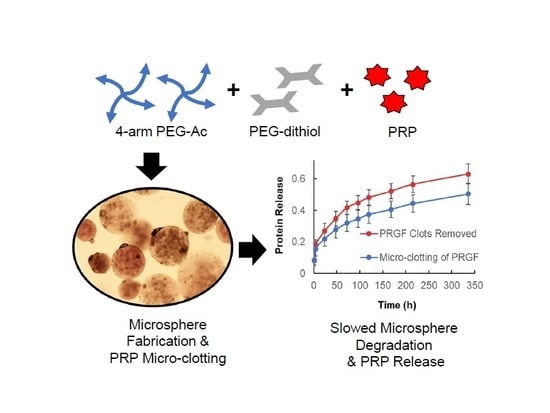
Micro-Clotting of Platelet-Rich Plasma Upon Loading in Hydrogel Microspheres Leads to Prolonged Protein Release and Slower Microsphere Degradation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
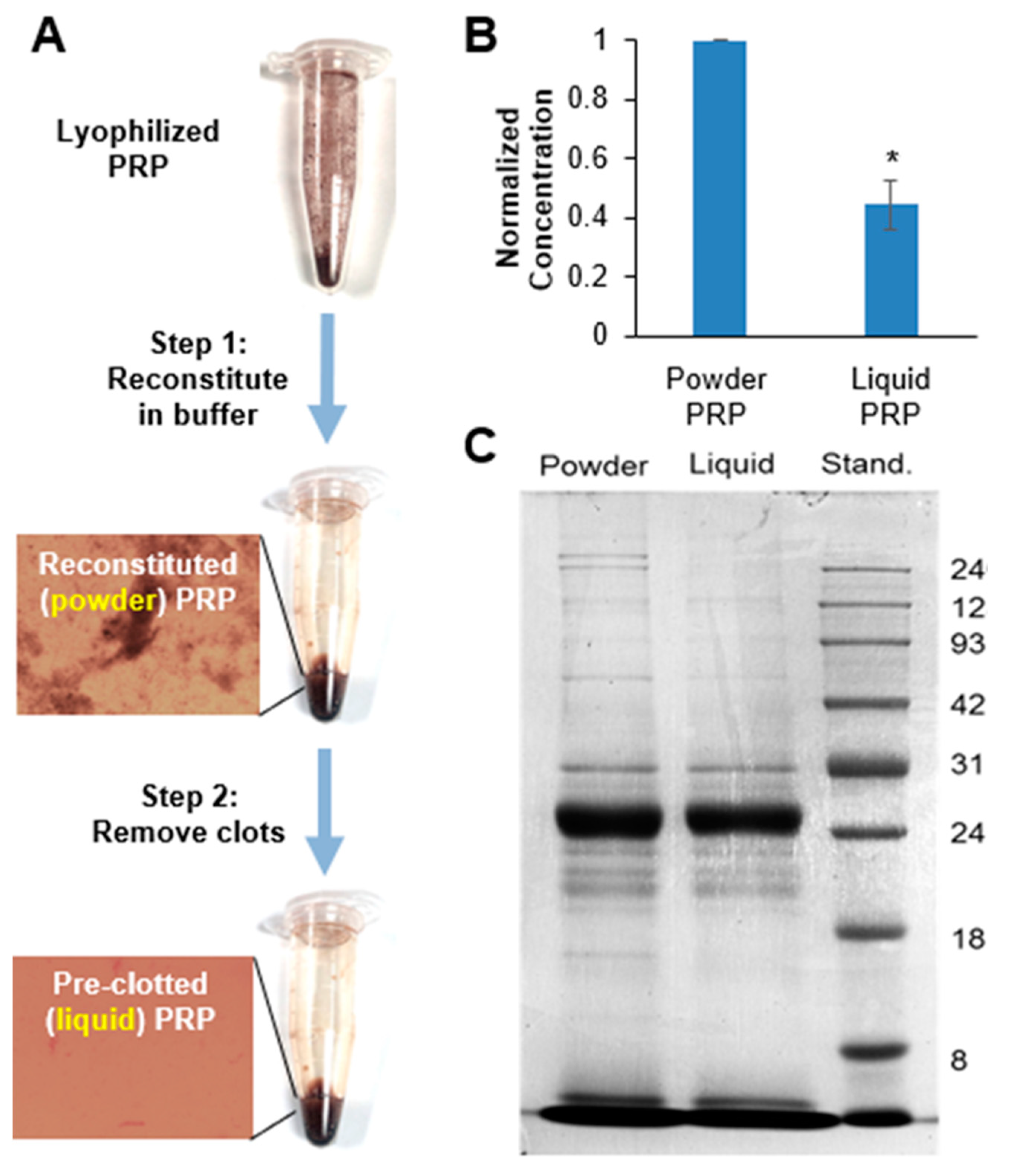
2.2. Platelet-Rich Plasma Preparation
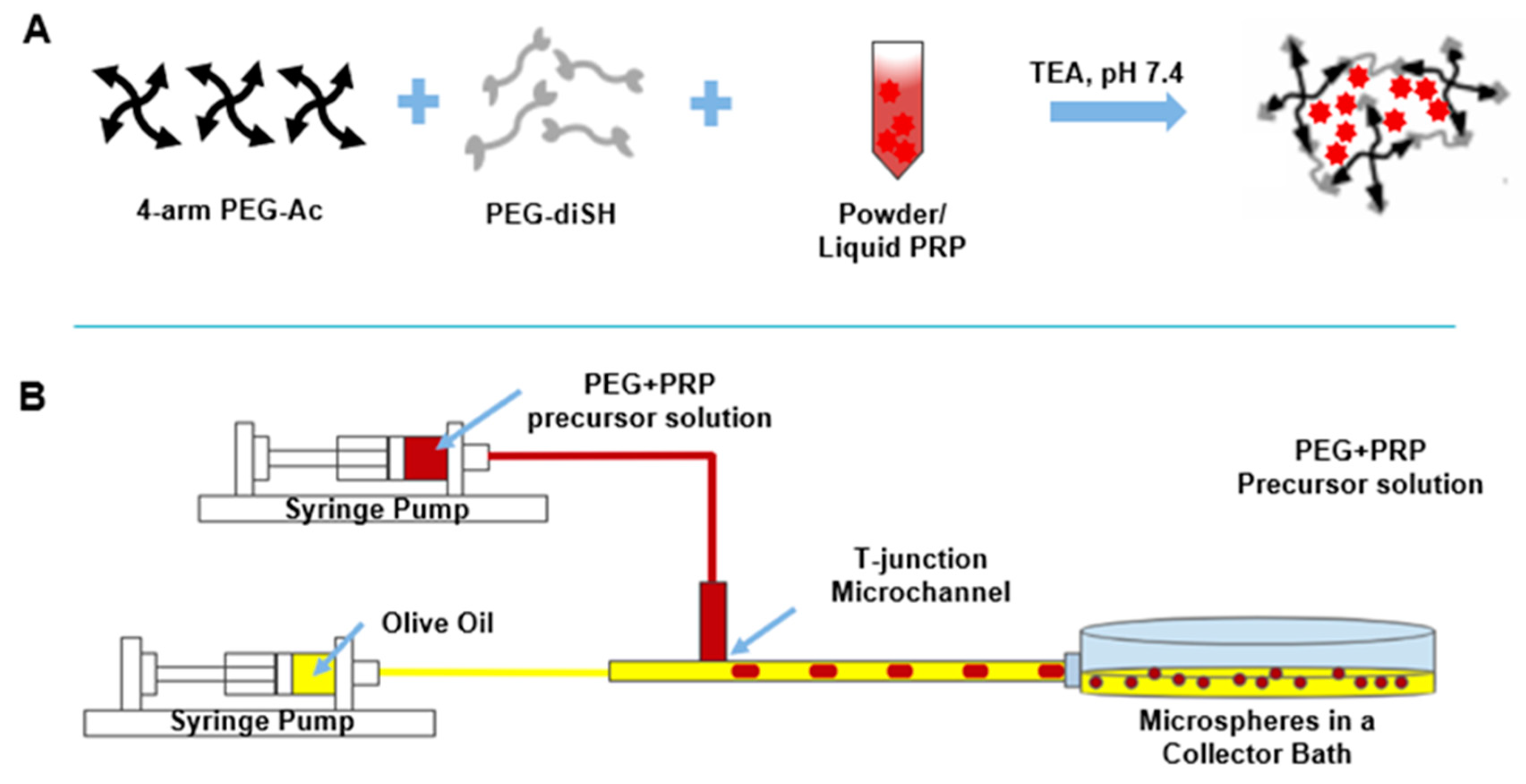
2.3. PRP-Loaded PEG Microsphere Fabrication Via Microfluidics
2.4. PRP Loading Efficiency
2.5. Characterization of Microsphere Diameter and Degradation via Microscopy
2.6. Rheology
2.7. Characterization of PRP Release from PEG Microspheres
2.8. In Vivo PRP-Loaded Microsphere Degradation
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
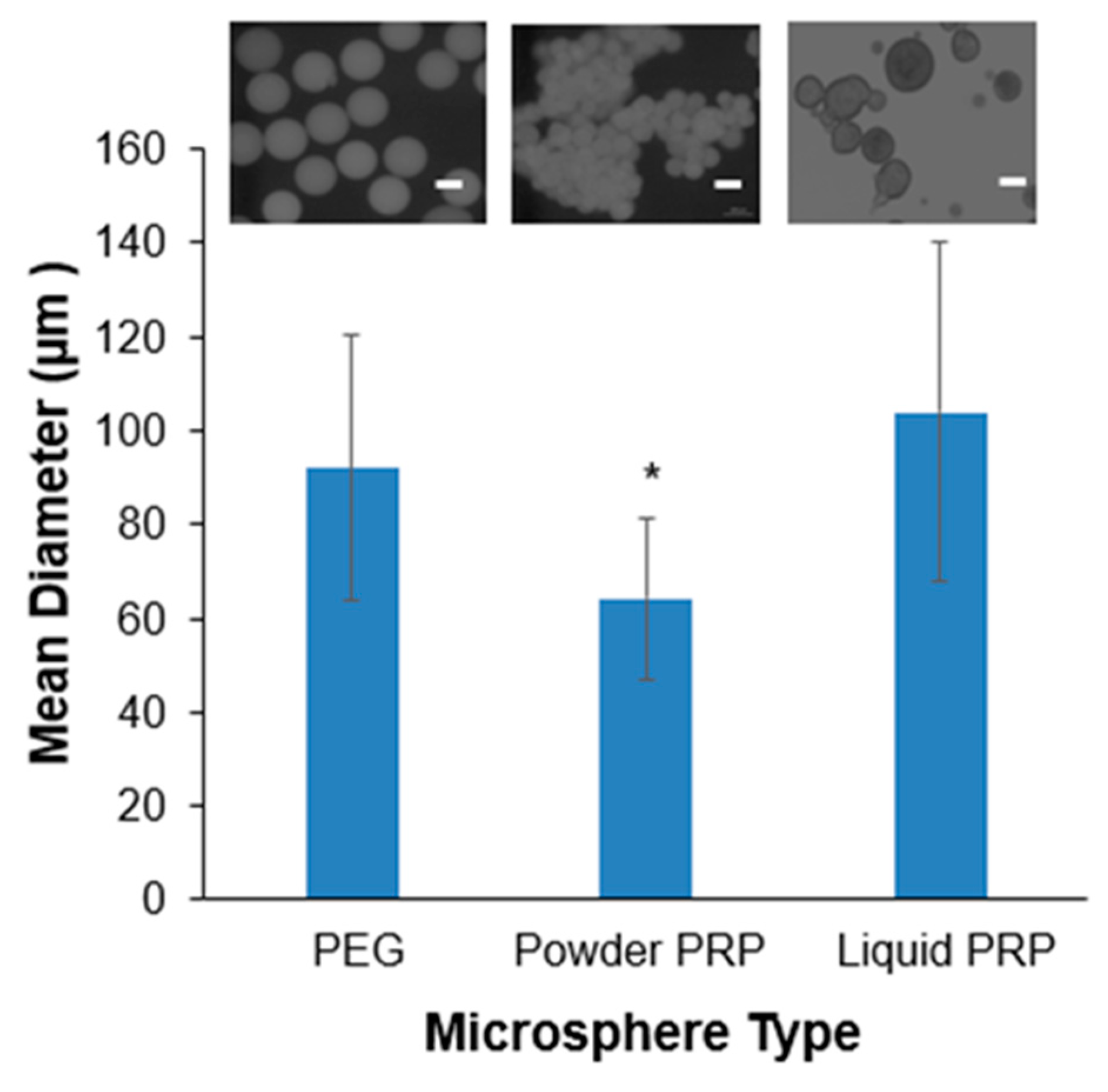
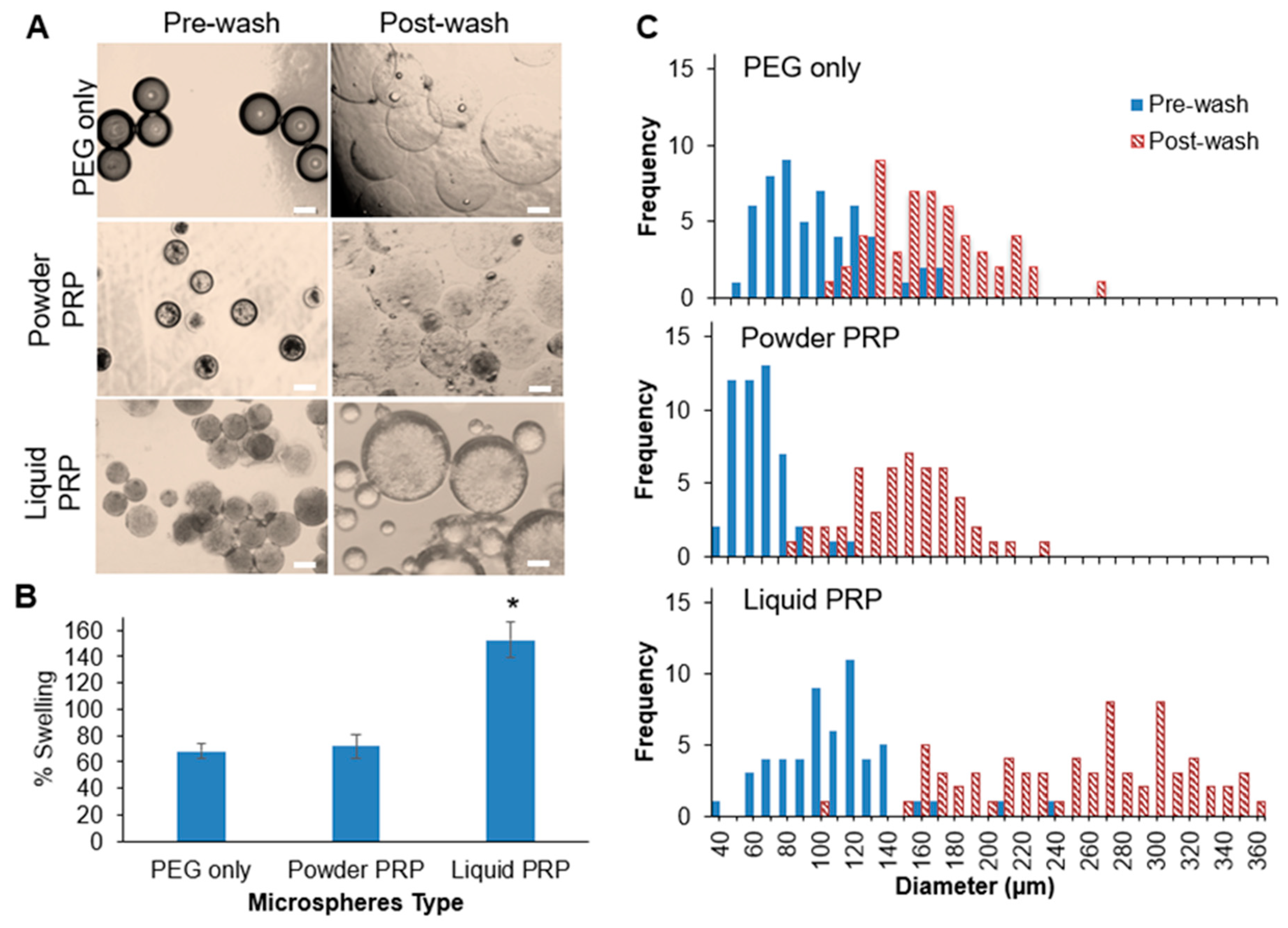
3.1. PRP-Loaded Microspheres Fabrication via Microfluidics
3.2. Microspheres Swelling and Modulus as a Function of PRP Loading
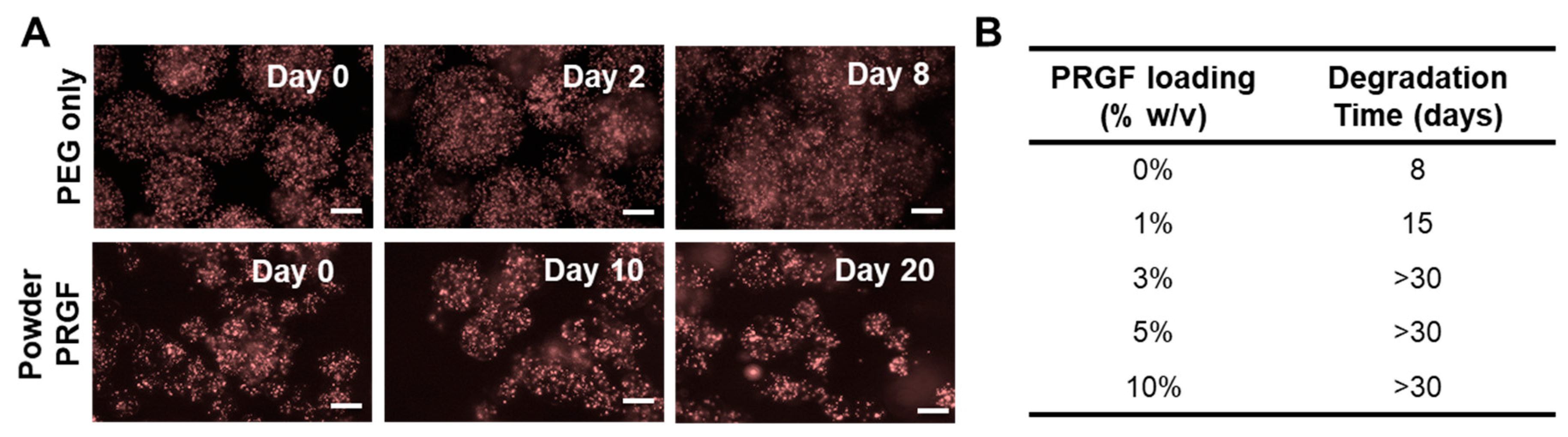
3.3. Microsphere Degradation in Vitro and in Vivo as a Function of PRP Loading
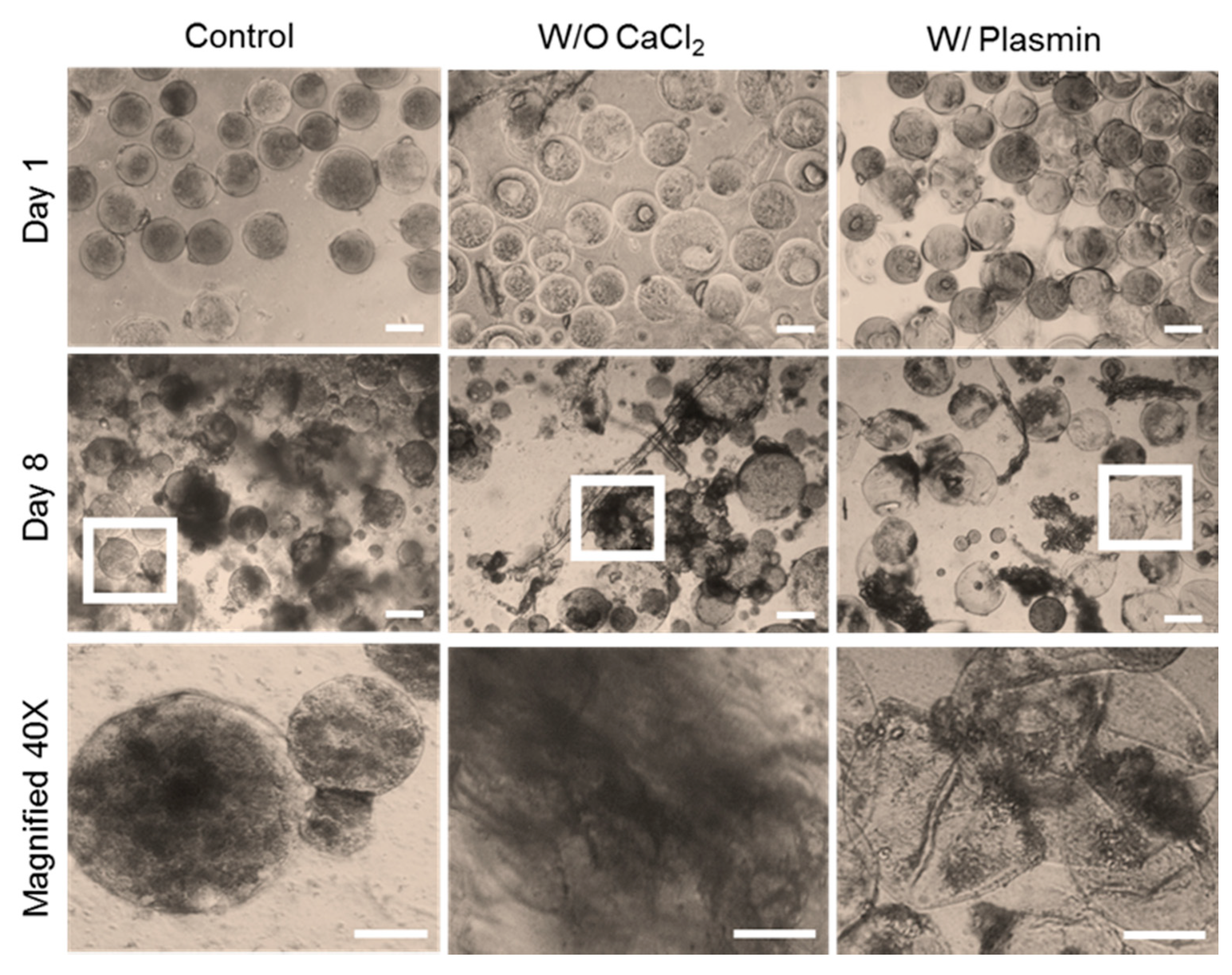
3.4. Effect of PRP Micro-Clotting on PRP-Loaded PEG Microsphere Degradation
3.5. PRP Release from Liquid and Powder PRP-Loaded PEG Microspheres
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Andia, I.; Sánchez, M.; Maffulli, N. Joint pathology and platelet-rich plasma therapies. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2012, 12, 7–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, T.E.; Puskas, B.L.; Mandelbaum, B.R.; Gerhardt, M.B.; Rodeo, S.A. Platelet-rich plasma: From basic science to clinical applications. Am. J. Sports Med. 2009, 37, 2259–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Yuan, M.; Meng, H.Y.; Wang, A.Y.; Guo, Q.Y.; Wang, Y.; Peng, J. Basic science and clinical application of platelet-rich plasma for cartilage defects and osteoarthritis: A review. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2013, 21, 1627–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saucedo, J.M.; Yaffe, M.A.; Berschback, J.C.; Hsu, W.K.; Kalainov, D.M. Platelet-rich plasma. J. Hand Surg. Am. 2012, 37, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Zhang, C.; Tuan, R.S. Biology of prp and its clinical application.pdf. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2014, 16, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boswell, S.G.; Cole, B.J.; Sundman, E.A.; Karas, V.; Fortier, L.A. Platelet-rich plasma: A milieu of bioactive factors. Arthrosc. J. Arthrosc. Relat. Surg. 2012, 28, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, E.; Chinzei, N.; Blanco, A.; Case, N.; Sandell, L.J.; Sell, S.; Rai, M.F.; Zustiak, S.P. Platelet-Rich Plasma Released From Polyethylene Glycol Hydrogels Exerts Beneficial Effects on Human Chondrocytes. J. Orthop. Res.® 2019, 37, 2401–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, E.; Sheth, S.; Dunn, A.; Zustiak, S.P.; Sell, S.A. Sustained release of multicomponent platelet-rich plasma proteins from hydrolytically degradable PEG hydrogels. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2017, 105, 3304–3314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.H.; Vo, J.M.; Chin, H.S.; Lin, J.; Cozin, M.; Tsay, R.; Eisig, S.; Landesberg, R. Controlled delivery of platelet-rich plasma-derived growth factors for bone formation. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2008, 86, 1128–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzocca, A.D.; McCarthy, M.B.R.; Chowaniec, D.M.; Cote, M.P.; Romeo, A.A.; Bradley, J.P.; Arciero, R.A.; Beitzel, K. Platelet-rich plasma differs according to preparation method and human variability. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2012, 94, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Dhillon, M.S.; Aggarwal, S.; Marwaha, N.; Jain, A. Treatment with platelet-rich plasma is more effective than placebo for knee osteoarthritis: A prospective, double-blind, randomized