Nanofibers-Based Piezoelectric Energy Harvester for Self-Powered Wearable Technologies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Preparation of Spinning Solutions
2.2.2. Preparation of the PVDF/LiCl Nanofibers Web
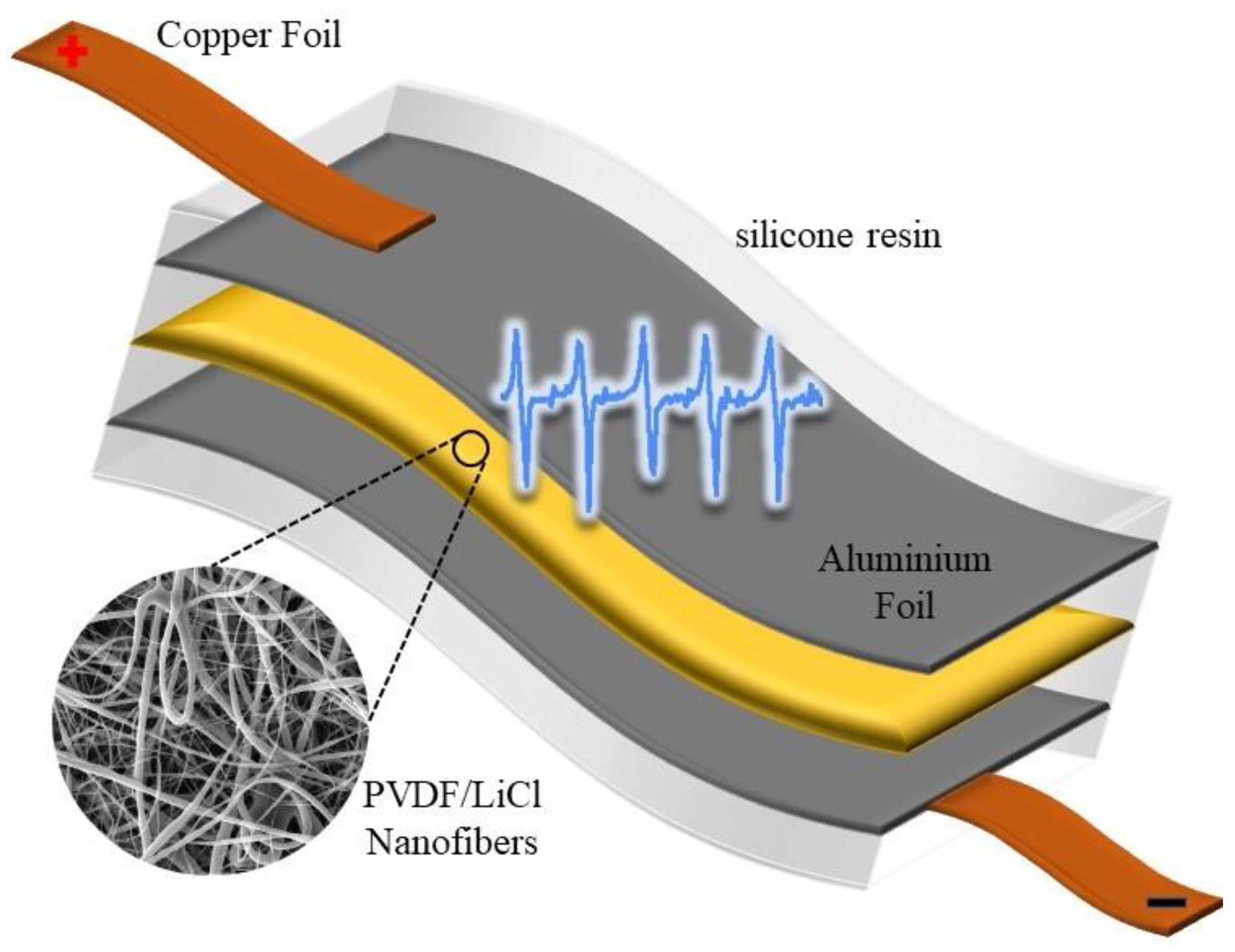
2.2.3. Fabrication of Power Generator Samples
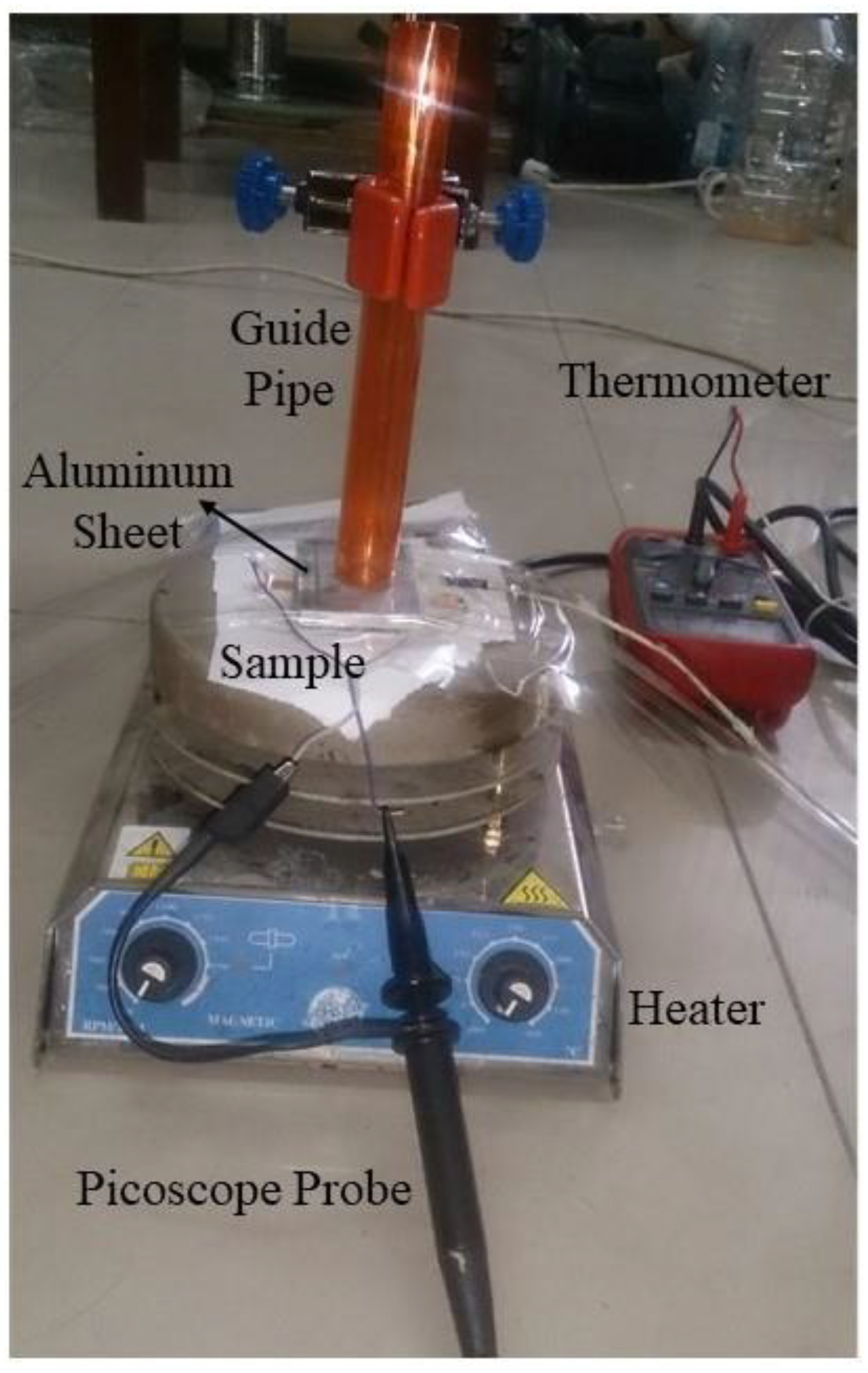
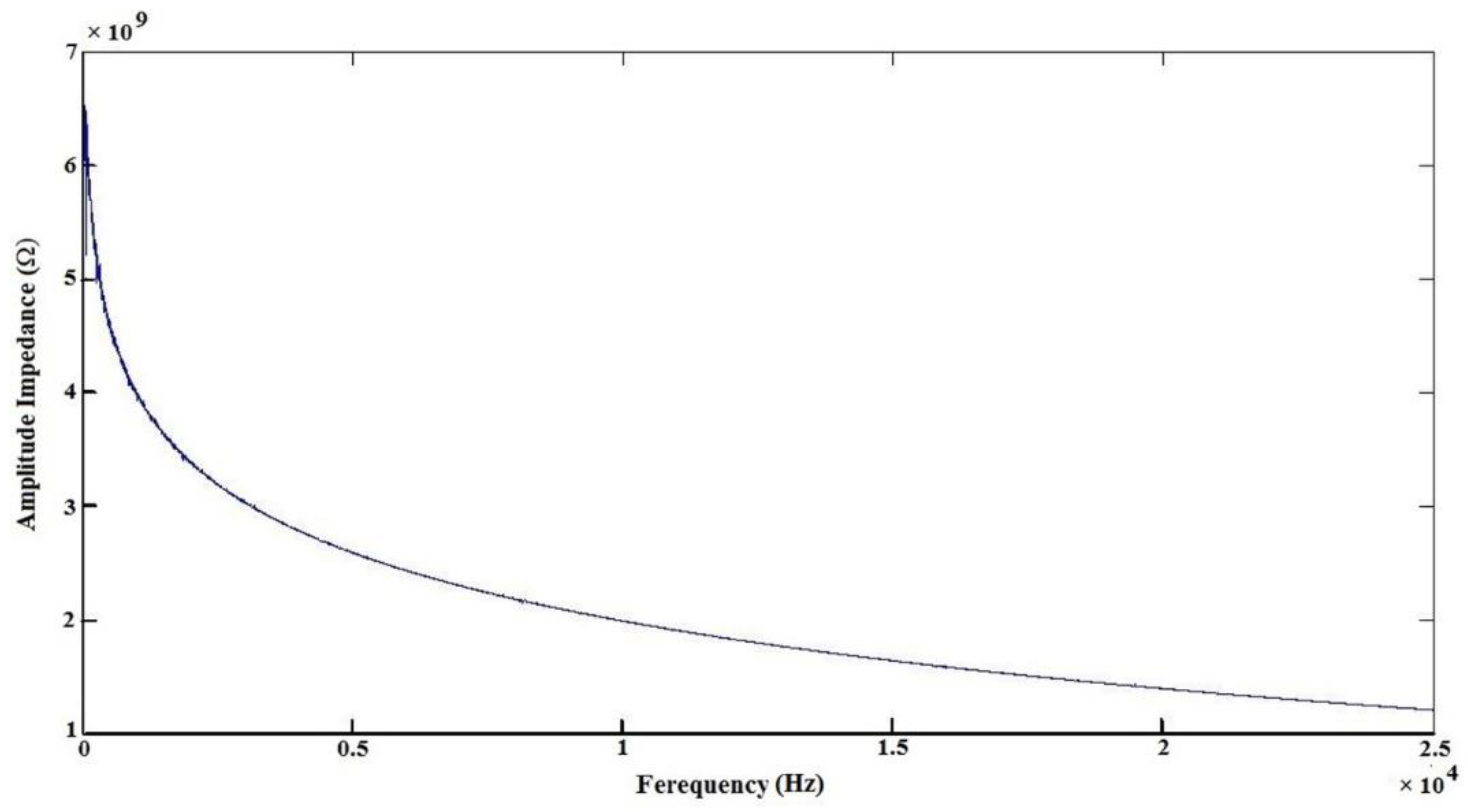
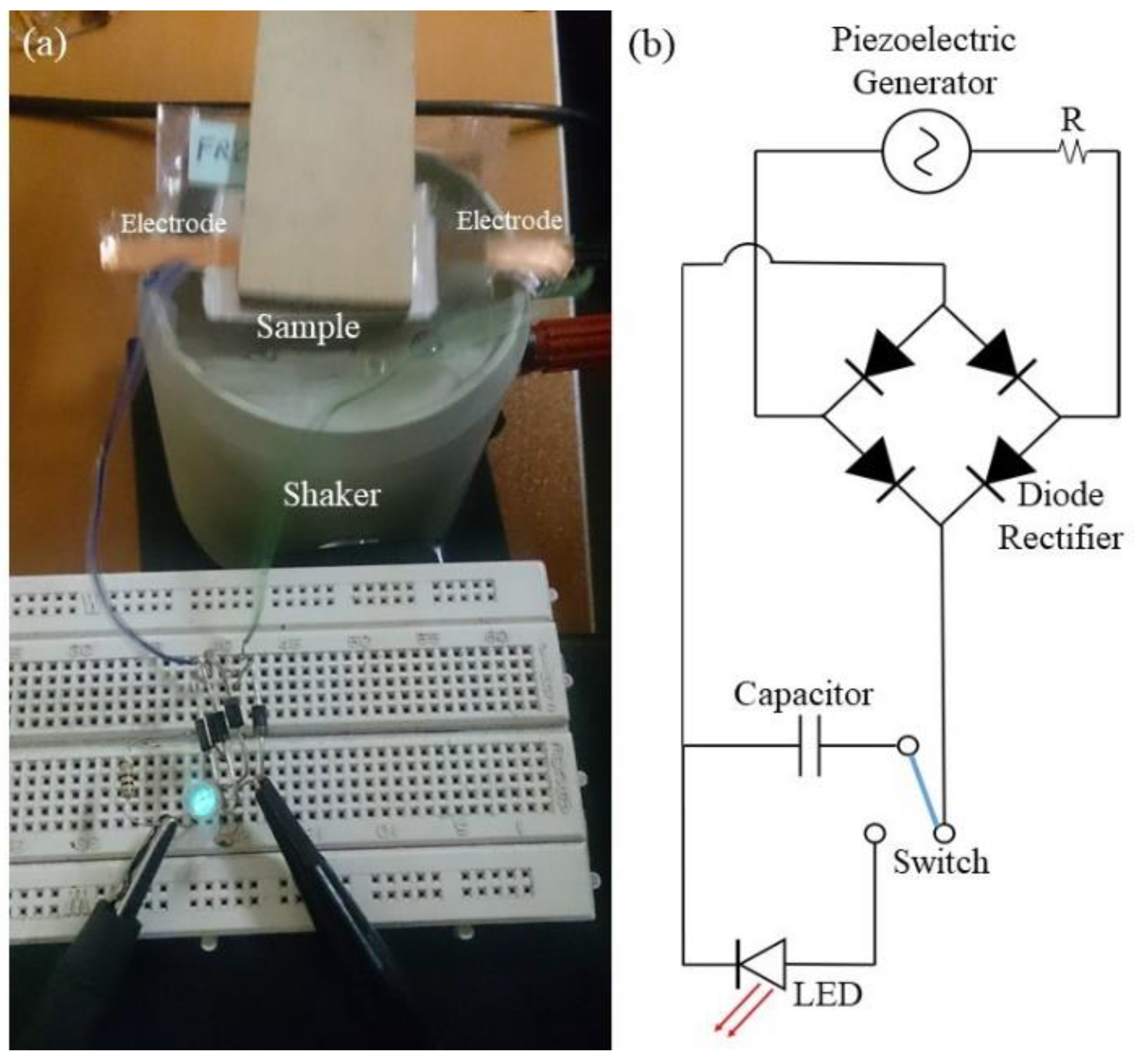
2.2.4. Measuring Output Voltage of PVDF/LiCl Nanogenerator
2.2.5. Measuring Output Voltage During Temperature Variations
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of LiCl on β Phase Formation
3.2. Effect of LiCl in Piezoelectric Response
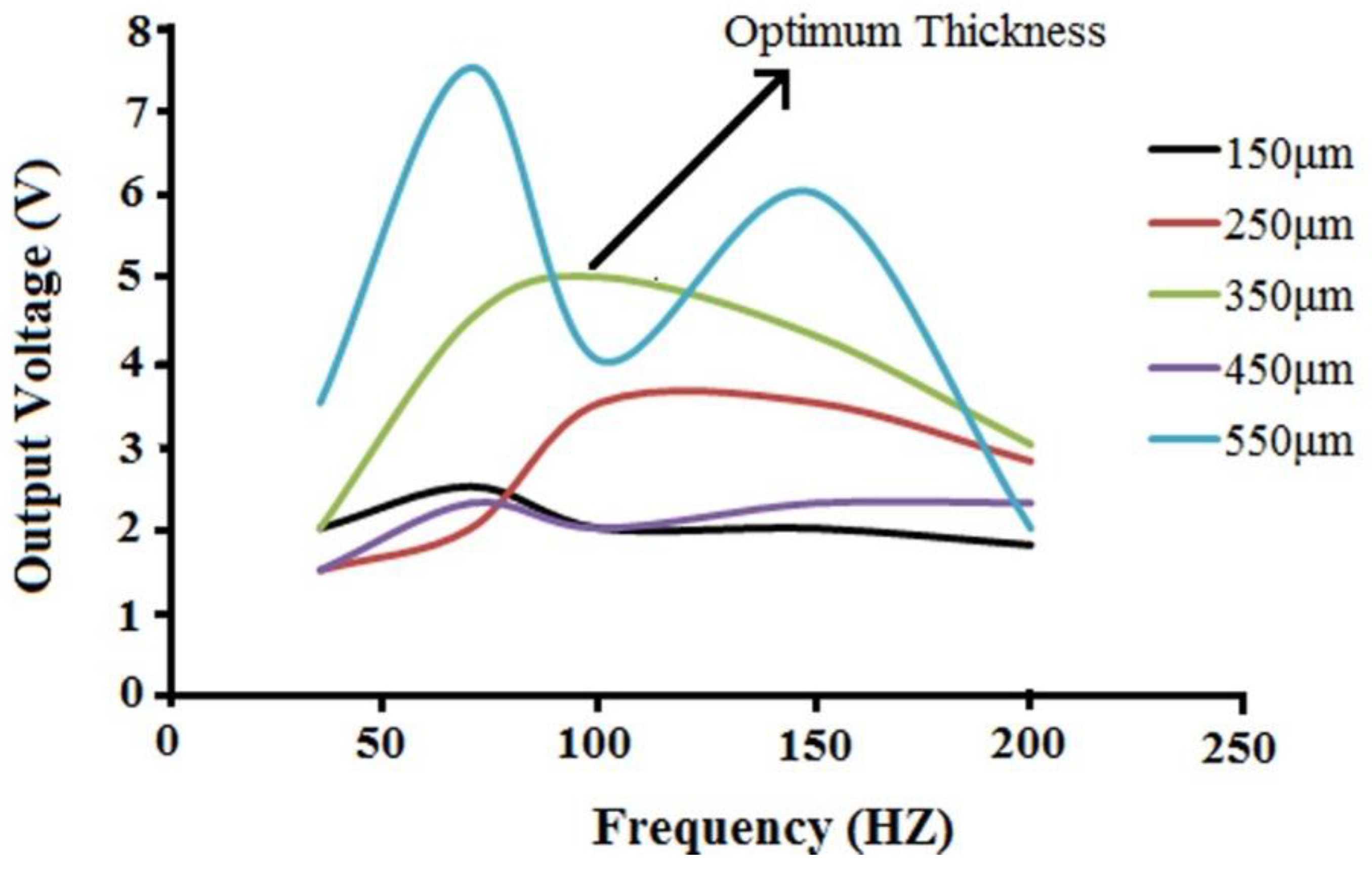
3.3. Effect of Electrospun Web Thickness on Piezoelectric Response
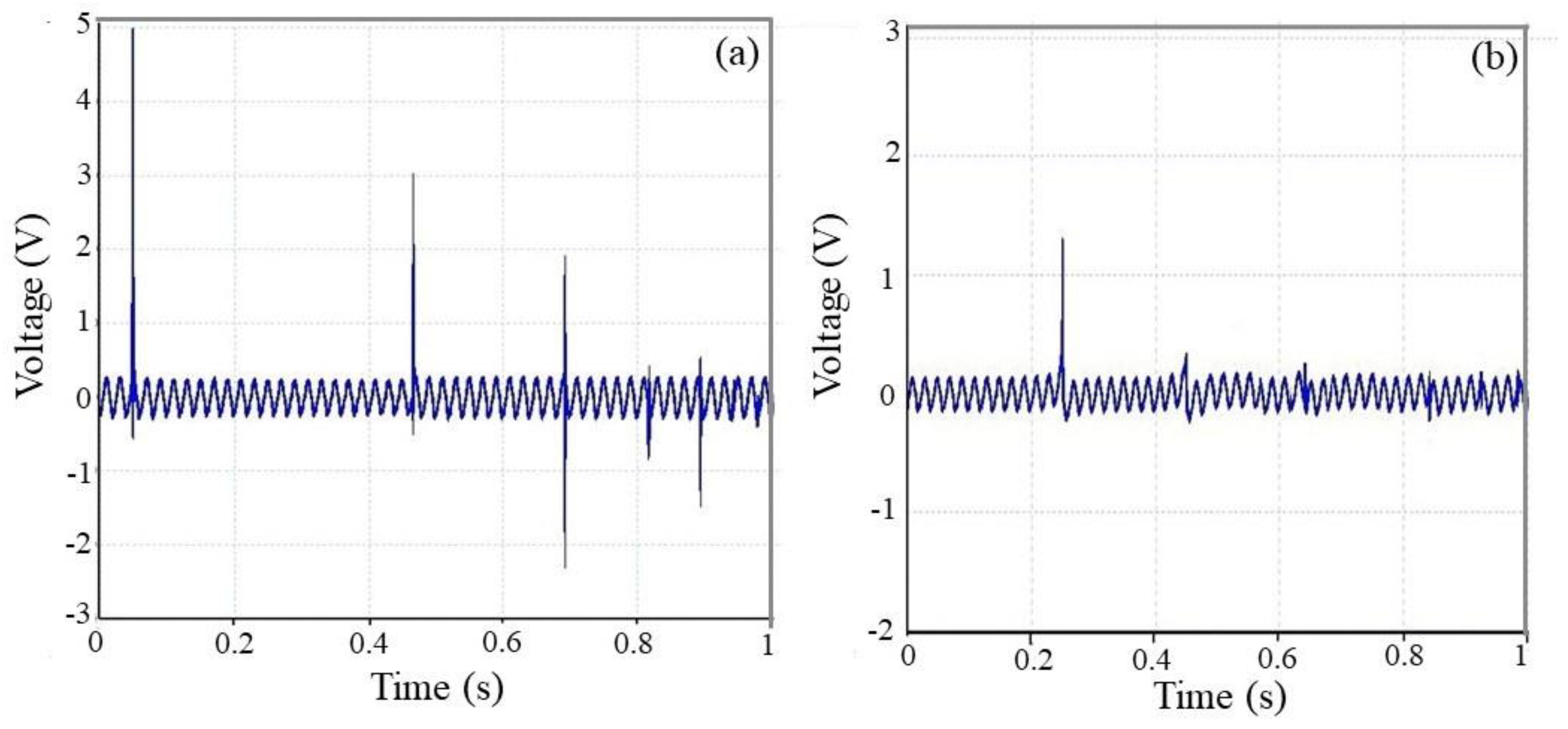
3.3.1. Vibration Test
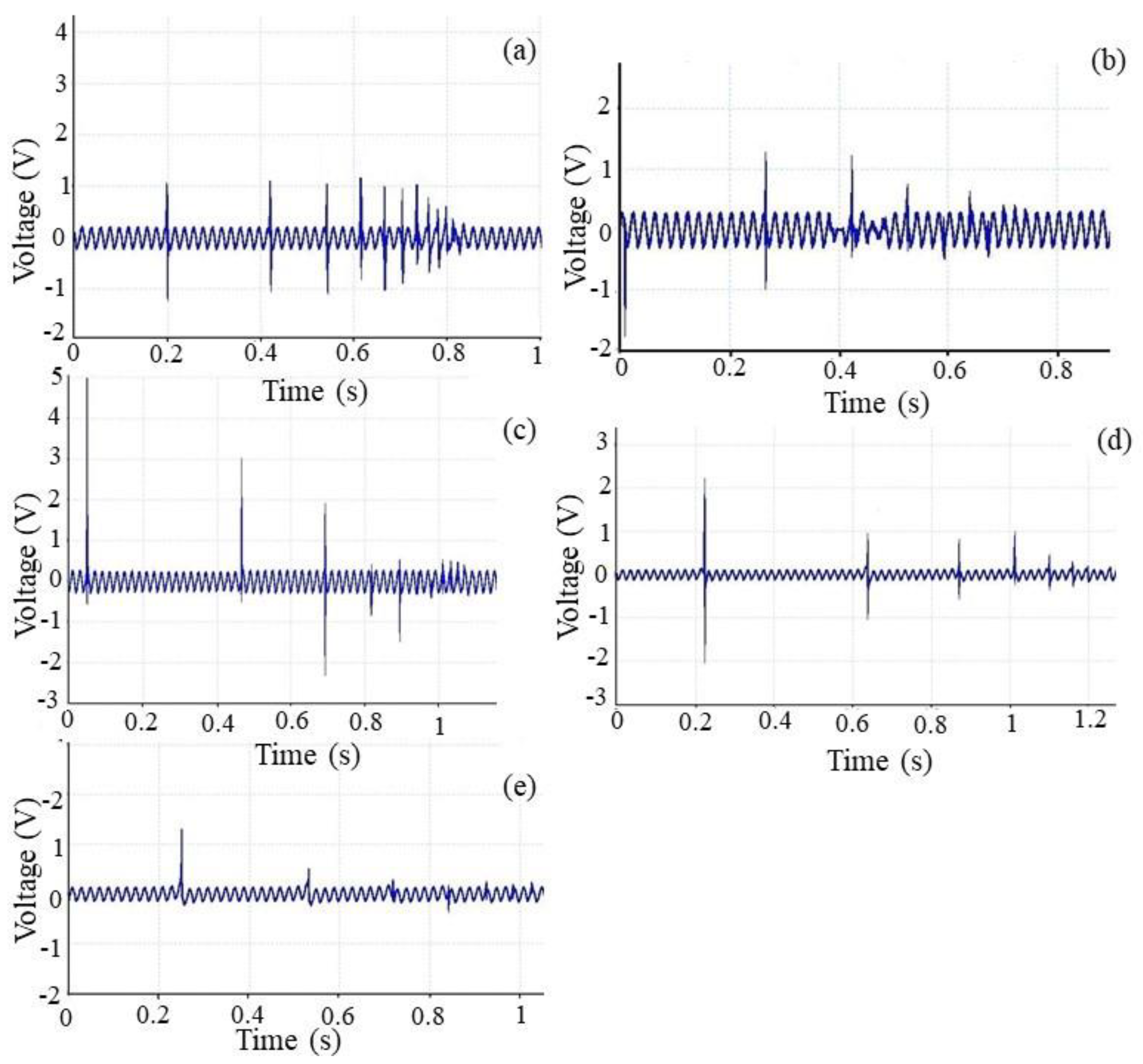
3.3.2. Impact Test
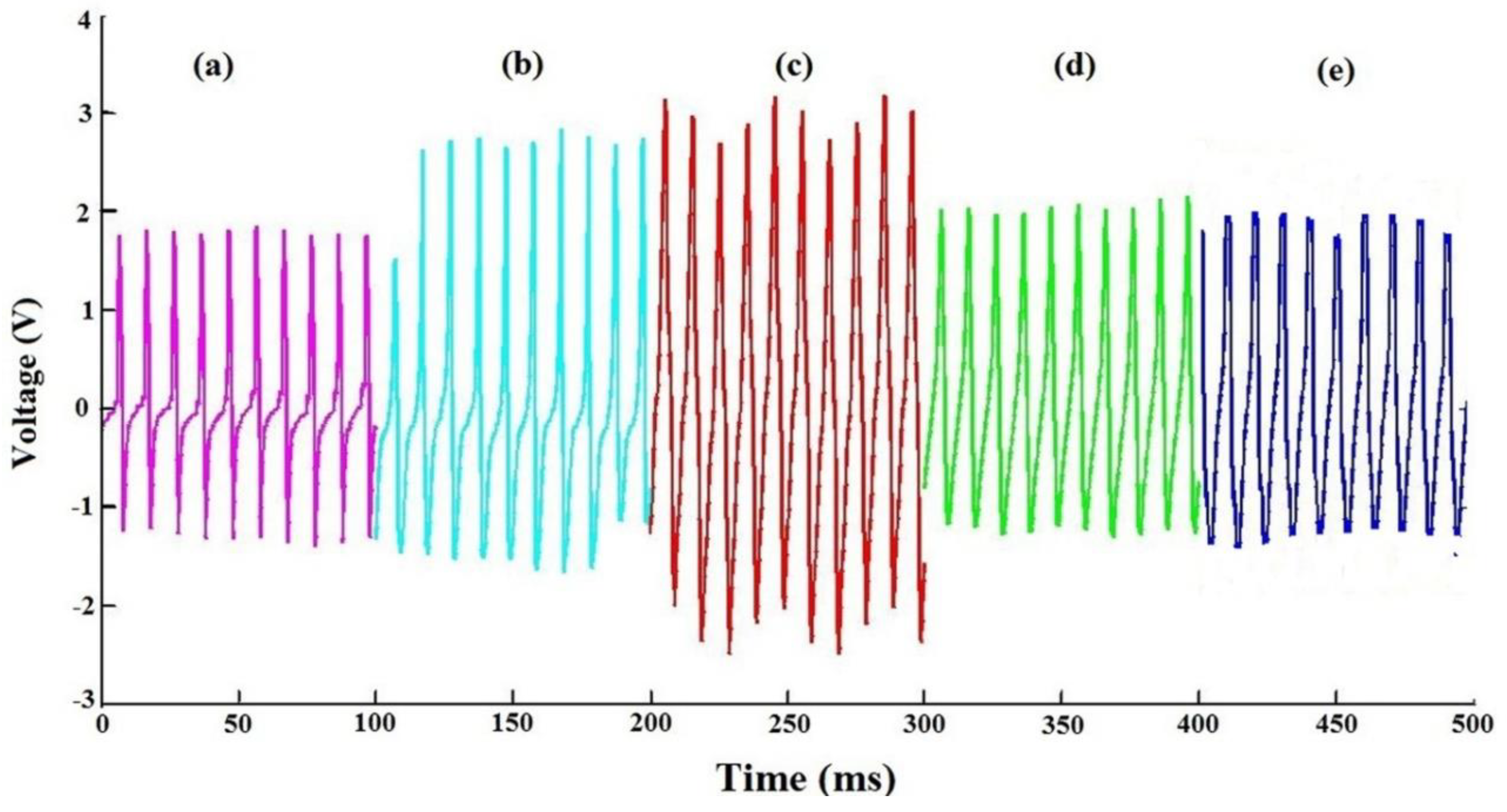
3.4. Effect of Temperature Variation on the Piezoelectric Response
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, S.; Skordos, A.; Thakur, V.K. Functional nanocomposites for energy storage: Chemistry and new horizons. Mater. Today Chem. 2020, 17, 100304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtari, F.; Latifi, M.; Shamshirsaz, M. Electrospinning/electrospray of polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF): Piezoelectric nanofibers. J. Text. Inst. 2016, 107, 1037–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Kim, H.; Kim, D.Y.; Seo, Y. Pure Piezoelectricity Generation by a Flexible Nanogenerator Based on Lead Zirconate Titanate Nanofibers. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 2610–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokhtari, F.; Foroughi, J.; Latifi, M. Enhancing β crystal phase content in electrospun PVDF nanofibers. In Energy Harvesting Properties of Electrospun Nanofibers; Fang, J., Lin, T., Eds.; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Mokhtari, F.; Cheng, Z.; Raad, R.; Xi, J.; Foroughi, J. Piezofibers to smart textiles: A review on recent advances and future outlook for wearable technology. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 9496–9522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Karakurt, I.; Wei, M.; Liu, N.; Chu, Y.; Zhong, J.; Lin, L. Lead iodide nanosheets for piezoelectric energy conversion and strain sensing. Nano Energy 2018, 49, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Hao, Z.; Yu, J.; Zhou, X.; Lee, P.S.; Sun, Y.; Mu, Z.; Zeng, F.L. A high-performance soft actuator based on a poly(vinylidene fluoride) piezoelectric bimorph. Smart Mater. Struct. 2019, 28, 055011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtari, F.; Foroughi, J.; Zheng, T.; Cheng, Z.; Spinks, G.M. Triaxial braided piezo fiber energy harvesters for self-powered wearable technologies. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 8245–8257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.-H.; Chang, S.-H. PVDF-based ferroelectric polymers and dielectric elastomers for sensor and actuator applications: A review. Funct. Compos. Struct. 2019, 1, 012003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtari, F.; Shamshirsaz, M.; Latifi, M. Investigation of β phase formation in piezoelectric response of electrospun polyvinylidene fluoride nanofibers: LiCl additive and increasing fibers tension. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2016, 56, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, K.Y.; Fang, F.; Wang, S.W.; Yang, W.; Sun, W.; Li, J.F. Hybridizing CNT/PMMA/PVDF towards high-performance piezoelectric nanofibers. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2018, 51, 265305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Wu, T.; Dai, Y.; Xia, Y. Electrospinning and Electrospun Nanofibers: Methods, Materials, and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 5298–5415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, S.; Gaur, A.; Kumar, C.; Maiti, P. Enhanced piezoelectric response in nanoclay induced electrospun PVDF nanofibers for energy harvesting. Energy 2019, 171, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafari, E.; Lu, N. Self-polarized electrospun polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) nanofiber for sensing applications. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 160, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szewczyk, P.K.; Gradys, A.; Kim, S.K.; Persano, L.; Marzec, M.; Kryshtal, A.; Busolo, T.; Toncelli, A.; Pisignano, D.; Bernasik, A.; et al. Enhanced Piezoelectricity of Electrospun Polyvinylidene Fluoride Fibers for Energy Harvesting. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 13575–13583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Xu, B.; Gong, J.J.N.E. Hierarchically architected polydopamine modified BaTiO3@P(VDF-TrFE) nanocomposite fiber mats for flexible piezoelectric nanogenerators and self-powered sensors. Nano Energy 2020, 70, 104516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azimi, B.; Milazzo, M.; Lazzeri, A.; Berrettini, S.; Uddin, M.J.; Qin, Z.; Buehler, M.J.; Danti, S. Electrospinning Piezoelectric Fibers for Biocompatible Devices. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2020, 9, 1901287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asai, H.; Zheng, W.; Nakane, K. Effects of ionic liquid/water addition and electrospinning conditions on the crystal structures of poly(vinylidene fluoride) nanofibers. Polymer 2020, 196, 122478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ren, L.F.; Shao, J.; Adeel, M.; Tu, Y.; Ma, Z.; He, Y. Effect of ionic liquid on the structure and desalination performance of PVDF-PTFE electrospun membrane. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, 48467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khayet, M.; García-Payo, M.; García-Fernández, L.; Contreras-Martínez, J. Dual-layered electrospun nanofibrous membranes for membrane distillation. Desalination 2018, 426, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janakiraman, S.; Surendran, A.; Ghosh, S.; Anandhan, S.; Venimadhav, A. A new strategy of PVDF based Li-salt polymer electrolyte through electrospinning for lithium battery application. Mater. Res. Express 2018, 6, 035303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Sun, B.; Huang, X.; Jiang, P. Synergistic effect of graphene nanosheet and BaTiO3 nanoparticles on performance enhancement of electrospun PVDF nanofiber mat for flexible piezoelectric nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2018, 52, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtari, F.; Spinks, G.M.; Fay, C.; Cheng, Z.; Raad, R.; Xi, J.; Foroughi, J. Wearable Electronic Textiles from Nanostructured Piezoelectric Fibers. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2020, 5, 1900900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-M.; Chou, M.-H.; Zeng, W.-Y. Piezoelectric Response of Aligned Electrospun Polyvinylidene Fluoride/Carbon Nanotube Nanofibrous Membranes. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abolhasani, M.M.; Shirvanimoghaddam, K.; Naebe, M. PVDF/graphene composite nanofibers with enhanced piezoelectric performance for development of robust nanogenerators. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2017, 138, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.H.; Singh, S.; Khare, N. Design of flexible PVDF/NaNbO3/RGO nanogenerator and understanding the role of nanofillers in the output voltage signal. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2017, 149, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; Tao, X.-M.; Chen, S.; Shang, S.; Chan, H.L.W.; Choy, S.H. Highly durable all-fiber nanogenerator for mechanical energy harvesting. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 2631–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, V.K.; Gupta, R.K. Recent Progress on Ferroelectric Polymer-Based Nanocomposites for High Energy Density Capacitors: Synthesis, Dielectric Properties, and Future Aspects. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 4260–4317. [Google Scholar]
- Abdolmaleki, H.; Agarwala, S. PVDF-BaTiO3 Nanocomposite Inkjet Inks with Enhanced β-Phase Crystallinity for Printed Electronics. Polymers 2020, 12, 2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponnamma, D.; Chamakh, M.M.; Alahzm, A.M.; Salim, N.; Hameed, N.; AlMaadeed, M.A.A. Core-Shell Nanofibers of Polyvinylidene Fluoride-based Nanocomposites as Piezoelectric Nanogenerators. Polymers 2020, 12, 2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arayanarakul, K.; Choktaweesap, N.; Aht-ong, D.; Meechaisue, C.; Supaphol, P. Effects of Poly(ethylene glycol), Inorganic Salt, Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate, and Solvent System on Electrospinning of Poly(ethylene oxide). Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2006, 291, 581–591. [Google Scholar]
- Khosravi, M.; Mansourpour, Z.; Ghaee, A. Effect of Additives (PEG400 and LiCl) on the Structure and Morphology of poly vinylidene fluoride (PVDF) Membranes. In Proceedings of the 11th International Seminar on Polymer Science and Technology, Tehran, Iran, 6–9 October 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Mokhtari, F.; Shamshirsaz, M.; Latifi, M.; Asadi, S. Comparative evaluation of piezoelectric response