Synthesis and Characterization of Polyaniline-Chitosan Patches with Enhanced Stability in Physiological Conditions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Chitosan Viscous Solution
2.3. Fabrication of Chitosan Film on Microscopic Glass Slides
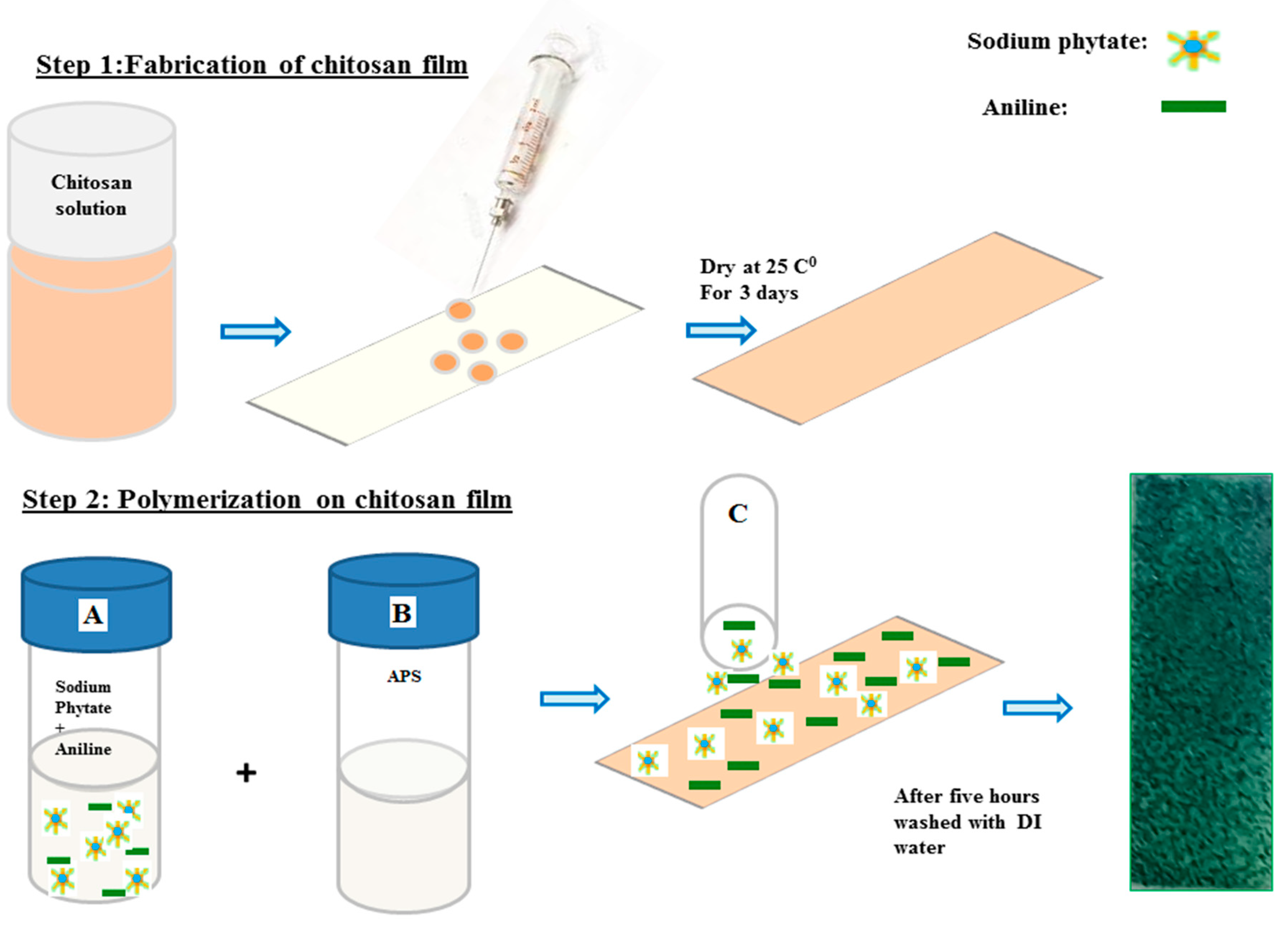
2.4. Fabrication of Chitosan-PAni Conductive Polymeric Patches
2.5. Material Characterization
2.5.1. In Vitro Characterization Physical Properties of the Patch
2.5.2. In Vitro Characterization/Electronic Properties of the Patch
3. Results and Discussion
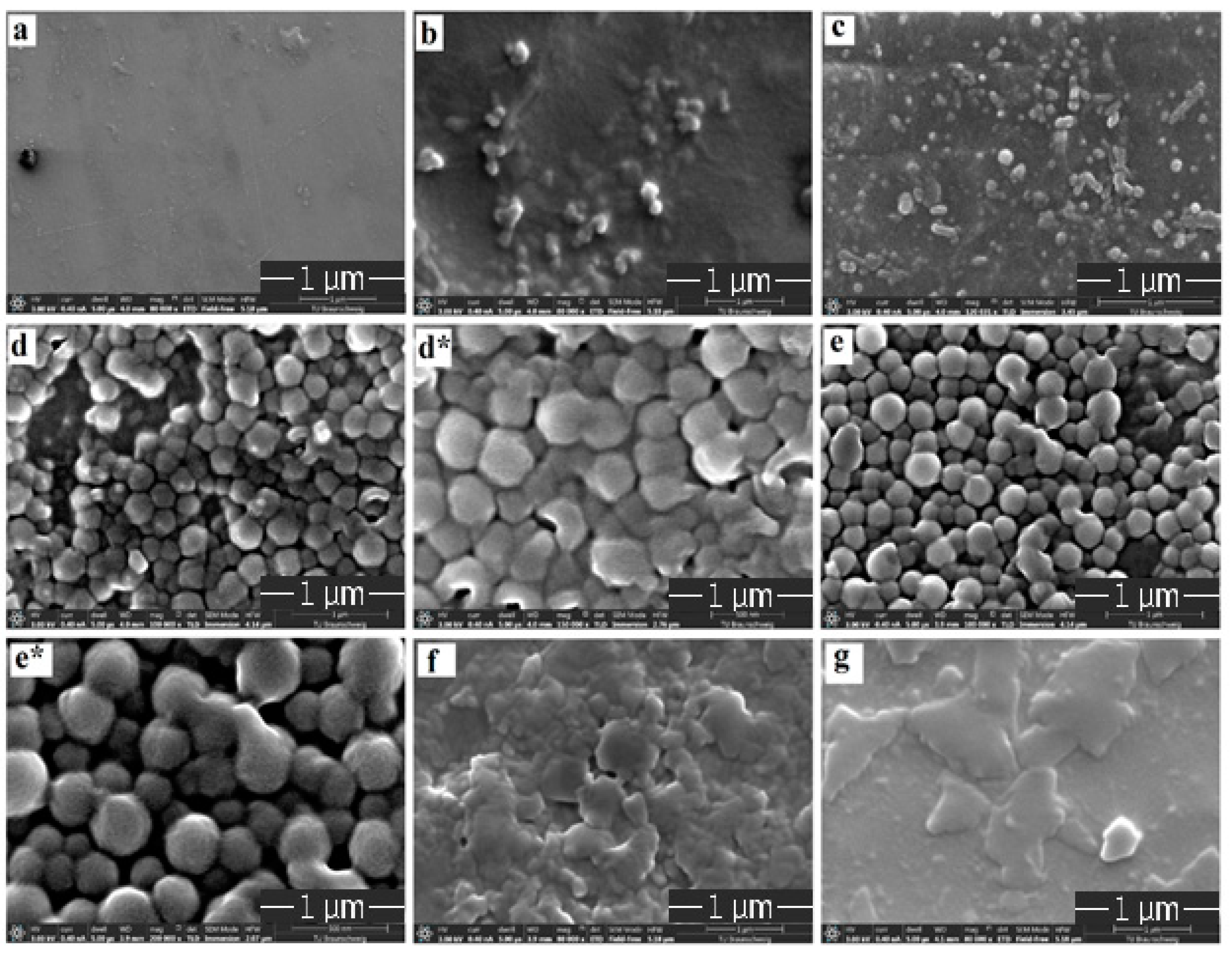
3.1. Surface Morphology of the Patches Using SEM
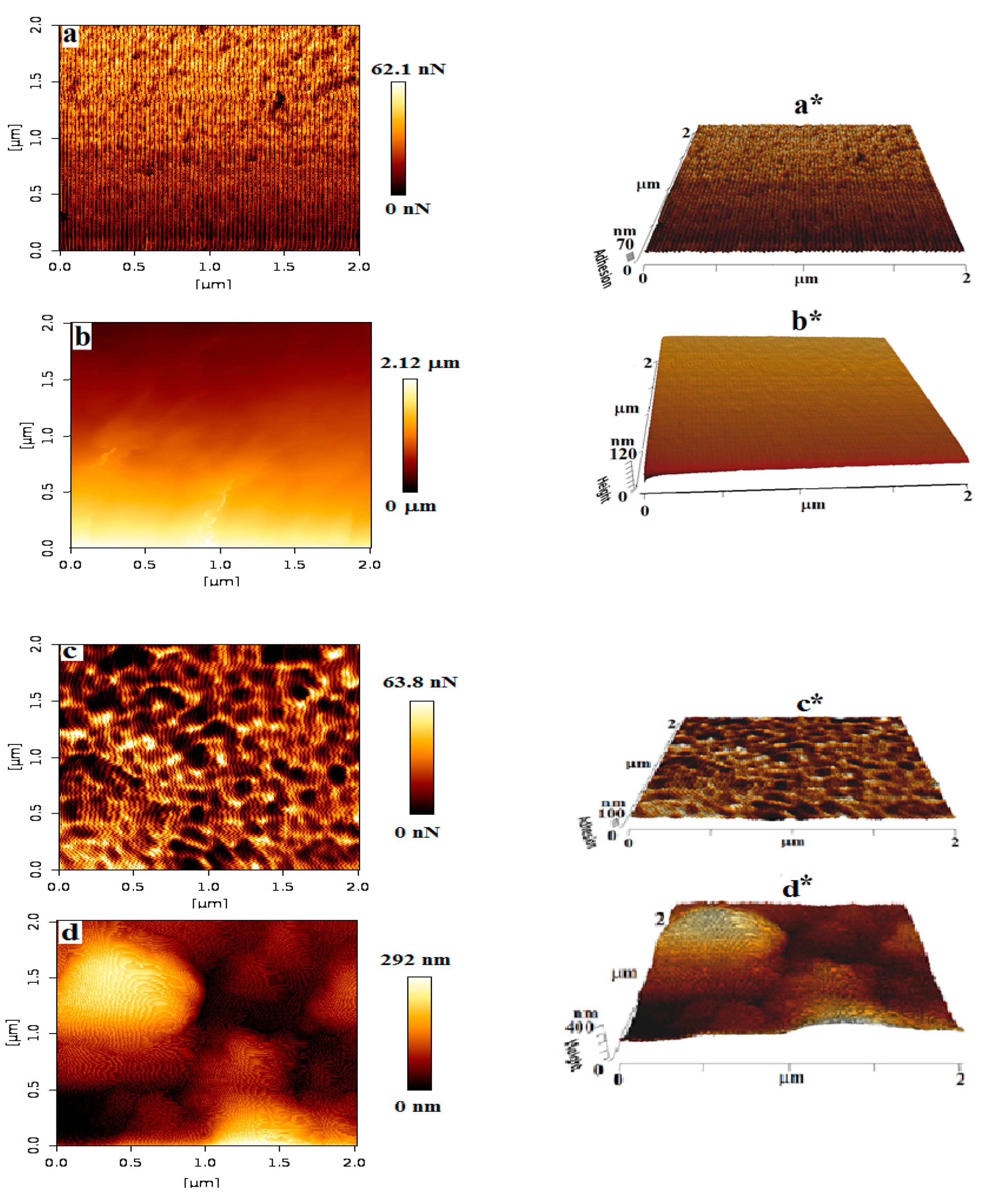
3.2. Morphological Studies of Patch-5 Using Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM)
3.3. Sheet Resistance of the Patch
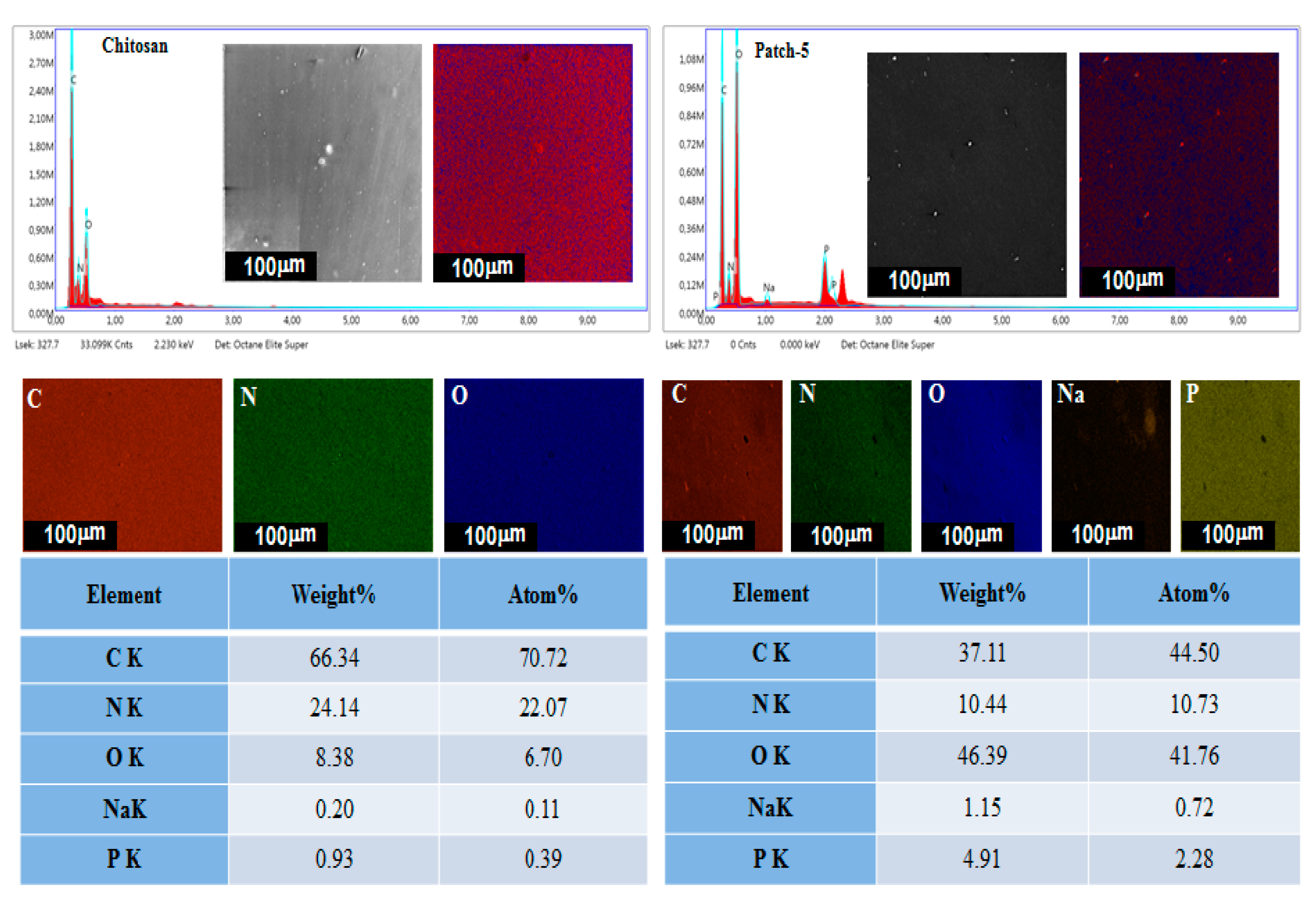
3.4. Energy-Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy and Elemental Mapping
3.5. FTIR Spectroscopy
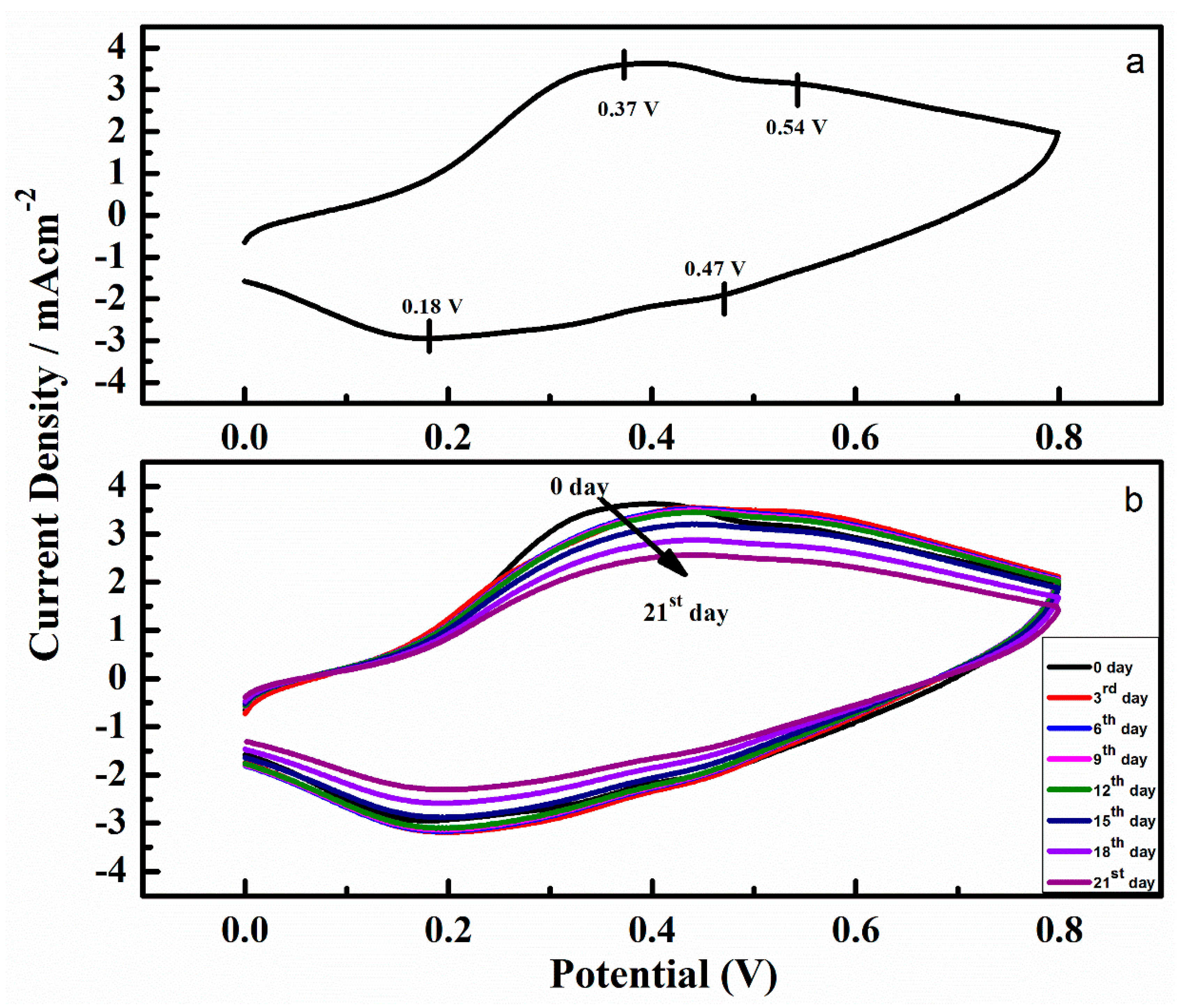
3.6. Cyclic Voltammetry (CV)
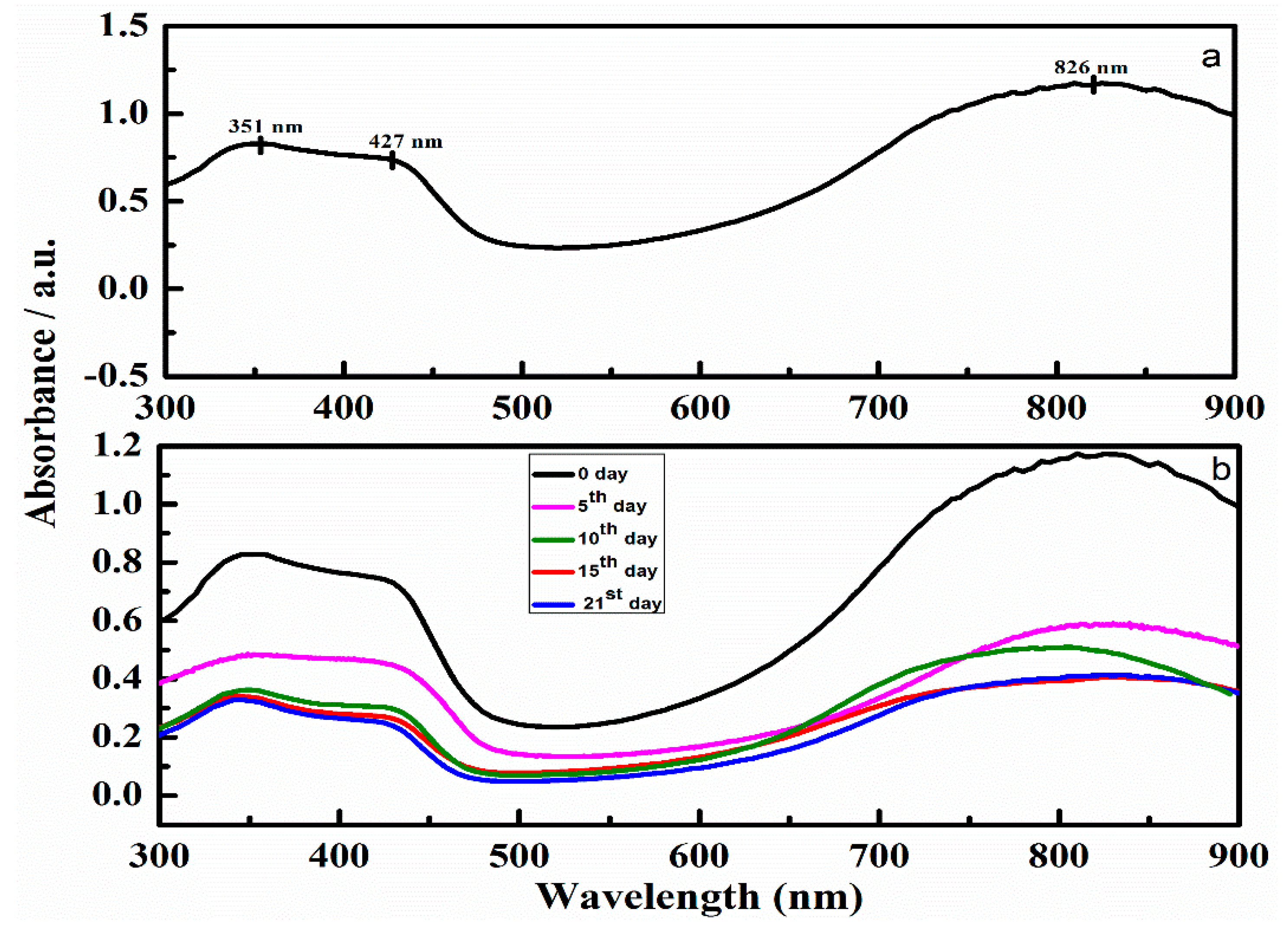
3.7. UV-Vis Spectroscopy
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Dedication
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Owens, M.R.; Malliaras, G.G. Organic electronics at the interface with biology. MRS Bull. 2010, 35, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mawad, D.; Stewart, E.; Officer, D.L.; Romeo, T.; Wanger, P.; Wanger, K.; Wallace, G. A single component conducting polymer hydrogel as a scaffold for tis sue engineering. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 2692–2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mawad, D.; Molino, J.P.; Gambhir, S.; Locke, M.J.; Officer, D.L.; Wallace, G.G. Electrically induced disassembly of electroactive multilayer films fabricated from water soluble polythiophenes. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 5020–5027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mawad, D.; Gilmore, K.; Molino, P.; Wagner, K.; Wagner, P.; Officer, D.L.; Wallace, G.G. An erodible polythiophene-based composite for biomedical applications. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 5555–5560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balint, R.; Cassidy, N.J.; Cartmell, S.H. Conductive polymers: Towards a smart biomaterial for tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 2341–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; MacDiarmid, A.G. New synthesis of phenyl/phenyl end-capped tetraaniline in the leucoemeraldine and emeraldine oxidation states. Synth. Met. 2002, 129, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garner, B.; Georgevich, A.; Hodgson, J.A.; Liu, L.; Wallace, G.G. Polypyrrole-heparin composites as stimulus-responsive substrates for endothelial cell growth. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1999, 44, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borriello, A.; Guarino, V.; Schiavo, L.; Alvarez-Perez, A.M.; Ambrosio, L. Optimizing PANi doped electroactive substrates as patches for the regeneration of cardiac muscle. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2011, 22, 1053–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.Q.; Yan, H.Y.; Li, P.S.; Feng, T. Synthesis of a novel biodegradable and electroactive polyphosphazene for biomedical application. Biomed. Mater. 2009, 4, 035008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedaghat, S. Synthesis and Evaluation of Chitosan-Polyaniline Copolymer in Presence of Ammonium Persulfate as Initiator. J. Appl. Chem. Res. 2014, 8, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, W.D.; Choi, R.H.; Keon, K.D. Stability constants of amidoximated chitosan-g-poly(acrylonitrile) copolymer for heavy metal ions. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1999, 73, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, F.W.; Chen, J.Y. Studies on preparation and swelling properties of the N-isopropylacrylamide/chitosan semi-IPN and IPN hydrogels. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2001, 82, 2487–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, K.S.; Tiwari, A. Synthesis of chemical responsive chitosan–grafted-polyaniline bio-composite. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 306, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihic, A.; Cui, Z.; Wu, J.; Vlacic, G.; Miyagi, Y.; Li, H.S.; Lu, S.; Sung, W.H.; Weisel, D.R.; Li, K.R. A conductive polymer hydrogel supports cell electrical signaling and improves cardiac function after implantation into myocardial infarct. Circulation 2015, 132, 