trial. Am. J. Sports Med. 2013, 41, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, R.P.; Apostolakos, J.; Hirose, T.; Cote, M.P.; Mazzocca, A.D. Variability of platelet-rich plasma preparations. Sports Med. Arthrosc. Rev. 2013, 21, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chahla, J.; Cinque, M.E.; Piuzzi, N.S.; Mannava, S.; Geeslin, A.G.; Murray, I.R.; Dornan, G.J.; Muschler, G.F.; LaPrade, R.F. A Call for Standardization in Platelet-Rich Plasma Preparation Protocols and Composition Reporting: A Systematic Review of the Clinical Orthopaedic Literature. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2017, 99, 1769–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khiste, S.V.; Naik Tari, R. Platelet-rich fibrin as a biofuel for tissue regeneration. ISRN Biomater. 2013, 2013, 627367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutlu, B.; Tiğlı Aydın, R.S.; Akman, A.C.; Gümüşderelioglu, M.; Nohutcu, R.M. Platelet-rich plasma-loaded chitosan scaffolds: Preparation and growth factor release kinetics. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2013, 101, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hokugo, A.; Ozeki, M.; Kawakami, O.; Sugimoto, K.; Mushimoto, K.; Morita, S.; Tabata, Y. Augmented bone regeneration activity of platelet-rich plasma by biodegradable gelatin hydrogel. Tissue Eng. 2005, 11, 1224–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notodihardjo, P.V.; Morimoto, N.; Kakudo, N.; Matsui, M.; Sakamoto, M.; Liem, P.H.; Suzuki, K.; Tabata, Y.; Kusumoto, K. Gelatin hydrogel impregnated with platelet-rich plasma releasate promotes angiogenesis and wound healing in murine model. J. Artif. Organs 2015, 18, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourcho, A.M.; Smith, J.; Wisniewski, S.J.; Sellon, J.L. Intraarticular platelet-rich plasma injection in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: Review and recommendations. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2014, 93, S108–S121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suthar, M.; Gupta, S.; Bukhari, S.; Ponemone, V. Treatment of chronic non-healing ulcers using autologous platelet rich plasma: A case series. J. Biomed. Sci. 2017, 24, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagae, M.; Ikeda, T.; Mikami, Y.; Hase, H.; Ozawa, H.; Matsuda, K.-I.; Sakamoto, H.; Tabata, Y.; Kawata, M.; Kubo, T. Intervertebral disc regeneration using platelet-rich plasma and biodegradable gelatin hydrogel microspheres. Tissue Eng. 2007, 13, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, M.; Takahashi, K.; Arai, E.; Inoue, A.; Sakao, K.; Tonomura, H.; Honjo, K.; Nakagawa, S.; Inoue, H.; Tabata, Y. Intra-articular administration of platelet-rich plasma with biodegradable gelatin hydrogel microspheres prevents osteoarthritis progression in the rabbit knee. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2009, 27, 201. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.-T.; Chang, W.-T.; Tsai, M.-L.; Chen, C.-H.; Chen, W.-Y.; Mi, F.-L. Development of injectable fucoidan and biological macromolecules hybrid hydrogels for intra-articular delivery of platelet-rich plasma. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, Y.; Ueda, M.; Naiki, T.; Takahashi, M.; Hata, K.-I.; Nagasaka, T. Autogenous injectable bone for regeneration with mesenchymal stem cells and platelet-rich plasma: Tissue-engineered bone regeneration. Tissue Eng. 2004, 10, 955–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salamanna, F.; Veronesi, F.; Maglio, M.; Della Bella, E.; Sartori, M.; Fini, M. New and emerging strategies in platelet-rich plasma application in musculoskeletal regenerative procedures: General overview on still open questions and outlook. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 846045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zustiak, S.P.; Leach, J.B. Hydrolytically degradable poly (ethylene glycol) hydrogel scaffolds with tunable degradation and mechanical properties. Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 1348–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, E.; Hill, L.; Canning, E.; Sell, S.A.; Zustiak, S.P. Control of gelation, degradation and physical properties of polyethylene glycol hydrogels through the chemical and physical identity of the crosslinker. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 2679–2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zustiak, S.P.; Boukari, H.; Leach, J.B. Solute diffusion and interactions in cross-linked poly (ethylene glycol) hydrogels studied by fluorescence correlation spectroscopy. Soft Matter 2010, 6, 3609–3618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, E.; Scott, K.M.; Zustiak, S.P.; Sell, S.A. Fabrication of Polyethylene Glycol-Based Hydrogel Microspheres Through Electrospraying. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2015, 300, 823–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, M.D.; Scott, E.A.; Elbert, D.L. Factors affecting size and swelling of poly (ethylene glycol) microspheres formed in aqueous sodium sulfate solutions without surfactants. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 5283–5291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritger, P.L.; Peppas, N.A. A simple equation for description of solute release I. Fickian and non-fickian release from non-swellable devices in the form of slabs, spheres, cylinders or discs. J. Control. Release 1987, 5, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zustiak, S.P.; Leach, J.B. Characterization of protein release from hydrolytically degradable poly (ethylene glycol) hydrogels. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2011, 108, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezihe-Ejiofor, J.A.; Hutchinson, N. Anticlotting mechanisms 1: Physiology and pathology. Contin. Educ. Anaesth. Crit. Care Pain 2013, 13, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyoda, T.; Isobe, K.; Tsujino, T.; Koyata, Y.; Ohyagi, F.; Watanabe, T.; Nakamura, M.; Kitamura, Y.; Okudera, H.; Nakata, K.; et al. Direct activation of platelets by addition of CaCl2 leads coagulation of platelet-rich plasma. Int. J. Implant Dent. 2018, 4, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, K.A.; Saltzman, B.M.; Mascarenhas, R.; Khair, M.M.; Verma, N.N.; Bach, B.R., Jr.; Cole, B.J. Does Intra-articular Platelet-Rich Plasma Injection Provide Clinically Superior Outcomes Compared With Other Therapies in the Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis? A Systematic Review of Overlapping Meta-analyses. Arthroscopy 2015, 31, 2213–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, G.; Hua, S.; Yang, T.; Ma, J.; Yu, W.; Chen, X. Platelet-rich plasma shows beneficial effects for patients with knee osteoarthritis by suppressing inflammatory factors. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 15, 3096–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duncanson, W.J.; Lin, T.; Abate, A.R.; Seiffert, S.; Shah, R.K.; Weitz, D.A. Microfluidic synthesis of advanced microparticles for encapsulation and controlled release. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 2135–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maham, A.; Tang, Z.; Wu, H.; Wang, J.; Lin, Y. Protein-based nanomedicine platforms for drug delivery. Small (Weinh. Bergstr. Ger.) 2009, 5, 1706–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deveza, L.; Ashoken, J.; Castaneda, G.; Tong, X.; Keeney, M.; Han, L.-H.; Yang, F. Microfluidic Synthesis of Biodegradable Polyethylene-Glycol Microspheres for Controlled Delivery of Proteins and DNA Nanoparticles. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2015, 1, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulina López-Juárez, B.; Alberto García-Ramírez, M.; Pérez-Luna, V.H.; Gonzalez-Reynoso, O. Formation of PEG-DA polymerized microparticles by different microfluidics devices: A T-junction device and a flow focusing device. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 13, 374–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baret, J.C. Surfactants in droplet-based microfluidics. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 422–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imaninezhad, M.; Hill, L.; Kolar, G.; Vogt, K.; Zustiak, S.P. Templated Macroporous Polyethylene Glycol Hydrogels for Spheroid and Aggregate Cell Culture. Bioconjugate Chem. 2018, 30, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoare, T.R.; Kohane, D.S. Hydrogels in drug delivery: Progress and challenges. Polymer 2008, 49, 1993–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Mooney, D.J. Designing hydrogels for controlled drug delivery. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2016, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.; Chen, T.T.; Iruela-Arispe, M.L.; Wu, B.M.; Dunn, J.C. Modulation of protein delivery from modular polymer scaffolds. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 1862–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaharwar, A.K.; Rivera, C.P.; Wu, C.-J.; Schmidt, G. Transparent, elastomeric and tough hydrogels from poly (ethylene glycol) and silicate nanoparticles. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 4139–4148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zustiak, S.P.; Durbal, R.; Leach, J.B. Influence of cell-adhesive peptide ligands on poly (ethylene glycol) hydrogel physical, mechanical and transport properties. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 3404–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chehreghanianzabi, Y.; Zustiak, S.P. Study of polyethylene glycol-fluorophore complex formation by fluorescence correlation spectroscopy. Macromol. Res. 2016, 24, 995–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veronese, F.M.; Pasut, G. PEGylation, successful