Bio-Based Epoxy Shape-Memory Thermosets from Triglycidyl Phloroglucinol
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of Triglycidyl Phlroglucinol Derivative
2.3. Preparation of Curing Mixtures
2.4. Thermal Characterization
2.5. Thermomechanical and Mechanical Characterization
2.6. Shape-Memory Properties Characterization
3. Results
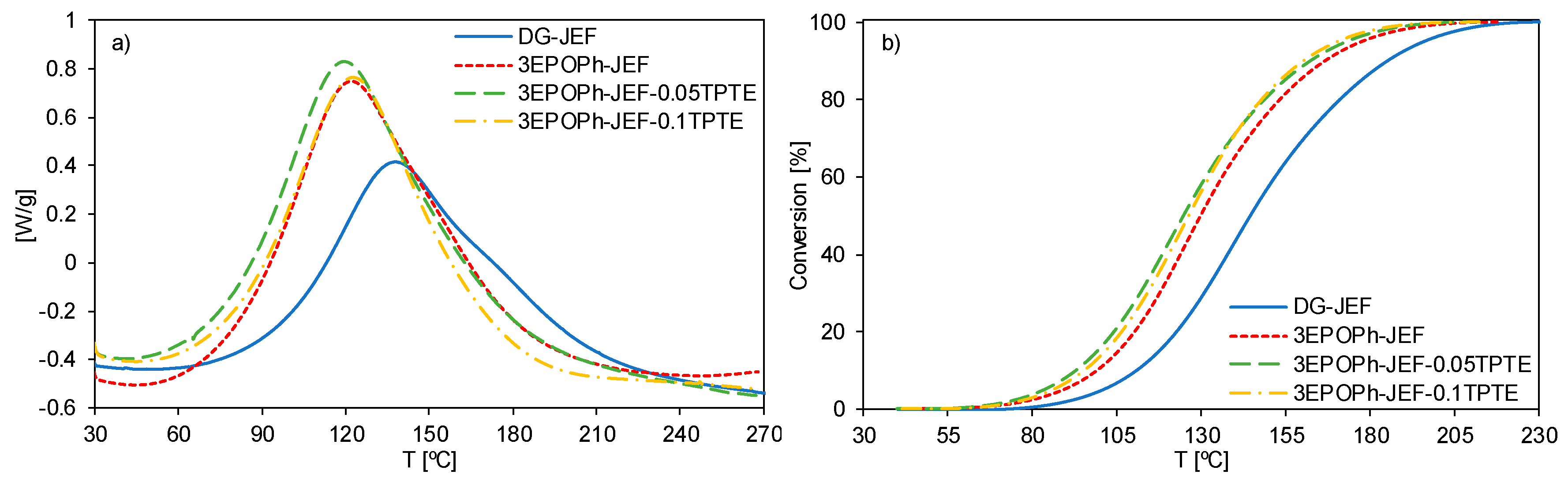
3.1. Thermal Characterization
3.2. Thermomechanical Characterization
3.3. Mechanical Characterization
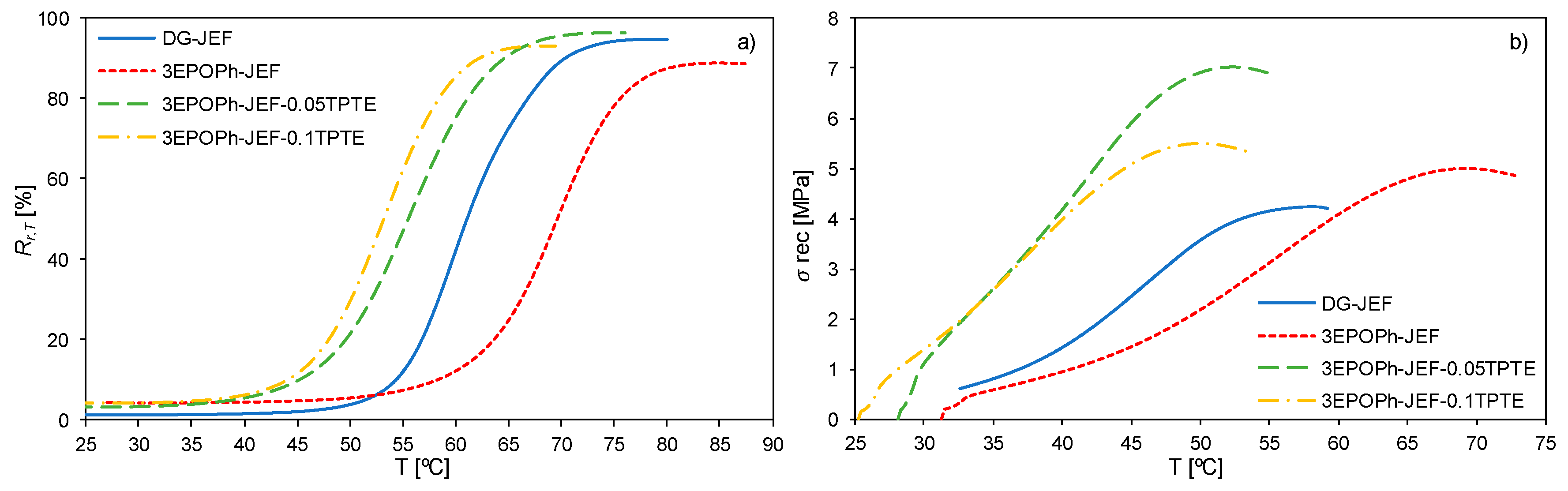
3.4. Shape-Memory Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Behl, M.; Lendlein, A. Shape-memory polymers. Mater. Today 2007, 10, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habault, D.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, Y. Light-triggered self-healing and shape-memory polymers. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 7244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Kong, D.; Ao, X.; Xiao, X. Electroactive High-Temperature Shape Memory Polymers with High Recovery Stress Induced by Ground Carbon Fibers. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2019, 220, 1900164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohr, R.; Kratz, K.; Weigel, T.; Lucka-Gabor, M.; Moneke, M.; Lendlein, A. Initiation of shape-memory effect by inductive heating of magnetic nanoparticles in thermoplastic polymers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 13, 3540–3545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Qin, H.; Mather, P.T. Review of progress in shape-memory polymers. J. Mater. Chem. 2007, 17, 1543–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousseau, I.A. Challenges of shape memory polymers: A review of the progress toward overcoming SMP’s limitations. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhosh Kumar, K.S.; Biju, R.; Reghunadhan Nair, C.P. Progress in shape memory epoxy resins. React. Func. Polym. 2013, 73, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karger-Kocsis, J.; Kéki, S. Review of progress in shape memory epoxies and their composites. Polymers 2017, 10, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, C. Epoxy Resins: Chemistry and Technology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, F.; Couture, G.; Philippe, C.; Boutevin, B.; Caillol, S. Bio-based aromatic epoxy monomers for thermoset materials. Molecules 2017, 22, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadam, A.; Pawar, M.; Yemul, O.; Thamke, V.; Kodam, K. Biodegradable biobased epoxy resin from karanja oil. Polymer 2015, 72, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, S.K.; Mohanty, S.; Nayak, S.K. Synthesis and characterization of bio-based epoxy blends from renewable resource based epoxidized soybean oil as reactive diluent. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2015, 33, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francucci, G.; Cardona, F.; Manthey, N.W. Cure kinetics of an acrylated epoxidized hemp oil-based bioresin system. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 128, 2030–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auvergne, R.; Caillol, S.; David, G.; Boutevin, B.; Pascault, J.P. Biobased thermosetting epoxy: Present and future. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 1082–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voirin, C.; Caillol, S.; Sadavarte, N.V.; Tawade, B.V.; Boutevin, B.; Wadgaonkar, P.P. Functionalization of cardanol: Towards biobased polymers and additives. Polym. Chem. 2014, 5, 3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salanti, A.; Zoia, L.; Simonutti, R.; Orlandi, M. Epoxidized lignin derivatives as bio-based crosslinkers used in the preparation of epoxy resins. BioResources 2018, 13, 2374–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Liu, X.; Jiang, Y.; Ma, S.; Zhu, J. Bio-based shape memory epoxy resin synthesized from rosin acid. Iran. Polym. J. 2016, 25, 957–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benyahya, S.; Aouf, C.; Caillol, S.; Boutevin, B.; Pascault, J.P.; Fulcrand, H. Functionalized green tea tannins as phenolic prepolymers for bio-based epoxy resins. Ind. Crops Prod. 2014, 53, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapi, Z. Synthesis and characterization of biobased epoxy monomers derived from d-glucose. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 67, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Wang, J.; Kou, Y.; Pang, H.; Zhang, S.; Li, N.; Liu, C.; Weng, Z.; Jian, X. Synthesis of an aromatic N-heterocycle derived from biomass and its use as a polymer feedstock. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Weng, Z.; Zhang, K.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; Liu, C.; Jian, X. Magnolol-based bio-epoxy resin with acceptable glass transition temperature, processability and flame retardancy. Chem. Eng. 2020, 387, 124115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Dai, J.; Liu, X.; Jiang, Y.; Ma, S.; Zhu, J. Green Synthesis of a Bio-Based Epoxy Curing Agent from Isosorbide in Aqueous Condition and Shape Memory Properties Investigation of the Cured Resin. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2016, 217, 1439–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujimoto, T.; Takeshita, K.; Uyama, H. Bio-based Epoxy Resins from Epoxidized Plant Oils and Their Shape Memory Behaviors. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2016, 93, 1663–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán, D.; Ramis, X.; Fernández-Francos, X.; De la Flor, S.; Serra, À. Preparation of new biobased coatings from a triglycidyl eugenol derivative through thiol-epoxy click reaction. Prog. Org. Coat. 2018, 114, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán, D.; Serra, À.; Ramis, X.; Fernández-Francos, X.; De la Flor, S. Fully renewable thermosets based on bis-eugenol prepared by thiol-click chemistry. React. Funct. Polym. 2019, 136, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago, D.; Guzmán, D.; Ramis, X.; Ferrando, F.; Serra, À. New Epoxy Thermosets Derived from Clove Oil Prepared by Epoxy-Amine Curing. Polymers 2019, 12, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán, D.; Santiago, D.; Serra, À.; Ferrando, F. Novel Bio-Based Epoxy Thermosets Based on Triglycidyl Phloroglucinol Prepared by Thiol-Epoxy Reaction. Polymers 2020, 12, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, M.T.H.; Bangoura, I.; Kang, J.Y.; Park, N.G.; Ahn, D.H.; Hong, Y.K. Distribution of phlorotannins in the brown alga Ecklonia cava and comparison of pretreatments for extraction. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2011, 14, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.Y.; Choi, H.; Jun, H.S. The effect of phloroglucinol, a component of ecklonia cava extract, on hepatic glucose production. Mar. Drugs. 2017, 15, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negrell, C.; Cornille, A.; de Andrade Nascimento, P.; Robin, J.J.; Caillol, S. New bio-based epoxy materials and foams from microalgal oil. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2017, 119, 1600214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noè, C.; Malburet, S.; Bouvet-Marchand, A.; Graillot, A.; Loubat, C.; Sangermano, M. Cationic photopolymerization of bio-renewable epoxidized monomers. Prog. Org. Coat. 2019, 133, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, F.; Bonnet, L.; David, G.; Caillol, S. Novel biobased and food contact epoxy coatings for glass toughening applications. Prog. Org. Coat. 2017, 109, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM E384-17. Standard Test Method for Microindentation Hardness of Materials; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2017.
