Novel Activated Carbon Nanofibers Composited with Cost-Effective Graphene-Based Materials for Enhanced Adsorption Performance toward Methane
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Graphene Preparation from Rice Husk Ash
2.2. Synthesis of Reduced Graphene Oxide (rGO)
2.3. Fabrication of Activated Carbon Nanofibers’ Nanocomposites (gACNFs)
2.4. Electrospinning and Pyrolysis of Nanofibers
2.5. Characterizations
2.6. Methane Adsorption Performance via Volumetric Method
2.7. Adsorption Kinetics
3. Results and Discussion
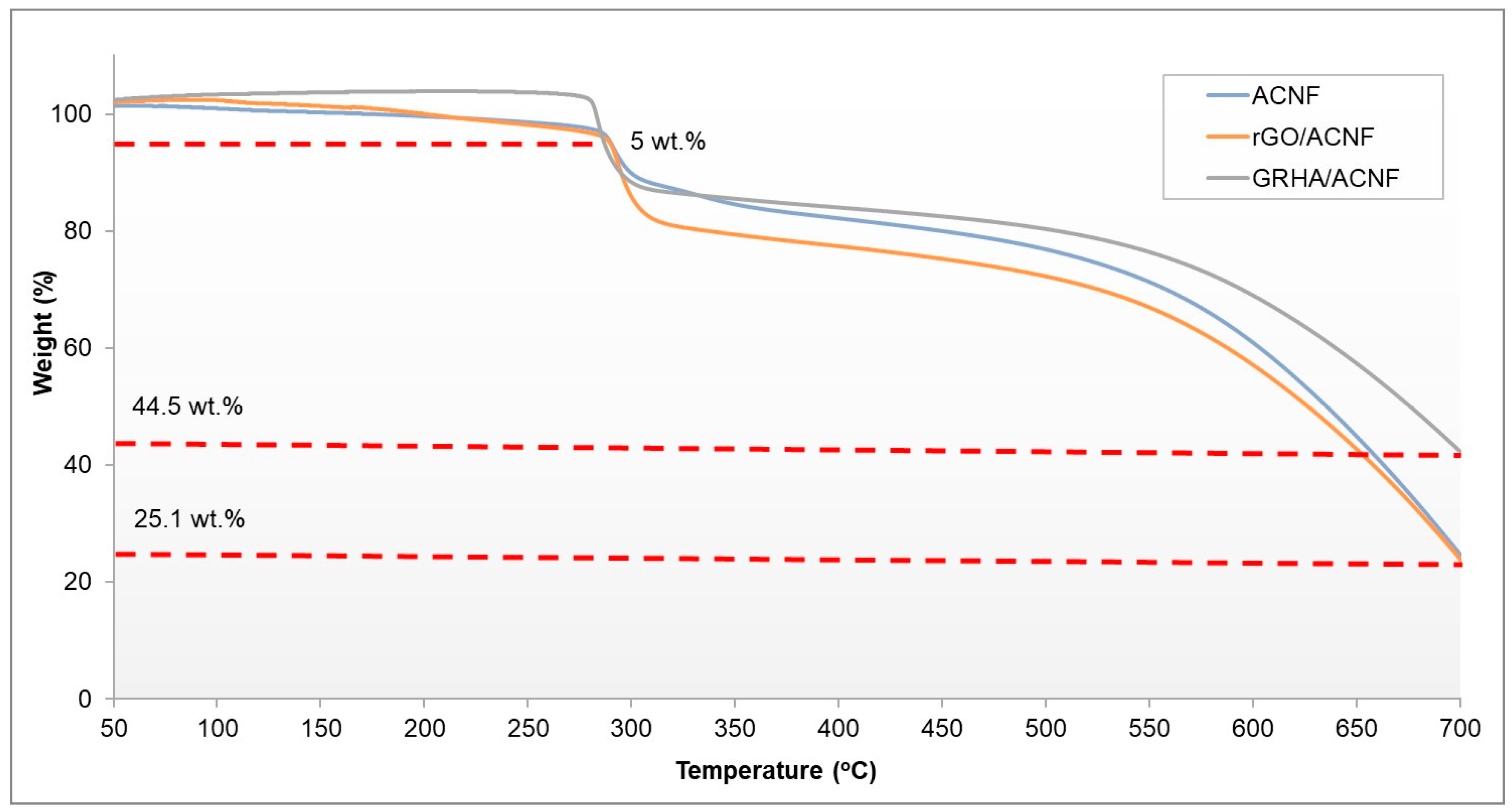
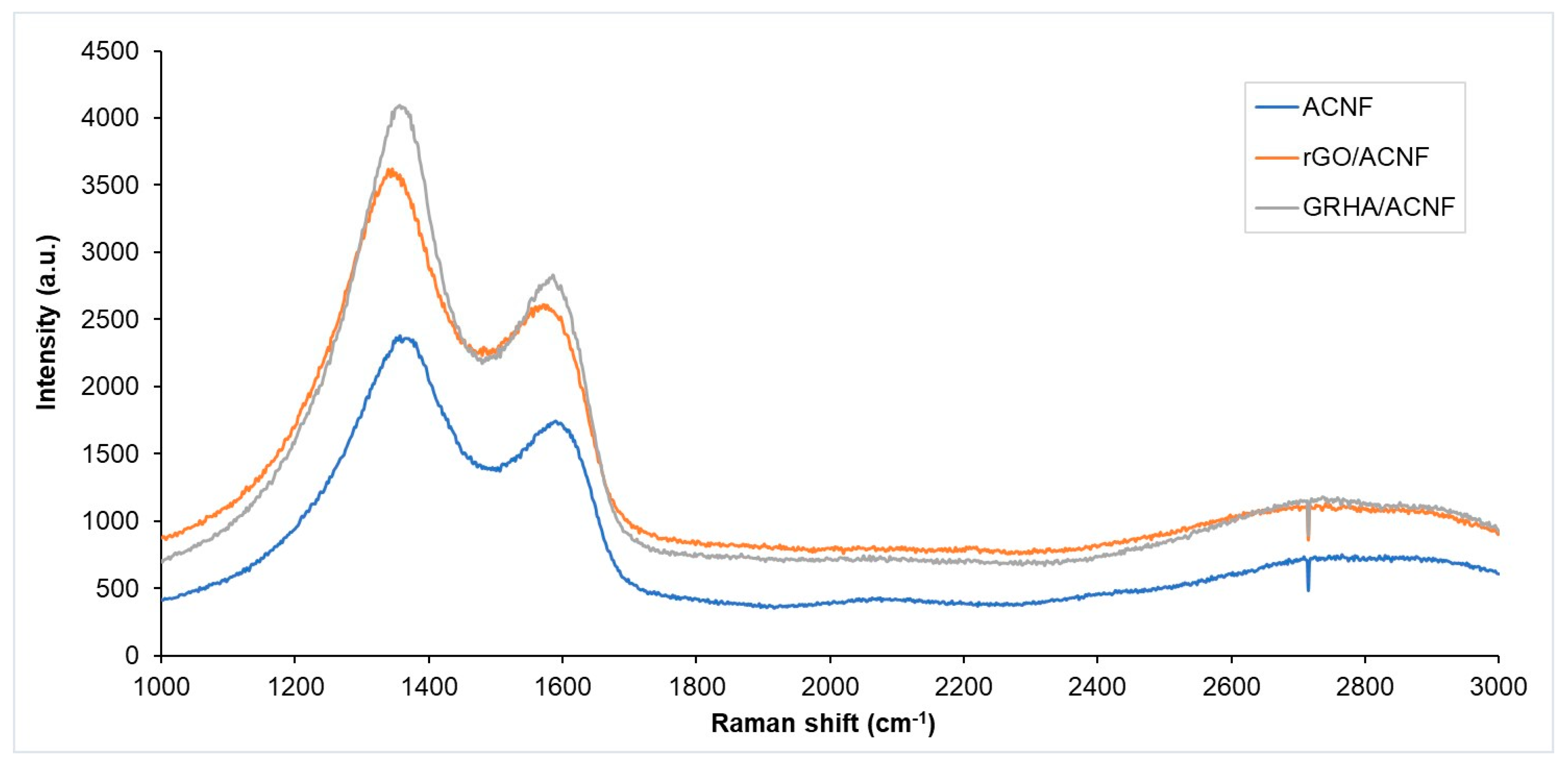
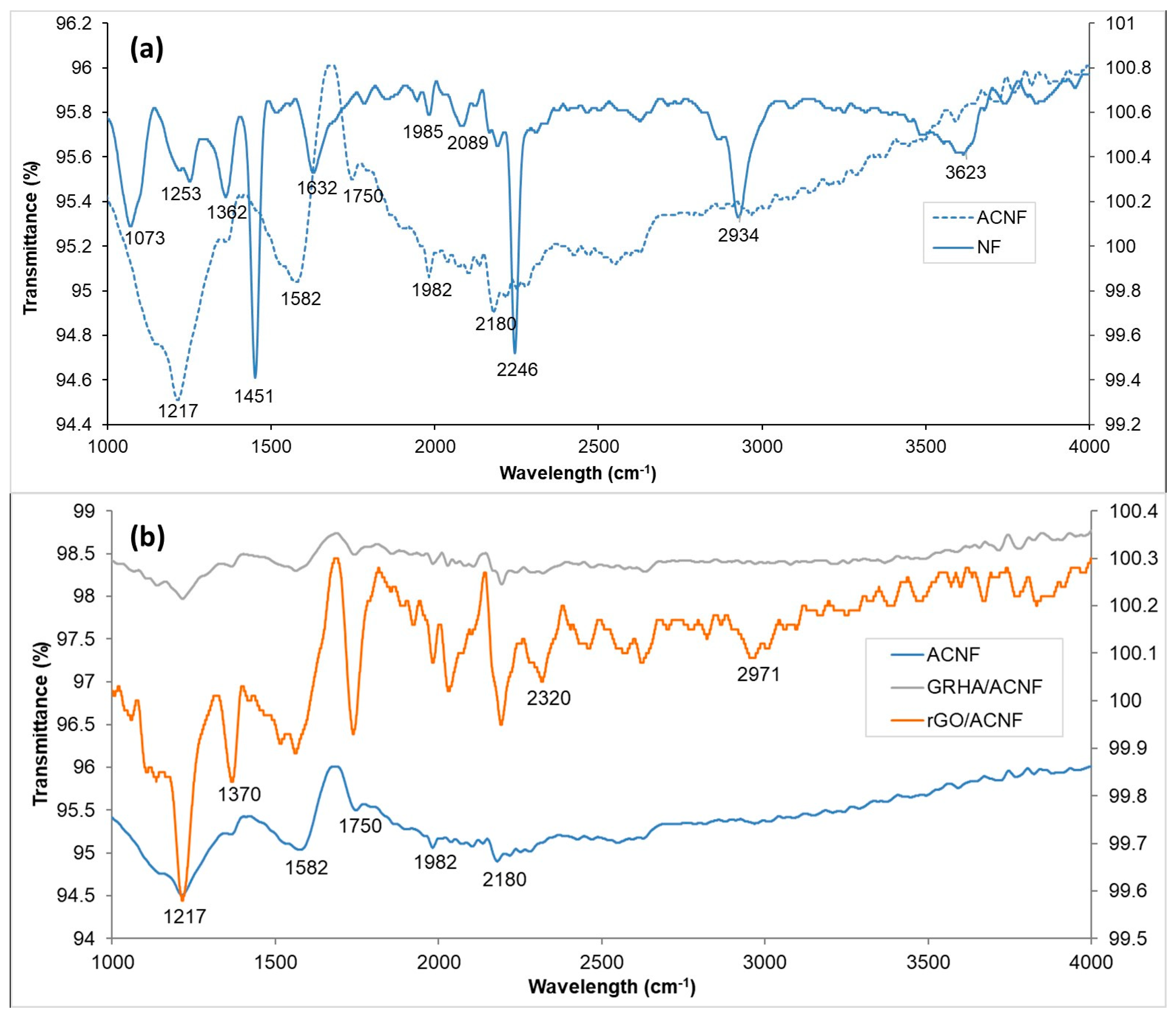
3.1. Physicochemical Properties of the gACNFs
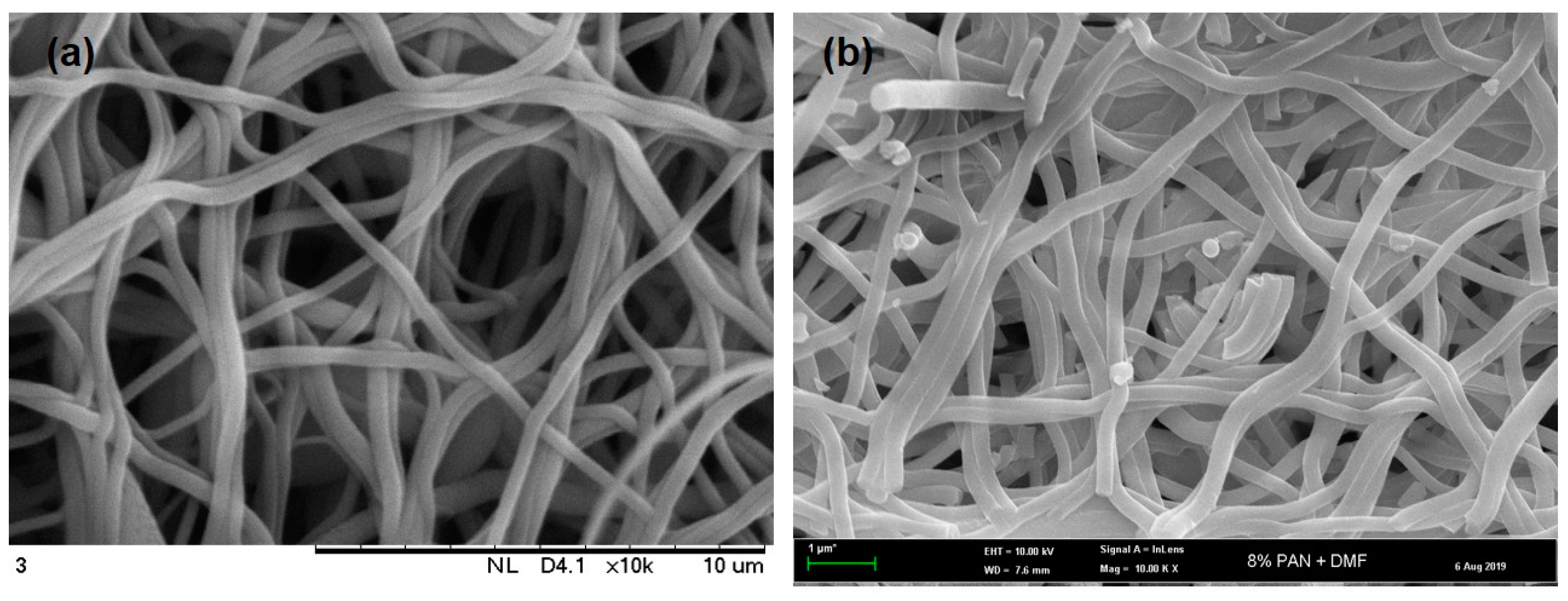
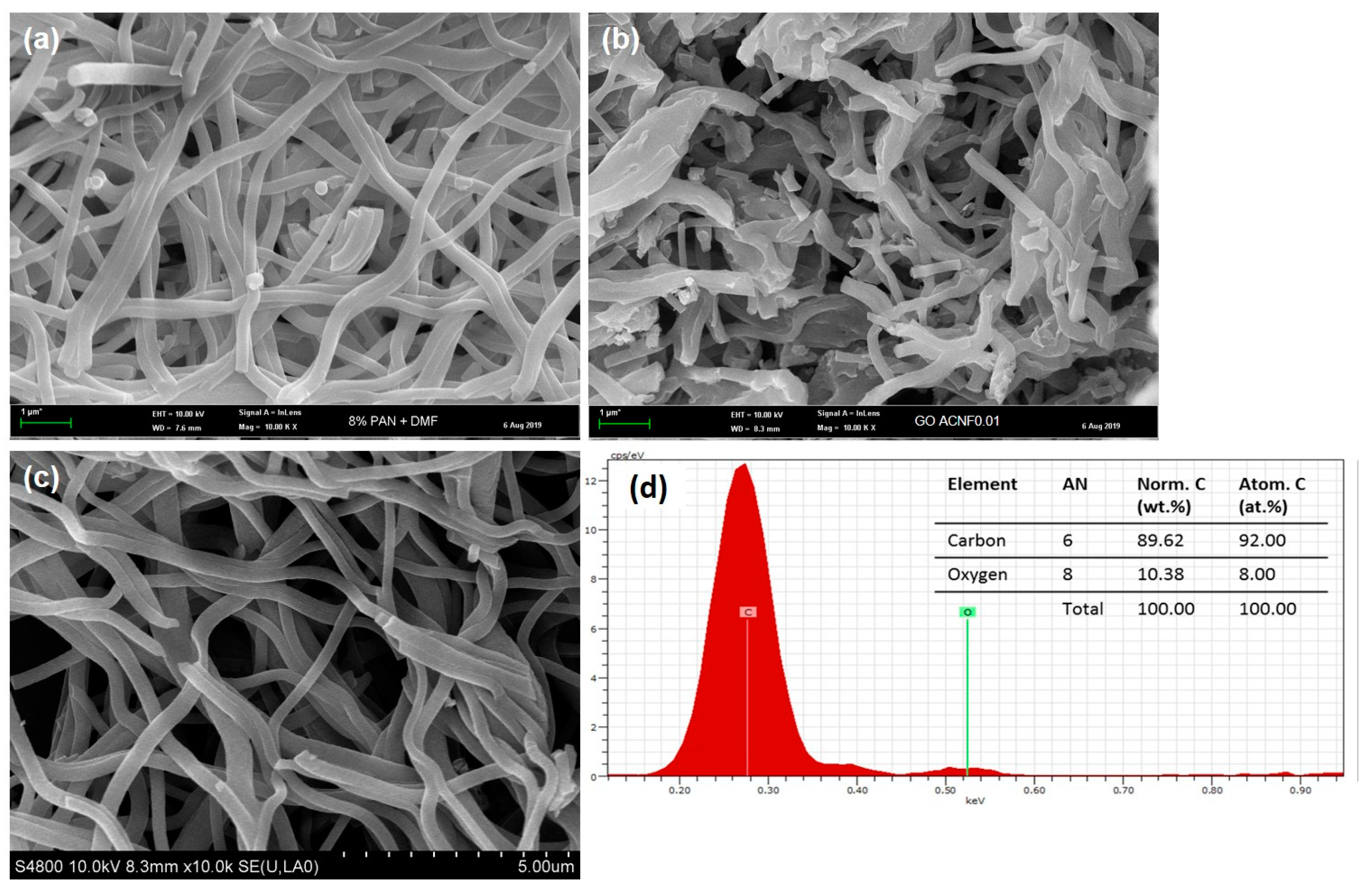
3.2. Morphologies and Structures
3.3. Pore Structure and Texture of gACNFs
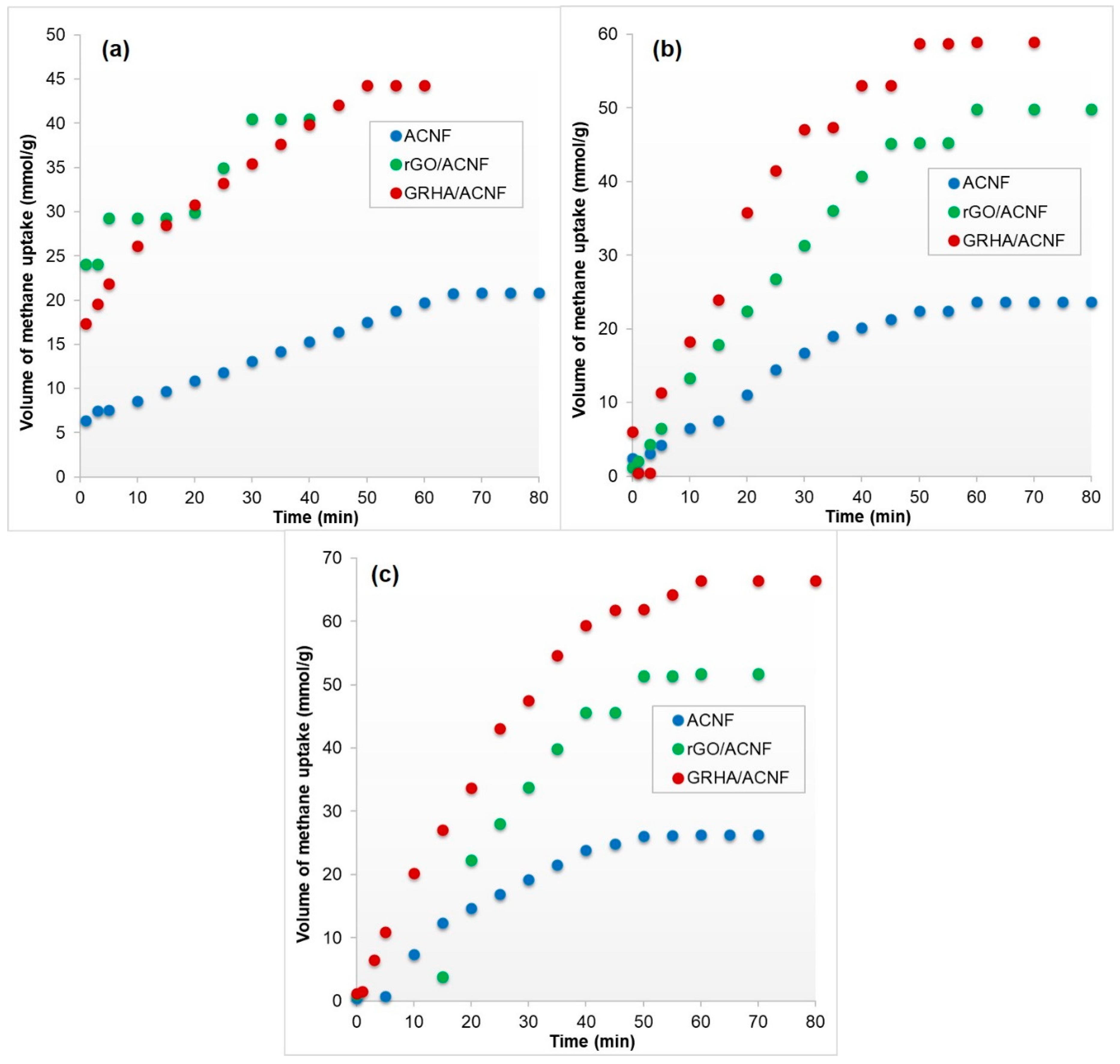
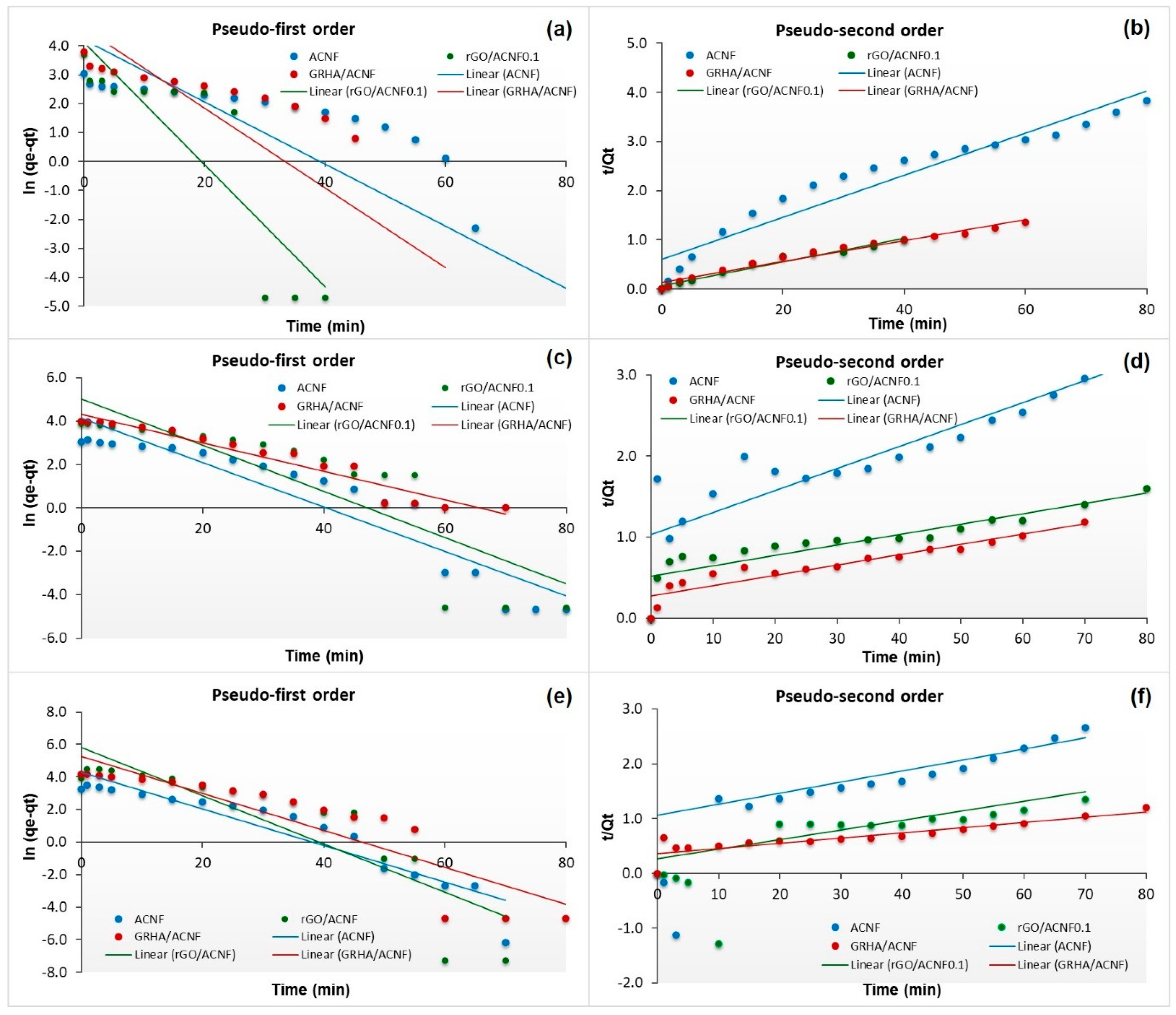
3.4. Adsorption Performance and Kinetic Study of gACNFs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lelieveld, J.; Klingmüller, K.; Pozzer, A.; Burnett, R.T.; Haines, A.P.; Ramanathan, V. Effects of fossil fuel and total anthropogenic emission removal on public health and climate. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 7192–7197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Perera, F. Pollution from fossil-fuel combustion is the leading environmental threat to global pediatric health and quity: Solutions exist. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Cassia, R.; Nocioni, M.; Correa-Aragunde, N.; Lamattina, L. Climate change and the impact of greenhouse gases: CO2 and NO, friends and foes of plant oxidative stress. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, L.C.; Nascimento, M.V.D.C.; Araújo, O.D.Q.F.; De Medeiros, J.L. A cleaner and more sustainable decarbonation process via ionic-liquid absorption for natural gas with high carbon dioxide content. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 242, 118421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Zhu, Z.; Feng, Y.; Wang, X. Development of composite adsorbents and storage vessels for domestically used adsorbed natural gas. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2016, 98, 778–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuliusman; Nasruddin; Sanal, A.; Bernama, A.; Haris, F.; Hardhi, M. Improved of natural gas storage with adsorbed natural gas technology using activated carbon from plastic waste polyethulene terephthalate. