Biocompatibility and Cytotoxicity Study of Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) and Palm Oil Fuel Ash (POFA) Sustainable Super-Hydrophobic Coating for Biomedical Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Method
2.1. Materials
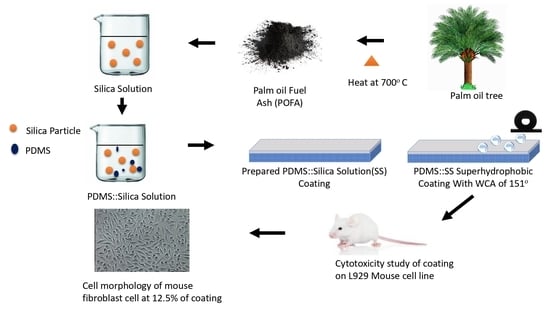
2.2. Synthesis of Silica Solution (SS)
2.3. Synthesis of PDMS: SS Super-Hydrophobic Solution
2.4. Deposition of Super-Hydrophobic Coating on Glass Surface
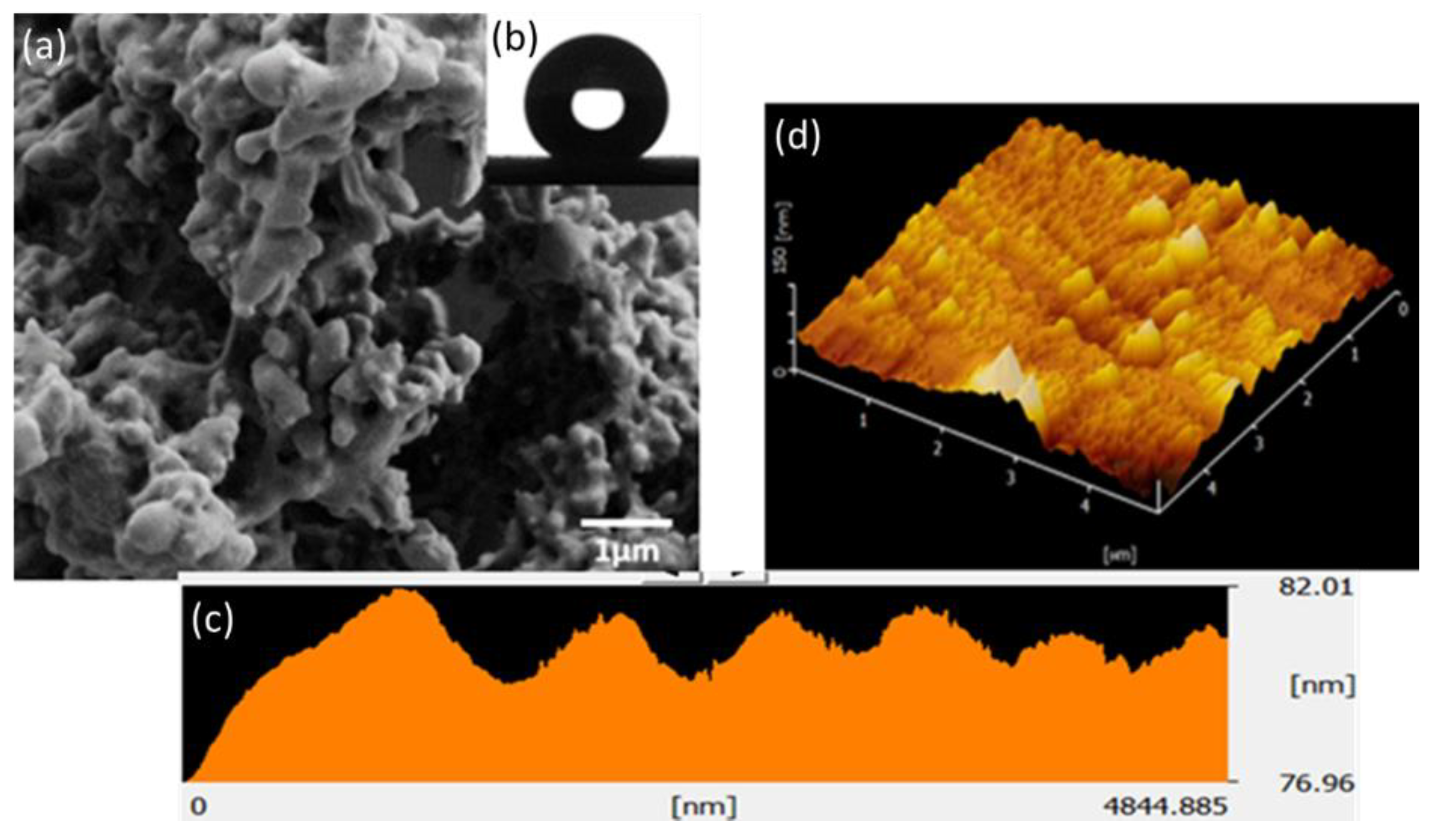
2.5. Physical Characterisation
2.6. Cell Line Culturing for Biocompatibility and Cytotoxicity Studies
2.7. Cell Viability Assay (MTT Assay)
2.8. Clonogenic Assay
2.9. Cell Proliferation Assay
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of PDMS: SS on Water Contact Angle
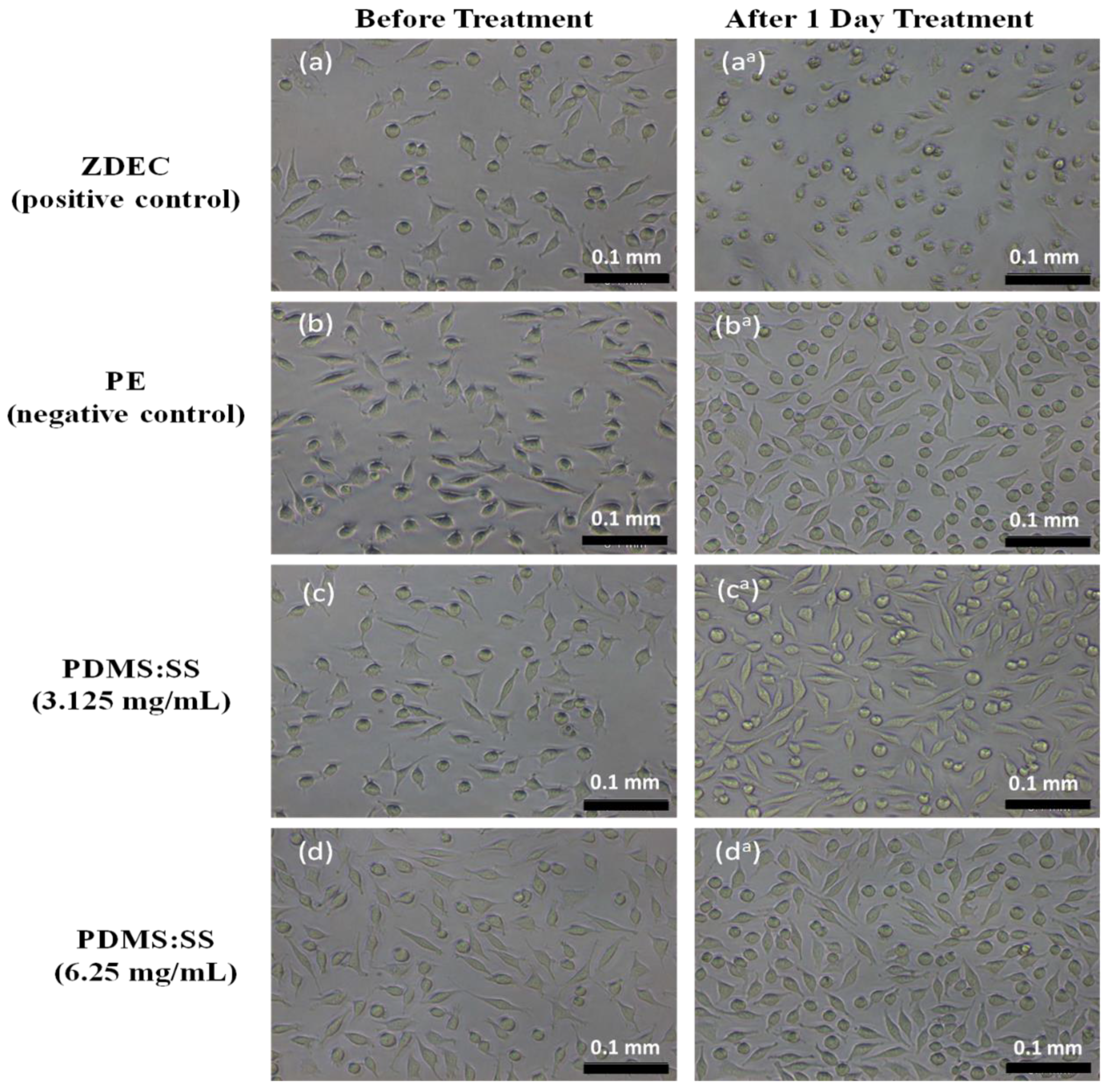
3.2. MTT Assay
3.3. Clonogenic Assay
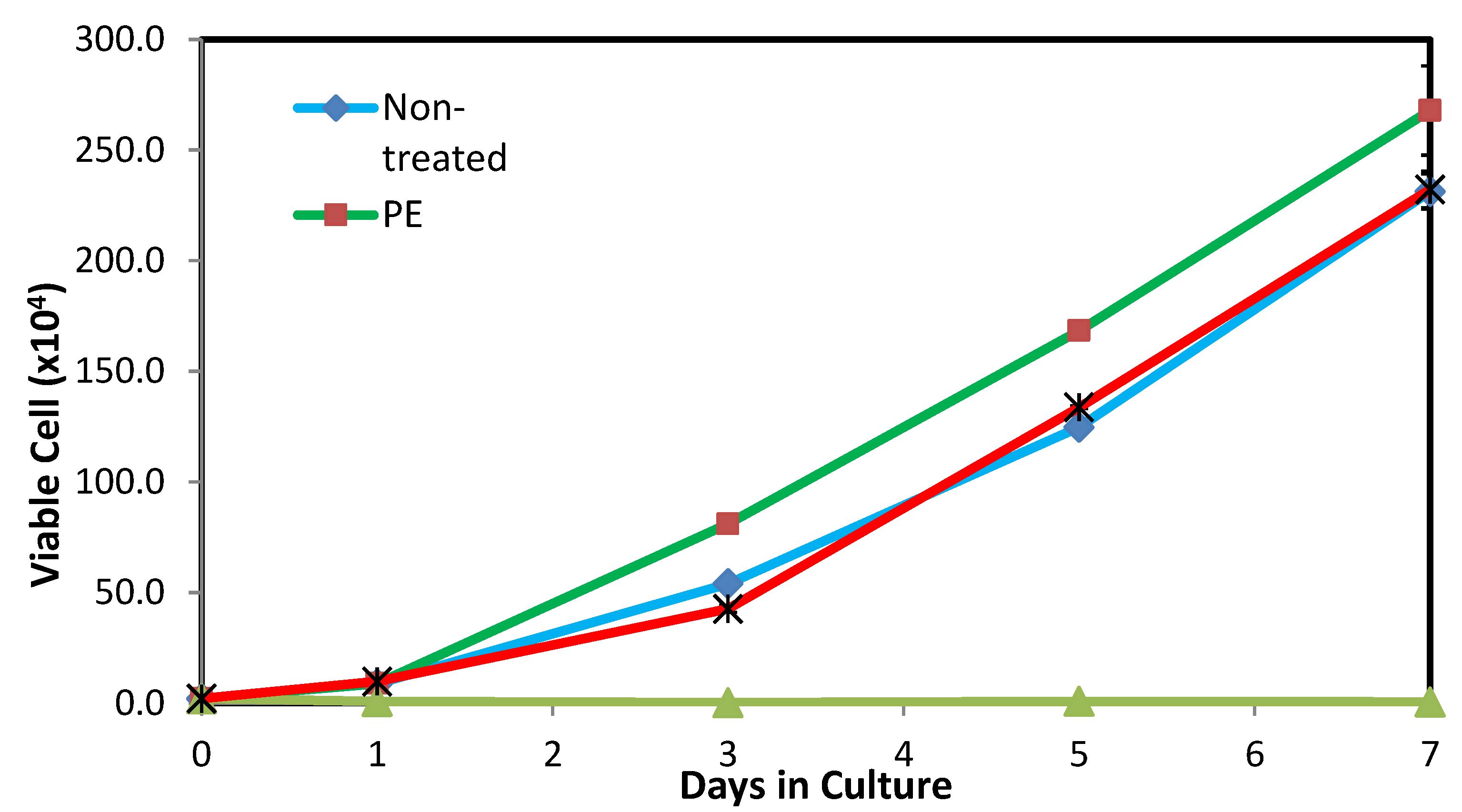
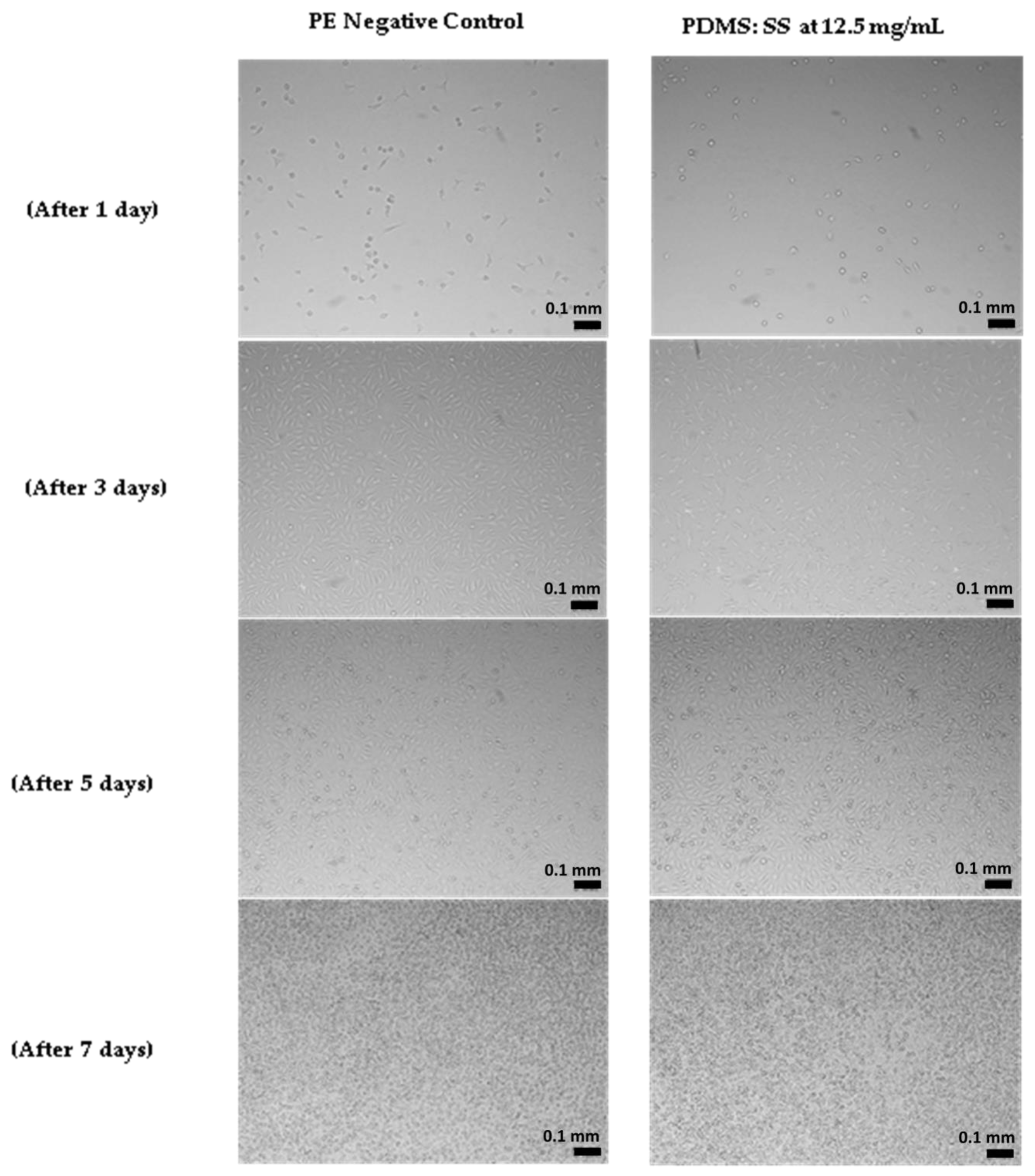
3.4. Cell Proliferation Assay
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nicol, E. The ageing population in healthcare: A challenge to, and in, the workforce. Clin. Med. 2017, 17, 291–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chung, J.W.; Meltzer, D.O. Estimate of the carbon footprint of the US health care sector. JAMA 2009, 302, 1970–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hamada, H.M.; Jokhio, G.A.; Yahaya, F.M.; Humada, A.M. Applications of Nano palm oil fuel ash and Nano fly ash in concrete. IOP Conf. Series: Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 342, 012068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamada, H.M.; Yahaya, F.; Muthusamy, K.; Humada, A. Comparison study between POFA and POCP in terms of chemical composition and physical properties-Review paper. IOP Conf. Series: Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 365, 