Design of Highly Adhesive and Water-Resistant UV/Heat Dual-Curable Epoxy–Acrylate Composite for Narrow Bezel Display Based on Reactive Organic–Inorganic Hybrid Nanoparticles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
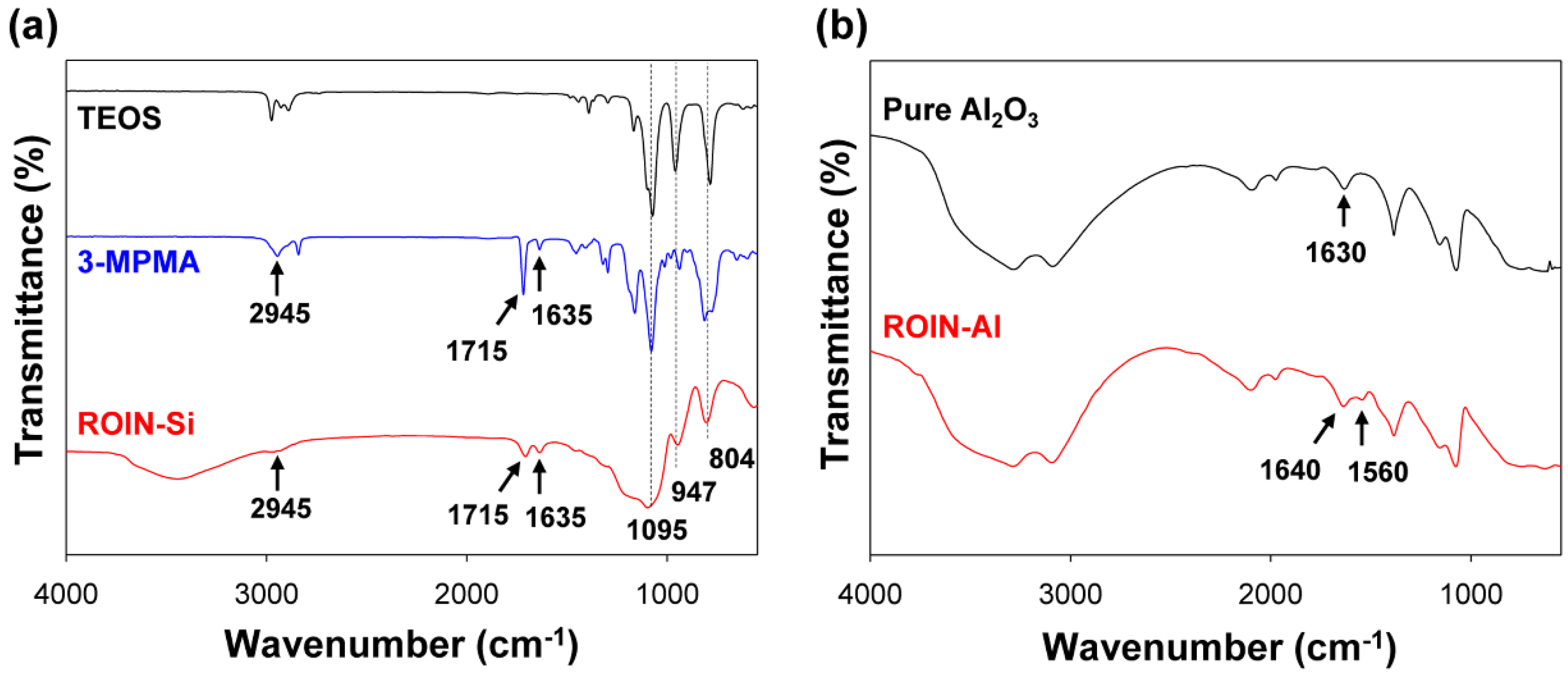
2.2. Synthesis of Reactive Organic–Inorganic Hybrid Silica Nanoparticles
2.3. Synthesis of Reactive Organic–Inorganic Hybrid Aluminum Oxide Nanoparticles
2.4. Preparation of UV/Heat Dual-Curable Epoxy–Acrylate Composites Embedded with Reactive Nanoparticles
2.5. Characterization
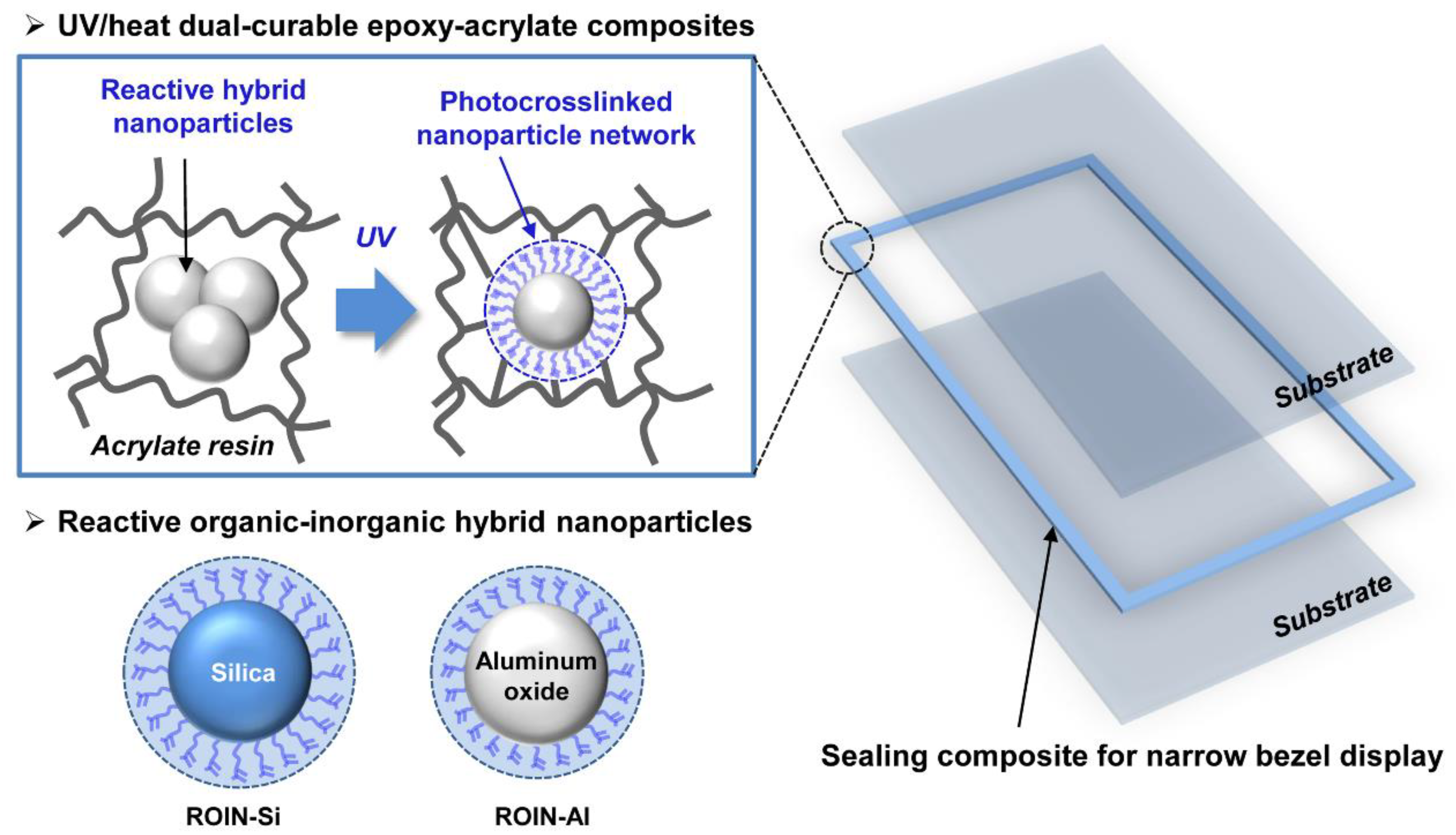
3. Results and Discussion
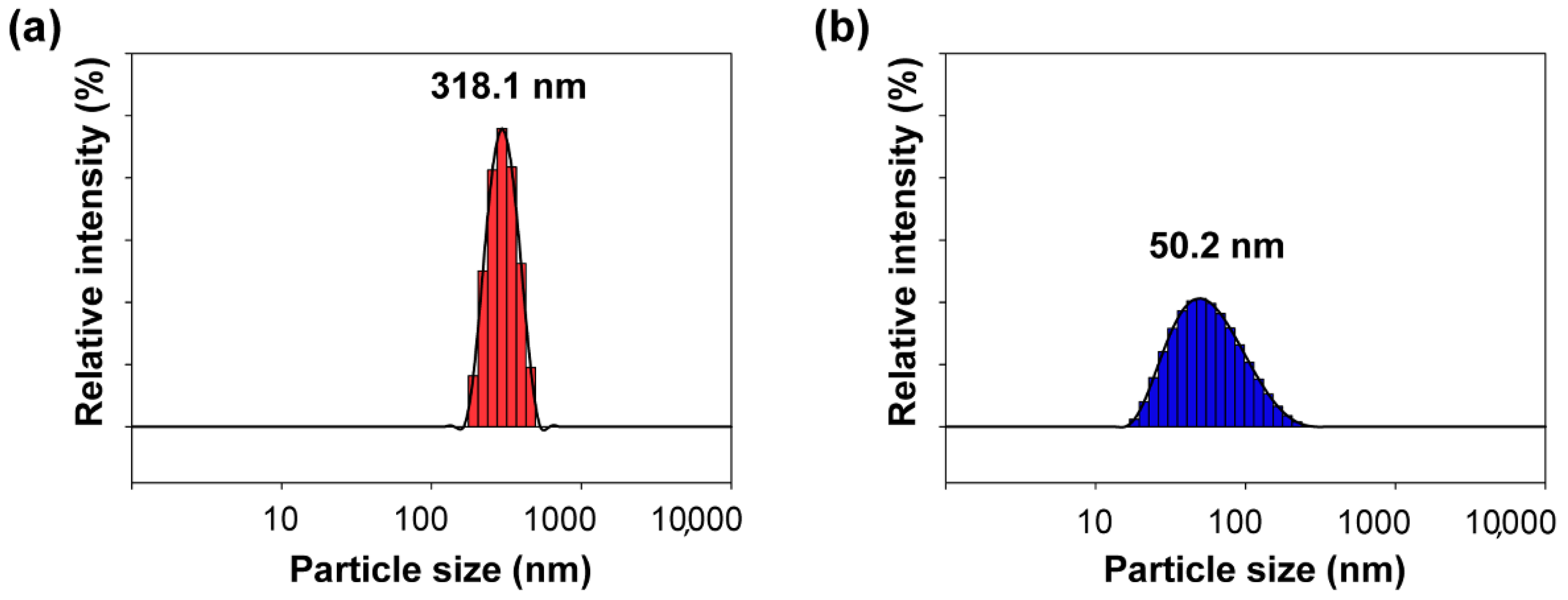
3.1. Preparation of Reactive Organic–Inorganic Hybrid Nanoparticles
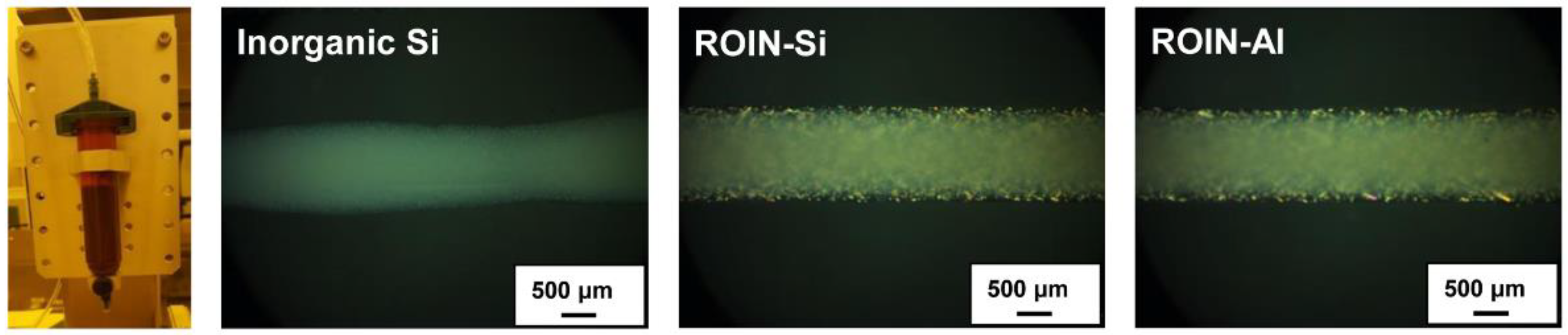
3.2. Viscosity and Narrow Dispensing Characteristics of UV/Heat Dual-Curable Epoxy–Acrylate Composites
3.3. Curing Behaviors of UV/Heat Dual-Curable Epoxy–Acrylate Composites
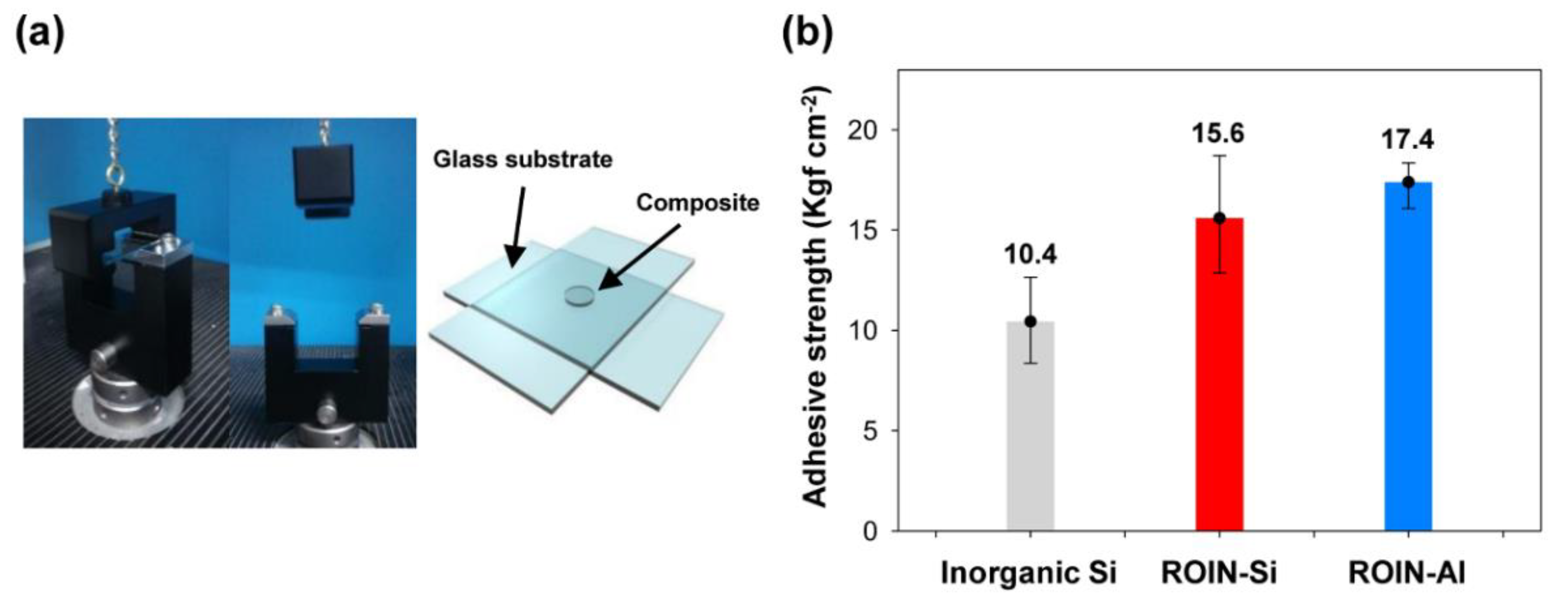
3.4. Adhesion Properties of UV/Heat Dual-Curable Epoxy–Acrylate Composites
3.5. Moisture Permeability Performance of UV/Heat Dual-Curable Epoxy–Acrylate Composites
4. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boer, W.D. Active Matrix Liquid Crystal Displays: Fundamentals and Applications, 1st ed.; Newnes: Oxford, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Hirai, A.; Abe, I.; Mitsumoto, M.; Ishida, S. One Drop Filling for Liquid Crystal Display Panel Produced from Larger-sized Mother Glass. Hitachi Rev. 2008, 57, 144. [Google Scholar]
- Mi, X.D.; Yang, D.K. Capillary filling of nematic liquid crystals. Phys. Rev. E 1998, 58, 1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.Y.; Son, I.; Lee, B.; Kim, C.; Cho, C.H.; Lee, J.H. Preparation and Characterization of UV/heat Dual-curable Adhesives for Liquid Crystal Device Using Multi-functional Heat-curing Agent. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2018, 662, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.; Cho, C.H.; Son, I.; Kim, J.H.; Yoo, J.Y.; Moon, G.; Lee, J.H. Preparation of a Carbon Nanotube-Reinforced UV/Heat Dual-Curable Adhesive for Liquid Crystal Displays. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2019, 678, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, C.A. Epoxy Resins: Chemistry and Technology, 2nd ed.; Marecl Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, F.L.; Li, X.; Park, S.J. Synthesis and Application of Epoxy Resins: A Review. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 29, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Wang, C.; Don, T. Mechanical Properties and Fracture Behavior of Dual-Curable Epoxyacrylate Composites Filled with Different Functionalized Silica Particles. Polym. Polym. Compos. 2014, 22, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes-Felipe, C.; Oliveira, J.; Etxebarria, I.; Vilas-Vilela, J.L.; Lanceros-Mendez, S. State-of-the-Art and Future Challenges of UV Curable Polymer-Based Smart Materials for Printing Technologies. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2019, 4, 1800618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayaman-Apohan, N.; Demirci, R.; Cakir, M.; Gungor, A. UV-Curable Interpenetrating Polymer Networks Based on acrylate/vinylether Functionalized Urethane Oligomers. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2005, 73, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decker, C.; Zahouily, K.; Keller, L.; Benfarhi, S.; Bendaikha, T.; Baron, J. Ultrafast Synthesis of Bentonite-Acrylate Nanocomposite Materials by UV-Radiation Curing. J. Mater. Sci. 2002, 37, 