Preparation and Characterization of Cellulose Acetate Propionate Films Functionalized with Reactive Ionic Liquids
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Reactive Ionic Liquids (RILs) Synthesis
2.2.1. 1-(1,3-Diethoxy-1,3-Dioxopropan-2-ylo)-3-Methylimidazolium Bromide (RIL1_ Br)
2.2.2. 1-(2-Etoxy-2-Oxoethyl)-3-Methylimidazolium Bromide (RIL2_Br)
2.2.3. 1-(2-Etoxy-2-Oxoethyl)-3-Methylimidazolium Tetrafluoroborate (RIL3_BF4)
2.3. Preparation of Cellulose Acetate Propionate-Reactive Ionic Liquids (CAP-RILs) Films
2.4. Characterization of CAP-RILs Films
2.5. Conversion Degree of RIL
2.6. Water Permeation Tests
3. Results
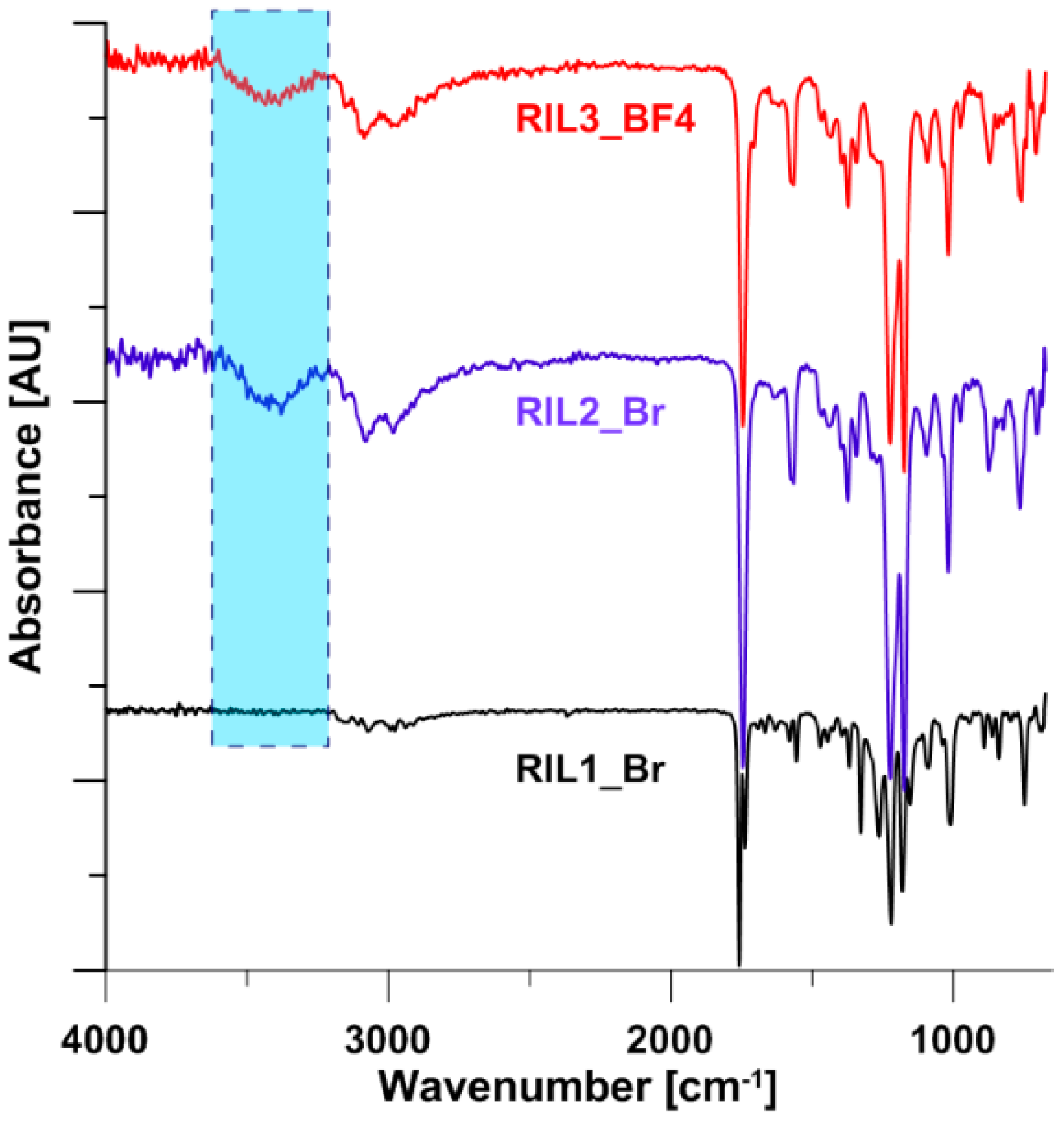
3.1. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Characterization
3.2. Subsection Conversion Degree of RIL
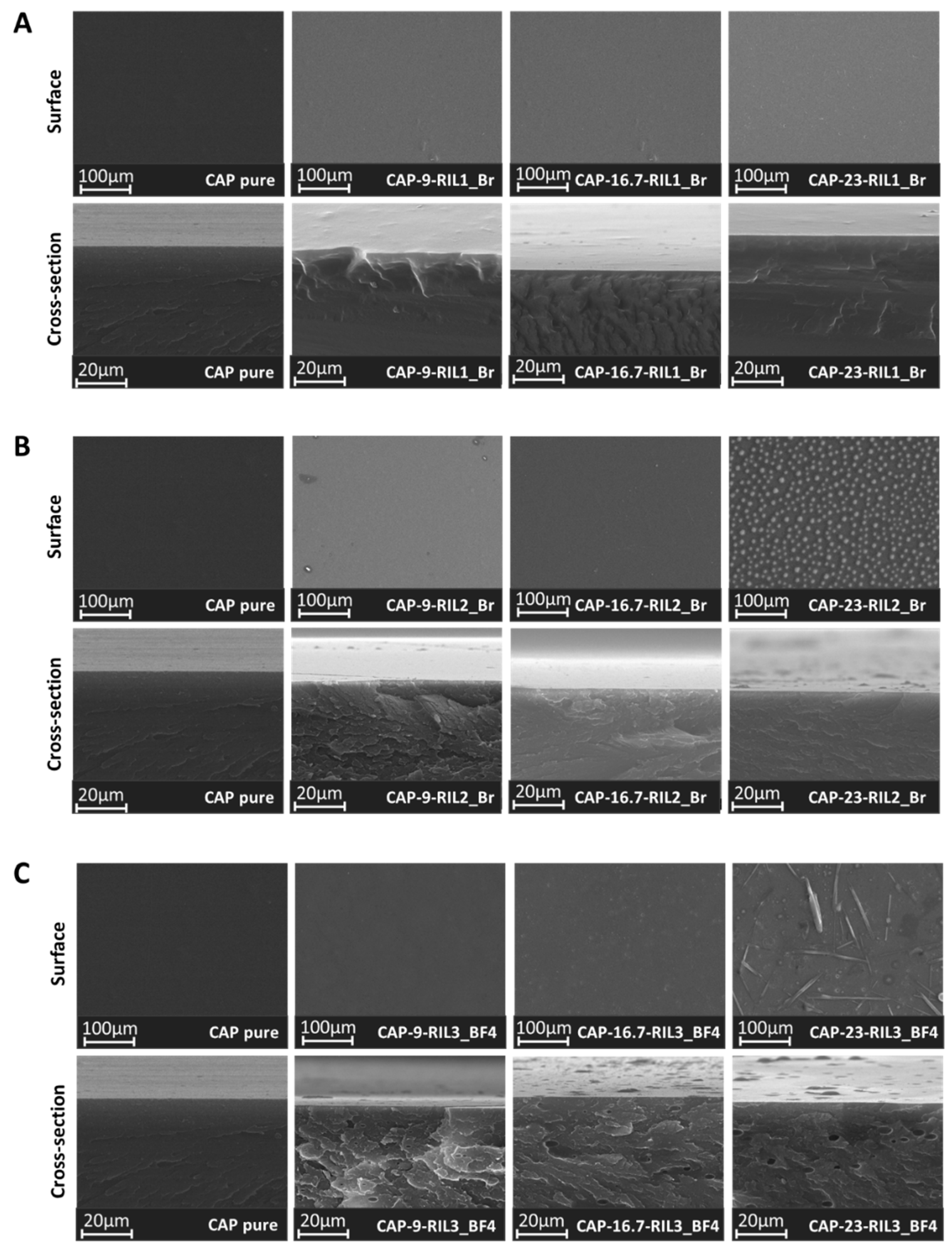
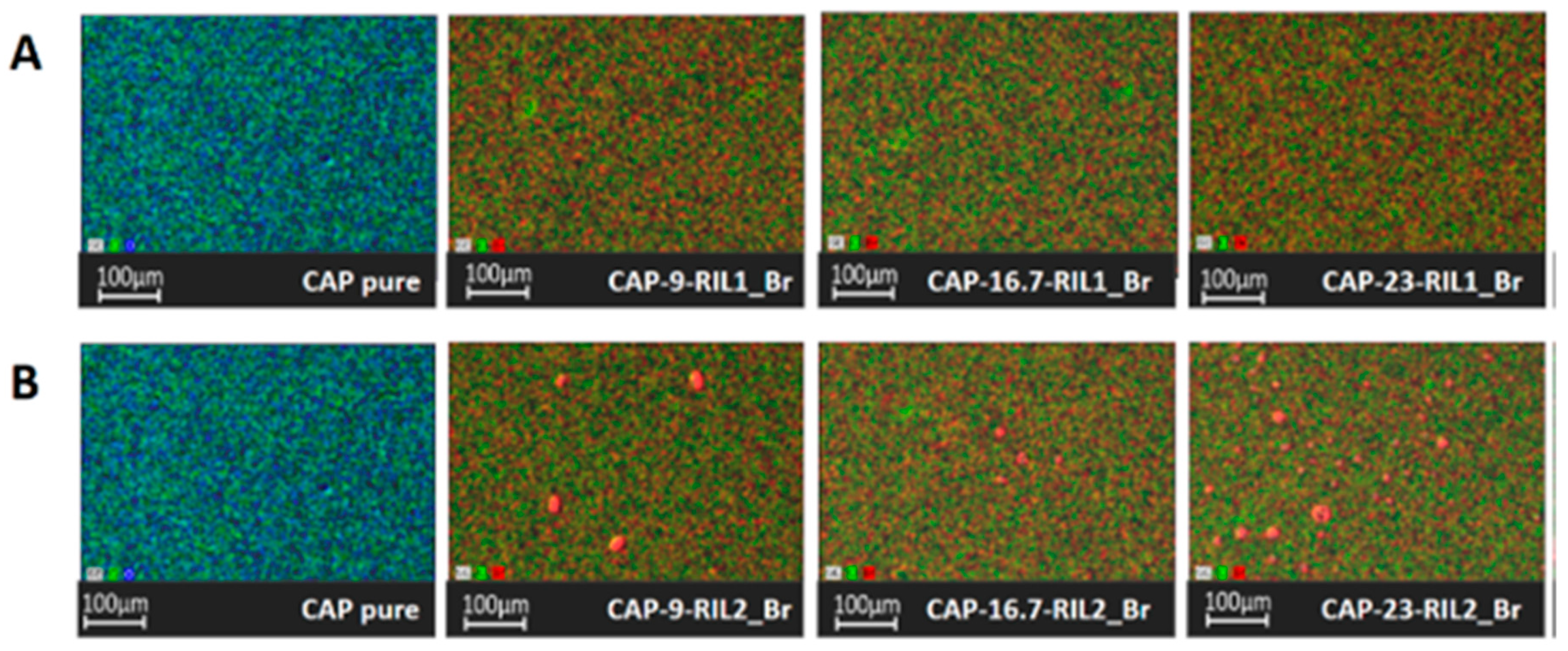
3.3. Morphology of CAP-RILs Films
3.4. Thermogravimetric (TGA) Analysis
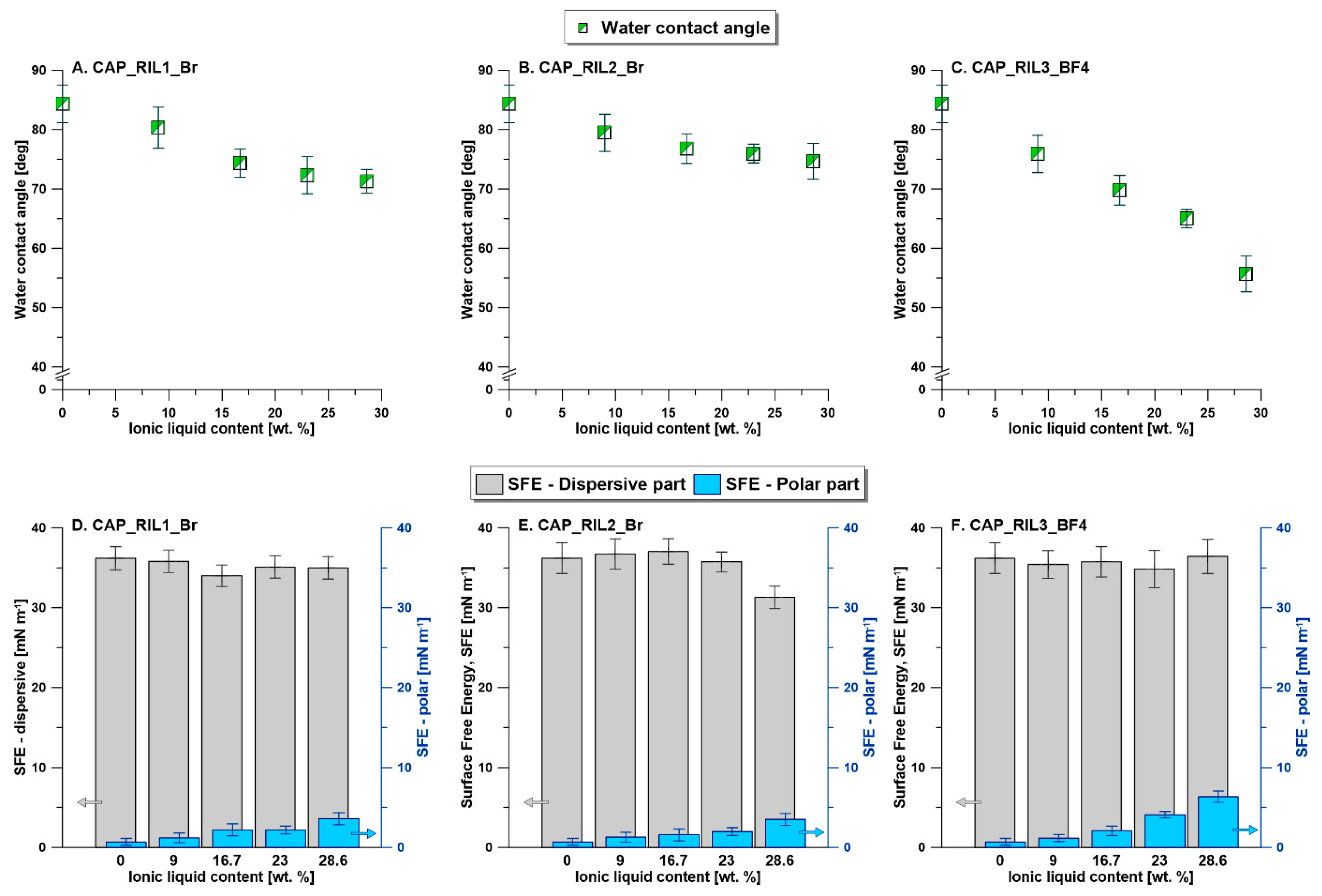
3.5. Membrane Surface Hydrophilicity
3.6. Mechanical Properties
3.7. Transport Properties
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bolto, B.; Tran, T.; Hoang, M.; Xie, Z. Crosslinked poly(vinyl alcohol) membranes. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2009, 34, 969–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.-S.; Rick, J.; Hwang, B.-J. Ionic liquid polymer electrolytes. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 2719–2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, R.W. Membrane Technology and Applications, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Ulbricht, M. Advanced functional polymer membranes. Polymer 2006, 47, 2217–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khulbe, K.C.; Feng, C.; Matsuura, T. The art of surface modification of synthetic polymeric membranes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 115, 855–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.S.; Bringas, E.; Tan, N.R.; Ortiz, I.; Ghahramani, M.; Alaei Shahmirzadi, M.A. Recent progress in development of high performance polymeric membranes and materials for metal plating wastewater treatment: A review. J. Water Process Eng. 2016, 9, 78–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunger, K.; Schmeling, N.; Jeazet, H.B.T.; Janiak, C.; Staudt, C.; Kleinermanns, K. Investigation of cross-linked and additive containing polymer materials for membranes with improved performance in pervaporation and gas separation. Membranes 2012, 2, 