Two Lanthanide Metal–Organic Frameworks Based on Semi-Rigid T-Shaped Tricarboxylate Ligand: Syntheses, Structures, and Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Synthesis of Compound 1
2.2. Synthesis of Compound 2
3. Results and Discussion
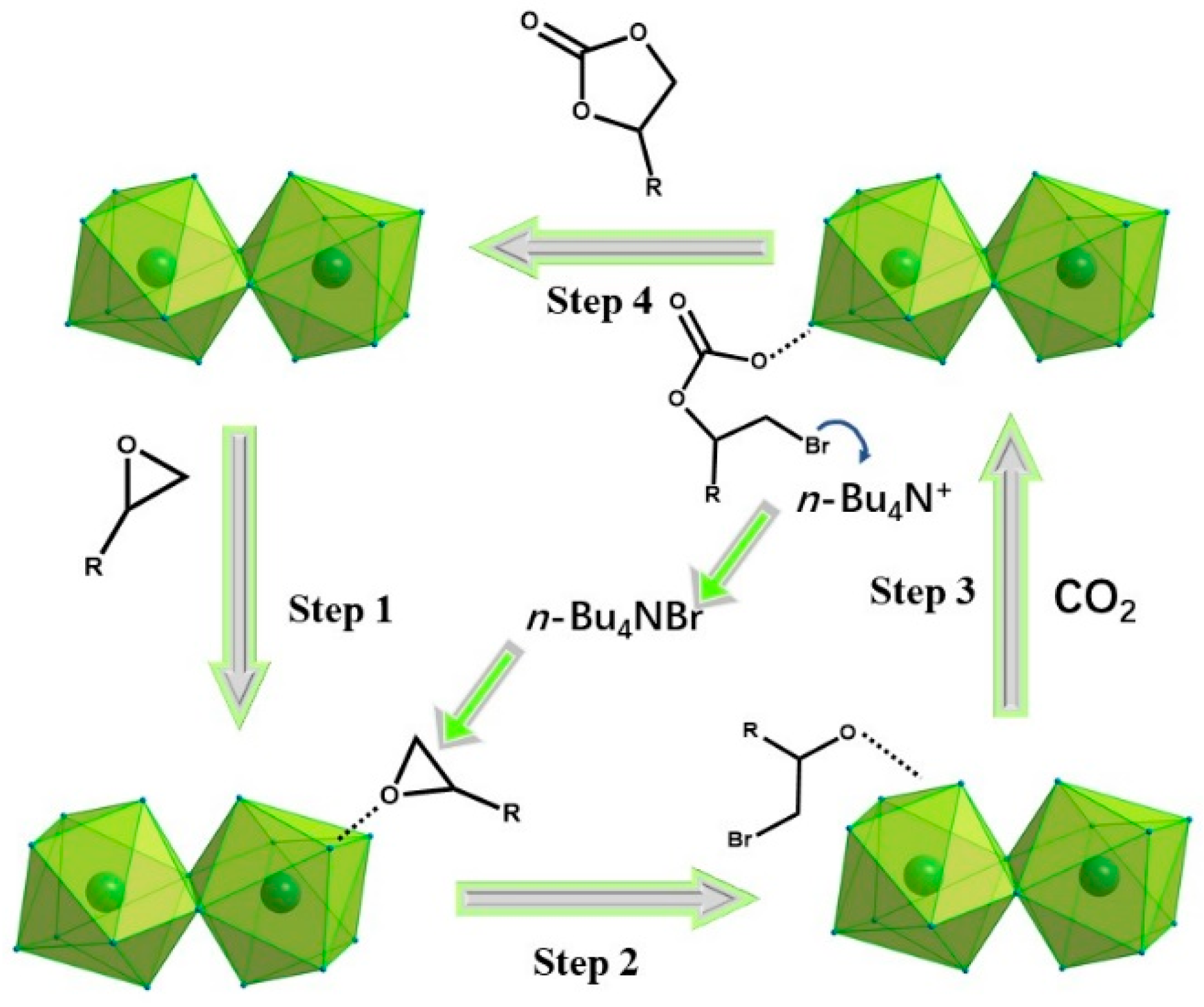
3.1. Synthesis
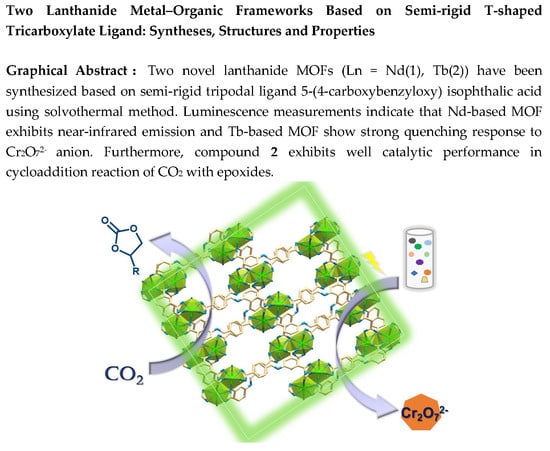
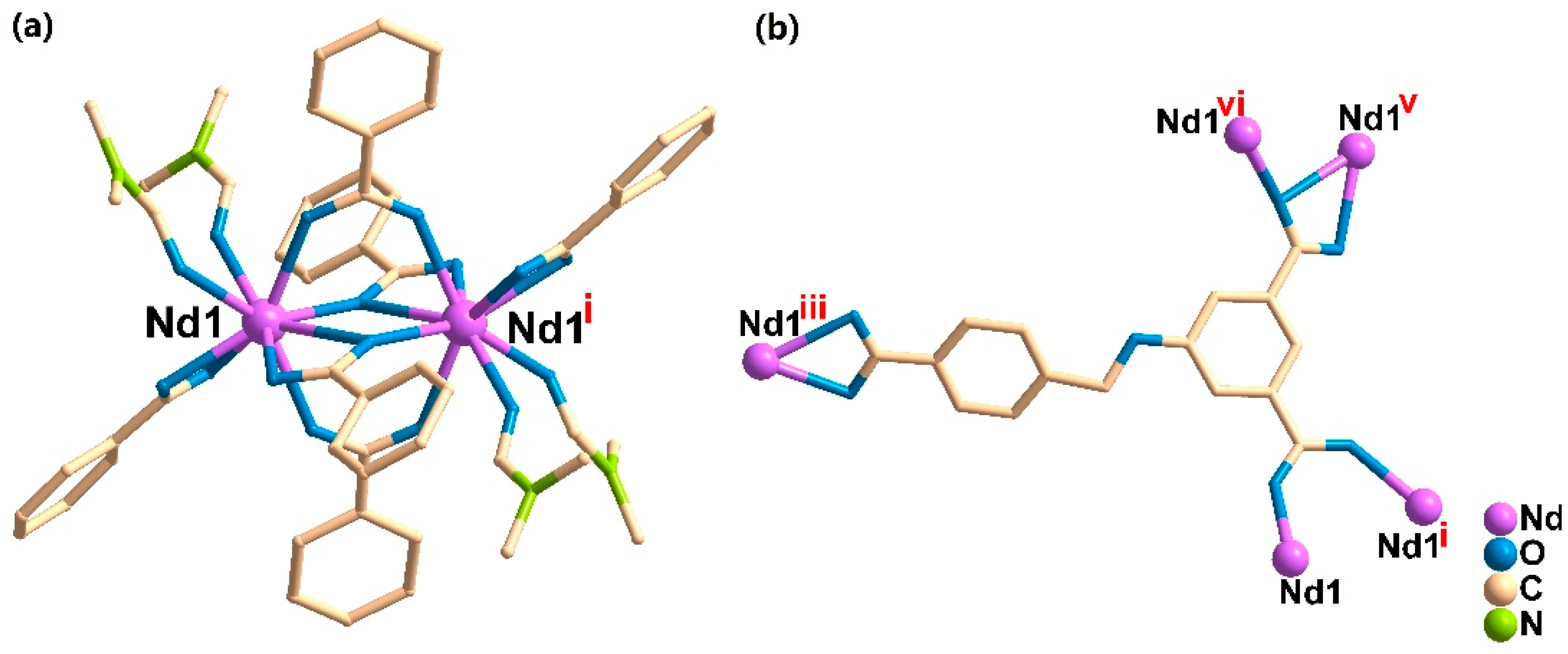
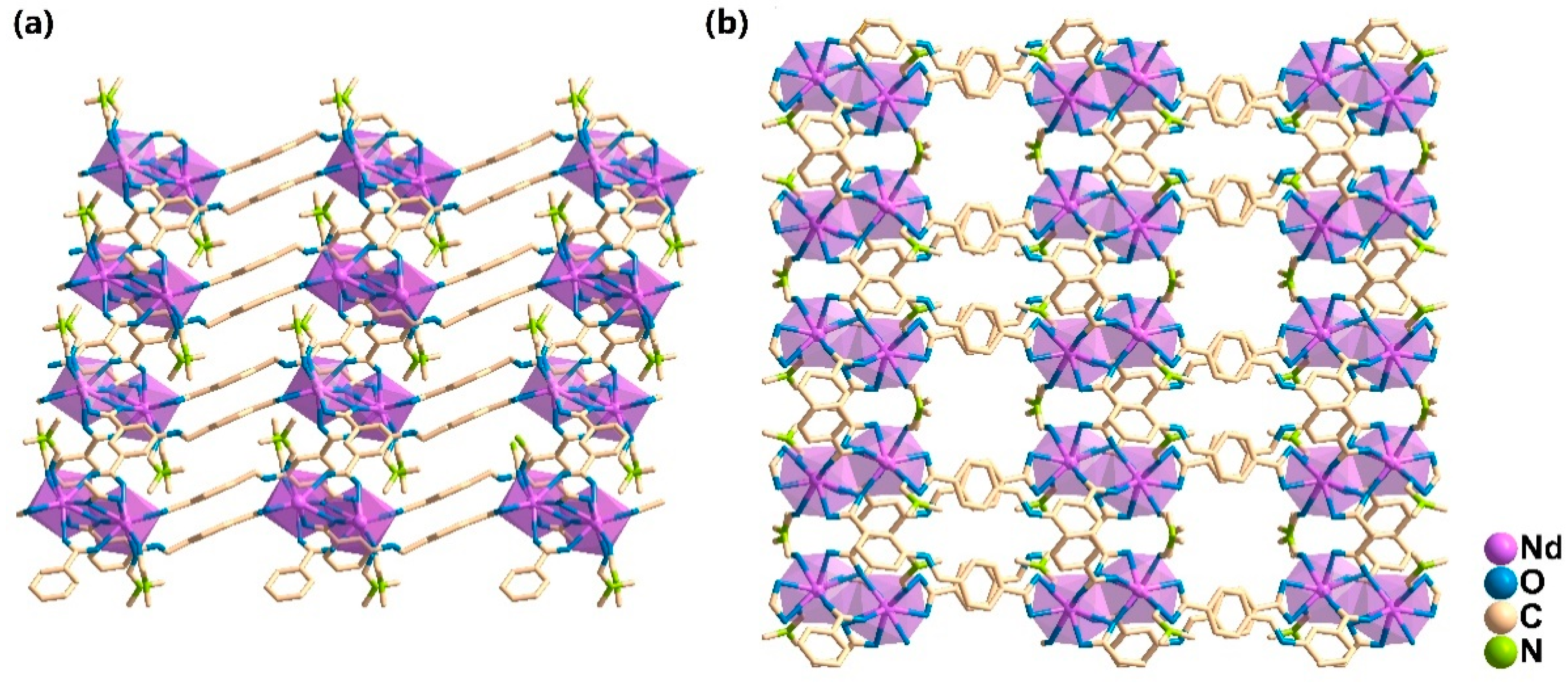
3.2. Crystal Structure Descriptions
3.3. Thermal Stability Analysis
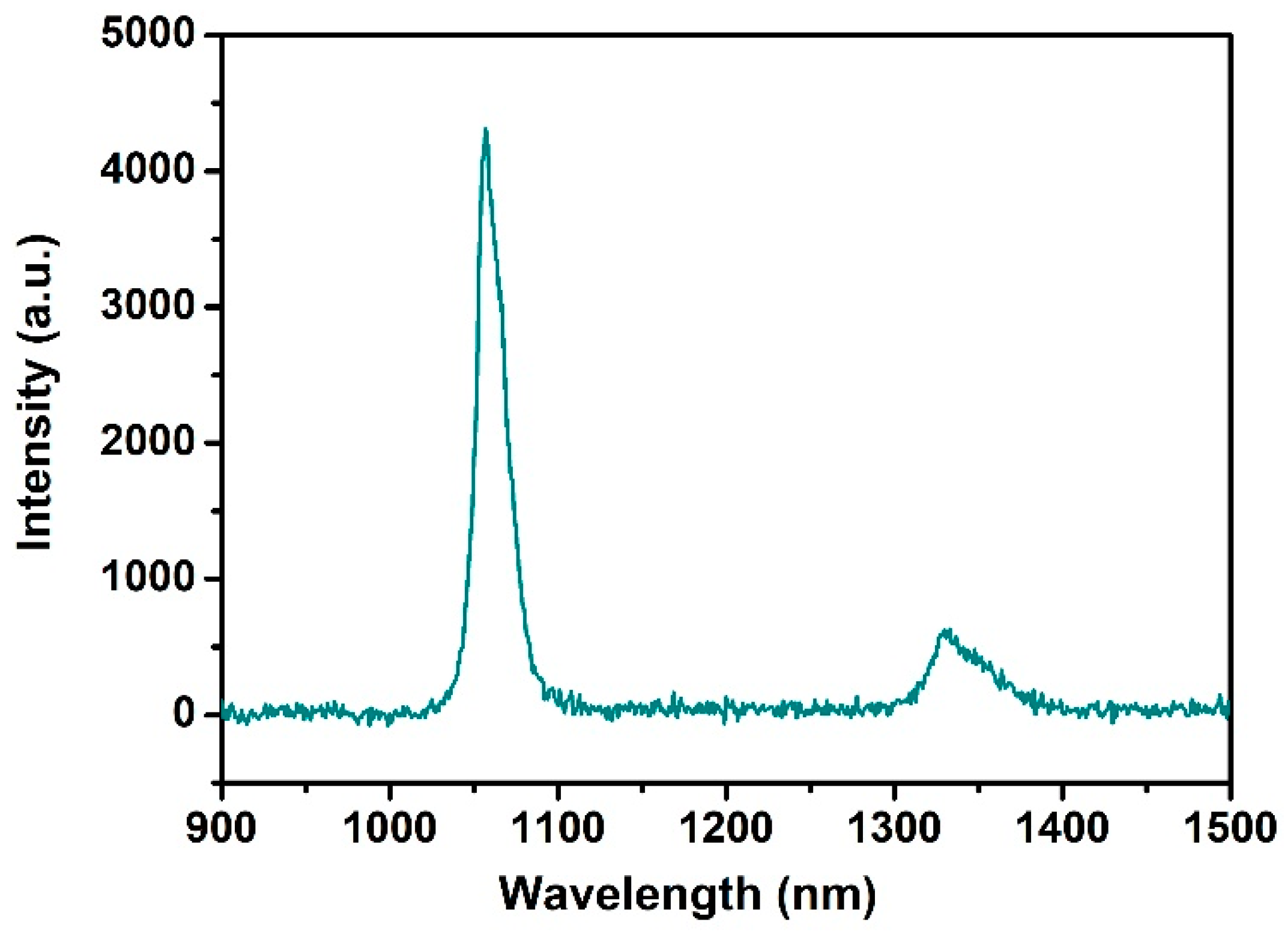
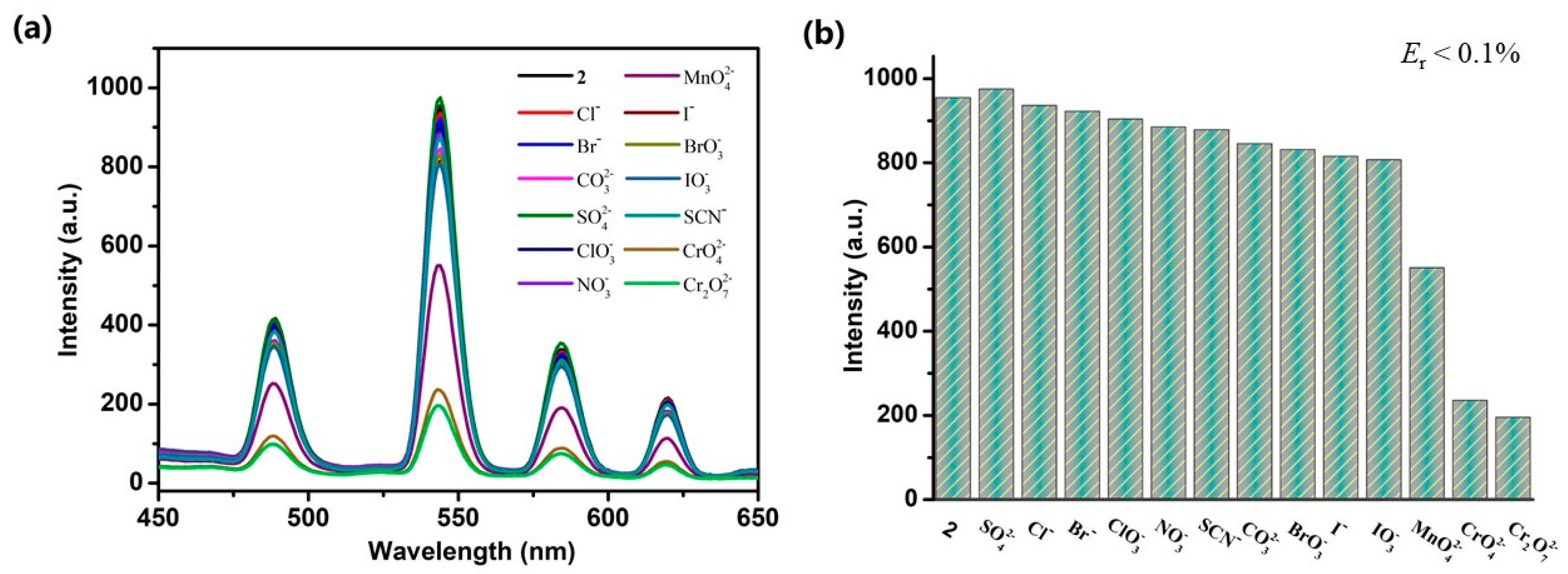
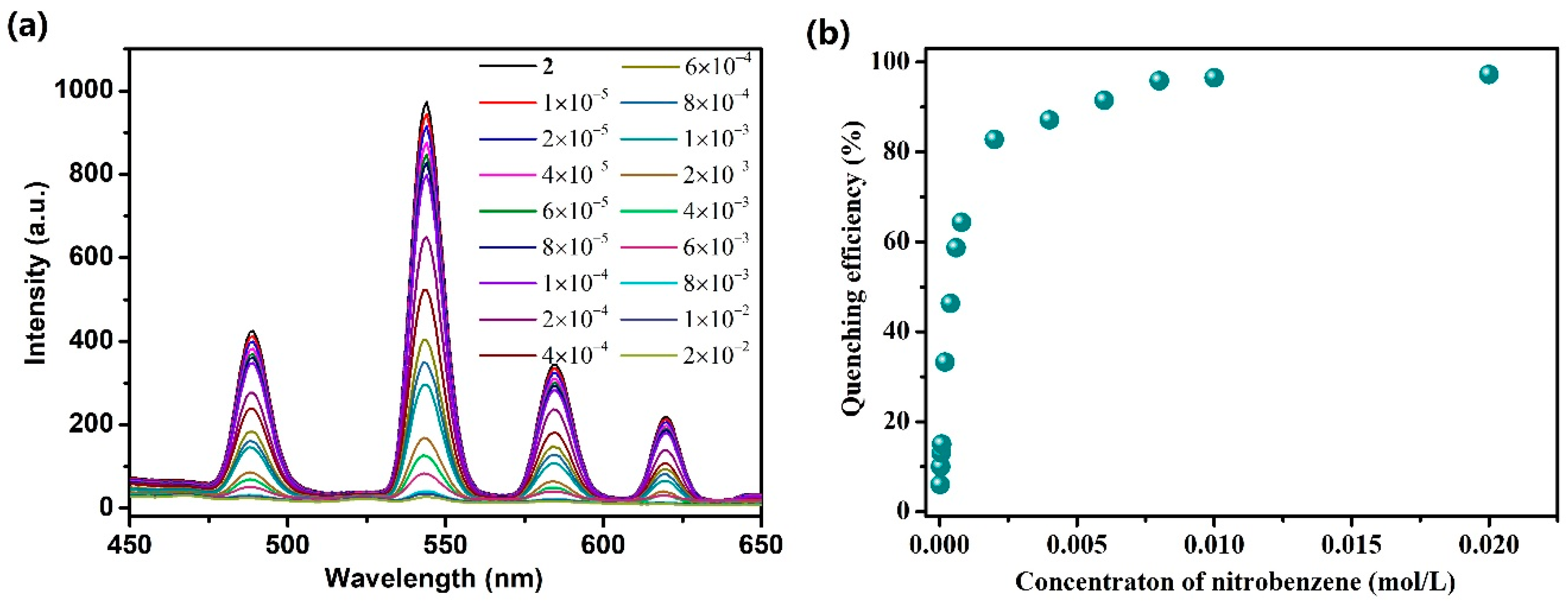
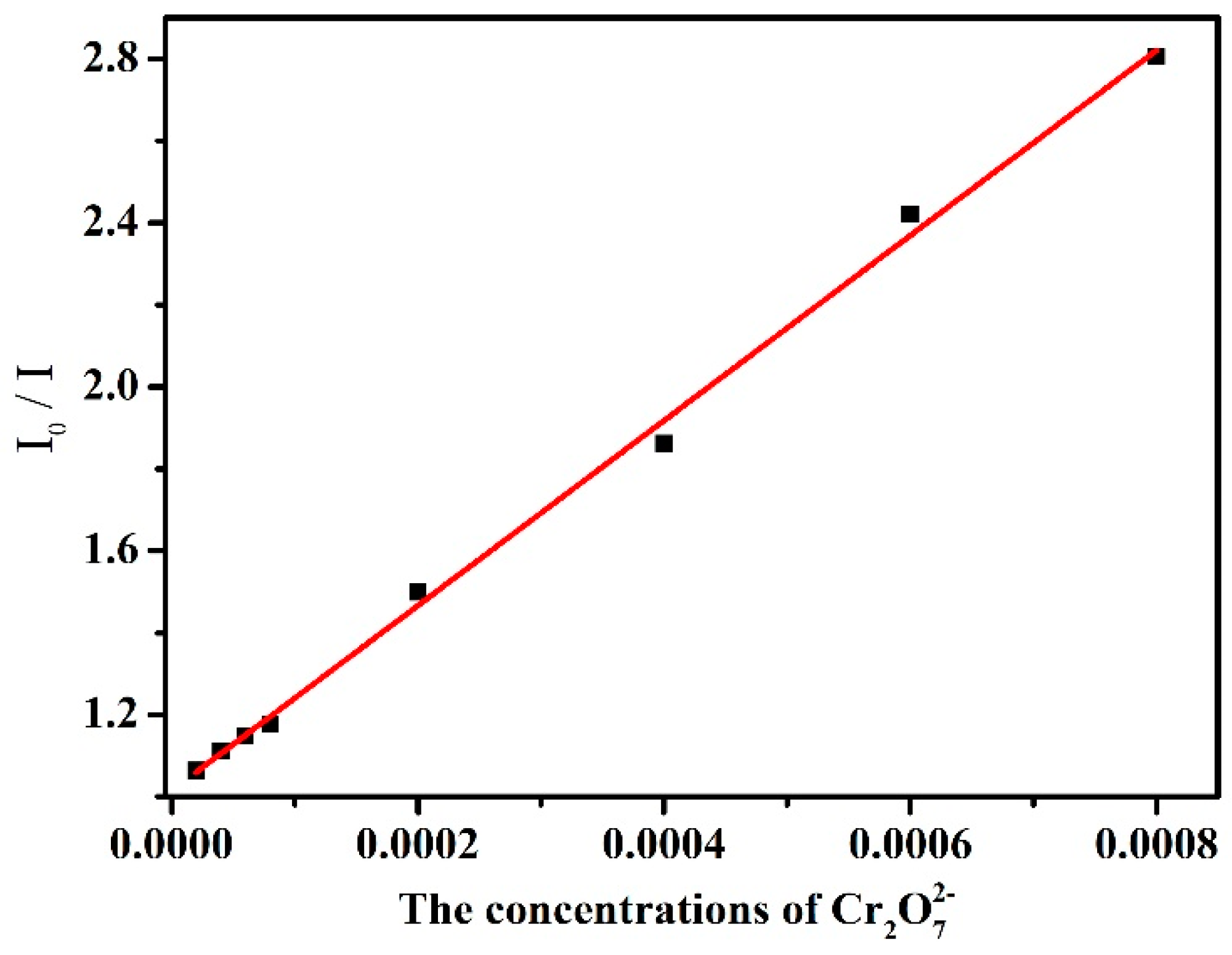
3.4. Photoluminescent Properties
3.5. Catalytic Performance
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Park, H.D.; Dincă, M.; Román-Leshkov, Y. Continuous-flow production of succinic anhydrides via catalytic β-lactone carbonylation by Co(CO)4⊂Cr-MIL-101. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 10669–10672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.W.; Yang, Y.; Che, J.X.; Zuo, J.; Li, X.H.; Gao, L.; Hu, Y.Z.; Liu, X.Y. Heterogenization of homogeneous chiral polymers in metal–organic frameworks with enhanced catalytic performance for asymmetric catalysis. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 4085–4093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Yun, Y.; Sheng, H.; Du, Y.; Ding, Y.; Wu, P.; Li, P.; Zhu, M. Rational encapsulation of atomically precise nanoclusters into metal–organic frameworks by electrostatic attraction for CO2 conversion. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 15371–15376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Peters, A.W.; Platero-Prats, A.E.; Liu, J.; Kung, C.W.; Noh, H.; DeStefano, M.R.; Schweitzer, N.M.; Chapman, K.W.; Hupp, J.T. Fine-tuning the activity of metal–organic framework-supported cobalt catalysts for the oxidative dehydrogenation of propane. