The Relationships between the Working Fluids, Process Characteristics and Products from the Modified Coaxial Electrospinning of Zein
Abstract
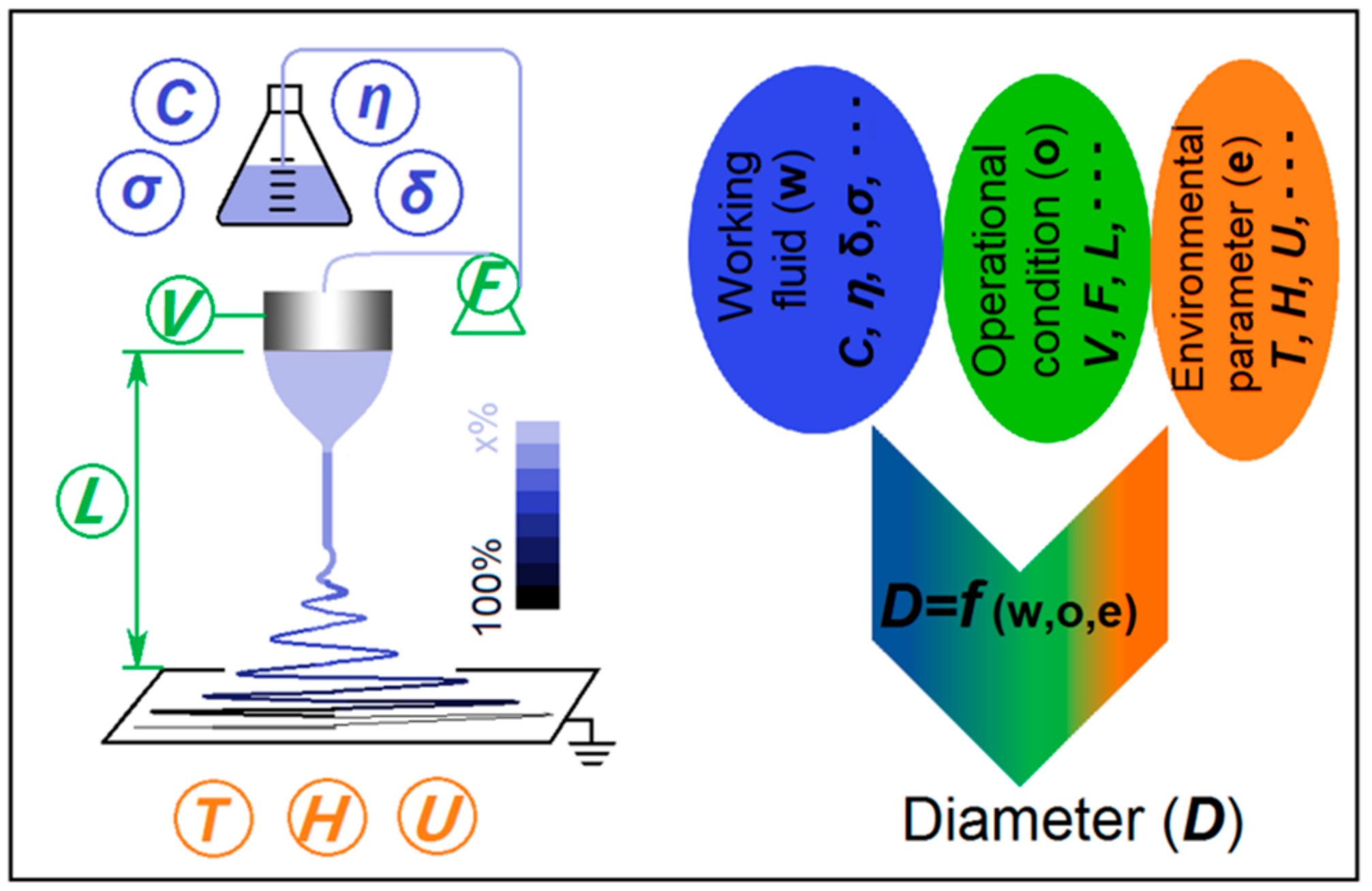
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
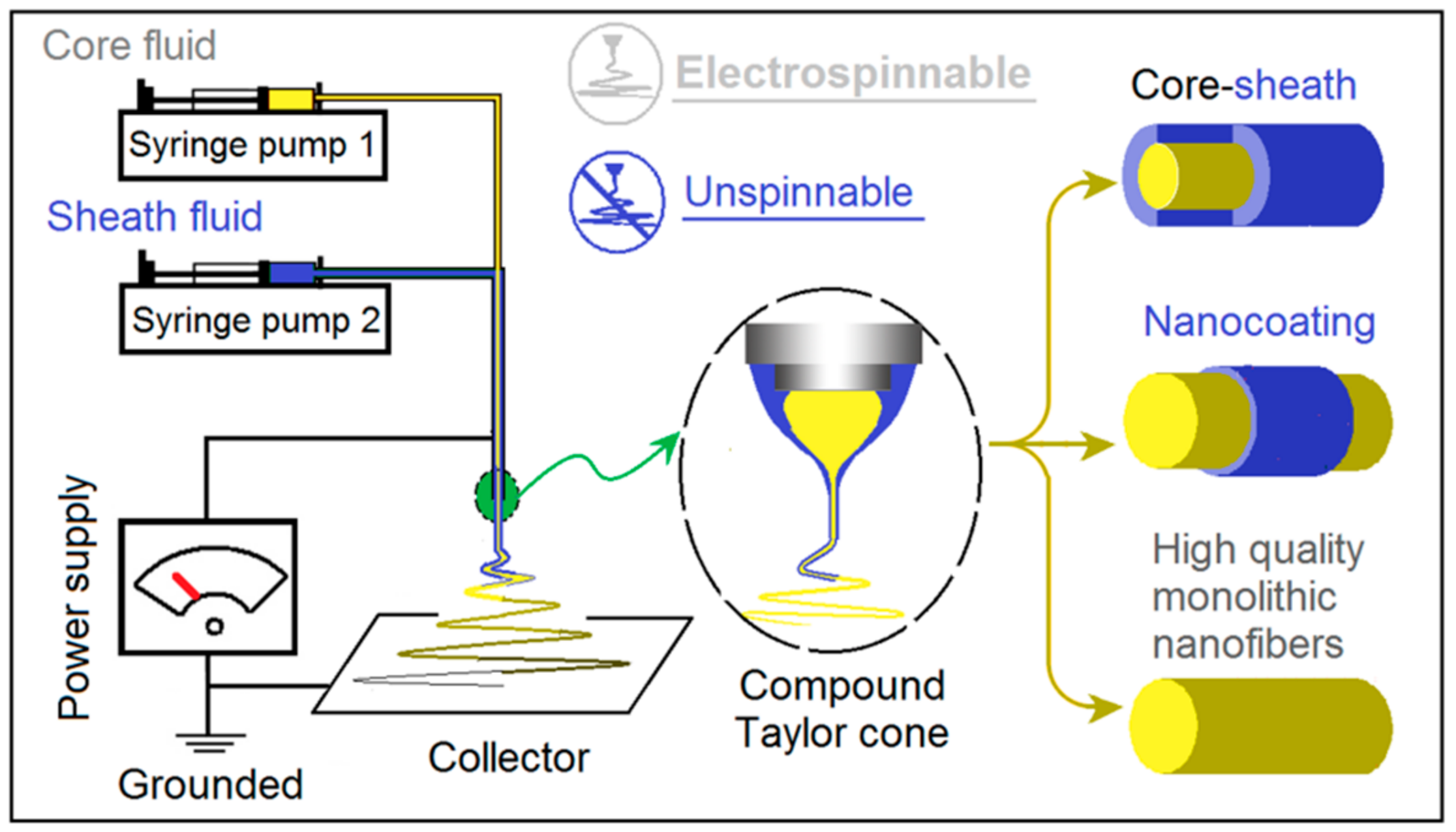
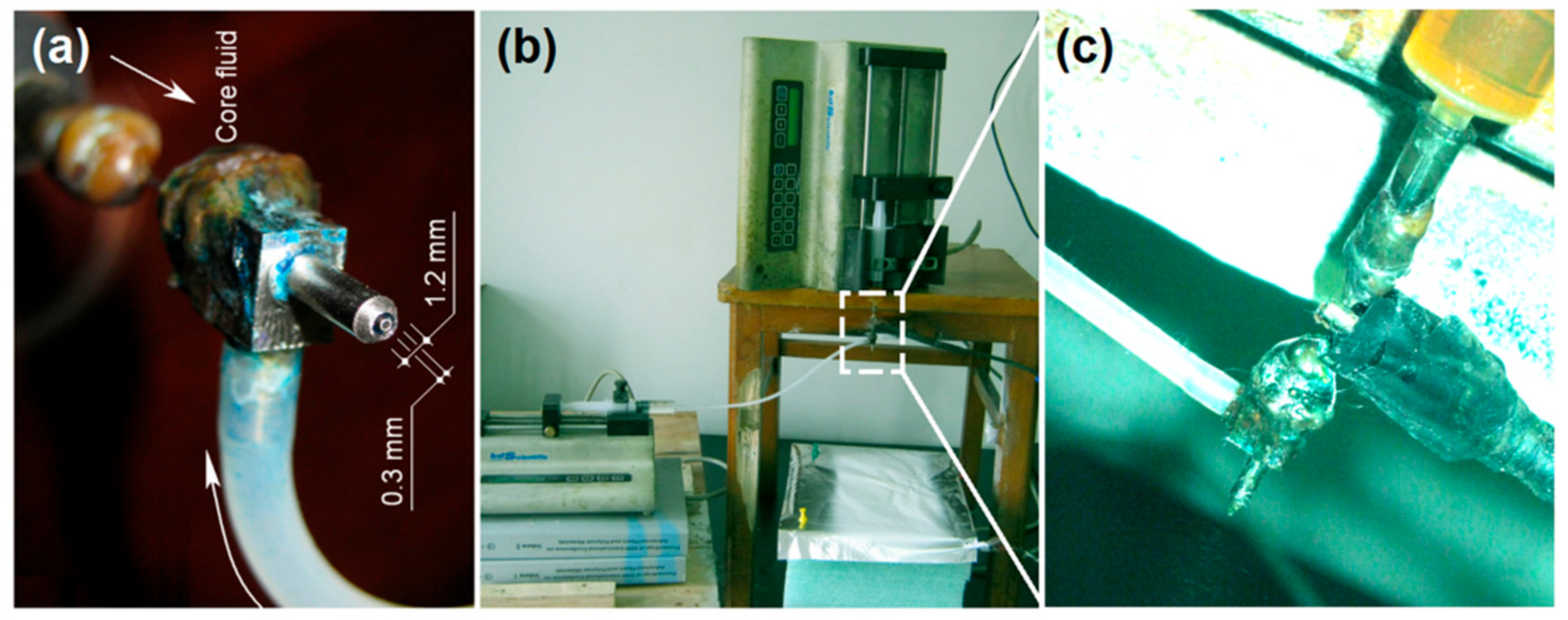
2.2. Modified Coaxial Electrospraying
2.3. Morphology of the Prepared Nanoparticles
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Implementation of Modified Coaxial Electrospinning
3.2. The Working Processes and the Resultant Zein Nanoribbons
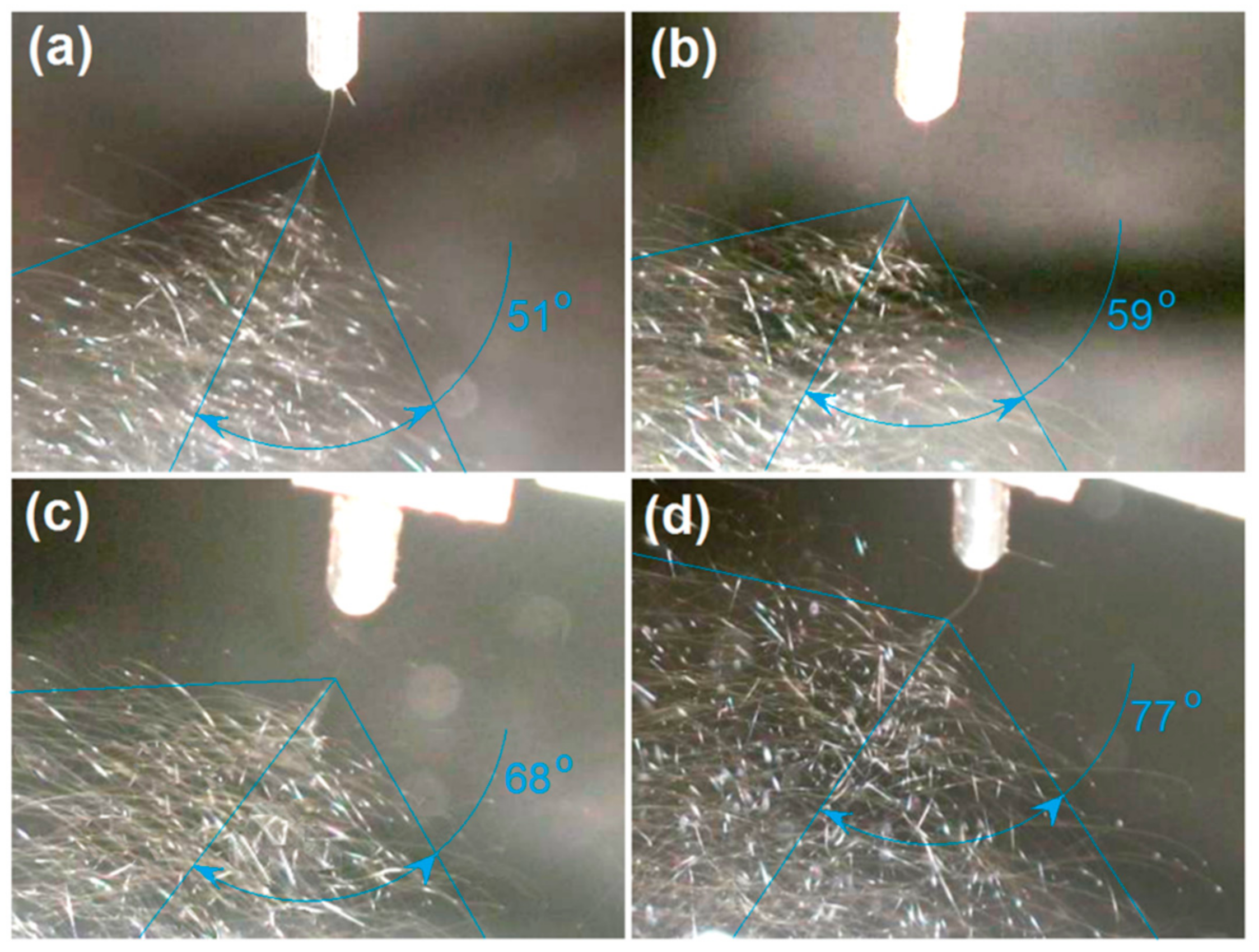
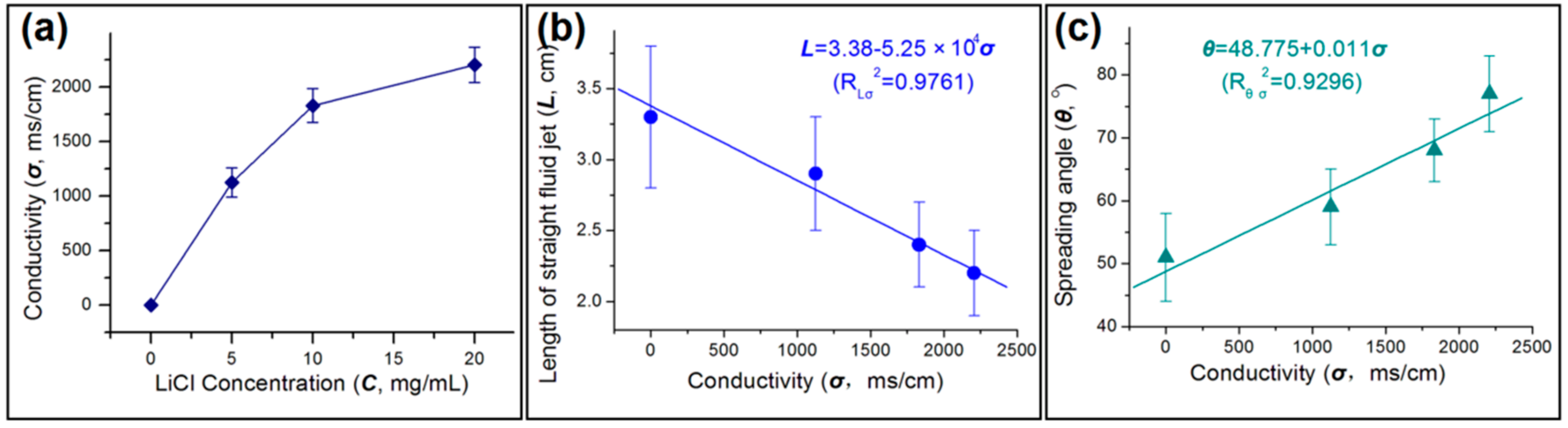
3.3. The Influence of Conductivity on the Behavior of the Working Fluids
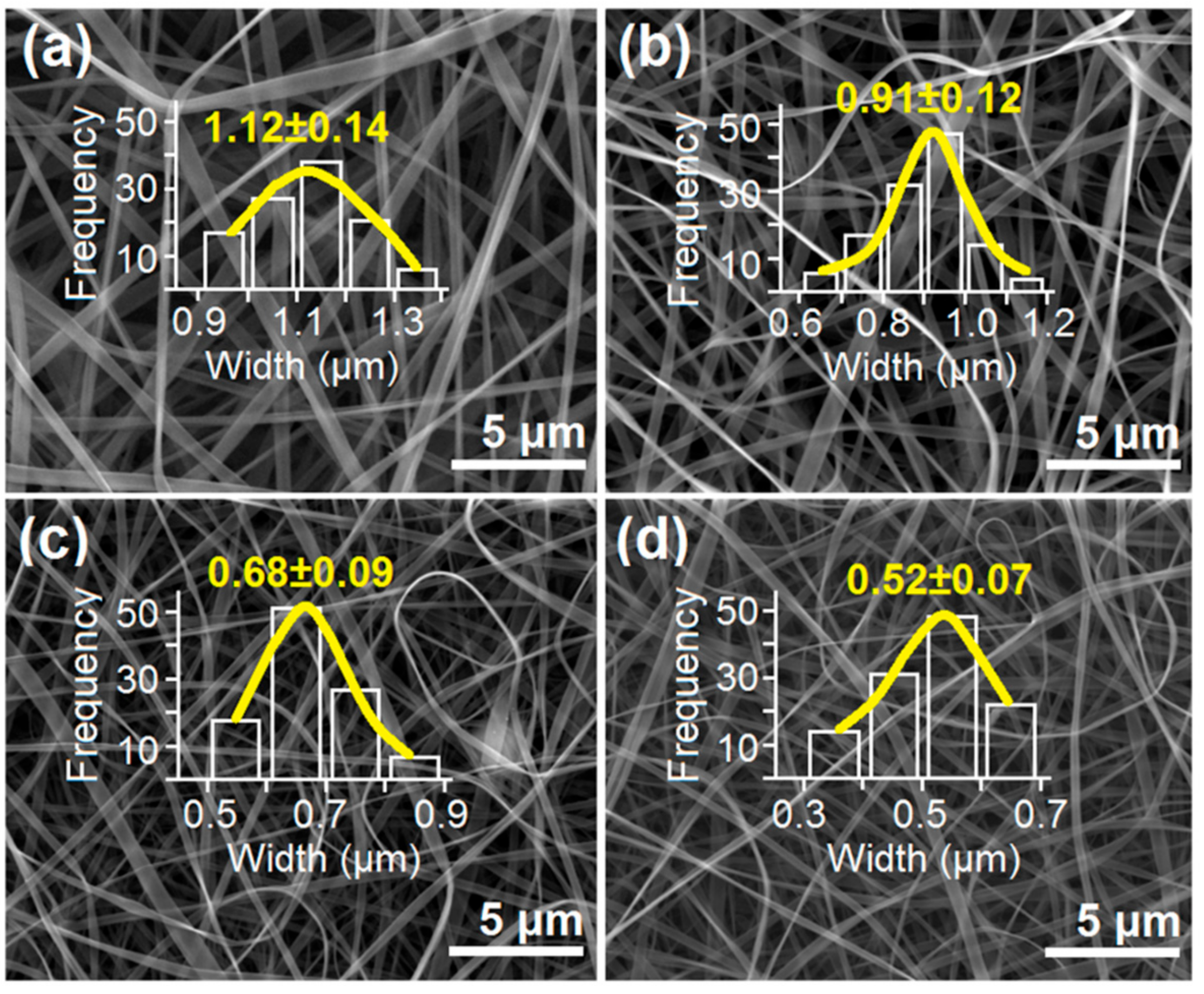
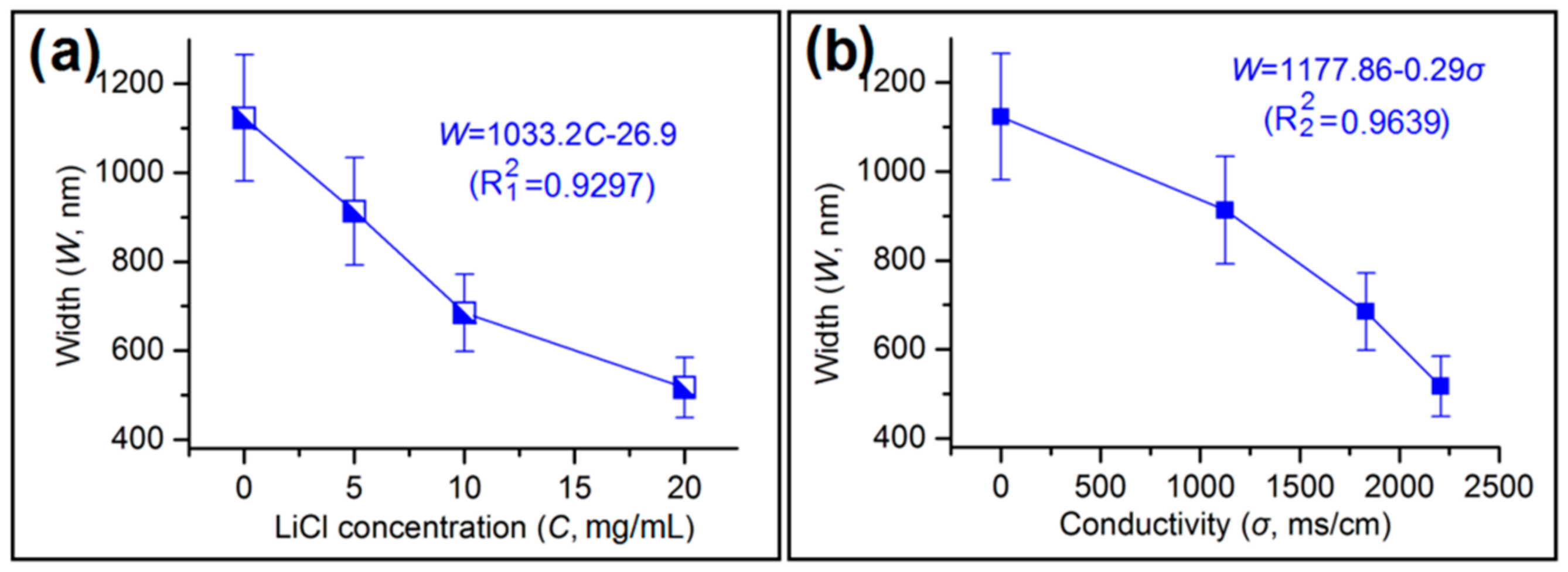
3.4. The Effect of Sheath Working Fluid Properties on the Width of Zein Nanoribbons
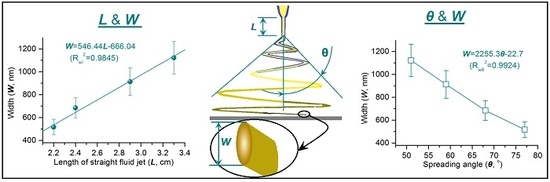
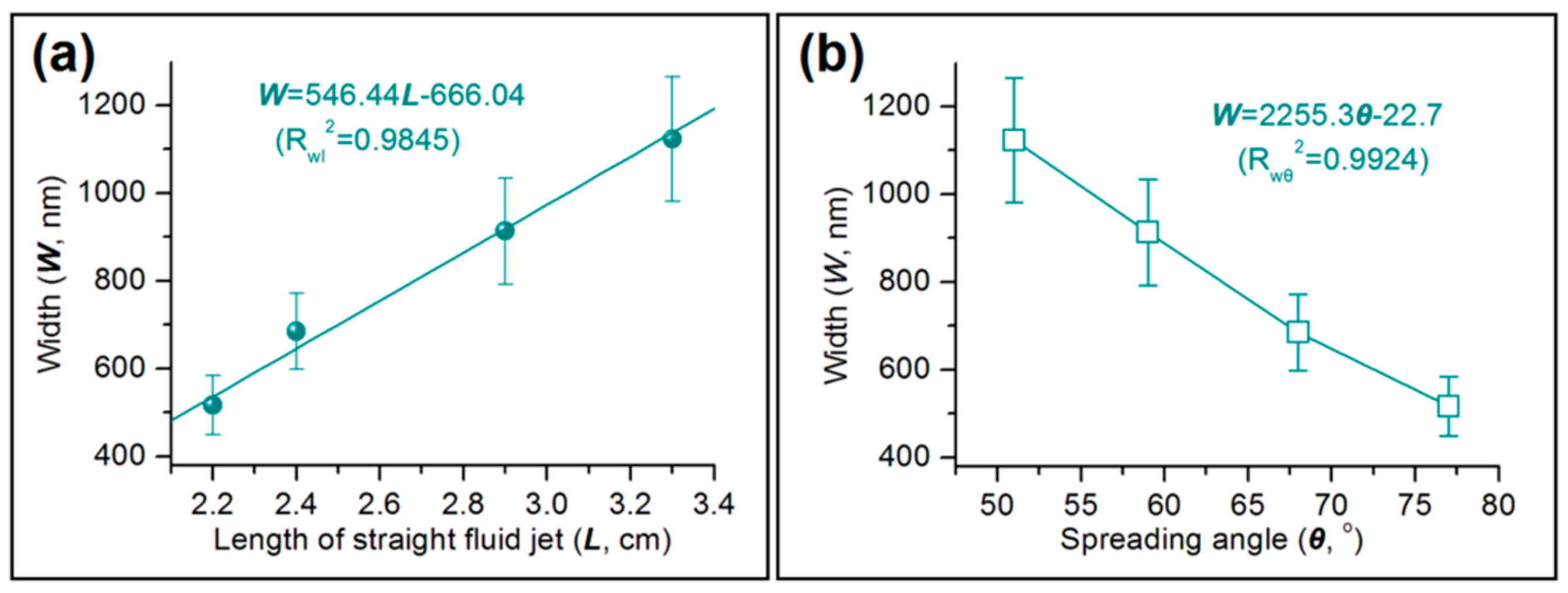
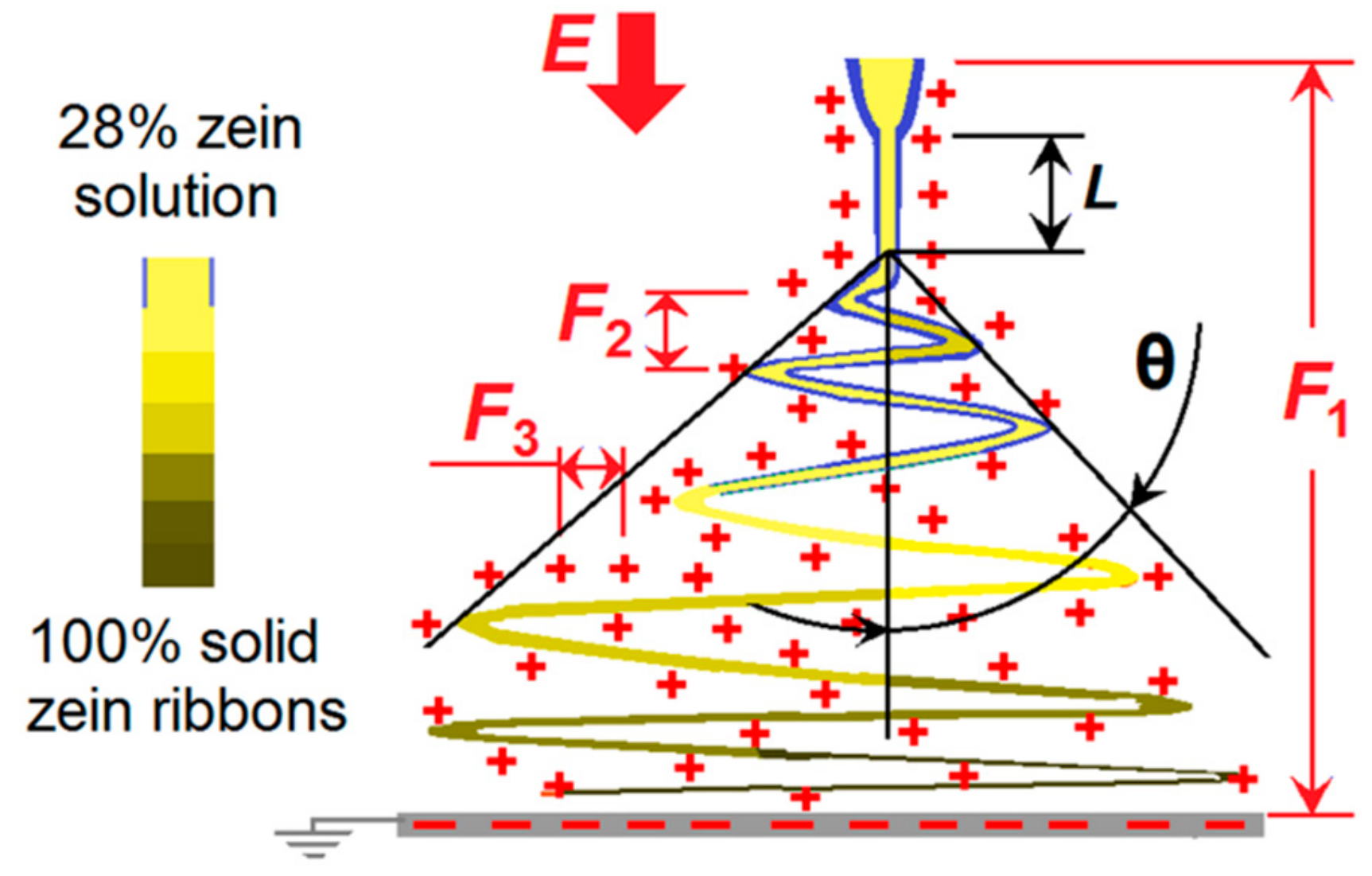
3.5. Correlations between the Width of Electrospun Zein Nanoribbons and the Detailed Steps of Electrospinning
3.6. The Role of Process Characteristics
4. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dotivala, A.C.; Puthuveetil, K.P.; Tang, C. Shear force fiber spinning: Process parameter and polymer solution property considerations. Polymers 2019, 11, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vass, P.; Démuth, B.; Hirsch, E.; Nagy, B.; Andersen, S.K.; Vigh, T.; Verreck, G.; Csontos, I.; Nagy, Z.K.; Marosi, G. Drying technology strategies for colontargeted oral delivery of biopharmaceuticals. J. Control. Release 2019, 296, 162–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Zhao, S.; Ding, W.; Han, L. Studies of interfacial interaction between polymer components on helical nanofiber formation via coelectrospinning. Polymers 2018, 10, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicente, A.C.B.; Medeiros, G.B.; do Carmo Vieira, D.; Garcia, F.P.; Nakamura, C.V.; Muniz, E.C.; Corradini, E. Influence of process variables on the yield and diameter of zeinpoly (n-isopropylacrylamide) fiber blends obtained by electrospinning. J. Mol. Liquids 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acik, G.; Cansoy, C.E.; Kamaci, M. Effect of flow rate on wetting and optical properties of electrospun poly (vinyl acetate) microfibers. