Erroneous or Arrhenius: A Degradation Rate-Based Model for EPDM during Homogeneous Ageing
Abstract
1. Introduction
- the Arrhenius treatment
- the time-temperature superposition technique
- the kinetic study
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Continuous Stress Relaxation Experiments
2.2.2. Compression Set
3. Modeling
3.1. Physical Relaxation
3.2. Chemical Ageing
4. Results and Discussion
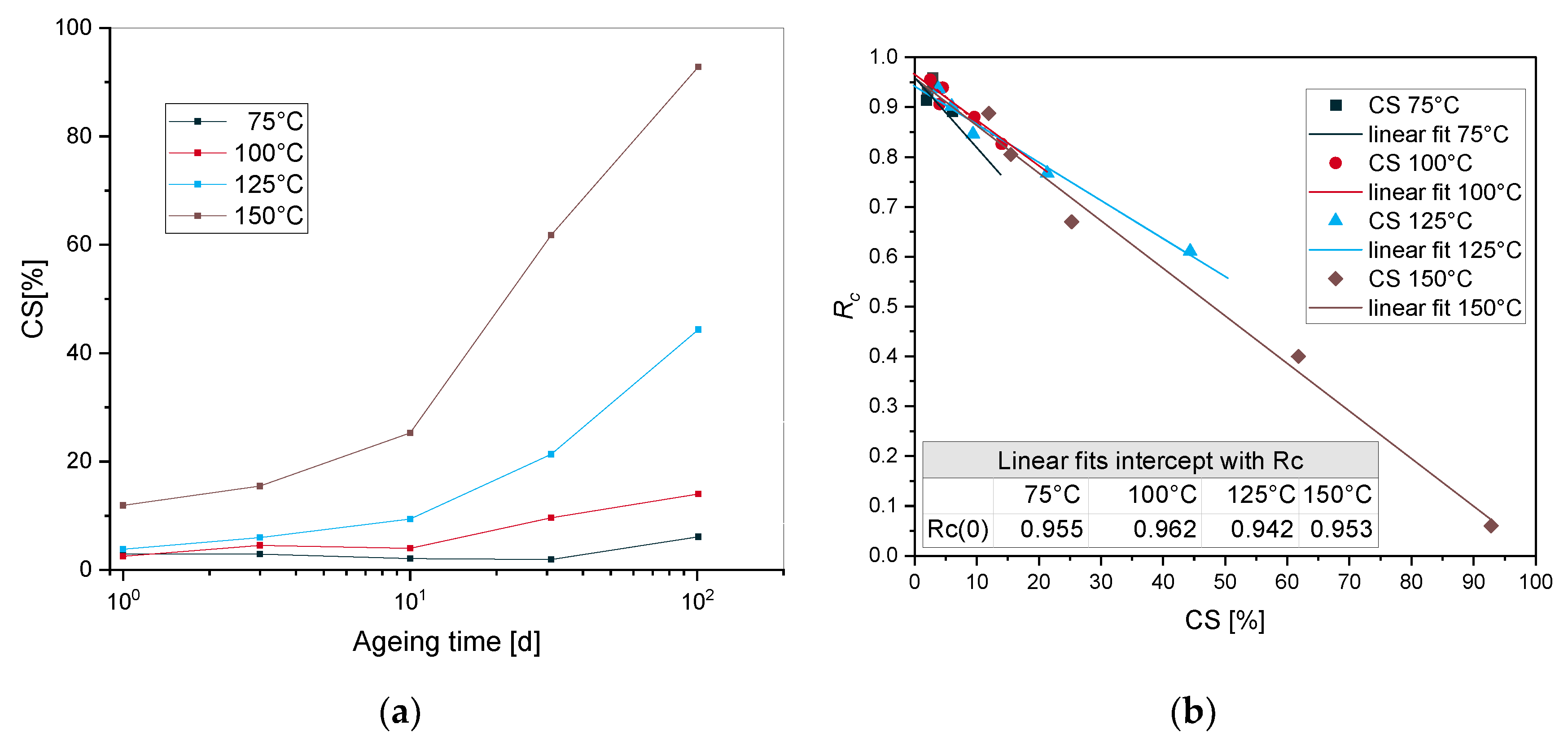
4.1. Continuous Stress Relaxation
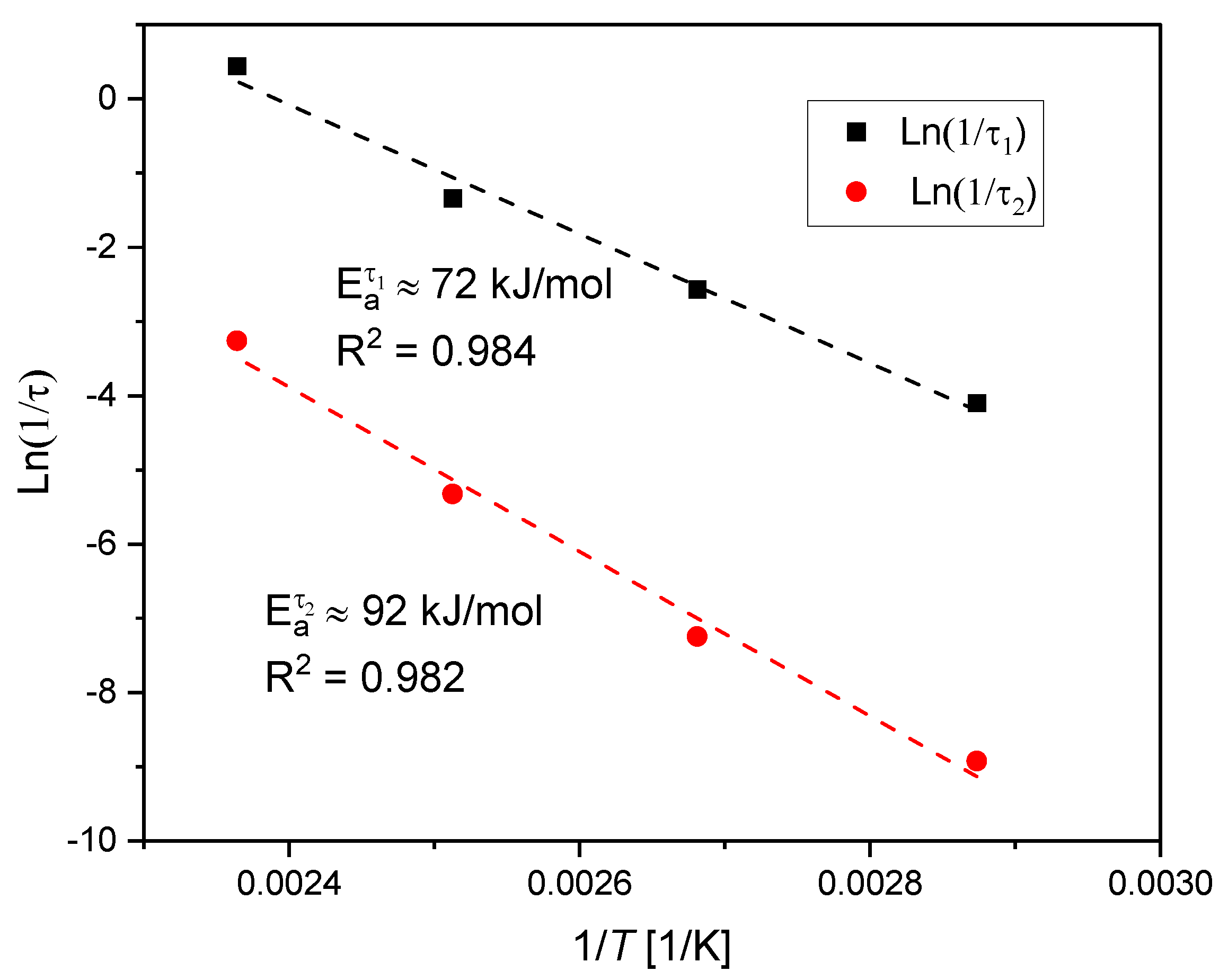
4.2. Kinetic Study
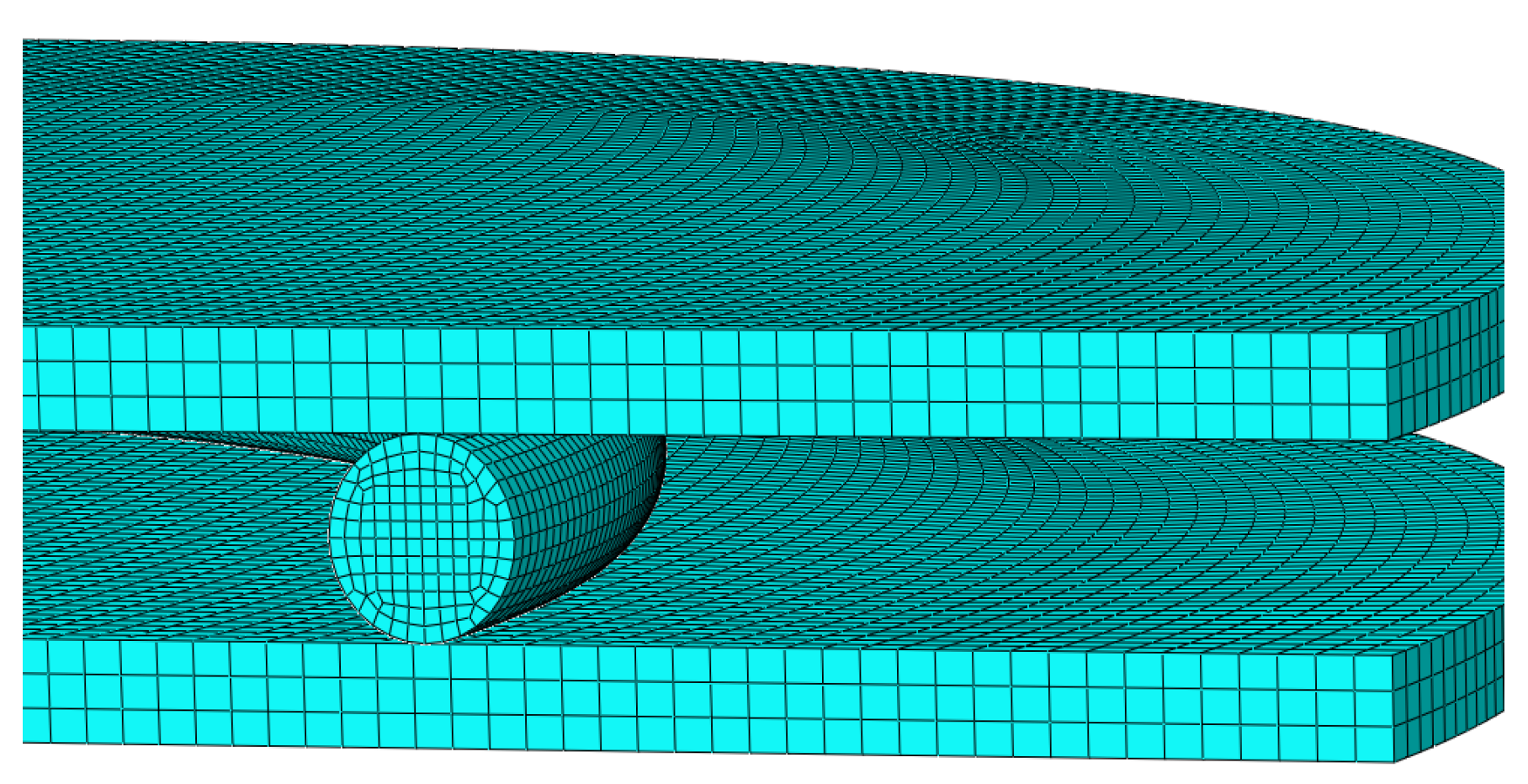
4.3. FE Simulation Results
4.4. Validation of the Model
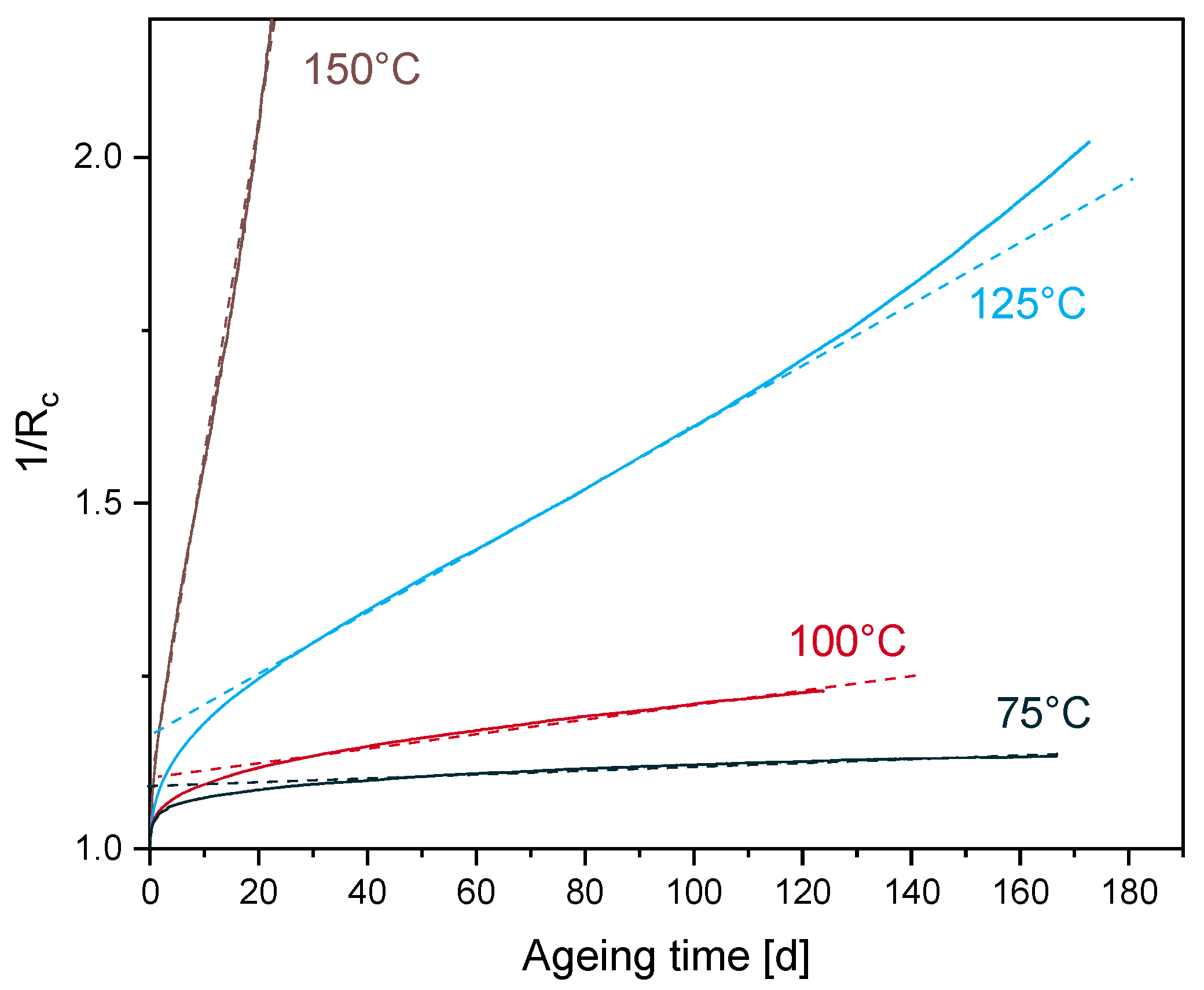
4.4.1. Time-Temperature Superposition
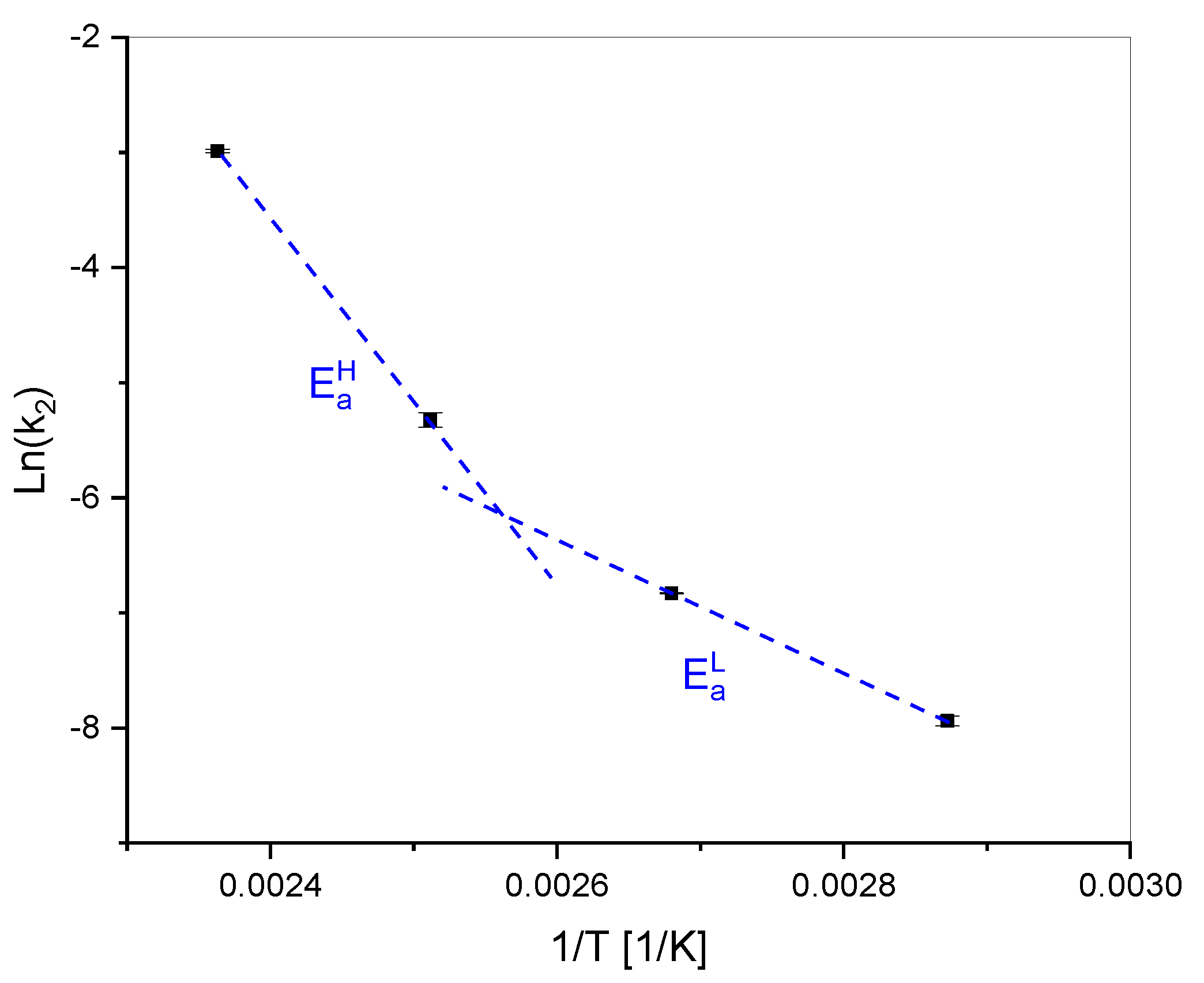
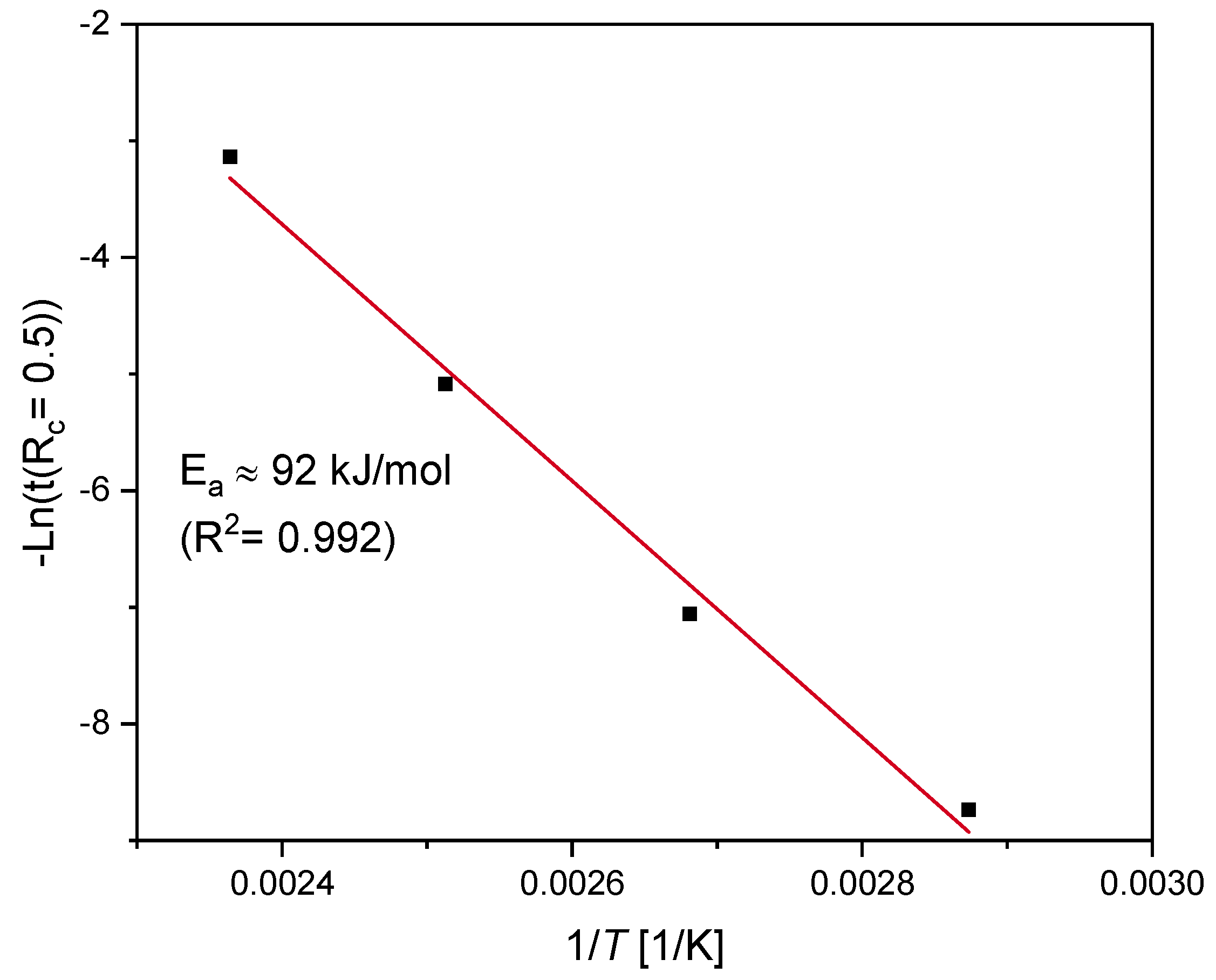
4.4.2. Arrhenius Approach
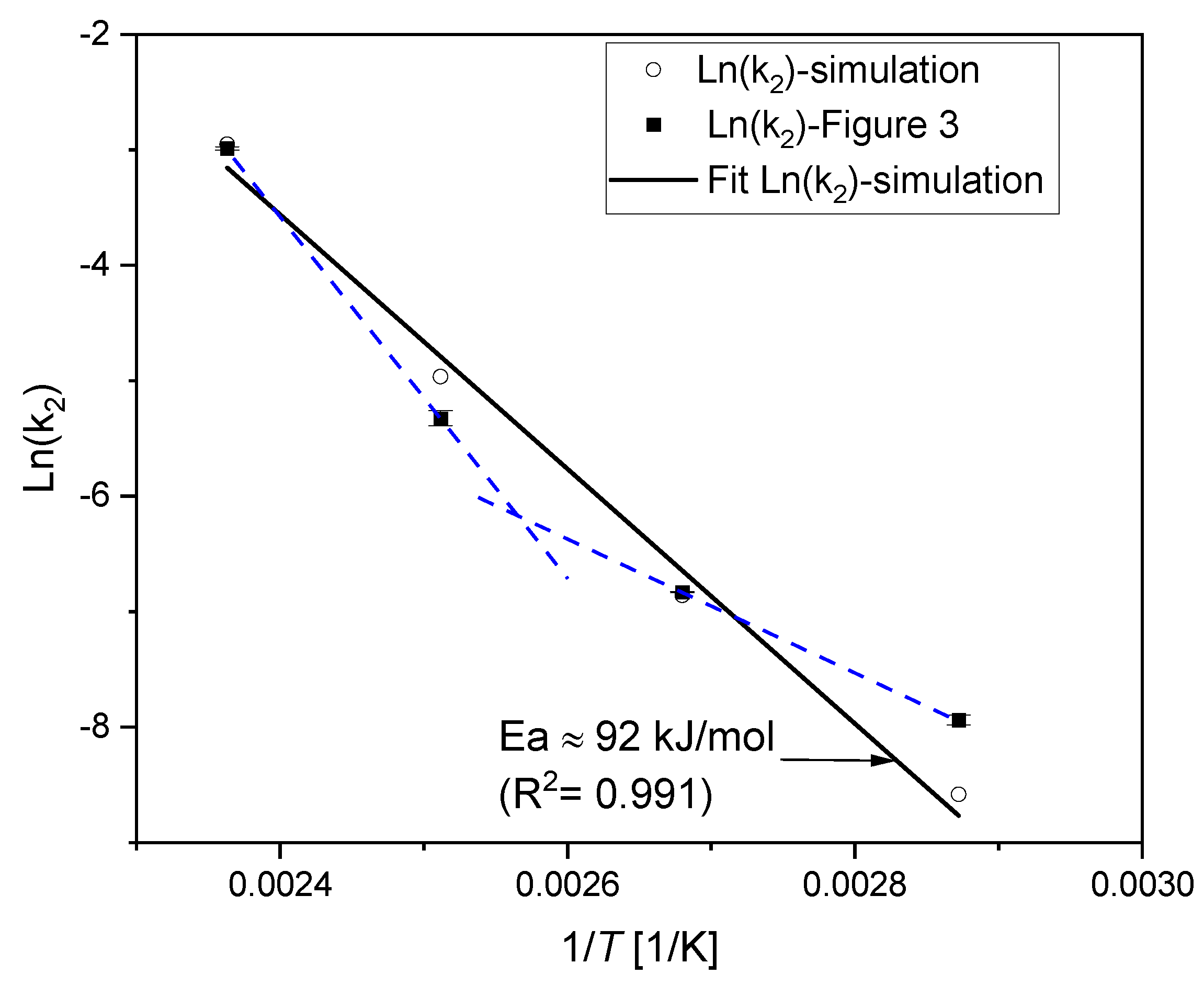
4.4.3. Kinetic Treatment
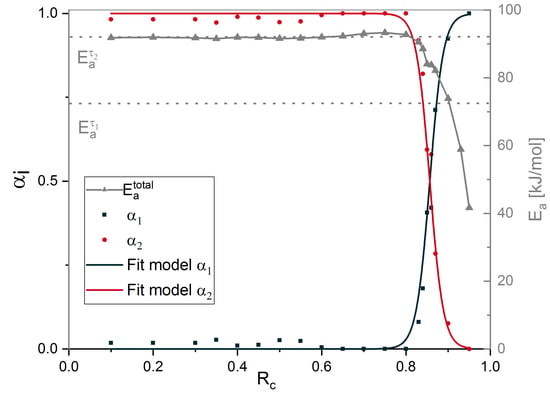
4.5. Contribution of Different Chemical Processes
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yoda, R. Elastomers for biomedical applications. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 1998, 9, 561–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, A.W.; Lin, A.N.; Martin, J.W. Performance of Elastomers in Isolation Bearings: A Literature Review. Earthq. Spectra 1992, 8, 279–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmas, P.; Colsenet, R.; Lemarié, L.; Sebban, M. Ageing of EPDM elastomers exposed to γ-radiation studied by 1H broadband and 13C high-resolution solid-state NMR. Polymer 2003, 44, 4889–4897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kass, M.D.; Janke, C.J.; Connatser, R.M.; Lewis, S.A.; Keiser, J.R.; Gaston, K. Compatibility Assessment of Fuel System Elastomers with