- Yakacki, C.M.; Willis, S.; Luders, C.; Gall, K. Deformation limits in shape-memory polymers. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2008, 10, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldkamp, D.M.; Rousseau, I.A. Effect of the deformation temperature on the shape-memory behavior of epoxy networks. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2010, 295, 726–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago, D.; Fernández-Francos, X.; Ferrando, F.; De la Flor, S. Shape-memory effect in hyperbranched poly(ethyleneimine)-modified epoxy thermosets. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2015, 53, 924–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozenberg, B.A. Kinetics, thermodynamics and mechanism of reactions of epoxy oligomers with amines. Adv. Polym. Sci. 1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.L.; Kang, S.F.; Xu, X.J.; Xiao, F.; Ge, X.L. Effect of the crosslinking density and programming temperature on the shape fixity and shape recovery in epoxy-anhydride shape-memory polymers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landel, R.F.; Nielsen, L.E. Mechanical Properties of Polymers and Composites; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, T.; Rousseau, I.A. Facile tailoring of thermal transition temperatures of epoxy shape memory polymers. Polymer 2009, 50, 1852–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, M.J.; Choi, H.; Jang, H.; Yu, W.-R.; Park, M.; Kim, Y.; Park, J.K.; Youk, J.H. Preparation of epoxy-based shape memory polymers for deployable space structures using diglycidyl ether of ethoxylated bisphenol-A. J. Polym. Res. 2019, 26, 1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldkamp, D.M.; Rousseau, I.A. Effect of chemical composition on the deformability of shape-memory epoxies. Macrom. Mater. Eng. 2011, 296, 1128–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belmonte, A.; Guzmán, D.; Fernández-Francos, X.; De la Flor, S. Effect of the network structure and programming temperature on the shape-memory response of thiol-epoxy ‘click’ systems. Polymers 2015, 7, 2146–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belmonte, A.; Fernández-Francos, X.; De la Flor, S.; Serra, À. Network structure dependence on unconstrained isothermal-recovery processes for shape-memory thiol-epoxy ‘click’ systems. Mech. Time-Depend. Mater. 