Generation of Core–Sheath Polymer Nanofibers by Pressurised Gyration
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Solution Preparation and Characterisation
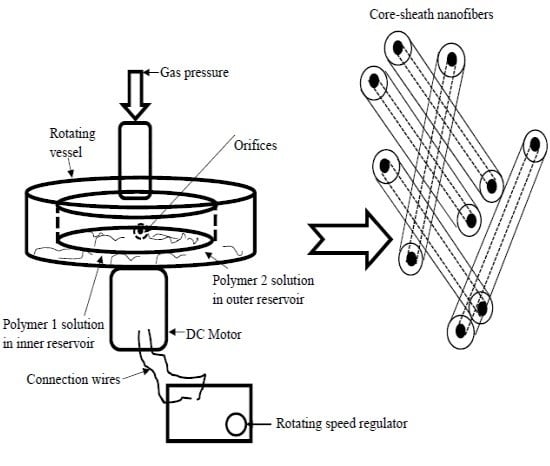
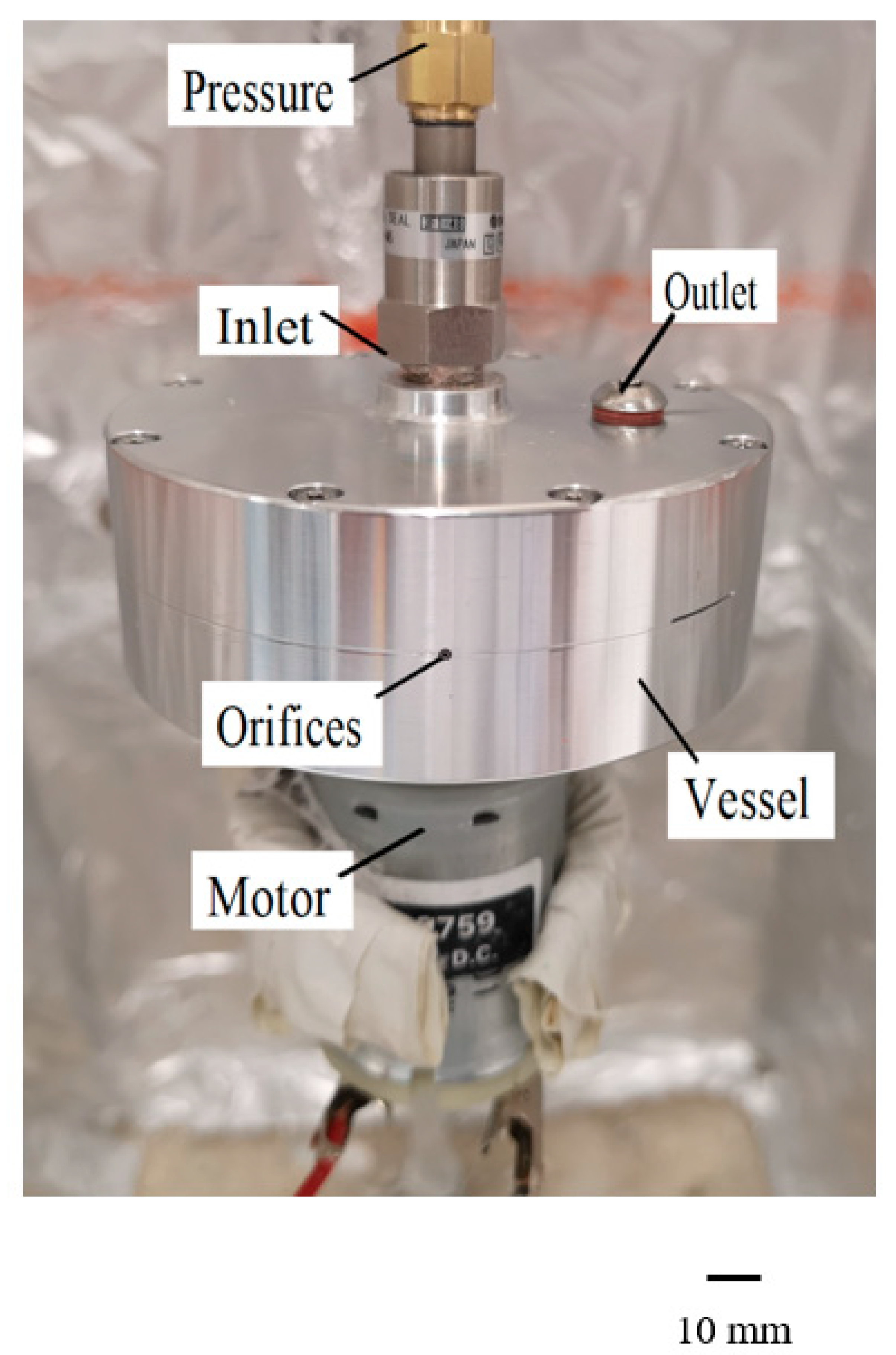
2.3. Experimental Set-Up
2.4. Core–Sheath Fibre Preparation
2.5. Characterisation of Core–Sheath Fibres
3. Results and Discussion
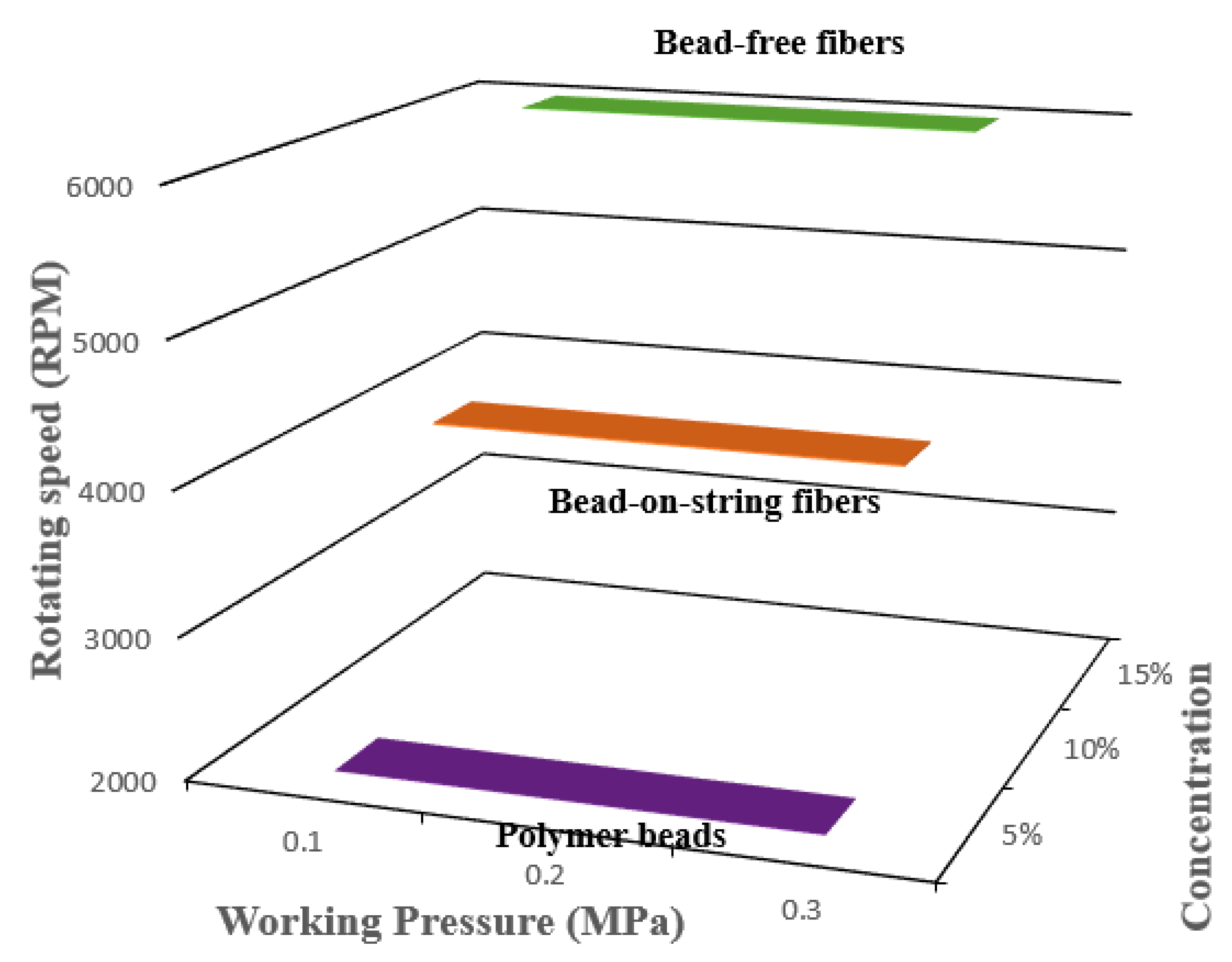
3.1. Effect of the Polymer Solution’s Physical Properties on Formability
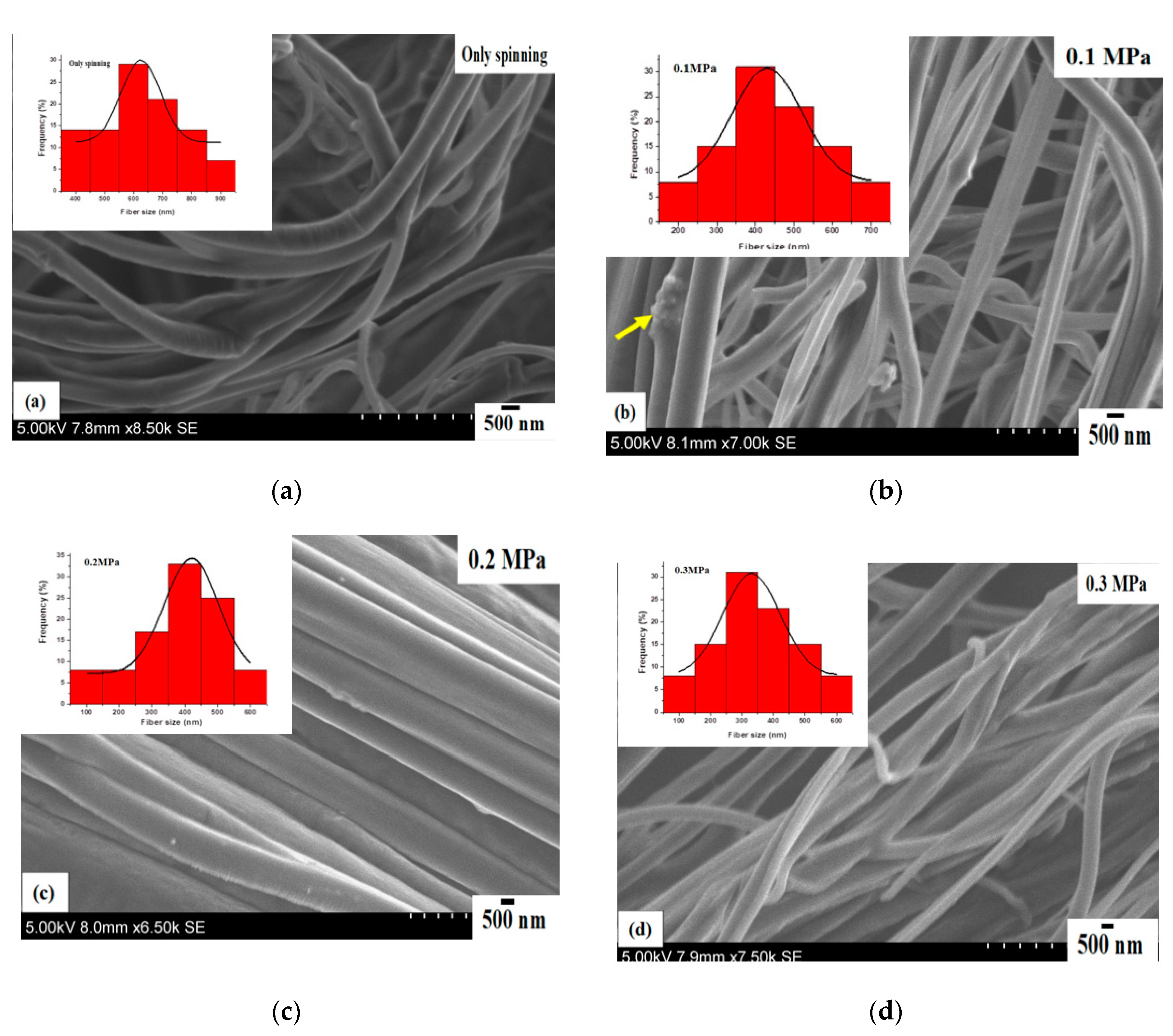
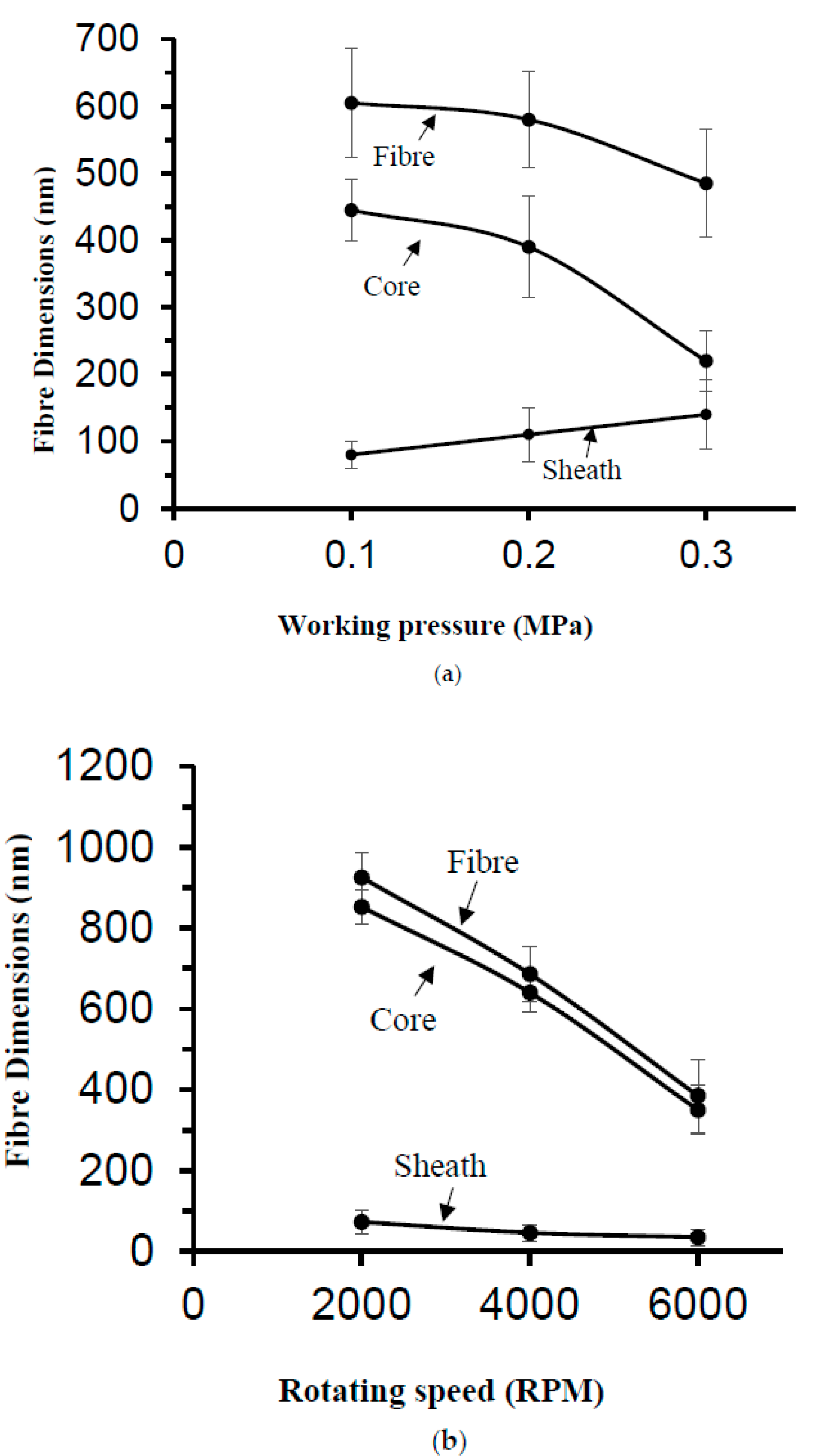
3.2. Effect of Working Pressure on Fibre Morphology
3.3. Effect of Working Pressure on Fibre Size and Size Distribution
3.4. Yield of the Core–Sheath Nanofibers
3.5. Applications of Water-Soluble Polymers
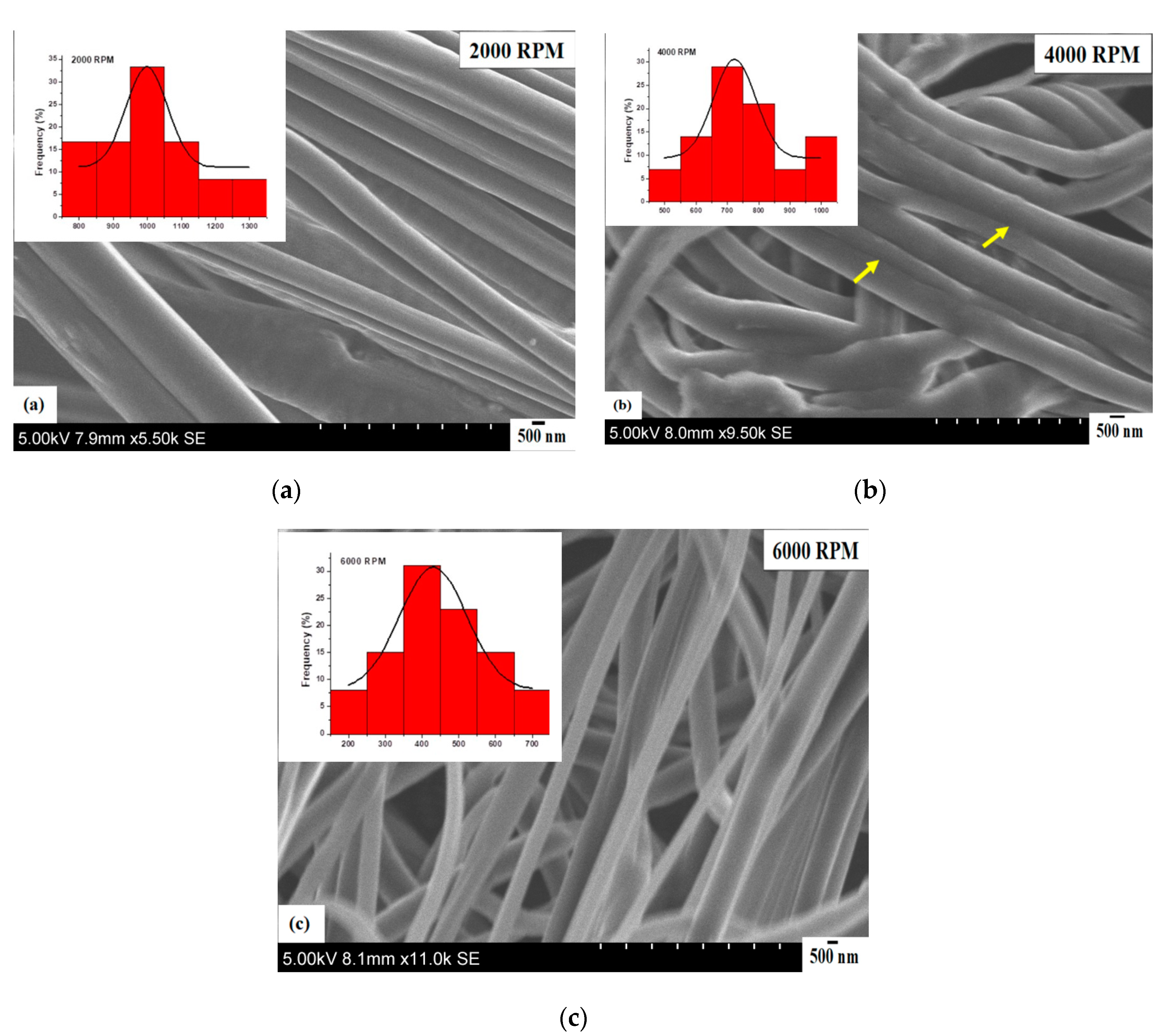
3.6. Effect of Rotating Speed on Fibre Morphology, Fibre Size and Size Distribution
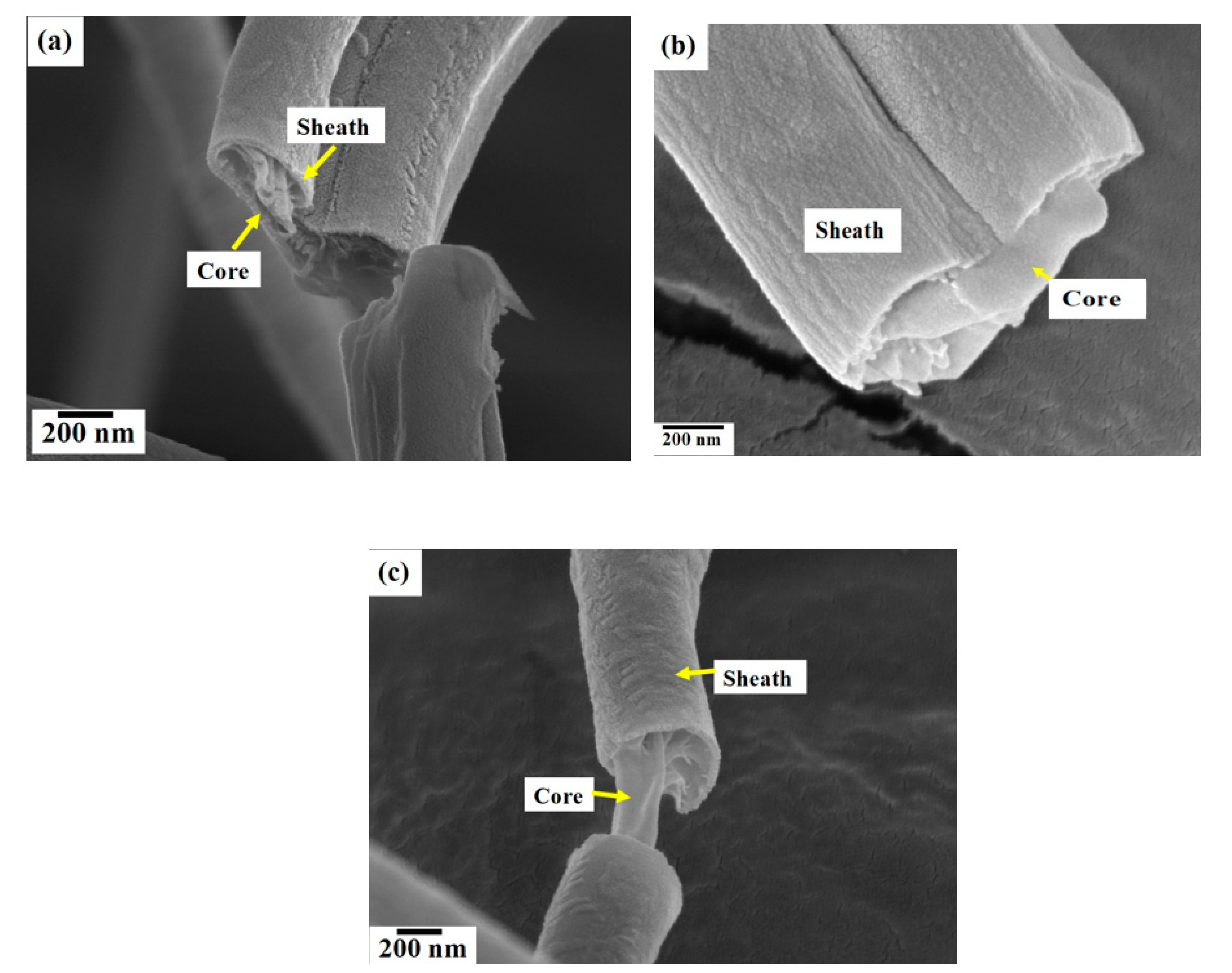
3.7. Focused Ion Beam Imaging and Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cleeton, C.; Keirouz, A.; Chen, X.; Radacsi, N. Electrospun Nanofibers for Drug Delivery and Biosensing. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 5, 4183–4205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, R.; Zhao, J.; Li, B.; Cai, P.; Loh, X.J.; Xu, C.; Chen, P.; Kai, D.; Zheng, L. Implantable and degradable antioxidant poly(ε-caprolactone)-lignin nanofiber membrane