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2019, 297, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, S.; Khan, A.R.; Ji, J.; Yang, M.; Zhai, G. Recent advances in electrospun for drug delivery purpose. J. Drug Target. 2019, 27, 270–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakrabarty, A.; Teramoto, Y. Recent advances in nanocellulose composites with polymers: A guide for choosing partners and how to incorporate them. Polymers 2018, 10, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, A.; Haider, S.; Kang, I.K. A comprehensive review summarizing the effect of electrospinning parameters and potential applications of nanofibers in biomedical and biotechnology. Arab. J. Chem. 2018, 11, 1165–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okutan, N.; Terzi, P.; Altay, F. Affecting parameters on electrospinning process and characterization of electrospun gelatin nanofibers. Food Hydrocolloids 2014, 39, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.Y.; Lung, Y.C.; Kuo, C.C.; Liang, F.C.; Tsai, T.L.; Jiang, D.H.; Satoh, T.; Jeng, R.J. Novel multifunctional luminescent electrospun fluorescent nanofiber chemosensorfilters and their versatile sensing of pH, temperature, and metal ions. Polymers 2018, 10, 1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.H.; Tsai, P.C.; Kuo, C.C.; Jhuang, F.C.; Guo, H.C.; Chen, S.P.; Tung, S.H. Facile preparation of Cu/Ag Core/Shell electrospun nanofibers as highly stable and flexible transparent conductive electrodes for optoelectronic devices. ACS Appl. Mat. Interfaces 2019, 11, 10118–10127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, D.G.; Zheng, X.L.; Yang, Y.; Li, X.Y.; Williams, G.R.; Zhao, M. Immediate release of helicid from nanoparticles produced by modified coaxial electrospraying. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 473, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Zheng, Z.B.; Yu, D.G.; Liu, X.K.; Qu, Y.L.; Li, H.L. Electrosprayed sperical ethylcellulose nanoparticles for an improved sustainedrelease profile of anticancer drug. Cellulose 2017, 24, 5551–5564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wen, H.F.; Yu, D.G.