727–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, B.P.; Das, P.; Simon, F.; Stamm, M. Ultralow fouling membranes by surface modification with functional polydopamine. Eur. Polym. J. 2018, 99, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Fan, H.; Zhou, J. Cellulose acetate/poly(vinyl alcohol) and cellulose acetate/crosslinked poly(vinyl alcohol) blend membranes: preparation, characterization, and antifouling properties. Desalin. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 10572–10584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Jiang, Z.; Li, W.; Mayta, J.Q.; Ding, H.; Song, Y.; Li, Z.; Dong, Z.; Pan, F.; Wang, B.; et al. Elevated performance of hybrid membranes by incorporating metal organic framework CuBTC for pervaporative desulfurization of gasoline. Chem. Eng. Process. 2018, 123, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livazovic, S.; Li, Z.; Behzad, A.R.; Peinemann, K.V.; Nunes, S.P. Cellulose multilayer membranes manufacture with ionic liquid. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 490, 282–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinkert, A.; Marsh, K.N.; Pang, S.; Staiger, M.P. Ionic Liquids and Their Interaction with Cellulose. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 6712–6728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Z.; Noble, R.D.; Gin, D.L.; Zhang, X.; Deng, L. Combination of ionic liquids with membrane technology: A new approach for CO2 separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 497, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunz, W.; Häckl, K. The hype with ionic liquids as solvents. Chem. Phys. Let. 2016, 661, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmad, S.; Mikkola, J.-P.; Ji, X. Carbon Dioxide Capture with Ionic Liquids and Deep Eutectic Solvents: A New Generation of Sorbents. ChemSusChem 2017, 10, 324–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, K.; Liu, X.; Dong, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S. Multiscale Studies on Ionic Liquids. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 6636–6695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowsari, E. Advanced applications of ionic liquids in polymer science. In Ionic Liquids Applications and Perspective, 1st ed.; Kokorin, A., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2011; Volume I, pp. 3–28. [Google Scholar]
