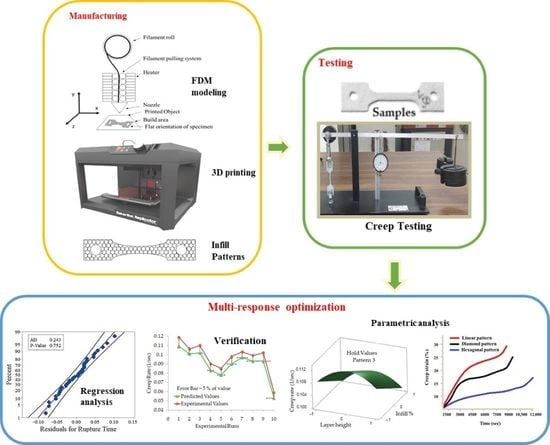
Multi-Response Optimization of Tensile Creep Behavior of PLA 3D Printed Parts Using Categorical Response Surface Methodology
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
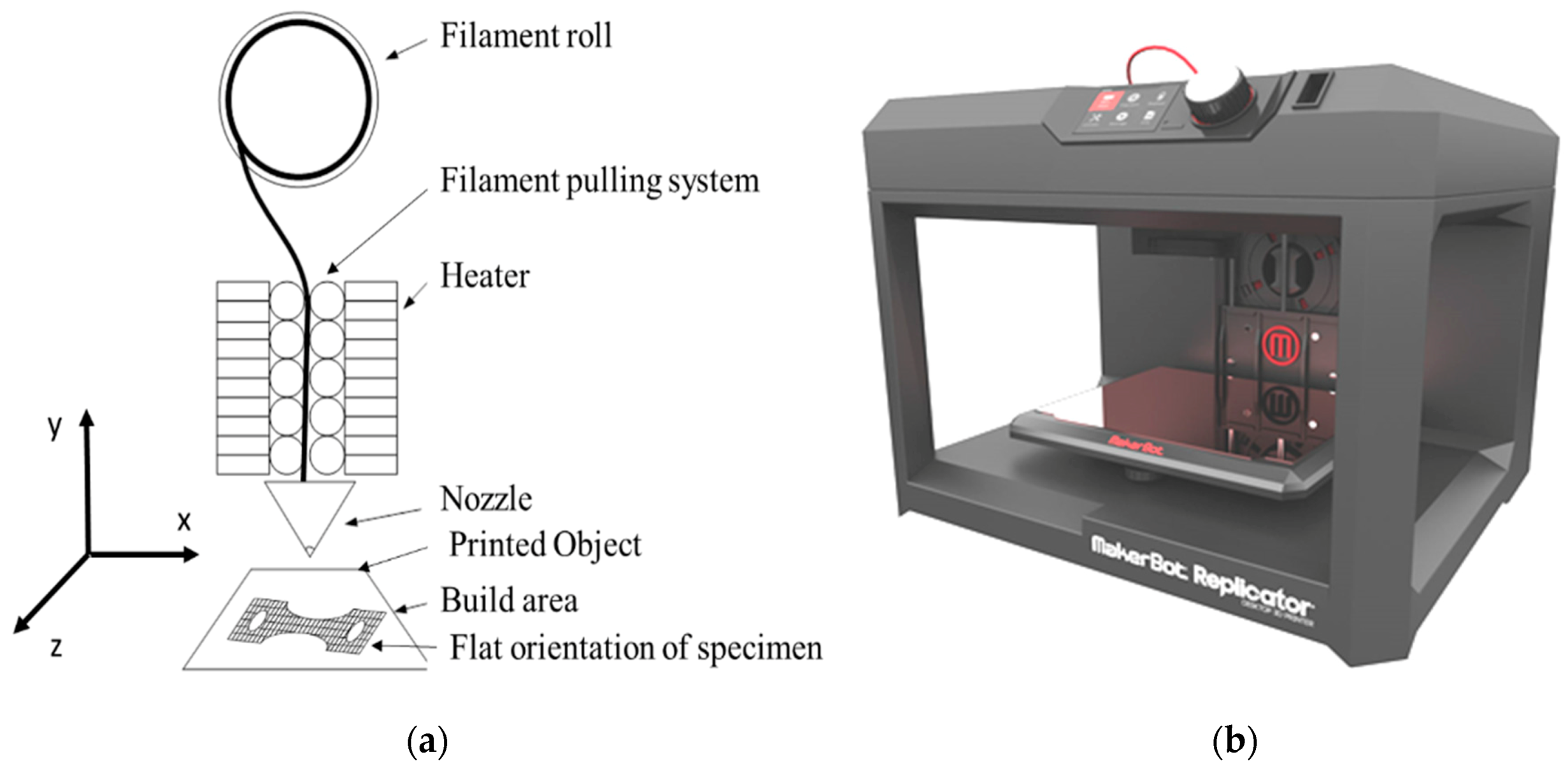
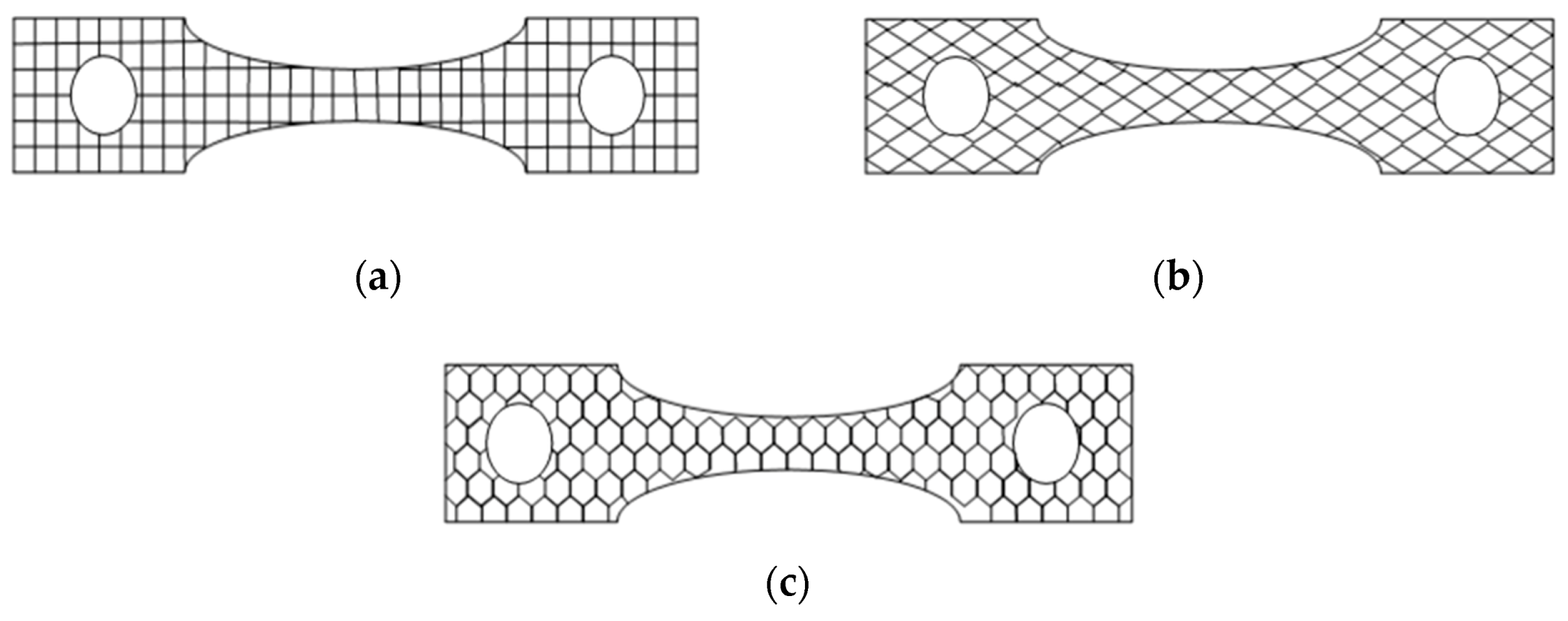
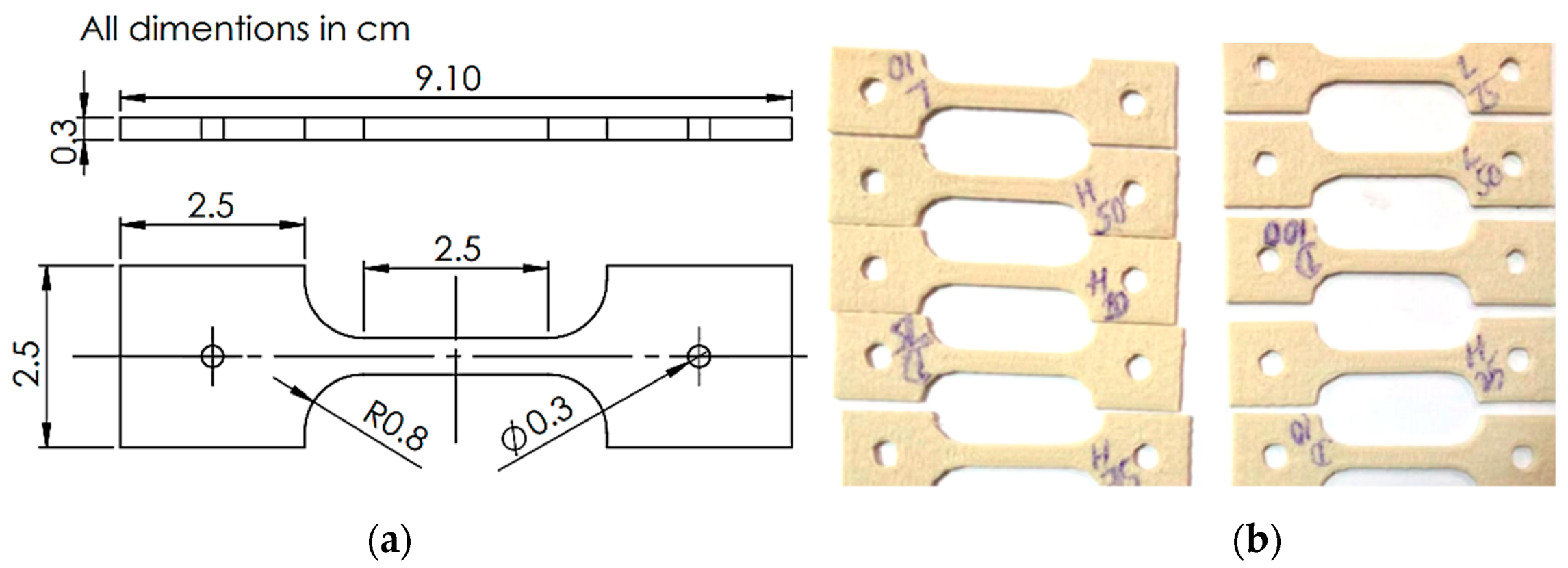
2.1. Experimental Setup
2.2. Experimental Design
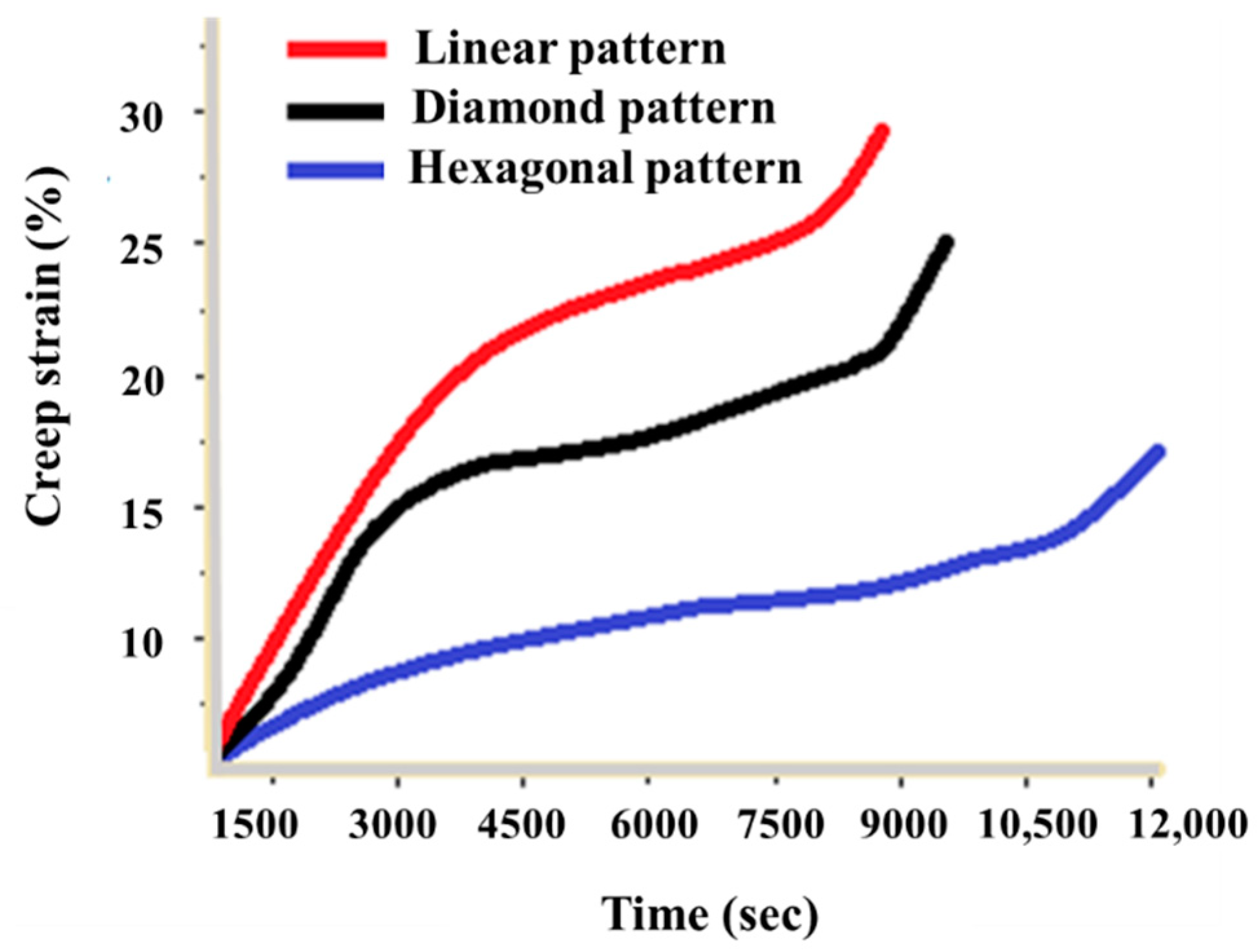
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Model Fitting and Analysis of Variance
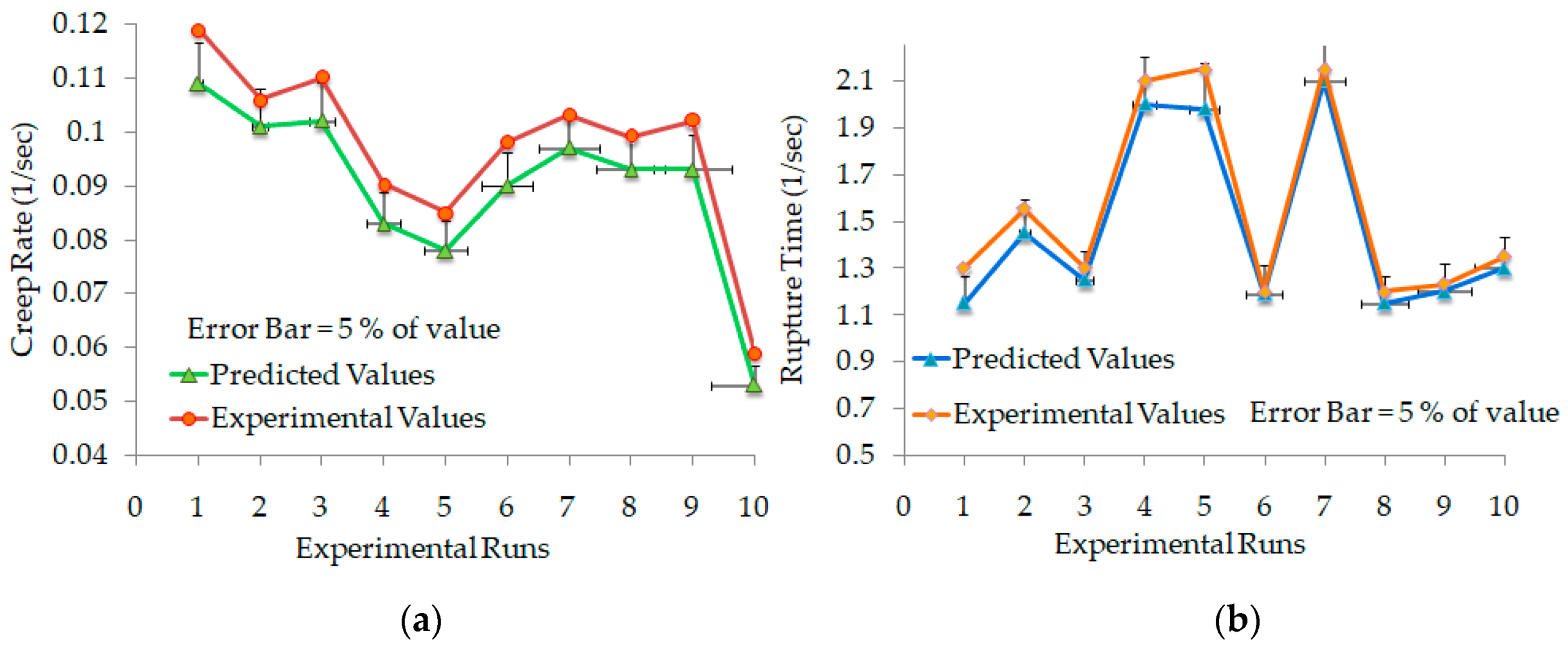
3.2. Regression Model Adequacy
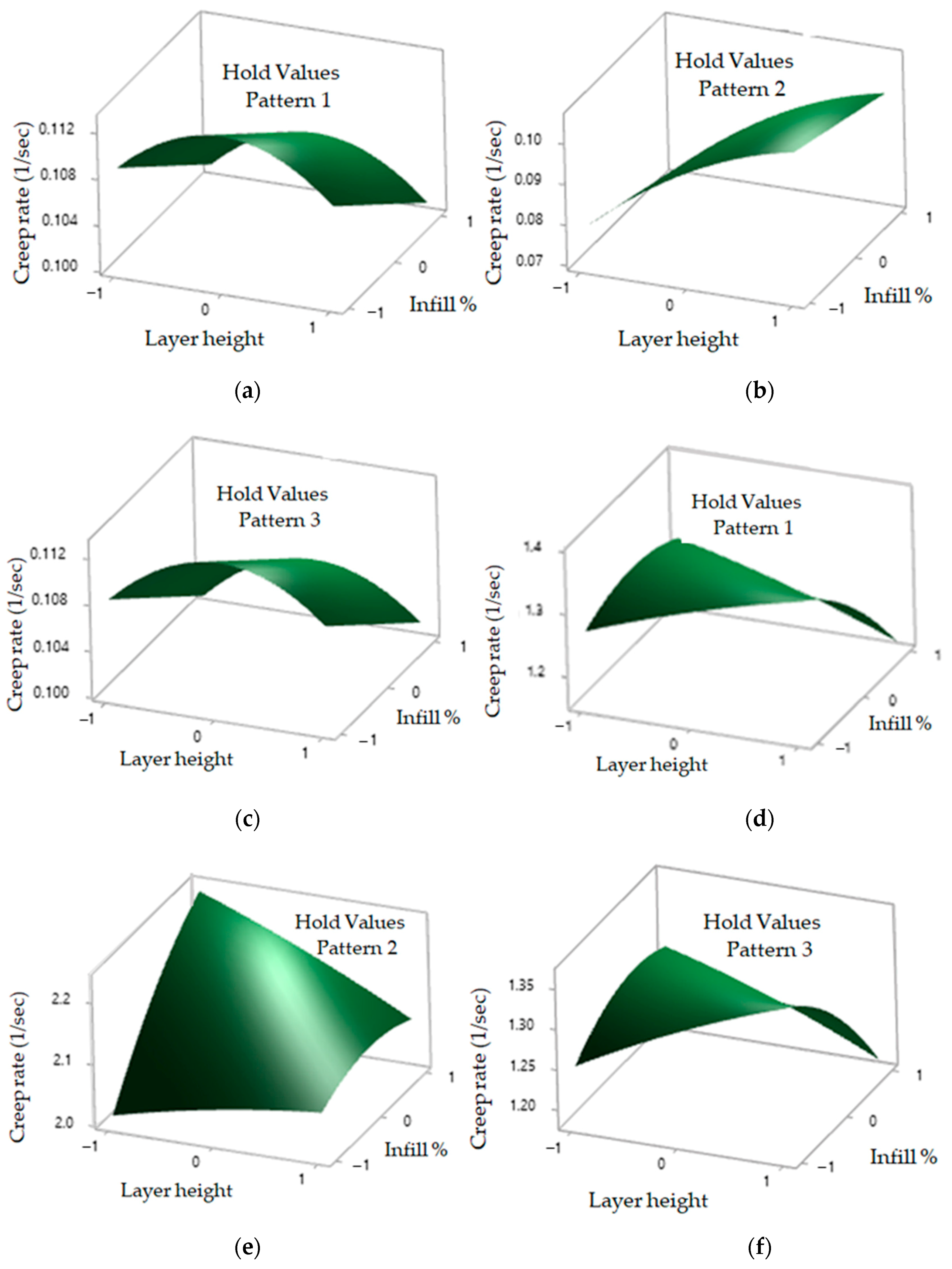
3.3. Effect of Process Parameters on Creep Rate and Rupture Time as 3D Surface Plots
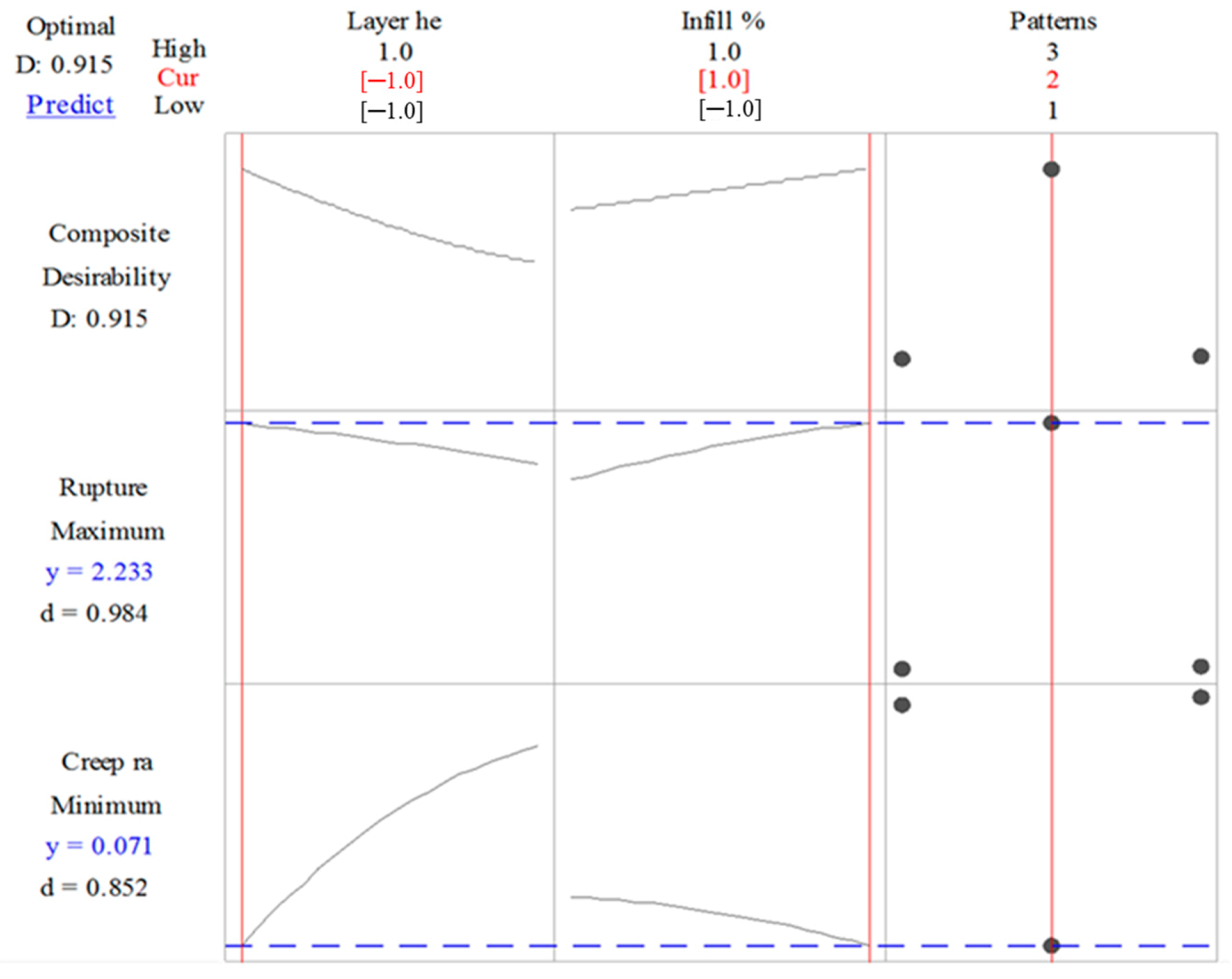
3.4. Multi-Response Optimization
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ngo, T.D.; Kashani, A.; Imbalzano, G.; Nguyen, K.T.; Hui, D. Additive manufacturing (3D printing): A review of materials, methods, applications and challenges. Compos. Part. B Eng. 2018, 143, 172–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheoran, A.J.; Kumar, H. Fused Deposition modeling process parameters optimization and effect on mechanical properties and part quality: Review and reflection on present research. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 21, 1659–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Singamneni, S. Adaptive slicing and speed- and time-dependent consolidation mechanisms in fused deposition modeling. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part. B J. Eng. Manuf. 2013, 228, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lou, Y. Tensile and Bending Strength Improvements in PEEK Parts Using Fused Deposition Modelling 3D Printing Considering Multi-Factor Coupling. Polymer 2020, 12, 2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parandoush, P.; Lin, D. A review on additive manufacturing of polymer-fiber composites. Compos. Struct. 2017, 182, 36–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasanasuk, K.; Tashiro, K. Crystal structure and disorder in Poly(l-lactic acid) δ form (α′ form) and the phase transition mechanism to the ordered α form. Polymer 2011, 52, 6097–6109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Lorenzo, M.L. Crystallization behavior of poly(l-lactic acid). Eur. Polym. J. 2005, 41, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marubayashi, H.; Asai, S.; Sumita, M. Complex Crystal Formation of Poly(l-lactide) with Solvent Molecules. Macromolecules 2012, 45, 1384–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, R.