Robust Superhydrophobic Cellulose Nanofiber Aerogel for Multifunctional Environmental Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Fabrication of Neat CNF Aerogels
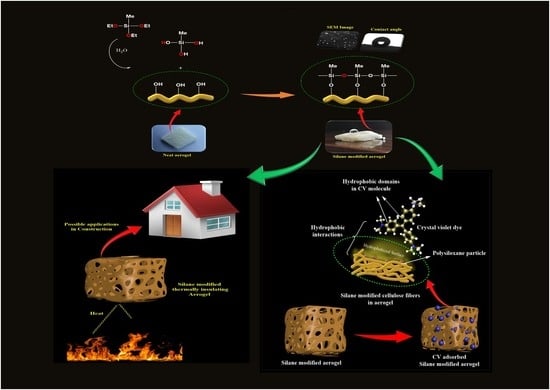
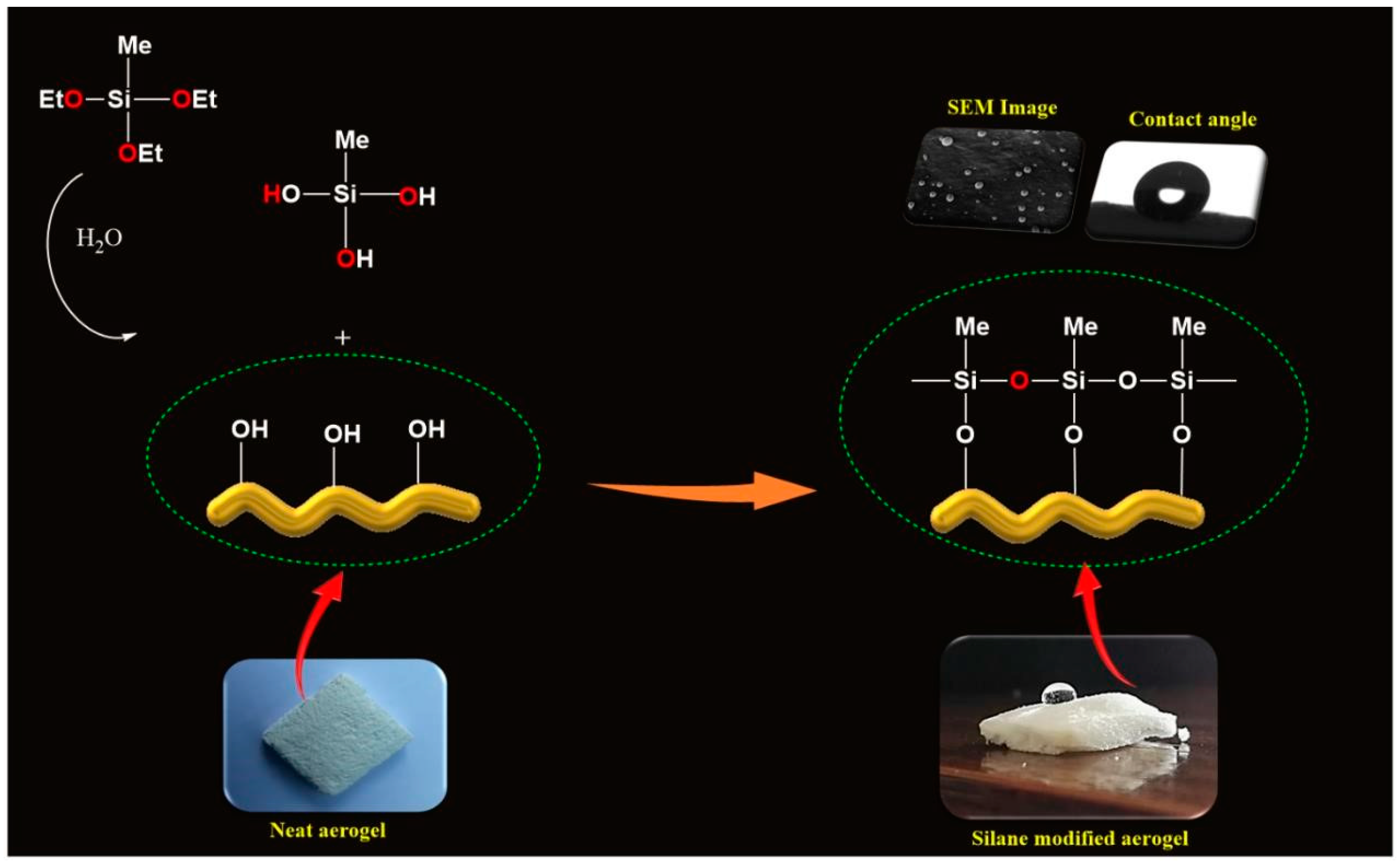
2.3. Fabrication of Silane-Modified CNF Aerogels
2.4. Aerogel Density Assay
2.5. Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.6. X-Ray Diffraction Analysis
2.7. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.8. Static Contact Angle and Surface Free Energy
2.9. UV-Visible Spectrophotometer
2.10. Evaluation of Adsorption Efficiency of Silane-Modified CNF Aerogels against Positively Charged Dyes
2.11. Thermal Conductivity Measurements
2.12. Evaluation of the Mechanical Properties
3. Results and Discussion
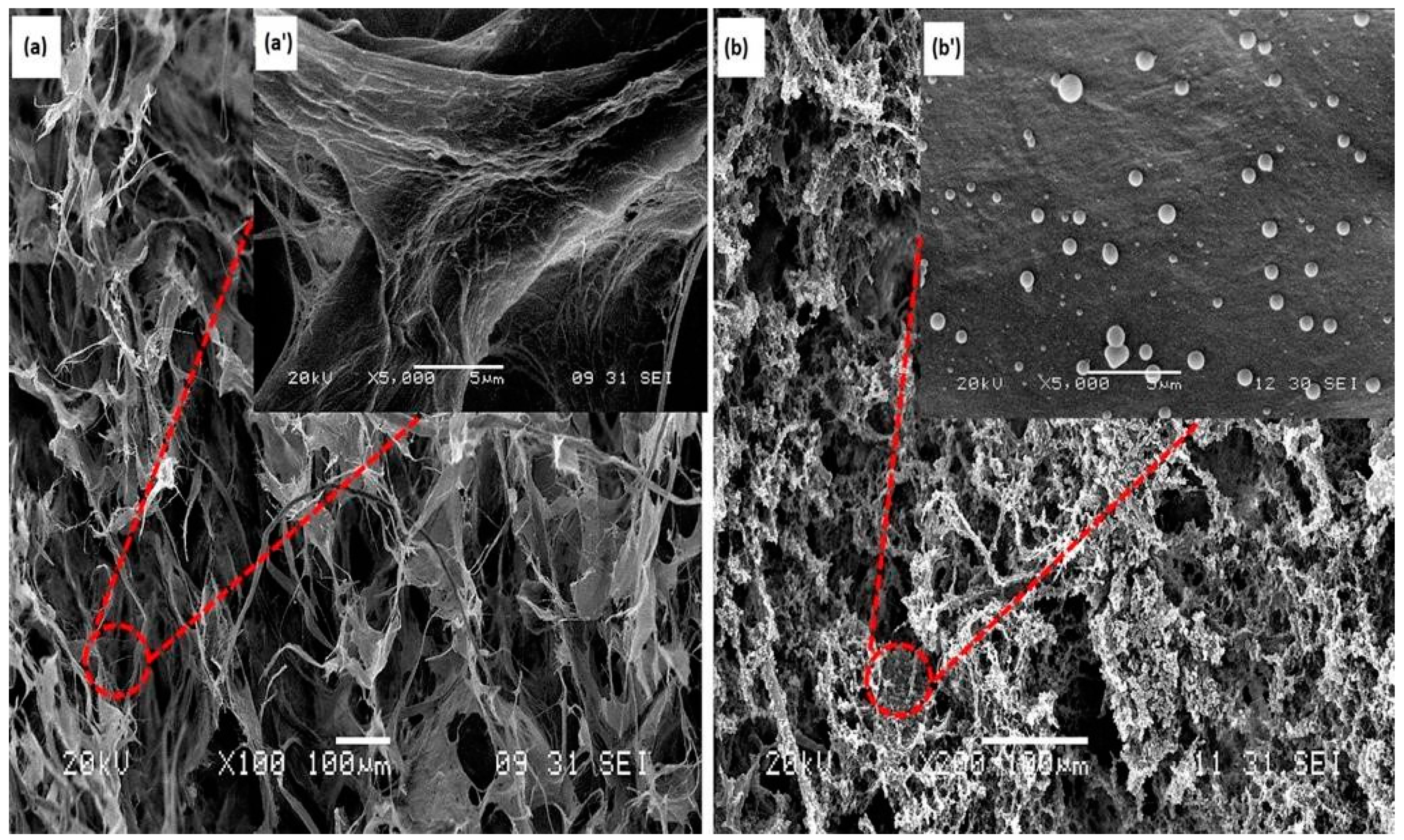
3.1. Morphology of CNF Aerogel and Silane-Modified CNF Aerogel
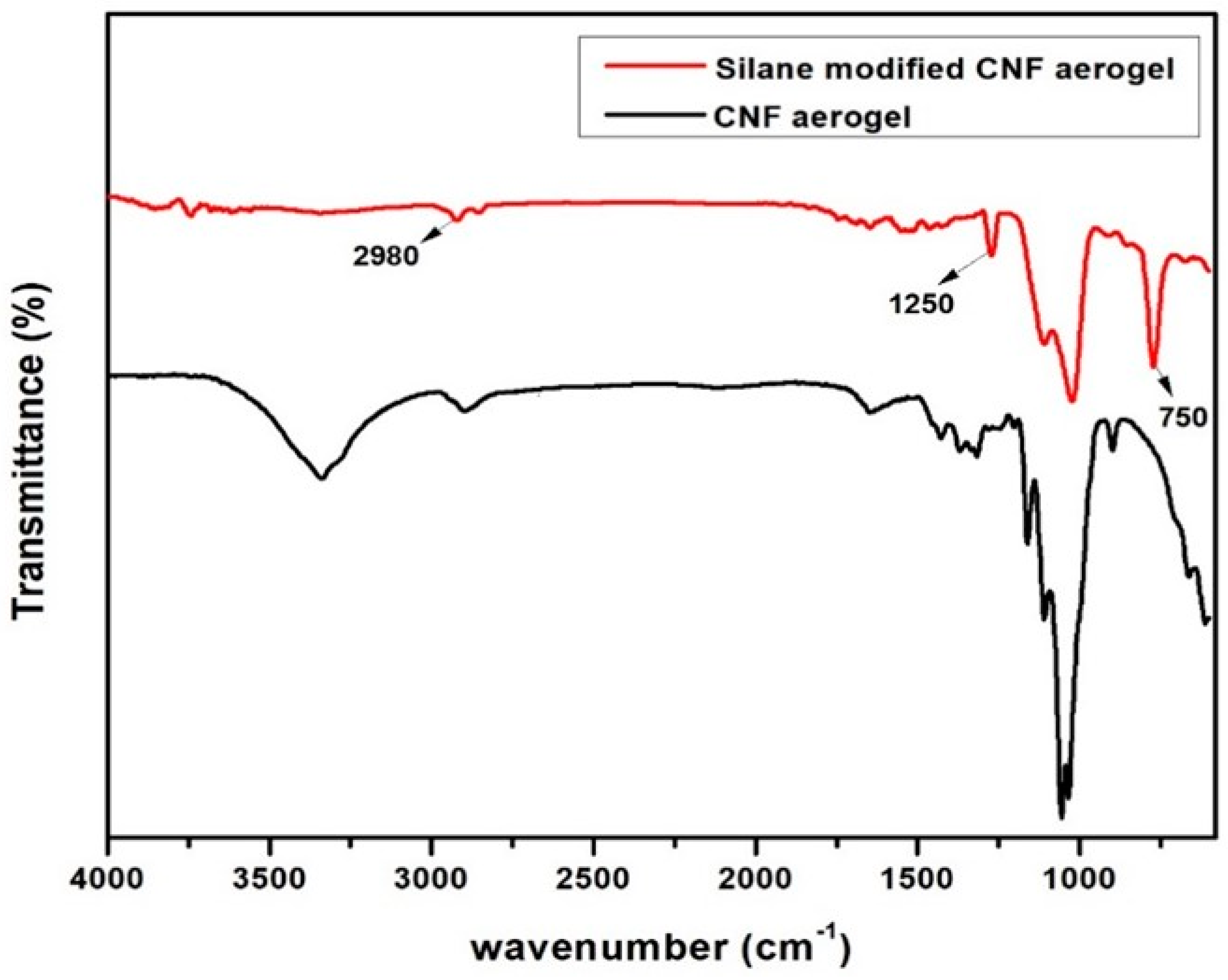
3.2. FTIR Studies
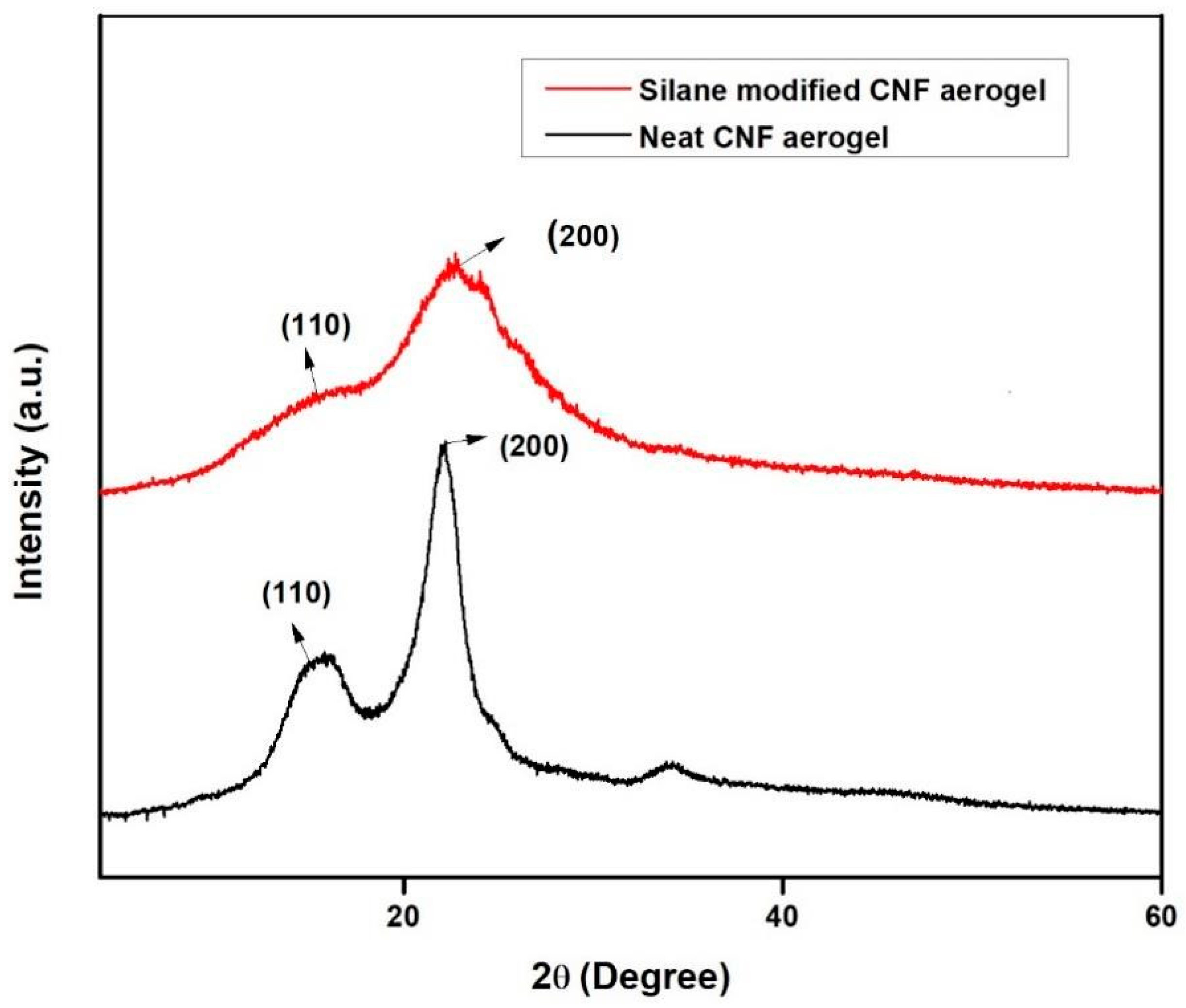
3.3. X-Ray Diffraction Studies
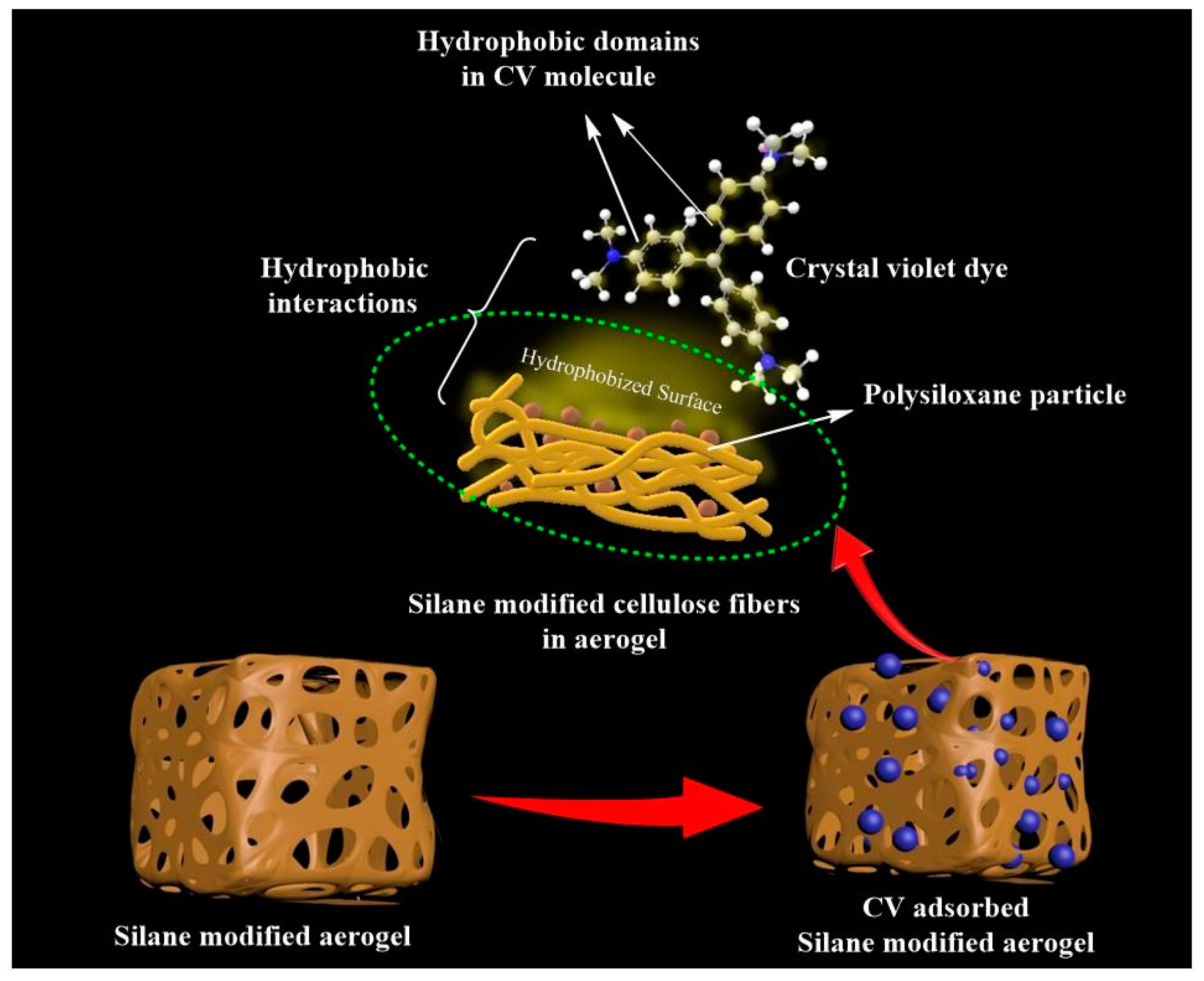
3.4. Interface Interaction between CNF and MTES
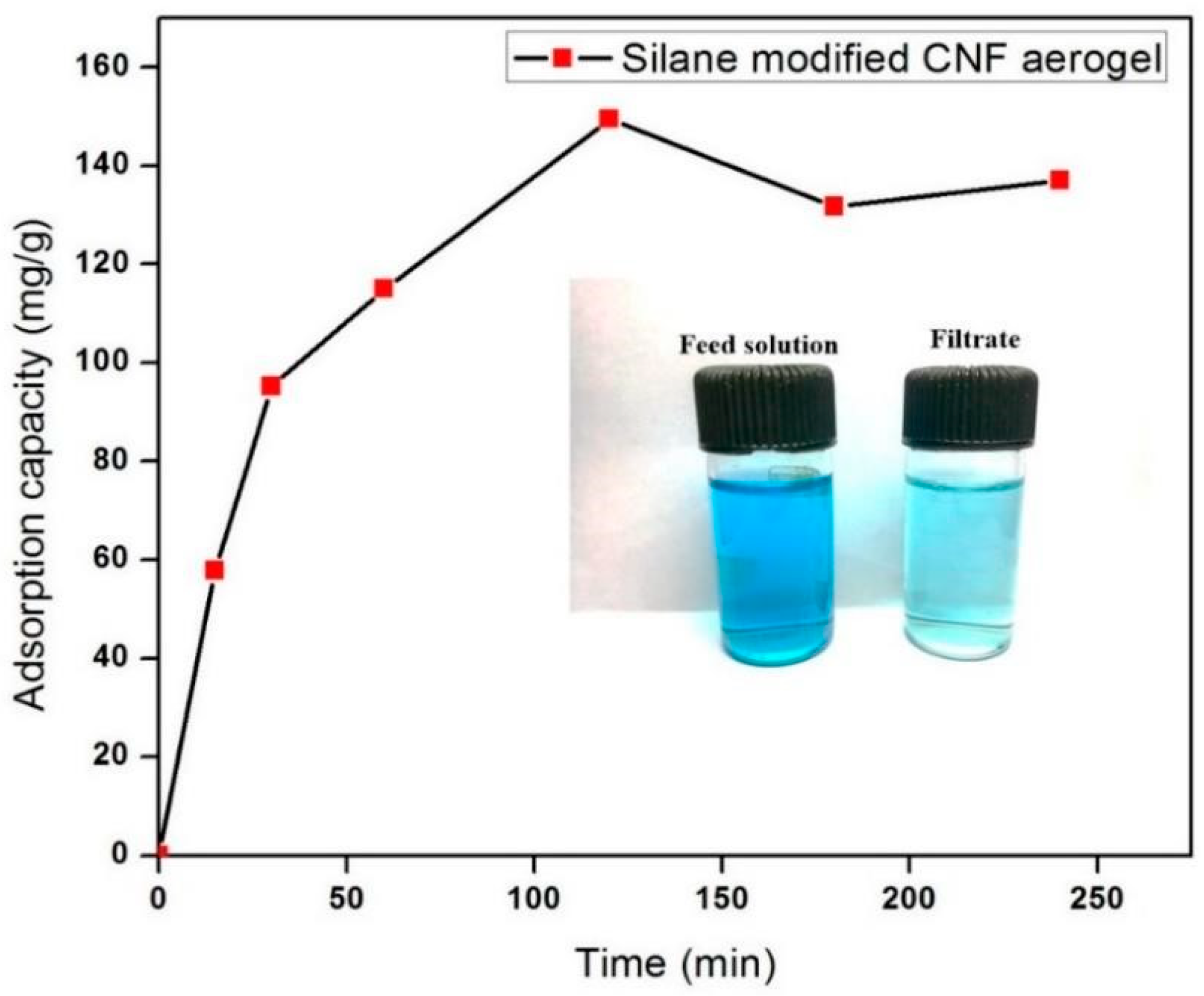
3.5. Dye Adsorption Capacity
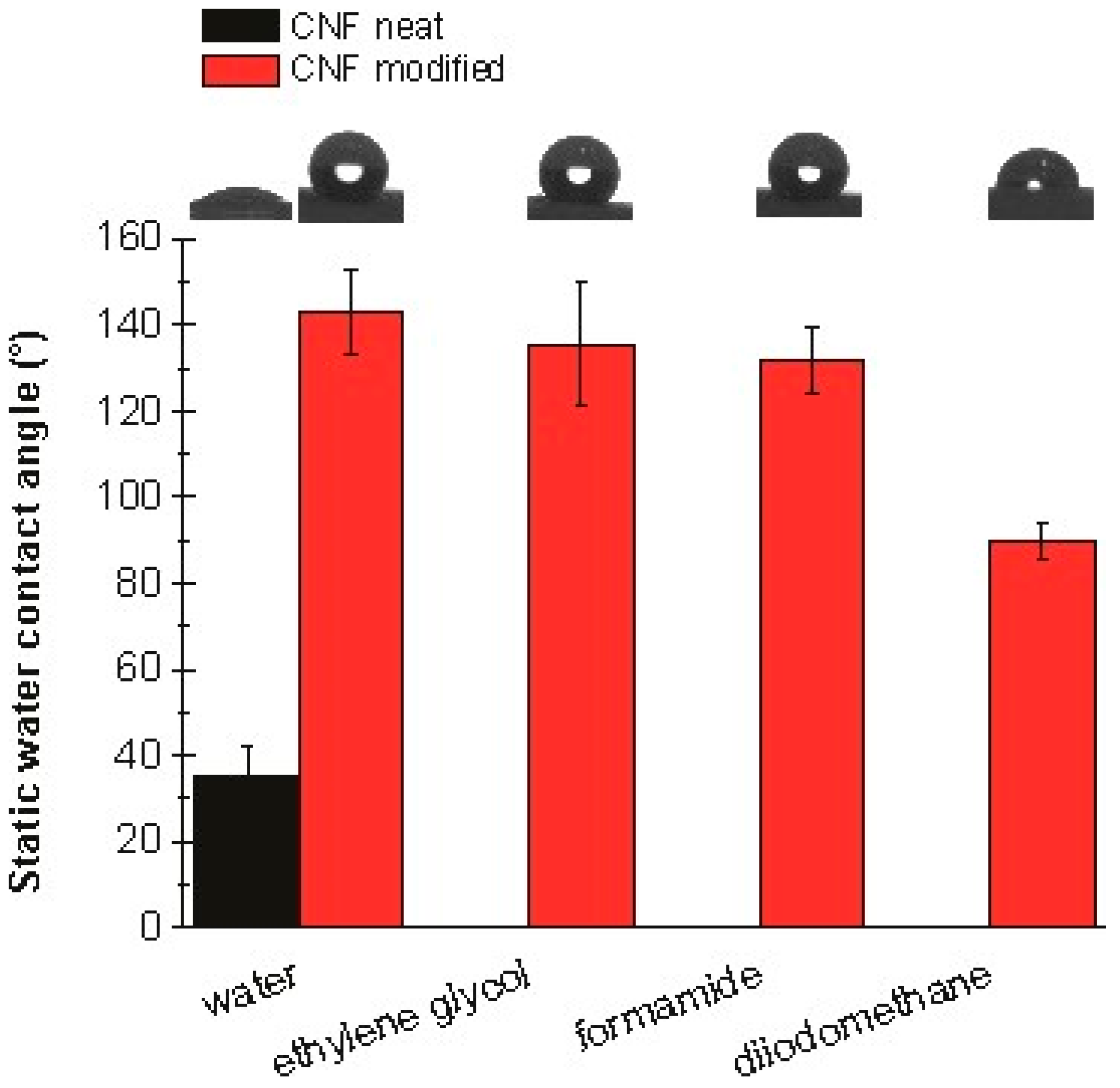
3.6. Contact Angle Studies
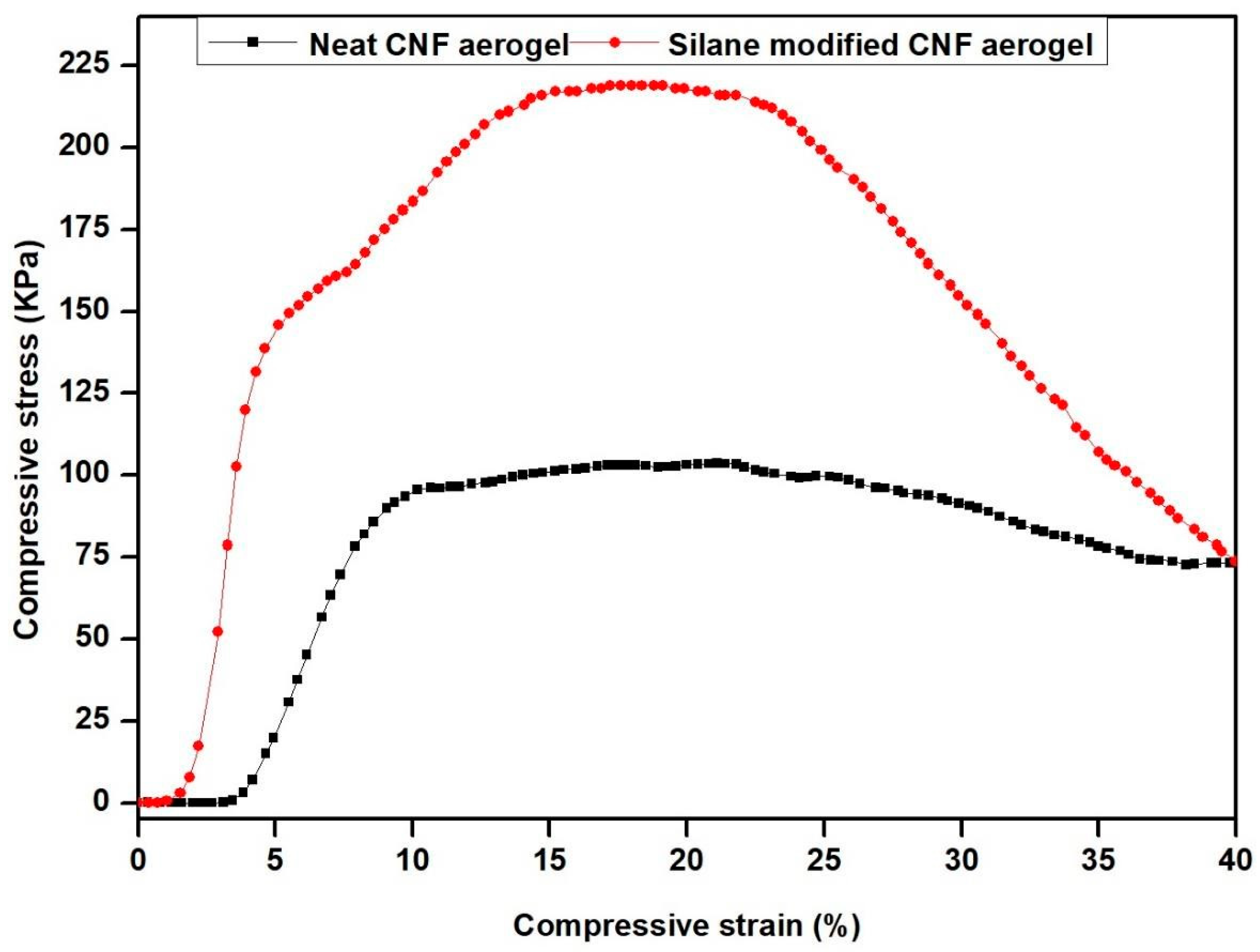
3.7. Mechanical Strength of Fabricated Silane-Modified CNF Aerogel
3.8. Thermal Conductivity Values of Neat CNF Aerogel and Silane-Modified CNF Aerogel
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Holt, M.S. Sources of chemical contaminants and routes into the freshwater environment. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2000, 38, S21–S27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, P.A.; Umbuzeiro, G.A.; Oliveira, D.P.; Zanoni, M.V.B. Assessment of water contamination caused by a mutagenic textile effluent/dyehouse effluent bearing disperse dyes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 174, 694–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandi, N.; Baral, A.; Basu, K.; Roy, S.; Banerjee, A. A dipeptide-based superhydrogel: Removal of toxic dyes and heavy metal ions from waste water. Biopolymers 2017, 108, e22915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Basu, K.; Nandi, N.; Mondal, B.; Dehsorkhi, A.; Hamley, I.W.; Banerjee, A. Peptide-based ambidextrous bifunctional gelator: Applications in oil spill recovery and removal of toxic organic dyes for waste water management. Interface Focus 2017, 7, 20160128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chawla, S.; Uppal, H.; Yadav, M.; Bahadur, N.; Singh, N. Zinc peroxide nanomaterial as an adsorbent for removal of Congo red dye from waste water. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 135, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirbas, A. Agricultural based activated carbons for the removal of dyes from aqueous solutions: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 167, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moosvi, S.; Keharia, H.; Madamwar, D. Decolourization of textile dye Reactive Violet 5 by a newly isolated bacterial consortium RVM 11.1. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2005, 21, 667–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, K.; Gondal, M.A. Removal of hazardous Rhodamine dye from water by adsorption onto exhausted coffee ground. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2017, 21, S120–S127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gopakumar, D.A.; Pasquini, D.; Henrique, M.A.; De Morais, L.C.; Grohens, Y.; Thomas, S. Meldrum’s acid modified cellulose nanofiber-based polyvinylidene fluoride microfiltration membrane for dye water treatment and nanoparticle removal. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 2026–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmen, Z.; Daniela, S. Textile Organic Dyes—Characteristics, Polluting Effects and Separation/Elimination Procedures from Industrial Effluents—A Critical Overview. In Organic Pollutants Ten Years after the Stockholm Convention—Environmental and Analytical Update; Intech Open: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Nauclér, T.; Enkvist, P. Pathways to a Low-Carbon Economy: Version 2 of the Global Greenhouse Gas Abatement Cost Curve. McKinsey Co. 2009, 192. [Google Scholar]
- Hüsing, N.; Schubert, U. Aerogels—Airy Materials: Chemistry, Structure, and Properties. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1998, 37, 22–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, K.; Norris, P.M.; Tien, C.-L. Aerogels—Applications, Structure, and Heat Transfer Phenomena. Annu. Rev. Heat Transf. 1995, 6, 61–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Sèbe, G.; Rentsch, D.; Zimmermann, T.; Tingaut, P. Ultralightweight and flexible silylated nanocellulose sponges for the selective removal of oil from water. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 2659–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y.; Yi, X.; Zeng, J.; Yu, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, J. Comparative study of aerogels obtained from differently prepared nanocellulose fibers. ChemSusChem 