Magnetic Properties of FeNi3 Nanoparticle Modified Pinus radiata Wood Nanocomposites
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
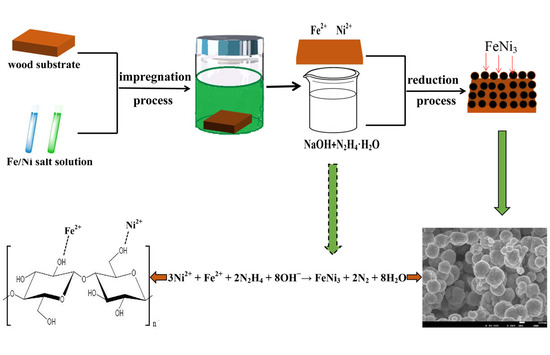
2.2. Preparation of FeNi3 Nanoparticle Magnetic Wood Composites
2.3. Characterization Techniques
3. Results and Discussion
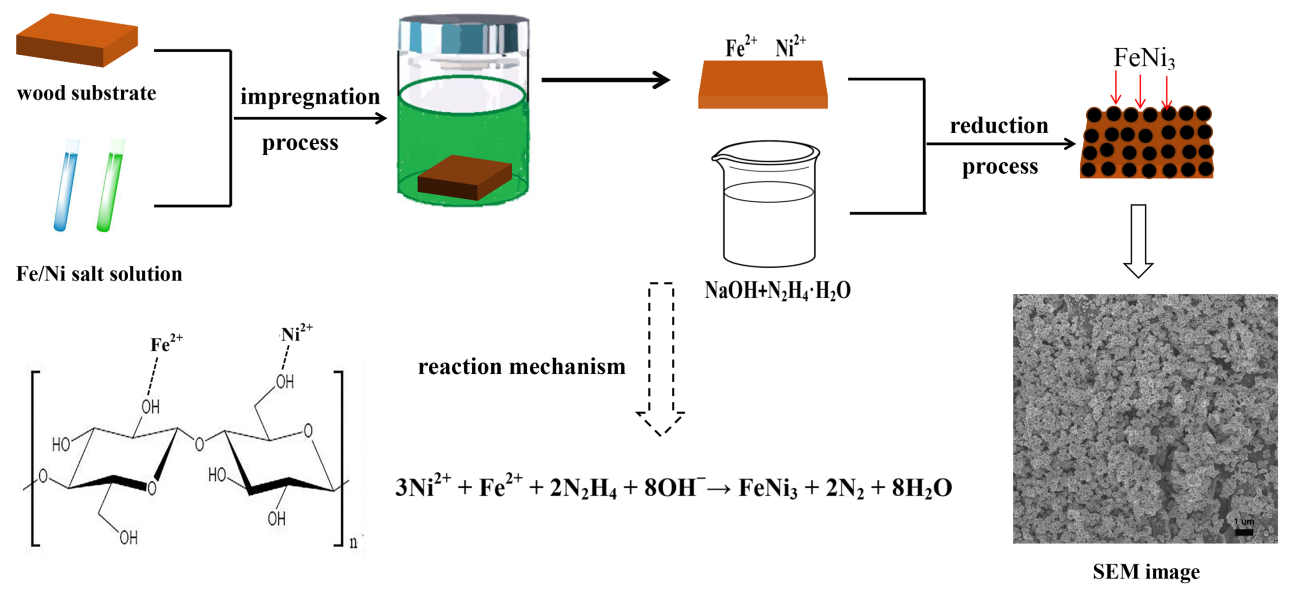
3.1. XRD Analysis of Unmodified and Modified Wood
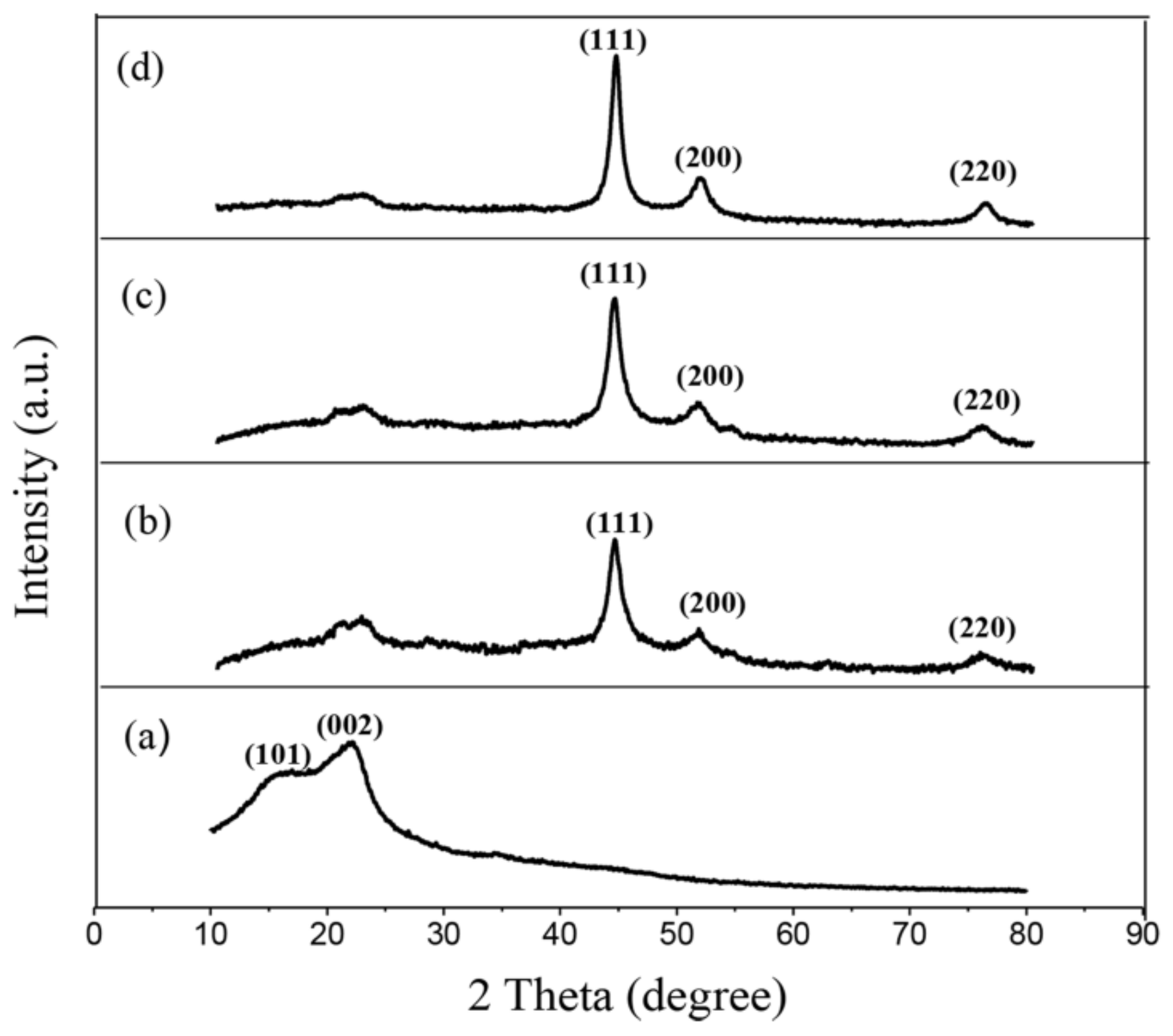
3.2. FTIR Analysis of Unmodified and Modified Wood
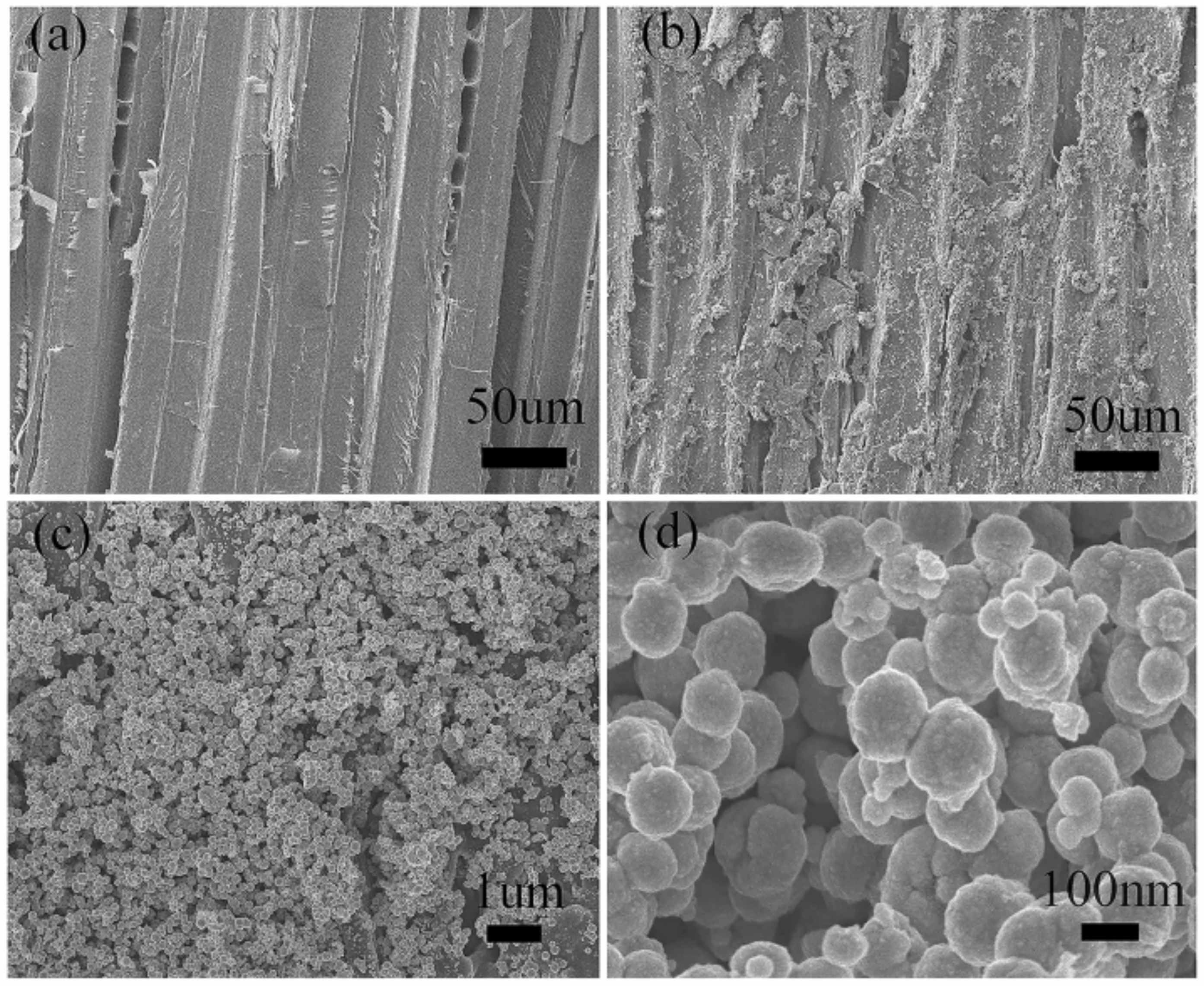
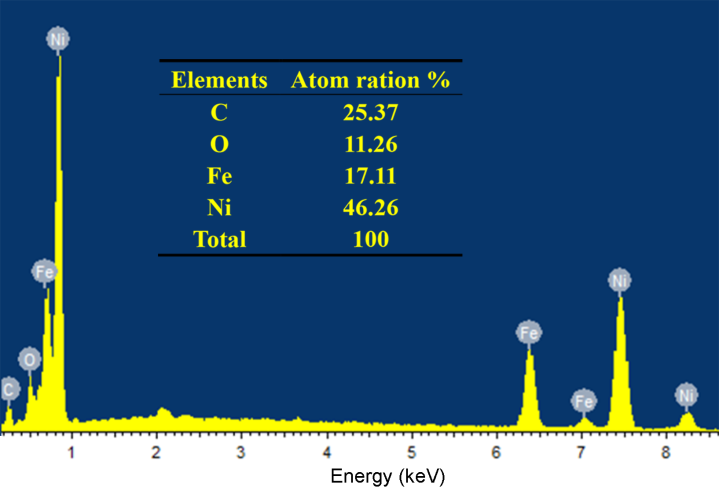
3.3. Morphology Analysis of Unmodified and Modified Wood Composites
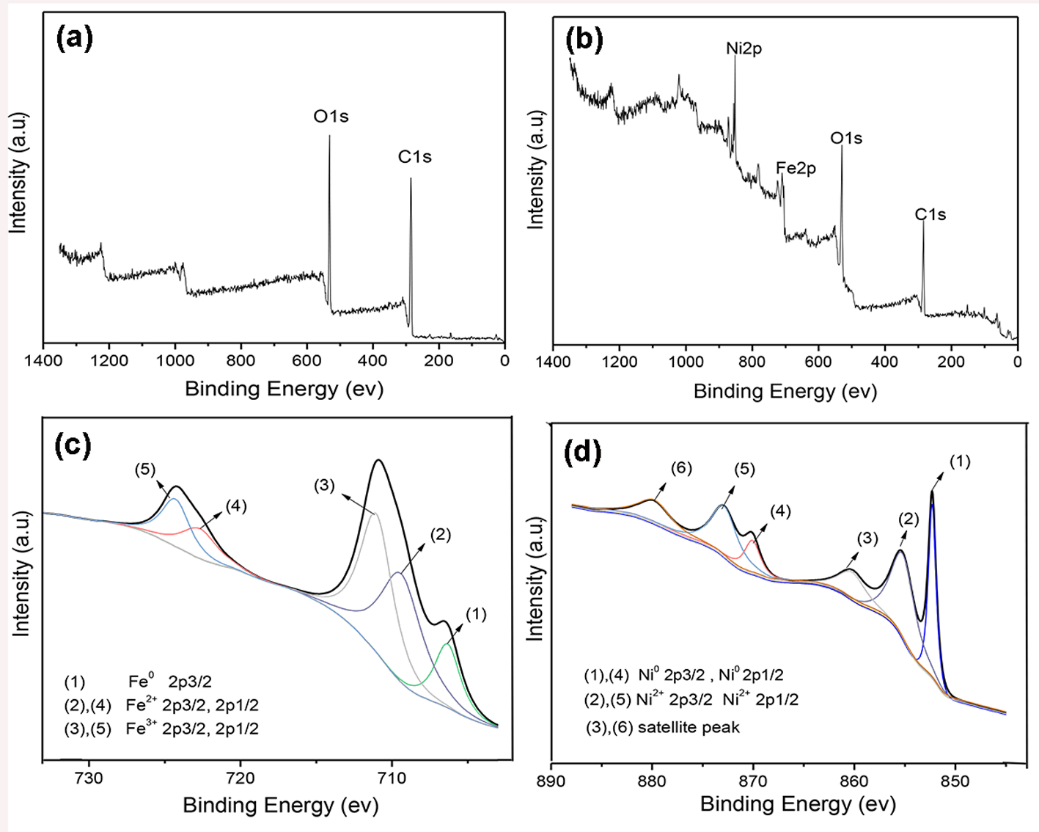
3.4. XPS Analysis of Unmodified Wood and MW–18 wt % Composite
3.5. Magnetism Analysis of Composites
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ugolev, B.N. Wood as a natural smart material. Wood Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 553–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lykidis, C.; Bak, M.; Mantanis, G.; Németh, R. Biological resistance of pine wood treated with nano-sized zinc oxide and zinc borate against brown-rot fungi. Eur. J. Wood Wood Prod. 2016, 74, 909–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.Z.; Javaid, A. Mechanical and rheological characterization of efficient and economical structural wood-plastic composite of wood and PVC. J. Chem. Soc. Pak. 2017, 39, 183. [Google Scholar]
- Hung, K.-C.; Wu, J.-H. Effect of SiO2 content on the extended creep behavior of SiO2-based wood-inorganic composites derived via the sol-gel process using the stepped isostress method. Polymers 2018, 10, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafezi, S.M.; Enayati, A.; Hosseini, K.D.; Tarmian, A.; Mirshokraii, S.A. Use of amino silane coupling agent to improve physical and mechanical properties of UF-bonded wheat straw (triticum aestivum I.) poplar wood particleboard. J. For. Res 2016, 27, 427–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, J.; Cha, S. Effect of chemical modification on mechanical properties of wood-plastic composite injection-molded parts. Polymers 2018, 10, 1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Declercq, N.F. Acoustic wood anomaly in transmitted diffraction field. J. Appl. Phys. 2017, 121, 114902–114921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, A.C.; Johnston, J.H. Novel hybrid materials of magnetic nanoparticles and cellulose fibers. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 331, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Yan, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Li, J. Combined treatment for conversion of fast-growing poplar wood to magnetic wood with high dimensional stability. Wood Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 503–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oka, H.; Hamano, H.; Chiba, S. Experimental study on actuation functions of coating-type magnetic wood. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2004, 272, E1693–E1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oka, H.; Kataoka, Y.; Osada, H.; Aruga, Y.; Izumida, F. Experimental study on electromagnetic wave absorbing control of coating-type magnetic wood using a grooving process. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2007, 310, e1028–e1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oka, H.; Uchidate, S.; Sekino, N.; Namizaki, Y.; Kubota, K.; Osada, H.; Dawson, F.P.; Lavers, J.D. Electromagnetic wave absorption characteristics of half carbonized powder-type magnetic wood. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2011, 47, 3078–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oka, H.; Hojo, A.; Osada, H.; Namizaki, Y.; Taniuchi, H. Manufacturing methods and magnetic characteristics of magnetic wood. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2004, 272, 2332–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, W.; Gao, L.; Xiao, S.; Zhang, W.; Zhan, X.; Jian, L. Transparent magnetic wood composites based on immobilizing Fe3O4 nanoparticles into a delignified wood template. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 3321–3329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, W.; Gao, L.; Ying, L.; Zhan, X.; Jian, L. The magnetic, mechanical, thermal properties and UV resistance of CoFe2O4/SiO2-coated film on wood. J. Wood Chem. Technol. 