-Y.; Yangb, W.; Jiang, W.-R.; Liu, Z.-Y.; Xie, B.-H.; Yang, M.-B. Polymorphism of Racemic Poly(l-lactide)/Poly(d-lactide) Blend: Effect of Melt and Cold Crystallization. J. Phys. Chem. B 2013, 117, 3667–3674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartier, L.; Okihara, T.; Ikada, Y.; Tsuji, H.; Puiggali, J.; Lotz, B. Epitaxial crystallization and crystalline polymorphism of polylactides. Polymer 2000, 41, 8909–8919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalish, J.P.; Aou, K.; Yang, X.; Hsu, S.L. Spectroscopic and thermal analyses of α′ and α crystalline forms of poly(l-lactic acid). Polymer 2011, 52, 814–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.; Montero, M.; Odell, D.; Roundy, S.; Wright, P.K. Anisotropic material properties of fused deposition modeling ABS. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2002, 8, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicala, G.; Giordano, D.; Tosto, C.; Filippone, G.; Recca, A.; Blanco, I. Polylactide (PLA) Filaments a Biobased Solution for Additive Manufacturing: Correlating Rheology and Thermomechanical Properties with Printing Quality. Materials 2018, 11, 1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olaiya, N.G.; Surya, I.; Oke, P.K.; Rizal, S.; Sadiku, E.R.; Ray, S.S.; Farayibi, P.K.; Hossain, S.; Khalil, H.P.S.A. Properties and Characterization of a PLA–Chitin–Starch Biodegradable Polymer Composite. Polymer 2019, 11, 1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramaniam, S.R.; Samykano, M.; Selvamani, S.K.; Ngui, W.K.; Kadirgama, K.; Sudhakar, K.; Idris, M.S. Preliminary investigations of polylactic acid (PLA) properties. In Proceedings of the AIP Conference Proceedings; AIP Publishing: Melville, NY, USA, 2019; Volume 2059, p. 020038. [Google Scholar]
- Getme, A.S.; Patel, B. A Review: Bio-fiber’s as reinforcement in composites of polylactic acid (PLA). In Proceedings of the Materials Today: Proceedings; Elsevier BV: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; Volume 26, pp. 2116–2122. [Google Scholar]
