Mechanical and Thermal Properties of All-Wood Biocomposites through Controllable Dissolution of Cellulose with Ionic Liquid
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
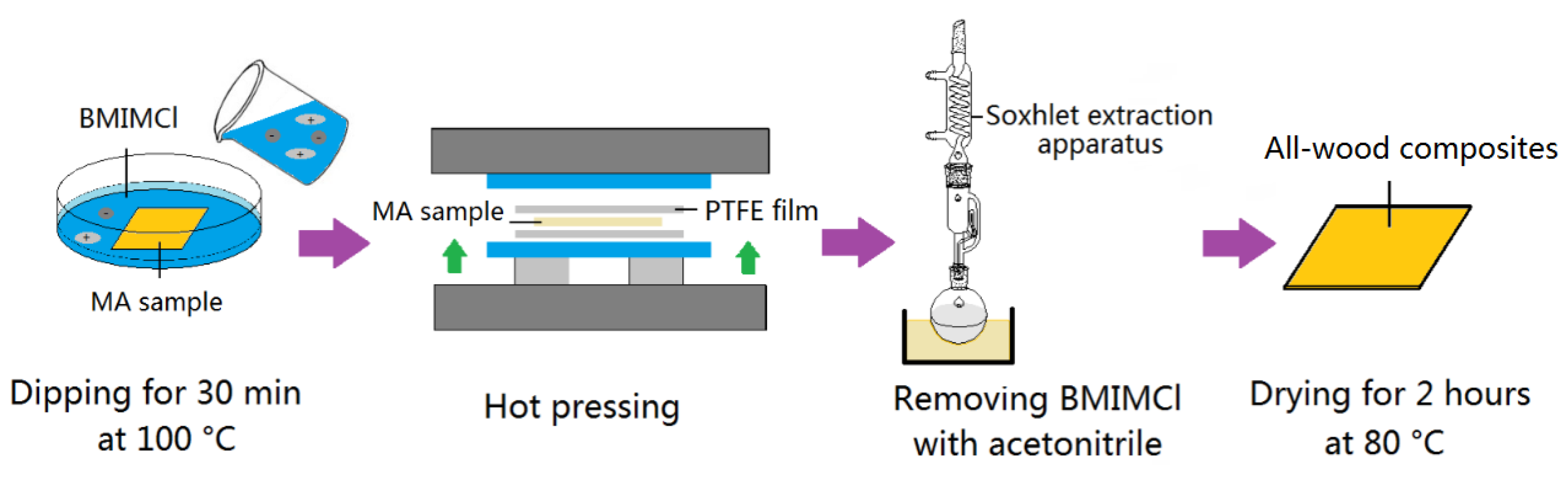
2.2. Preparation of the All-Wood Biocomposites
2.3. Characterization
2.3.1. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Study
2.3.2. X-ray Diffraction Analysis
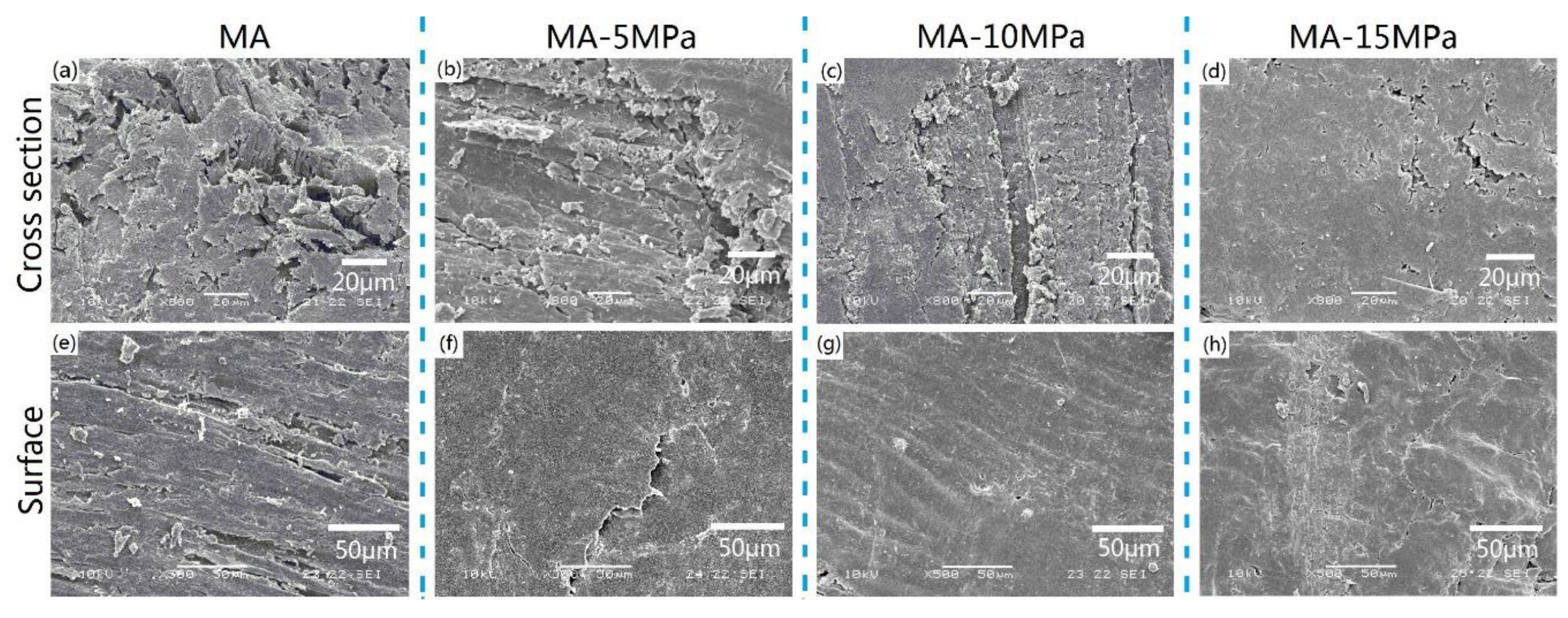
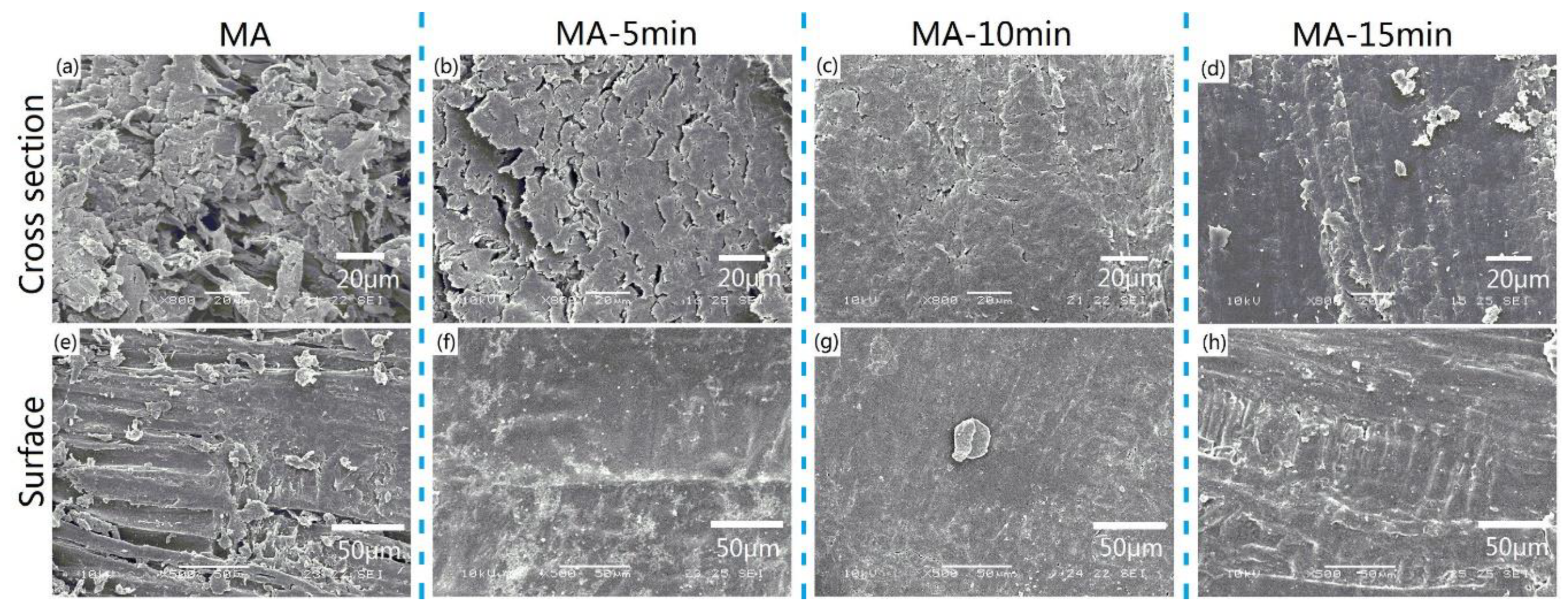
2.3.3. Scanning Electron Microscope
2.3.4. Thermal Gravimetric Analysis
2.3.5. Mechanical Properties
3. Results and Discussion
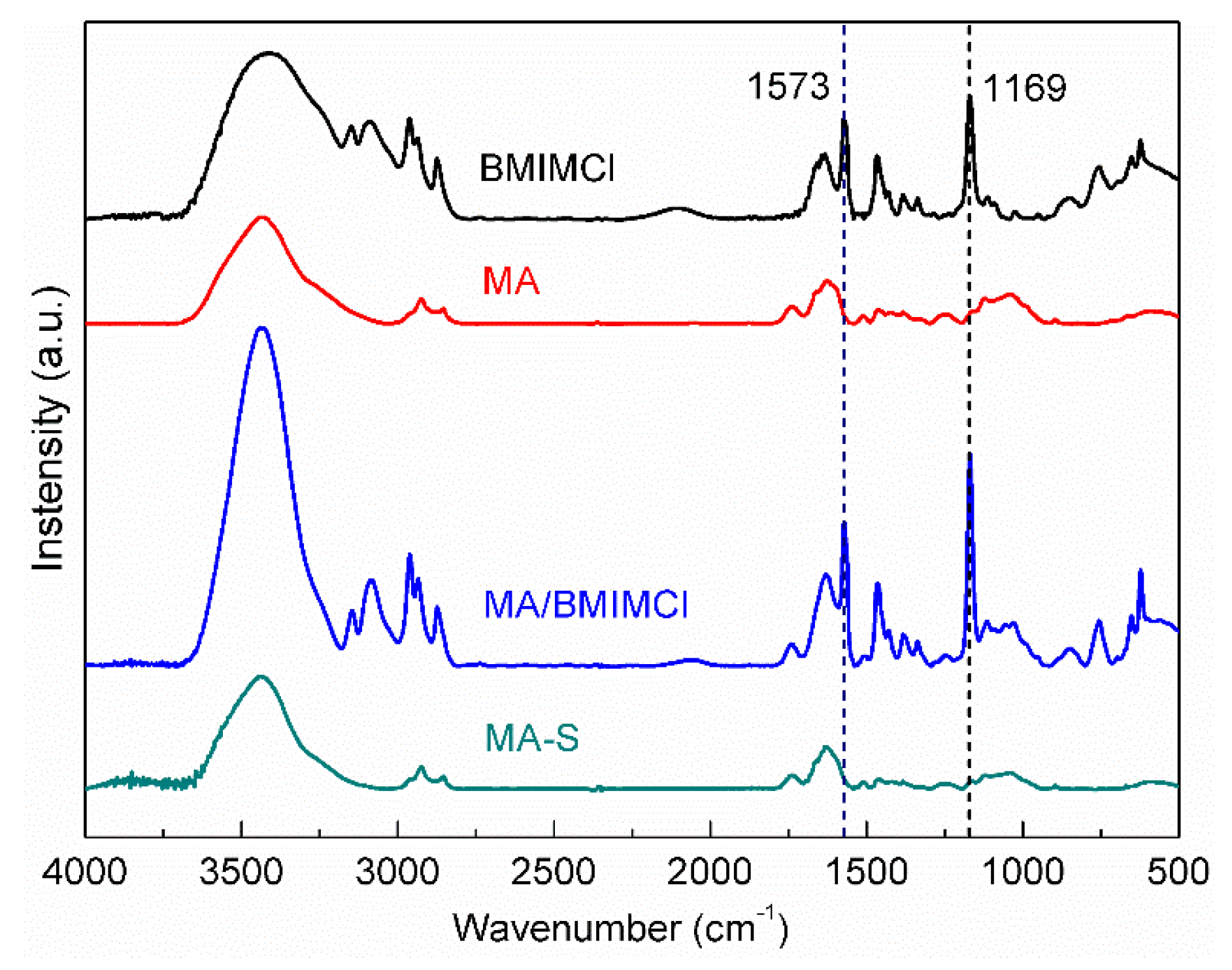
3.1. FTIR Characterization of Composites Samples
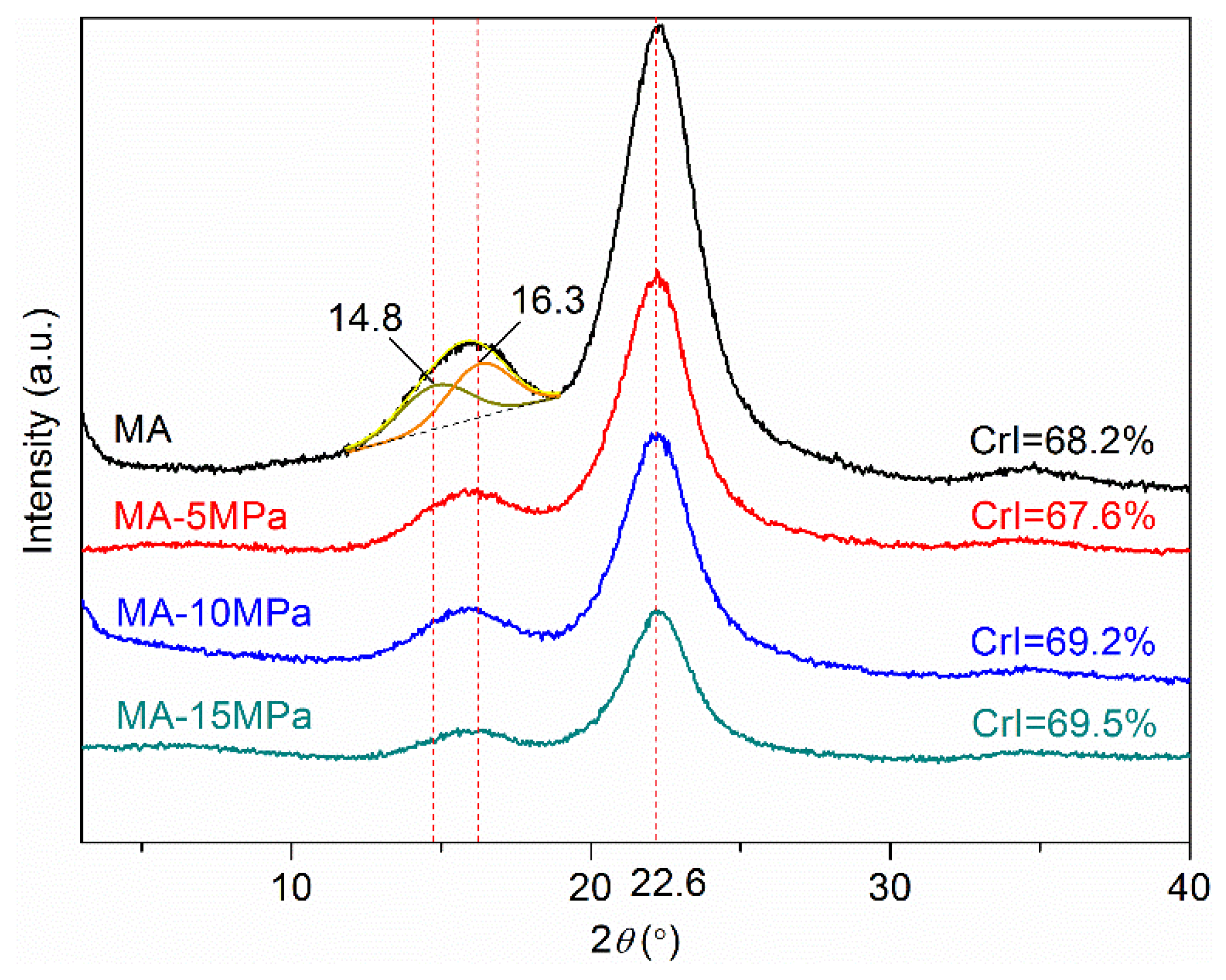
3.2. Crystallinity
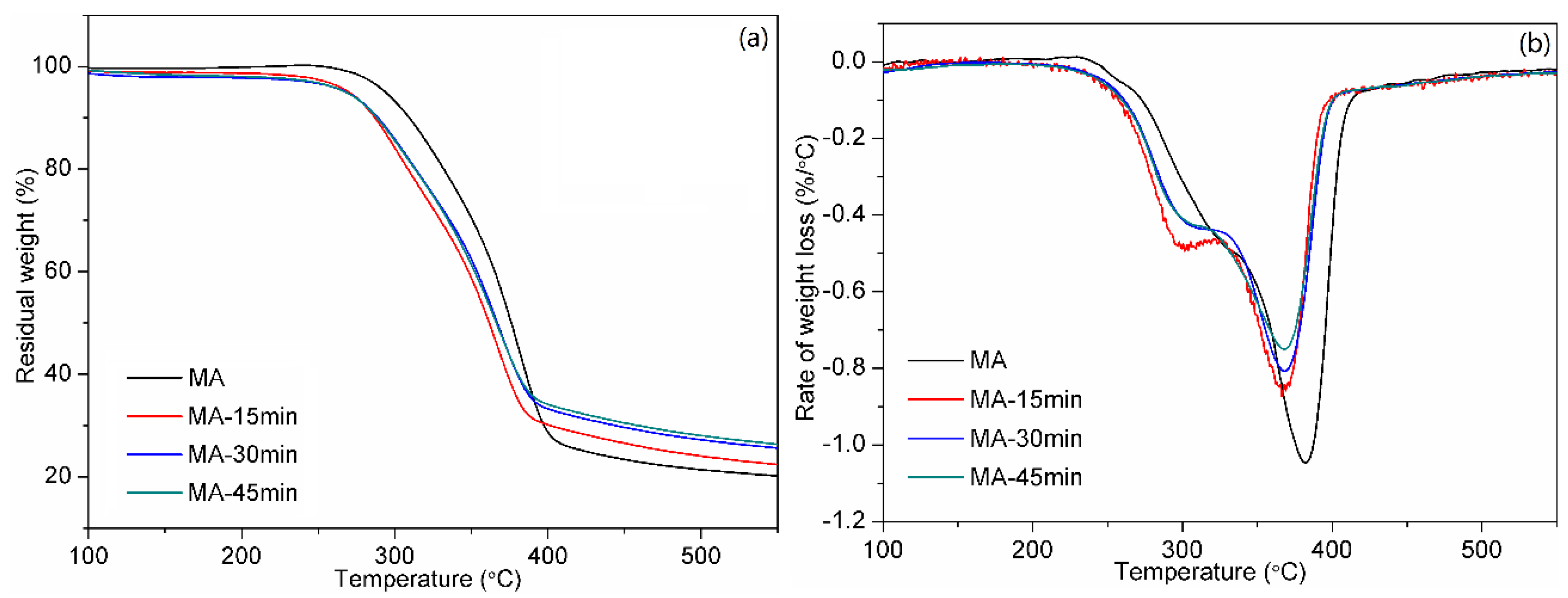
3.3. Thermal Properties