2017, 21, 133–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakacki, C.M.; Shandas, R.; Safranski, S.; Ortega, A.M.; Sassaman, K.; Gall, K. Strong, tailored, biocompatible shape-memory polymer networks. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2008, 18, 2428–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega, A.M.; Yakacki, C.M.; Dixon, S.A.; Likos, R.; Greenberg, A.R.; Gall, K. Effect of crosslinking and long-term storage on the shape-memory behavior of (meth)acrylate-based shape-memory polymers. Soft Matter. 2012, 8, 7381–7392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago, D.; Fabregat-Sanjuan, A.; Ferrando, F.; De la Flor, S. Recovery stress and work output in hyperbranched poly(ethyleneimine)-modified shape-memory epoxy polymers. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2016, 54, 1002–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belmonte, A.; Russo, C.; Ambrogi, V.; Fernández-Francos, X.; De la Flor, S. Epoxy-based shape-memory actuators obtained via dual-curing of off-stoichiometric ‘thiol-epoxy’ mixtures. Polymers 2017, 9, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Li, L.; Deng, X.Y.; Cheng, C.Y.; Yang, K.K.; Wang, Y.Z. Reinforcement of shape-memory poly(ethylene-co-vinyl acetate) by carbon fibre to access robust recovery capability under resistant condition. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2018, 157, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthamatten, M.; Cavicchi, K.; Li, G.; Wang, A. Cold, warm, and hot programming of shape memory polymers. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2016, 54, 1319–1339. [Google Scholar]
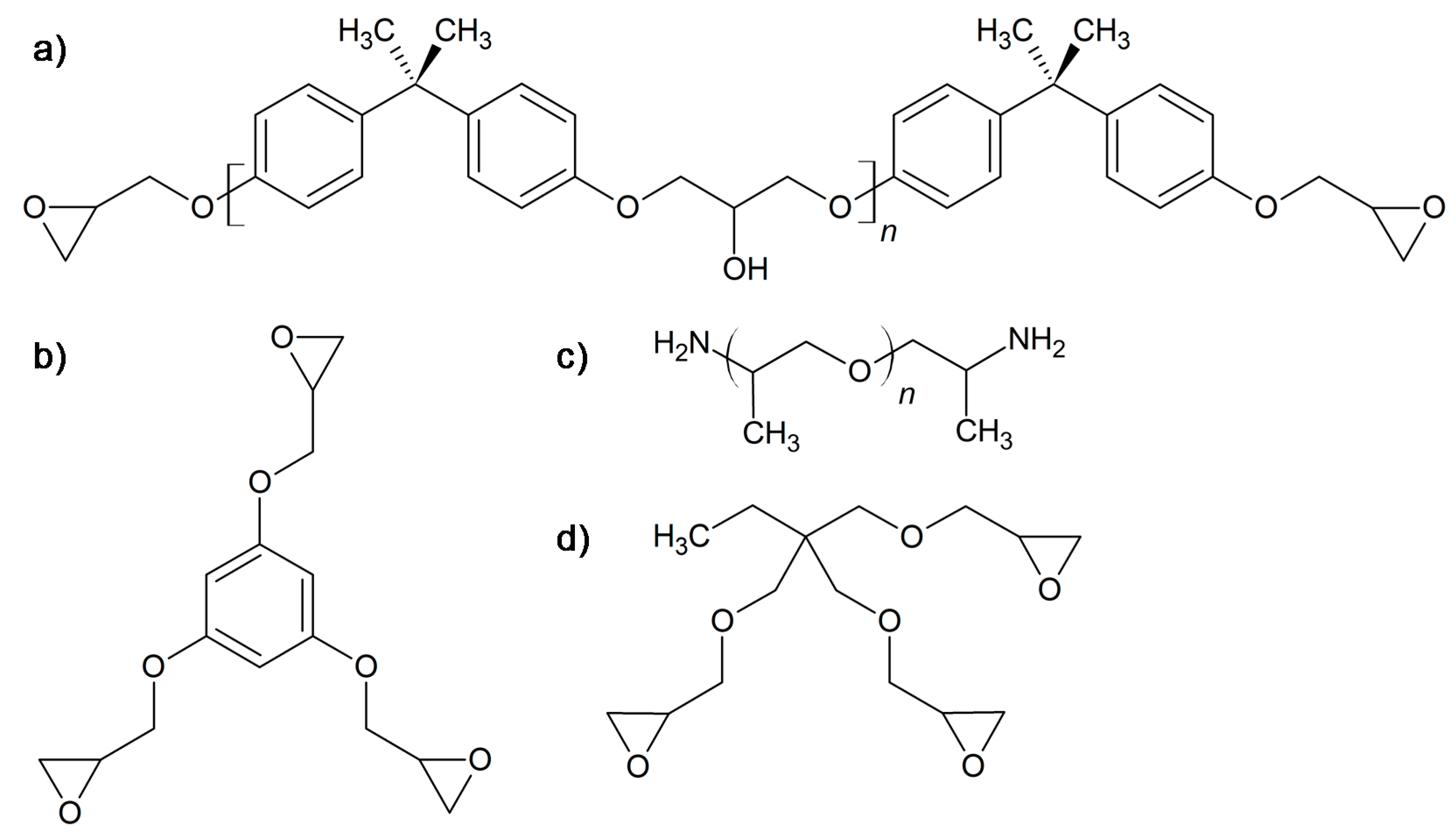




| Sample | DGEBA [wt. %] | 3EPOPh [wt. %] | TPTE [wt. %] | JEF [wt. %] | υc 1 [mol/g] | υe 2 [mol/g] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DG-JEF | 62.9 | 0 | 0 | 37.1 | 0.0017 | 0.0014 |
| 3EPOPh-JEF | 0 | 47.7 | 0 | 52.3 | 0.0024 | 0.0039 |
| 3EPOPh-JEF-0.05TPTE | 0 | 45.3 | 2.4 | 52.3 | 0.0024 | 0.0027 |
| 3EPOPh-JEF-0.1TPTE | 0 | 43.0 | 4.8 | 52.2 | 0.0024 | 0.0024 |
| Sample | Tpeak [°C] | ΔH [J/g] 1 | ΔH [kJ/eq] 2 | Tg [°C] 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DG-JEF | 140 | 386 | 112 | 56 |
| 3EPOPh-JEF | 124 | 488 | 100 | 61 |
| 3EPOPh-JEF-0.05TPTE | 121 | 504 | 105 | 48 |
| 3EPOPh-JEF-0.1TPTE | 125 | 429 | 88 | 34 |
| Sample | T5% [°C] 1 | Tmax [°C] 2 | Char Residue [%] |