4831–4838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, L.; Decker, C.; Zahouily, K.; Benfarhi, S.; Le Meins, J.; Miehe-Brendle, J. Synthesis of Polymer Nanocomposites by UV-Curing of organoclay–acrylic Resins. Polymer 2004, 45, 7437–7447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangnaik, A.S.; Georgiev, Y.M.; Holmes, J.D. New Generation Electron Beam Resists: A Review. Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 1898–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.; Park, J.; Koo, K.; Jang, Y. Structural and Physical Properties of Sealant Paste Prepared by Silica/Polymer Composites. KIEE 2012, 61, 916–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Choi, S.; Lee, E.; Choi, S. Effects of Silane-Treated Silica on the Cure Temperature and Mechanical Properties of Elastomeric Epoxy. Elastomers Compos. 2008, 43, 147–156. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, S.; Sun, Z.; Huang, P.; Li, Y.; Hu, N. Some Basic Aspects of Polymer Nanocomposites: A Critical Review. Nano Mater. Sci. 2019, 1, 2–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, Y.; Yamaguchi, M.; Okubo, M.; Matsumoto, T. Effects of Particle Size on Mechanical and Impact Properties of Epoxy Resin Filled with Spherical Silica. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1992, 45, 1281–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagwe, R.P.; Hilliard, L.R.; Tan, W. Surface Modification of Silica Nanoparticles to Reduce Aggregation and Nonspecific Binding. Langmuir 2006, 22, 4357–4362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Hong, R.; Xie, H.; Feng, W. One-Step Synthesis of Functional Silica Nanoparticles for Reinforcement of Polyurethane Coatings. Powder Technol. 