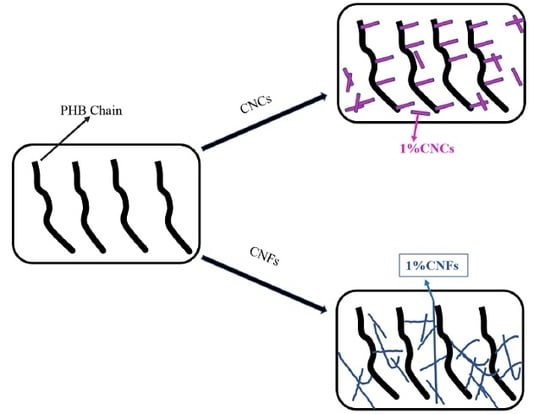
Effects of Cellulose Nanocrystals and Cellulose Nanofibers on the Structure and Properties of Polyhydroxybutyrate Nanocomposites
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Cellulose Nanocrystals (CNCs)
2.3. Preparation of Cellulose Nanofibers (CNFs)
2.4. Preparation of Nanocellulose Chloroform Suspension
2.5. Preparation of Nanocellulose/PHB Composite Film
2.6. Characterization
2.6.1. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Analysis
2.6.2. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) Analysis
2.6.3. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) Analysis
2.6.4. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) Test
2.6.5. Thermal Characterization
2.6.6. Mechanical Performance Test
2.6.7. Barrier Performance Test
2.6.8. Optical Properties by UV–Vis Spectroscopy
2.6.9. Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) Test
3. Results and Discussion
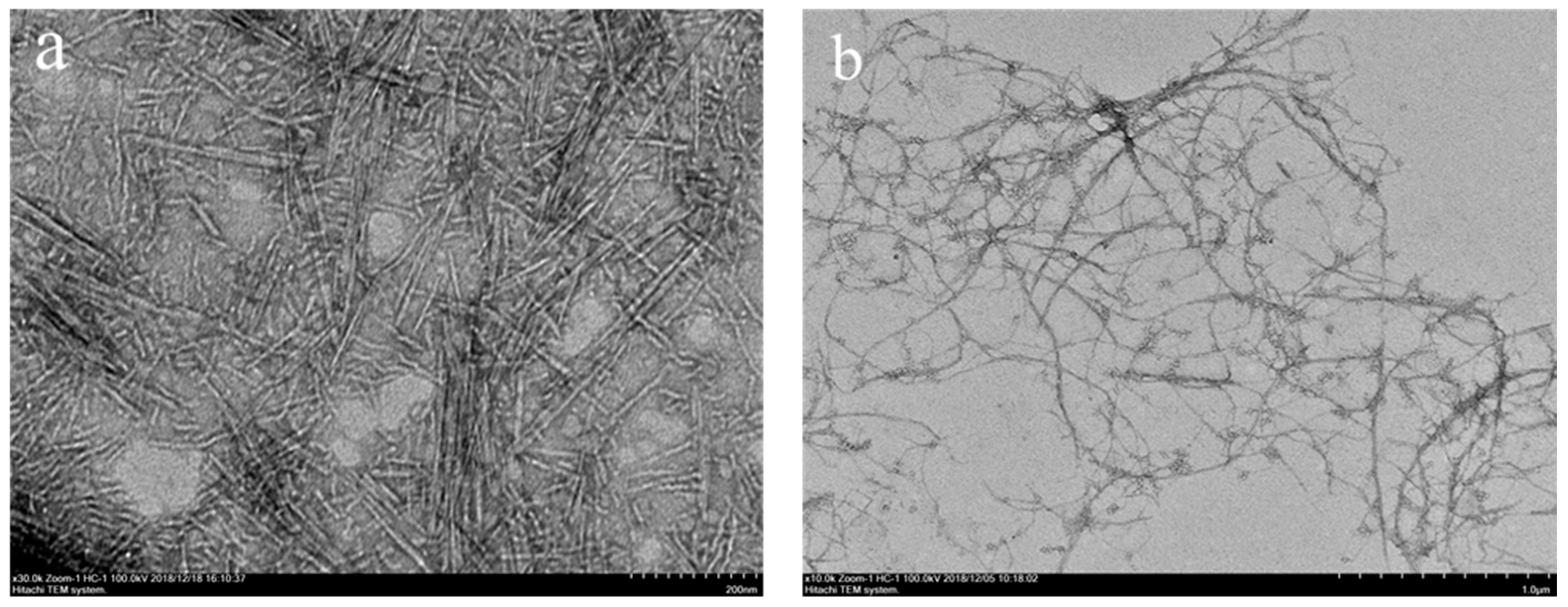
3.1. Morphology of CNCs and CNFs
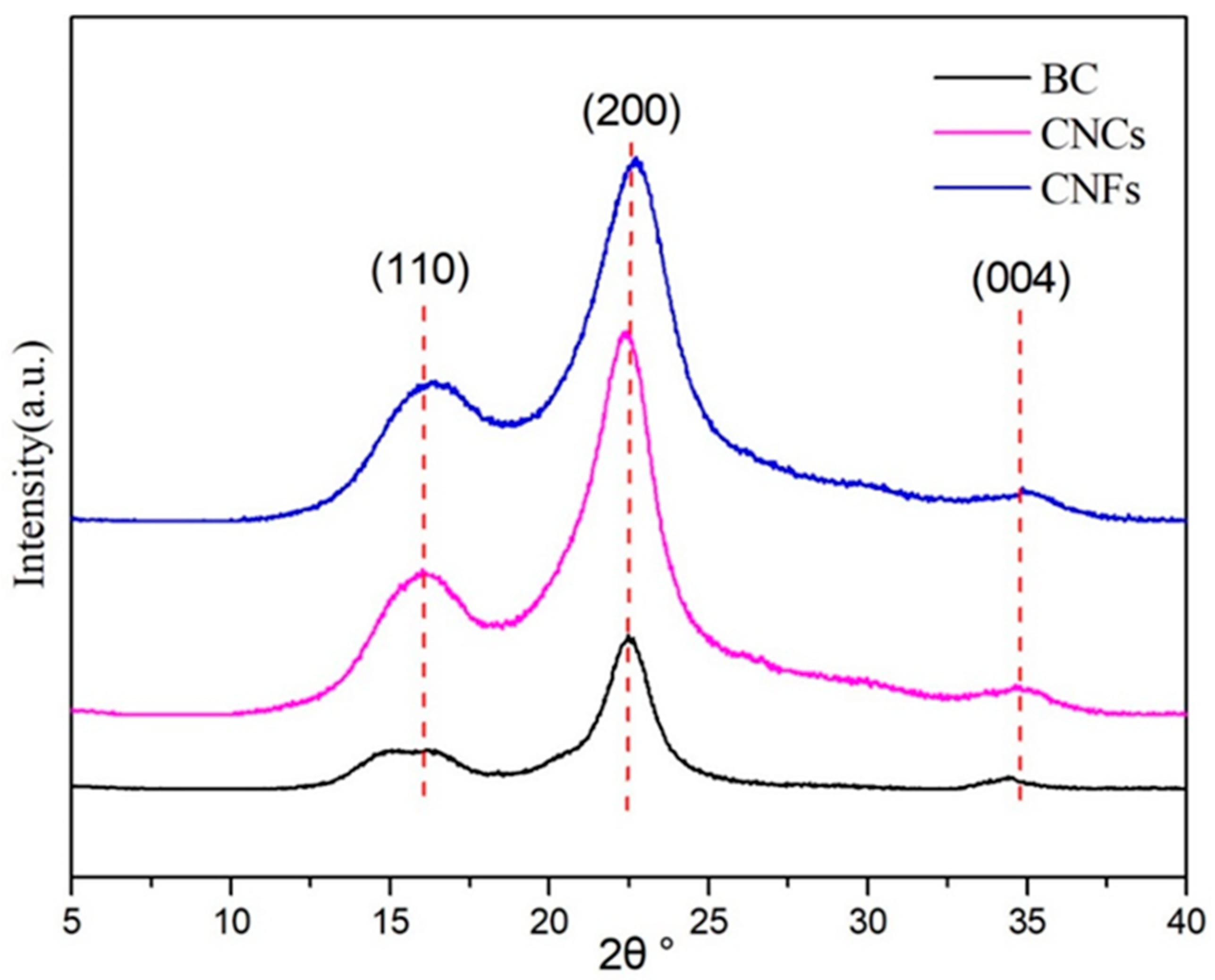
3.2. Crystal Structure Analysis of CNCs and CNFs
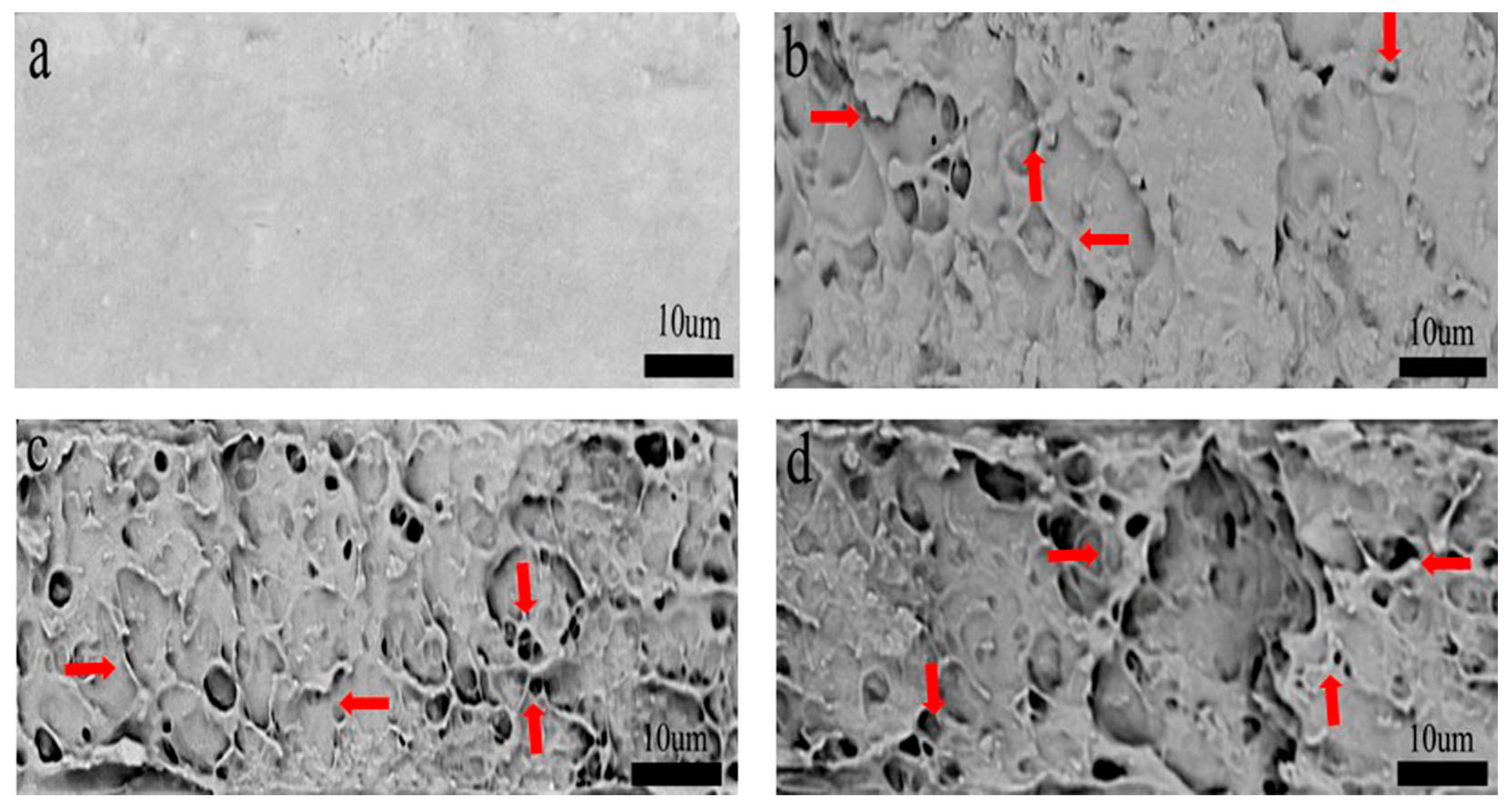
3.3. Fracture Morphology Analysis of Nanocellulose/PHB Composite Film
3.4. Crystal Structure Analysis of Nanocellulose/PHB Composite Film
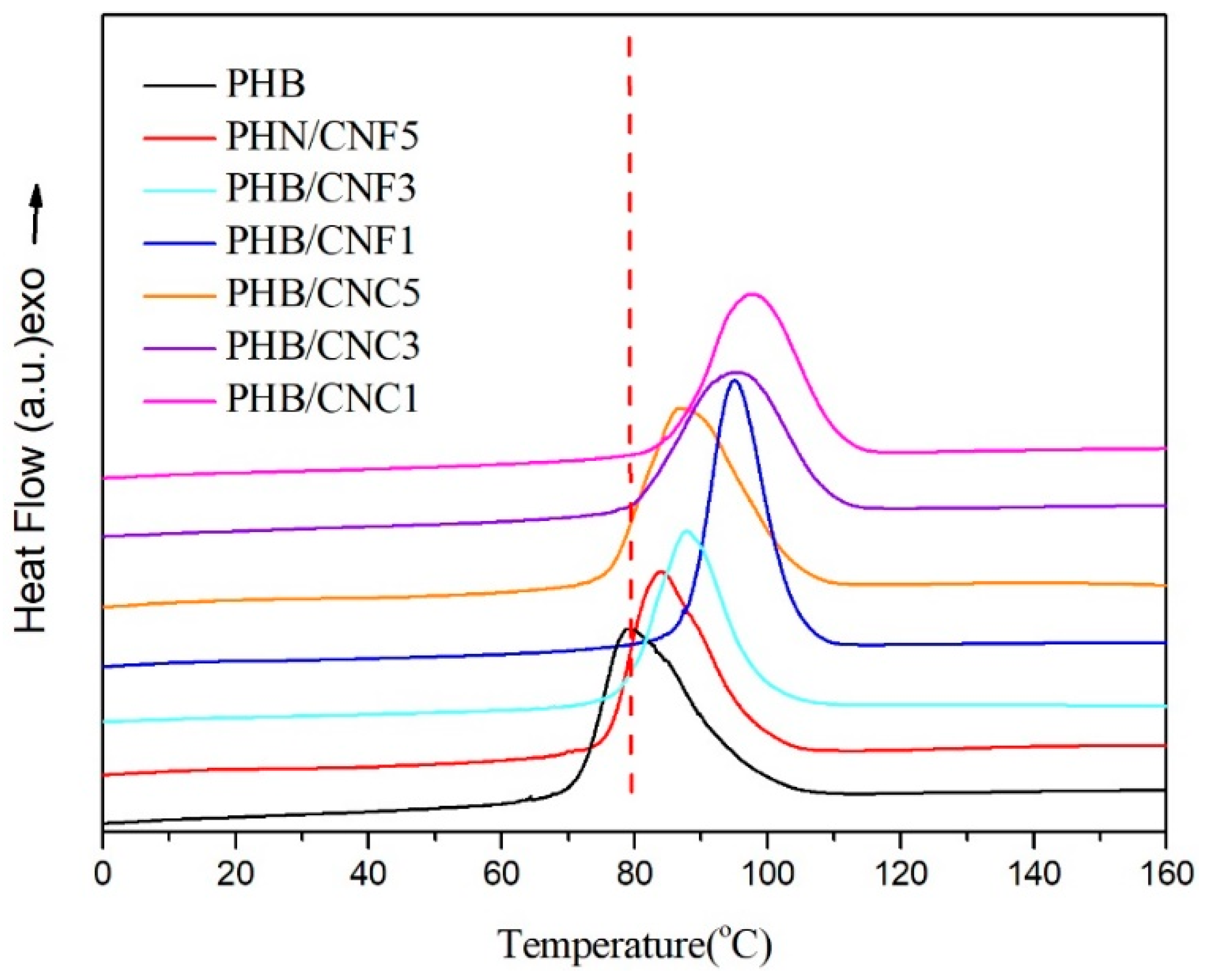
3.5. Melting and Non-Isothermal Crystallization Behavior of Nanocellulose/PHB Composite Film
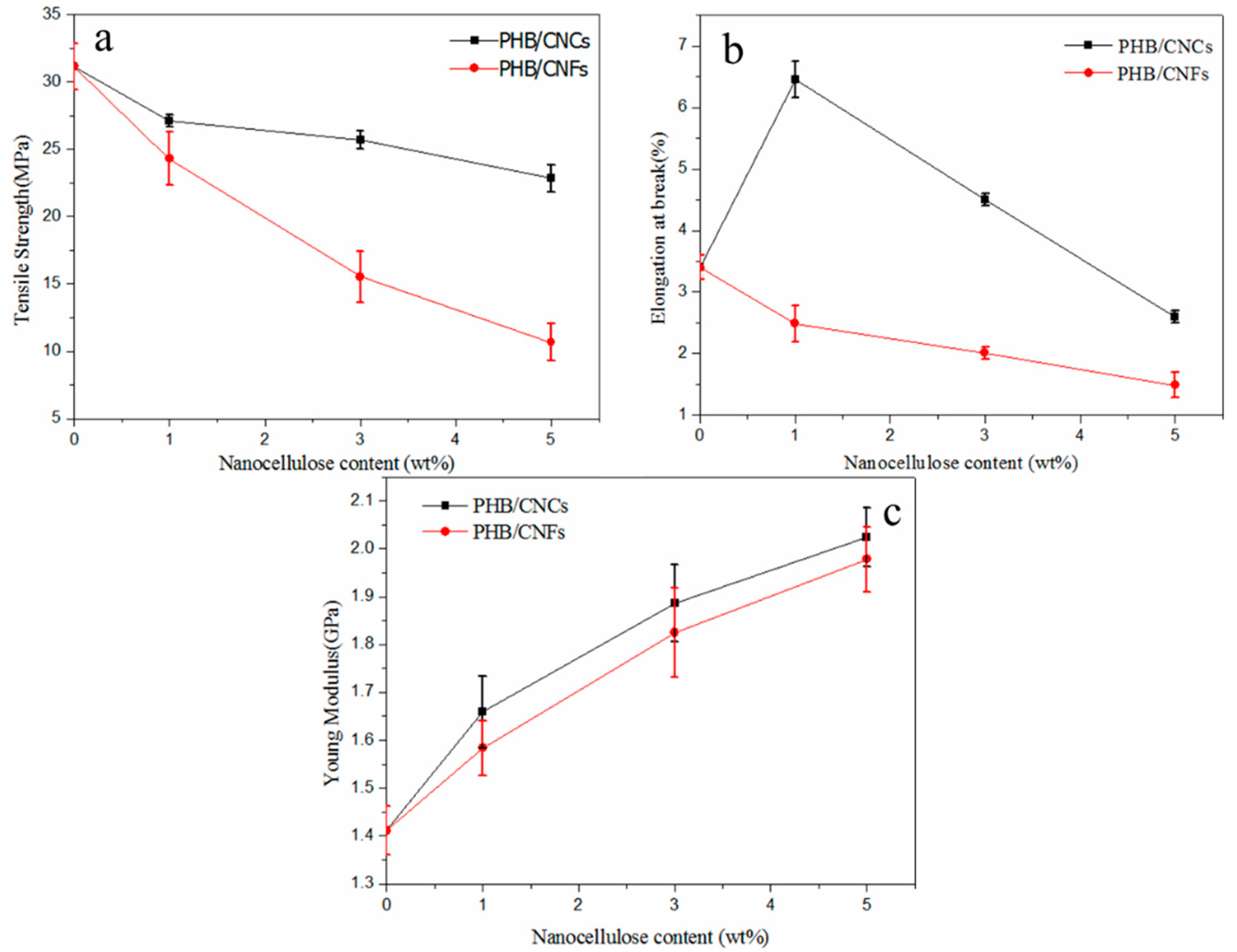
3.6. Effect of Nanocellulose on the Mechanical Properties of PHB
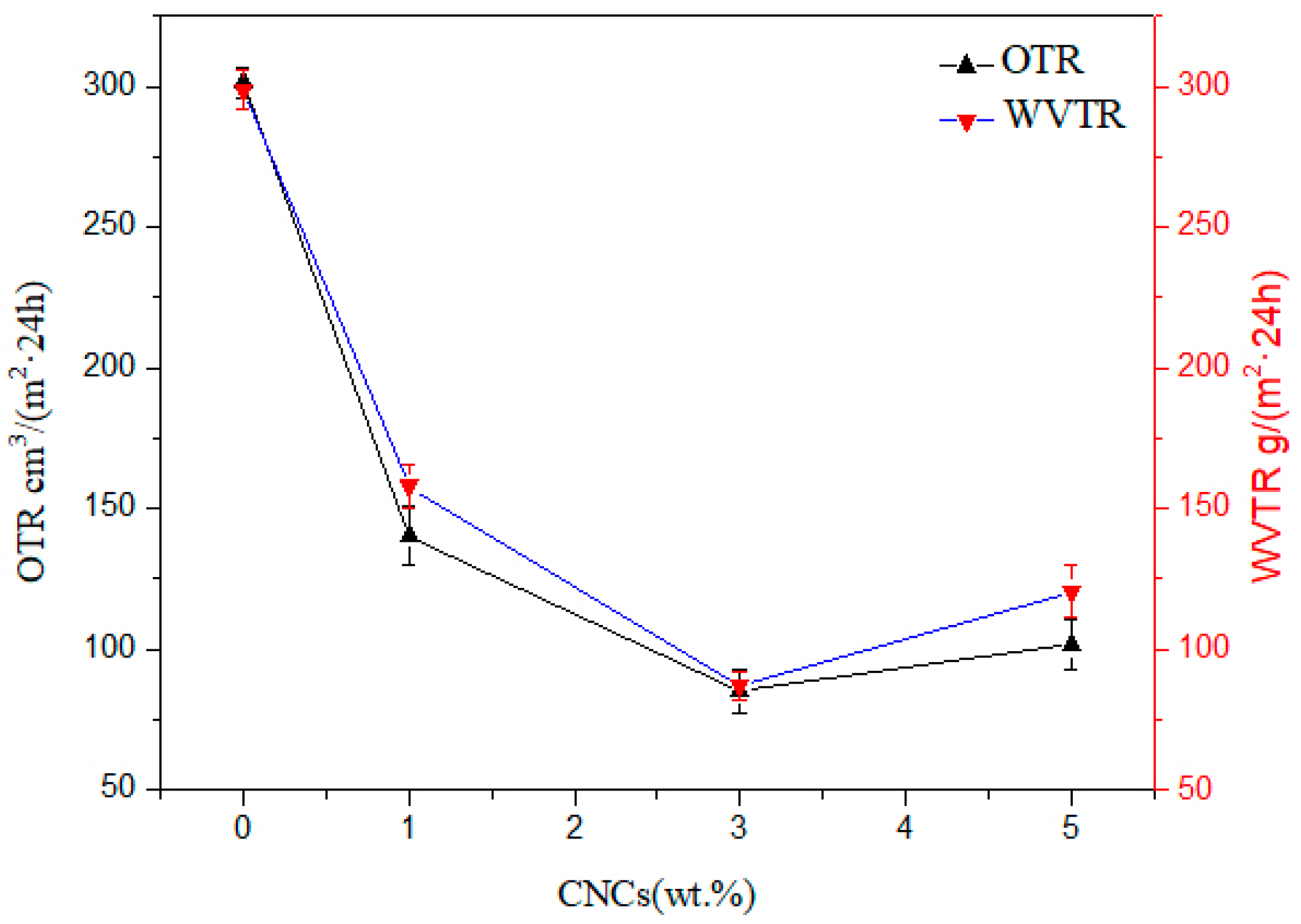
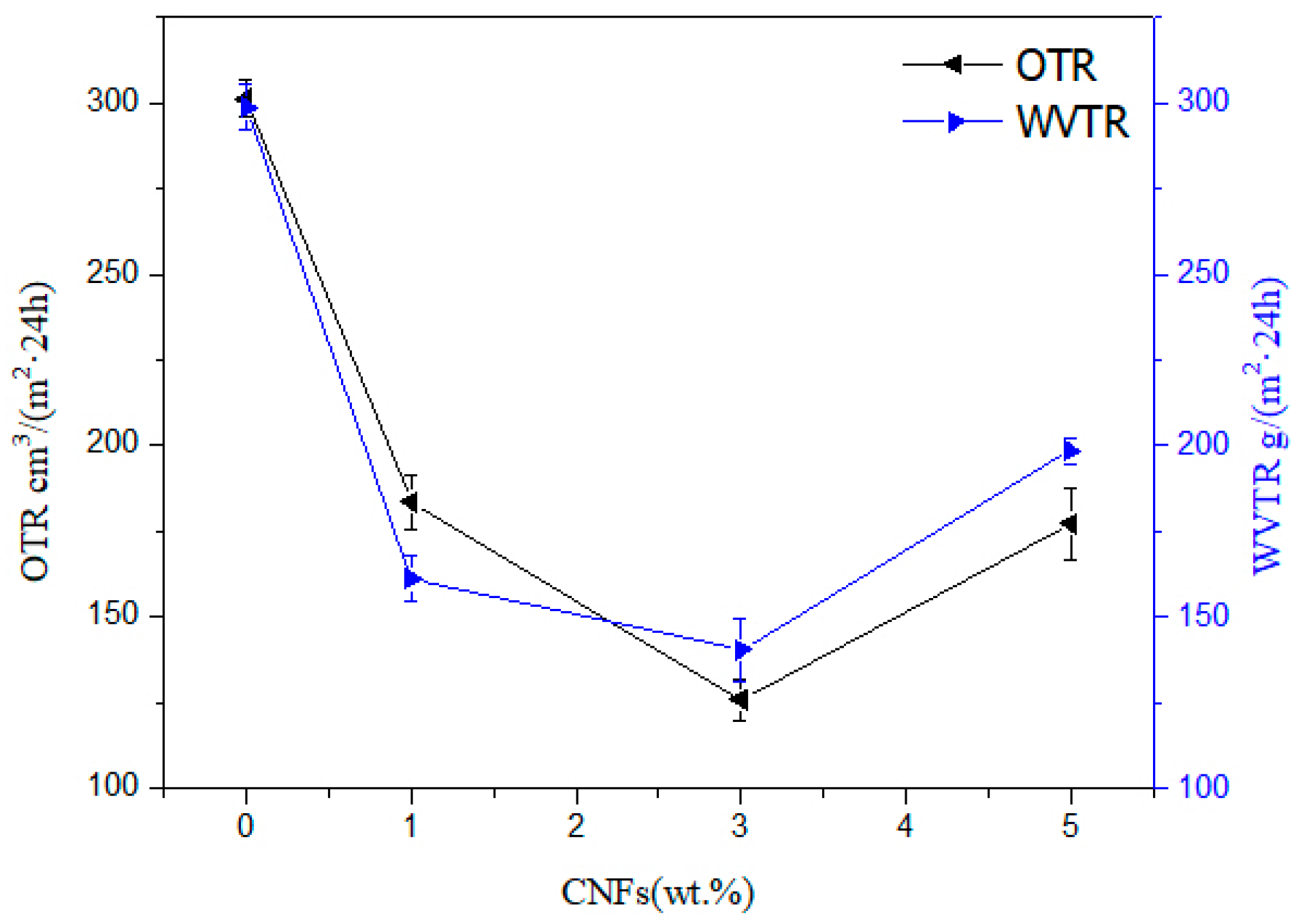
3.7. Barrier Properties of Nanocellulose/PHB Composite Film
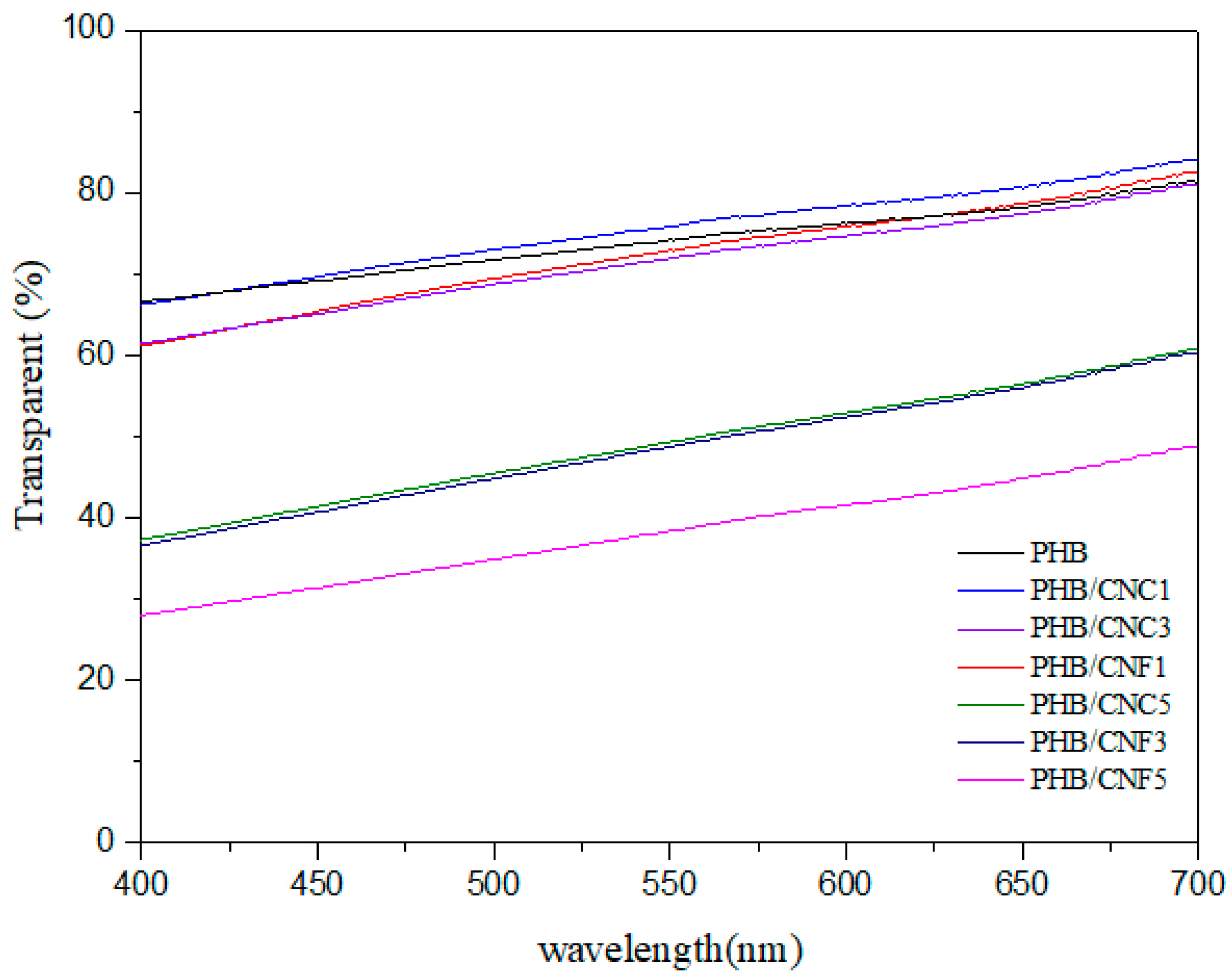
3.8. Transparency of Nanocellulose/PHB Composite Films
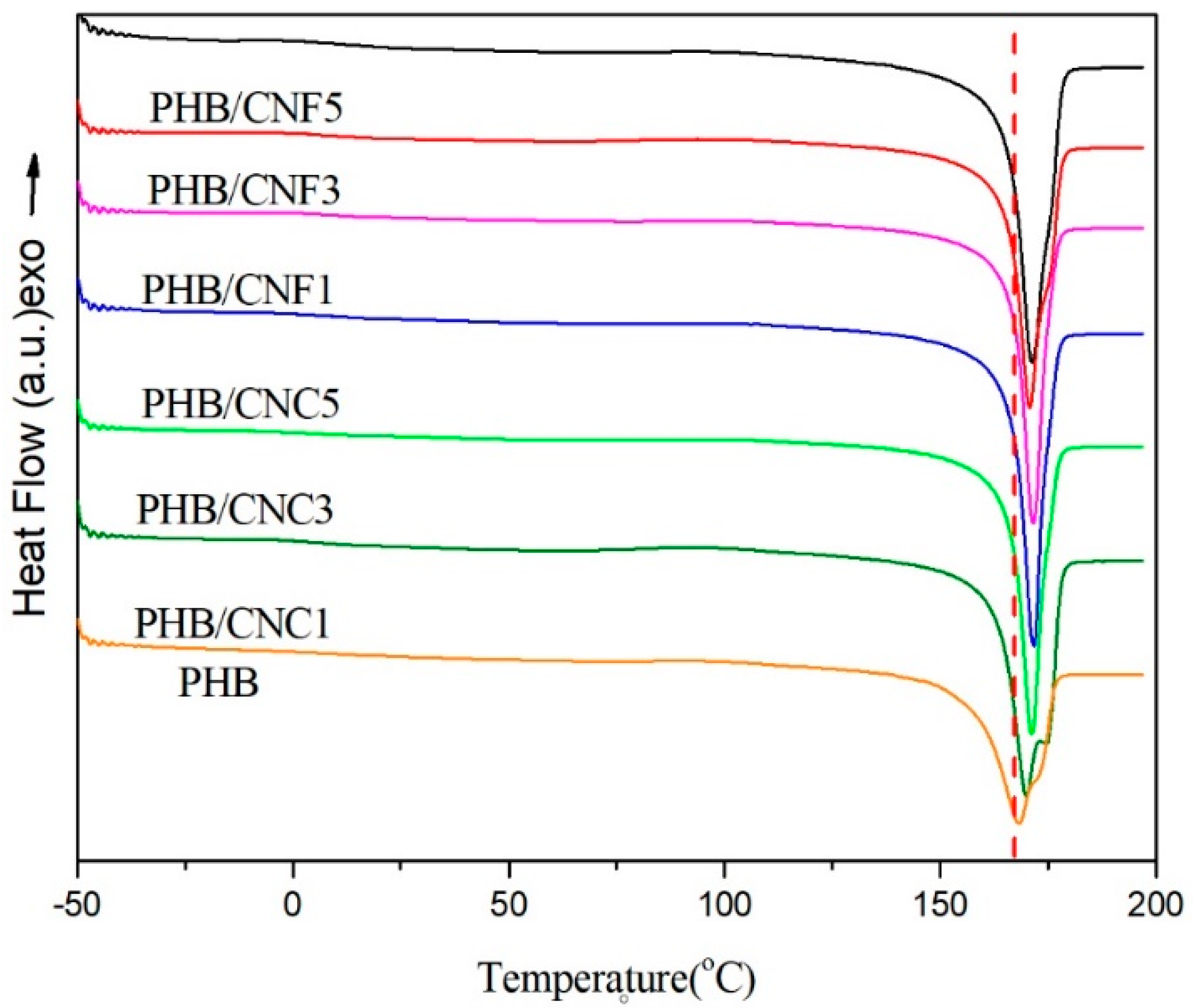
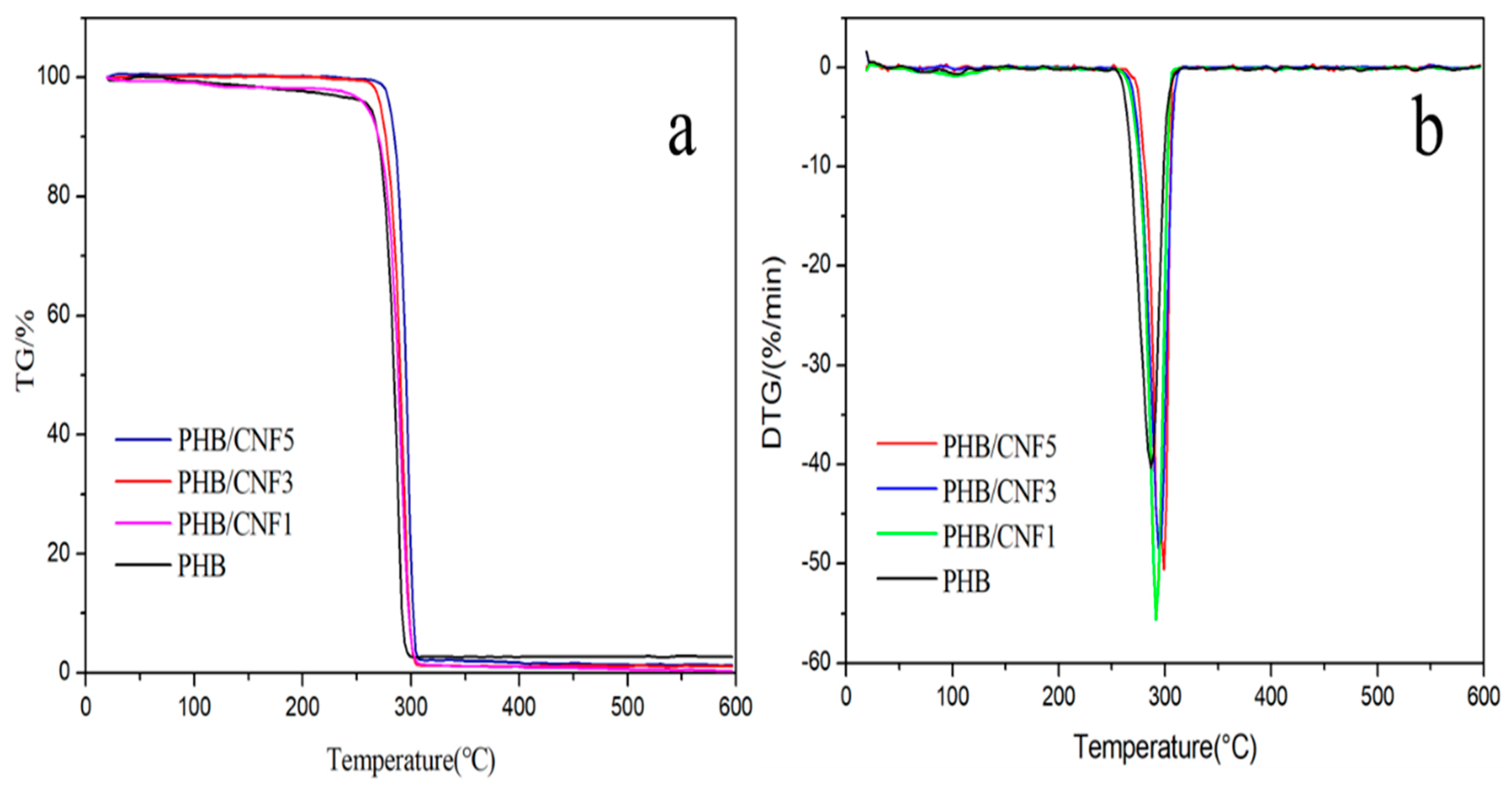
3.9. Thermal Stability of Nanocellulose/PHB Composite Films
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Utekar, P.; Gabale, H.; Khandelwal, A.; Mhaske, S.T. Hot-Melt Adhesives from Renewable Resources: A Critical Review. Rev. Adhes. Adhes. 