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 15251–15258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Huang, Y.; Yue, D.; Cui, Y.; Yang, Y.; Qian, G. A luminescent turn-up metal–organic framework sensor for tryptophan based on singlet–singlet Förster energy transfer. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 5174–5180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Li, P.; Wu, P.; Zhang, F.; Tian, X.; Deng, C.; Wang, J. A squaramide-based metal–organic framework as a luminescent sensor for the detection of lactose in aqueous solution and in milk. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 9131–9134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Yao, S.; Yu, C.; Li, G.; Liu, C.; Huo, Q.; Liu, Y. An ultrastable Zr-MOF for fast capture and highly luminescence detection of Cr2O72− simultaneously in an aqueous phase. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 6363–6369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marti, A.M.; Venna, S.R.; Roth, E.A.; Culp, J.T.; Hopkinson, D.P. Simple fabrication method for mixed matrix membranes with in situ MOF growth for gas separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 24784–24790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasetya, N.; Donose, B.C.; Ladewig, B.P. A new and highly robust light-responsive Azo-UiO-66 for highly selective and low energy post-combustion CO2 capture and its application in a mixed matrix membrane for CO2/N2 separation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 16390–16402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhou, W.; Pham, T.; Forrest, K.A.; Liu, W.; He, Y.; Wu, H.; Yildirim, T.; Chen, B.; Space, B. Fine tuning of MOF-505 analogues to reduce low-pressure methane uptake and enhance methane working capacity. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 11426–11430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Wen, H.M.; Cui, Y.; Zhou, W.; Qian, G.; Chen, B. Emerging multifunctional metal–organic framework materials. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 8819–8860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.; Zhang, X.; Bing, Y.; Xu, N.; Shi, W.; Cheng, P. In situ generation of NiO nanoparticles in a magnetic metal–organic framework exhibiting three-dimensional magnetic ordering. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 55, 12938–12943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Wang, D.; Du, Y.H.; Xi, S.; Hong, J.; Yin, S.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, T.; Xu, R. Metal–organic framework immobilized cobalt oxide nanoparticles for efficient photocatalytic water oxidation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 20607–20613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armelaoa, L.; Quici, S.; Barigelletti, F.; Accorsic, G.; Bottaro, G.; Cavazzini, M.; Tondello, E. Design of luminescent lanthanide complexes: From molecules to highly efficient photo-emitting materials. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2010, 254, 487–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliseeva, S.V.; Bünzli, J.C.G. Lanthanide luminescence for functional materials and bio-sciences. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 189–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joao, R.; Luis, D.C.; Filipe, A.A.P.; Duarte, A. Luminescent multifunctional lanthanides-based metal–organic frameworks. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 926–940. [Google Scholar]
- White, K.A.; Chengelis, D.A.; Gogick, K.A.; Stehman, J.; Rosi, N.L.; Petoud, S. Near-Infrared Luminescent Lanthanide MOF Barcodes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 18069–18071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.L.; Wang, L.B.; Zapata, F.; Qian, G.D.; Lobkovsky, E.B. A luminescent microporous metal−organic framework for the recognition and sensing of anions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 6718–6719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Z.S.; Yu, J.C.; Cui, Y.J.