2012, 218, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Hong, S.I.; Choe, C.R.; Park, M.; Rim, S.; Kim, J. Preparation and Characterization of Epoxy Composites Filled with Functionalized Nanosilica Particles obtained Via sol–gel Process. Polymer 2001, 42, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zukas, W.X.; Craven, K.J.; Wentworth, S.E. Effects of Aluminum Oxide Surfaces on Epoxy Cure Reactions. Surf. Interface Anal. 1991, 17, 530–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bintijamaludin, N.A.; Anithambigai, P.; Shanmugan, S.; Mutharasu, D. Performance and Thermal Analysis of Aluminium Oxide Filled Epoxy Composite as TIM for LEDs. Mater. Sci. Res. India 2014, 11, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosso, P.; Ye, L.; Friedrich, K.; Sprenger, S. A Toughened Epoxy Resin by Silica Nanoparticle Reinforcement. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 100, 1849–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Pearson, R. Toughening Mechanisms in epoxy–silica Nanocomposites (ESNs). Polymer 2009, 50, 4895–4905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Hsu, C.; Hsu, K. Poly (Methylmethacrylate)-Silica Nanocomposites Films from Surface-Functionalized Silica Nanoparticles. Polymer 2005, 46, 1851–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Jean, J.; Li, C. Dispersion of nano-sized γ-alumina Powder in non-polar Solvents. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2006, 89, 882–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anaya, S.; Serrano, B.; Herrero, B.; Cervera, A.; Baselga, J. Γ-Alumina Modification with Long Chain Carboxylic Acid Surface Nanocrystals for Biocompatible Polysulfone Nanocomposites. Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 14460–14468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Condrate, R., Sr. An FTIR Spectral Investigation of the Structural Species found on Alumina Surfaces. Mater. Lett. 1995, 23, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Fu, L.; Su, M.; Aslam, M.; Wong, K.C.; Dravid, V.P. Interaction of Fatty Acid Monolayers with Cobalt Nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2004, 4, 383–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, T.V.; Prabhakar, S.; Raju, G.B. Adsorption of Oleic Acid at sillimanite/water Interface. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2002, 247, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Han, S.W.; Choi, H.J.; Kim, K. Structure and Thermal Behavior of a Layered Silver Carboxylate. J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106, 2892–2900. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wong, C. Study on Mono-Dispersed Nano-Size Silica by Surface Modification for Underfill Applications. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 292, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanemann, T. Influence of Particle Properties on the Viscosity of polymer–alumina Composites. Ceram. Int. 2008, 34, 2099–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, F.; Gläsel, H.; Hartmann, E.; Langguth, H.; Hinterwaldner, R. Functionalized inorganic/organic Nanocomposites as New Basic Raw Materials for Adhesives and Sealants. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2004, 24, 519–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, D.; Panda, S.S.; Raju, K. Thermal and Mechanical Properties of Epoxy acrylate/methacrylates UV Cured Coatings. Prog. Org. Coat. 2005, 54, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, Y.; He, Y.; Zhao, L.; Kowalczyk, A.; Yang, W.; Nie, J. Effect of Monomer Structure on Real-Time UV-Curing Shrinkage Studied by a Laser Scanning Approach. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2013, 32, 21331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Composition | Chemical Compound | Conventional Composite (wt.%) | New Epoxy–Acrylate Composites with Reactive Nanoparticles (wt.%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resin | YD-128 | 40 | 40 | 40 |