772–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tiwari, A.; Singh, V. Synthesis and characterization of electrical conducting chi-tosan-graft-polyaniline. Express Polym. Lett. 2007, 5, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moutsatsou, P.; Coopman, K.; Georgiadou, S. Biocompatibility assessment of conducting PANI/Chitosan nanofibers for wound healing applications. Polymers 2017, 9, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kushwaha, S.C.; Singh, P.; Shukla, K.S.; Dubey, G.C. Electrochemical urea sensing over polyaniline grafted chitosan copolymer. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 15253–15260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasela, R.B.; Castillo, P.A.; Simon, R.; Pulido, T.M.; Manaay, H.; Abiquibil, R.M.; Montecillo, R.; Thumanu, K.; Tumacder, V.D.; Tacca, L.K. Synthesis and characterization of acetic acid doped Polyaniline and Polyaniline-chitosan composite. Biomimetics 2019, 4, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.; Choi, D.; Son, Y. Hazardous acid detection based on chitosan-grafted polyaniline copolymer. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2019, 59, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, J.A.; Ginder, M.J.; Zuo, F.; Woo, S.H.; Tanner, B.D.; Richter, F.A.; Angelopoulos, M.; Huang, S.W.; MacDiarmid, G.A. Insulator-to-metal transition in polyaniline: Effect of protonation in emeraldine. Synth. Met. 1987, 21, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.; Faraji, N.; Lauto, A.; Travaglini, L.; Tonkin, J.; Mahns, D.; Humphrey, E.; Terracciano, C.; Gooding, J.J.; Seidel, J.; et