Micellization of Pluronic P123 in Water/Ethanol/Turpentine Oil Mixed Solvents: Hybrid Particle–Field Molecular Dynamic Simulation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Simulation Method
2.2. Coarse-Grained (CG) Model
3. Results and Discussion
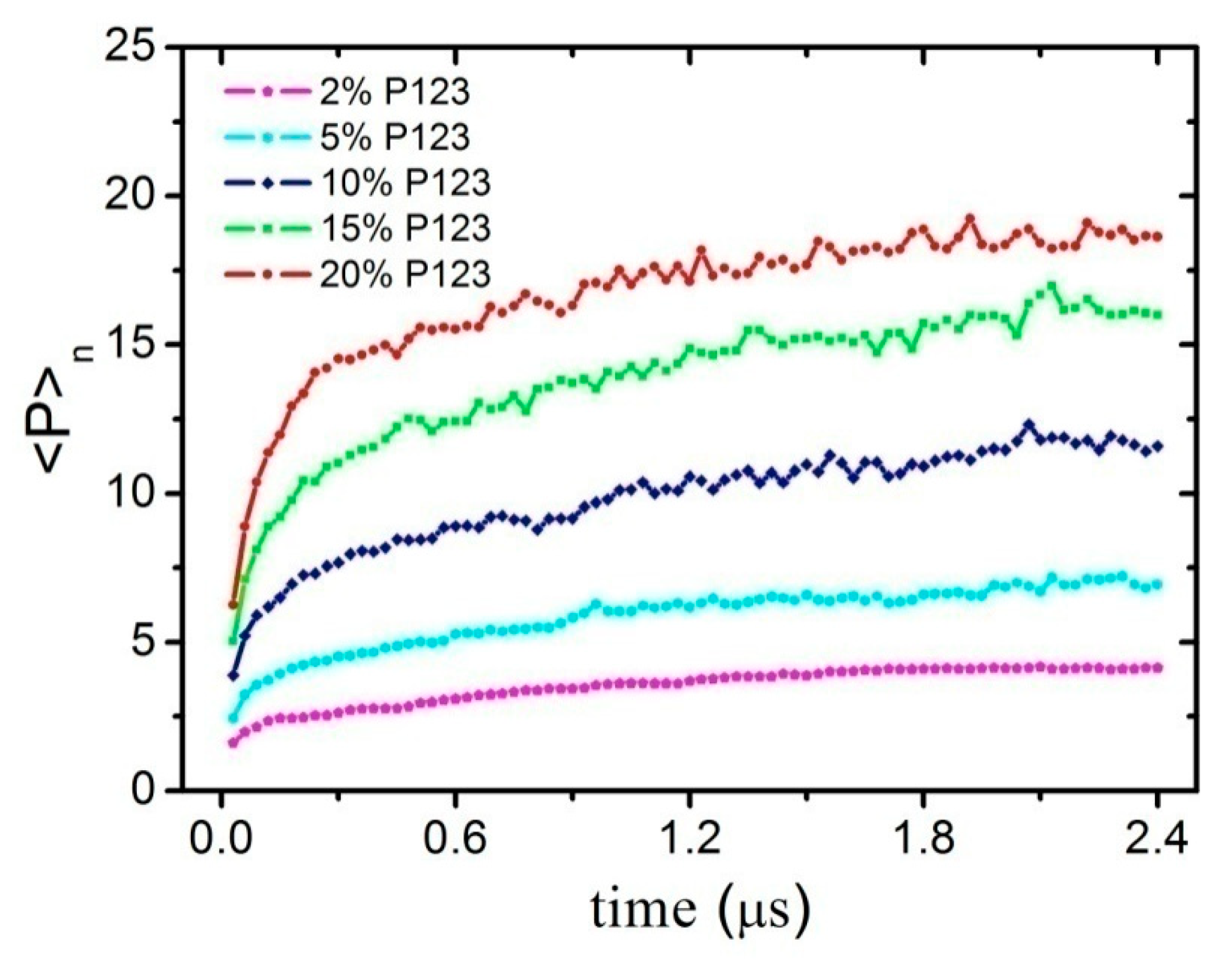
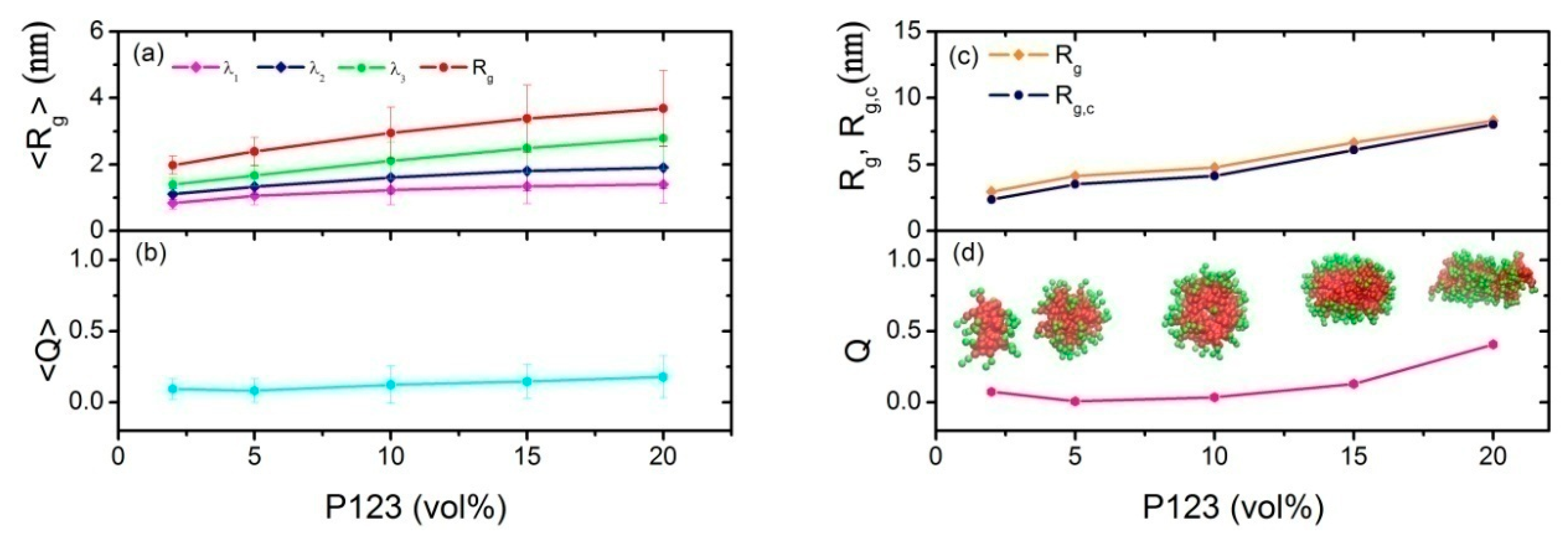
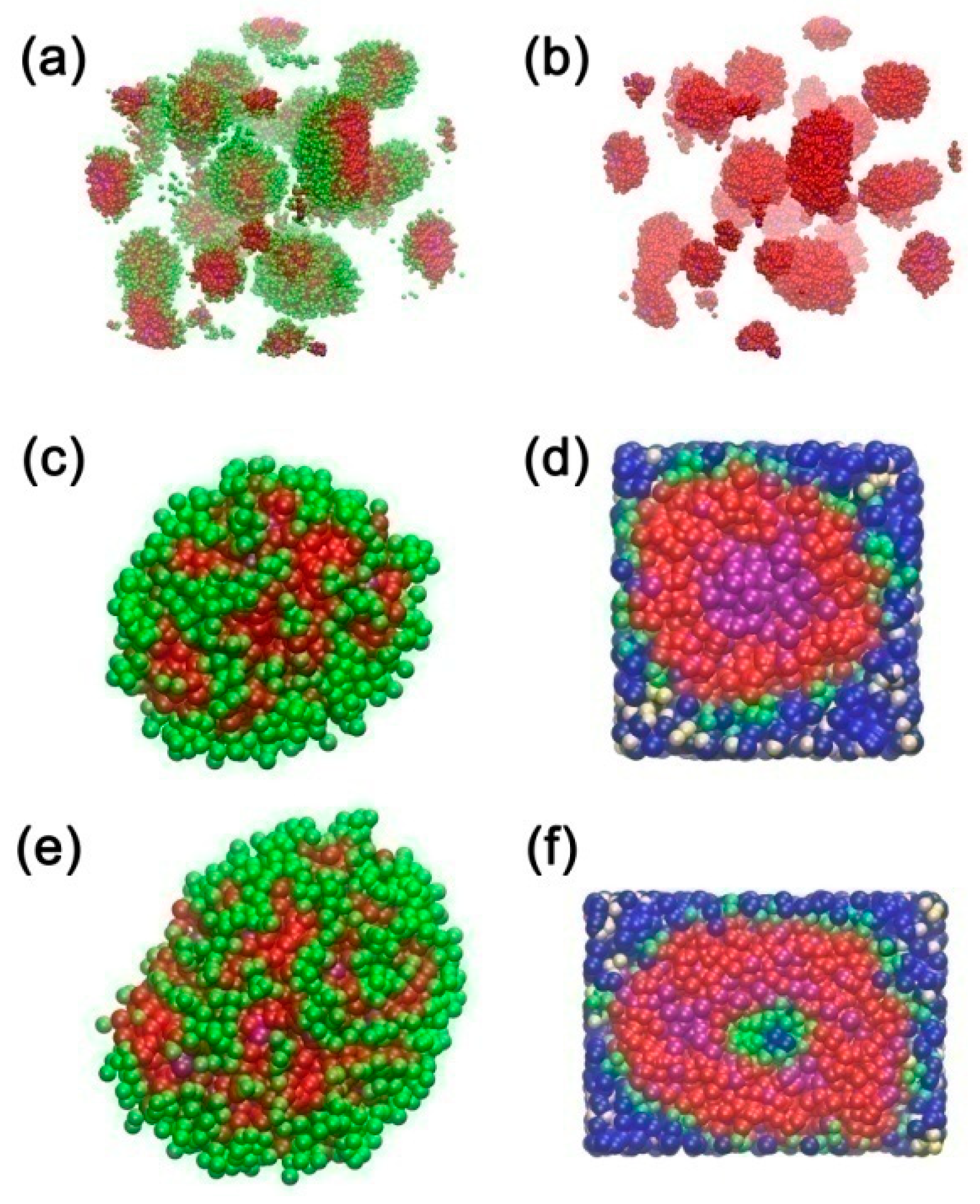
3.1. Effect of Concentration on the Micelles Structure of P123 in Water
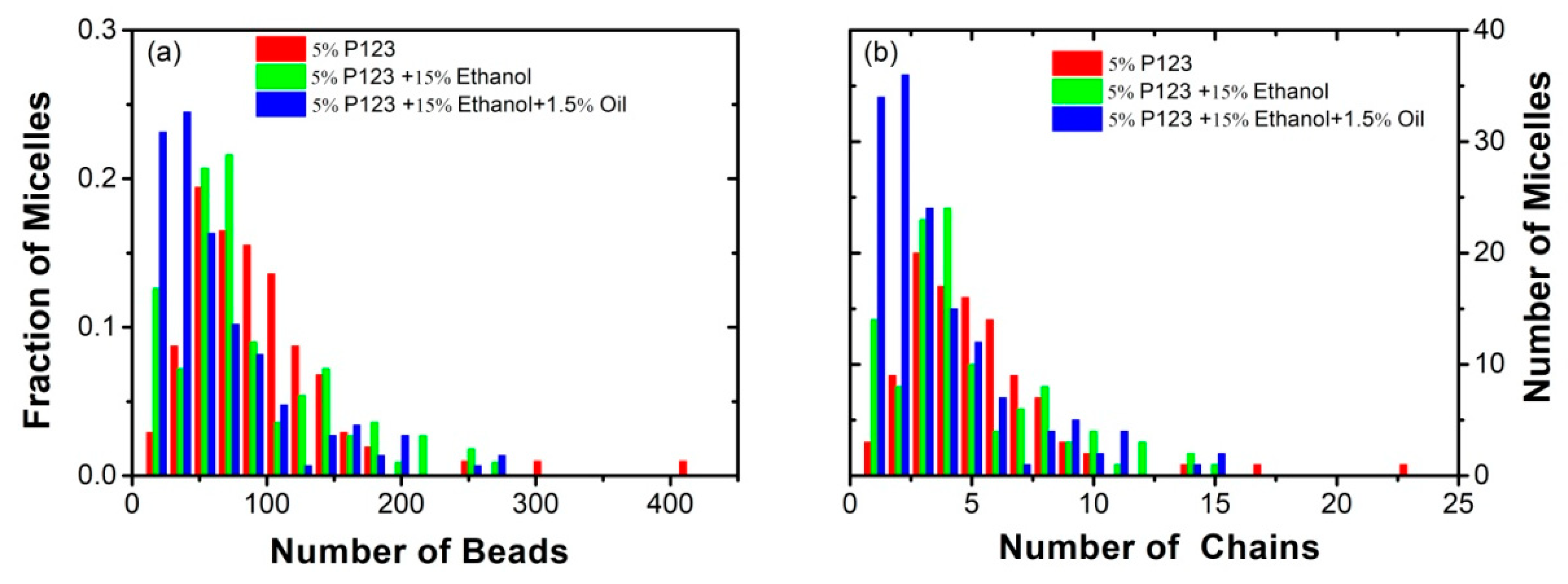
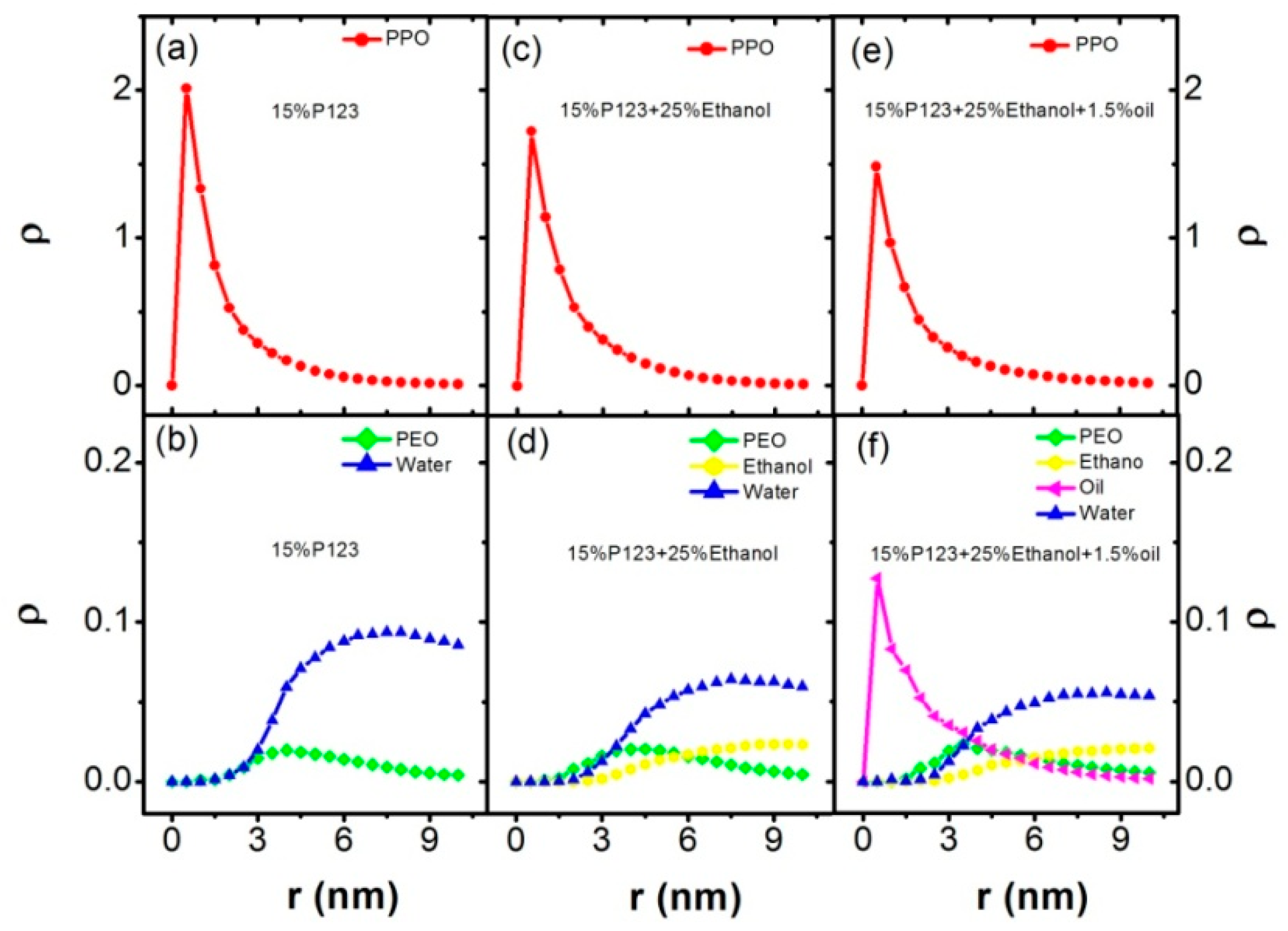
3.2. Effect of Ethanol on the Micelles Structure of P123 in the Mixed Ethanol-Water Solvent
3.3. Effect of Turpentine Oil on the Micelles’ Structure of P123 in the Mixed Solvent
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kundu, A.; Verma, P.K.; Cho, M. Role of solvent water in the temperature-induced self-assembly of a triblock copolymer. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2017, 8, 3040–3047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X. Amphiphilic building blocks for self-assembly: From amphiphiles to supra-amphiphiles. Acc. Chem. Res. 2012, 45, 608–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mai, Y.; Eisenberg, A. Self-Assembly of block copolymers. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 5969–5985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atanase, L.; Riess, G. Self-Assembly of block and graft copolymers in organic solvents: An overview of recent advances. Polymers 2018, 10, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parent, L.R.; Bakalis, E.; Ramírez-Hernández, A.; Kammeyer, J.K.; Park, C.; de Pablo, J.; Zerbetto, F.; Patterson, J.P.; Gianneschi, N.C. Directly observing micelle fusion and growth in solution by liquid-cell transmission electron microscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 17140–17151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nace, V. Contrasts in the surface activity of polyoxypropylene and polyoxybutylene-based block copolymer surfactants. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1996, 73, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmolka, I.R. Artificial skin I. Preparation and properties of pluronic F-127 gels for treatment of burns. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1972, 6, 571–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batrakova, E.V.; Kabanov, A.V. Pluronic block copolymers: Evolution of drug delivery concept from inert nanocarriers to biological response modifiers. J. Control. Release 2008, 130, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yasuda, S.; Townsend, D.; Michele, D.E.; Favre, E.G.; Day, S.M.; Metzger, J.M. Dystrophic heart failure blocked by membrane sealant poloxamer. Nature 2005, 436, 1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, G.G.; Dimer, F.A.; Guterres, S.S.; Kechinski, C.P.; Granada, J.E.; Cardozo, N.S.M. Formulation and characterization of poloxamer 407®: Thermoreversible gel containing polymeric microparticles and hyaluronic acid. Quim. Nova 2013, 36, 1121–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, U.; Goliaei, A.; Tsereteli, L.; Berkowitz, M.L. Properties of poloxamer molecules and poloxamer micelles dissolved in water and next to lipid bilayers: Results from computer simulations. J. Phys. Chem. B 2016, 120, 5823–5830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houang, E.M.; Bates, F.S.; Sham, Y.Y.; Metzger, J.M. All-Atom molecular dynamics-based analysis of membrane-stabilizing copolymer interactions with lipid bilayers probed under constant surface tensions. J. Phys. Chem. B 2017, 121, 10657–10664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rikiyama, K.; Horiuchi, T.; Koga, N.; Sanada, Y.; Watanabe, K.; Aida, M.; Katsumoto, Y. Micellization of poly (ethylene oxide)-poly (propylene oxide) alternating multiblock copolymers in water. Polymer 2018, 156, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Liu, T.; Chu, B.; Schneider, D.K.; Graziano, V. Characterization of the PEO− PPO− PEO triblock copolymer and its application as a separation medium in capillary electrophoresis. Macromolecules 1997, 30, 4574–4583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanka, G.; Hoffmann, H.; Ulbricht, W. Phase diagrams and aggregation behavior of poly (oxyethylene)-poly (oxypropylene)-poly (oxyethylene) triblock copolymers in aqueous solutions. Macromolecules 1994, 27, 4145–4159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandridis, P.; Nivaggioli, T.; Hatton, T.A. Temperature effects on structural properties of Pluronic P104 and F108 PEO-PPO-PEO block copolymer solutions. Langmuir 1995, 11, 1468–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Alexandridis, P. Micellization thermodynamics of Pluronic P123 (EO20PO70EO20) amphiphilic block copolymer in aqueous ethylammonium nitrate (EAN) solutions. Polymers 2017, 10, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaibundit, C.; Ricardo, N.M.; Ricardo, N.M.; Costa, F.V.D.M.; Wong, M.G.; Hermida-Merino, D.; Rodriguez-Perez, J.; Hamley, I.W.; Yeates, S.G.; Booth, C. Effect of ethanol on the micellization and gelation of pluronic P123. Langmuir 2008, 24, 12260–12266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandridis, P.; Yang, L. SANS investigation of polyether block copolymer micelle structure in mixed solvents of water and formamide, ethanol, or glycerol. Macromolecules 2000, 33, 5574–5587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chat, O.A.; Nazir, N.; Bhat, P.A.; Hassan, P.; Aswal, V.; Dar, A.A. Aggregation and rheological behavior of the lavender oil–pluronic P123 microemulsions in water–ethanol mixed solvents. Langmuir 2017, 34, 1010–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, R.; Kunwar, A.; Kota, S.; Kumar, S.; Aswal, V. Micellar structural transitions and therapeutic properties in tea tree oil solubilized pluronic P123 solution. Colloid Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 537, 478–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qavi, S.; Firestone, M.; Foudazi, R. Elasticity and yielding of mesophases of block copolymers in water-oil mixtures. Soft Matter. 2019, 15, 5626–5637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Bautista, M.C.; Avendaño-Alejo, M.; Castañeda, L.; Peralta-Ángeles, J.A.; Reyes-Esqueda, J.A. Study of nonlinear properties of N-(2-hydroxyphenyl)-2-propylpentanamide in polymeric solution. Optik 2019, 180, 724–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, V.; Bharatiya, B.; Patel, V.; Mishra, M.; Shukla, A.; Shah, D. Interaction of salicylic acid analogues with Pluronic® micelles: Investigations on micellar growth and morphological transition. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 277, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Droghetti, H.; Pagonabarraga, I.; Carbone, P.; Asinari, P.; Marchisio, D. Dissipative particle dynamics simulations of tri-block co-polymer and water: Phase diagram validation and microstructure identification. J. Chem. Phys. 2018, 149, 184903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, P.; Li, X.; Kou, D.; Deng, M.; Liang, H. Complex micelles from the self-assembly of amphiphilic triblock copolymers in selective solvents. J. Chem. Phys. 2010, 132, 204905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, J.-H.; Fan, Z.-X.; Ma, Z.-X. Dissipative particle dynamics simulations on self-assembly of rod-coil-rod triblock copolymers in a rod-selective solvent. J. Chem. Phys. 2013, 139, 064905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo-Shen, X.; Ying, Z.; Shen, X.L.; Yue, C.; Yin, X.M.; Wang, X.P.; Yuan, Q.; Nai-Sen, Y.; Dong, B. Dissipative particle dynamics simulation of multicompartment micelles self-assembled from a blend of triblock copolymers and diblock copolymers in an aqueous solution. Acta Physico Chimica Sinica 2014, 30, 646–653. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Xie, Y.; Zhong-Yuan, L.; Sun, C.C. Dissipative particle dynamics simulation of physical gelation behavior of P123(PEO (20)-PPO (70)-PEO (20)) block copolymer aqueous solution. Chem. J. Chin. Univ. Chin. 2009, 30, 2455–2459. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; You, L.-Y.; Lu, Z.-Y.; Sun, C.-C. Dissipative particle dynamics study on the multicompartment micelles self-assembled from the mixture of diblock copolymer poly (ethyl ethylene)-block-poly (ethylene oxide) and homopolymer poly (propylene oxide) in aqueous solution. Polymer 2009, 50, 5333–5340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Chen, X.; Yang, C.; Zhang, G. Mesoscopic simulation on phase behavior of pluronic P123 aqueous solution. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 13937–13942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Xie, T.; Jiang, R.; Wang, Z.; Yin, Y.; Li, B.; Shi, A.-C. Effect of chain architecture on self-assembled aggregates from cyclic AB diblock and linear ABA triblock copolymers in solution. Langmuir 2018, 34, 4013–4023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Yu, H.; Du, H.; Jiang, W. Effect of selective solvent addition rate on the pathways for spontaneous vesicle formation of ABA amphiphilic triblock copolymers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 1144–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milano, G.; Kawakatsu, T. Hybrid particle-field molecular dynamics simulations for dense polymer systems. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 130, 214106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; De Nicola, A.; Kawakatsu, T.; Milano, G. Hybrid particle-field molecular dynamics simulations: Parallelization and benchmarks. J. Comput. Chem. 2012, 33, 868–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Nicola, A.; Zhao, Y.; Kawakatsu, T.; Roccatano, D.; Milano, G. Hybrid particle-field coarse-grained models for biological phospholipids. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2011, 7, 2947–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzirusso, A.; De Nicola, A.; Sevink, G.A.; Correa, A.; Cascella, M.; Kawakatsu, T.; Rocco, M.; Zhao, Y.; Celino, M.; Milano, G. Biomembrane solubilization mechanism by Triton X-100: A computational study of the three stage model. PCCP 2017, 19, 29780–29794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Nicola, A.; Kawakatsu, T.; Rosano, C.; Celino, M.; Rocco, M.; Milano, G. Self-Assembly of triton X-100 in water solutions: A multiscale simulation study linking mesoscale to atomistic models. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2015, 11, 4959–4971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Nicola, A.; Kawakatsu, T.; Milano, G. A hybrid particle-field coarse-grained molecular model for pluronics water mixtures. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2013, 214, 1940–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Milano, G.; Cong, Y.; Yu, N.; He, Y.; Cong, Y.; Yuan, Q.; Dong, B. Self-Assembled morphologies and percolation probability of mixed carbon fillers in the diblock copolymer template: Hybrid particle-field molecular dynamics simulation. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 25009–25022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Byshkin, M.; Cong, Y.; Kawakatsu, T.; Guadagno, L.; De Nicola, A.; Yu, N.; Milano, G.; Dong, B. Self-Assembly of carbon nanotubes in polymer melts: Simulation of structural and electrical behaviour by hybrid particle-field molecular dynamics. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 15538–15552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groot, R.D.; Rabone, K. Mesoscopic simulation of cell membrane damage, morphology change and rupture by nonionic surfactants. Biophys. J. 2001, 81, 725–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, V.; Nielsen, S.O.; Discher, D.E.; Klein, M.L.; Lipowsky, R.; Shillcock, J. Dissipative particle dynamics simulations of polymersomes. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 17708–17714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.; Hou, T.; Xu, X. Simulation of the phase behavior of the (EO) 13 (PO) 30 (EO) 13 (pluronic L64)/water/p-xylene system using MesoDyn. J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106, 11397–11403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Vlimmeren, B.; Maurits, N.; Zvelindovsky, A.; Sevink, G.; Fraaije, J. Simulation of 3D mesoscale structure formation in concentrated aqueous solution of the triblock polymer surfactants (ethylene oxide) 13 (propylene oxide) 30 (ethylene oxide) 13 and (propylene oxide) 19 (ethylene oxide) 33 (propylene oxide) 19. Application of dynamic mean-field density functional theory. Macromolecules 1999, 32, 646–656. [Google Scholar]