- Cobos, C.M.; Garzón, L.; López-Martínez, J.; Fenollar, O.; Ferrandiz, S. Study of thermal and rheological properties of PLA loaded with carbon and halloysite nanotubes for additive manufacturing. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2019, 25, 738–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez-Robles, J.; Martin, N.K.; Fong, M.L.; Stewart, S.A.; Irwin, N.J.; Rial-Hermida, M.I.; Donnelly, R.F.; Larrañeta, E. Antioxidant PLA Composites Containing Lignin for 3D Printing Applications: A Potential Material for Healthcare Applications. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeStefano, V.; Khan, S.; Tabada, A. Applications of PLA in Modern Medicine. Eng. Regen. 2020, 1, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luchian-Lupu, A.-M.; Zaharescu, T.; Lungulescu, E.-M.; Râpă, M.; Iovu, H. Availability of PLA/SIS blends for packaging and medical applications. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2020, 172, 108696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, J.C.; Machado, Á.R.; Almeida, E.C.; Silva, E.F.M.S. Mechanical properties of PLA-graphene filament for FDM 3D printing. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 103, 2423–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casavola, C.; Cazzato, A.; Moramarco, V.; Pappalettere, C. Orthotropic mechanical properties of fused deposition modelling parts described by classical laminate theory. Mater. Des. 2016, 90, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baich, L.; Manogharan, G.; Marie, H. Study of infill print design on production cost-time of 3D printed ABS parts. Int. J. Rapid Manuf. 2015, 5, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farbman, D.; McCoy, C. Materials Testing of 3D Printed ABS and PLA Samples to Guide Mechanical Design. In Proceedings of the 11th International Manufacturing Science and Engineering Conference, Blacksburg, VA, USA, 27 June 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caminero, M.; Rodríguez, G.; Muñoz, V. Effect of stacking sequence on Charpy impact and flexural damage behavior of composite laminates. Compos. Struct. 2016, 136, 345–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamoona, S.N.; Masood, S.H.; Mohamed, O.A. Experimental investigation on flexural properties of FDM processed Nylon 12 parts using RSM. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2018; Volume 377, p. 12137. [Google Scholar]