al. A flexible polyaniline-based bioelectronic patch. Biomater. Sci. 2018, 6, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, L.; Yu, G.; Zhai, D.; Lee, R.H.; Zhao, W.; Liu, N.; Wang, H.; Tee, K.C.B.; Shi, Y.; Cui, Y.; et al. Hierarchical nanostructured conducting polymer hydrogel with high Electrochemical activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 9287–9292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, H.; Jeong, C.; Ghafoor, K.; Cho, S.; Park, J. Oral delivery of insulin using chitosan capsules cross-linked with phytic acid. Biomed. Mater. Eng. 2011, 21, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konyushenko, E.; Trchova, M.; Stejskal, J.; Sapurina, I. The role of acidity profile in the nanotubular growth of polyaniline. Chem. Pap. 2010, 64, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Kaner, B.R. A general chemical route to polyaniline nanofibers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 851–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Ni, C.N.; Wu, J.; Du, Q.G.; He, S.; Yau, M.T.; Weisel, D.R.; Sung, W.H.; Li, K.R. Polypyrrole-chitosan conductive biomaterial synchronizes cardiomyocyte contraction and improves myocardial electrical impulse propagation. Theranostics 2018, 8, 2752–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Lei, B.; Li, P.; Ma, X.P. Functionalized scaffolds to enhance tissue regeneration. Regen. Biomater. 2015, 2, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, X.; Jing, X.; Li, Y.