approach to drug delivery. Drug Discov. Today 2005, 10, 1451–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.C.; Anseth, K.S. PEG hydrogels for the controlled release of biomolecules in regenerative medicine. Pharm. Res. 2009, 26, 631–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larraneta, E.; Stewart, S.; Ervine, M.; Al-Kasasbeh, R.; Donnelly, R.F. Hydrogels for Hydrophobic Drug Delivery. Classification, Synthesis and Applications. J. Funct. Biomater. 2018, 9, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, M.H.; Blanco, A.; Stealey, S.; Duan, X.; Case, N.; Sell, S.A.; Rai, M.F.; Zustiak, S.P. Micro-Clotting of Platelet-Rich Plasma Upon Loading in Hydrogel Microspheres Leads to Prolonged Protein Release and Slower Microsphere Degradation. Polymers 2020, 12, 1712. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12081712
Choi MH, Blanco A, Stealey S, Duan X, Case N, Sell SA, Rai MF, Zustiak SP. Micro-Clotting of Platelet-Rich Plasma Upon Loading in Hydrogel Microspheres Leads to Prolonged Protein Release and Slower Microsphere Degradation. Polymers. 2020; 12(8):1712. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12081712
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Miran Hannah, Alexandra Blanco, Samuel Stealey, Xin Duan, Natasha Case, Scott Allen Sell, Muhammad Farooq Rai, and Silviya Petrova Zustiak. 2020. "Micro-Clotting of Platelet-Rich Plasma Upon Loading in Hydrogel Microspheres Leads to Prolonged Protein Release and Slower Microsphere Degradation" Polymers 12, no. 8: 1712. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12081712
APA StyleChoi, M. H., Blanco, A., Stealey, S., Duan, X., Case, N., Sell, S. A., Rai, M. F., & Zustiak, S. P. (2020). Micro-Clotting of Platelet-Rich Plasma Upon Loading in Hydrogel Microspheres Leads to Prolonged Protein Release and Slower Microsphere Degradation. Polymers, 12(8), 1712. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12081712