- Tymrak, B.M.; Kreiger, M.; Pearce, J.M. Mechanical properties of components fabricated with open-source 3-D printers under realistic environmental conditions. Mater. Des. 2014, 58, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanzotti, A.; Grasso, M.; Staiano, G.; Martorelli, M. The impact of process parameters on mechanical properties of parts fabricated in PLA with an open-source 3-D printer. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2015, 21, 604–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaezi, M.; Chua, C.K. Effects of layer thickness and binder saturation level parameters on 3D printing process. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2010, 53, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovo, J.F.P.; Fortulan, C.A.; Da Silva, M.M.M. Optimal deposition orientation in fused deposition modeling for maximizing the strength of three-dimensional printed truss-like structures. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part. B J. Eng. Manuf. 2018, 233, 1206–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, O.A.; Masood, S.; Bhowmik, J.L. Investigation on the Flexural Creep Stiffness Behavior of PC–ABS Material Processed by Fused Deposition Modeling Using Response Surface Definitive Screening Design. JOM 2016, 69, 498–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, T.; Selvaraj, R.; Hong, S.; Kim, N. Creep Behavior of ABS Polymer in Temperature–Humidity Conditions. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2017, 29494, 304–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.D.; Rhee, J.M.; Nah, C.; Lee, S.-H.; Lyu, M.-Y. Predicting the Long-term Creep Behavior of Plastics Using the Short-term Creep Test. Int. Polym. Process. 2004, 19, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tezel, T.; Kovan, V.; Topal, E.S. Effects of the printing parameters on short-term creep behaviors of three-dimensional printed polymers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dave, H.K.; Patadiya, N.H.; Prajapati, A.R.; Rajpurohit, S.R. Effect of infill pattern and infill density at varying part orientation on tensile properties of fused deposition modeling-printed poly-lactic acid part. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part. C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasong, W.; Muanchan, P.; Ishigami, A.; Thumsorn, S.; Kurose, T.; Ito, H. Properties of 3D Printable Poly(lactic acid)/Poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) Blends and Nano Talc Composites. J. Nanomater. 2020, 2020, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanzotti, A.; Martorelli, M.; Maietta, S.; Gerbino, S.; Penta, F.; Gloria, A. A comparison between mechanical properties of specimens 3D printed with virgin and recycled PLA. Procedia CIRP 2019, 79, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, S.A.; Muthukumaran, E.; Jayakrishna, K. A Case Study of 3D Printed PLA and Its Mechanical Properties. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 11219–11226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, W.N.F.W.; Ismail, M.A.; Lee, H.-S.; Meddah, M.S.; Singh, J.K.; Hussin, M.W.; Ismail, M. Mixture optimization of high-strength blended concrete using central composite design. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 243, 118251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abas, M.; Salman, Q.; Khan, A.M.; Rahman, K. Direct ink writing of flexible electronic circuits and their characterization. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2019, 41, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, D.E.; Montgomery, D.C. A Systematic Approach to Planning for a Designed Industrial Experiment. Technometrics 1993, 35, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ait-Amir, B.; Pougnet, P.; El Hami, A. Meta-Model Development. In Embedded Mechatronic Systems 2; Elsevier BV: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 151–179. [Google Scholar]
- Sood, A.K.; Ohdar, R.; Mahapatra, S. Parametric appraisal of mechanical property of fused deposition modelling processed parts. Mater. Des. 2010, 31, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovan, V.; Altan, G.; Topal, E.S. Effect of layer thickness and print orientation on strength of 3D printed and adhesively bonded single lap joints. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2017, 31, 2197–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeykoon, C.; Sri-Amphorn, P.; Fernando, A. Optimization of fused deposition modeling parameters for improved PLA and ABS 3D printed structures. Int. J. Lightweight Mater. Manuf. 