012004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Tang, W.; Lee, H.; Vimonsatit, V.; Htut, T.; Singh, J.K.; Hassan, W.N.F.W.; Ismail, M.A.; Seikh, A.H.; Alharthi, N.H. Optimization of micro and nano palm oil fuel ash to determine the carbonation resistance of the concrete in accelerated condition. Materials 2019, 12, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hamada, H.M.; Jokhio, G.A.; Yahaya, F.M.; Humada, A.M. Properties of fresh and hardened sustainable concrete due to the use of palm oil fuel ash as cement replacement. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 342, 012035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Tian, T.; Yao, J.; Huang, C.; Tang, W.; Xiang, Z.; Xu, X.; Min, J. Superhydrophobic organosilicon-based coating system by a novel ultravoiletcurable method. Nanomater. Nanotechnol. 2016, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Xu, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, R.; Song, X.; Li, J. One-step preparation of durable super-hydrophobic MSR/SiO 2 coatings by suspension air spraying. Micromachines 2018, 9, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Falde, E.J.; Yohe, S.T.; Colson, Y.L.; Grinstaff, M.W. Superhydrophobic materials for biomedical applications. Biomaterials 2016, 104, 87–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahadik, S.A.; Pedraza, F.; Mahadik, S.S.; Relekar, B.P.; Thorat, S.S. Biocompatible superhydrophobic coating material for biomedical applications. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2016, 81, 791–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peifu, T.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Wang, H.; Lin, C.; Zhang, L. Effect of superhydrophobic surface of titanium on staphylococcus aureus adhesion. J. Nanomater. 2011, 2011, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Levänen, E. Superhydrophobic surfaces for the reduction of bacterial adhesion. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 12003–12020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, W.; Shi, Q.; Hou, J.; Jin, J.; Fan, Q.; Wong, S.-C.; Xu, X.; Yin, J. Superhydrophobic coating of elastomer on different substrates using a liquid template to construct a biocompatible and antibacterial surface. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 7186–7191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junaidi, M.U.M.; Ahmad, N.; Leo, C.; Yee, H. Near superhydrophobic coating synthesized from rice husk ash: Anti-fouling evaluation. Prog. Org. Coatings. 2016, 99, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husni, H.; Nazari, M.; Yee, H.; Rohim, R.; Yusuff, A.; Ariff, M.A.M.; Ahmad, N.; Leo, C.; Junaidi, M. Superhydrophobic rice husk ash coating on concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 144, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Sun, Q.; Guo, Y.; Dong, S. Effects of modifiers on the hydrophobicity of SiO 2 films from nano-husk ash. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 276, 796–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anitha, C.; Azim, S.S.; Mayavan, S.; Chandrasekaran, A. Fluorine free superhydrophobic surface textured silica particles and its dynamics–Transition from impalement to impingement. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 711, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yang, G.; Lyu, W.; Yan, W. Thorny TiO2 nanofibers: Synthesis, enhanced photocatalytic activity and supercapacitance. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 659, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, S.; Subramaniyam, S.T.; Kumaravel, V. Fabrication of Hydrophobic Coatings Using Sugarcane Bagasse Waste Ash as Silica Source. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spathi, C.; Young, N.; Heng, J.Y.Y.; Vandeperre, L.J.M.; Cheeseman, C.R. Cheeseman, A simple method for preparing super-hydrophobic powder from paper sludge ash. Mater. Lett. 2015, 142, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saharudin, K.A.; Sreekantan, S.; Basiron, N.; Chun, L.K.; Kumaravel, V.; Abdullah, T.K.; Ahmad, Z.A. Improved super-hydrophobicity of eco-friendly coating from palm oil fuel ash (POFA) waste. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 337, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vagos, M.R.; Gomes, M.; Moreira, J.M.R.; Soares, O.S.G.P.; Pereira, M.F.R.; Mergulhão, F.J. Carbon nanotube/poly (dimethylsiloxane) composite materials to reduce bacterial adhesion. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, X.; Cai, D.; Ruan, X.; Cai, A. Research on the selective adhesion characteristics of polydimethylsiloxane layer. AIP Adv. 2018, 8, 095004. [Google Scholar]
- Brix, N.; Samaga, D.; Hennel, R.; Gehr, K.; Zitzelsberger, H.; Lauber, K. The clonogenic assay: Robustness of plating efficiency-based analysis is strongly compromised by cellular cooperation. Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 15, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, S.; Bhushan, B. Transparent, wear-resistant, superhydrophobic and superoleophobic poly (dimethylsiloxane)(PDMS) surfaces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 488, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenço, B.D.N.; Marchioli, G.; Song, W.; Reis, R.L.; Van Blitterswijk, C.A.; Karperien, M.; Van Apeldoorn, A.; Mano, J.F. Wettability influences cell behavior on superhydrophobic surfaces with different topographies. Biointerphases 2012, 7, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, M.; Cirisano, F.; Morán, M.C. Regenerable Superhydrophobic Coatings for Biomedical Fabrics. Coatings 2020, 10, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, K.; Jo, Y.Y.; Park, C.-K.; Cho, H. Synthesis of graphene oxide using atmospheric plasma for prospective biological applications. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 5813–5824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, S.Z.; Tabatabaei-Panah, P.-S.; Seyfi, J. Emphasizing the role of surface chemistry on hydrophobicity and cell adhesion behavior of polydimethylsiloxane/TiO2 nanocomposite films. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 2018, 167, 492–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchiya, T.; Ikarashi, Y.; Hata, H.; Toyoda, K.; Takahashi, M.; Uchima, T.; Tanaka, N.; Sasaki, T.; Nakamura, A. Comparative studies of the toxicity of standard reference materials in various cytotoxicity tests and in vivo implantation tests. J. Appl. Biomater. 1993, 4, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Mendis, N.; Trigui, H.; Oliver, J.D.; Faucher, S.P. The importance of the viable but non-culturable state in human bacterial pathogens. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dascalu, M.; Cazacu, M.; Vlad, S.; Iacomi, F. Polydimethylsiloxane-silica composites. Influence of the silica on the morphology and the surface, thermal, mechanical properties. High Perform. Polym. 2008, 21, 379–392. [Google Scholar]
- Dollase, T.; Spiess, H.W.; Gottlieb, M.; Yerushalmi-Rozen, R. Crystallization of PDMS: The effect of physical and chemical crosslinks. Europhys. Lett. 2002, 60, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.-M.; Huang, G.; Feng, S.; McShane, G.; Stronge, W.J. Static and dynamic properties of semi-crystalline polyethylene. Polymers 2016, 8, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Waste Material | Functionalizing Agent | Substrate | Coating Method | WCA (°) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RHA | 1H,1H,2H,2H-perfluorodecyltriethoxysilane | Glass | Spraying | 144° | [14] |
| RHA | 1H,1H,2H,2H-perfluorodecyltriethoxysilane | Concrete | Spraying | 152° | [15] |
| RHA | Hydroxyl silicone oil | Glass | Spraying | 160° | [16] |