2014, 7, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pääkkö, M.; Vapaavuori, J.; Silvennoinen, R.; Kosonen, H.; Ankerfors, M.; Lindström, T.; Berglund, L.A.; Ikkala, O. Long and entangled native cellulose I nanofibers allow flexible aerogels and hierarchically porous templates for functionalities. Soft Matter 2008, 4, 2492–2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Hsieh, Y. Lo Amphiphilic superabsorbent cellulose nanofibril aerogels. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 6337–6342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Peng, X.; Zhong, L.; Tan, J.; Jing, S.; Cao, X.; Chen, W.; Liu, C.; Sun, R. An ultralight, elastic, costeffective, and highly recyclable superabsorbent from microfibrillated cellulose fibers for oil spillage cleanup. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 8772–8781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudemanche, C.; Navard, P. Swelling and dissolution mechanisms of regenerated Lyocell cellulose fibers. Cellulose 2011, 18, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Liu, P.; Wang, M.; Zhao, H.; Yang, J.; Xu, F. Sustainable, Reusable, and Superhydrophobic Aerogels from Microfibrillated Cellulose for Highly Effective Oil/Water Separation. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 6409–6416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korhonen, J.T.; Kettunen, M.; Ras, R.H.A.; Ikkala, O. Hydrophobic nanocellulose aerogels as floating, sustainable, reusable, and recyclable oil absorbents. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 1813–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Han, S.; Li, J.; Sun, Q. Fabrication of cellulose-based aerogels from waste newspaper without any pretreatment and their use for absorbents. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 123, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.; Li, A.; Zheng, T.; Lu, L.; Cao, Y. Hydrophobic and flexible cellulose aerogel as an efficient, green and reusable oil sorbent. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 82027–82033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Yu, H.; Fan, X.; Gu, J.; Ye, S.; Yao, J.; Ni, Q. High Aspect Ratio Carboxylated Cellulose Nanofibers Cross-linked to Robust Aerogels for Superabsorption–Flocculants: Paving Way from Nanoscale to Macroscale. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 20755–20766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Dinh, D.M.; Hsieh, Y. Lo Adsorption and desorption of cationic malachite green dye on cellulose nanofibril aerogels. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 173, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Saelices, C.; Seantier, B.; Cathala, B.; Grohens, Y. Spray freeze-dried nanofibrillated cellulose aerogels with thermal superinsulating properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 157, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthuraj, R.; Grohens, Y.; Seantier, B. Mechanical and thermal insulation properties of elium acrylic resin/cellulose nanofiber based composite aerogels. Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects 2017, 12, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Saelices, C.; Seantier, B.; Cathala, B.; Grohens, Y. Effect of freeze-drying parameters on the microstructure and thermal insulating properties of nanofibrillated cellulose aerogels. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2017, 84, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopakumar, D.A.; Pai, A.R.; Pottathara, Y.B.; Pasquini, D.; Carlos De Morais, L.; Luke, M.; Kalarikkal, N.; Grohens, Y.; Thomas, S. Cellulose Nanofiber-Based Polyaniline Flexible Papers as Sustainable Microwave Absorbers in the X-Band. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 20032–20043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segal, L.; Creely, J.J.; Martin, A.E.; Conrad, C.M. An Empirical Method for Estimating the Degree of Crystallinity of Native Cellulose Using the X-Ray Diffractometer. Text. Res. J. 1959, 29, 786–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, H.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, F.; Wang, E.; Min, Y.; Huang, Q.; Pang, L.; Ma, T. Effective removal of cationic dyes using carboxylate-functionalized cellulose nanocrystals. Chemosphere 2015, 141, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, M.; Yin, T.; Shen, W. The Interaction Between Crystal Violet and Bovine Serum Albumin: Spectroscopic and Molecular Docking Investigations. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2016, 37, 1623–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S. Removal of crystal violet from aqueous solution by sorption into semi-interpenetrated networks hydrogels constituted of poly(acrylic acid-acrylamide-methacrylate) and amylose. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 2197–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Homoud, M.S. Performance characteristics and practical applications of common building thermal insulation materials. Build. Environ. 