Aging Mechanism and Rejuvenating Possibility of SBS Copolymers in Asphalt Binders
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Experiments
2.1. Materials
2.2. Experiments
2.2.1. Preparation of Penetrative Rejuvenator
2.2.2. SBS Copolymers
2.2.3. SBS-Modified Asphalt
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Characteristics of Aged SBS Copolymers
3.2. Characteristics of SBS-Modified Asphalt
3.2.1. Physical Properties Analysis
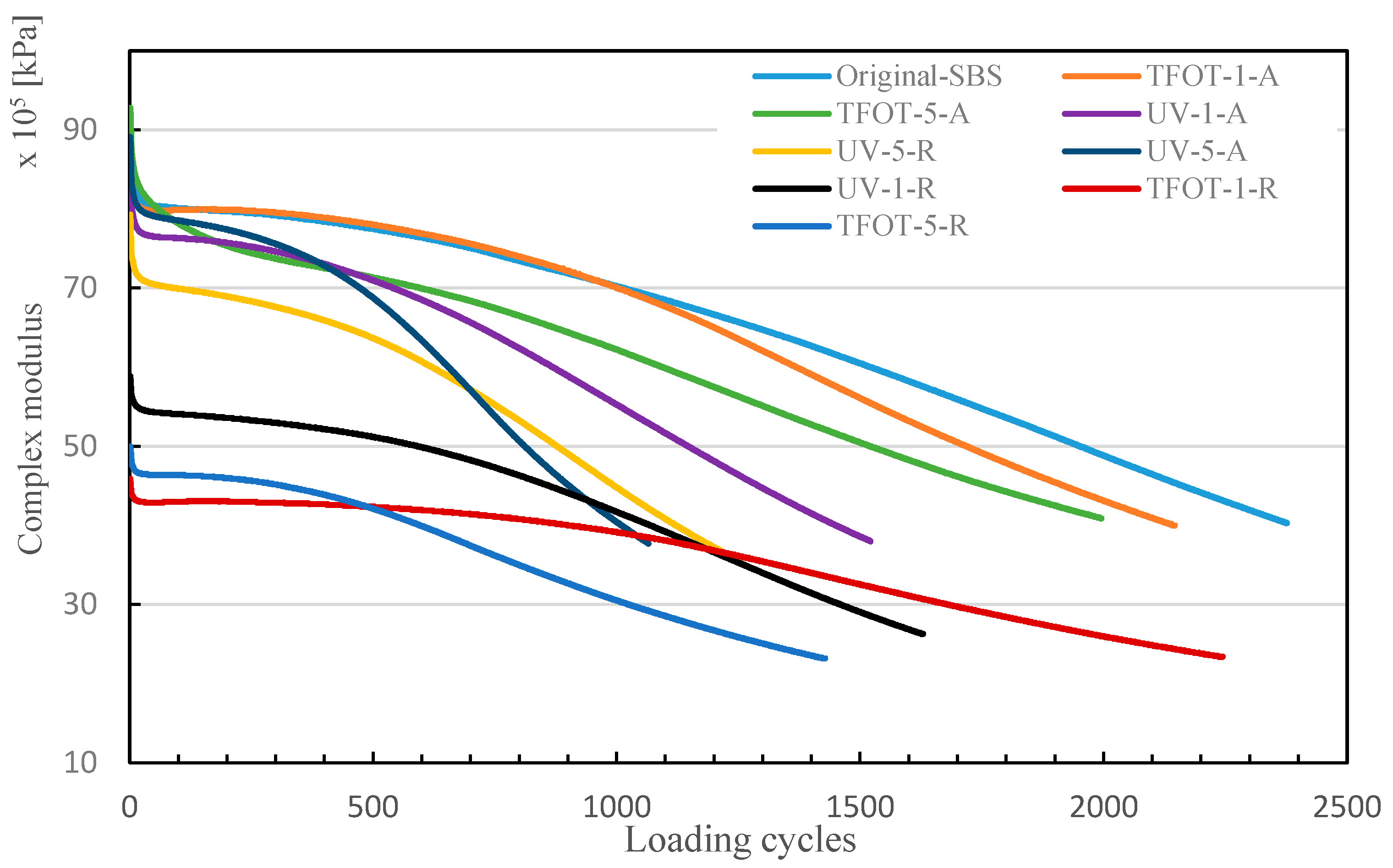
3.2.2. Rheological Properties Analysis
3.2.3. Chemical Structure Integration
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- SBS copolymer could be easily aged in thermal and UV conditions from oxidation reactions, accompanied with their quality increasing and yellowing as they age. Besides, the ozone generated from the ultraviolet circumstance played a critical effect in the aging process.