| RHA | Vinyl triethoxysilane | Porous silica | - | 158° | [17] |
| FA | Dodecyltrimethoxysilane | Cotton textile | Dip coating | 152° | [18] |
| SBA | Dimethyldiethoxysilane | Tiles | Drop-casting | 135° | [19] |
| PSA | Stearic acid | Disc | Pressing | 153° | [20] |
| POFA | Polydimethylsiloxane | Glass | Spraying | 171° | [21] |
| Substrate | WCA | TA |
|---|---|---|
| Bare Tile | 53° ± 2° | - |
| PDMS: SS 1:2 | 151° ± 1° | 7° ± 1° |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sreekantan, S.; Hassan, M.; Sundera Murthe, S.; Seeni, A. Biocompatibility and Cytotoxicity Study of Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) and Palm Oil Fuel Ash (POFA) Sustainable Super-Hydrophobic Coating for Biomedical Applications. Polymers 2020, 12, 3034. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12123034
Sreekantan S, Hassan M, Sundera Murthe S, Seeni A. Biocompatibility and Cytotoxicity Study of Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) and Palm Oil Fuel Ash (POFA) Sustainable Super-Hydrophobic Coating for Biomedical Applications. Polymers. 2020; 12(12):3034. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12123034
Chicago/Turabian StyleSreekantan, Srimala, Mohd Hassan, Satisvar Sundera Murthe, and Azman Seeni. 2020. "Biocompatibility and Cytotoxicity Study of Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) and Palm Oil Fuel Ash (POFA) Sustainable Super-Hydrophobic Coating for Biomedical Applications" Polymers 12, no. 12: 3034. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12123034
APA StyleSreekantan, S., Hassan, M., Sundera Murthe, S., & Seeni, A. (2020). Biocompatibility and Cytotoxicity Study of Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) and Palm Oil Fuel Ash (POFA) Sustainable Super-Hydrophobic Coating for Biomedical Applications. Polymers, 12(12), 3034. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12123034