2016, 36, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yao, Q.; Wang, C.; Ma, Z.; Sun, Q.; Fan, B.; Jin, C.; Chen, Y. Hydrothermal synthesis of nanooctahedra MnFe2O4 onto the wood surface with soft magnetism, fire resistance and electromagnetic wave absorption. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, X.; He, J.; Xia, Z.; Jing, A.; Hao, J.; Xiang, Y.; He, S.; Zhao, D. Optimized microwave magnetic characteristics for patterned FeNi nanoparticle films manufactured by electric field-assisted deposition. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 447, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butta, M.; Ripka, P.; Janosek, M.; Pribil, M. Electroplated FeNi ring cores for fluxgates with field induced radial anisotropy. J. Appl. Phys. 2015, 117, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chlenova, A.A.; Svalov, A.V.; Kurlyandskaya, G.V.; Volchkov, S.O. Magnetoimpedance of FeNi-based asymmetric sensitive elements. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2016, 415, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurlyandskaya, G.V.; Chlenova, A.A.; Fernández, E.; Lodewijk, K.J. FeNi-based flat magnetoimpedance nanostructures with open magnetic flux: New topological approaches. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2015, 383, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zhu, Z.; Xiong, C.; Xu, X.; Lin, Q. The effect of transverse magnetic field treatment on wave-absorbing properties of FeNi alloy powders. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 422, 402–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Lv, J.; Xiang, Z.; Zheng, J.; Yao, Y.; Liang, Q.; Jing, Y.; Che, S. Enhanced and broadband microwave absorption of flake-shaped Fe and FeNi composite with Ba ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2016, 426, 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Liang, G.; Zhang, Y. Synthesis and characterization of magnetic FeNi3 particles obtained by hydrazine reduction in aqueous solution. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2007, 139, 124–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.L.; Tao, J.H.; Yu, L.; Song, C.; Qiu, G.Z.; Li, Y.; Xu, Z.H. Synthesis and magnetic properties of Fe–Ni alloy nanoparticles obtained by hydrothermal reaction. Adv. Mater. Res 2011, 239–242, 748–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Wang, L.; Wang, L. Preparation of corrosion-resistant, EMI shielding and magnetic veneer-based composite via Ni–Fe–p alloy deposition. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2015, 26, 7096–7103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, M.; Yuan, M.; Islam, S.M.; Li, H.; Ma, S.; Sun, G.; Yang, X. FeNi3 alloy nanocrystals grown on graphene: Controllable synthesis, in-depth characterization and enhanced electromagnetic performance. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 678, 468–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Li, J.; Ren, B.; Li, T.; Ma, X. Synthesis and characterization of wooden magnetic activated carbon fibers with hierarchical pore structures. Polymers 2018, 10, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, R.; Langenfeld-Heyser, R.; Finkeldey, R.; Polle, A. FTIR spectroscopy, chemical and histochemical characterisation of wood and lignin of five tropical timber wood species of the family of dipterocarpaceae. Wood Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 225–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.; Hao, J.; Wang, W. Ultraviolet weathering performance of high-density polyethylene/wood-flour composites with a basalt-fiber-included shell. Polymers 2018, 10, 831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.T.; Chang, S.T. Modification of wood with isopropyl glycidyl ether and its effects on decay resistance and light stability. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 1265–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, H.L.; Wu, G.Y.; Guan, H.T.; Zhang, G.L. In situ preparation and magnetic properties of Fe3O4/wood composite. Mater. Technol. 2012, 27, 101–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bheki Magagula, N.N.; Focke, W.W. Mn2al-ldh- and co2al-ldh-stearate as photodegradants for ldpe film. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2009, 94, 947–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alekseeva, T.; Prevot, V.; Sancelme, M.; Forano, C.; Besse-Hoggan, P. Enhancing atrazine biodegradation by pseudomonas sp. Strain ADP adsorption to layered double hydroxide bionanocomposites. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 191, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, R.Y.; Zhang, S.Z.; Han, Y.P.; Li, H.Z.; Ding, J.; Zheng, Y. Preparation, characterization and application of bilayer surfactant-stabilized ferrofluids. Powder Technol. 2006, 170, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, B.; Li, G.; Han, G.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, J. Fabrication of magnetic response composite based on wood veneers by a simple in situ synthesis method. Wood Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 755–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesinger, M.C.; Payne, B.P.; Grosvenor, A.P.; Lau, L.W.M.; Gerson, A.R.; Smart, R.S.C. Resolving surface chemical states in XPS analysis of first row transition metals, oxides and hydroxides: Cr, Mn, Fe, Co and Ni. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 2717–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokare, A.D.; Chikate, R.C.; Rode, C.V.; Paknikar, K.M. Iron-nickel bimetallic nanoparticles for reductive degradation of azo dye Orange G in aqueous solution. Appl. Catal. B 2008, 79, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo-cheng, H.; Ehrman, S.H. Synthesis of iron nanoparticles via chemical reduction with palladium ion seeds. Langmuir 2007, 23, 1419–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, Y.; Teramoto, Y.; Nishio, Y. Preparation of thermoplastic magnetic wood via etherification and in-situ synthesis of iron oxide. J. Wood Chem. Technol. 2010, 30, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, W.; Gao, L.; Zhan, X.; Li, J. Hydrothermal synthesis of magnetic wood composites and improved wood properties by precipitation with CoFe2O4/hydroxyapatite. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 45919–45927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.P.; Wang, H.W.; Yao, Q.F.; Fan, B.T.; Wang, C.; Xiong, Y.; Jin, C.D.; Sun, Q.F. Biomimetic taro leaf-like films decorated on wood surfaces using soft lithography for superparamagnetic and superhydrophobic performance. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 7428–7438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhang, R.; Liu, X.X.; Lin, D.D.; Pan, W. Electrospinning of Fe, Co, and Ni nanofibers: Synthesis, assembly, and magnetic properties. Chem. Mater. 2007, 19, 3506–3511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bremaud, I.; Gril, J.; Thibaut, B. Anisotropy of wood vibrational properties: Dependence on grain angle and review of literature data. Wood Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 735–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merk, V.; Chanana, M.; Gierlinger, N.; Hirt, A.M.; Burgert, I. Hybrid wood materials with magnetic anisotropy dictated by the hierarchical cell structure. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 9760–9767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trey, S.; Olsson, R.T.; Strom, V.; Berglund, L.; Johansson, M. Controlled deposition of magnetic particles within the 3-D template of wood: Making use of the natural hierarchical structure of wood. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 35678–35685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Li, N.; Zhao, T.; Li, B.; Ji, Y. Magnetic Properties of FeNi3 Nanoparticle Modified Pinus radiata Wood Nanocomposites. Polymers 2019, 11, 421. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11030421
Wang L, Li N, Zhao T, Li B, Ji Y. Magnetic Properties of FeNi3 Nanoparticle Modified Pinus radiata Wood Nanocomposites. Polymers. 2019; 11(3):421. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11030421
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, LiLi, Na Li, Tiqi Zhao, Bin Li, and Yali Ji. 2019. "Magnetic Properties of FeNi3 Nanoparticle Modified Pinus radiata Wood Nanocomposites" Polymers 11, no. 3: 421. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11030421
APA StyleWang, L., Li, N., Zhao, T., Li, B., & Ji, Y. (2019). Magnetic Properties of FeNi3 Nanoparticle Modified Pinus radiata Wood Nanocomposites. Polymers, 11(3), 421. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11030421