Poly(Lactic Acid)/ZnO Bionanocomposite Films with Positively Charged ZnO as Potential Antimicrobial Food Packaging Materials
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of ZnO NPs
2.3. Preparation of Bionanocomposite Films
2.4. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. FT-IR Analysis
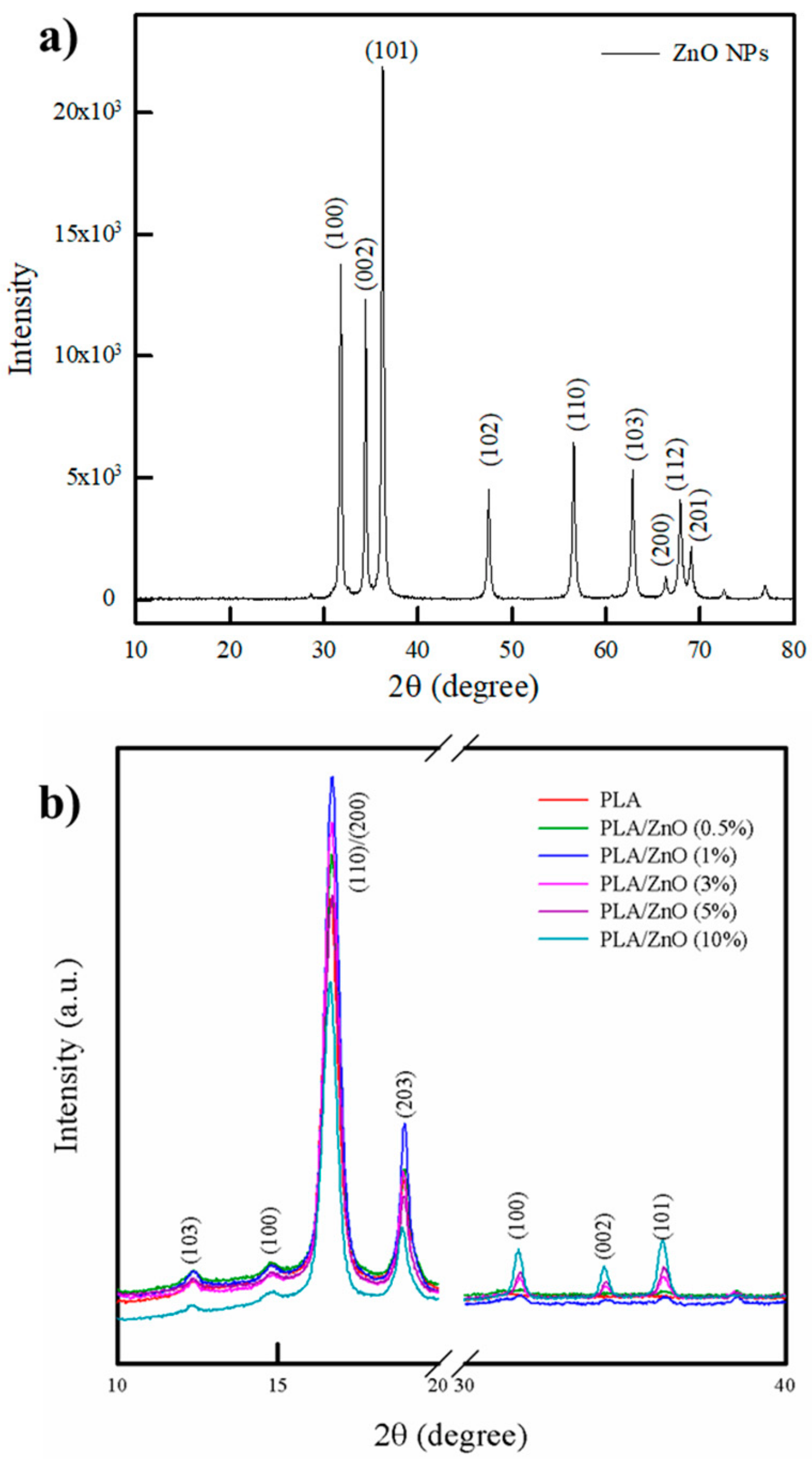
3.2. XRD Analysis
3.3. Optical Property
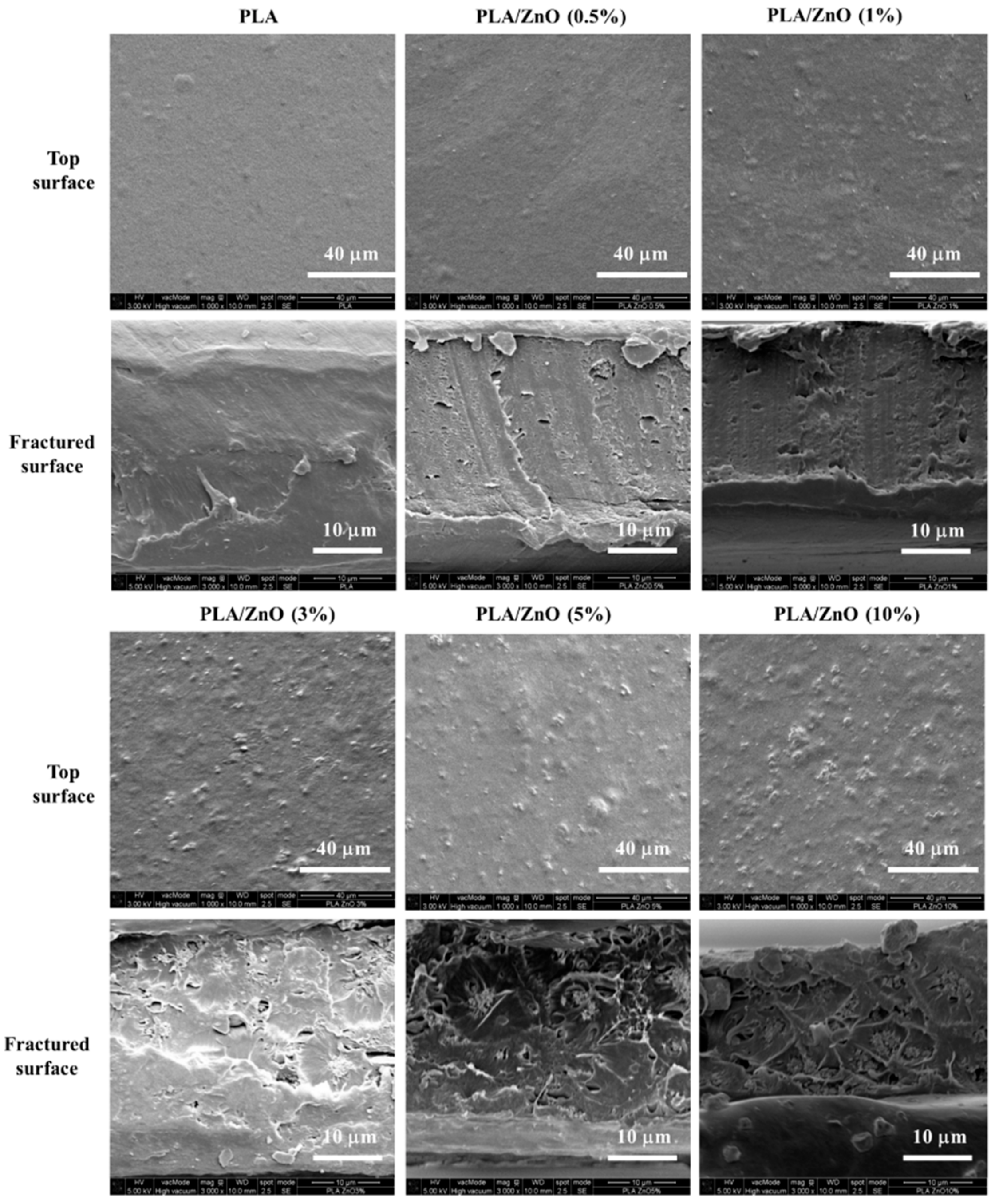
3.4. Morphology
3.5. Thermal Properties
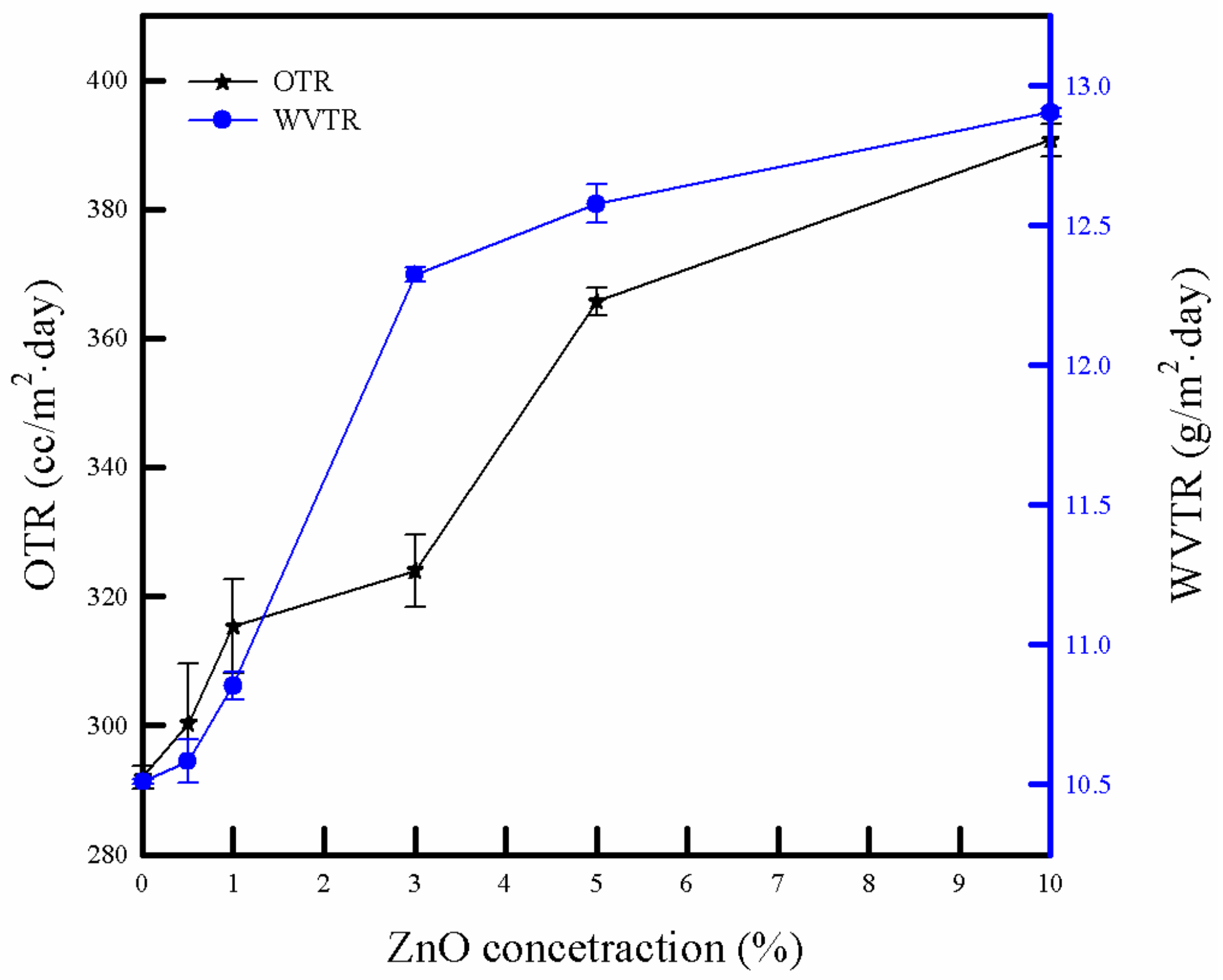
3.6. Barrier Property
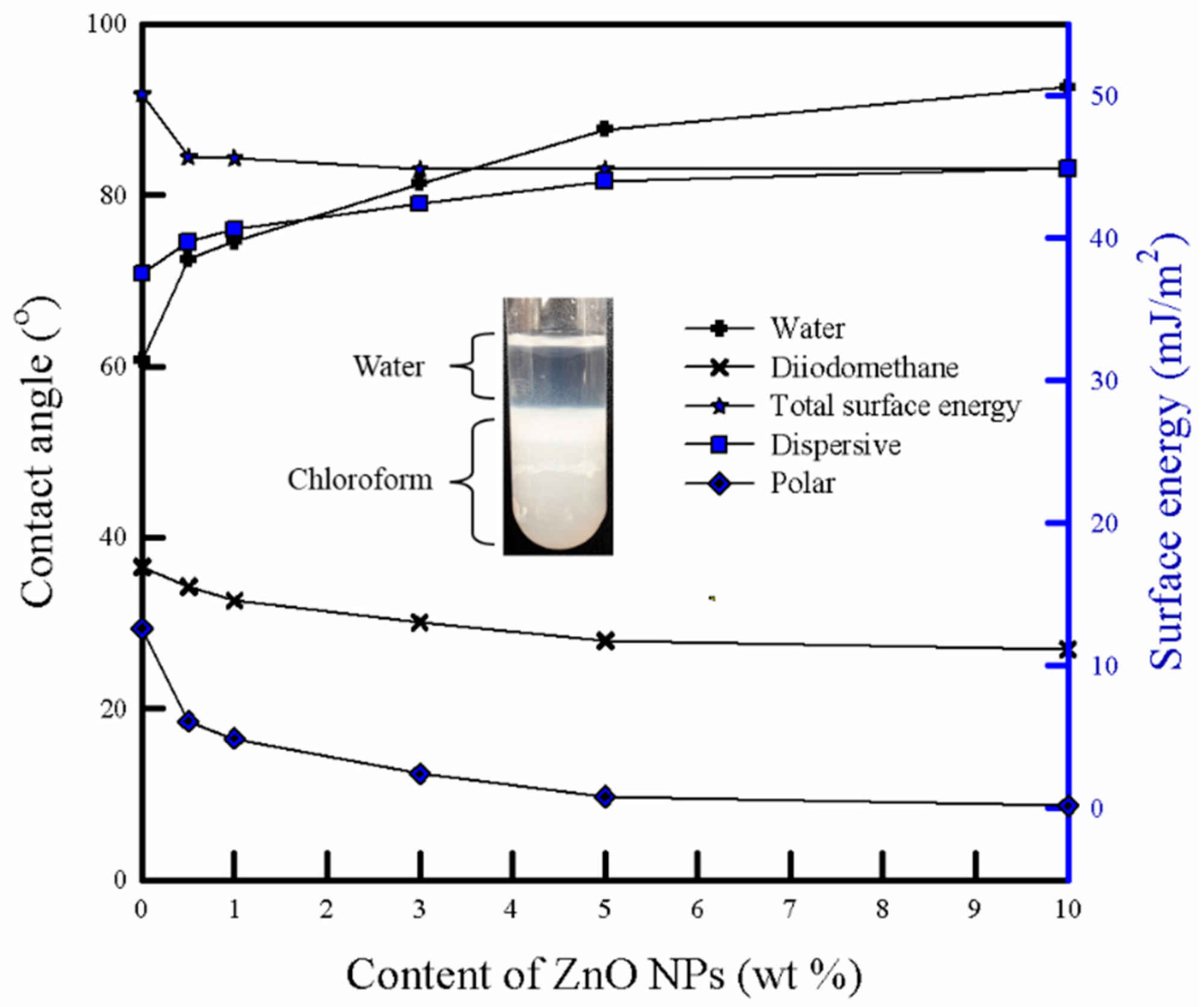
3.7. Surface Energy and Water Sorption
3.8. Antibacterial Activity of PLA/ZnO Bionanocomposite Films
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Díez-Pascual, A.M.; Díez-Vicente, A.L. Poly (3-hydroxybutyrate)/ZnO bionanocomposites with improved mechanical, barrier and antibacterial properties. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 10950–10973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Therias, S.; Larché, J.F.; Bussière, P.O.; Gardette, J.L.; Murariu, M.; Dubois, P. Photochemical behavior of polylactide/ZnO nanocomposite films. Biomacromolecules 2012, 13, 3283–3291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, Z.; Zhao, T.; Li, L.; Fan, J.; Qin, Y. Characterization of antimicrobial poly (lactic acid)/nano-composite films with silver and zinc oxide nanoparticles. Materials 2017, 10, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murariu, M.; Paint, Y.; Murariu, O.; Raquez, J.M.; Bonnaud, L.; Dubois, P. Current progress in the production of PLA–ZnO nanocomposites: Beneficial effects of chain extender addition on key properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 42480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hegyesi, N.; Zhang, Y.; Mao, Z.; Feng, X.; Wang, B.; Pukánszky, B.; Sui, X. Poly (lactic acid)/lignin blends prepared with the Pickering emulsion template method. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 110, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marra, A.; Silvestre, C.; Duraccio, D.; Cimmino, S. Polylactic acid/zinc oxide biocomposite films for food packaging application. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 88, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorgan, J.R. Rheology of Poly (Lactic Acid). In Poly (Lactic Acid): Synthesis, Structures, Properties, Processing, and Applications; Auras, R.A., Lim, L.T., Selke, S.E., Tsuji, H., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 125–139. [Google Scholar]
- Lunt, J. Large-scale production, properties and commercial applications of polylactic acid polymers. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 1998, 59, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudnik, E. Compostable Polymer Materials; Elsevier: Newnes, Australia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Vasile, C. Polymeric nanocomposites and nanocoatings for food packaging. Materials 2018, 11, 1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Silva, R.T.; Pasbakhsh, P.; Lee, S.M.; Kit, A.Y. ZnO deposited/encapsulated halloysite–poly (lactic acid) (PLA) nanocomposites for high performance packaging films with improved mechanical and antimicrobial properties. Appl. Clay Sci. 2015, 111, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantani, R.; Gorrasi, G.; Vigliotta, G.; Murariu, M.; Dubois, P. PLA-ZnO nanocomposite films: Water vapor barrier properties and specific end-use characteristics. Eur. Polym. J. 2013, 49, 3471–3482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, M.; Gupta, S.; Zafeiropoulos, N.E.; Oertel, U.; Häßler, R.; Stamm, M. Nano-Level Mixing of ZnO into Poly (methyl methacrylate). Macromolecular Chemistry and Physics. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2010, 211, 1925–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, R.; Karan, R.; Sinha, A.; Khare, S.K. Interaction and nanotoxic effect of ZnO and Ag nanoparticles on mesophilic and halophilic bacterial cells. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 1516–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yildirim, S.; Röcker, B.; Pettersen, M.K.; Nilsen-Nygaard, J.; Ayhan, Z.; Rutkaite, R.; Radusin, T.; Suminska, P.; Marcos, B.; Coma, V. Active packaging applications for food. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2018, 17, 165–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.; Viswanathan, K.; Kasi, G.; Seo, J. Preparation and characterization of positively surface charged zinc oxide nanoparticles against bavterial pathrogens. Microb. Pathog. 2019, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Hameed, A.S.H.; Karthikeyan, C.; Ahamed, A.P.; Thajuddin, N.; Alharbi, N.S.; Alharbi, S.A.; Ravi, G. In vitro antibacterial activity of ZnO and Nd doped ZnO nanoparticles against ESBL producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arakha, M.; Saleem, M.; Mallick, B.C.; Jha, S. The effects of interfacial potential on antimicrobial propensity of ZnO nanoparticle. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, J.; Liang, Y.; Kwong, F.L.; Ding, Z.; Ng, D.H. Template-free solvothermal synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles with controllable size and their size-dependent optical properties. Mater. Lett. 2012, 66, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanakkasaranee, S.; Kim, D.; Seo, J. Preparation and characterization of poly (ether-block-amide)/polyethylene glycol composite films with temperature-dependent permeation. Polymers 2018, 10, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergstrom, J.S. Mechanics of Solid Polymers: Theory and Computational Modeling; William Andrew: San Diego, CA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.; Jeon, K.; Lee, Y.; Seo, J.; Seo, K.; Han, H.; Khan, S. Preparation and characterization of UV-cured polyurethane acrylate/ZnO nanocomposite films based on surface modified ZnO. Prog. Org. Coat. 2012, 74, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.; Jeon, G.; Jang, E.S.; Khan, S.B.; Han, H. Preparation and properties of poly (propylene carbonate) and nanosized ZnO composite films for packaging applications. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 122, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Lee, Y.; Seo, J.; Han, H.; Khan, S.B. Preparation and properties of poly (urethane acrylate) (PUA) and tetrapod ZnO whisker (TZnO-W) composite films. Polym. Int. 2013, 62, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, W.C. Thermal Behavior and Crystal Structure of Poly (l-lactic acid) with 1, 3: 2, 4-Dibenzylidene-d-sorbitol. J. Phys. Chem. B 2011, 115, 11029–11037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vestena, M.; Gross, I.P.; Müller, C.M.; Pires, A.T. Nanocomposite of poly (lactic acid)/cellulose nanocrystals: Effect of CNC content on the polymer crystallization kinetics. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2016, 27, 905–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Liu, T. Polymer/calcium carbonate nanocomposites. In Polymer Nanocomposites; Mai, Y.W., Yu, Z.Z., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2006; pp. 412–439. [Google Scholar]
- Eiras, D.; Pessan, L.A. Influence of calcium carbonate nanoparticles on the crystallization of polypropylene. Mat. Res. 2009, 12, 523–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auras, R.; Harte, B.; Selke, S. An overview of polylactides as packaging materials. Macromol. Biosci. 2004, 4, 835–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Kemary, M.; El-Shamy, H.; El-Mehasseb, I. Photocatalytic degradation of ciprofloxacin drug in water using ZnO nanoparticles. J. Lumin. 2010, 130, 2327–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.W.; Park, M.; Kim, J.; Lee, J.I.; Yoon, H.G. Enhanced thermal conductivity of polymer composites filled with hybrid filler. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2006, 37, 727–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizundia, E.; Ruiz-Rubio, L.; Vilas, J.L.; León, L.M. Poly (l-lactide)/zno nanocomposites as efficient UV-shielding coatings for packaging applications. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133, 42426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benali, S.; Aouadi, S.; Dechief, A.L.; Murariu, M.; Dubois, P. Key factors for tuning hydrolytic degradation of polylactide/zinc oxide nanocomposites. Nanocomposites 2015, 1, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Hu, D.; Deng, S.; Han, B.; Wang, Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, Y. Isopropanol sensing properties of coral-like ZnO–CdO composites by flash preparation via self-sustained decomposition of metal–organic complexes. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 198, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Tobías, H.; Morales, G.; Grande, D. Improvement of mechanical properties and antibacterial activity of electrospun poly (d, l-lactide)-based mats by incorporation of ZnO-graft-poly (d, l-lactide) nanoparticles. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2016, 182, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheewawuttipong, W.; Fuoka, D.; Tanoue, S.; Uematsu, H.; Iemoto, Y. Thermal and mechanical properties of polypropylene/boron nitride composites. Energy Procedia 2013, 34, 808–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karak, N. Nanomaterials and Polymer Nanocomposites: Raw Materials to Applications; Elsevier Science: Taramani, India, 2018; pp. 1–432. [Google Scholar]
- Aggarwal, S.; Sajwan, M.; Singh, R.B. Crystallinity of hdpe pipes by dsc, xrd and ftir spectroscopy-a Forensic comparison. Indian J. Criminol. Crim. 2008, 2, 141–148. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, K.K.; Mishra, P.K.; Srivastava, P.; Gangwar, M.; Nath, G.; Maiti, P. Hydrothermal in situ preparation of TiO2 particles onto poly (lactic acid) electrospun nanofibres. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 264, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhoodi, M.; Dadashi, S.; Mousavi, S.M.A.; Sotudeh-Gharebagh, R.; Emam-Djomeh, Z.; Oromiehie, A.; Hemmati, F. Influence of TiO2 Nanoparticle Filler on the Properties of PET and PLA Nanocomposites. Polym. Korea 2012, 36, 745–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y. Biodegradable Poly (Lactic Acid) Nanocomposites: Synthesis and Characterization. Ph.D. Thesis, Kansas State University, Manhattan, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Cirillo, G.; Kozlowski, M.A.; Spizzirri, U.G. Composite Materials for Food Packaging; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, R.; Deng, H.; Putz, K.W.; Brinson, L.C. Effect of particle agglomeration and interphase on the glass transition temperature of polymer nanocomposites. J. Polym. Sci. Pol. Phys. 2011, 49, 740–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Restrepo, I.; Benito, N.; Medinam, C.; Mangalaraja, R.V.; Flores, P.; Rodriguez-Llamazares, S. Development and characterization of polyvinyl alcohol stabilized polylactic acid/ZnO nanocomposites. Mater. Res. Express 2017, 4, 105019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaroop, C.; Shukla, M. Nano-magnesium oxide reinforced polylactic acid biofilms for food packaging applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 113, 729–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereda, M.; Ponce, A.G.; Marcovich, N.E.; Ruseckaite, R.A.; Martucci, J.F. Chitosan-gelatin composites and bi-layer films with potential antimicrobial activity. Food Hydrocoll. 2011, 25, 1372–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Kuc, A.; Frauenheim, T.; Heine, T. Stabilization mechanism of ZnO nanoparticles by Fe doping. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 112, 106102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Lang, J.; Liu, F.; Yang, L.; Zhai, H.; Gao, M.; Zhao, X. Effect of polar and non-polar surfaces of ZnO nanostructures on photocatalytic properties. J. Alloy. Compd. 