Bio-oil and Diesel Fuel. Energy Fuels 2016, 30, 6486–6494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrenstein, G.W.; Pongratz, S. Beständigkeit von Kunststoffen; Carl Hanser: München, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson, J.M. Physical aging of polymers. Prog. Polym. Sci. 1995, 20, 703–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R. Physical test Methods for Elastomers; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Arrhenius, S. Über die Reaktionsgeschwindigkeit bei der Inversion von Rohrzucker durch Säuren. Z. Phys. Chem. 1889, 4U, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.L.; Landel, R.F.; Ferry, J.D. The Temperature Dependence of Relaxation Mechanisms in Amorphous Polymers and Other Glass-forming Liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1955, 77, 3701–3707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, P. Glossary of terms used in physical organic chemistry (IUPAC Recommendations 1994). Pure Appl. Chem. 1994, 66, 1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyazovkin, S.; Burnham, A.K.; Criado, J.M.; Pérez-Maqueda, L.A.; Popescu, C.; Sbirrazzuoli, N. ICTAC Kinetics Committee recommendations for performing kinetic computations on thermal analysis data. Thermochim. Acta 2011, 520, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.; Morrell, P.R.; Murphy, J.J. Continuous and intermittent stress relaxation studies on foamed polysiloxane rubber. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2005, 87, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillen, K.T.; Celina, M.; Clough, R.L.; Wise, J. Extrapolation of accelerated aging data-Arrhenius or erroneous? Trends Polym. Sci. 1997, 8, 250–257. [Google Scholar]
