In Situ Preparation of Novel Porous Nanocomposite Hydrogel as Effective Adsorbent for the Removal of Cationic Dyes from Polluted Water
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
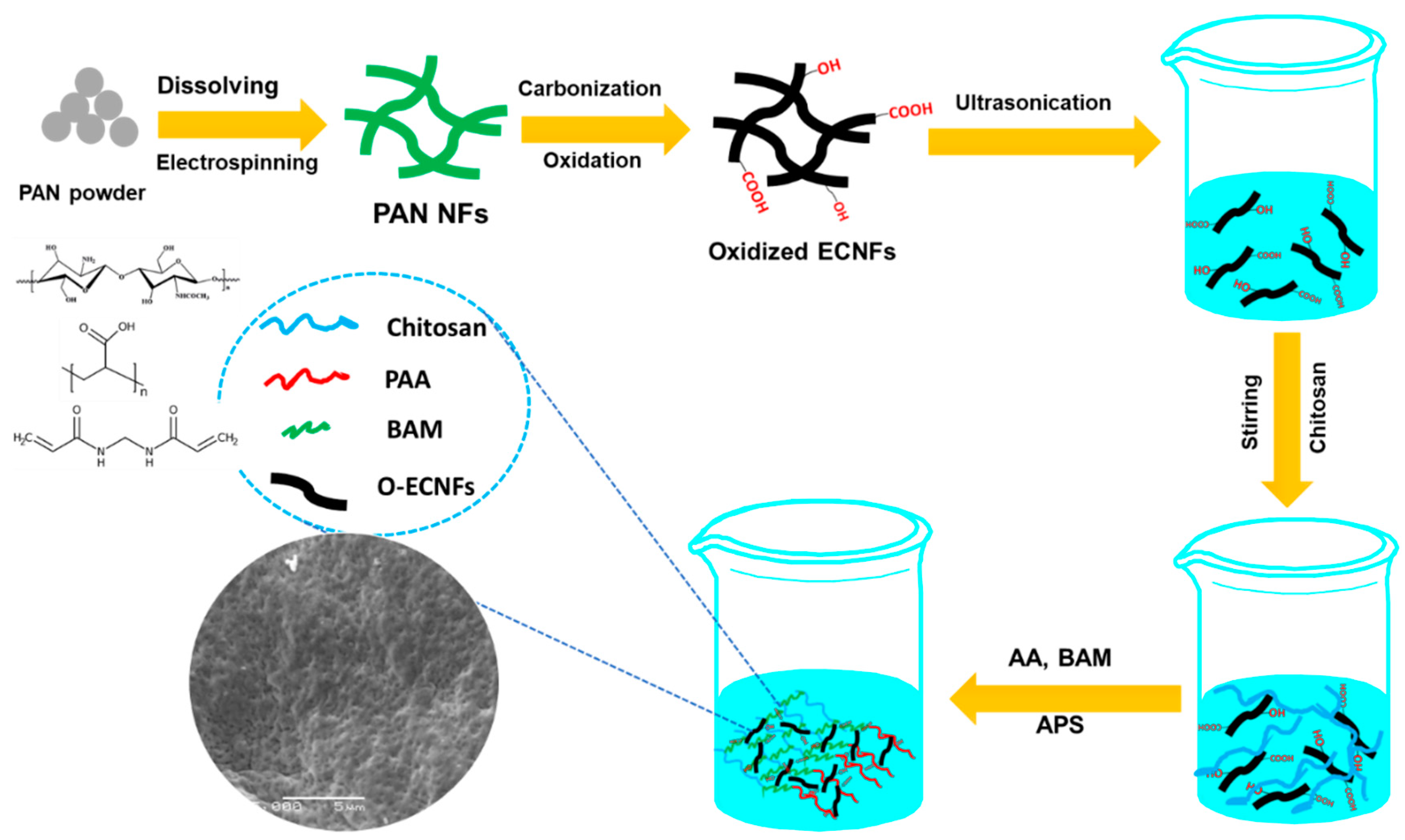
2.2. Preparation of Hydrogel Nanocomposite
2.3. Characterization of Hydrogel Nanocomposite
2.4. Adsorption Study
2.5. Reusability of Hydrogel Nanocomposite
2.6. Swelling Test of Hydrogel Nanocomposite
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Hydrogel Nanocomposite
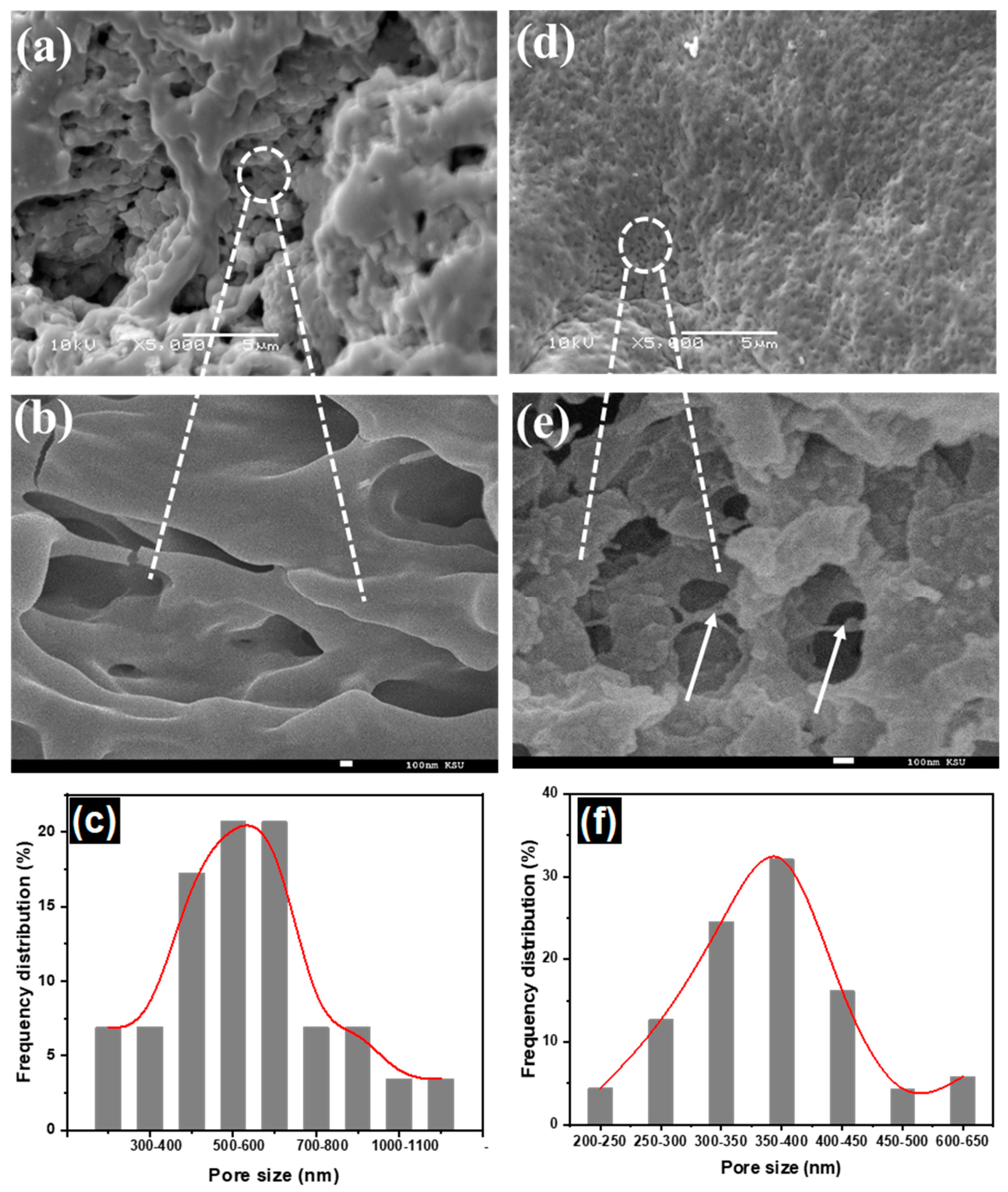
3.1.1. The Morphology of Hydrogel Nanocomposite
3.1.2. FTIR Spectra
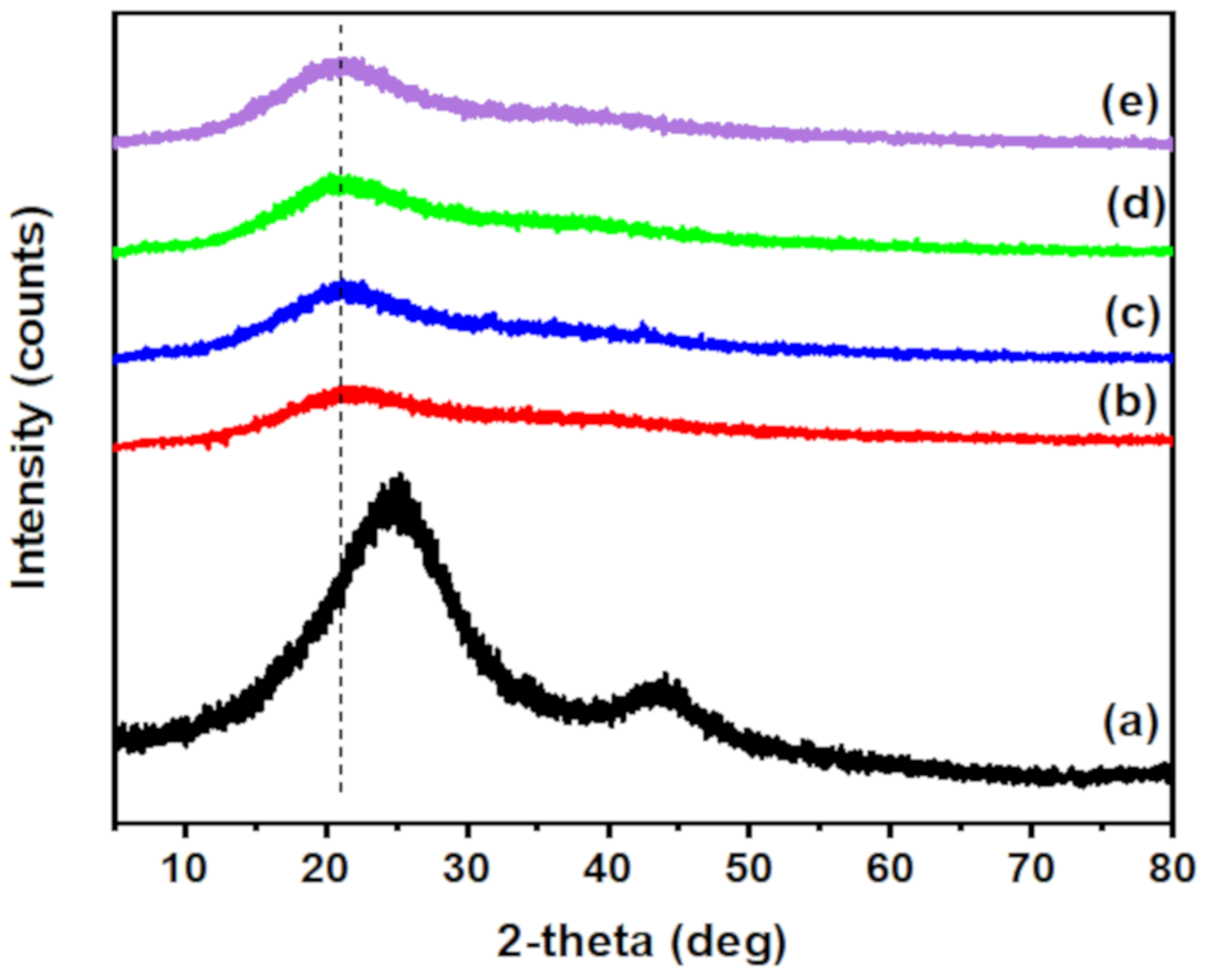
3.1.3. XRD Analysis
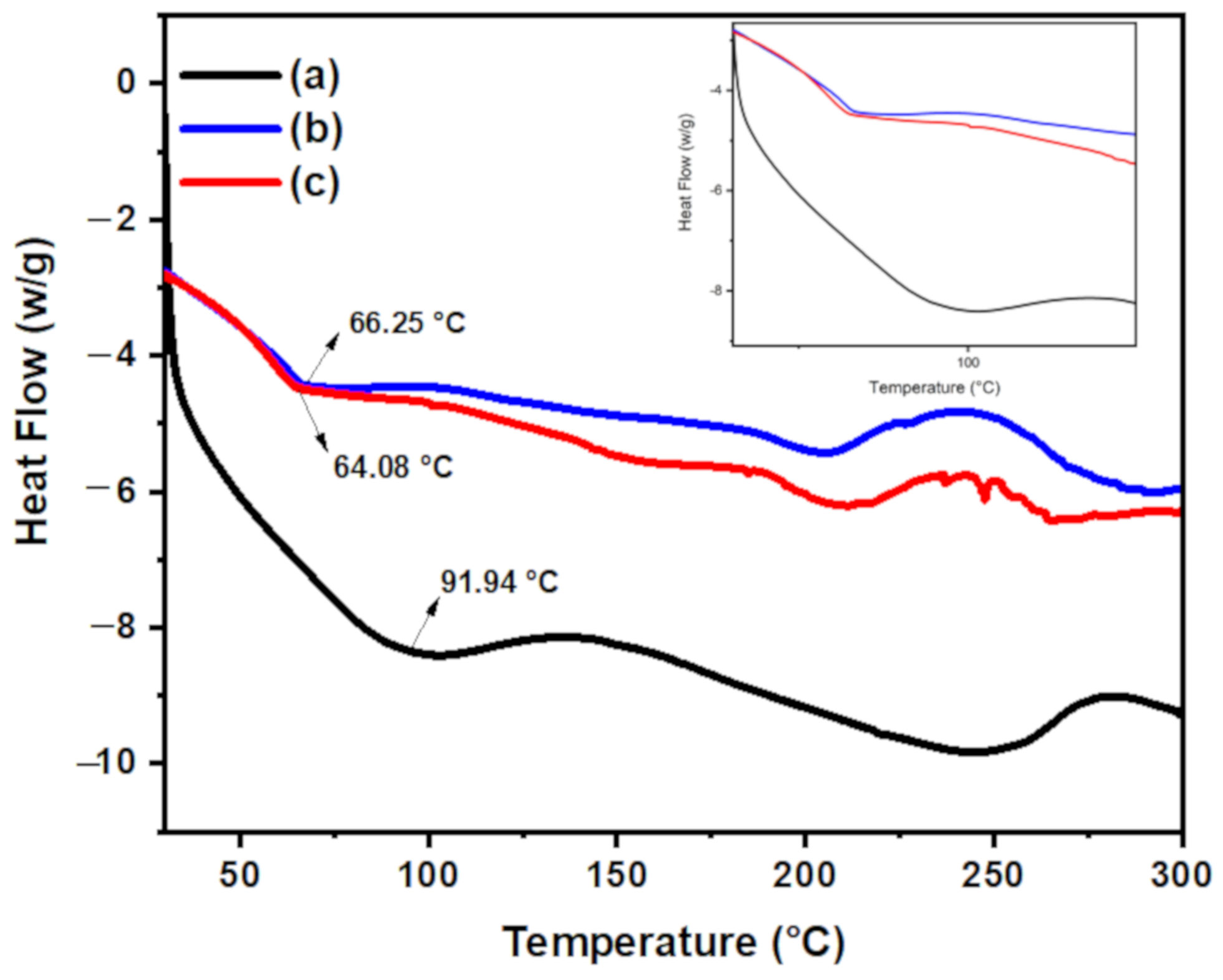
3.1.4. DSC Analysis
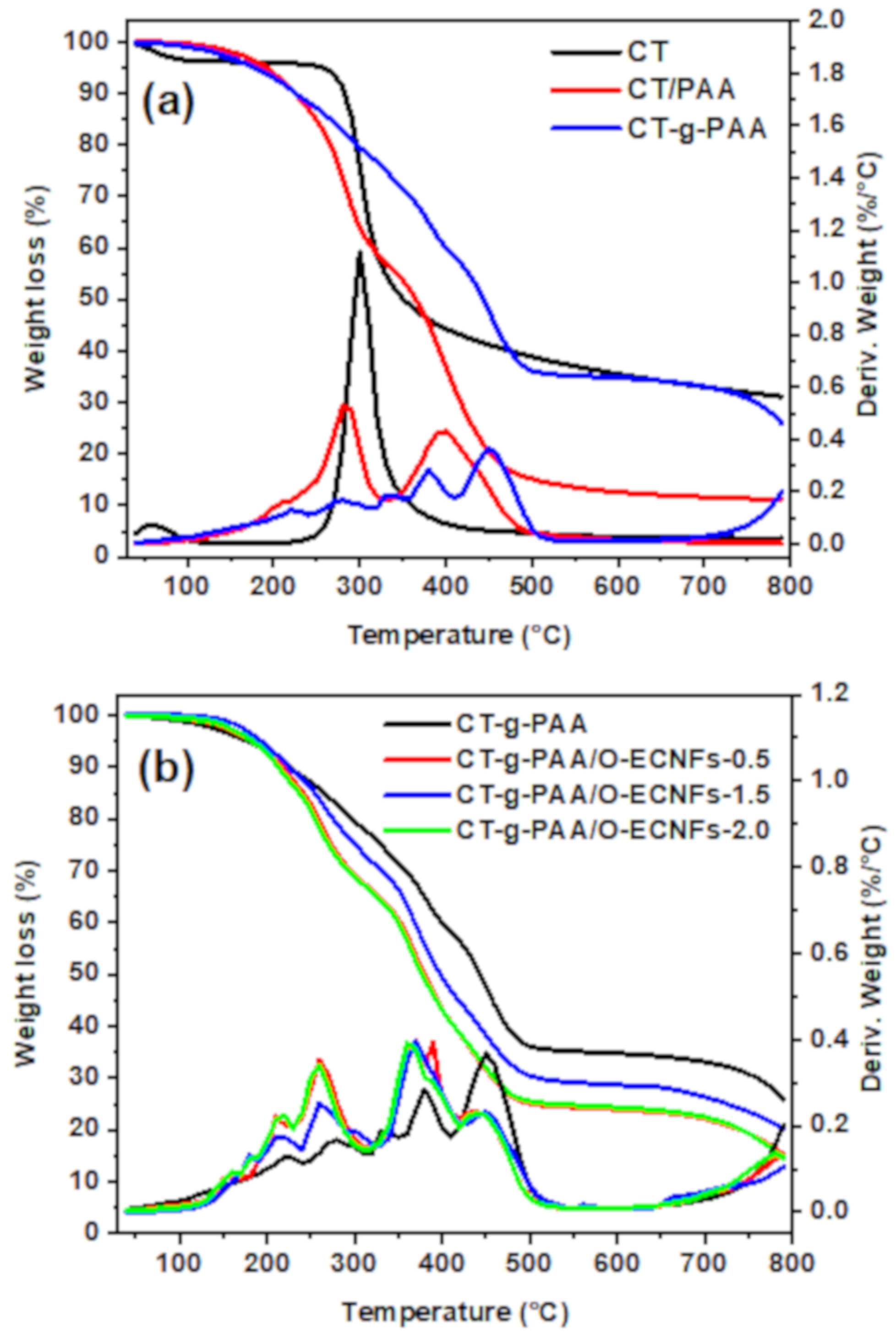
3.1.5. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
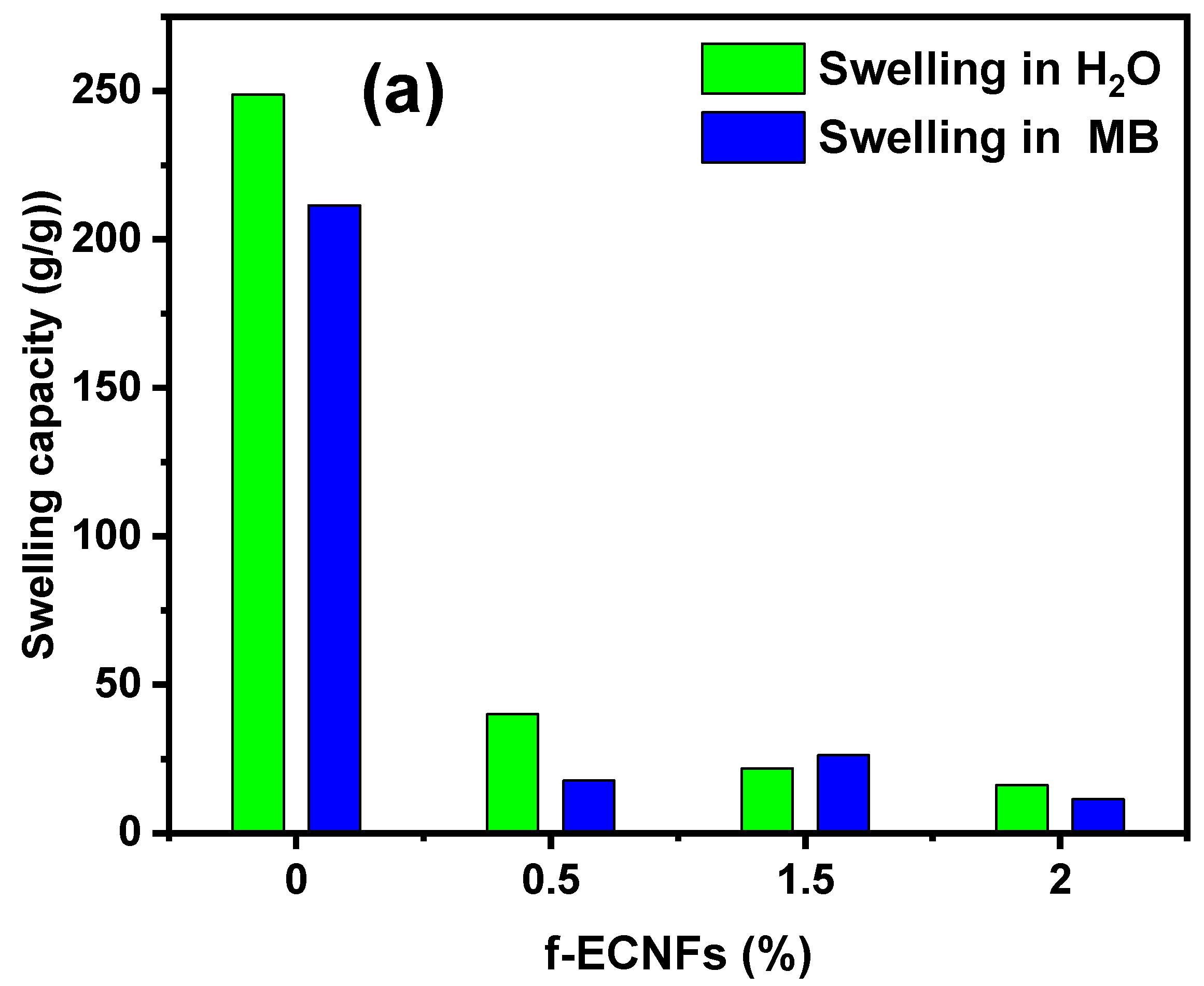
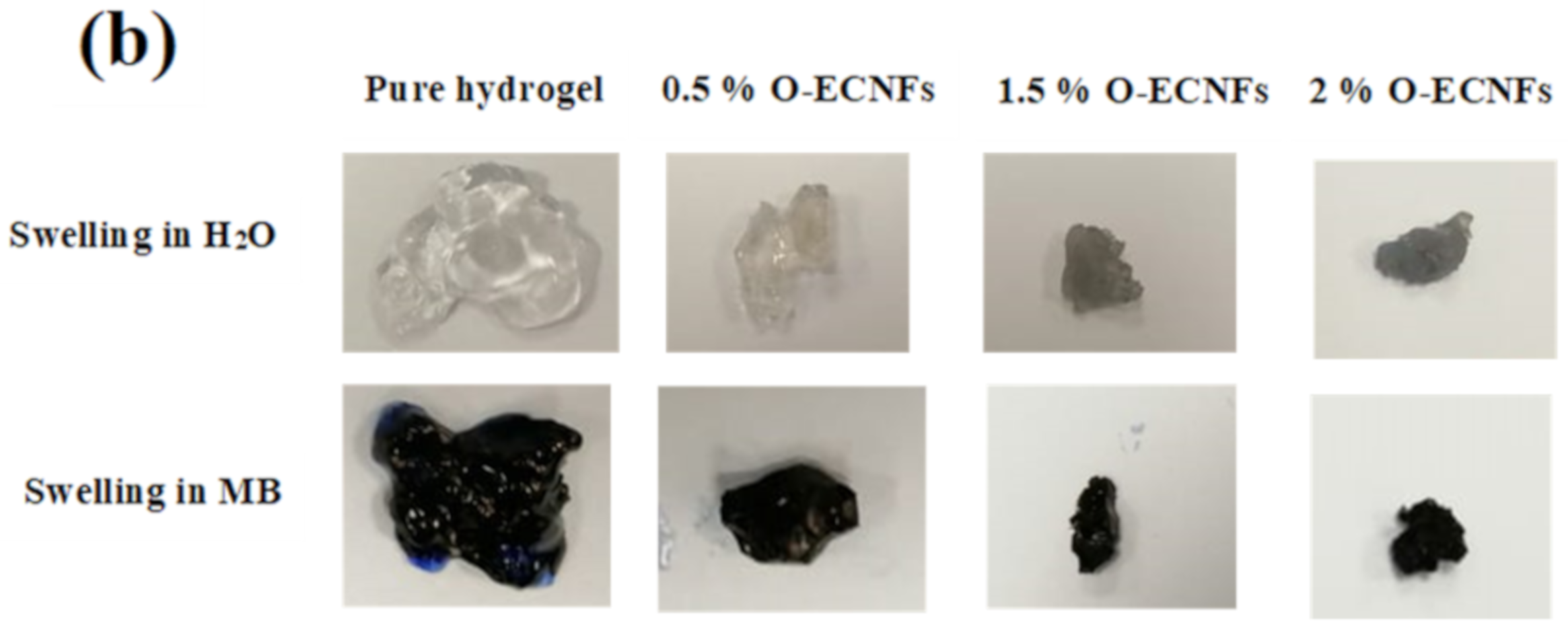
3.2. Swelling Capacity of Hydrogel Nanocomposite
3.3. Adsorption Study
3.3.1. Effect of Incorporated Amount of O-ECNFs into Hydrogel
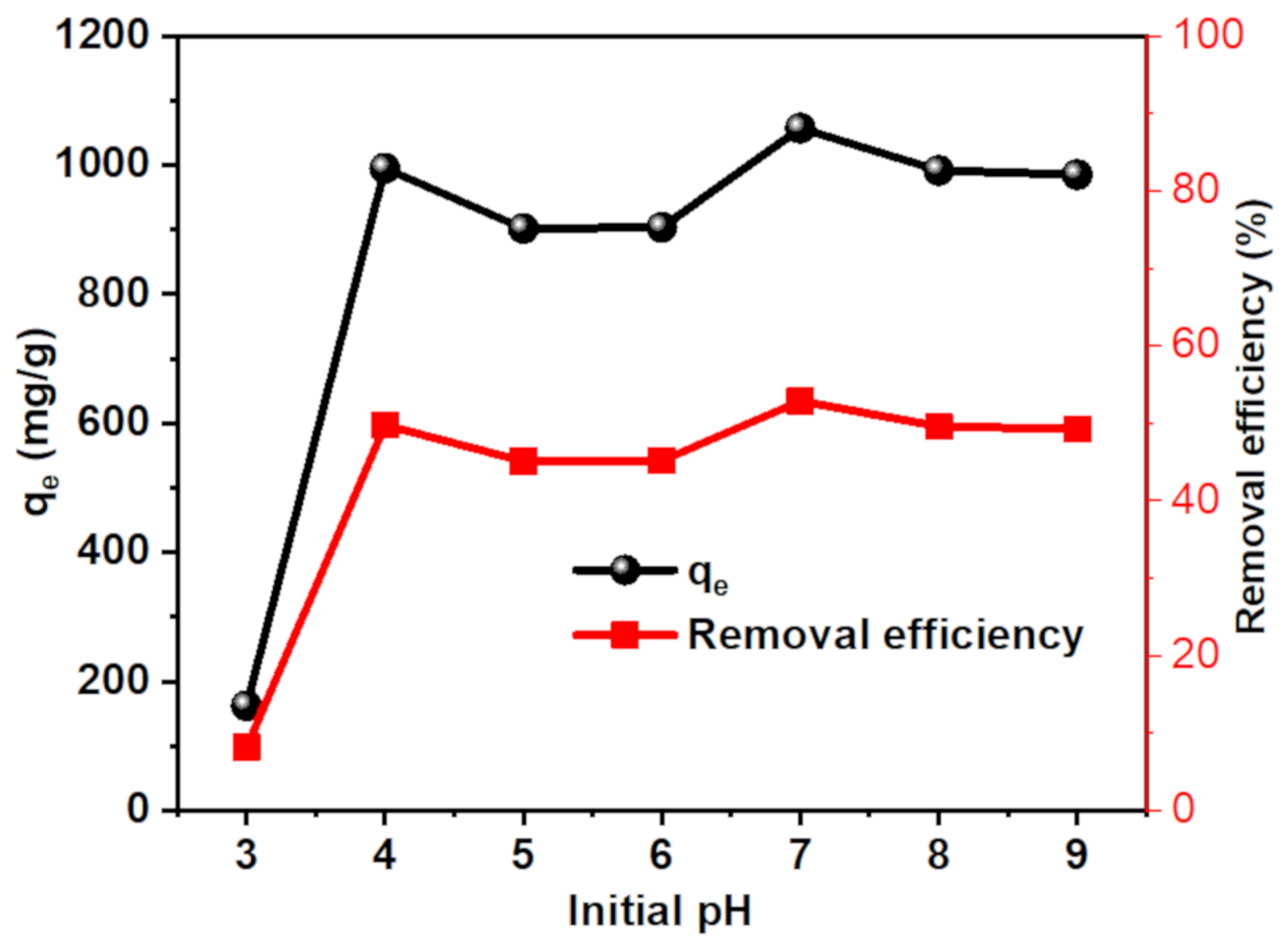
3.3.2. Effect of pH
3.3.3. Effect of Initial Concentration and Isotherm Study
3.3.4. The Effect of Contact Time and Kinetic Study
3.3.5. Thermodynamic Study
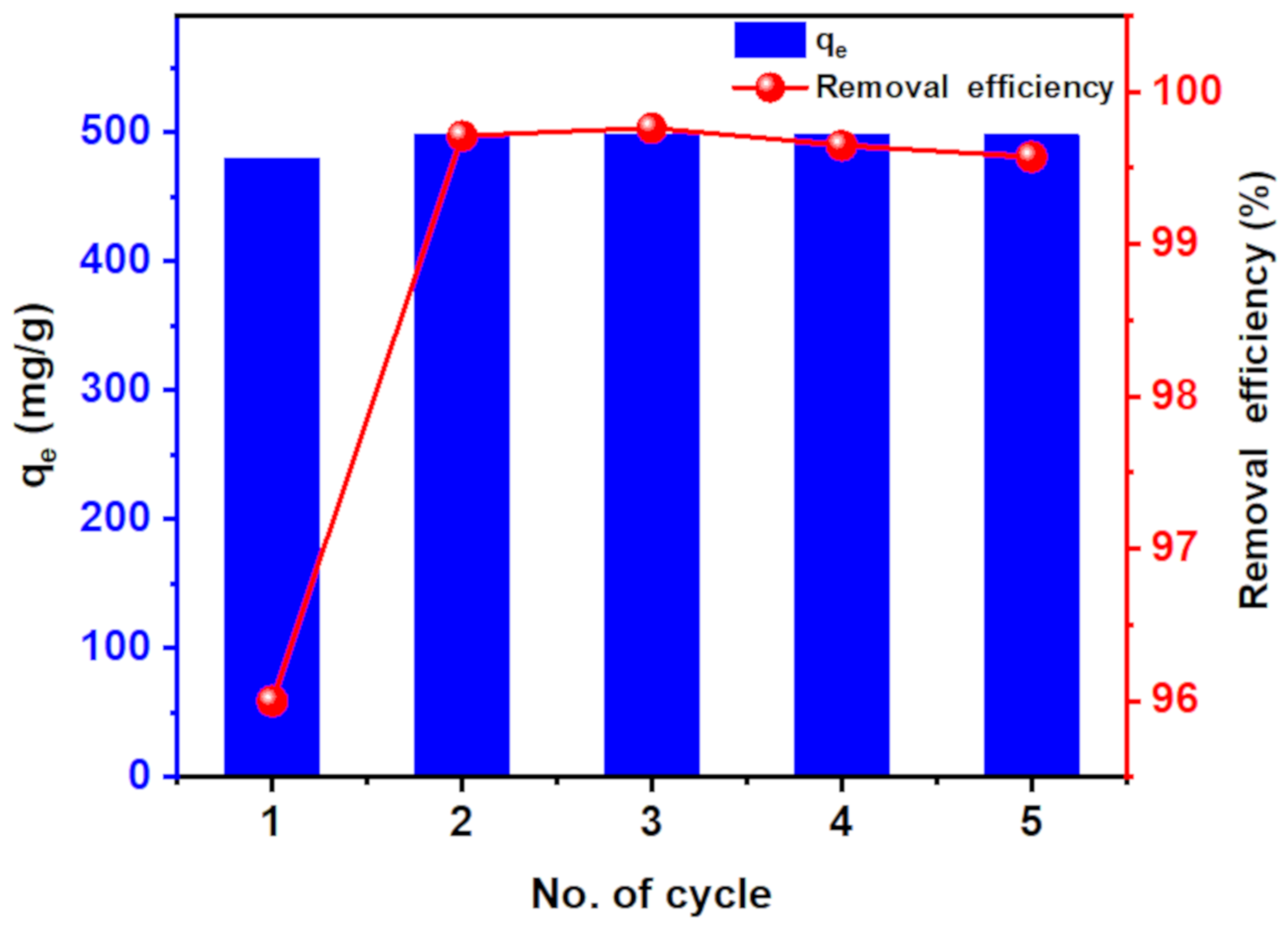
3.3.6. Reusability
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eckenfelder, W.W. Industrial Water Pollution Control, 3rd ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Yaseen, D.A.; Scholz, M. Textile dye wastewater characteristics and constituents of synthetic effluents: A critical review. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 1193–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lellis, B.; Fávaro-Polonio, C.Z.; Pamphile, J.A.; Polonio, J.C. Effects of textile dyes on health and the environment and bioremediation potential of living organisms. Biotechnol. Res. Innov. 2019, 3, 275–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kant, R. Textile dyeing industry an environmental hazard. Nat. Sci. 2012, 04, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salgot, M.; Folch, M. Wastewater treatment and water reuse. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2018, 2, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai, F.I.; Yamamoto, K.; Fukushi, K. Hybrid Treatment Systems for Dye Wastewater. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 37, 315–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajeshwari, K.V.; Balakrishnan, M.; Kansal, A.; Lata, K.; Kishore, V.V.N. State-of-the-art of anaerobic digestion technology for industrial wastewater treatment. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2000, 4, 135–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katheresan, V.; Kansedo, J.; Lau, S.Y. Efficiency of various recent wastewater dye removal methods: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 4676–4697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Türgay, O.; Ersöz, G.; Atalay, S.; Forss, J.; Welander, U. The treatment of azo dyes found in textile industry wastewater by anaerobic biological method and chemical oxidation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2011, 79, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.H.; Chen, M.L. Treatment of textile wastewater by-chemical methods for reuse. Water Res. 1997, 31, 868–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrelkas, F.; Azizi, A.; Yaacoubi, A.; Benhammou, A.; Pons, M.N. Treatment of textile dye effluents using coagulation-flocculation coupled with membrane processes or adsorption on powdered activated carbon. Desalination 2009, 235, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crini, G. Non-conventional low-cost adsorbents for dye removal: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 1061–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thamer, B.M.; Aldalbahi, A.; Moydeen A, M.; Al-Enizi, A.M.; El-Hamshary, H.; El-Newehy, M.H. Fabrication of functionalized electrospun carbon nanofibers for enhancing lead-ion adsorption from aqueous solutions. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kausar, A.; Iqbal, M.; Javed, A.; Aftab, K.; Nazli, Z.i.H.; Bhatti, H.N.; Nouren, S. Dyes adsorption using clay and modified clay: A review. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 256, 395–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.Y.; Muralidhara, H.B.; Nayaka, Y.A.; Balasubramanyam, J.; Hanumanthappa, H. Low-cost synthesis of metal oxide nanoparticles and their application in adsorption of commercial dye and heavy metal ion in aqueous solution. Powder Technol. 2013, 246, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.K.; Kumar, R.; Nayak, A.; Saleh, T.A.; Barakat, M.A. Adsorptive removal of dyes from aqueous solution onto carbon nanotubes: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 193–194, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thamer, B.M.; Aldalbahi, A.; Moydeen A, M.; Al-Enizi, A.M.; El-Hamshary, H.; Singh, M.; Bansal, V.; El-Newehy, M.H. Alkali-activated electrospun carbon nanofibers as an efficient bifunctional adsorbent for cationic and anionic dyes. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 582, 123835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thamer, B.M.; Aldalbahi, A.; Moydeen A, M.; El-Hamshary, H.; Al-Enizi, A.M.; El-Newehy, M.H. Effective adsorption of Coomassie brilliant blue dye using poly(phenylene diamine)grafted electrospun carbon nanofibers as a novel adsorbent. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2019, 234, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monte Blanco, S.P.D.; Scheufele, F.B.; Módenes, A.N.; Espinoza-Quiñones, F.R.; Marin, P.; Kroumov, A.D.; Borba, C.E. Kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic phenomenological modeling of reactive dye adsorption onto polymeric adsorbent. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 307, 466–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, E.; Jun, J.W.; Jhung, S.H. Adsorptive removal of methyl orange and methylene blue from aqueous solution with a metal-organic framework material, iron terephthalate (MOF-235). J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 185, 507–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakhjiri, M.T.; Marandi, G.B.; Kurdtabar, M. Poly(AA-co-VPA) hydrogel cross-linked with N-maleyl chitosan as dye adsorbent: Isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamic investigation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 117, 152–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, N.; Grishkewich, N.; Berry, R.M.; Tam, K.C. Cellulose nanocrystal–alginate hydrogel beads as novel adsorbents for organic dyes in aqueous solutions. Cellulose 2015, 22, 3725–3738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.S.; Liang, R.; Sun, G. Super-adsorbent hydrogel for removal of methylene blue dye from aqueous solution. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 17612–17624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anseth, K.S.; Bowman, C.N.; Brannon-Peppas, L. Mechanical properties of hydrogels and their experimental determination. Biomaterials 1996, 17, 1647–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Lo, I.M.C. A holistic review of hydrogel applications in the adsorptive removal of aqueous pollutants: Recent progress, challenges, and perspectives. Water Res. 2016, 106, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, L.; Li, H.; Chen, L.; Xu, L.; Liu, J.; Geng, A.; Mei, C.; Shang, S. Graphene oxide incorporated alginate hydrogel beads for the removal of various organic dyes and bisphenol A in water. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2018, 296, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, N.; Hu, D.; Zeng, J.; Li, Y.; Liang, L.; Chang, C. Superabsorbent Cellulose-Clay Nanocomposite Hydrogels for Highly Efficient Removal of Dye in Water. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 7217–7224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Jiao, T.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, W.; Peng, Q.; Yan, X. Preparation of Graphene Oxide-Based Hydrogels as Efficient Dye Adsorbents for Wastewater Treatment. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chatterjee, S.; Lee, M.W.; Wooa, S.H. Adsorption of congo red by chitosan hydrogel beads impregnated with carbon nanotubes. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 1800–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zeng, M.; Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Q. Multi-structural network design and mechanical properties of graphene oxide filled chitosan-based hydrogel nanocomposites. Mater. Des. 2018, 148, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thamer, B.M.; El-Hamshary, H.; Al-Deyab, S.S.; El-Newehy, M.H. Functionalized electrospun carbon nanofibers for removal of cationic dye. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 747–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaz, T.; Zeeshan, R.; Zarif, F.; Ilyas, K.; Muhammad, N.; Safi, S.Z.; Rahim, A.; Rizvi, S.A.A.; Rehman, I.U. FTIR analysis of natural and synthetic collagen. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2018, 53, 703–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, M.; Feng, Z.; Huang, Y.; Liu, J.; Ren, J.; Xu, Q.; Fan, L. Chemical structure and remarkably enhanced mechanical properties of chitosan-graft-poly(acrylic acid)/polyacrylamide double-network hydrogels. Polym. Bull. 2017, 74, 55–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queiroz, M.F.; Melo, K.R.T.; Sabry, D.A.; Sassaki, G.L.; Rocha, H.A.O. Does the use of chitosan contribute to oxalate kidney stone formation? Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 141–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Zeng, M.; Feng, Z.; Yin, D.; Xu, Q.; Fan, L. Graphene oxide-based composite hydrogels with self-assembled macroporous structures. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 3561–3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Simeon, F.; Hatton, T.A.; Rutledge, G.C. Polyacrylonitrile-based electrospun carbon paper for electrode applications. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 124, 3861–3870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmed, E.M. Hydrogel: Preparation, characterization, and applications: A review. J. Adv. Res. 2015, 6, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Langmuir, I. The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1918, 40, 1361–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Freundlich, H. Über die adsorption in lösungen. Z. Phys. Chem. 1907, 57, 385–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sips, R. Combined form of Langmuir and Freundlich equations. J. Chem. Phys. 1948, 16, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubinin, M.M.; Radushkevich, L.V. Equation of the characteristic curve of activated charcoal. Chem. Zentr. 1947, 1, 857. [Google Scholar]