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Z.Y.; Yang, D.; Qian, G.D. Luminescent metal–organic framework films as highly sensitive and fast-response oxygen sensors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 5527–5530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Tian, J.S.; Qi, X.H.; Han, Z.N.; Zhuang, Y.Y.; He, L.N. Quaternary ammonium salt-functionalized chitosan: An easily recyclable catalyst for efficient synthesis of cyclic carbonates from epoxides and carbon dioxide. J. Mol. Catal. A 2007, 271, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Song, S.Y.; Ma, J.F.; Liu, Y.Y.; Yu, Z.T. Syntheses, structures, photoluminescence, and gas adsorption of rare earth–organic frameworks based on a flexible tricarboxylate. Cryst. Growth Des. 2011, 11, 5469–5474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, X.C.; Sun, Y.Q.; Lei, R.; Chen, Y.P.; Zhang, S.; Cao, Y.N.; Zhang, H.H. A series of lanthanide frameworks with a flexible ligand, N,N’-diacetic acid imidazolium, in different coordination modes. Cryst. Growth Des. 2010, 10, 658–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spek, A.L. Single-crystal structure validation with the program PLATON. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2003, 36, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blatov, V.A. TOPOS, A Multipurpose Crystallochemical Analysis with the Program Package; Samara State University: Samara Oblast, Russia, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Lakowicz, J.R. Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy, 3rd ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2006; pp. 63–95. [Google Scholar]