|---|---|---|---|
| DG-JEF | 354 | 381 | 7.6 |
| 3EPOPh-JEF | 304 | 338 | 12.0 |
| 3EPOPh-JEF-0.05TPTE | 303 | 332 | 11.5 |
| 3EPOPh-JEF-0.1TPTE | 301 | 331 | 11.1 |
| Sample | Tg1 [°C] | TgE′2 [°C] | tan δ Peak | FWHM 3 [°C] | E′g4 [MPa] | E′r5 [MPa] | E′g/E′r |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DG-JEF | 65 | 57 | 1.5 | 10 | 2770 | 14 | 198 |
| 3EPOPh-JEF | 73 | 60 | 0.7 | 17 | 2942 | 39 | 75 |
| 3EPOPh-JEF-0.05TPTE | 63 | 49 | 0.9 | 18 | 2584 | 26 | 99 |
| 3EPOPh-JEF-0.1TPTE | 56 | 42 | 0.9 | 18 | 2460 | 23 | 107 |
| Sample | Troom | TgE′ | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| σb1 [MPa] | εb2 [%] | Micro-Indendation [HV] | E3 [MPa] | σb1 [MPa] | εb2 [%] | σmax4 [MPa] | εmax5 [%] | |
| DG-JEF | 30.0 | 10.7 | 5.4 ± 0.4 | 1318 | 6.0 | 63.3 | 4.5 | 46.8 |
| 3EPOPh-JEF | 28.0 | 3.2 | 8.7 ± 0.2 | 2222 | 8.2 | 27.1 | 6.1 | 16.0 |
| 3EPOPh-JEF-0.05TPTE | 27.7 | 10.4 | 5.8 ± 0.9 | 1592 | 11.7 | 36.8 | 8.7 | 25.5 |
| 3EPOPh-JEF-0.1TPTE | 27.0 | 29.8 | 4.1 ± 0.2 | 1372 | 9.7 | 37.9 | 7.3 | 27.0 |
| Sample | Rr [%] | Rf [%] | Vr [%/min] | σrec1 [MPa] | σrec/σmax2 [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DG-JEF | 94.6 | 98.8 | 19.8 | 4.3 | 94.2 |
| 3EPOPh-JEF | 88.7 | 95.7 | 15.3 | 5.0 | 83.7 |
| 3EPOPh-JEF-0.05TPTE | 96.2 | 96.6 | 16.8 | 7.0 | 80.8 |
| 3EPOPh-JEF-0.1TPTE | 93.1 | 95.6 | 18.4 | 5.5 | 75.2 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Santiago, D.; Guzmán, D.; Ferrando, F.; Serra, À.; De la Flor, S. Bio-Based Epoxy Shape-Memory Thermosets from Triglycidyl Phloroglucinol. Polymers 2020, 12, 542. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12030542
Santiago D, Guzmán D, Ferrando F, Serra À, De la Flor S. Bio-Based Epoxy Shape-Memory Thermosets from Triglycidyl Phloroglucinol. Polymers. 2020; 12(3):542. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12030542
Chicago/Turabian StyleSantiago, David, Dailyn Guzmán, Francesc Ferrando, Àngels Serra, and Silvia De la Flor. 2020. "Bio-Based Epoxy Shape-Memory Thermosets from Triglycidyl Phloroglucinol" Polymers 12, no. 3: 542. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12030542
APA StyleSantiago, D., Guzmán, D., Ferrando, F., Serra, À., & De la Flor, S. (2020). Bio-Based Epoxy Shape-Memory Thermosets from Triglycidyl Phloroglucinol. Polymers, 12(3), 542. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12030542