- (2)
- Partial double bonds in SBS copolymers were degraded during aging, and oxidized to oxygen-containing groups, such as hydroxyl, carbonyl and ether bonds. Nevertheless, rarely evident chemical reactions take place between PR and SBS copolymer.
- (3)
- Aged SBS copolymers would deteriorate the physical properties of modified asphalt with a higher possibility in generating cracks at lower temperature, as well as shorter fatigue life by considering the changes of rheological properties.
- (4)
- UV would be a major adverse factor in the aging SBS copolymer and brings about servicing time decrease in the field. Although PR contains sufficient oil components which can alleviate the negative influences in aged SBS asphalt with adjusting the composition of asphalt binder, PR has little rejuvenating effects in SBS copolymers directly.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khodaii, A.; Mehrara, A. Evaluation of permanent deformation of unmodified and SBS modified asphalt mixtures using dynamic creep test. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 2586–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, D.O.; Alessandrini, J.L.; Bosch, A.; Cortizo, M.S. Micro-structural and rheological characteristics of SBS-asphalt blends during their manufacturing. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 2769–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, S.; Muhammad, Y.; Li, J.; Maria, S.; Meng, F.; Wei, Y.; Su, Z.; Yang, H. Enhancing effect of microalgae biodiesel incorporation on the performance of crumb Rubber/SBS modified asphalt. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 237, 117725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Jia, X.; Yu, J.; Xue, L. Effect of expanded vermiculite on microstructures and aging properties of styrene–butadiene–styrene copolymer modified bitumen. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 40, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.B.; Wan, L.; Peng, Z.Q.; Cui, P.Q.; Wu, S.P. Effects of Various Rejuvenator Sealer Materials on Rheological Properties of Aged SBS Modified Asphalt. Key Eng. Mater. 2014, 599, 155–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Wang, L.; Zeng, X.; Wu, S.; Li, B. Effect of montmorillonite on properties of styrene-butadiene-styrene copolymer modified bitumen. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2007, 47, 1289–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Isacsson, U. Influence of styrene-butadiene-styrene polymer modification on bitumen viscosity. Fuel 1997, 76, 1353–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Qin, Y.; Huang, S.; Xu, J. Laboratory Evaluation of Aging Behaviour of SBS Modified Asphalt. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 2017, 3154634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adedeji, A.; Grünfelder, T.; Bates, F.S.; Macosko, C.W.; Stroup-Gardiner, M.; Newcomb, D.E. Asphalt Modified by SBS Triblock Copolymer: Structures and Properties. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1996, 36, 1707–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, K.; Wang, X.; Huang, G.; Zheng, J.; Huang, J.; Li, G. Thermal ageing behavior of styrene–butadiene random copolymer: A study on the ageing mechanism and relaxation properties. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2012, 97, 1704–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Luo, Z. Wavelength sensitivity of photooxidation of styrene-butadiene-styrene copolymer. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 1995, 48, 99–102. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, R.P.; Desai, S.M.; Solanky, S.S.; Thanki, P.N. Photodegradation and stabilization of styrene–butadiene–styrene rubber. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 75, 1103–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Gu, F.; Zhao, Y. Thermal oxidative aging characterization of SBS modified asphalt. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. Mater. Sci. Ed. 2013, 28, 88–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortizo, M.S.; Larsen, D.O.; Bianchetto, H.; Alessandrini, J.L. Effect of the thermal degradation of SBS copolymers during the ageing of modified asphalts. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2004, 86, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucena, M.D.C.C.; Soares, S.D.A.; Soares, J.B. Characterization and thermal behavior of polymer-modified asphalt. Mater. Res. Ibero Am. J. Mater. 2004, 7, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, L.; Qin, Y. Aging mechanism of SBS modified asphalt based on chemical reaction kinetics. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 91, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, A.; Zhou, T.; Cao, X.; Xie, Z. A study on thermal oxidation mechanism of styrene–butadiene–styrene block copolymer (SBS). Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2007, 92, 1682–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, P.; Luo, W.; Xu, P.; Zhao, H. Investigation on recycling of SBS modified asphalt binders containing fresh asphalt and rejuvenating agents. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 91, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, C. Effect of different rejuvenators on the properties of aged SBS modified asphalt. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2017, 35, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Yu, J.; Hu, C.; Qin, D.; Xue, L. Laboratory evaluation of rejuvenation effect of reactive rejuvenator on aged SBS modified bitumen. Mater. Struct. 2017, 50, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Tan, Y.; Luo, D.; Li, Y.; Farooq, A.; Mo, L.; Jiao, Y. Effect of Recycling Agents on Rheological and Micromechanical Properties of SBS-Modified Asphalt Binders. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 2018, 5482368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Yu, J.; Zhang, C.; Cao, Z.; Gu, Y.; Xue, L. Effect of reactive rejuvenators on structure and properties of UV-aged SBS modified bitumen. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 155, 780–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões, D.; Almeida-Costa, A.; Benta, A. Preventive maintenance of road pavement with microsurfacing—An economic and sustainable strategy. Int. J. Sustain. Transp. 2017, 11, 670–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giustozzi, F.; Crispino, M.; Flintsch, G. Multi-attribute life cycle assessment of preventive maintenance treatments on road pavements for achieving environmental sustainability. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2012, 17, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, I.A.; Al Mehthel, M.H.; Wahhab, H.I.A.-A.; Al Idi, S.H.; Akhtar, J.S. Sulfur Extended Polymer for Use in Asphalt Binder and Road Maintenance. U.S. Patents 9012542B2, 21 April 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, M.; Ghaly, N.; Ibrahim, I. Modified Hot Mix Asphalt for Road Maintenance. World Appl. Sci. J. 2008, 5, 236–245. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.B. Asphalt Pavement Preventive Maintenance Technology Overview. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2014, 638–640, 1135–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Hong, J.; Huang, C.; Liu, J.; Wu, S. Effectiveness of rejuvenator seal materials on performance of asphalt pavement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 55, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prapaitrakul, N.; Freeman, T.J.; Glover, C.J. Analyze Existing Fog Seal Asphalts and Additives: Literature Review. Asph. Emuls. 2005, 12, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.P.; Luo, P.F.; Xu, L.; Ma, X.J. Laboratory Study on the Permeability and Skid Resistance of Asphalt Pavement Fog Seal Layer. In Proceedings of the 15th COTA International Conference of Transportation, Beijing, China, 24–27 July 2015; pp. 949–956. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Y.; Van De Ven, M.; Molenaar, A.; Su, Z.; Zandvoort, F. Characteristics of two-component epoxy modified bitumen. Mater. Struct. 2011, 44, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhang, L.; Yan, B.; Kong, D.; Li, Y.; Wu, S. Diffusion Mechanism of Rejuvenator and Its Effects on the Physical and Rheological Performance of Aged Asphalt Binder. Materials 2019, 12, 4130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klint, A. Amphiphilic Surface Modification of Colloidal Silica Sols; Chalmers University of Technology: Göteborg, Sweden, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Dong, Z.J.; Tan, Y.Q.; Liu, Z.Y. Investigating the Interactions of SARA Four-Fraction in Asphalt Binders by Molecular Simulations. Energy Fuels 2015, 29, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Guo, P.; Wan, L.; Wu, S. Laboratory investigation of rejuvenator seal materials on performances of asphalt mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 37, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D2872-19. Standard test method for effect of heat and air on a moving film of asphalt (rolling thin-film oven test); ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM G154-16. Standard Practice for Operating Fluorescent Ultraviolet (UV) Lamp Apparatus for Exposure of Nonmetallic Materials; ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, A.; Micaelo, R.; Quaresma, L.; Cidade, M.T. Evaluation of Different Methods for the Estimation of the Bitumen Fatigue Life with DSR Testing. In 8th RILEM International Symposium on Testing and Characterization of Sustainable and Innovative Bituminous Materials; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2016; Volume 11, pp. 1017–1028. [Google Scholar]
- Moyo, S.; Mphuthi, D.; Cukrowska, E.; Henshilwood, C.S.; Niekerk, K.V.; Chimuka, L. Blombos Cave: Middle Stone Age ochre differentiation through FTIR, ICP OES, ED XRF and XRD. Quat. Int. 2016, 404, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.P.; Pang, L.; Mo, L.T.; Chen, Y.C.; Zhu, G.J. Influence of aging on the evolution of structure, morphology and rheology of base and SBS modified bitumen. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 1005–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendessi, S.; Klerk, A.D. Ozonation of Oilsands Bitumen. Energy Fuels 2016, 30, 8941–8951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Cai, H.M.; Zhang, Y.Z. Research about the Mechanism of SBS Modified Asphalt. Pet. Asphalt 2008, 22, 10–14. [Google Scholar]
- Romera, R.; Santamaría, A.; Peña, J.J.; Muñoz, M.E.; Barral, M.; García, E.; Jañez, V. Rheological aspects of the rejuvenation of aged bitumen. Rheol. Acta 2006, 45, 474–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Zhang, H.; Shi, C. Investigation of aging performance of SBS modified asphalt with various aging methods. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 145, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
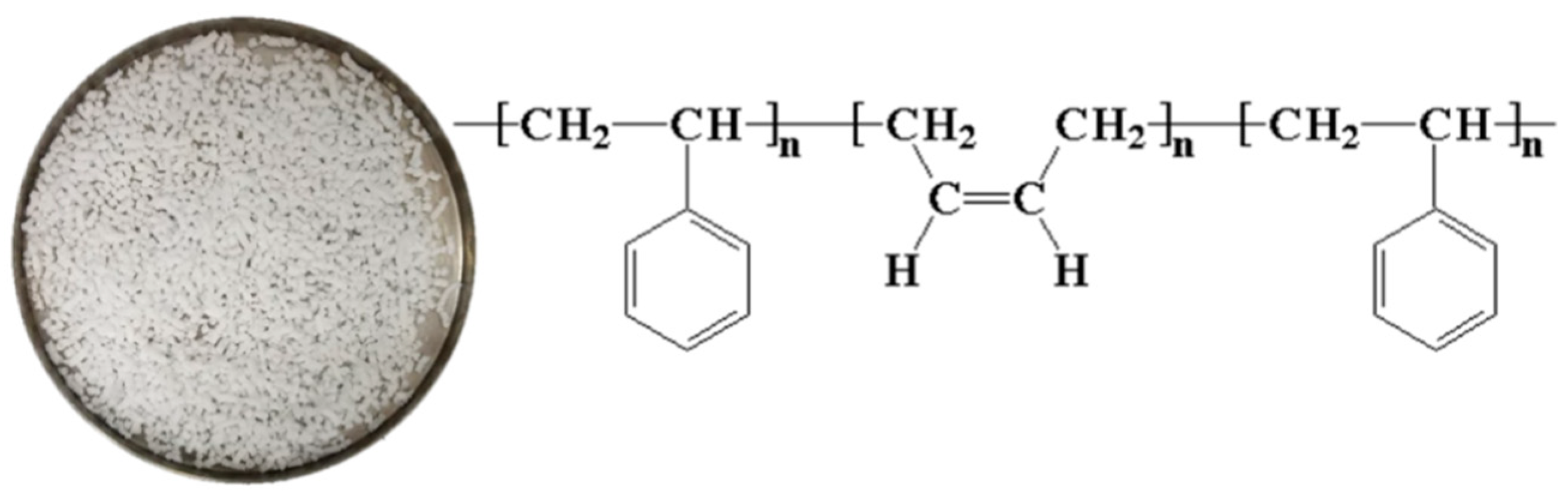
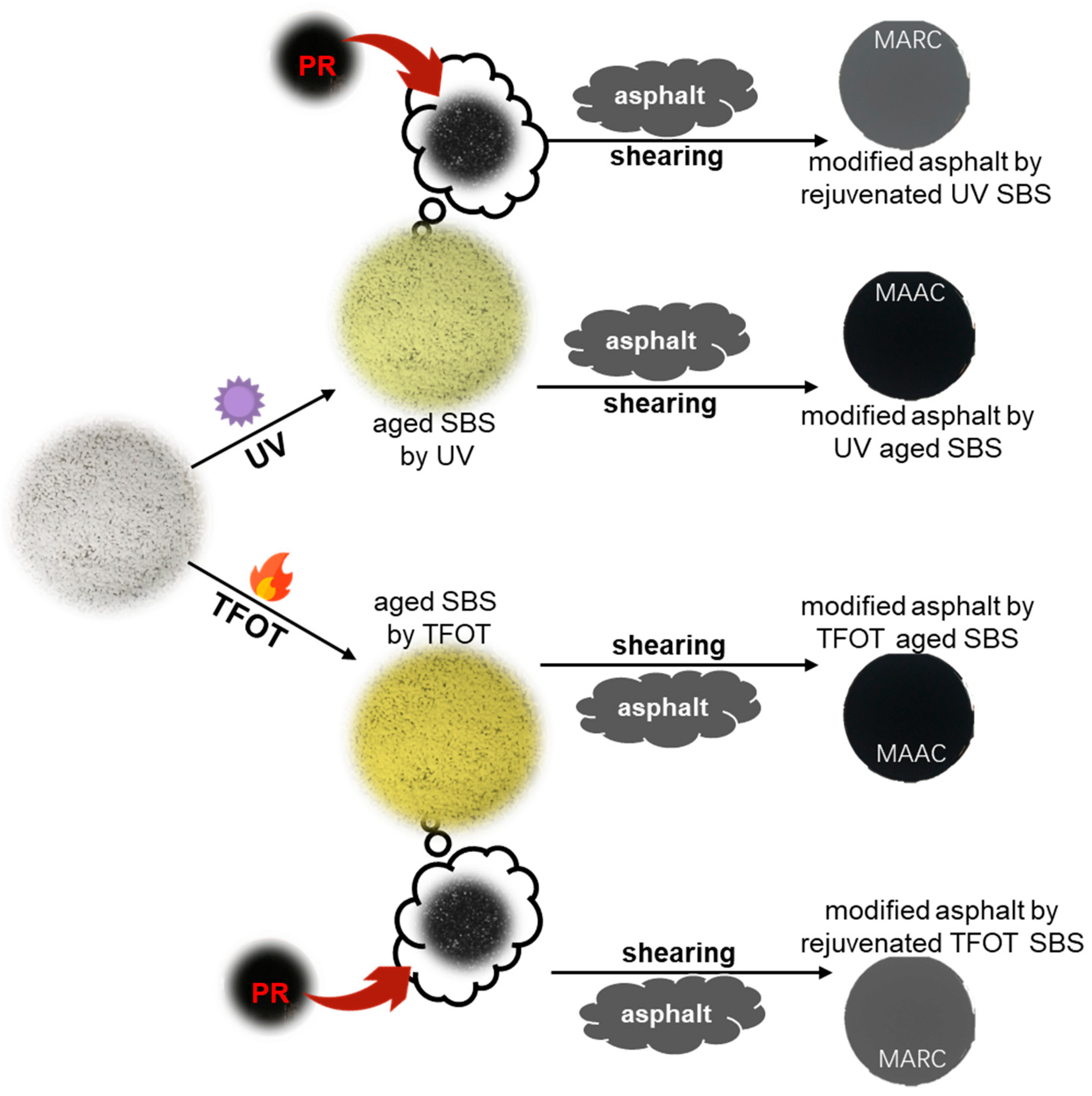











| Sample | S/B Ratio | Volatiles [%] | Total Ash [%] | Tensile Strength [MPa] | Density [g/cm3] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SBS copolymer | 40/60 | <0.7 | <0.2 | >24.0 | 1.32 |
| Items | Results | |
|---|---|---|
| Physical properties | Penetration (25 °C) [0.1 mm] | 80.5 |
| Ductility (10 °C) [cm] | >100 | |
| Softening point [°C] | 41.3 | |
| Viscosity (135 °C) [cP] | 533 | |
| Chemical compositions | Saturates [%] | 14.68 |
| Aromatics [%] | 43.28 | |
| Resins [%] | 32.85 | |
| Asphaltenes [%] | 9.19 | |
| Items | Results | |
|---|---|---|
| Physical properties | pH values | 5.6 |
| Density [g·mL−1] | 0.97 | |
| Viscosity (25 °C) [cP] | 478 | |