2020, 3, 284–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Xie, X.; Wang, J.; Zhao, A.; Peng, Y.; Rao, Y. Effects of infill characteristics and strain rate on the deformation and failure properties of additively manufactured polyamide-based composite structures. Results Phys. 2020, 18, 103346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alafaghani, A.; Qattawi, A. Investigating the effect of fused deposition modeling processing parameters using Taguchi design of experiment method. J. Manuf. Process. 2018, 36, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Mechanical Properties | |
| Elastic (Young’s, Tensile) Modulus, GPa | 3.5 |
| Elongation at Break, % | 6 |
| Flexural Modulus, GPa | 4 |
| Flexural Strength, MPa | 80 |
| Tensile Strength: Ultimate (UTS), MPa | 50 |
| Molecular weight, Mn (g/mol) (103) | 4.7–16.8 |
| Thermal Properties | |
| Heat Deflection Temperature At 455 kPa (66 psi), °C | 65 |
| Density, g/cm3 | 1.3 |
| Common Calculations | |
| Stiffness to Weight: Axial, points | 1.6 |
| Stiffness to Weight: Bending, points | 40 |
| Strength to Weight: Axial, points | 11 |
| Strength to Weight: Bending, points | 24 |
| Factors | Levels | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symbols | −1 | 0 | 1 | |
| Continuous | ||||
| Layer height (mm) | L | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 |
| Infill percentage | I | 10 | 55 | 100 |
| Categorical | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| Infill Pattern | Pt | Linear | Hexagonal | Diamond |
| Coded Variable | Responses | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Std Order | Run Order | Layerheight | Infill % | Patterns | Creep rate (1/s) | Rupture time (h) |
| 27 | 1 | −1 | −1 | 3 | 0.108 | 1.296 |
| 16 | 2 | −1 | 1 | 1 | 0.105 | 1.260 |
| 39 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0.109 | 1.308 |
| 7 | 4 | 0 | −1 | 2 | 0.094 | 2.021 |
| 10 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0.087 | 2.088 |
| 30 | 6 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 0.101 | 1.212 |
| 18 | 7 | −1 | 0 | 1 | 0.104 | 1.248 |
| 19 | 8 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0.103 | 1.236 |
| 31 | 9 | −1 | 0 | 3 | 0.101 | 1.212 |
| 25 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.110 | 1.320 |
