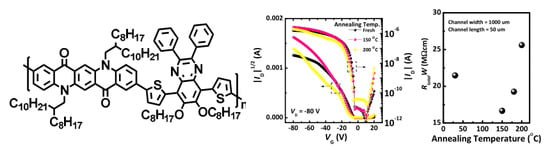
A Quinacridone-Diphenylquinoxaline-Based Copolymer for Organic Field-Effect Transistors
Abstract
Share and Cite
Jeong, Y.J.; Oh, J.H.; Song, H.J.; An, T.K. A Quinacridone-Diphenylquinoxaline-Based Copolymer for Organic Field-Effect Transistors. Polymers 2019, 11, 563. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11030563
Jeong YJ, Oh JH, Song HJ, An TK. A Quinacridone-Diphenylquinoxaline-Based Copolymer for Organic Field-Effect Transistors. Polymers. 2019; 11(3):563. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11030563
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeong, Yong Jin, Jeong Hyun Oh, Ho Jun Song, and Tae Kyu An. 2019. "A Quinacridone-Diphenylquinoxaline-Based Copolymer for Organic Field-Effect Transistors" Polymers 11, no. 3: 563. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11030563
APA StyleJeong, Y. J., Oh, J. H., Song, H. J., & An, T. K. (2019). A Quinacridone-Diphenylquinoxaline-Based Copolymer for Organic Field-Effect Transistors. Polymers, 11(3), 563. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11030563