of electrospun PVDF (polyvinilydine fluoride) nanofiber with various additives for energy scavenging application. J. Text. Inst. 2017, 108, 906–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forouharshad, M.; King, S.G.; Buxton, W.; Kunovski, P.; Stolojan, V. Textile-Compatible, Electroactive Polyvinylidene Fluoride Electrospun Mats for Energy Harvesting. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2019, 220, 1900364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-H.; Lee, H.B.; Yeon, S.M.; Park, J.; Lee, N.K. Flexible and Stretchable Piezoelectric Sensor with Thickness-Tunable Configuration of Electrospun Nanofiber Mat and Elastomeric Substrates. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 24773–24781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gheibi, A.; Bagherzadeh, R.; Merati, A.A.; Latifi, M. Electrical power generation from piezoelectric electrospun nanofibers membranes: Electrospinning parameters optimization and effect of membranes thickness on output electrical voltage. J. Polym. Res. 2014, 21, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, T.; Sen, S.; Seal, A.; Sen, A. Temperature Dependent Electrical Properties of PZT Wafer. J. Electron. Mater. 2016, 45, 2252–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, I.; Siores, E.; Shah, T. Utilisation of smart polymers and ceramic based piezoelectric materials for scavenging wasted energy. Sens. Actuator. A Phys. 2010, 159, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-B.; Park, J.-H.; Ahn, H.; Liu, D.; Kim, D.-J. Temperature effects on output power of piezoelectric vibration energy harvesters. Microelectron. J. 2011, 42, 988–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satthiyaraju, M.; Ramesh, T. Effect of annealing treatment on PVDF nanofibers for mechanical energy harvesting applications. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 105366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaik, H.; Rachith, S.; Rudresh, K.; Sheik, A.S.; Raman, K.T.; Kondaiah, P.; Rao, G.M. Towards β-phase formation probability in spin coated PVDF thin films. J. Polym. Res. 2017, 24, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Y.; Qi, X.; Tian, H.; Guo, C.; Li, X.; Lin, J.; Wang, C. Full-fiber piezoelectric sensor by straight PVDF/nanoclay nanofibers. Mater. Lett. 2016, 164, 136–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Li, Z.; Deng, N.; Kang, W.; Fan, J.; Liu, Y. PVDF/TBAPF6 hierarchical nanofiber gel membrane for lithium ion capacitor with ultrahigh ion conductivity and excellent interfacial compatibility. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 318, 801–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunithamani, S.; Lakshmi, P. Simulation study on performance of MEMS piezoelectric energy harvester with optimized substrate to piezoelectric thickness ratio. Microsyst. Technol. 2015, 21, 733–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persano, L.; Dagdeviren, C.; Su, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Girardo, S.; Pisignano, D.; Huang, Y.; Rogers, J.A. High performance piezoelectric devices based on aligned arrays of nanofibers of poly(vinylidenefluoride-co-trifluoroethylene). Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanda, K.; Saito, T.; Iga, Y.; Higuchi, K.; Maenaka, K. Influence of parasitic capacitance on output voltage for series-connected thin-film piezoelectric devices. Sensors 2012, 12, 16673–16684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popovici, D.; Gheorghe, A.; Hantila, F.I.; Constantinescu, F.; Maricaru, M.; Nitescu, M. Modeling and simulation of piezoelectric devices. In Modelling and Simulation; Petrone, G., Cammarata, G., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Y.; Chen, X.; Ni, Q.; Li, L.; Ju, C. Dependence