for effective osteoarthritis treatment. Biomaterials 2020, 230, 119601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattarai, R.S.; Bachu, R.D.; Boddu, S.H.S.; Bhaduri, S. Biomedical Applications of Electrospun Nanofibers: Drug and Nanoparticle Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Homaeigohar, S.; Boccaccini, A.R. Antibacterial biohybrid nanofibers for wound dressings. Acta Biomater. 2020, 107, 25–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, Y.; Ge, J.; Wang, M.; Chen, M.; Niu, W.; Cheng, W.; Xue, Y.; Lin, C.; Lei, B. Bioactive Anti-inflammatory, Antibacterial, Antioxidative Silicon-Based Nanofibrous Dressing Enables Cutaneous Tumor Photothermo-Chemo Therapy and Infection-Induced Wound Healing. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 2904–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celebioglu, A.; Uyar, T. Fast Dissolving Oral Drug Delivery System Based on Electrospun Nanofibrous Webs of Cyclodextrin/Ibuprofen Inclusion Complex Nanofibers. Mol. Pharm. 2019, 16, 4387–4398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, N.; Yu, C.; Jiao, L.; Chen, J. MnFe2O4@C Nanofibers as High-Performance Anode for Sodium-Ion Batteries. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 3321–3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solaberrieta, I.; Jimenez, A.; Cacciotti, I.; Garrigos, M.C. Encapsulation of bioactive compounds from aloe