3.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy Study of the Composites
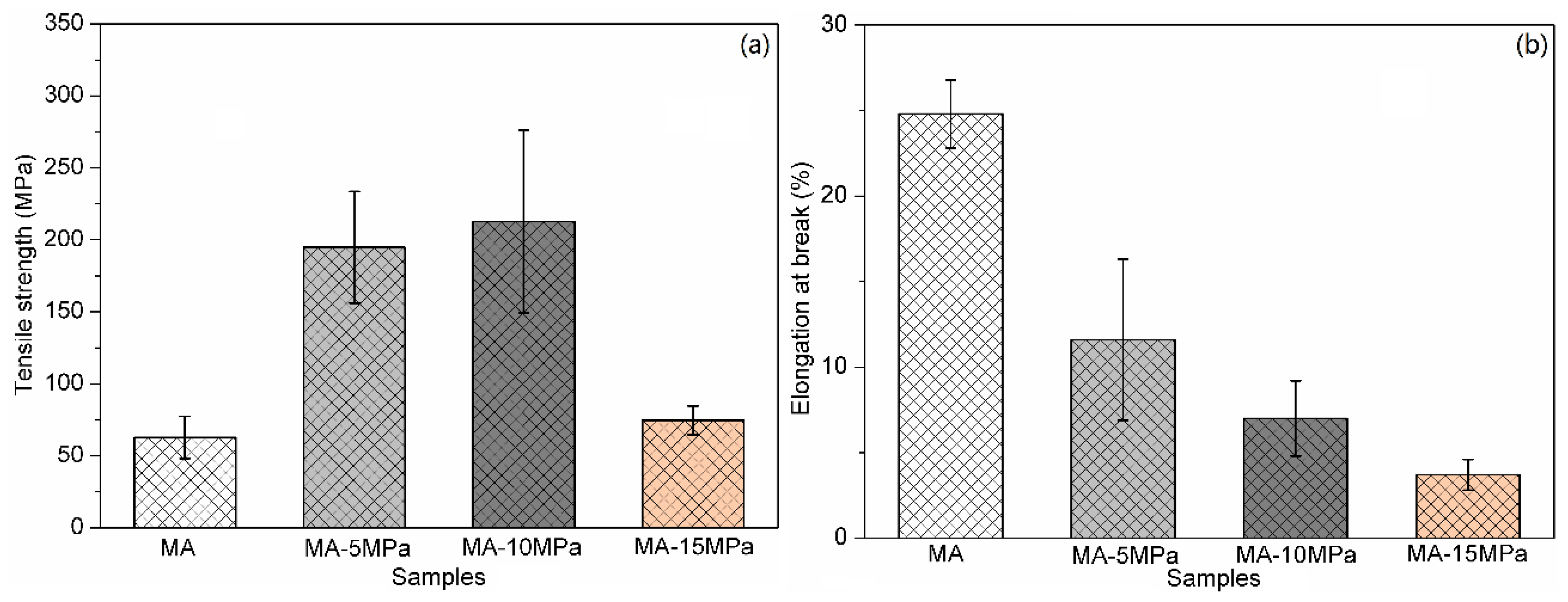
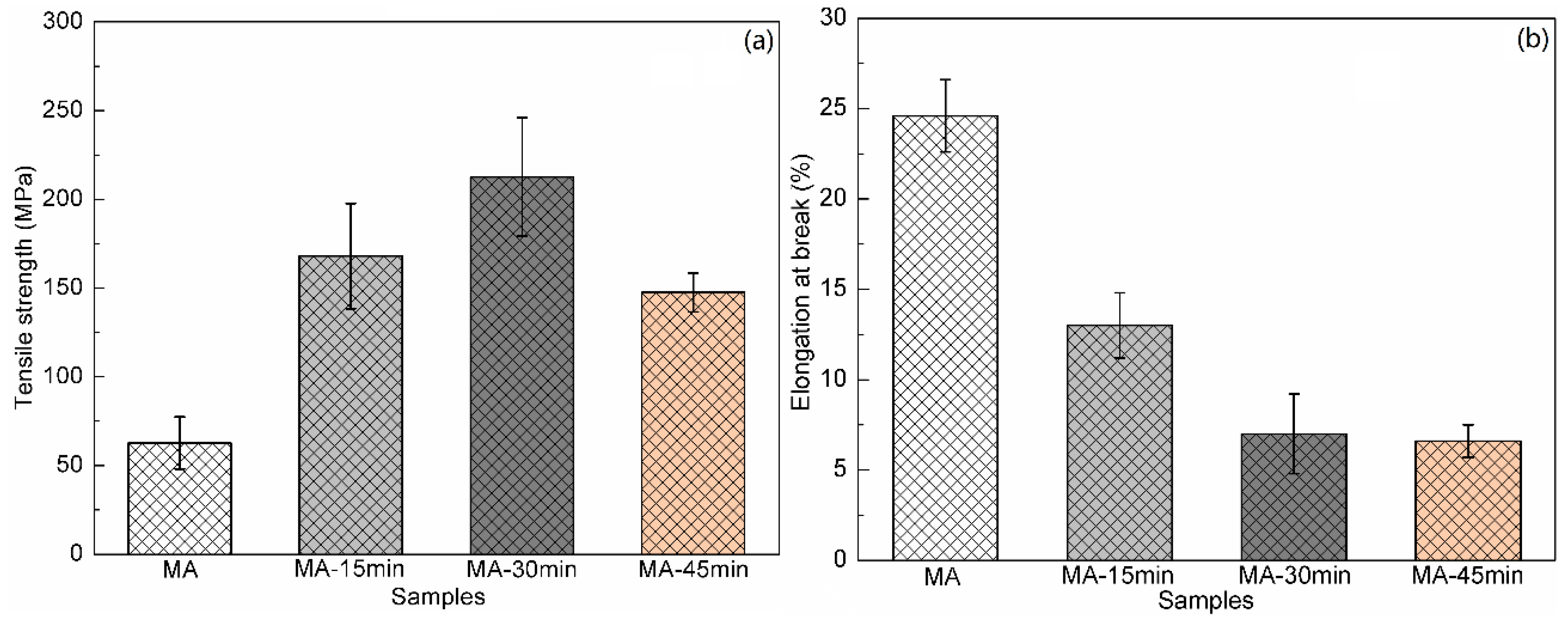
3.5. Mechanical Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xie, H.; Jarvi, P.; Karesoja, M.; King, A.; Kilpelainen, I.; Argyropoulos, D.S. Highly compatible wood thermoplastic composites from lignocellulosic material modified in ionic liquids: Preparation and thermal properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 111, 2468–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Chen, K.; Jia, M.; Xue, P. Effect of processing conditions on the microstructure of microcellular PP/WF composites prepared by the continuous extrusion molding technology. Mater. Res. Express 2020, 7, 015308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, M.J.; Thomas, S. Biofibres and biocomposites. Carbohyd. Polym. 