2005, 40, 353–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, N.; Jiao, D.; Ding, P.; Cui, S.; Tang, S.; Shi, L. Anisotropic thermally conductive flexible films based on nanofibrillated cellulose and aligned graphene nanosheets. J. Mater. Chem. C 2016, 4, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Le, D.; Nguyen, S.T.; Tan Chin Nien, V.; Jewell, D.; Duong, H.M. Silica–cellulose hybrid aerogels for thermal and acoustic insulation applications. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2016, 506, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, N.; Jiao, D.; Cui, S.; Hou, X.; Ding, P.; Shi, L. Highly anisotropic thermal conductivity of layer-bylayer assembled nanofibrillated cellulose/graphene nanosheets hybrid films for thermal management. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 2924–2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seantier, B.; Bendahou, D.; Bendahou, A.; Grohens, Y.; Kaddami, H. Multi-scale cellulose based new bioaerogel composites with thermal super-insulating and tunable mechanical properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 138, 335–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, B.; Chen, S.; Yao, Q.; Sun, Q.; Jin, C. Fabrication of cellulose nanofiber/AlOOH aerogel for flame retardant and thermal insulation. Materials 2017, 10, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
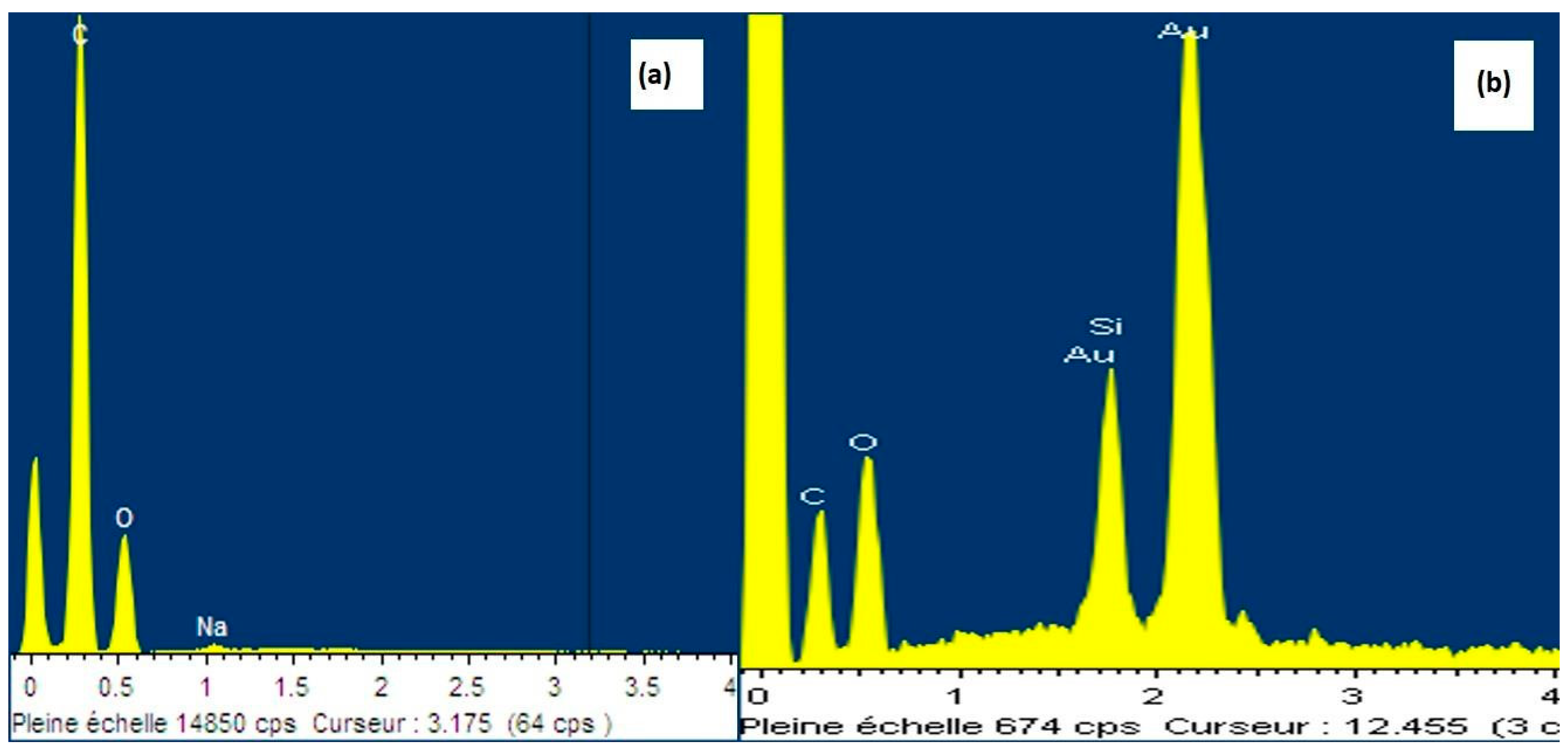
| Element | Silane-Modified CNF Aerogel % Mass | Neat CNF Aerogel % Mass |
|---|---|---|
| C | 42.00 | 73.16 |
| O | 52.02 | 26.84 |
| Si | 5.98 | 0.00 |
| Total | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| Materials | Thermal Conductivity (W·m−1·K−1) | References |
|---|---|---|
| Ag2O/Nanofibrillated cellulose aerogels | 0.072 | [35] |