| Chemical compositions | Saturates [%] | 25.57 |
| Aromatics [%] | 29.91 | |
| Resins [%] | 39.98 | |
| Asphaltenes [%] | 4.41 | |
| Copolymers | Temperature [°C] | Time [h] | UV Intensity [uw/cm2] | Rejuvenated Labels |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Origin-SBS | N/A | N/A | N/A | Origin-SBS-R |
| UV-1 | 50 | 24 | 998 | UV-1-R |
| UV-5 | 50 | 120 | 998 | UV-5-R |
| TFOT-1 | 163 | 1 | N/A | TFOT-1-R |
| TFOT-5 | 163 | 5 | N/A | TFOT-5-R |
| Copolymers | MAAC | MARC |
|---|---|---|
| Origin-SBS | SBS-A | N/A |
| UV-1 | UV-1-A | UV-1-R |
| UV-5 | UV-5-A | UV-5-R |
| TFOT-1 | TFOT-1-A | TFOT-1-R |
| TFOT-5 | TFOT-5-A | TFOT-5-R |
| Wavenumber (cm−1) | Assignments | Origin of the Chemical Structures |
|---|---|---|
| 3460 | Hydroxyl (O–H) stretching | Carboxyl acids, alcohols, hydroperoxides and etc. |
| 2919 | Methylene C–H anti-symmetry stretching | Methylene units |
| 2845 | Methyl C–H symmetry stretching | Methylene units |
| 1780 | Carbonyl (C=O) stretching | Anhydrides, lactones, peracids and so on. |
| 1725 | Carbonyl (C=O) stretching | Aliphatic ketones, aldehydes, etc. |
| 1700 | Carbonyl (C=O) stretching | α, β unsaturated acids, ketones, aldehydes and acetophenone groups |
| 1160 | Ether bond (–O–) stretching | Fatty ethers or aromatic ethers |
| 1030 | Sulfoxide (S=O) stretching | Thioether and sulfoxide units |
| 967 | C-H bending vibration | 1-4 trans olefinic groups |
| 910 | C-H bending vibration | 1-2 vinyl olefinic groups |
| ICH=CH | IC=O | IS=O | |
|---|---|---|---|
| UV-5-A | 0.01915 | 0.03857 | 0.02696 |
| UV-5-R | 0.02534 | 0.04003 | 0.02061 |
| UV-1-A | 0.03273 | 0.02088 | 0.02159 |
| UV-1-R | 0.03934 | 0.03543 | 0.02075 |
| TFOT-5-A | 0.02520 | 0.02769 | 0.02054 |
| TFOT-5-R | 0.02970 | 0.03283 | 0.01748 |
| TFOT-1-A | 0.03225 | 0.01968 | 0.01957 |
| TFOT-1-R | 0.03560 | 0.02840 | 0.01456 |
| SBS-A | 0.03565 | 0.01773 | 0.01987 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, F.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Wu, S. Aging Mechanism and Rejuvenating Possibility of SBS Copolymers in Asphalt Binders. Polymers 2020, 12, 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12010092
Wang F, Zhang L, Zhang X, Li H, Wu S. Aging Mechanism and Rejuvenating Possibility of SBS Copolymers in Asphalt Binders. Polymers. 2020; 12(1):92. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12010092
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Fusong, Lei Zhang, Xiaoshan Zhang, Hechuan Li, and Shaopeng Wu. 2020. "Aging Mechanism and Rejuvenating Possibility of SBS Copolymers in Asphalt Binders" Polymers 12, no. 1: 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12010092
APA StyleWang, F., Zhang, L., Zhang, X., Li, H., & Wu, S. (2020). Aging Mechanism and Rejuvenating Possibility of SBS Copolymers in Asphalt Binders. Polymers, 12(1), 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12010092