| 11 | 11 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0.089 | 2.136 |
| 1 | 12 | −1 | −1 | 2 | 0.082 | 1.994 |
| 34 | 13 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 0.099 | 1.188 |
| 12 | 14 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0.098 | 2.058 |
| 22 | 15 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.110 | 1.320 |
| 13 | 16 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0.093 | 2.093 |
| 21 | 17 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0.100 | 1.200 |
| 14 | 18 | −1 | −1 | 1 | 0.105 | 1.260 |
| 3 | 19 | −1 | 1 | 2 | 0.064 | 2.240 |
| 26 | 20 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.110 | 1.320 |
| 36 | 21 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0.111 | 1.332 |
| 37 | 22 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0.108 | 1.350 |
| 23 | 23 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.113 | 1.356 |
| 15 | 24 | 1 | −1 | 1 | 0.112 | 1.344 |
| 8 | 25 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0.095 | 2.233 |
| 2 | 26 | 1 | −1 | 2 | 0.105 | 2.153 |
| 32 | 27 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 0.108 | 1.296 |
| 28 | 28 | 1 | −1 | 3 | 0.110 | 1.320 |
| 20 | 29 | 0 | −1 | 1 | 0.112 | 1.344 |
| 24 | 30 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.110 | 1.320 |
| 4 | 31 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0.097 | 2.037 |
| 9 | 32 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0.098 | 2.058 |
| 38 | 33 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0.111 | 1.332 |
| 6 | 34 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0.100 | 2.150 |
| 35 | 35 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0.110 | 1.320 |
| 33 | 36 | 0 | −1 | 3 | 0.108 | 1.296 |
| 17 | 37 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.098 | 1.176 |
| 29 | 38 | −1 | 1 | 3 | 0.108 | 1.296 |
| 5 | 39 | −1 | 0 | 2 | 0.075 | 2.250 |
| Source | † DF | Sum of Square | Mean Square | F-Value | ǂp-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Creep rate (1/s) | |||||
| Model | 11 | 0.003943 | 0.000358 | 22.48 | <0.0001 * |
| L | 1 | 0.000374 | 0.000374 | 23.43 | <0.0001 * |
| I | 1 | 0.000264 | 0.000264 | 16.59 | <0.0001 * |
| Pt | 2 | 0.002371 | 0.001185 | 74.34 | <0.0001 * |
| L2 | 1 | 0.000128 | 0.000128 | 8.03 | 0.009 * |