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, M. Synthesis and characterization of phosphorized polyaniline doped with phytic acid and its anticorrosion properties for Mg-Li alloy. J. Macromol. Sci. A 2018, 55, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, A.Y.; Shin, R.S.; Shin, M.K.; Yoon, G.S.; Shon, K.; Kim, I.S. Electrochemical actuation in chitosan/polyaniline microfibers for artificial muscles fabricated using an in situ polymerization. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2008, 129, 834–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavuz, G.A.; Uygun, A.; Bhethanabotla, R.V. Substituted polyaniline/chitosan composites: Synthesis and characterization. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 75, 448–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.X.; Ren, L.G.; Chen, J.G.; Liu, Q.; Li, G.D.; Chen, Q. Selfassembly of polyaniline-grafted chitosan/glucose oxidase nanolayered films for electrochemical biosensor applications. J. Mater. Sci. 2006, 41, 4974–4977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavuz, G.A.; Uygun, A.; Bethanabotla, R.V. Preparation of substituted polyaniline/chitosan composites by in situ electropolymerization and their application to glucose sensing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 81, 712–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanathana, S.; Ponnuswamya, V.; Gowthama, B.; Premnazeerb, K.; Murugavelc, C.S. Effect of aniline concentration on chitosan-grafted polyaniline. J. Optoelectron. Adv. Mater. 