2008, 71, 343–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Xue, P.; Jia, M.; Chen, K. Extrusion foaming behavior of wood plastic composites based on PP/POE blends. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 115345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faruk, O.; Bledzki, A.K.; Fink, H.P.; Sain, M. Biocomposites reinforced with natural fibers: 2000–2010. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2012, 37, 1552–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spörl, J.M.; Batti, F.; Vocht, M.P.; Raab, R.; Müller, A.; Hermanutz, F.; Buchmeiser, M.R. Ionic Liquid Approach Toward Manufacture and Full Recycling of All-Cellulose Composites. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2018, 303, 1700335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinkert, A.; Marsh, K.N.; Pang, S.; Staiger, M.P. Ionic liquids and their interaction with cellulose. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 6712–6728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogoeva-Gaceva, G.; Avella, M.; Malinconico, M.; Buzarovska, A.; Grozdanov, A.; Gentile, G.; Errico, M.E. Natural fiber eco-composites. Polym. Compos. 2007, 28, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Jia, M.; Sun, H.; Xue, P. Thermoplastic Reaction Injection Pultrusion for Continuous Glass Fiber-Reinforced Polyamide-6 Composites. Materials 2019, 12, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominkovics, Z.; Dányádi, L.; Pukanszky, B. Surface modification of wood flour and its effect on the properties of PP/wood composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2007, 38, 