| Silica/cellulose hybrid aerogels | 0.040 | [36] |
| Nanofibrillated cellulose/graphene films | 0.042 | [37] |
| Multi-scale cellulose bio-aerogel composites | 0.023 | [38] |
| CNF/AlOOH aerogel | 0.039 | [39] |
| Silane-modified CNF aerogel | 0.037 | This work |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
M., H.; Gopakumar, D.A.; Arumughan, V.; Pottathara, Y.B.; K. S., S.; Pasquini, D.; Bračič, M.; Seantier, B.; Nzihou, A.; Thomas, S.; et al. Robust Superhydrophobic Cellulose Nanofiber Aerogel for Multifunctional Environmental Applications. Polymers 2019, 11, 495. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11030495
M. H, Gopakumar DA, Arumughan V, Pottathara YB, K. S. S, Pasquini D, Bračič M, Seantier B, Nzihou A, Thomas S, et al. Robust Superhydrophobic Cellulose Nanofiber Aerogel for Multifunctional Environmental Applications. Polymers. 2019; 11(3):495. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11030495
Chicago/Turabian StyleM., Hasan., Deepu A. Gopakumar, Vishnu Arumughan, Yasir Beeran Pottathara, Sisanth K. S., Daniel Pasquini, Matej Bračič, Bastien Seantier, Ange Nzihou, Sabu Thomas, and et al. 2019. "Robust Superhydrophobic Cellulose Nanofiber Aerogel for Multifunctional Environmental Applications" Polymers 11, no. 3: 495. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11030495
APA StyleM., H., Gopakumar, D. A., Arumughan, V., Pottathara, Y. B., K. S., S., Pasquini, D., Bračič, M., Seantier, B., Nzihou, A., Thomas, S., Rizal, S., & H. P. S., A. K. (2019). Robust Superhydrophobic Cellulose Nanofiber Aerogel for Multifunctional Environmental Applications. Polymers, 11(3), 495. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11030495