- Valeur, B. Molecular Fluorescence: Principles and Application; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2002; pp. 34–70. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.Y.; Ohulchanskyy, T.Y.; Liu, S.; Law, W.C.; Wu, F.; Swihart, M.T.; Agren, H.; Prasad, P.N. Core/Shell NaGdF4: Nd3+/NaGdF4 nanocrystals with efficient near-infrared to near-infrared downconversion photoluminescence for bioimaging applications. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 2969–2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marciniak, L.; Strek, W.; Guyot, Y.; Hreniak, D.; Boulon, G. Synthesis and Nd3+ luminescence properties of ALa1–xNdxP4O12 (A = Li, Na, K, Rb) tetraphosphate nanocrystals. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 5160–5167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Xu, H.; Yue, Y.; Guo, Z.; Yu, J.; Chen, Z.; Gao, J.; Yang, Y.; Qian, G.; Chen, B. A luminescent mixed-lanthanide metal-organic framework thermometer. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 3979–3982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, W.G.; Jiang, L.; Feng, X.L.; Lu, T.B. Three-dimensional lanthanide anionic metal-organic frameworks with tunable luminescent properties induced by cation exchange. Inorg. Chem. 2009, 48, 6997–6999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, Y.N.; Dong, W.W.; Wu, Y.P.; Li, D.S.; Zhang, Q.C. A Robust Luminescent Tb(III)-MOF with Lewis Basic Pyridyl Sites for the Highly Sensitive Detection of Metal Ions and Small Molecules. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 55, 3265–3271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.S.; Shi, D.; Zhang, H.; Ju, W.; Mei, H.; Xu, Y. A series of color-tunable light-emitting open-framework lanthanide sulfates containing extra-large 36-membered ring channels. CrystEngComm 2017, 19, 5989–5994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.L.; Tian, D.; Gao, Q.; Sun, H.W.; Xu, J.; Bu, X.H. A chiral lanthanide metal–organic framework for selective sensing of Fe(III) ions. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 1040–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yue, Q.; Li, G.D.; Cao, J.J.; Li, G.H.; Chen, J.S. Structures, photoluminescence, up-conversion, and magnetism of 2D and 3D rare-earth coordination polymers with multicarboxylate linkages. Inorg. Chem. 2006, 45, 2857–2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.Y.; Wang, R.; Wang, J.Z.; Zang, S.Q.; Mak, T.C.W. Highly selective Fe3+ sensing and proton conduction in a water-stable sulfonate−carboxylate Tb−organic-framework. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.S.; He, Y.; Zhou, L.; Chen, F.J.; Xu, Y.; Du, H.B.; You, X.Z.; Chen, B. A photoluminescent microporous metal organic anionic framework for nitroaromatic explosive sensing. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 4525–4530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Wang, L.; Xiao, Y.; Fronczek, F.R.; Xue, M.; Cui, Y.; Qian, G. A luminescent metal-organic framework with Lewis basic pyridyl sites for the sensing of metal ions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 500–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Cao, C.S.; Zhao, B. A water-stable lanthanide-organic framework as a recyclable luminescent probe for detecting pollutant phosphorus anions. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 10280–10283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.; Xu, H.; Hou, S.L.; Wu, Z.L.; Zhao, B. Metal−organic frameworks with Tb4 clusters as nodes: Luminescent detection of chromium(VI) and chemical fixation of CO2. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 56, 6244–6250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojtas, L.; Cai, J.; Chen, Y.S.; Ma, S. Crystal engineering of an nbo topology metal–organic framework for chemical fixation of CO2 under ambient conditions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 2615–2619. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, W.Y.; Wojtas, L.; Ma, S.Q. A porous metal–metalloporphyrin framework featuring high-density active sites for chemical fixation of CO2 under ambient conditions. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 5316–5318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.Y.; Tsai, C.Y.; Wojtas, L.; Thiounn, T.; Lin, C.C.; Ma, S. Interpenetrating metal–metalloporphyrin framework for selective CO2 uptake and chemical transformation of CO2. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 55, 7291–7294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Chen, C.; Chen, X.; Zhang, N. Isomorphic MOFs functionalized by free-standing acylamide and organic groups serving as self-supported catalysts for the CO2 cycloaddition reaction. New J. Chem. 2016, 40, 2904–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, T.; Tsutsumi, Y.; Ema, T. Highly active and robust organic–inorganic hybrid catalyst for the synthesis of cyclic carbonates from carbon dioxide and epoxides. Green Chem. 2008, 10, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.Z.; Wang, X.J.; Liu, J.; Lim, J.S.; Zou, R.; Zhao, Y. A triazole-containing metal–organic framework as a highly effective and substrate size-dependent catalyst for CO2 conversion. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 2142–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kathalikkattil, A.C.; Roshan, R.; Tharun, J.; Babu, R.; Jeong, G.S.; Kim, D.W.; Cho, S.J.; Park, D.W. A sustainable protocol for the facile synthesis of zinc-glutamate MOF: An efficient catalyst for room temperature CO2 fixation reactions under wet conditions. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 280–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
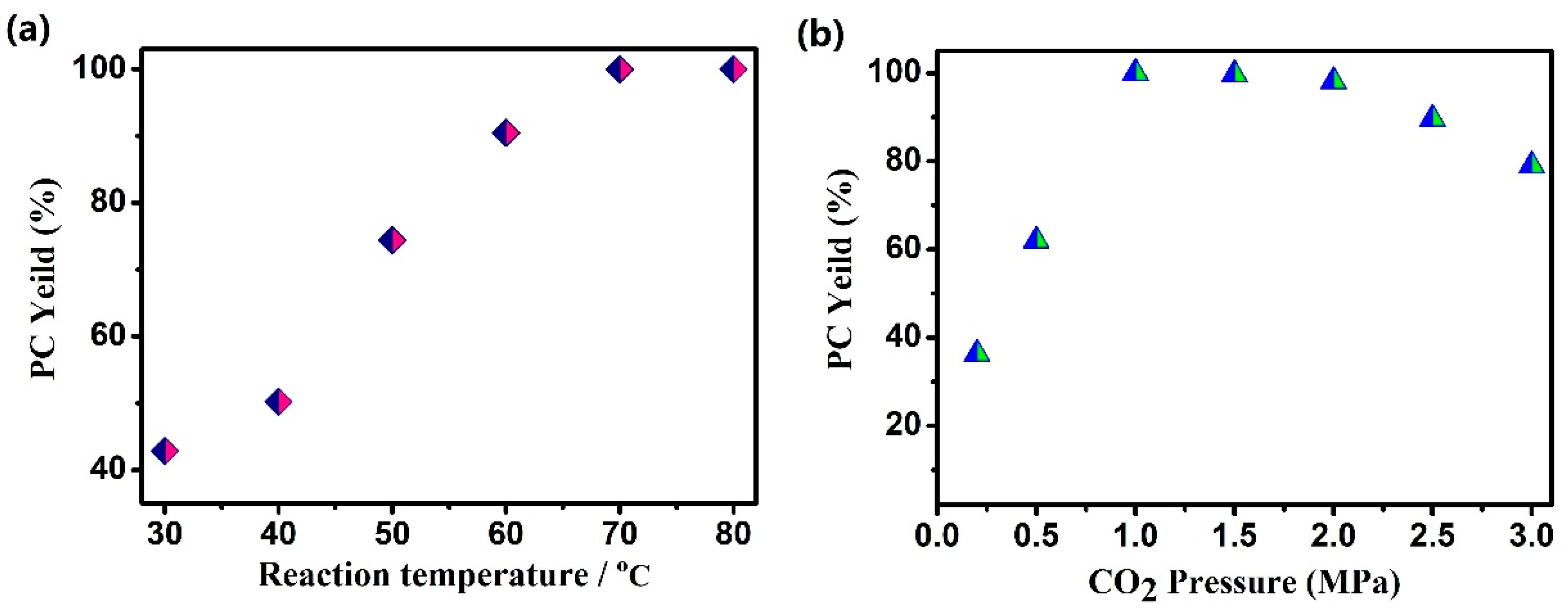
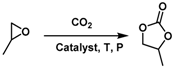
| Entry | Temperature (°C) | Pressure (MPa) | Time (h) | Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 30 | 0.2 | 12 | 4.7 |