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2017, 75, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feroldi, M.; Neves, A.; Borba, C.E.; Alves, H. Methane storage in activated carbon at low pressure under different temperatures and flow rates of charge. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 921–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, O.F., Jr.; Silvestre-Albero, J.; Casco, M.E.; Hotza, D.; Rambo, C.R. Activated nanocarbons produced by microwave-assisted hydrothermal carboniozation of Amazonian fruit waste for methane storage. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 216, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-M.; Lee, B.-H.; Park, S.-J.; An, K.-H.; Kim, B.-J. Pitch-Derived Activated Carbon Fibers for Emission Control of Low-Concentration Hydrocarbon. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Sharkawy, I.I.; Mansour, M.H.; Awad, M.M.; El-Ashry, R. Investigation of Natural Gas Storage through Activated Carbon. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2015, 60, 3215–3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergna, D.; Varila, T.; Romar, H.; Lassi, U. Comparison of the Properties of Activated Carbons Produced in One-Stage and Two-Stage Processes. C J. Carbon Res. 2018, 4, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jahangiri, M.; Adl, J.; Shahtaheri, S.J.; Rashidi, A.; Ghorbanali, A.; Kakooe, H.; Rahimiforoushani, A.; Ganjali, M.R. Preparation of a new adsorbent from activated carbon and carbon nanofiber (AC/CNF) for manufacturing organic-vacbpour respirator cartridge. Iran. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2013, 10, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Othman, F.E.C.; Yusof, N.; Hasbullah, H.; Othman, M.H.D.; Ismail, A.; Abdullah, N.; Nordin, N.A.H.M.; Aziz, F.; Salleh, W.N.W. Polyacrylonitrile/magnesium oxide-based activated carbon nanofibers with well-developed microporous structure and their adsorption performance for methane. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2017, 51, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Fan, Z. Design of advanced porous graphene materials: From graphene nanomesh to 3D architectures. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 1922–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, R.; Chowdhury, S. Recent advances and progress in the development of graphene-based adsorbents for CO 2 capture. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 21968–21989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Bahadur, J.; Pal, K. One-Step One Chemical Synthesis Process of Graphene from Rice Husk for Energy Storage Applications. Graphene 2017, 6, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oliveira, A.E.; Braga, G.B.; Tarley, C.R.T.; Pereira, A.C. Thermally reduced graphene oxide: Synthesis, studies and characterization. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 12005–12015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muramatsu, H.; Kim, Y.A.; Yang, K.-S.; Cruz-Silva, R.; Toda, I.; Yamada, T.; Terrones, M.; Endo, M.; Hayashi, T.; Saitoh, H. Rice Husk-Derived Graphene with Nano-Sized Domains and Clean Edges. Small 2014, 10, 2766–2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, S.N.; Sharma, N.; Kumar, L. Synthesis of Graphene Oxide (GO) by Modified Hummers Method and Its Thermal Reduction to Obtain Reduced Graphene Oxide (rGO)*. Graphene 2017, 6, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, J.; Pei, S.; Ren, W.; Gao, L.; Cheng, H.-M. Efficient Preparation of Large-Area Graphene Oxide Sheets for Transparent Conductive Films. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 5245–5252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, F.E.C.; Yusof, N.; Jaafar, J.; Ismail, A.; Hasbullah, H.; Abdullah, N.; Ismail, M.S. Preparation and characterization of Polyacrylonitrile/ Manganese Dioxides- based Carbon Nanofibers via electrospinning process. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2016, 36, 12006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, A.; Haider, S.; Kang, I.-K. A comprehensive review summarizing the effect of electrospinning parameters and potential applications of nanofibers in biomedical and biotechnology. Arab. J. Chem. 2018, 11, 1165–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasri, N.S.; Hamza, U.D.; Ismail, S.N.; Ahmed, M.M.; Mohsin, R. Assessment of porous carbons derived from sustainable palm solid waste for carbon dioxide capture. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 71, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, M.; Kong, H.; Ding, X.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Cao, Y.; Yu, M. Study on the Changes of Structures and Properties of PAN Fibers during the Cyclic Reaction in Supercritical Carbon Dioxide. Polymers 2019, 11, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tiwari, D.; Goel, C.; Bhunia, H.; Bajpai, P.K. Dynamic CO 2 capture by carbon adsorbents: Kinetics, isotherm and thermodynamic studies. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 181, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, R.F.; Pardini, L.C.; Alves, N.P.; Júnior, C.A.R.B. Thermal Stabilization study of polyacrylonitrile fiber obtained by extrusion. Polímeros 2015, 25, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pashaloo, F.; Bazgir, S.; Tamizifar, M.; Faghihisani, M.; Zakerifar, S. Preparation and characterization of carbon nanofibers via electrospun PAN nanofibers. Text. Sci. Technol. J. 2009, 3, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, X.; Li, L.; Xu, R.; Liu, Q.; Ding, L.; Pan, Y.; Wang, C.; Hung, W.-S.; Lee, K.-R.; Wang, T. Effects of Thermal Cross-Linking on the Structure and Property of Asymmetric Membrane Prepared from the Polyacrylonitrile. Polymers 2018, 10, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hossain, S.; Mathur, L.; Roy, P. Rice husk/rice husk ash as an alternative source of silica in ceramics: A review. J. Asian Ceram. Soc. 2018, 6, 299–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, I.J.; Calheiro, D.; Sánchez, F.A.L.; Camacho, A.L.D.; Rocha, T.L.A.D.C.; Moraes, C.A.M.; Sousa, V. Characterization of Silica Produced from Rice Husk Ash: Comparison of Purification and Processing Methods. Mater. Res. 2017, 20, 512–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusof, N.; Ismail, A.; Rana, D.; Matsuura, T. Effects of the activation temperature on the polyacrylonitrile/acrylamide-based activated carbon fibers. Mater. Lett. 2012, 82, 16–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kshetri, T.; Tran, D.T.; Singh, T.I.; Kim, N.H.; Lau, K.-T.; Lee, J.H. Effects of the composition of reduced graphene oxide/carbon nanofiber nanocomposite on charge storage behaviors. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 178, 107500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brownson, D.A.C.; Varey, S.; Hussain, F.; Haigh, S.J.; Banks, C.E. Electrochemical properties of CVD grown pristine graphene: Monolayer- vs. quasi-graphene. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 1607–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Z.; Wu, X.-F. Graphene-beaded carbon nanofibers for use in supercapacitor electrodes: Synthesis and electrochemical characterization. J. Power Sources 2013, 222, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wolfe, D.; Terrones, M.; Haque, A.; Ganguly, S.; Roy, A. Electro-graphitization and exfoliation of graphene on carbon nanofibers. Carbon 2017, 117, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wilcox, J. CO2Adsorption on Carbon Models of Organic Constituents of Gas Shale and Coal. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 809–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankar, S.; Lee, H.; Jung, H.; Kim, A.; Ahmed, A.T.A.; Inamdar, A.I.; Kim, H.; Lee, S.; Im, H.; Kim, D.Y. Ultrathin grapheme nanosheets derived from rice husks for sustainable supercapacitor electrodes. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 13792–13797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin Ali, A.; Renz, F.; Koch, J.; Tegenkamp, C.; Sindelar, R. Graphene Nanoplatelet (GNPs) Doped Carbon Nanofiber (CNF) System: Effect of GNPs on the Graphitic Structure of Creep Stress and Non-Creep Stress Stabilized Polyacrylonitrile (PAN). Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, Q.; Wang, G.; Qian, B.; Hu, C.; Wang, Y.; Qiu, J. Electrospun Composites Made of Reduced Graphene Oxide and Activated Carbon Nanofibers for Capacitive Deionization. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 137, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusof, N.; Rana, D.; Ismail, A.; Matsuura, T. Microstructure of polyacrylonitrile-based activated carbon fibers prepared from solvent-free coagulation process. J. Appl. Res. Technol. 2016, 14, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petuhov, O.; Lupaşcu, T.; Behunová, D.M.; Povar, I.; Mitina, T.; Rusu, M. Microbiological Properties of Microwave-Activated Carbons Impregnated with Enoxil and Nanoparticles of Ag and Se. C J. Carbon Res. 2019, 5, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Minceva-Sukarova, B.; Mangovska, B.; Bogova-Gaceva, G.; Petrusevski, V.M. Micro-Raman and micro-FTIR spectroscopic investigation of raw and dyed PAN fibers. Croat. Chem. Acta 2012, 85, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baby, T.T.; Aravind, S.J.; Arockiadoss, T.; Rakhi, R.; Ramaprabhu, S. Metal decorated graphene nanosheets as immobilization matrix for amperometric glucose biosensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 145, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Tan, T.; Bakenov, Z.; Zhang, Y. Synthesis of a Flexible Freestanding Sulfur/Polyacrylonitrile/Graphene Oxide as the Cathode for Lithium/Sulfur Batteries. Polymers 2018, 10, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, E.S.; Ro, H.W.; Nguyen, C.V.; Jaffe, R.L.; Yoon, D.Y. Infrared Spectroscopy Study of Microstructures of Poly(silsesquioxane)s. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 1548–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, C.J.; Chase, G.; Yarin, A.; Reneker, D. Effects of parameters on nanofiber diameter determined from electrospinning model. Polymer 2007, 48, 6913–6922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzmenko, V.; Wang, N.; Haque, M.; Naboka, O.; Flygare, M.; Svensson, K.; Gatenholm, P.; Liu, J.; Enoksson, P. Cellulose-derived carbon nanofibers/graphene composite electrodes for powerful compact supercapacitors. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 45968–45977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Othman, F.E.C.; Yusof, N.; Ismail, A.F.; Jaafar, J.; Salleh, W.N.W.; Aziz, F. Preparation and characterization of polyacrylonitrile-based activated carbon nanofibers/graphene (gACNFs) composite synthesized by electrospinning. AIP Adv. 2020, 10, 055117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Sabio, M.; Rodrigue-Reinoso, F. Role of chemical activation in the development of carbon porosity. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2004, 241, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Ding, W.; Lei, S.; Tian, X.; Zhou, F. Selective adsorption of CH4/N2 on Ni-based MOF/SBA-15 composite materials. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, J.; Zhao, G. Preparation and Characterization of High Surface Area Activated Carbon Fibers from Lignin. Polymers 2016, 8, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, D.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Z.; Li, L.; Tian, Y.; Lu, Y.; Qiao, Y.; Li, J.; Wen, L. Improving low-pressure CO2 capture performance of N-doped active carbons by adjusting flow rate of protective gas during alkali activation. Carbon 2017, 114, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makal, T.A.; Li, J.-R.; Lu, W.; Zhou, H.-C. Methane storage in advanced porous materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 7761–7779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, D.; Li, F.; Liu, W. Methane adsorption study using activated carbon fiber and coal based activated carbon. China Pet. Process. Petrochem. Technol. 2013, 15, 20–25. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.E.; Lee, G.B.; Hwang, S.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Hong, B.U.; Kim, H.; Kim, S. The Effects of Methane Storage Capacity Using Upgraded Activated Carbon by KOH. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Im, J.S.; Jung, M.J.; Lee, Y.-S. Effects of fluorination modification on pore size controlled electrospun activated carbon fibers for high capacity methane storage. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 339, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano-Castello, D.; Cazorla-Amorós, D.; Linares-Solano, A. Powdered Activated Carbons and Activated Carbon Fibers for Methane Storage: A Comparative Study. Energy Fuels 2002, 16, 1321–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.; Wang, W.; Zhang, X. Experimental measurements and computer simulation of methane adsorption on activated carbon fibers. Carbon 2007, 45, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, F.E.C.; Yusof, N.; Hasbullah, H.; Jaafar, J.; Ismail, A.F.; Nasri, N.S. Physicochemical properties and methane adsorption performance of activated carbon nanofibers with different types of metal oxides. Carbon Lett. 2017, 24, 82–89. [Google Scholar]
- Guerrero-Fajardo, C.A.; Giraldo, L.; Moreno-Piraján, J.C. Preparation and Characterization of Graphene Oxide for Pb(II) and Zn(II) Ions Adsorption from Aqueous Solution: Experimental, Thermodynamic and Kinetic Study. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Zheng, Z.; Lin, K.; Luan, J.; Zhang, J. Adsorption of p-nitrophenol from aqueous solutions onto activated carbon fiber. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 143, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Activation | Sample Name | PAN to Graphene Ratio | PAN wt. (g) | Graphene wt. (g) | Graphene |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prior | NF | - | 4 | - | - |
| GRHA/NF | 100:1 | 4 | 0.04 | GRHA | |
| rGO/NF | 100:1 | 4 | 0.04 | rGO | |
| After | ACNF | - | 4 | - | - |
| GRHA/ACNF | 100:1 | 4 | 0.04 | GRHA | |
| rGO/ACNF | 100:1 | 4 | 0.04 | rGO |
| Samples | SSA (m2/g) | TPV (cm3/g) | Vmicro (cm3/g) | DPAve (nm) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prior activation | NF | 17.1723 | 0.1364 | −0.0064 * | 31.7692 |
| rGO/NF | 10.2330 | 0.0737 | −0.0008 | 28.8255 | |
| GRHA/NF | 17.8035 | 0.1423 | −0.0072 | 31.9677 | |
| After activation | ACNF | 137.0900 | 0.0807 | 0.0534 | 2.3559 |
| rGO/ACNF | 205.3000 | 0.1665 | 0.0825 | 3.2884 | |
| GRHA/ACNF | 384.6500 | 0.1785 | 0.1580 | 1.8564 |
| Materials | SSA (m2/g) | TPV (cm3/g) | Vol. of CH4 adsorbed (mmol/g) | Temp; Pressure | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACNF | 137 | 0.0807 | 20.84 | 25 °C; 4 bar | This work |
| rGO/ACNF | 205 | 0.1665 | 40.52 | 25 °C; 4 bar | |
| GRHA/ACNF | 384 | 0.1785 | 44.32 | 25 °C; 4 bar | |
| GRHA/ACNF | 384 | 0.1785 | 58.94 | 25 °C; 8 bar | |
| GRHA/ACNF | 384 | 0.1785 | 66.40 | 25 °C; 12 bar | |
| ACF-K2CO3 | 2500 | 0.8 | 191.3 V/V | 25 °C; 35 bar | [56] |