- Izák, P.; Ruth, W.; Fei, Z.; Dyson, P.J.; Kragl, U. Selective removal of acetone and butan-1-ol from water with supported ionic liquid–polydimethylsiloxane membrane by pervaporation. Chem. Eng. J. 2008, 139, 318–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rynkowska, E.; Dzieszkowski, K.; Lancien, A.; Fatyeyeva, K.; Szymczyk, A.; Kujawa, J.; Koter, S.; Marais, S.; Wolan, A.; Kujawski, W. Physicochemical properties and pervaporation performance of dense membranes based on cellulose acetate propionate (CAP) and containing polymerizable ionic liquid (PIL). J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 544, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heitmann, S.; Krings, J.; Kreis, P.; Lennert, A.; Pitner, W.R.; Górak, A.; Schulte, M.M. Recovery of n-butanol using ionic liquid-based pervaporation membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 97, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Wu, L.; Li, B.-G. Preparation and CO2 Sorption/Desorption of N-(3-Aminopropyl)Aminoethyl Tributylphosphonium Amino Acid Salt Ionic Liquids Supported into Porous Silica Particles. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 7901–7909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasikumar, B.; Arthanareeswaran, G.; Ismail, A.F. Recent progress in ionic liquid membranes for gas separation. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 266, 330–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-Y.; Ogawa, A.; Kanno, M.; Nakamoto, H.; Yasuda, T.; Watanabe, M. Nonhumidified Intermediate Temperature Fuel Cells Using Protic Ionic Liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 9764–9773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.H.; Henderson, W.A.; Appetecchi, G.B.; Alessandrini, F.; Passerini, S. Recent developments in the ENEA lithium metal battery project. Electrochim. Acta 2005, 50, 3859–3865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokorin, A. Ionic Liquids: Applications and Perspectives; Kokorin, A., Ed.; Intech Europe: Rijeka, Croatia, 2011; pp. 1–674. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández-Fernández, F.J.; de los Ríos, A.P.; Tomás-Alonso, F.; Palacios, J.M.; Víllora, G. Preparation of supported ionic liquid membranes: Influence of the ionic liquid immobilization method on their operational stability. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 341, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Fernández, F.J.; de los Ríos, A.P.; Mateo-Ramírez, F.; Juarez, M.D.; Lozano-Blanco, L.J.; Godínez, C. New application of polymer inclusion membrane based on ionic liquids as proton exchange membrane in microbial fuel cell. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 160, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasahara, S.; Kamio, E.; Ishigami, T.; Matsuyama, H. Effect of water in ionic liquids on CO2 permeability in amino acid ionic liquid-based facilitated transport membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 415–416, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahi, A.; Fatyeyeva, K.; Langevin, D.; Chappey, C.; Rogalsky, S.P.; Tarasyuk, O.P.; Marais, S. Polyimide/ionic liquid composite membranes for fuel cells operating at high temperatures. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 130, 830–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Chen, J. Preparation of PVDF-based polymer inclusion membrane using ionic liquid plasticizer and Cyphos IL 104 carrier for Cr(VI) transport. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 372, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Luo, J.; Feng, S.; Li, H.; Wan, Y.; Zhang, X. Recent development of ionic liquid membranes. Green Energ. Environ. 2016, 1, 43–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, M.-a.; Kaneko, Y.; Kadokawa, J.-i. Preparation of cellulose-polymerized ionic liquid composite by in-situ polymerization of polymerizable ionic liquid in cellulose-dissolving solution. Carbohydr. Polym. 2007, 69, 378–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, K.; Endo, T. Preparation and properties of ionic-liquid-containing poly(ethylene glycol)-based networked polymer films having lithium salt structures. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2011, 49, 3582–3587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izák, P.; Kockerling, M.; Kragl, U. Stability and selectivity of a multiphase membrane, consisting of dimethylpolysiloxane on an ionic liquid, used in the separation of solutes from aqueous mixtures by pervaporation. Green Chem. 2006, 8, 947–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardo, P.; Jansen, J.C.; Bazzarelli, F.; Tasselli, F.; Fuoco, A.; Friess, K.; Izák, P.; Jarmarová, V.; Kačírková, M.; Clarizia, G. Gas transport properties of Pebax®/room temperature ionic liquid gel membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 97, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pospiech, B.; Kujawski, W. Ionic liquids as selective extractants and ion carriers of heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions utilized in extraction and membrane separation. Rev. Chem. Eng. 2015, 31, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teramoto, M.; Sakaida, Y.; Fu, S.S.; Ohnishi, N.; Matsuyama, H.; Maki, T.; Fukui, T.; Arai, K. An attempt for the stabilization of supported liquid membrane. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2000, 21, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Manna, M.S.; Ghoshal, A.K.; Saha, P. Study of the supported liquid membrane for the estimation of the synergistic effects of influential parameters on its stability. J. Environ. Chem. Protect. 2016, 4, 943–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; He, G.; Nie, F.; Zhang, L.; Feng, H.; Liu, H. Membrane liquid loss mechanism of supported ionic liquid membrane for gas separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 411–412, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan Hassan Abdellatif, F.; Babin, J.; Arnal-Herault, C.; David, L.; Jonquieres, A. Grafting of cellulose acetate with ionic liquids for biofuel purification by a membrane process: Influence of the cation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 147, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodge, T.P. A unique platform for materials design. Science 2008, 321, 50–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodge, T.P.; Ueki, T. Mechanically tunable, readily processable ion gels by self-assembly of block copolymers in ionic liquids. Acc. Chem. Res. 2016, 49, 2107–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rynkowska, E.; Fatyeyeva, K.; Kujawa, J.; Dzieszkowski, K.; Wolan, A.; Kujawski, W. The effect of reactive ionic liquid or plasticizer incorporation on the physicochemical and transport properties of cellulose acetate propionate-based membranes. Polymers 2018, 10, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isik, M.; Sardon, H.; Mecerreyes, D. Ionic Liquids and Cellulose: Dissolution, Chemical Modification and Preparation of New Cellulosic Materials. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 11922–11940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooshyari, K.; Javanbakht, M.; Adibi, M. Novel composite membranes based on dicationic ionic liquid and polybenzimidazole mixtures as strategy for enhancing thermal and electrochemical properties of proton exchange membrane fuel cells applications at high temperature. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 10870–10883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulder, M. Basic Principles of Membrane Technology, 2nd ed.; Publishers, K.A., Ed.