2016, 4, 104–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, C.; Hamad, W.Y. Cellulose reinforced polymer composites and nanocomposites: A critical review. Cellulose 2013, 20, 2221–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopera-Valle, A.; Caputo, J.V.; Leao, R.; Sauvageau, D.; Luz, S.M.; Elias, A. Influence of Epoxidized Canola Oil (eCO) and Cellulose Nanocrystals (CNCs) on the Mechanical and Thermal Properties of Polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB)-Poly(lactic acid) (PLA) Blends. Polymers 2019, 11, 933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, K.C.C.D.; Montoro, S.R.; Cioffi, M.O.H.; Voorwald, H.J.C. Chapter 13—Polyhydroxyalkanoates and Their Nanobiocomposites With Cellulose Nanocrystals. In Design & Applications of Nanostructured Polymer Blends & Nanocomposite Systems; William Andrew Publishing: Boston, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 261–285. [Google Scholar]
- Chiulan, I.; Mihaela, P.D.; Nicoleta, F.A.; Teodorescu, M.; Nicolae, C.A.; Căşărică, A.; Tofan, V.; Sălăgeanu, A. Biocompatible polyhydroxyalkanoates/bacterial cellulose composites: Preparation, characterization and in vitro evaluation. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2016, 104, 2576–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teresita Seoane, I.; Beatriz Manfredi, L.; Paola Cyras, V.; Torre, L.; Fortunati, E.; Puglia, D. Effect of Cellulose Nanocrystals and Bacterial Cellulose on Disintegrability in Composting Conditions of Plasticized PHB Nanocomposites. Polymers 2017, 9, 561. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Xu, C.; Wu, D.; Pan, K.; Qian, A.; Sha, Y.; Wang, L.; Tong, W. Insights into the nucleation role of cellulose crystals during crystallization of poly( β -hydroxybutyrate). Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 134, 508–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Zhao, G.; Pan, M.; Zhuang, L.; Li, D.; Rui, Z. Crystallization and mechanical properties of reinforced PHBV composites using melt compounding: Effect of CNCs and CNFs. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 168, 255. [Google Scholar]
- Prakobna, K.; Galland, S.; Berglund, L.A. High-Performance and Moisture-Stable Cellulose-Starch Nanocomposites Based on Bioinspired Core-Shell Nanofibers. Biomacromolecules 2015, 16, 904–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Wang, S.; Rials, T.G. Poly(vinyl alcohol) nanocomposites reinforced with cellulose fibrils isolated by high intensity ultrasonication. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2009, 40, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santamaria-Echart, A.; Ugarte, L.; Arbelaiz, A.; Barreiro, F.; Angeles Corcuera, M.; Eceiza, A. Modulating the microstructure of waterborne polyurethanes for preparation of environmentally friendly nanocomposites by incorporating cellulose nanocrystals. Cellulose 2017, 24, 823–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Liu, M.; Gao, Q.; Yang, D.; Zhang, Z.; Xiong, X.; Yuan, J.; Xiang, Y.L. Design of Heterogeneous Nuclei Composed of Uniaxial Cellulose Nanocrystal Assemblies for Epitaxial Growth of Poly(ε-caprolactone). Macromolecules 2017, 50, 3355–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariano, M.; Pilate, F.; de Oliveira, F.B.; Khelifa, F.; Dubois, P.; Raquez, J.-M.; Dufresne, A. Preparation of Cellulose Nanocrystal-Reinforced Poly(lactic acid) Nanocomposites through Noncovalent Modification with PLLA-Based Surfactants. Acs Omega 2017, 2, 2678–2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saba, N.; Mohammad, F.; Pervaiz, M.; Jawaid, M.; Alothman, O.Y.; Sain, M. Mechanical, morphological and structural properties of cellulose nanofibers reinforced epoxy composites. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 97, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, T.; Bordeanu, N.; Strub, E. Properties of nanofibrillated cellulose from different raw materials and its reinforcement potential. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 79, 1086–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwamoto, S.; Nakagaito, A.N.; Yano, H. Nano-fibrillation of pulp fibers for the processing of transparent nanocomposites. Appl. Phys. A 2007, 89, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Cheng, Q. A novel process to isolate fibrils from cellulose fibers by high-intensity ultrasonication, Part 1: Process optimization. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 113, 1270–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nechyporchuk, O.; Belgacem, M.N.; Bras, J. Production of cellulose nanofibrils: A review of recent advances. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2016, 93, 2–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, W.; Holbery, J.; Li, K. A technique for production of nanocrystalline cellulose with a narrow size distribution. Cellulose 2009, 16, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samira, E.H.; Yoshiharu, N.; Jean-Luc, P.; Laurent, H.; Frédéric, D.; Cyrille, R. The shape and size distribution of crystalline nanoparticles prepared by acid hydrolysis of native cellulose. Biomacromolecules 2008, 9, 57–65. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Negi, Y.S.; Choudhary, V.; Bhardwaj, N. Sugarcane Bagasse: A Promising Source for the Production of Nano-Cellulose. J. Polym. Compos. 2014, 2, 23–27. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Negi, Y.S.; Choudhary, V.; Bhardwaj, N.K. Characterization of Cellulose Nanocrystals Produced by Acid-Hydrolysis from Sugarcane Bagasse as Agro-Waste. J. Mater. Phys. Chem. 2014, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Srithep, Y.; Ellingham, T.; Peng, J.; Sabo, R.; Clemons, C.; Turng, L.S.; Pilla, S. Melt compounding of poly (3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate)/nanofibrillated cellulose nanocomposites. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2013, 98, 1439–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherpinski, A.; Torres-Giner, S.; Vartiainen, J.; Peresin, M.S.; Lahtinen, P.; Lagaron, J.M. Improving the water resistance of nanocellulose-based films with polyhydroxyalkanoates processed by the electrospinning coating technique. Cellulose 2018, 25, 1291–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seoane, I.T.; Fortunati, E.; Puglia, D.; Cyras, V.P.; Manfredi, L.B. Development and characterization of bionanocomposites based on poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) and cellulose nanocrystals for packaging applications. Polym. Int. 2016, 65, 1046–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, H.; Lucia, L.A.; Rojas, O.J. Cellulose nanocrystals: Chemistry, self-assembly, and applications. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 3479–3500. [Google Scholar]
- Seoane, I.T.; Cerrutti, P.; Vazquez, A.; Manfredi, L.B.; Cyras, V.P. Polyhydroxybutyrate-Based Nanocomposites with Cellulose Nanocrystals and Bacterial Cellulose. J. Polym. Environ. 