of the Impact Response of Polyvinylidene Fluoride Sensors on Their Supporting Materials’ Elasticity. Sensors 2013, 13, 8669–8678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Wu, Y.S.; Kan, E.C.; Fan, J. Breathable and Flexible Piezoelectric ZnO@PVDF Fibrous Nanogenerator for Wearable Applications. Polymers 2018, 10, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, M.F.; Giurgiutiu, V.; Lin, B.; Yu, L. Irreversibility effects in piezoelectric wafer active sensors after exposure to high temperature. Smart Mater. Struct. 2017, 26, 095019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, K.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Xu, Z. A triboelectric nanogenerator as self-powered temperature sensor based on PVDF and PTFE. Appl. Phys. A 2018, 124, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mokhtari, F.; Shamshirsaz, M.; Latifi, M.; Foroughi, J. Nanofibers-Based Piezoelectric Energy Harvester for Self-Powered Wearable Technologies. Polymers 2020, 12, 2697. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12112697
Mokhtari F, Shamshirsaz M, Latifi M, Foroughi J. Nanofibers-Based Piezoelectric Energy Harvester for Self-Powered Wearable Technologies. Polymers. 2020; 12(11):2697. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12112697
Chicago/Turabian StyleMokhtari, Fatemeh, Mahnaz Shamshirsaz, Masoud Latifi, and Javad Foroughi. 2020. "Nanofibers-Based Piezoelectric Energy Harvester for Self-Powered Wearable Technologies" Polymers 12, no. 11: 2697. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12112697
APA StyleMokhtari, F., Shamshirsaz, M., Latifi, M., & Foroughi, J. (2020). Nanofibers-Based Piezoelectric Energy Harvester for Self-Powered Wearable Technologies. Polymers, 12(11), 2697. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12112697