vera agrowastes in electrospun poly (ethylene oxide) nanofibers. Polymers 2020, 12, 1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.; Delaney, M.; Frey, M. Anti-Escherichia coli functionalized silver-doped carbon nanofibers for capture of E. coli in microfluidic. Polymers 2020, 12, 1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abudula, T.; Gauthaman, K.; Hammad, A.H.; Navare, K.J.; Alshahrie, A.A.; Bencherif, S.A.; Tamayol, A.; Memic, A. Oxygen-releasing antibacterial nanofibrous scaffolds for tissue engineering applications. Polymers 2020, 12, 1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghe, A.K.; Gupta, B.S. Co-axial electrospinning for nanofiber structures: Preparation and applications. Polym. Rev. 2008, 48, 353–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeimirad, M.; Zadhoush, A.; Kotek, R.; Neisiany, R.M.; Khorasani, S.N.; Ramakrishna, S. Recent advances in core/shell bicomponent fibers and nanofibers: A. review. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 46265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borah, R.; Ingavle, G.C.; Sandeman, S.R.; Kumar, A.; Mikhalovsky, S.V. Amine-Functionalized Electrically Conductive Core-Sheath MEH-PPV: PCL Electrospun Nanofibers for Enhanced Cell-Biomaterial Interactions. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 4, 3327–3346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, E.M.; Yang, L.; Ye, C.Y.; Zhang, W.; Ran, J.S.; Xue, D.T.; Wang, Z.K.; Pan, Z.L.; Hu, Q.L. An asymmetric chitosan scaffold for tendon tissue engineering: In vitro and In Vivo evaluation with rat tendon stem/progenitor cells. Acta Biomater. 2018, 73, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Steckl, A.J. Selective pH-Responsive Core Sheath Nanofiber Membranes for Chem/Bio/Med Applications: Targeted Delivery of Functional Molecules. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 42653–42660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuysinuan, P.; Pengsuk, C.; Lirdprapamongkol, K.; Techasakul, S.; Svasti, J.; Nooeaid, P. Enhanced Structural Stability and Controlled Drug Release of Hydrophilic Antibiotic-Loaded Alginate/Soy Protein Isolate Core-Sheath Fibers for Tissue Engineering Applications. Fibers Polym. 2019, 20, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekh, M.I.; Patel, K.P.; Patel, R.M. Electrospun ZnO Nanoparticles Doped Core-Sheath Nanofibers: Characterization and Antimicrobial Properties. J. Polym. Environ. 2018, 26, 4376–4387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoes, M.C.R.; Cragg, S.M.; Barbu, E.; De Sousa, F.B. The potential of electrospun poly (methyl methacrylate)/polycaprolactone core-sheath fibers for drug delivery applications. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 5712–5725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, X.; Qu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, Q. Photothermally Activated Electrospun Nanofiber Mats for High-Efficiency Surface-Mediated Gene Transfection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 7905–7914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankar, S.S.; Karthick, K.; Sangeetha, K.; Karmakar, A.; Kundu, S. Transition-Metal-Based Zeolite Imidazolate Framework Nanofibers via an Electrospinning Approach: A Review. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, S.; John, J.V.; McCarthy, A.; Xie, J. New forms of electrospun nanofiber materials for biomedical applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 3733–3746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doostmohammadi, M.; Forootanfar, H.; Ramakrishna, S. Regenerative medicine and drug delivery: Progress via electrospun biomaterials. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 109, 110521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahalingam, S.; Edirisinghe, M. Forming of Polymer Nanofibers by a Pressurised Gyration Process. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2013, 34, 1134–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alenezi, H.; Cam, M.E.; Edirisinghe, M. Experimental and theoretical investigation of the fluid behaviour during polymeric fiber formation with and without pressure. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2019, 6, 041401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.Q.; Karaca, B.T.; VanOosten, S.K.; Yuca, E.; Mahalingam, S.; Edirisinghe, M.; Tamerler, C. Coupling Infusion and Gyration for the Nanoscale Assembly of Functional Polymer Nanofibers Integrated with Genetically Engineered Proteins. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2015, 36, 1322–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, X.Z.; Mahalingam, S.; Edirisinghe, M. Simultaneous Application of Pressure-Infusion-Gyration to Generate Polymeric Nanofibers. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2017, 302, 1600564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Z.W.; Mahalingam, S.; Basnett, P.; Raimi-Abraham, B.; Roy, I.; Craig, D.; Edirisinghe, M. Making Nonwoven Fibrous Poly(epsilon-caprolactone) Constructs for Antimicrobial and Tissue Engineering Applications by Pressurized Melt Gyration. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2016, 301, 922–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahalingam, S.; Homer-Vanniasinkam, S.; Edirisinghe, M. Novel pressurised gyration device for making core-sheath polymer fibres. Mater. Des. 2019, 178, 107846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illangakoon, U.E.; Mahalingam, S.; Matharu, R.K.; Edirisinghe, M. Evolution of surface nanopores in pressurised gyrospun polymeric microfibers. Polymers 2017, 9, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, X.Z.; Mahalingam, S.; Edirisinghe, M. Bead, beaded-fibres, and fibres: Tailoring the morphology of poly(caprolactone) using pressurised gyration. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 69, 1373–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raimi-Abraham, B.T.; Mahalingam, S.; Edirisinghe, M.; Craig, D.Q.M. Generation of poly (N-vinylprrolidone) nanofibers using pressurised gyration. Mater. Sci. Eng C 2014, 39, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, C.J.; Stoyanov, S.D.; Stride, E.; Pelan, E.; Edirisinghe, M. Electrospinning versus fibre production methods: From specifics to technological convergence. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 4708–4735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malkan, S.R. An overview of spun-bonding and melt-blowing technologies. Tappi J. 1995, 78, 185–190. [Google Scholar]
- Mahalingam, S.; Raimi-Abraham, B.T.; Craig, D.Q.M.; Edirisinghe, M. Solubility-spinnability map and model for the preparation of fibres of polyethylene (terephthalate) using gyration and pressure. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 280, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kadajji, V.W.; Betageri, G.V. Water-soluble polymers for pharmaceutical applications. Polymers 2011, 3, 1972–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanda, T.; Kitawaki, M.; Arata, T.; Matsuki, Y.; Fujiwara, T. Structural analysis of cross-linked poly(vinyl alcohol) using high-field DNP-NMR. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 8039–8043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noreen, A.; Zia, K.M.; Tabasum, S.; Khalid, S.; Shareef, R. A review on grafting of hydroxyethylene cellulose for versatile applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 150, 289–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mahalingam, S.; Huo, S.; Homer-Vanniasinkam, S.; Edirisinghe, M. Generation of Core–Sheath Polymer Nanofibers by Pressurised Gyration. Polymers 2020, 12, 1709. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12081709
Mahalingam S, Huo S, Homer-Vanniasinkam S, Edirisinghe M. Generation of Core–Sheath Polymer Nanofibers by Pressurised Gyration. Polymers. 2020; 12(8):1709. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12081709
Chicago/Turabian StyleMahalingam, Suntharavathanan, Suguo Huo, Shervanthi Homer-Vanniasinkam, and Mohan Edirisinghe. 2020. "Generation of Core–Sheath Polymer Nanofibers by Pressurised Gyration" Polymers 12, no. 8: 1709. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12081709
APA StyleMahalingam, S., Huo, S., Homer-Vanniasinkam, S., & Edirisinghe, M. (2020). Generation of Core–Sheath Polymer Nanofibers by Pressurised Gyration. Polymers, 12(8), 1709. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12081709