Novel PEEK Copolymer Synthesis and Biosafety—I: Cytotoxicity Evaluation for Clinical Application
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. PEEK Polymerization and Composite Preparation
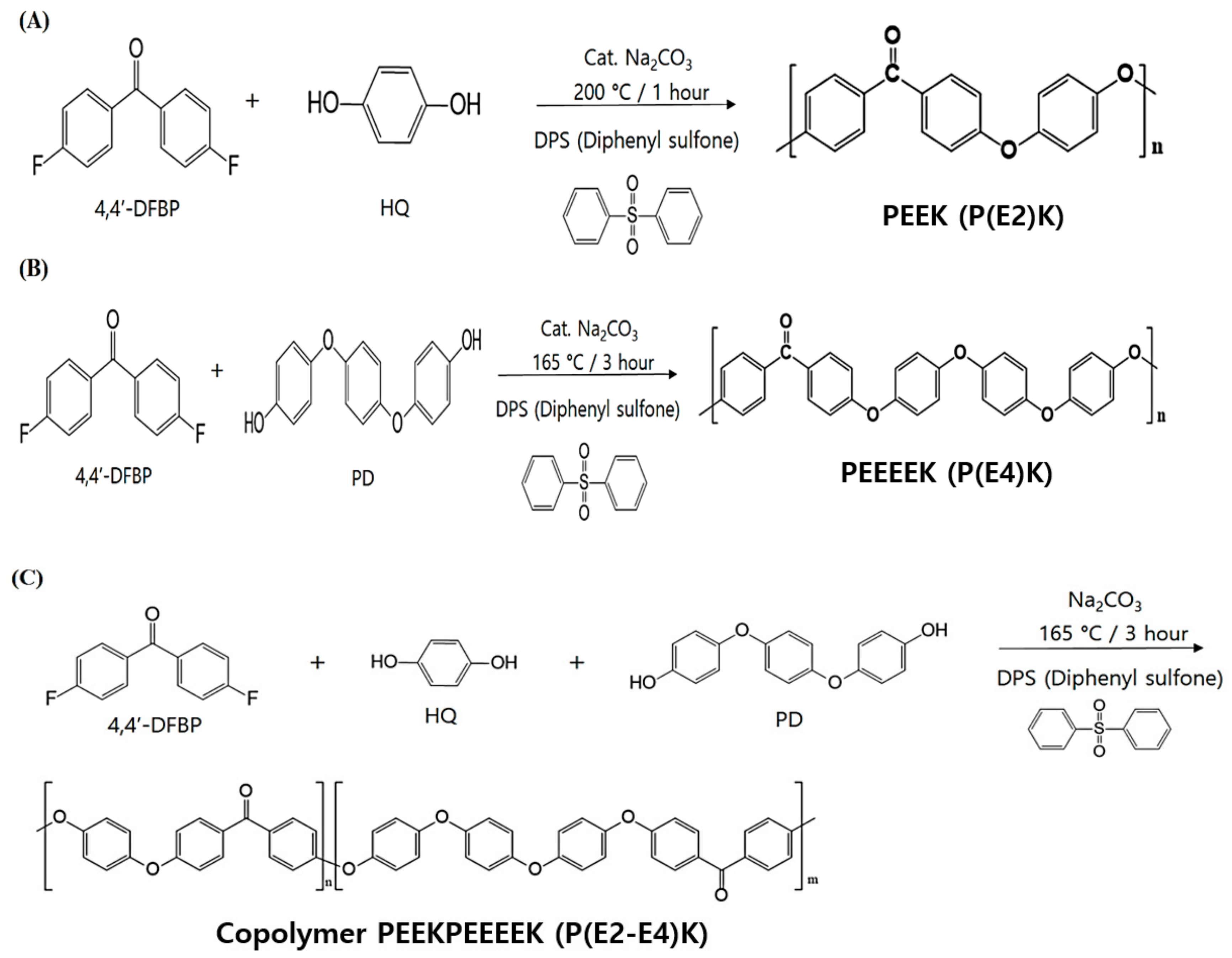
2.2.1. Synthesis of Poly(ether ether ketone) P(E2)K
2.2.2. Synthesis of Poly(ether ether ether ether ketone) P(E4)K
2.2.3. Synthesis of the Random Copolymer P(E2–E4)K
2.2.4. Fabrication of the PEEK Composite
2.3. Characterization and Mechanical Properties of the Synthesized PEEK Polymers and Composites
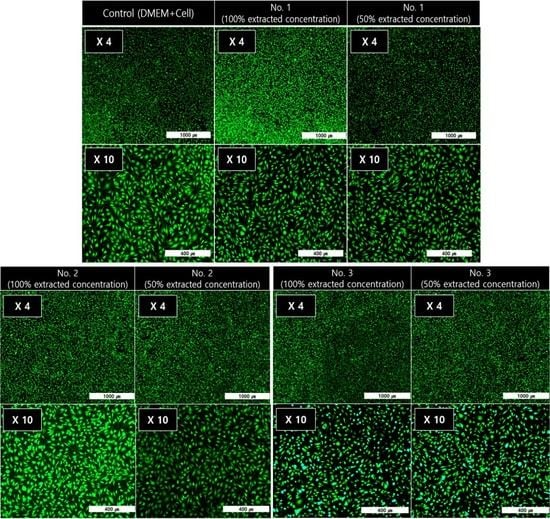
2.4. In vitro Cytotoxicity Test of the PEEK Composites
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis and Characterizations of P(E2)K, P(E4)K, and P(E2–E4)K
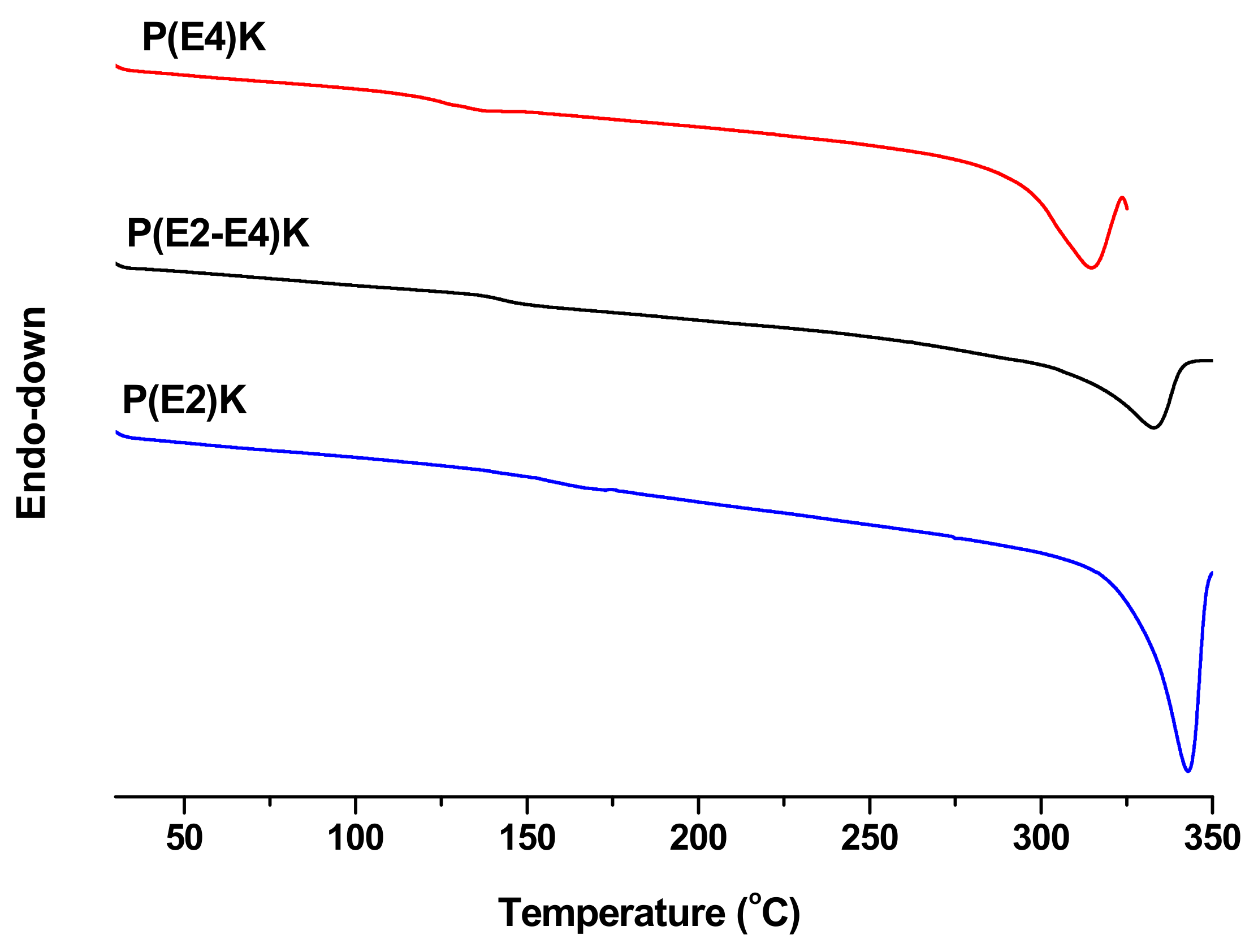
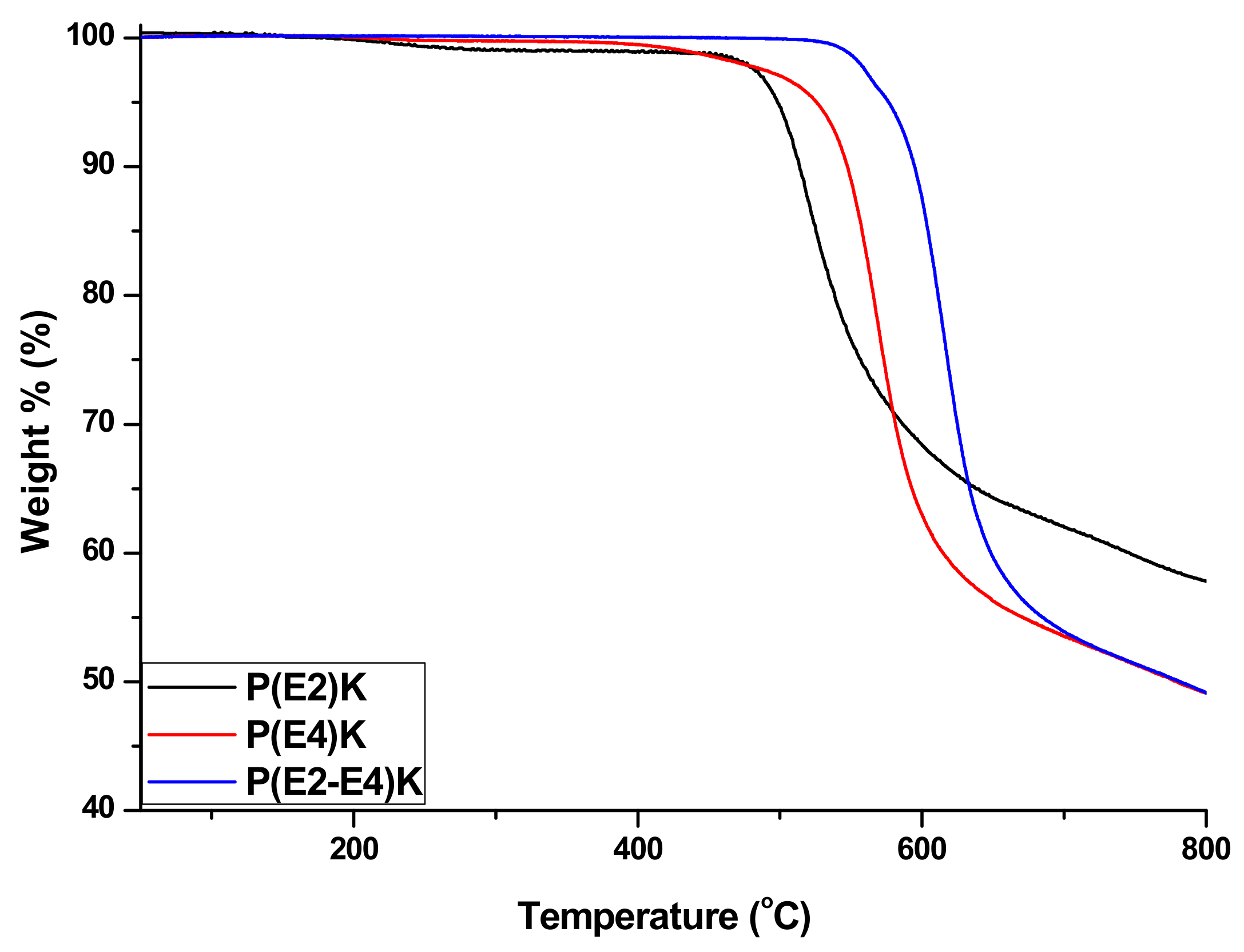
3.2. Thermal Properties of P(E2)K, P(E4)K, and P(E2–E4)K
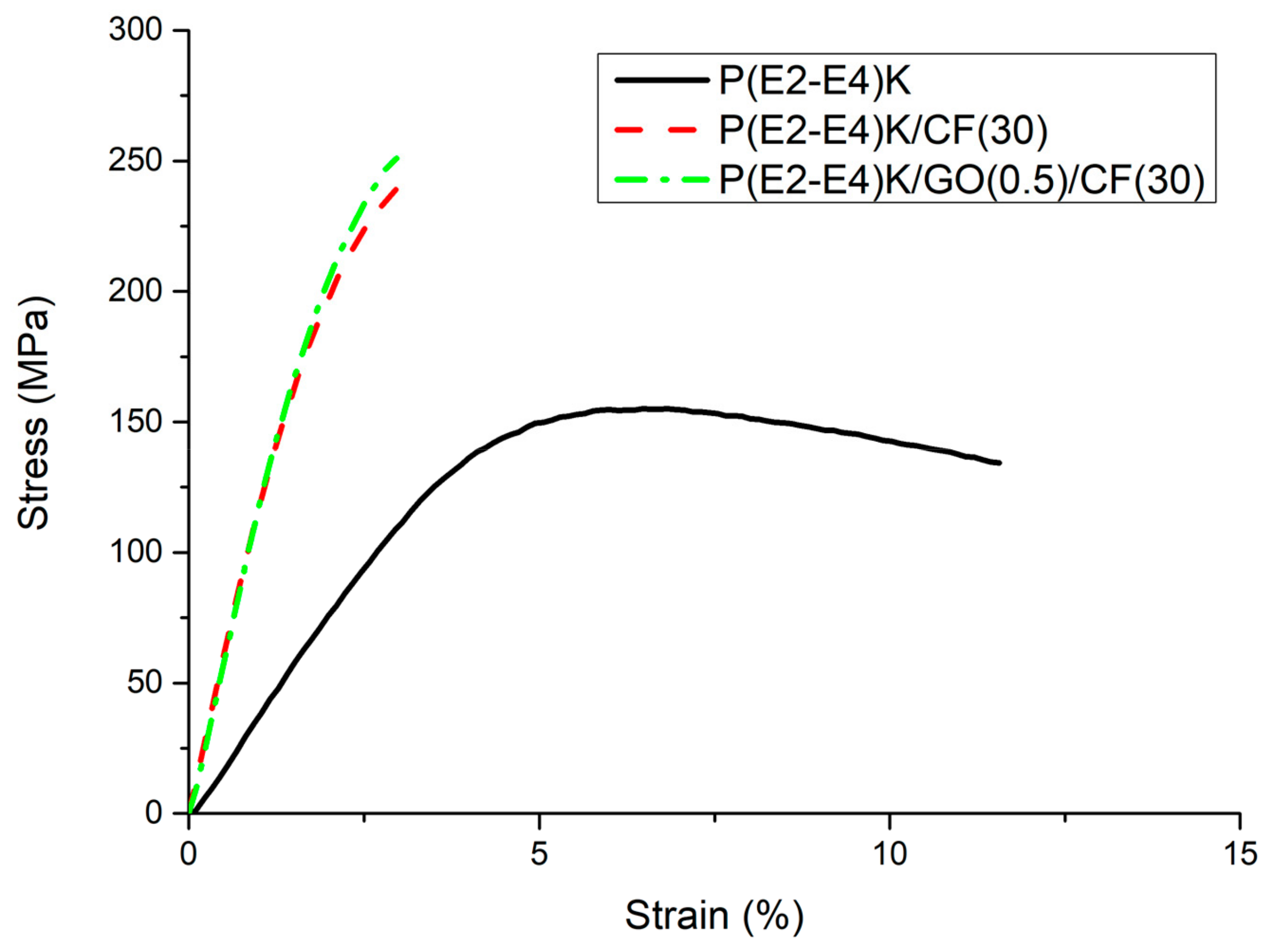
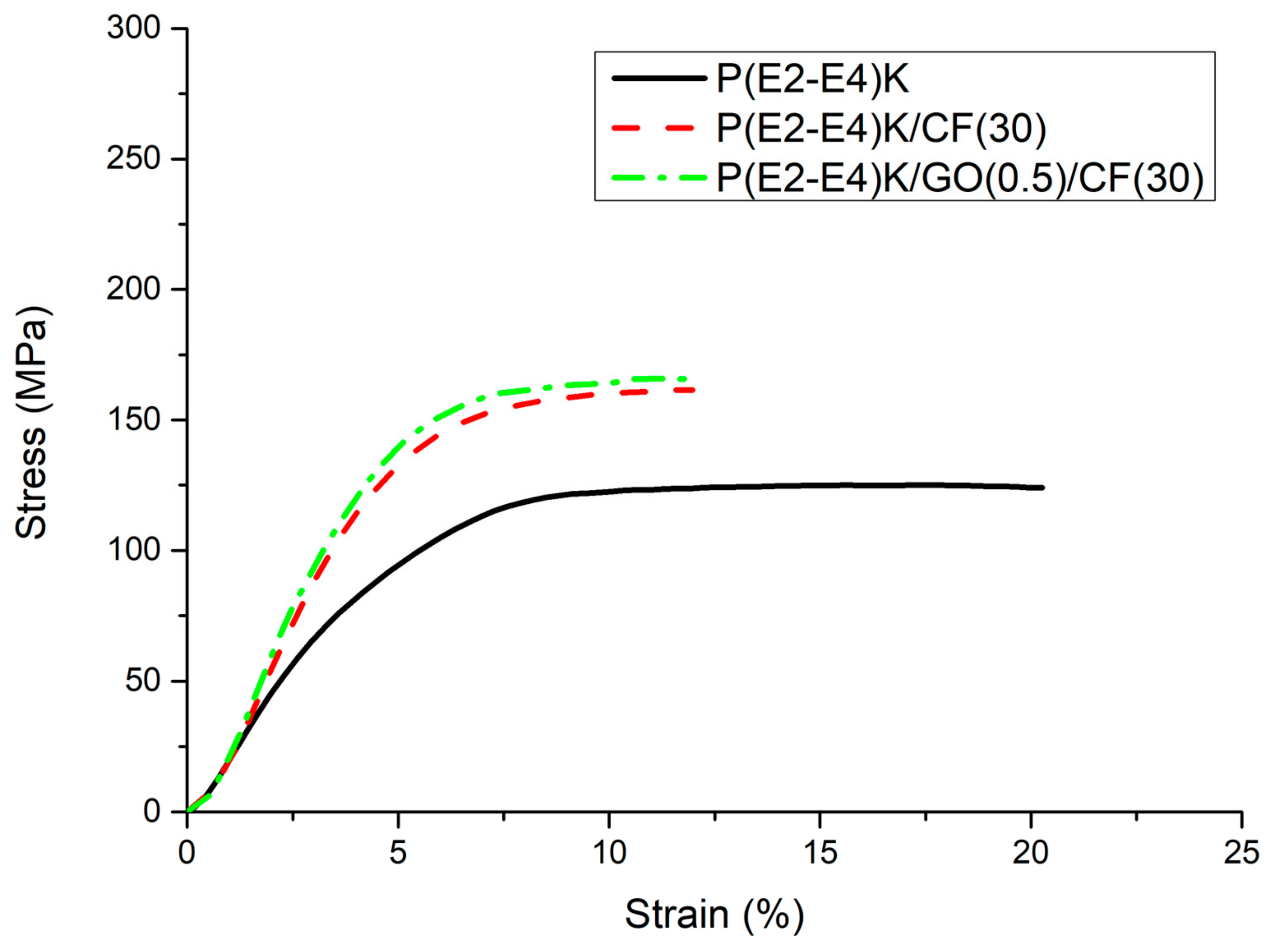
3.3. Mechanical Properties
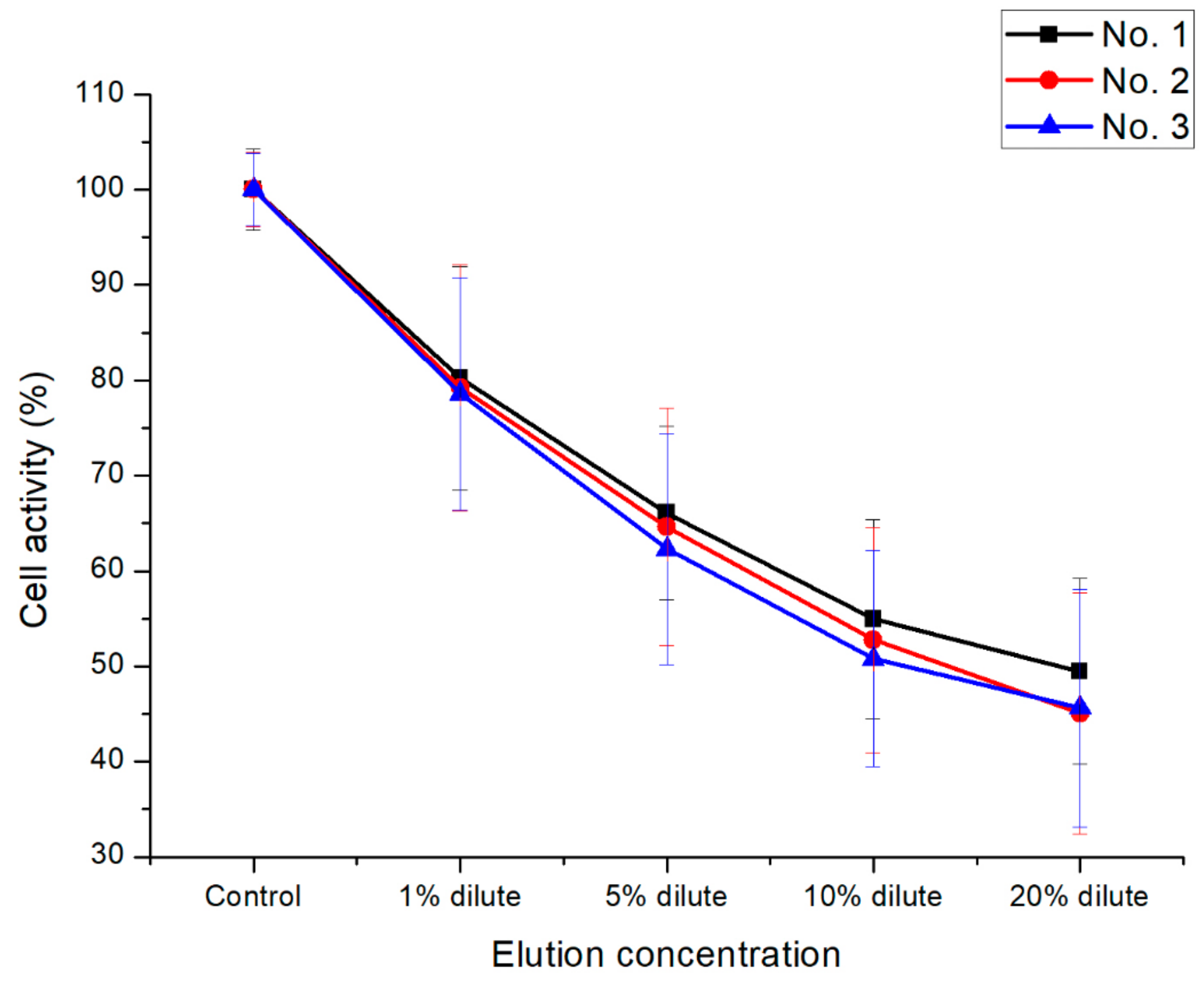
3.4. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Test of the PEEK Composites