2017, 25, 586–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barham, P.J.; Keller, A.; Otun, E.L.; Holmes, P.A. Crystallization and morphology of a bacterial thermoplastic: Poly-3-hydroxybutyrate. J. Mater. Sci. 1984, 19, 2781–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroda, M.; Ohta, T.; Uchiyama, I.; Baba, T.; Yuzawa, H.; Kobayashi, I.; Cui, L.; Oguchi, A.; Aoki, K.; Nagai, Y. Whole genome sequencing of meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Lancet 2001, 357, 1225–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, F.B.; Bras, J.; Borges Pimenta, M.T.; da Silva Curvelo, A.A.; Belgacem, M.N. Production of cellulose nanocrystals from sugarcane bagasse fibers and pith. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2016, 93, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.M.; Revol, J.F.; Gray, D.G. Effect of microcrystallite preparation conditions on the formation of colloid crystals of cellulose. Cellulose 1998, 5, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Yu, H.; Liu, Y.; Chen, P.; Zhang, M.; Hai, Y. Individualization of cellulose nanofibers from wood using high-intensity ultrasonication combined with chemical pretreatments. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 1804–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gicquel, E.; Bras, J.; Rey, C.; Putaux, J.-L.; Pignon, F.; Jean, B.; Martin, C. Impact of sonication on the rheological and colloidal properties of highly concentrated cellulose nanocrystal suspensions. Cellulose 2019, 26, 7619–7634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlem, M.A.; Borsoi, C.; Hansen, B.; Catto, A.L. Evaluation of different methods for extraction of nanocellulose from yerba mate residues. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 218, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goswami, N.; Lin, F.; Liu, Y.; Leong, D.T.; Xie, J. Highly Luminescent Thiolated Gold Nanoclusters Impregnated in Nanogel. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 4009–4016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Renneckar, S. Supramolecular Structure Characterization of Molecularly Thin Cellulose I Nanoparticles. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 650–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodin, A.; Backdahl, H.; Risberg, B.; Gatenholm, P. Nano cellulose as a scaffold for tissue engineered blood vessels. Tissue Eng. 2007, 13, 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Abraham, E.; Deepa, B.; Pothen, L.A.; Cintil, J.; Thomas, S.; John, M.J.; Anandjiwala, R.; Narine, S.S. Environmental friendly method for the extraction of coir fibre and isolation of nanofibre. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 92, 1477–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirayil, C.J.; Joy, J.; Mathew, L.; Mozetic, M.; Koetz, J.; Thomas, S. Isolation and characterization of cellulose nanofibrils from Helicteres isora plant. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2014, 59, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.-S.; Zhu, M.-F.; Wu, W.-H.; Qin, Z.-Y. Reducing the formation of six-membered ring ester during thermal degradation of biodegradable PHBV to enhance its thermal stability. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2009, 94, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, N.; Dufresne, A. Physical and/or Chemical Compatibilization of Extruded Cellulose Nanocrystal Reinforced Polystyrene Nanocomposites. Macromolecules 2013, 46, 5570–5583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhar, P.; Bhardwaj, U.; Kumar, A.; Katiyar, V. Poly (3-hydroxybutyrate)/cellulose nanocrystal films for food packaging applications: Barrier and migration studies. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2015, 55, 2388–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, M.D.; Li, J.; Yang, J.; Liu, J.J.; Tong, X.; Cheng, H.M. The morphology and thermal properties of multi-walled carbon nanotube and poly(hydroxybutyrate-co-hydroxyvalerate) composite. Polym. Int. 2004, 53, 1479–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Guo, L.; Sato, H.; Ozaki, Y.; Yan, S.; Takahashi, I. A study on the crystallization behavior of poly(β-hydroxybutyrate) thin films on Si wafers. Polymers 2011, 52, 3865–3870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mottin, A.C.; Ayres, E.; Oréfice, R.L.; Câmara, J.J.D. What Changes in Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate) (PHB) When Processed as Electrospun Nanofibers or Thermo-Compression Molded Film? Mater. Res. 2016, 19, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ten, E.; Jiang, L.; Wolcott, M.P. Preparation and properties of aligned poly(3-hydroxybutyrate- co -3-hydroxyvalerate)/cellulose nanowhiskers composites. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 92, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janne, L.; Junji, S.; Malin, G.; Linda, F.; Markus, L.; Teeri, T.T. The binding specificity and affinity determinants of family 1 and family 3 cellulose binding modules. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 484–489. [Google Scholar]