1893–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, J.; Yu, J.; Zhang, X.; He, J.; Zhang, J. Application of ionic liquids for dissolving cellulose and fabricating cellulose-based materials: State of the art and future trends. Mater. Chem. Front. 2017, 1, 1273–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, Y.C.; Yano, H.; Nogi, M.; Eichhorn, S.J. An estimation of the Young’s modulus of bacterial cellulose filaments. Cellulose 2008, 15, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Luo, N.; Zhang, X.; Xu, L.; Wu, J.; Yu, J.; Zhang, J. All-cellulose nanocomposites reinforced with in situ retained cellulose nanocrystals during selective dissolution of cellulose in an ionic liquid. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 4417–4423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Nawaz, H.; Wu, J.; Zhang, J.; Wan, J.; Mi, Q.; Yu, J.; Zhang, J. All-cellulose composites based on the self-reinforced effect. Compos. Commun. 2018, 9, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishino, T.; Matsuda, I.; Hirao, K. All-cellulose composite. Macromolecules 2004, 37, 7683–7687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gindl-Altmutter, W.; Keckes, J.; Plackner, J.; Liebner, F.; Englund, K.; Laborie, M.P. All-cellulose composites prepared from flax and lyocell fibres compared to epoxy-matrix composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2012, 72, 1304–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, T.; Pang, S.; Staiger, M.P. All-cellulose composite laminates. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2012, 43, 1738–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, M.; Yamazoe, K.; Kuribayashi, M.; Okuyama, Y. All-wood biocomposites by partial dissolution of wood flour in 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 127, 4802–4808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, M.; Teramoto, N.; Nakamura, T.; Saitoh, Y. All-cellulose and all-wood composites by partial dissolution of cotton fabric and wood in ionic liquid. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 98, 1532–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pullawan, T.; Wilkinson, A.N.; Zhang, L.N.; Eichhorn, S.J. Deformation micromechanics of all-cellulose nanocomposites: Comparing matrix and reinforcing components. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 100, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D-1708 Standard Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics by Use of Microtensile Specimens; ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2018.