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, D.F. Electrosprayed hydrophilic nanocomposites coated with shellac for colonspecific delayed drug delivery. Mat. Design 2018, 143, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.P.; Zhang, L.L.; Yang, Y.Y.; Wu, D.; Jiang, G.; Yu, D.G. Preparing composite nanoparticles for immediate drug release by modifying electrohydrodynamic interfaces during electrospraying. Powder Technol. 2018, 327, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yew, C.; Azari, P.; Choi, J.; Muhamad, F.; PingguanMurphy, B. Electrospun polycaprolactone nanofibers as a reaction membrane for lateral flow assay. Polymers 2018, 10, 1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kijeńska, E.; Swieszkowski, W. General requirements of electrospun materials for tissue engineering: Setups and strategy for successful electrospinning in laboratory and industry. Electrospun Mat. Tissue Eng. Biomed. Appl. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Shi, Z.; Wan, X.; Fang, H.; Yu, D.G.; Chen, X.; Liu, P. The relationships between the process parameters and the polymeric nanofibers fabricated using a modified coaxial electrospinning. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chlanda, A.; Kijeńska, E.; Rinoldi, C.; Tarnowski, M.; Wierzchoń, T.; Swieszkowski, W. Structure and physicomechanical properties of low temperature plasma treated electrospun nanofibrous scaffolds examined with atomic force microscopy. Micron 2018, 107, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.H.; Li, H.P.; Shi, X.X.; Wan, J.; Liu, Y.F.; Yu, D.G. Effective utilization of the electrostatic repulsion for improved alignment of electrospun nanofibers. J. Nanomat. 2016, 2016, 2067383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.H.; Yang, S.P.; Chen, Y.S.; Chen, K.Y. Electrospun poly (γ–glutamic acid)/β–tricalcium phosphate composite fibrous mats for bone regeneration. Polymers 2019, 11, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Liang, X.; Wang, S.; Qin, W.; Zhang, Q. Electrospun antimicrobial polylactic acid/tea polyphenol nanofibers for foodpackaging