- Celina, M.; Gillen, K.T.; Assink, R.A. Accelerated aging and lifetime prediction: Review of non-Arrhenius behaviour due to two competing processes. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2005, 90, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillen, K. New Methods For Predicting Lifetimes In Weapons. Part 1-Ultrasensitive Oxygen Consumption Measurements To Predict The Lifetime Of Epdm O-Rings; Technical Report, SAND-98-1942, TIC Foreign Exchange Reports; Sandia National Laboratories: Albuquerque, NM, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Kömmling, A.; Jaunich, M.; Wolff, D. Effects of heterogeneous aging in compressed HNBR and EPDM O-ring seals. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2016, 126, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, I. Lifetime Prediction of Polymers: To Bet, or Not to Bet-Is This the Question? Materials 2018, 11, 1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaghdoudi, M.; Kömmling, A.; Jaunich, M.; Wolff, D. Scission, Cross-Linking, and Physical Relaxation during Thermal Degradation of Elastomers. Polymers 2019, 11, 1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, I.; Abate, L.; Antonelli, M.L. The regression of isothermal thermogravimetric data to evaluate degradation Ea values of polymers: A comparison with literature methods and an evaluation of lifetime prediction reliability. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2011, 96, 1947–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobolsky, A.V.; Prettyman, I.B.; Dillon, J.H. Stress Relaxation of Natural and Synthetic Rubber Stocks. J. Appl. Phys. 1944, 15, 380–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobolsky, A.V.; Norling, P.M.; Frick, N.H.; Yu, H. On the mechanism of autoxidation of three vinyl polymers: Polypropylene, ethylene-propylene rubber, and poly(ethyl acrylate). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1964, 86, 3925–3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huggins, M.L. Properties and structure of polymers, A.T. Tobolsky. Wiley, New York, 1960, IX + 331 pp. $14.50. J. Polym. Sci. 1960, 47, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, R.D.; Tobolsky, A.V.; Hanson, E.E. The Theory of Permanent Set at Elevated Temperatures in Natural and Synthetic Rubber Vulcanizates. J. Appl. Phys. 1946, 17, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johlitz, M.; Retka, J.; Lion, A. Chemical Ageing of Elastomers: Experiments and Modelling. In Proceedings of the 7th European Conference on Constitutive Models for Rubber, ECCMR, Dublin, Ireland, 20–23 September 2011; pp. 113–118. [Google Scholar]
- Johlitz, M.; Diercks, N.; Lion, A. Thermo-oxidative ageing of elastomers: A modelling approach based on a finite strain theory. Int. J. Plast. 2014, 63, 138–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal, H.; Kaliske, M. A micro-continuum-mechanical material model for failure of rubber-like materials: Application to ageing-induced fracturing. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2009, 57, 1340–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, H.; Dargazany, R. A micro-mechanical approach to model thermal induced aging in elastomers. Int. J. Plast. 2019, 118, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouaziz, R.; Ahose, K.D.; Lejeunes, S.; Eyheramendy, D.; Sosson, F. Characterization and modeling of filled rubber submitted to thermal aging. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2019, 169, 122–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, J.A.; Jones, A.S.; Wineman, A.S. Chemorheological response of elastomers at elevated temperatures: Experiments and simulations. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2005, 53, 2758–2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wineman, A. On the mechanics of elastomers undergoing scission and cross-linking. Int. J. Adv. Eng. Sci. Appl. Math. 2009, 1, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronan, S.; Alshuth, T.; Jerrams, S. An Approach to the Estimation of Long-Term Stress Relaxation in Elastomers. KGK 2007, 60, 559–563. [Google Scholar]
- Ronan, S.; Santoso, M.; Alshuth, T.; Giese, U.; Schuster, R. The impact of chain oxidation on stress relaxation of NR-elastomers and life-time prediction. Kautsch. Gummi Kunstst. 2009, 62, 182–186. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammadi, H.; Morovati, V.; Poshtan, E.; Dargazany, R. Understanding decay functions and their contribution in modeling of thermal-induced aging of cross-linked polymers. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2020, 175, 109108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kömmling, A.; Jaunich, M.; Pourmand, P.; Wolff, D.; Gedde, U.W. Influence of Ageing on Sealability of Elastomeric O-Rings. Macromol. Symp. 2017, 373, 1600157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillen, K.T.; Bernstein, R.; Wilson, M.H. Predicting and confirming the lifetime of o-rings. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2005, 87, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kömmling, A.; Jaunich, M.; Goral, M.; Wolff, D. Insights for lifetime predictions of O-ring seals from five-year long-term aging tests. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2020, 179, 109278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wineman, A.; Shaw, J. Combined deformation-and temperature-induced scission in a rubber cylinder in torsion. Int. J. Non Linear Mech. 2007, 42, 330–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wineman, A. Some Comments on the Mechanical Response of Elastomers Undergoing Scission and Healing at Elevated Temperatures. Math. Mech. Solids 2005, 10, 673–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehret, A.E.; Itskov, M. Modeling of anisotropic softening phenomena: Application to soft biological tissues. Int. J. Plast. 2009, 25, 901–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göktepe, S.; Miehe, C. A micro–macro approach to rubber-like materials. Part III: The micro-sphere model of anisotropic Mullins-type damage. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2005, 53, 2259–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ABAQUS®. ABAQUS; Dassault Systèmes Simulia Corp.: Providence, RI, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Musil, B.; Böhning, M.; Johlitz, M.; Lion, A. On the inhomogenous chemo-mechanical ageing behaviour of nitrile rubber: Experimental investigations, modelling and parameter identification. Contin. Mech. Thermodyn. 2020, 32, 127–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lion, A.; Johlitz, M. On the representation of chemical ageing of rubber in continuum mechanics. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2012, 49, 1227–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saanouni, K.; Sidoroff, F.; Andrieux, F. Damaged hyperelastic solid with an induced volume variation. Effect of loading paths. In Studies in Applied Mechanics; Voyiadjis, G.Z., Ju, J.-W.W., Chaboche, J.-L., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1998; Volume 46, pp. 503–522. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, R.P.; Forrest, M.J.; Soulagnet, G. Long-Term and Accelerated Ageing Tests on Rubbers; Rapra Technology Limited: Shrewsbury, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Li, X.; Xu, L.; He, T. Service Lifetime Estimation of EPDM Rubber Based on Accelerated Aging Tests. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2017, 26, 1735–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albihn, P. Chapter 1—The 5-year Accelerated Ageing Project for Thermoset and Thermoplastic Elastomeric Materials: A Service Life Prediction Tool. In Elastomers and Components; Coveney, V.A., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, Cambridge, UK, 2006; pp. 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kömmling, A.; Jaunich, M.; Pourmand, P.; Wolff, D.; Hedenqvist, M. Analysis of O-Ring Seal Failure under Static Conditions and Determination of End-of-Lifetime Criterion. Polymers 2019, 11, 1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roper, L.D. Depletion of nonrenewable resources. Am. J. Phys. 1979, 47, 467–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J.R.; Turnbull, A. Weathering of polymers: Mechanisms of degradation and stabilization, testing strategies and modelling. J. Mater. Sci. 1994, 29, 584–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| 150 °C | 125 °C | 100 °C | 75 °C | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| tinitiation [d] | 0.13 | 1 | 1.3 | 0.19 |
| Physical Relaxation Parameters | Chemical Relaxation Parameters | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature | 150 °C | 0.0043 | 0.003 | 0.11 | 0.87 | 0.64 | 26 |
| 0.03 | 0.3 | ||||||
| 125 °C | 0.0043 | 0.003 | 0.12 | 0.85 | 3.8 | 205 | |
| 0.03 | 0.3 | ||||||