- Fortunati, E.; Peltzer, M.; Armentano, I.; Torre, L.; Jiménez, A.; Kenny, J.M. Effects of modified cellulose nanocrystals on the barrier and migration properties of PLA nano-biocomposites. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 90, 948–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthet, M.A.; Angellier-Coussy, H.; Chea, V.; Guillard, V.; Gastaldi, E.; Gontard, N. Sustainable food packaging: Valorising wheat straw fibres for tuning PHBV-based composites properties. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2015, 72, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhar, P.; Bhardwaj, U.; Kumar, A.; Katiyar, V. Investigations on Rheological and Mechanical Behavior of Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate)/Cellulose Nanocrystal Based Nanobiocomposites. Polym. Compos. 2017, 38, E392–E401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, U.; Dhar, P.; Kumar, A.; Katiyar, V. Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA)-Cellulose Based Nanobiocomposites for Food Packaging Applications. In Food Additives and Packaging; American Chemical Society: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 275–314. [Google Scholar]
- Fraga, A.; Ruseckaite, R.A.; Jiménez, A. Thermal degradation and pyrolysis of mixtures based on poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-8%-3-hydroxyvalerate) and cellulose derivatives. Polym. Test. 2005, 24, 526–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhena, T.C.; Sefadi, J.S.; Sadiku, E.R.; John, M.J.; Mochane, M.J.; Mtibe, A. Thermoplastic Processing of PLA/Cellulose Nanomaterials Composites. Polymers 2018, 10, 1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Sample Serial Number | PHB (wt %) | Percentage of Absolute Dry Mass and PHB Mass of Nanocellulose (wt %) |
|---|---|---|
| PHB | 100 | 0 |
| PHBCNC1 | 100 | 1 |
| PHBCNC3 | 100 | 3 |
| PHBCNC5 | 100 | 5 |
| PHBCNF1 | 100 | 1 |
| PHBCNF3 | 100 | 3 |
| PHBCNF5 | 100 | 5 |
| Sample | Crystallinity (%) |
|---|---|
| PHB | 56.61 |
| PHB/CNC1 | 54.6 |
| PHB/CNC3 | 56.85 |
| PHB/CNC5 | 59.37 |
| PHB/CNF1 | 57.9 |
| PHB/CNF3 | 59.5 |
| PHB/CNF5 | 60.1 |
| Sample | Second Melting | First Melting | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tm/°C | ΔHm/(J/g) | Xc/% | Tc /°C | |