- Fraaije, J.; Sevink, G. Model for pattern formation in polymer surfactant nanodroplets. Macromolecules 2003, 36, 7891–7893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.; Li, Y.; Wang, D.; Bao, M.; Tong, L. Mesoscopic simulation studies on the self-assembly of pluronic at oil/water interface. Acta Chim. Sinica 2013, 71, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, B.; Ravi, V.; Alexandridis, P. Micellization of amphiphilic block copolymers in binary and ternary solvent mixtures. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 390, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandrup, J.; Immergut, E.H.; Grulke, E.A. (Eds.) Polymer Handbook; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Mississauga, ON, Canada, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Zhao, L.; Qian, H.-J.; Lu, Z.-Y. Coarse-Grained simulation study on the self-assembly of miktoarm star-like block copolymers in various solvent conditions. Soft Matter. 2014, 10, 2245–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.-Y.; Li, Y.-C.; Lu, Z.-Y. The important role of cosolvent in the amphiphilic diblock copolymer self-assembly process. Polymer 2019, 171, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, N.; Biswas, P. Size, shape, and flexibility of proteins and DNA. J. Chem. Phys. 2009, 131, 165104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexandridis, P.; Hatton, T.A. Poly(ethylene oxide)-poly(propylene oxide)-poly(ethylene oxide) block copolymer surfactants in aqueous solutions and at interfaces: Thermodynamics, structure, dynamics, and modeling. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1995, 96, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
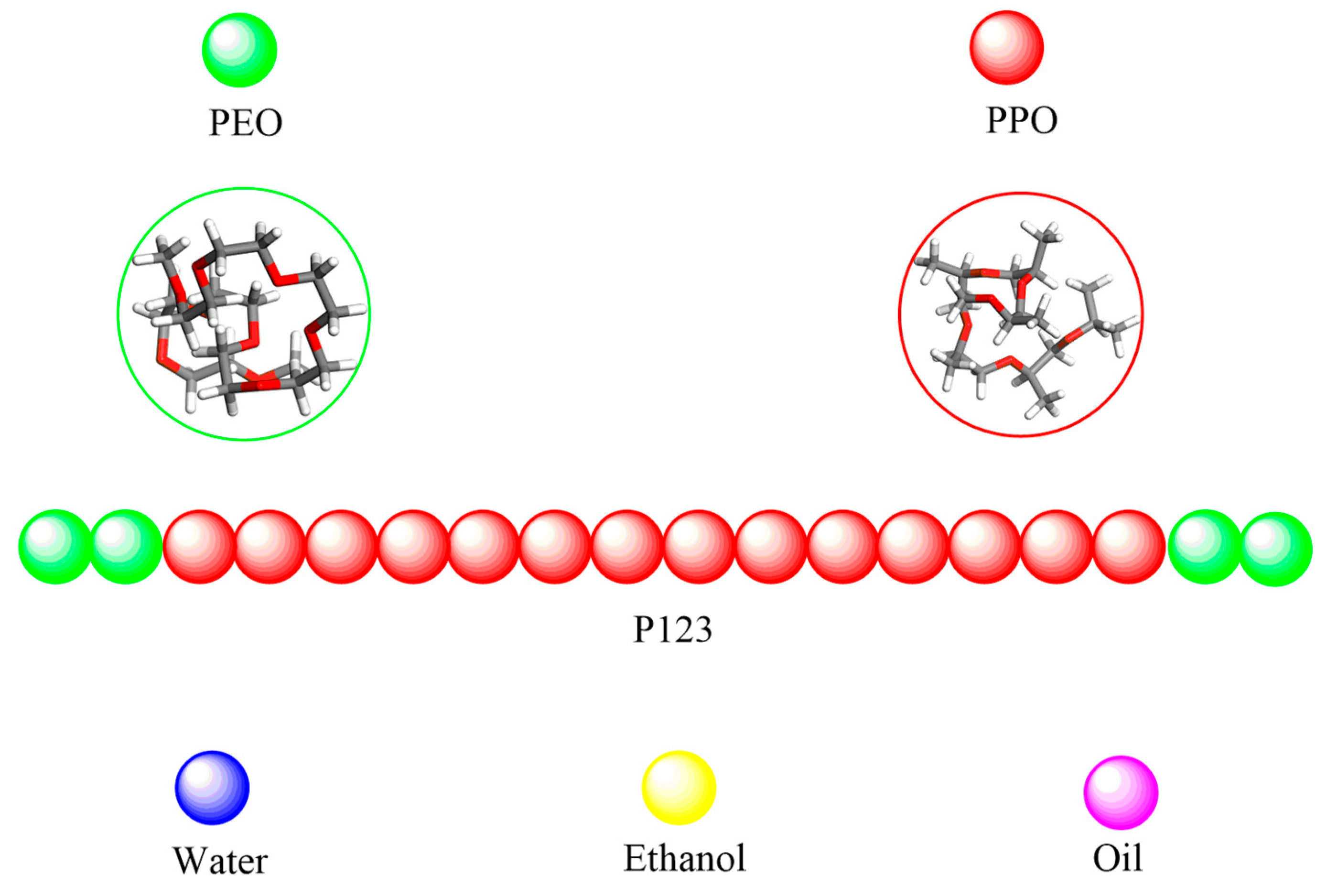


| Volume Fraction (vol %) | P123 No. of Atoms | Water No. of Atoms | Particle No. of Atoms | Box Length (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 3834 | 188,166 | 192,000 | 64.25 |
| 5 | 9594 | 182,406 | 192,000 | 64.25 |
| 10 | 19,206 | 172,794 | 192,000 | 64.25 |
| 15 | 28,800 | 163,200 | 192,000 | 64.25 |
| 20 | 38,394 | 153,606 | 192,000 | 64.25 |
| System | P123 No. of Atoms | Water No. of Atoms | Ethanol No. of Atoms | Turpentine Oil No. of Atoms |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | 9576 (5%) | 153,624 | 28,800 (15%) | 0 |
| II | 9576 (5%) | 134,424 | 48,000 (25%) | 0 |
| III | 28,800 (15%) | 115,200 | 48,000 (25%) | 0 |
| IV | 9576 (5%) | 150,744 | 28,800 (15%) | 2880 (1.5%) |