- Lagergren, S.K. About the theory of so-called adsorption of soluble substances. Sven. Vetenskapsakad. Handingar 1898, 24, 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Blanchard, G.; Maunaye, M.; Martin, G. Removal of heavy metals from waters by means of natural zeolites. Water Res. 1984, 18, 1501–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, S.H.; Clayton, W.R. Application of Elovich Equation to the Kinetics of Phosphate Release and Sorption in Soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1980, 44, 265–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Huang, Y.; Huang, H. Eco-friendly polyvinyl alcohol/carboxymethyl cellulose hydrogels reinforced with graphene oxide and bentonite for enhanced adsorption of methylene blue. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 185, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Wu, Q.; Lei, T.; Negulescu, I.I. Adsorption kinetic and equilibrium studies for methylene blue dye by partially hydrolyzed polyacrylamide/cellulose nanocrystal nanocomposite hydrogels. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 251, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, S.; Pandey, S.; Arotiba, O.A. Development of a sodium alginate-based organic/inorganic superabsorbent composite hydrogel for adsorption of methylene blue. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 153, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhang, T.; Chen, T.; Yi, H.; Rao, F.; Song, S. Removal of methylene blue from water with montmorillonite nanosheets/chitosan hydrogels as adsorbent. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 448, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhado, E.; Pandey, S.; Ramontja, J. Microwave assisted synthesis of xanthan gum-cl-poly (acrylic acid) based-reduced graphene oxide hydrogel composite for adsorption of methylene blue and methyl violet from aqueous solution. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 119, 255–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, G.; Zhang, F.; Cheng, Z.; Zhou, L. Facile fabrication of magnetic carboxymethyl starch/poly(vinyl alcohol) composite gel for methylene blue removal. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 81, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, S.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, Y. Fabrication of three-dimensional porous β-cyclodextrin/chitosan functionalized graphene oxide hydrogel for methylene blue removal from aqueous solution. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 539, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhado, E.; Pandey, S.; Nomngongo, P.N.; Ramontja, J. Preparation and characterization of xanthan gum-cl-poly(acrylic acid)/o-MWCNTs hydrogel nanocomposite as highly effective re-usable adsorbent for removal of methylene blue from aqueous solutions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 513, 700–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


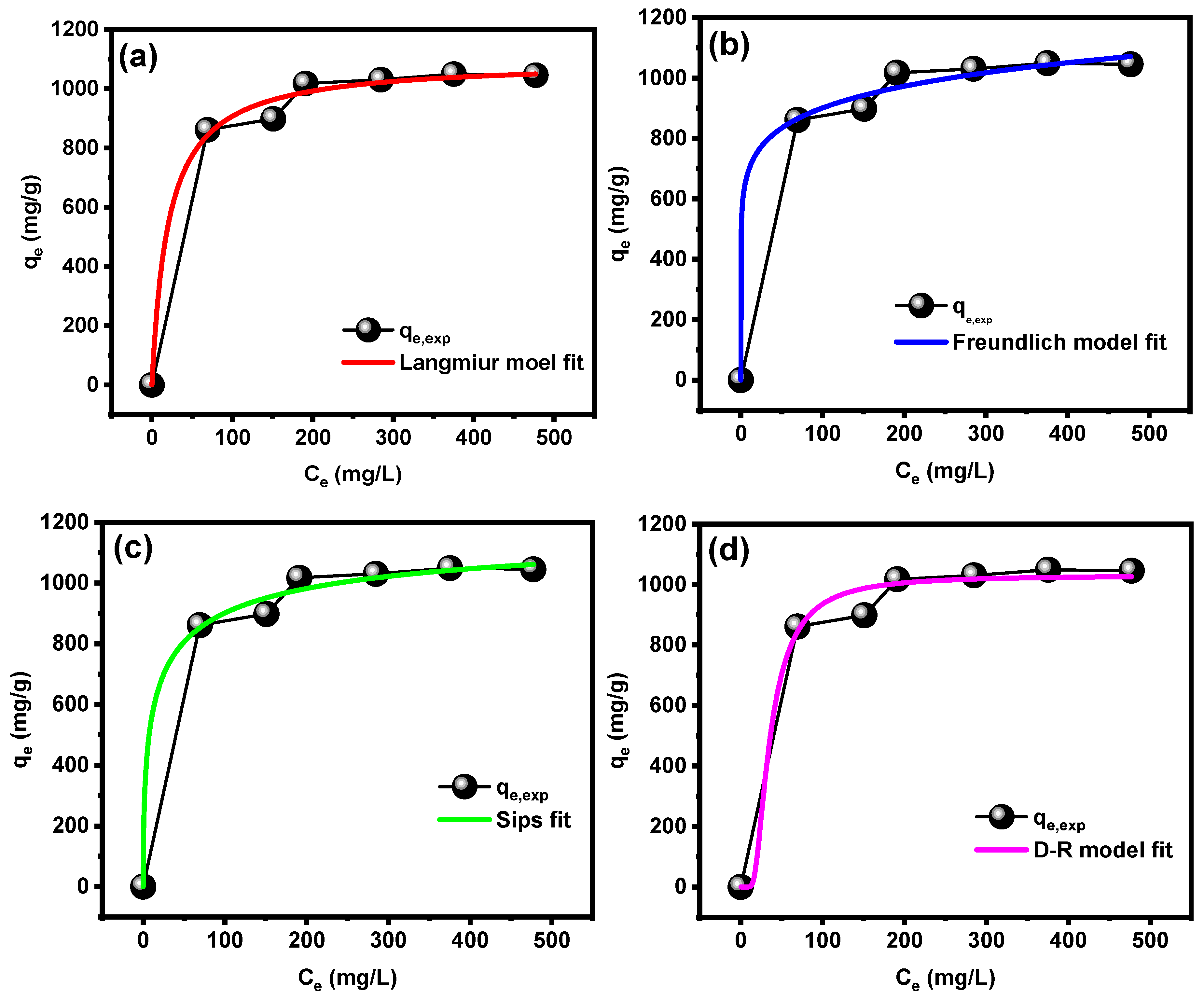


| Model | Equation | Parameters | R2 | χ2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Langmuir | Qo | KL | 0.99349 | 5.87 | ||
| 1095.11 ± 28.86 | 0.0482 ± 0.0116 | |||||
| Freundlich | KF | 1/n | 0.99358 | 5.69 | ||
| 540.93 ± 67.10 | 0.1108 ± 0.0227 | |||||
| Sips | qs | Ks | ns | 0.9942 | 5.16 | |
| 1231.38 ± 43.07 | 0.2388 ± 0.0467 | 0.5292 ± 0.0709 | ||||
| D-R | qo | KD-R | E | 0.9888 | 9.80 | |
| 1030.39 ± 22.49 | 159.24 ± 47.57 | 0.05603 ± 0.0006 | ||||
| Model | Equation | Parameters | R2 | χ2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PFO | qt.exp | qt.cal | K1 | 0.9790 | 539.80 | ||
| 1052.37 | 1049.33 ± 2.68 | 0.0096 ± 2.59 × 10−4 | |||||
| PSO | qt.cal | K2 | 0.9987 | 4.45 | |||
| 1155.26 ± 15.83 | 1.38 × 10−5 ± 1.82 × 10−6 | ||||||
| Elovich | α | β | 0.9956 | 17.72 | |||
| 181.87 ± 131.25 | 0.00628 ± 8.29 × 10−4 | ||||||
| Intraparticle diffusion | Kid1 | Kid2 | C1 | C2 | 0.9923 | -- | |