| PHB | 168.2 | 94.6 | 64.8 | 79.2 |
| PHB/CNC1 | 169.5 | 88.3 | 61.1 | 97.5 |
| PHB/CNC3 | 170.9 | 90.8 | 64.2 | 96.1 |
| PHB/CNC5 | 171.0 | 93.1 | 67.1 | 86.8 |
| PHB/CNF1 | 170.8 | 91.2 | 63.1 | 94.8 |
| PHB/CNF3 | 171.3 | 94.8 | 66.9 | 87.5 |
| PHB/CNF5 | 172.5 | 96,8 | 69.8 | 83.5 |
| Sample | Transmittance (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 400 nm | 500 nm | 600 nm | 700 nm | |
| PHB | 66.69 | 71.84 | 76.25 | 82.56 |
| PHB/CNC1 | 66.3 | 73.04 | 78.43 | 84.14 |
| PHB/CNC3 | 61.46 | 69.47 | 75.83 | 81.42 |
| PHB/CNC5 | 37.36 | 45.52 | 52.96 | 60.85 |
| PHB/CNF1 | 61.2 | 68.76 | 74.71 | 81.06 |
| PHB/CNF3 | 36.69 | 44.85 | 52.45 | 60.44 |
| PHB/CNF5 | 28.08 | 34.93 | 41.6 | 48.88 |
| Sample | T0/°C | Tmax/°C | 600 °C Residual Ash (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PHB | 254.0 | 286.5 | 1.12 |
| PHB/CNC1 | 254.1 | 288.4 | 0.97 |
| PHB/CNC3 | 250.7 | 290.2 | 1.01 |
| PHB/CNC5 | 252.7 | 291.7 | 1.76 |
| PHB/CNF1 | 254.4 | 291.4 | 2.42 |
| PHB/CNF3 | 255.2 | 294.6 | 2.86 |
| PHB/CNF5 | 255.6 | 298.2 | 1.17 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, B.; Huang, C.; Zhao, H.; Wang, J.; Yin, C.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, Y. Effects of Cellulose Nanocrystals and Cellulose Nanofibers on the Structure and Properties of Polyhydroxybutyrate Nanocomposites. Polymers 2019, 11, 2063. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11122063
Zhang B, Huang C, Zhao H, Wang J, Yin C, Zhang L, Zhao Y. Effects of Cellulose Nanocrystals and Cellulose Nanofibers on the Structure and Properties of Polyhydroxybutyrate Nanocomposites. Polymers. 2019; 11(12):2063. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11122063
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Bobo, Chongxing Huang, Hui Zhao, Jian Wang, Cheng Yin, Lingyun Zhang, and Yuan Zhao. 2019. "Effects of Cellulose Nanocrystals and Cellulose Nanofibers on the Structure and Properties of Polyhydroxybutyrate Nanocomposites" Polymers 11, no. 12: 2063. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11122063
APA StyleZhang, B., Huang, C., Zhao, H., Wang, J., Yin, C., Zhang, L., & Zhao, Y. (2019). Effects of Cellulose Nanocrystals and Cellulose Nanofibers on the Structure and Properties of Polyhydroxybutyrate Nanocomposites. Polymers, 11(12), 2063. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11122063