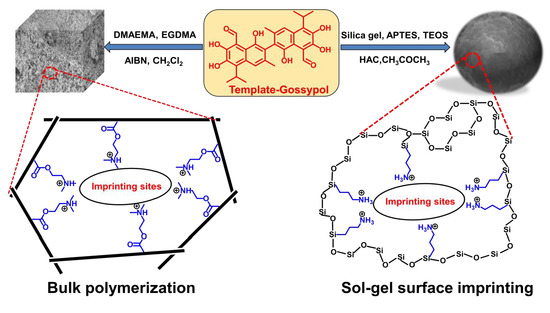
Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Gossypol via Sol–Gel, Bulk, and Surface Layer Imprinting—A Comparative Study
Abstract
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Zhi, K.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yasin, A.; Lin, Q. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Gossypol via Sol–Gel, Bulk, and Surface Layer Imprinting—A Comparative Study. Polymers 2019, 11, 602. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11040602
Wang L, Zhi K, Zhang Y, Liu Y, Zhang L, Yasin A, Lin Q. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Gossypol via Sol–Gel, Bulk, and Surface Layer Imprinting—A Comparative Study. Polymers. 2019; 11(4):602. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11040602
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Lulu, Keke Zhi, Yagang Zhang, Yanxia Liu, Letao Zhang, Akram Yasin, and Qifeng Lin. 2019. "Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Gossypol via Sol–Gel, Bulk, and Surface Layer Imprinting—A Comparative Study" Polymers 11, no. 4: 602. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11040602
APA StyleWang, L., Zhi, K., Zhang, Y., Liu, Y., Zhang, L., Yasin, A., & Lin, Q. (2019). Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Gossypol via Sol–Gel, Bulk, and Surface Layer Imprinting—A Comparative Study. Polymers, 11(4), 602. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11040602