applications. Polymers 2018, 10, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caimi, S.; Wu, H.; Morbidelli, M. PVdF-HFP and ionic-liquid-based, freestanding thin separator for lithium-ion batteries. ACS Appl. Energy Mat. 2018, 1, 5224–5232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.G.; Li, J.J.; Williams, G.R.; Zhao, M. Electrospun amorphous solid dispersions of poorly watersoluble drugs: A review. J. Control. Release 2018, 292, 91–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, M.; Yu, D.G.; Wang, X.; Geraldes, C.F.G.C.; Williams, G.R.; Annie Bligh, S.W. Electrospun contrast agent-loaded fibers for colon-targeted MRI. Adv. Healthc. Mat. 2016, 5, 977–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Inoue, Y.; Kim, M.; Ren, X.; Kim, I. Effective formation of welldefined polymeric microfibers and nanofibers with exceptional uniformity by simple mechanical needle spinning. Polymers 2018, 10, 980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domokos, A.; Balogh, A.; Dénes, D.; Nyerges, G.; Ződi, L.; Farkas, B.; Marosi, G.; Nagy, Z.K. Continuous manufacturing of orally dissolving webs containing a poorly soluble drug via electrospinning. Euro. J. Pharma. Sci. 2019, 130, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saghazadeh, S.; Rinoldi, C.; Schot, M.; Kashaf, S.S.; Sharifi, F.; Jalilian, E.; Nuutila, K.; Giatsidis, G.; Mostafalu, P.; Derakhshandeh, H. Drug delivery systems and materials for wound healing applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2018, 127, 138–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Zhang, M.; Li, X.; Jiang, J.; Sousa, A.M.; Zhao, Q.; Pontious, S.; Liu, L. Incorporation of tannic acid in foodgrade guar gum fibrous mats by electrospinning technique. Polymers 2019, 11, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Jiao, X.; Shang, Y.; Wen, Y. Encapsulation of thymol in biodegradable nanofiber via coaxial eletrospinning and applications in fruit preservation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 1736–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.; Zhao, X.; Shi, L.; Zhang, G.; Wang, S.; Kang, W.; Zhuang, X. Preparation and properties of SCPLA/PMMA transparent nanofiber air filter. Polymers 2018, 10, 996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Yang, Y.; Yu, D.G.; Zhu, M.J.; Zhao, M.; Williams, G.R. Tunable zeroorder drug delivery systems created by modified triaxial electrospinning. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 356, 886–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, W.; Yu, D.G.; Wang, G.; Williams, G.R.; Zhang, Z. Tunable drug release from nanofibers coated with blank cellulose acetate layers fabricated using triaxial electrospinning. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 203, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guarino, V.; Caputo, T.; Calcagnile, P.; Altobelli, R.; Demitri, C.; Ambrosio, L. Core/shell cellulose-based microspheres for oral administration of ketoprofen lysinate. J. Biomed. Mat. Res. Part B 2018, 106, 2636–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costantini, M.; Colosi, C.; Święszkowski, W.; Barbetta, A. Coaxial wetspinning in 3d bioprinting: State of the art and future perspective of microfluidic integration. Biofabrication 2018, 11, 012001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caimi, S.; Timmerer, E.; Banfi, M.; Storti, G.; Morbidelli, M. Core-shell morphology of redispersible powders in polymer-cement waterproof mortars. Polymers 2018, 10, 1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, D.G.; Yang, C.; Jin, M.; Williams, G.R.; Zou, H.; Wang, X.; Bligh, S.A. Medicated Janus fibers fabricated using a tefloncoated sidebyside spinneret. Colloids Surf. B 2016, 138, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Wang, Y.; Xue, H.; Dou, Y. Biomimetic growth of hydroxyapatite on electrospun CA/PVP core–shell nanofiber membranes. Polymers 2018, 10, 1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Loh, C.H.; Tian, M.; Wang, R.; Fane, A.G. Progress in electrospun polymeric nanofibrous membranes for water treatment: Fabrication, modification and applications. Progr. Polym. Sci. 2018, 77, 69–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, V.D.; Cerqueira, M.A.; Fuciños, P.; GarridoMaestu, A.; Curto, J.M.; Pastrana, L.M. Active bilayer cellulosebased films: Development and characterization. Cellulose 2018, 25, 