2012, 528, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohara, S.; Mousavand, T.; Sasaki, T.; Umetsu, M.; Naka, T.; Adschiri, T. Continuous production of fine zinc oxide nanorods by hydrothermal synthesis in supercritical water. J. Mater. Sci. 2008, 43, 2393–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, S.; Teng, X.; Li, G.; Rhim, J.W. Preparation, characterization, and antimicrobial activity of gelatin/ZnO nanocomposite films. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 45, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmi Prasanna, V.; Vijayaraghavan, R. Insight into the mechanism of antibacterial activity of ZnO: Surface defects mediated reactive oxygen species even in the dark. Langmuir 2015, 31, 9155–9162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghupathi, K.R.; Koodali, R.T.; Manna, A.C. Size-dependent bacterial growth inhibition and mechanism of antibacterial activity of zinc oxide nanoparticles. Langmuir 2011, 27, 4020–4028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Hortal, M.; Jordá-Beneyto, M.; Rosa, E.; Lara-Lledo, M.; Lorente, I. ZnO-PLA nanocomposite coated paper for antimicrobial packaging application. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 78, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Sample Code | DSC | TGA | DVS | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tg (°C) a | Tm (°C) b | ΔHm (J/g) c | Tc (°C) d | ΔHc (J/g) e | Td3% (°C) f | Td10% (°C) g | Residual Content (%) h | Water Uptake (3h) | |
| ZnO NPs | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 98.8 | - |
| PLA | 62.5 ± 0.05 | 165.6 ± 0.3 | 46.2 ± 1.4 | 110.6 ± 0.1 | 43.1 ± 0.2 | 324.8 | 341.7 | 2.6 | 0.82 ± 0.04 |
| PLA/ZnO (0.5%) | 62.1 ± 0.03 | 166.5 ± 0.3 | 43.8 ± 0.8 | 104.5 ± 0.1 | 35.7 ± 3.1 | 281.4 | 300.4 | 2.8 | 0.92 ± 0.04 |
| PLA/ZnO (1%) | 61.7 ± 0.05 | 166.6 ± 1.8 | 40.6 ± 0.1 | 101.5 ± 2.3 | 30.9± 0.5 | 275.7 | 295.7 | 3.1 | 0.94 ± 0.02 |
| PLA/ZnO (3%) | 61.3 ± 0.05 | 166.7 ± 2.4 | 40.4 ± 1.1 | 101.1 ± 1.2 | 30.2 ± 0.5 | 273.6 | 294.8 | 5.2 | 0.90 ± 0.02 |
| PLA/ZnO (5%) | 60.9 ± 0.03 | 166.8 ± 2.5 | 38.9 ± 1.8 | 99.1 ± 4.2 | 28.7 ± 1.3 | 273.1 | 293.7 | 7.1 | 0.97 ± 0.01 |