| BisGMA | 40 | 40 | 40 | |
| Hardener | ADH | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 |
| Photoinitiator | Irgacure 651 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 2.5 |
| Filler | Fumed silica | 16 | - | - |
| Reactive hybrid silica nanoparticles (ROIN-Si) | - | 16 | - | |
| Reactive hybrid aluminum oxide nanoparticles (ROIN-Al) | - | - | 16 | |
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.H. Design of Highly Adhesive and Water-Resistant UV/Heat Dual-Curable Epoxy–Acrylate Composite for Narrow Bezel Display Based on Reactive Organic–Inorganic Hybrid Nanoparticles. Polymers 2020, 12, 2178. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12102178
Lee JH. Design of Highly Adhesive and Water-Resistant UV/Heat Dual-Curable Epoxy–Acrylate Composite for Narrow Bezel Display Based on Reactive Organic–Inorganic Hybrid Nanoparticles. Polymers. 2020; 12(10):2178. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12102178
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Jun Hyup. 2020. "Design of Highly Adhesive and Water-Resistant UV/Heat Dual-Curable Epoxy–Acrylate Composite for Narrow Bezel Display Based on Reactive Organic–Inorganic Hybrid Nanoparticles" Polymers 12, no. 10: 2178. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12102178
APA StyleLee, J. H. (2020). Design of Highly Adhesive and Water-Resistant UV/Heat Dual-Curable Epoxy–Acrylate Composite for Narrow Bezel Display Based on Reactive Organic–Inorganic Hybrid Nanoparticles. Polymers, 12(10), 2178. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12102178