6361–6375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeem, M.; Lv, P.; Zhou, H.; Naveed, T.; Wei, Q. A novel in situ selfassembling fabrication method for bacterial celluloseelectrospun nanofiber hybrid structures. Polymers 2018, 10, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.; Yang, H.S.; Lee, B.S.; Yu, W.R. Recent progress in coaxial electrospinning: New parameters, various structures, and wide applications. Adv. Mat. 2018, 30, 1704765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xu, S.; Hassan, M.; Shao, J.; Ren, L.F.; He, Y. Effective modeling and optimization of pvdf–ptfe electrospinning parameters and membrane distillation process by response surface methodology. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 47125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.Q.; He, C.H.; Li, X.X.; He, J.H. Fabrication of beltlike fibers by electrospinning. Polymers 2018, 10, 1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abudula, T.; Saeed, U.; Salah, N.; Memic, A.; AlTuraif, H. Study of electrospinning parameters and collection methods on size distribution and orientation of PLA/PBS hybrid fiber using digital image processing. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2018, 18, 8240–8251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Chen, T.; Hu, C.; Xie, K. Recent advances of the polymer micro/nanofiber fluorescence wave guide. Polymers 2018, 10, 1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabó, E.; Démuth, B.; Nagy, B.; Molnár, K.; Farkas, A.; Szabó, B.; Balogh, A.; Hirsch, E.; Marosi, G.; Nagy, Z. Scaledup preparation of drugloaded electrospun polymer fibres and investigation of their continuous processing to tablet form. Express Polym. Lett. 2018, 12, 436–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutledge, G.C.; Fridrikh, S.V. Formation of fibers by electrospinning. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 1384–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, L.Y.; Friend, J.R. Electrospinning carbon nanotube polymer composite nanofibers. J. Exp. Nanosci. 2006, 1, 177–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yu, D.G.; Zhang, L.L.; Liu, X.K.; Deng, Y.C.; Zhao, M. Electrospun hypromellosebased hydrophilic composites for rapid dissolution of poorly watersoluble drug. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 174, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai, T.; Wan, X.; Yu, D.G.; Wang, K.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Z.P. Electrospun lipidcoated medicated nanocomposites for an improved drug sustainedrelease profile. Mat. Design 2019, 162, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.P.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Yu, D.G.; Wu, D.; Li, H.L. Fabrication of sustained-release zein nanoparticles via modified coaxial electrospraying. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 334, 807–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehcheshmeh, M.A.; Fathi, M. Production of coreshell nanofibers from zein and tragacanth for encapsulation of saffron extract. Int. J. Bio. Macromol. 2019, 122, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghalei, S.; Asadi, H.; Ghalei, B. Zein nanoparticle-embedded electrospun PVA nanofibers as wound dressing for topical delivery of anti-inflammatory diclofenac. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 46643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Que, F.; Kang, X.; Liu, Y.; Feng, F.; Zhang, H. Characterization of gelatin/zein nanofibers by hybrid electrospinning. Food Hydrocolloids 2018, 75, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.H.; Yang, C.; Li, X.Y.; Zhu, J.Y.; Yu, D.G. Medicated nanofibers fabricated using NaCl solutions as shell fluids in a modified coaxial electrospinning. J. Nanomat. 2016, 2016, 8970213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouhi, M.; Fathi, M.; Reddy, V.J.; Ramakrishna, S. Bredigite reinforced electrospun nanofibers for bone tissue engineering. Mat. Today Proc. 2019, 7, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngadiman, N.; Yusof, N.; Idris, A.; Fallahiarezoudar, E.; Kurniawan, D. Novel processing technique to produce three dimensional polyvinyl alcohol/maghemite nanofiber scaffold suitable for hard tissues. Polymers 2018, 10, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sill, T.J.; von Recum, H.A. Electrospinning: Applications in drug delivery and tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 1989–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Tang, G.; Hua, D.; Xiong, R.; Han, J.