| 100 °C | 0.05 | 0.31 | 0.08 | 0.871 | 13 | 1400 | |
| 75 °C | 0.024 | 0.113 | 0.073 | 0.873 | 60 | 7500 | |
| 0.095 | 2.23 | ||||||
| Regression Coefficient | ||
|---|---|---|
| 0.95 | 42 | 0.966 |
| 0.93 | 59 | 0.989 |
| 0.9 | 74 | 0.995 |
| 0.88 | 83 | 0.997 |
| 0.85 | 84 | 0.994 |
| 0.83 | 91 | 0.998 |
| 0.8 | 93 | 0.994 |
| 0.75 | 93 | 0.992 |
| 0.7 | 93 | 0.991 |
| 0.65 | 92 | 0.991 |
| 0.6 | 92 | 0.991 |
| 0.55 | 92 | 0.991 |
| 0.5 | 92 | 0.992 |
| 0.45 | 92 | 0.991 |
| 0.4 | 92 | 0.990 |
| 0.35 | 92 | 0.990 |
| 0.3 | 92 | 0.990 |
| 0.2 | 92 | 0.995 |
| 0.1 | 92 | 0.995 |
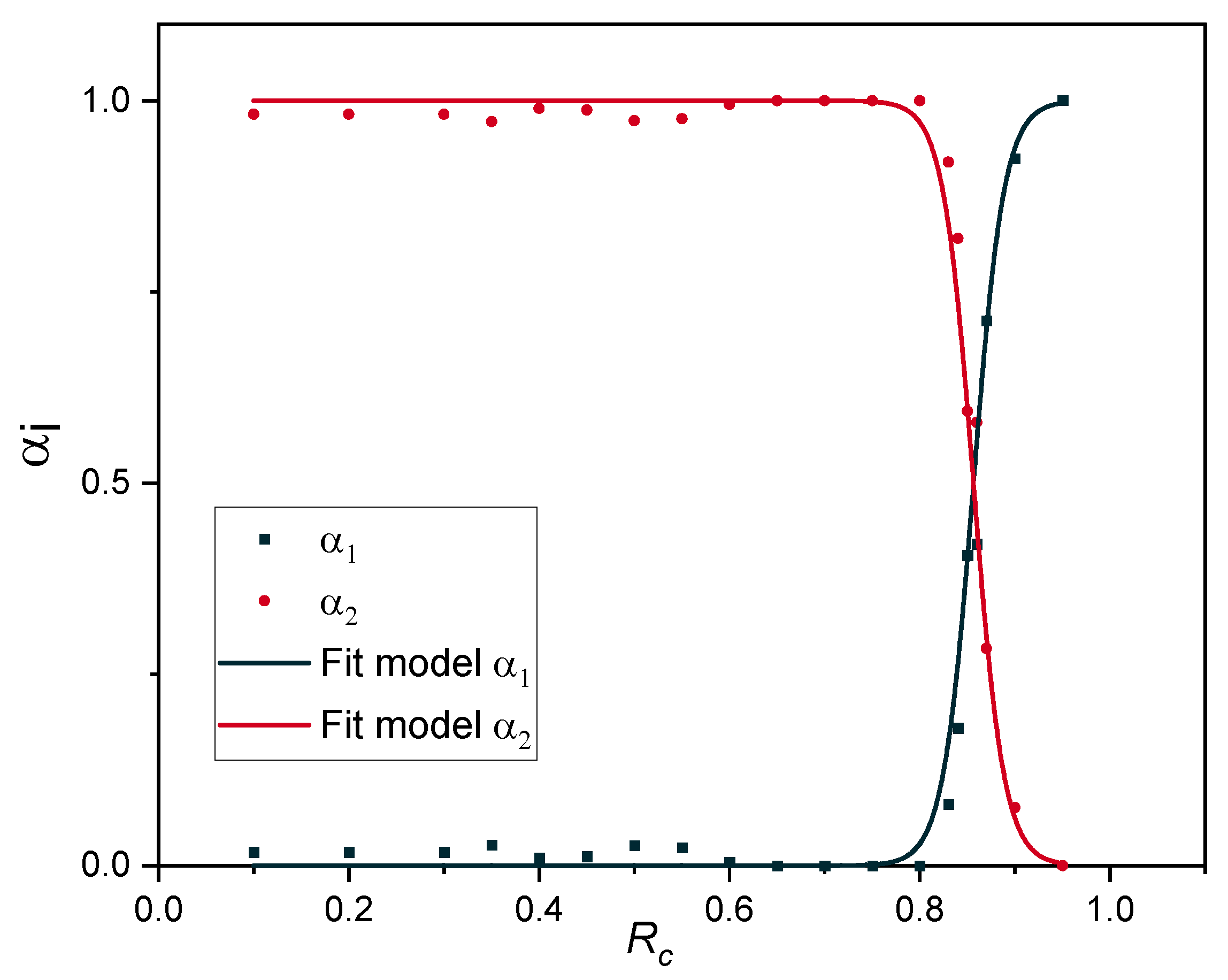
| A | x | l | Regression Coefficient |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 | 0.856 | 0.032 | 0.997 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zaghdoudi, M.; Kömmling, A.; Jaunich, M.; Wolff, D. Erroneous or Arrhenius: A Degradation Rate-Based Model for EPDM during Homogeneous Ageing. Polymers 2020, 12, 2152. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12092152
Zaghdoudi M, Kömmling A, Jaunich M, Wolff D. Erroneous or Arrhenius: A Degradation Rate-Based Model for EPDM during Homogeneous Ageing. Polymers. 2020; 12(9):2152. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12092152
Chicago/Turabian StyleZaghdoudi, Maha, Anja Kömmling, Matthias Jaunich, and Dietmar Wolff. 2020. "Erroneous or Arrhenius: A Degradation Rate-Based Model for EPDM during Homogeneous Ageing" Polymers 12, no. 9: 2152. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12092152
APA StyleZaghdoudi, M., Kömmling, A., Jaunich, M., & Wolff, D. (2020). Erroneous or Arrhenius: A Degradation Rate-Based Model for EPDM during Homogeneous Ageing. Polymers, 12(9), 2152. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12092152