2014, 16, 973–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khairkar, R.S.; Raut, R.A. Synthesis of chitosan-graft-polyaniline-based composites. Am. J. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2014, 2, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arefinia, R.; Shojaei, A.; Shariatpanahi, H.; Neshati, J. Anticorrosion properties of smart coating based on polyaniline nanoparticles/epoxy-ester system. Prog. Org. Coat. 2012, 75, 502–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Im, S.; Kim, J.C.; Hong, W.G.; Shin, K.; Jeong, H.Y.; Hong, J.H. Phytic acid doped polyaniline nanofibers for enhanced aqueous copper(II) adsorption capability. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 6654–6664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trchova, M.; Stejskal, J. The infrared spectroscopy of conducting polymer nanotubes. Pure Appl. Chem. 2011, 83, 1803–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarver, J.; Yoo, J.E.; Dennes, T.J.; Schwartz, J.; Loo, Y.L. Polymer acid doped polyaniline is electrochemically stable beyond pH 9. Chem. Mater. 2009, 21, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, A.F.; Logan, J.A. Electroactive polyaniline films. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1980, 111, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Levon, K. Influence of dopant on electroactivity of polyaniline. Macromol. Symp. 2012, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.G.; Cho, S.K.; Oh, S.G.; Im, S.S. Preparation