| ACF | 1965 | 0.41 | 7.40 | 25 °C; 40 bar | [57] |
| ACF-NH3 | 1795 | 1.0231 | 8.45 | 25 °C; 55 bar | [54] |
| ACF | 1511 | - | 9.83 wt% | 25 °C; 18 bar | [58] |
| MgO/ACNF | 1893 | 0.6212 | 2.37 | 25 °C; 3.5 bar | [59] |
| MnO2/ACNF | 431 | 0.1861 | 1.35 | 25 °C; 3.5 bar | |
| ACNF | 478 | 0.2097 | 1.42 | 25 °C; 3.5 bar |
| Sample | Pressure (bar) | qe, exp (mmol/g) | Pseudo-First Order | Pseudo-Second Order | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1 | R2 | k2 | R2 | |||
| ACNF | 4 | 20.87 | 0.1382 | 0.7004 | 0.0791 | 0.9262 |
| rGO/ACNF | 40.52 | 0.2209 | 0.7679 | 0.3785 | 0.9685 | |
| GRHA/ACNF | 44.33 | 0.1645 | 0.7299 | 0.1765 | 0.9737 | |
| ACNF | 8 | 23.67 | 0.1102 | 0.8773 | 0.0408 | 0.8184 |
| rGO/ACNF | 49.88 | 0.1202 | 0.8577 | 0.0385 | 0.8048 | |
| GRHA/ACNF | 58.94 | 0.1577 | 0.9369 | 0.0619 | 0.8780 | |
| ACNF | 12 | 26.32 | 0.1495 | 0.8817 | 0.0358 | 0.0911 |
| rGO/ACNF | 51.76 | 0.1869 | 0.7677 | 0.0737 | 0.1325 | |
| GRHA/ACNF | 66.40 | 0.1246 | 0.8054 | 0.0415 | 0.7875 | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Che Othman, F.E.; Yusof, N.; Yub Harun, N.; Bilad, M.R.; Jaafar, J.; Aziz, F.; Wan Salleh, W.N.; Ismail, A.F. Novel Activated Carbon Nanofibers Composited with Cost-Effective Graphene-Based Materials for Enhanced Adsorption Performance toward Methane. Polymers 2020, 12, 2064. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12092064
Che Othman FE, Yusof N, Yub Harun N, Bilad MR, Jaafar J, Aziz F, Wan Salleh WN, Ismail AF. Novel Activated Carbon Nanofibers Composited with Cost-Effective Graphene-Based Materials for Enhanced Adsorption Performance toward Methane. Polymers. 2020; 12(9):2064. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12092064
Chicago/Turabian StyleChe Othman, Faten Ermala, Norhaniza Yusof, Noorfidza Yub Harun, Muhammad Roil Bilad, Juhana Jaafar, Farhana Aziz, Wan Norharyati Wan Salleh, and Ahmad Fauzi Ismail. 2020. "Novel Activated Carbon Nanofibers Composited with Cost-Effective Graphene-Based Materials for Enhanced Adsorption Performance toward Methane" Polymers 12, no. 9: 2064. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12092064
APA StyleChe Othman, F. E., Yusof, N., Yub Harun, N., Bilad, M. R., Jaafar, J., Aziz, F., Wan Salleh, W. N., & Ismail, A. F. (2020). Novel Activated Carbon Nanofibers Composited with Cost-Effective Graphene-Based Materials for Enhanced Adsorption Performance toward Methane. Polymers, 12(9), 2064. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12092064