| 2 | 30 | 0.2 | 24 | 8.3 |
| 3 | 30 | 0.2 | 36 | 9.9 |
| 4 | 30 | 1.0 | 12 | 42.8 |
| 5 | 60 | 1.0 | 24 | 98.7 |
| 6 | 70 | 1.0 | 12 | >99 |
| 7 [a] | 70 | 1.0 | 12 | 10.7 |
| 8 [b] | 70 | 1.0 | 12 | 17.3 |
| 9 [c] | 70 | 1.0 | 12 | 94.2 |
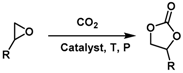
| Entry | Substrate | Products | Yield (%) [b] |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 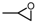 |  | >99.0 |
| 2 | 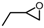 | 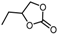 | >99.0 |
| 3 |  |  | 90.8 |
| 4 | 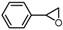 | 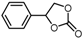 | 88.4 |
| 5 | 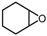 | 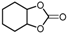 | 43.2 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xue, Y.-S.; Chen, Z.-L.; Dong, Y.; Cheng, W.-W. Two Lanthanide Metal–Organic Frameworks Based on Semi-Rigid T-Shaped Tricarboxylate Ligand: Syntheses, Structures, and Properties. Polymers 2019, 11, 868. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11050868
Xue Y-S, Chen Z-L, Dong Y, Cheng W-W. Two Lanthanide Metal–Organic Frameworks Based on Semi-Rigid T-Shaped Tricarboxylate Ligand: Syntheses, Structures, and Properties. Polymers. 2019; 11(5):868. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11050868
Chicago/Turabian StyleXue, Yun-Shan, Zhuo-Lin Chen, Youzhen Dong, and Wei-Wei Cheng. 2019. "Two Lanthanide Metal–Organic Frameworks Based on Semi-Rigid T-Shaped Tricarboxylate Ligand: Syntheses, Structures, and Properties" Polymers 11, no. 5: 868. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11050868
APA StyleXue, Y.-S., Chen, Z.-L., Dong, Y., & Cheng, W.-W. (2019). Two Lanthanide Metal–Organic Frameworks Based on Semi-Rigid T-Shaped Tricarboxylate Ligand: Syntheses, Structures, and Properties. Polymers, 11(5), 868. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11050868