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Vijayaraghavan, R.; MacFarlane, D.R.; Izgorodina, E.I. Ab Initio Prediction of Proton NMR Chemical Shifts in Imidazolium Ionic Liquids. J. Phys. Chem. B 2013, 117, 3186–3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Xie, H.; Liu, E. Acylation of cellulose in reversible ionic liquids. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 3018–3023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Matson, J.B.; Edgar, K.J. Olefin cross-metathesis, a mild, modular approach to functionalized cellulose esters. Pol. Chem. 2014, 5, 7021–7033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheiner, S. Assessment of the Presence and Strength of H-Bonds by Means of Corrected NMR. Molecules 2016, 21, 1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, N.; Kwon, S.; Moon, S.; Hong, C.H.; Kim, Y.G. Ionic liquid-mediated deoxydehydration reactions: Green synthetic process for bio-based adipic acid. Tetrahedron 2017, 73, 4758–4765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Fu, Y.; Qin, M.; Shao, Z.; Xu, Q. Homogeneous acylation and regioselectivity of cellulose with 2-chloro-2-phenylacetyl chloride in ionic liquid. BioResources 2014, 9, 5134–5146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, E.S.; Sánchez, R.J.; Tavares, M.I.B.; Lamônica, Á.C. Characterization and properties of hydrophilic cellulose acetate propionate derivative. J. Polym. Environ. 2010, 18, 661–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crépy, L.; Chaveriat, L.; Banoub, J.; Martin, P.; Joly, N. Synthesis of cellulose fatty esters as plastics-influence of the degree of substitution and the fatty chain length on mechanical properties. ChemSusChem 2009, 2, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinze, T.; Dorn, S.; Schöbitz, M.; Liebert, T.; Köhler, S.; Meister, F. Interactions of Ionic Liquids with Polysaccharides–2: Cellulose. In Macromolecular Symposia; WILEY-VCH Verlag: Weinheim, Germany, 2008; Volume 262, pp. 8–22. [Google Scholar]
- Ríos, A.P.d.l.; Hernández-Fernández, F.J.; Tomás-Alonso, F.; Palacios, J.M.; Gómez, D.; Rubio, M.; Víllora, G. A SEM–EDX study of highly stable supported liquid membranes based on ionic liquids. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 300, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, T.; Tang, L.; Hao, W.; Yao, L.; Cui, P. Morphology and pervaporation performance of ionic liquid and waterborne polyurethane composite membranes. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 7792–7799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalu; Singh, V.K.; Singh, R.K. Development of ion conducting polymer gel electrolyte membranes based on polymer PVdF-HFP, BMIMTFSI ionic liquid and the Li-salt with improved electrical, thermal and structural properties. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 7305–7318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, Q.; Yue, J. Polymerized imidazolium ionic liquids crosslinking sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone) (SPEEK) for high-temperature proton exchange membrane. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 111729–111738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdmenger, T.; Vitz, J.; Wiesbrock, F.; Schubert, U.S. Influence of different branched alkyl side chains on the properties of imidazolium-based ionic liquids. J. Mater. Chem. A 2008, 18, 5267–5273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, J.J.; Wilfred, C.D.; Shah, S.N.; Pranesh, M.; Abdul Mutalib, M.I.; Lethesh, K.C. Physicochemical and thermodynamic properties of imidazolium ionic liquids with nitrile and ether dual functional groups. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 225, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Mu, T. Comprehensive Investigation on the Thermal Stability of 66 Ionic Liquids by Thermogravimetric Analysis. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 8651–8664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, K.-Y.; Zhao, H. Determination of Solid Surface Tension by Contact Angle. In Surface Wetting: Characterization, Contact Angle, and Fundamentals; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 135–148. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, C.; Glück, T.; Schmidt-Naake, G. Modification of Nafion membranes by impregnation with ionic liquids. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2008, 31, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Guo, Q.; Li, D.; Tong, J.; Li, X. Properties improvement of SPEEK based proton exchange membranes by doping of ionic liquids and Y2O3. Prog. Nat. Sci. 2012, 22, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlon, S.; Follain, N.; Chappey, C.; Dargent, E.; Soulestin, J.; Sclavons, M.; Marais, S. Improvement of barrier properties of bio-based polyester nanocomposite membranes by water-assisted extrusion. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 496, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.; Patel, J.M.; Lemberger, A.P. Water vapor permeation of selected cellulose ester films. J. Pharm. Sci. 1964, 53, 286–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dushman, S. Diffusion In and Through Solids (Barrer, Richard M.). J. Chem. Educ. 1942, 19, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