| PLA/ZnO (10%) | 58.2 ± 0.07 | 166.9 ± 3.0 | 33.9 ± 5.1 | 98.6 ± 1.8 | 24.8 ± 4.0 | 272.6 | 293.1 | 11.1 | 0.94 ± 0.03 |
| Sample Code | S. aureus | R (%) | E. coli | R (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10−7 | 10−5 | |||
| PLA |  | - |  | - |
| PLA/ZnO (0.5%) | 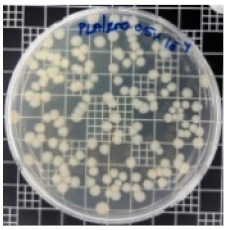 | 23.3 | 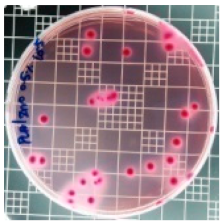 | 51.7 |
| PLA/ZnO (1%) | 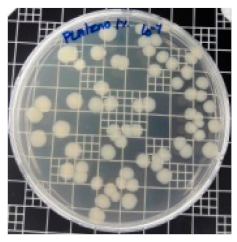 | 69.2 |  | 69.0 |
| PLA/ZnO (3%) |  | 83.7 | 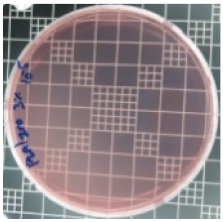 | 100 |
| PLA/ZnO (5%) | 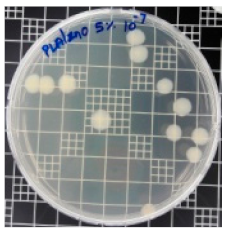 | 90.2 | 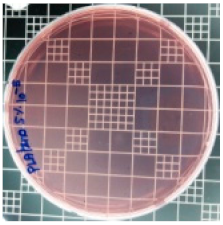 | 100 |
| PLA/ZnO (10%) | 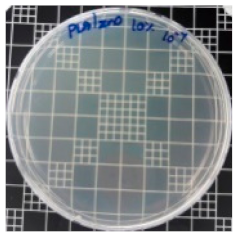 | 100 |  | 100 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, I.; Viswanathan, K.; Kasi, G.; Sadeghi, K.; Thanakkasaranee, S.; Seo, J. Poly(Lactic Acid)/ZnO Bionanocomposite Films with Positively Charged ZnO as Potential Antimicrobial Food Packaging Materials. Polymers 2019, 11, 1427. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11091427
Kim I, Viswanathan K, Kasi G, Sadeghi K, Thanakkasaranee S, Seo J. Poly(Lactic Acid)/ZnO Bionanocomposite Films with Positively Charged ZnO as Potential Antimicrobial Food Packaging Materials. Polymers. 2019; 11(9):1427. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11091427
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Insoo, Karthika Viswanathan, Gopinath Kasi, Kambiz Sadeghi, Sarinthip Thanakkasaranee, and Jongchul Seo. 2019. "Poly(Lactic Acid)/ZnO Bionanocomposite Films with Positively Charged ZnO as Potential Antimicrobial Food Packaging Materials" Polymers 11, no. 9: 1427. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11091427
APA StyleKim, I., Viswanathan, K., Kasi, G., Sadeghi, K., Thanakkasaranee, S., & Seo, J. (2019). Poly(Lactic Acid)/ZnO Bionanocomposite Films with Positively Charged ZnO as Potential Antimicrobial Food Packaging Materials. Polymers, 11(9), 1427. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11091427