and characterization of polyaniline nanoparticles synthesized from DBSA micellar solution. Synth. Met. 2002, 126, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sample Code | Roughness | Sheet Resistance (Ohm/cm2) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Average Resistance (Ra) | Root Mean Square Resistance (Rq) | ||
| Pristine chitosan | 13.52 nm | 20.19 nm | - |
| Patch-5 | 51.86 nm | 66.31 nm | 14.15 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rahman, S.U.; Bilal, S.; ul Haq Ali Shah, A. Synthesis and Characterization of Polyaniline-Chitosan Patches with Enhanced Stability in Physiological Conditions. Polymers 2020, 12, 2870. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12122870
Rahman SU, Bilal S, ul Haq Ali Shah A. Synthesis and Characterization of Polyaniline-Chitosan Patches with Enhanced Stability in Physiological Conditions. Polymers. 2020; 12(12):2870. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12122870
Chicago/Turabian StyleRahman, Sami Ur, Salma Bilal, and Anwar ul Haq Ali Shah. 2020. "Synthesis and Characterization of Polyaniline-Chitosan Patches with Enhanced Stability in Physiological Conditions" Polymers 12, no. 12: 2870. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12122870
APA StyleRahman, S. U., Bilal, S., & ul Haq Ali Shah, A. (2020). Synthesis and Characterization of Polyaniline-Chitosan Patches with Enhanced Stability in Physiological Conditions. Polymers, 12(12), 2870. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12122870