| V | 9576 (5%) | 131,544 | 48,000 (25%) | 2880 (1.5%) |
| VI | 28,800 (15%) | 112,320 | 48,000 (25%) | 2880 (1.5%) |
| PEO | PPO | Water | Ethanol | Turpentine Oil | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PEO | 0.0 | 30.3 | 0.76 | 16.0 | 21.0 |
| PPO | 30.3 | 0.0 | 21.2 | 25.4 | 2.3 |
| Water | 0.76 | 21.2 | 0.0 | 0.76 | 42.3 |
| Ethanol | 16.0 | 25.4 | 0.76 | 0.0 | 36.0 |
| TurpentineOil | 21.0 | 2.3 | 42.3 | 36.0 | 0.0 |
| System | Component | <P>n | <Rg> (nm) | <Q> |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | 5% P123 + 15% Ethanol | 6.890 | 2.304 | 0.1085 |
| II | 5% P123 + 25% Ethanol | 8.876 | 2.451 | 0.1216 |
| III | 15% P123 + 25% Ethanol | 16.80 | 3.463 | 0.1634 |
| IV | 5% P123 + 15% Ethanol + 1.5% Oil | 6.095 | 2.462 | 0.1608 |
| V | 5% P123 + 25% Ethanol + 1.5% Oil | 8.558 | 3.038 | 0.1241 |
| VI | 15% P123 + 25% Ethanol + 1.5% Oil | 14.25 | 3.544 | 0.1899 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Y.; Ma, S.-M.; Li, B.; De Nicola, A.; Yu, N.-S.; Dong, B. Micellization of Pluronic P123 in Water/Ethanol/Turpentine Oil Mixed Solvents: Hybrid Particle–Field Molecular Dynamic Simulation. Polymers 2019, 11, 1806. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11111806
Zhao Y, Ma S-M, Li B, De Nicola A, Yu N-S, Dong B. Micellization of Pluronic P123 in Water/Ethanol/Turpentine Oil Mixed Solvents: Hybrid Particle–Field Molecular Dynamic Simulation. Polymers. 2019; 11(11):1806. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11111806
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Ying, Su-Min Ma, Bin Li, Antonio De Nicola, Nai-Sen Yu, and Bin Dong. 2019. "Micellization of Pluronic P123 in Water/Ethanol/Turpentine Oil Mixed Solvents: Hybrid Particle–Field Molecular Dynamic Simulation" Polymers 11, no. 11: 1806. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11111806
APA StyleZhao, Y., Ma, S.-M., Li, B., De Nicola, A., Yu, N.-S., & Dong, B. (2019). Micellization of Pluronic P123 in Water/Ethanol/Turpentine Oil Mixed Solvents: Hybrid Particle–Field Molecular Dynamic Simulation. Polymers, 11(11), 1806. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11111806