| I2 | 1 | 0.00001 | 0.00001 | 0.63 | 0.436 |
| L × I | 1 | 0.000014 | 0.000014 | 0.88 | 0.356 |
| L × Pt | 2 | 0.000721 | 0.00036 | 22.6 | <0.0001 * |
| I × Pt | 2 | 0.000006 | 0.000003 | 0.2 | 0.821 |
| Error | 27 | 0.000431 | 0.000016 | ||
| Lack-of-Fit | 15 | 0.000315 | 0.000021 | 2.17 | 0.091 |
| Pure Error | 12 | 0.000116 | 0.00001 | ||
| Total | 38 | 0.004374 | |||
| Rupture time (h) | |||||
| Model | 11 | 6.04684 | 0.54971 | 206.1 | <0.0001 |
| L | 1 | 0.00098 | 0.00098 | 0.37 | 0.55 |
| I | 1 | 0.00192 | 0.00192 | 0.72 | 0.403 |
| Pt | 2 | 5.95786 | 2.97893 | 1116.89 | <0.0001 * |
| L2 | 1 | 0.0004 | 0.0004 | 0.15 | 0.701 |
| I2 | 1 | 0.00534 | 0.00534 | 2 | 0.169 |
| L × I | 1 | 0.03387 | 0.03387 | 12.7 | 0.001 * |
| L × Pt | 2 | 0.00262 | 0.00131 | 0.49 | 0.617 |
| I × Pt | 2 | 0.04157 | 0.02079 | 7.79 | 0.002 * |
| Error | 27 | 0.07201 | 0.00267 | ||
| Lack-of-Fit | 15 | 0.06588 | 0.00439 | 2.2 | 0.097 |
| Pure Error | 12 | 0.00613 | 0.00051 | ||
| Total | 38 | 6.11885 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Waseem, M.; Salah, B.; Habib, T.; Saleem, W.; Abas, M.; Khan, R.; Ghani, U.; Siddiqi, M.U.R. Multi-Response Optimization of Tensile Creep Behavior of PLA 3D Printed Parts Using Categorical Response Surface Methodology. Polymers 2020, 12, 2962. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12122962
Waseem M, Salah B, Habib T, Saleem W, Abas M, Khan R, Ghani U, Siddiqi MUR. Multi-Response Optimization of Tensile Creep Behavior of PLA 3D Printed Parts Using Categorical Response Surface Methodology. Polymers. 2020; 12(12):2962. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12122962
Chicago/Turabian StyleWaseem, Muhammad, Bashir Salah, Tufail Habib, Waqas Saleem, Muhammad Abas, Razaullah Khan, Usman Ghani, and Muftooh Ur Rehman Siddiqi. 2020. "Multi-Response Optimization of Tensile Creep Behavior of PLA 3D Printed Parts Using Categorical Response Surface Methodology" Polymers 12, no. 12: 2962. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12122962
APA StyleWaseem, M., Salah, B., Habib, T., Saleem, W., Abas, M., Khan, R., Ghani, U., & Siddiqi, M. U. R. (2020). Multi-Response Optimization of Tensile Creep Behavior of PLA 3D Printed Parts Using Categorical Response Surface Methodology. Polymers, 12(12), 2962. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12122962