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, Q.L.; Huang, C. Stimuli-responsive bio-based polymeric systems and their applications. J. Mat. Chem. B 2019, 7, 709–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, D.; Zhu, M.; Jiang, Z.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Xiong, R.; Huang, C. Green electrospun nanofibers and their application in air filtration. Macromol. Mat. Eng. 2018, 303, 1800336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, G.; Greiner, A. Air-blowing-assisted coaxial electrospinning toward high productivity of core/sheath and hollow fibers. Macromol. Mat. Eng. 2019, 304, 1800669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Hou, Y.; Lu, X.; Gong, Z.; Yang, Y.; Lu, X.J.; Liu, X.L.; Yu, D.G. The process–property–performance relationship of medicated nanoparticles prepared by modified coaxial electrospraying. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, M.; Hai, T.; Feng, Z.; Yu, D.-G.; Yang, Y.; Annie Bligh, S. The Relationships between the Working Fluids, Process Characteristics and Products from the Modified Coaxial Electrospinning of Zein. Polymers 2019, 11, 1287. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11081287
Wang M, Hai T, Feng Z, Yu D-G, Yang Y, Annie Bligh S. The Relationships between the Working Fluids, Process Characteristics and Products from the Modified Coaxial Electrospinning of Zein. Polymers. 2019; 11(8):1287. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11081287
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Menglong, Tao Hai, Zhangbin Feng, Deng-Guang Yu, Yaoyao Yang, and SW Annie Bligh. 2019. "The Relationships between the Working Fluids, Process Characteristics and Products from the Modified Coaxial Electrospinning of Zein" Polymers 11, no. 8: 1287. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11081287
APA StyleWang, M., Hai, T., Feng, Z., Yu, D.-G., Yang, Y., & Annie Bligh, S. (2019). The Relationships between the Working Fluids, Process Characteristics and Products from the Modified Coaxial Electrospinning of Zein. Polymers, 11(8), 1287. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11081287