- Ma, H.; Zhou, B.; Li, H.S.; Li, Y.Q.; Ou, S.Y. Green composite films composed of nanocrystalline cellulose and a cellulose matrix regenerated from functionalized ionic liquid solution. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 84, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilpeläinen, I.; Xie, H.; King, A.; Granstrom, M.; Heikkinen, S.; Argyropoulos, D.S. Dissolution of wood in ionic liquids. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 9142–9148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, N.; Rahman, M.; Qin, Y.; Maxim, M.L.; Rodríguez, H.; Rogers, R.D. Complete dissolution and partial delignification of wood in the ionic liquid 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium acetate. Green Chem. 2009, 11, 646–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, T.; Bickerton, S.; Müssig, J.; Pang, S.; Staiger, M.P. Solvent infusion processing of all-cellulose composite materials. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 90, 730–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Sample Code | Hot-Pressing Temperature (°C) | Hot-Pressing Pressure (MPa) | Hot-Pressing Time (min) |
|---|---|---|---|
| MA | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MA-5MPa | 190 | 5 | 30 |
| MA-10MPa | 190 | 10 | 30 |
| MA-15MPa | 190 | 15 | 30 |
| MA-15min | 190 | 10 | 15 |
| MA-30min | 190 | 10 | 30 |
| MA-45min | 190 | 10 | 45 |
| Sample Code | Tensile Strength (MPa) | σt (MPa) | Elongation at Break (%) | σe (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MA | 62.7 | 14.7 | 24.8 | 2 |
| MA-5MPa | 194.8 | 38.8 | 11.6 | 4.7 |
| MA-10MPa | 212.6 | 63.4 | 7 | 2.2 |
| MA-15MPa | 74.6 | 9.9 | 3.7 | 0.9 |
| MA-15min | 168.0 | 29.6 | 13 | 1.8 |
| MA-30min | 214.1 | 32.8 | 6.7 | 2.4 |
| MA-45min | 147.5 | 11 | 6.6 | 0.9 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, K.; Xu, W.; Ding, Y.; Xue, P.; Sheng, P.; Qiao, H.; Wang, S.; Yu, Y. Mechanical and Thermal Properties of All-Wood Biocomposites through Controllable Dissolution of Cellulose with Ionic Liquid. Polymers 2020, 12, 361. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12020361
Chen K, Xu W, Ding Y, Xue P, Sheng P, Qiao H, Wang S, Yu Y. Mechanical and Thermal Properties of All-Wood Biocomposites through Controllable Dissolution of Cellulose with Ionic Liquid. Polymers. 2020; 12(2):361. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12020361
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Ke, Weixin Xu, Yun Ding, Ping Xue, Pinghou Sheng, Hui Qiao, Suwei Wang, and Yang Yu. 2020. "Mechanical and Thermal Properties of All-Wood Biocomposites through Controllable Dissolution of Cellulose with Ionic Liquid" Polymers 12, no. 2: 361. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12020361
APA StyleChen, K., Xu, W., Ding, Y., Xue, P., Sheng, P., Qiao, H., Wang, S., & Yu, Y. (2020). Mechanical and Thermal Properties of All-Wood Biocomposites through Controllable Dissolution of Cellulose with Ionic Liquid. Polymers, 12(2), 361. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12020361