| 58 ± 1.92 | 1.2 ± 0.426 | 30.1 ± 17.78 | 1018.6 ± 10.77 | ||||
| T (K) | Van’t Hoff Equation | Kc | ΔG° (kJ/mol) | ΔH° (kJ/mol) | ΔS° (kJ/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 298 | y = −8204x + 27.47 R2 = 0.9348 | 1.095 | −0.2257 | 68.21 ± 12.35 | 0.228 ± 0.0408 |
| 308 | 1.20 | −0.4716 | |||
| 318 | 2.49 | −2.3387 | |||
| 328 | 3.66 | −3.3809 |
| Adsorbent | Qe (mg/g) | Regeneration Number/Removal Efficiency (%) | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|
| PVA/PCMC/GO/bentonite | 136.56 | 4/93.4 * | [45] |
| polyacrylamide/cellulose | 326 | - | [46] |
| SA-g-PAA/TiO2 | 2257.36 | 5/91.4 | [47] |
| Chitosan/montmorillonite | 387 | - | [48] |
| XG-cl-PAA/rGO hydrogel | 793.6 | 4/96 | [49] |
| Magnetic Starch/PVA | 23.53 | 8/85 | [50] |
| 3D-GO/CS/β-CD | 1134 | 5/75 | [51] |
| XG-cl-PAA/o-MWCNTs | 521 | 4/74.8 | [52] |
| CT-g-PAA/O-ECNFs | 1095 | 5/99 | This study |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Thamer, B.M.; Aldalbahi, A.; Moydeen A., M.; El-Newehy, M.H. In Situ Preparation of Novel Porous Nanocomposite Hydrogel as Effective Adsorbent for the Removal of Cationic Dyes from Polluted Water. Polymers 2020, 12, 3002. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12123002
Thamer BM, Aldalbahi A, Moydeen A. M, El-Newehy MH. In Situ Preparation of Novel Porous Nanocomposite Hydrogel as Effective Adsorbent for the Removal of Cationic Dyes from Polluted Water. Polymers. 2020; 12(12):3002. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12123002
Chicago/Turabian StyleThamer, Badr M., Ali Aldalbahi, Meera Moydeen A., and Mohamed H. El-Newehy. 2020. "In Situ Preparation of Novel Porous Nanocomposite Hydrogel as Effective Adsorbent for the Removal of Cationic Dyes from Polluted Water" Polymers 12, no. 12: 3002. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12123002
APA StyleThamer, B. M., Aldalbahi, A., Moydeen A., M., & El-Newehy, M. H. (2020). In Situ Preparation of Novel Porous Nanocomposite Hydrogel as Effective Adsorbent for the Removal of Cationic Dyes from Polluted Water. Polymers, 12(12), 3002. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12123002