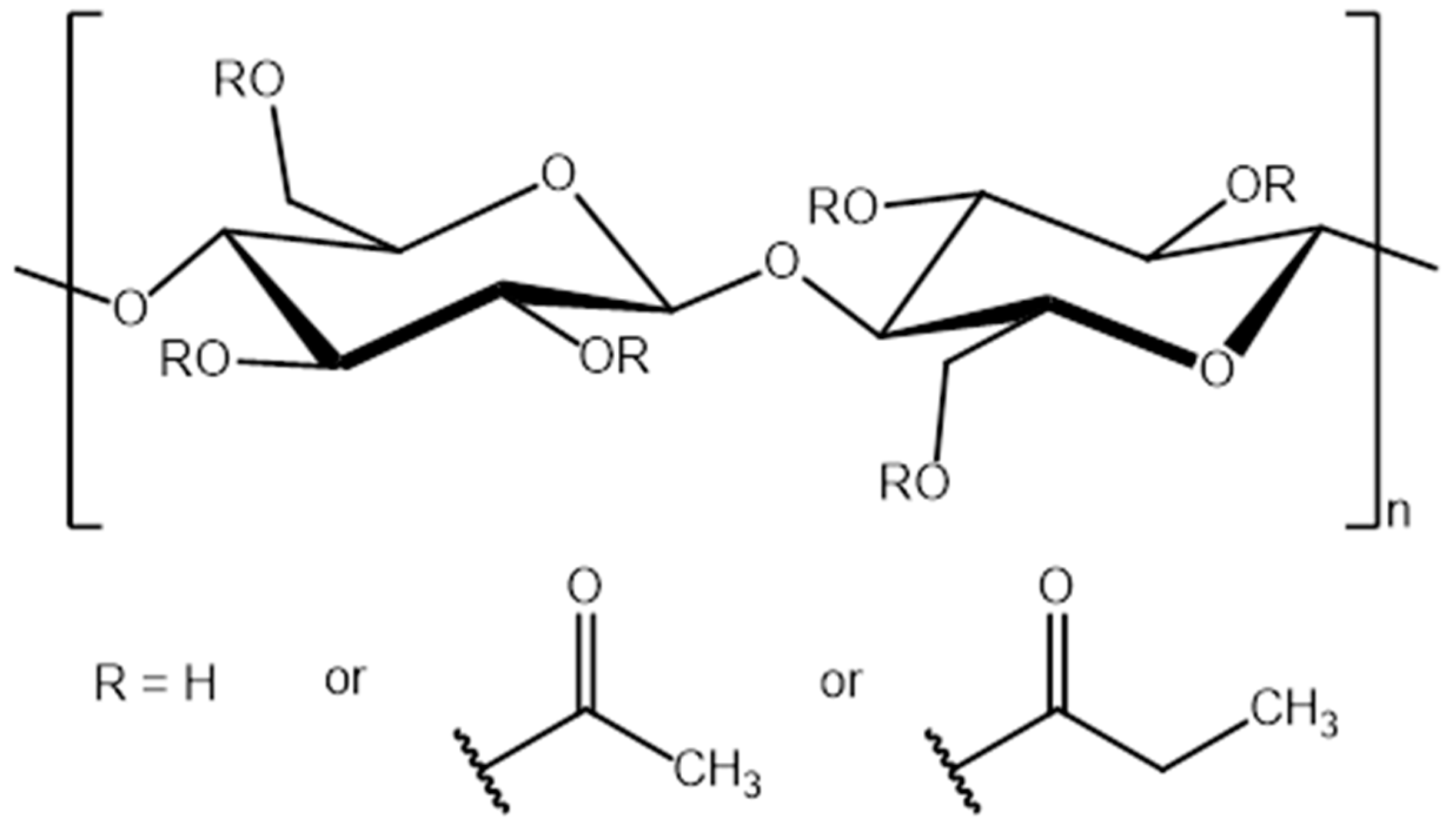
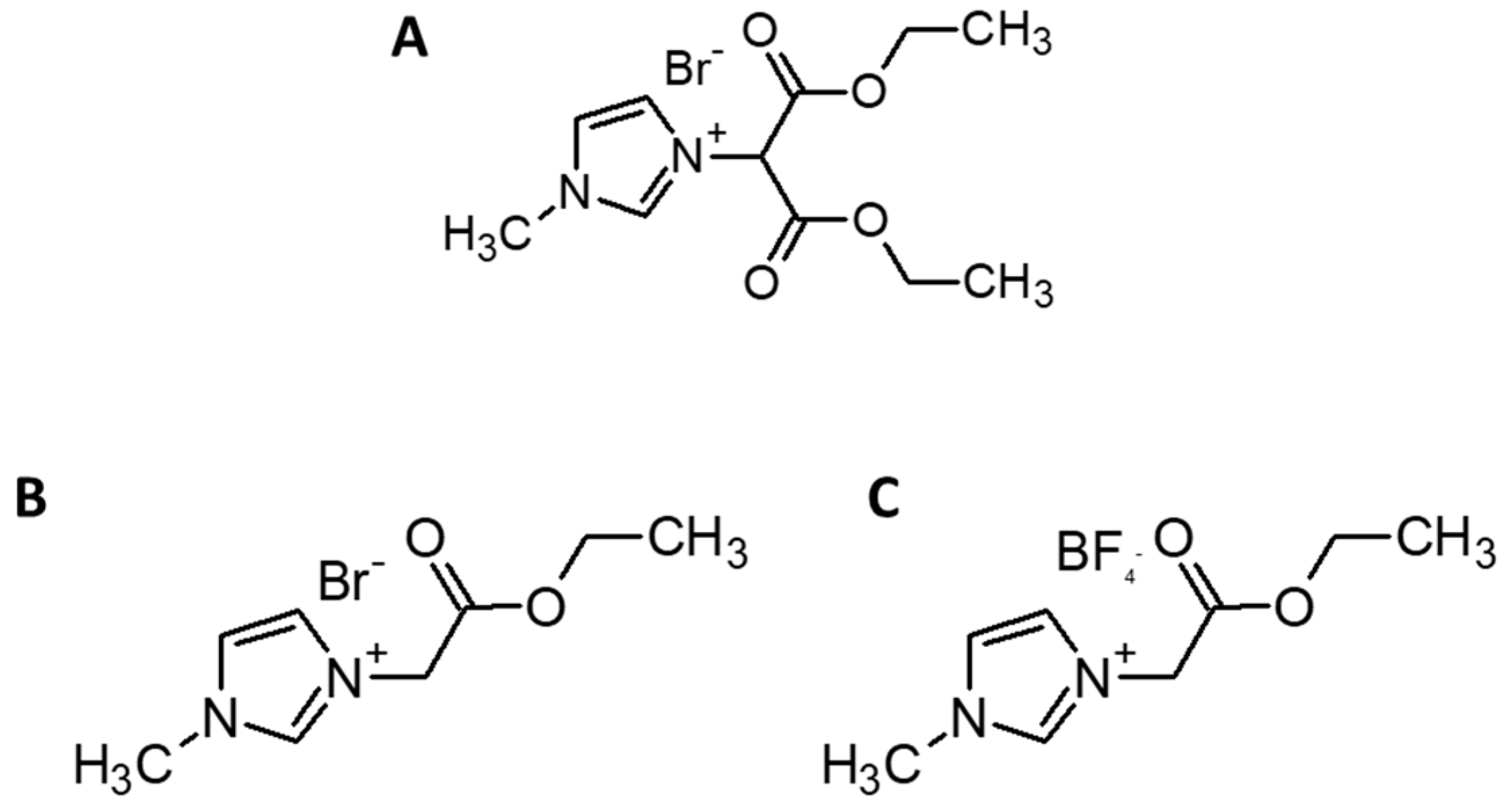

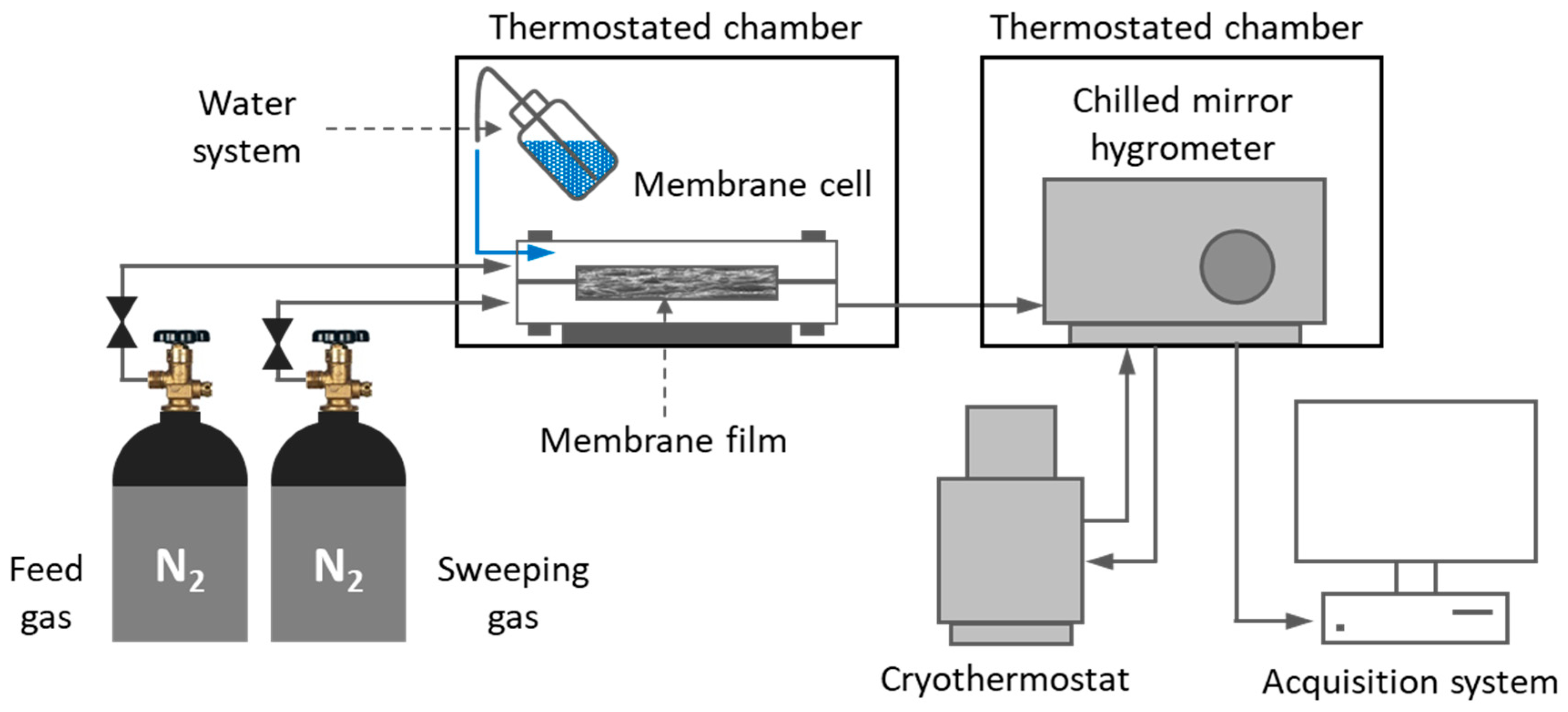

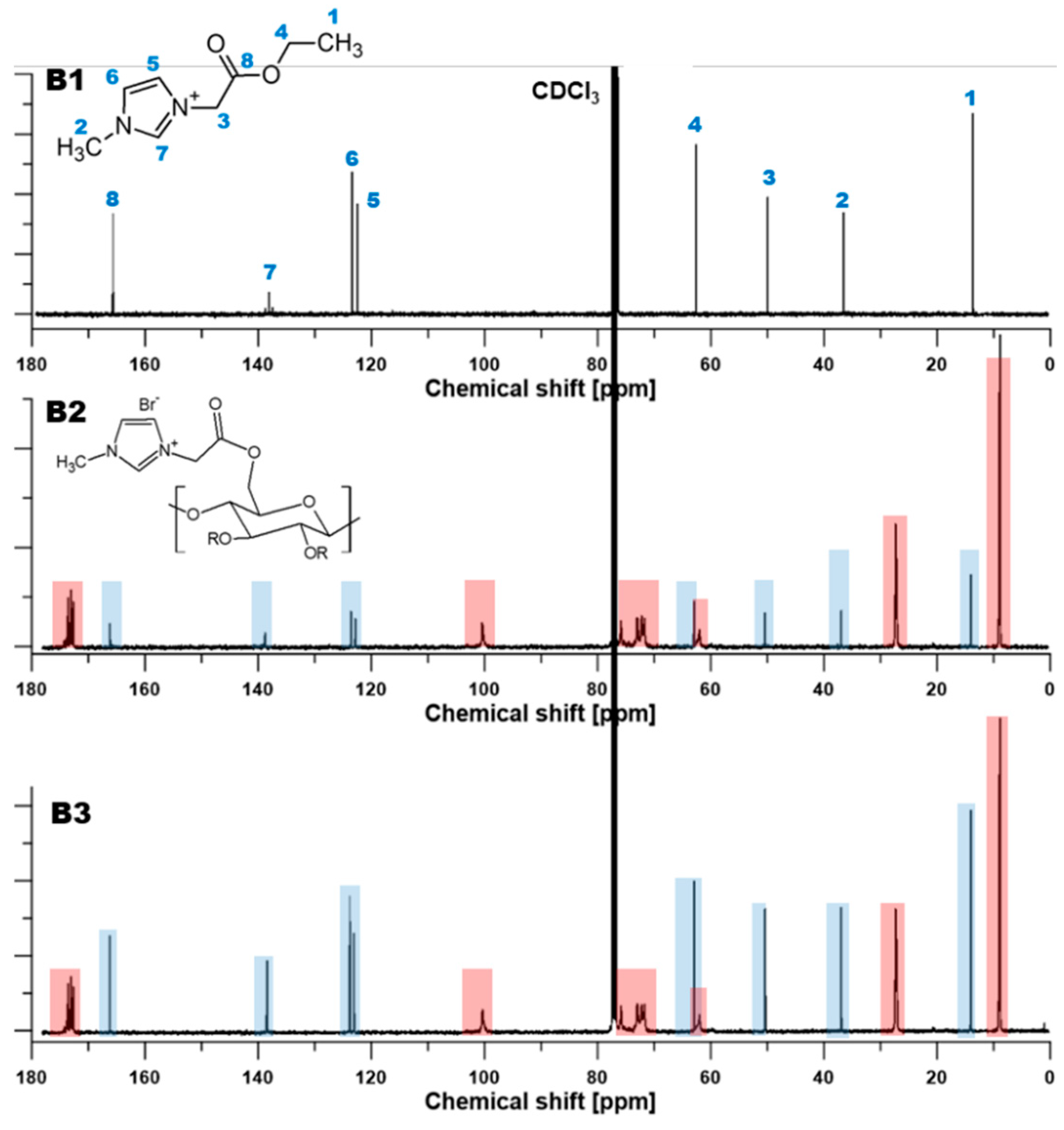



| Films | Signals Position of a Proton (ppm) | |
|---|---|---|
| H2 | H4 and H5 | |
| Pure RIL1_Br | 10.55 | 7.58 |
| CAP-9-RIL1_Br | 11.02 | 7.24 |
| CAP-23-RIL1_Br | 11.01 | 7.21 |
| Pure RIL2_Br | 10.17 | 7.48 |
| CAP-9-RIL2_Br | 10.56 | 7.21 |
| CAP-23-RIL2_Br | 10.58 | 7.24 |
| Integral of Resonance (-) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Films | CAP-9-RIL1_Br | CAP-23-RIL1_Br |
| S1 | 1.00 (at 7.81 ppm) | 1.00 (at 7.82 ppm) |
| S2 | 11.43 (at 5.10 ppm) | 3.53 (at 5.09 ppm) |
| DS | 0.087 | 0.283 |
| DSmax | 0.099 | 0.295 |
| Films | CAP-9-RIL2_Br | CAP-23-RIL2_Br |
| S1 | 1.00 (at 7.41 ppm) | 1.00 (at 7.24 ppm) |
| S2 | 36.88 (at 5.07 ppm) | 13.10 (at 5.07 ppm) |
| DS | 0.027 | 0.076 |
| DSmax | 0.076 | 0.229 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kujawa, J.; Rynkowska, E.; Fatyeyeva, K.; Knozowska, K.; Wolan, A.; Dzieszkowski, K.; Li, G.; Kujawski, W. Preparation and Characterization of Cellulose Acetate Propionate Films Functionalized with Reactive Ionic Liquids. Polymers 2019, 11, 1217. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11071217
Kujawa J, Rynkowska E, Fatyeyeva K, Knozowska K, Wolan A, Dzieszkowski K, Li G, Kujawski W. Preparation and Characterization of Cellulose Acetate Propionate Films Functionalized with Reactive Ionic Liquids. Polymers. 2019; 11(7):1217. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11071217
Chicago/Turabian StyleKujawa, Joanna, Edyta Rynkowska, Kateryna Fatyeyeva, Katarzyna Knozowska, Andrzej Wolan, Krzysztof Dzieszkowski, Guoqiang Li, and Wojciech Kujawski. 2019. "Preparation and Characterization of Cellulose Acetate Propionate Films Functionalized with Reactive Ionic Liquids" Polymers 11, no. 7: 1217. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11071217
APA StyleKujawa, J., Rynkowska, E., Fatyeyeva, K., Knozowska, K., Wolan, A., Dzieszkowski, K., Li, G., & Kujawski, W. (2019). Preparation and Characterization of Cellulose Acetate Propionate Films Functionalized with Reactive Ionic Liquids. Polymers, 11(7), 1217. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11071217