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Park, J.B.; Lakes, R.S. Biomaterials: An Introduction, 3rd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 100–136. [Google Scholar]
- Blackwood, D.J. Biomaterials: Past Successes and Future Problems. Corros. Rev. 2003, 21, 97–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seal, C.K.; Vince, K.; Hodgson, M.A. Biodegradable surgical implants based on magnesium alloys—A review of current research. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2009, 4, 012011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salahshoor, M.; Guo, Y. Biodegradable Orthopedic Magnesium-Calcium (MgCa) Alloys, Processing, and Corrosion Performance. Materials 2012, 5, 135–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kurtz, S.M.; Devine, J.N. PEEK biomaterials in trauma, orthopedic, and spinal implants. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 4845–4869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- James, C.S. Polyetheretherketone (PEEK): Processing-structure and properties studies for a matrix in high performance composites. Polym. Compos. 1986, 7, 159–169. [Google Scholar]
- Christian, B.; David, J.W.; Frank, E.K.; William, J.M. The sodium salts of sulphonated poly(aryl-ether-ether-ketone) (PEEK): Preparation and characterization. Polymer 1987, 28, 1009–1016. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Dawson, P.C.; Blundell, D.J. X-ray data for poly(aryl ether ketones). Polymer 1980, 21, 577–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmet-Alkan, A.A.; Hay, J.N. The crystallinity of PEEK composites. Polymer 1993, 34, 3529–3531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attwood, T.E.; Dawson, P.C.; Freeman, J.L.; Hoy, L.R.; Rose, J.B.; Staniland, P.A. Synthesis and properties of polyaryletherketones. Polymer 1981, 22, 1096–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clendlinning, R.A. Poly(aryl ether ketone) Block Copolymers. U.S. Patent 4,786,694, 22 November 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Clendlinning, R.A. Modified poly(aryl ether ketones) derived from biphenol. E.P. Patent 0,266,132, 4 May 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Skinner, H.B. Composite technology for total hip arthroplasty. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1988, 235, 224–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mark, H.F.; Bikales, N.M.; Overberger, C.G.; Menges, G.; Kroschiwitz, J.I. Encyclopedia of Polymer Science and Engineering, 2nd ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1988; pp. 313–320. [Google Scholar]
- Roel, F.M.R.K.; Steven, M.V.G.; Arthur, D.G.; Oner, F.C. Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) cages in cervical applications: A systematic review. Spine J. 2015, 15, 1446–1460. [Google Scholar]
- Hongli, P.; Hailong, T.; Shaobo, Q.; Ning, W.; Yu, Q.W. Progress of titanium strut for cervical reconstruction with nano-graphene oxide loaded hydroxyapatite/polyamide composite and interbody fusion after corpectomy with anterior plate fixation. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 3094–3100. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Caeiro, J.R.; González, P.; Guede, D. Biomechanics and bone (& II): Trials in different hierarchical levels of bone and alternative tools for the determination of bone strength. Rev. Osteoporos. Metab. Miner. 2013, 5, 99–108. [Google Scholar]
- Zioupos, P.; Currey, J.D. Changes in the stiffness, strength, and toughness of human cortical bone with age. Bone 1998, 22, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, A.; Frormann, L.; Iqbal, A. High performance thermoplastic composites: Study on the mechanical, thermal, and electrical resistivity properties of carbon fiber-reinforced polyetheretherketone and polyethersulphone. Polym. Compos. 2007, 28, 785–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, R.; Beredjiklian, P.; Rhoad, R.; Theiss, S.; Cuckler, J.; Ducheyne, P.; Baker, D.G. A comparison of the inflammatory potential of particulates derived from two composite materials. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1997, 34, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.R.; Zihlmann, C.; Akbari, M.; Assawes, P.; Cheung, L.; Zhang, K.; Manoharan, V.; Zhang, Y.S.; Yüksekkaya, M.; Wan, K.-T.; et al. Reduced graphene oxide-GelMA hybrid hydrogels as scaffolds for cardiac tissue engineering. Small 2016, 12, 3677–3689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, W.; Ni, Z.; Chen, G.; Huang, G.; Huang, H.; Zhao, Y. Mechanical and thermal properties of graphene oxide/ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene nanocomposites. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 63063–63072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shi, Z.; Fang, J.; Xu, H.; Yin, J. Graphene oxide/polybenzimidazole composites fabricated by a solvent-exchange method. Carbon 2011, 49, 1199–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Chen, X.; Guo, Z.; Qiu, X.; Yang, Y.; Su, C.; Jiang, N.; Li, Y.; Sun, D.; Zhang, L. Super tough graphene oxide reinforced polyetheretherketone for potential hard tissue repair applications. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2019, 174, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, K.; Ruan, J.; Song, H.; Zhang, J.; Wo, Y.; Guo, S.; Cui, D. Biocompatibility of graphene oxide. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2011, 6, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girase, B.; Shah, J.S.; Misra, R.D.K. Cellular mechanics of modulated osteoblasts functions in graphene oxide reinforced elastomers. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2012, 14, B101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.; Kim, Y.K.; Shin, D.; Ryoo, S.R.; Hong, B.H.; Min, D.H. Biomedical applications of graphene and graphene oxide. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 2211–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO 10993-5. International Standard, 3rd ed.; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Mitsuru, U.; Masaki, S. Synthesis of Aromatic Poly (ether ketones). Macromolecules 1987, 20, 2675–2678. [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh, K.H.; Chern, Y.C.; Ho, K.S.; Wang, Y.Z.; Chan, B.W.; Chen, L.W. Effect of dihydroxydiphenyl ether on Poly (ether ether ketone). J. Polym. Res. 1996, 3, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, V.L.; Sivadasan, P. Synthesis and properties of polyether ketones. Eur. Polym. J. 1994, 30, 1381–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, P.; Goel, A. Carbon Fibres: Production, Properties and Potential Use. Mater. Sci. Res. India 2017, 14, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Feng, P.; Wu, P.; Huang, W.; Yang, Y.; Guo, W.; Gao, C.; Shuai, C. Graphene oxide as an interface phase between polyetheretherketone and hydroxyapatite for tissue engineering scaffolds. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, Y.; Im, H.; Kim, J. The effect of sulfonated graphene oxide on Sulfonated Poly (Ether Ether Ketone) membrane for direct methanol fuel cells. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 425, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johan, V.M.; Gertjan, J.L.K.; Jacqueline, C. Cancer Cell Culture; Humana Press: Totawa, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 237–245. [Google Scholar]




| Sample No. | Samples Composition (wt %) |
|---|---|
| No. 1 | P(E2-E4)K only |
| No. 2 | P(E2-E4)K/CF(30) |
| No. 3 | P(E2-E4)K/GO(0.5)/CF(30) |
| Polymer | Polymerization Solvent | Polymerization Temperature (°C) | Reaction Time (hr) | Yield (%) | ηinh* (dL/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P(E2)K | Ph2SO2 (DPS) | 160/250/320 | 2/2/1 | 96 | 1.20 |
| P(E4)K | Ph2SO2 (DPS) | 160/235/290 | 2/2/5 | 94 | 0.63 |
| P(E2–E4)K | Ph2SO2 (DPS) | 160/240/300 | 2/4/5 | 97 | 1.43 |
| Sample Name | Sample Composition (wt %) | Flexural Strength (MPa) | Compressive Strength (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| No. 1 | P(E2–E4)K | 155 ± 3.6 | 125 ± 1.5 |
| No. 2 | P(E2–E4)K/CF(30) | 240 ± 3.9 | 161 ± 2.9 |
| No. 3 | P(E2–E4)K/GO(0.5)/CF(30) | 250 ± 4.0 | 164 ± 3.1 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chon, J.W.; Yang, X.; Lee, S.M.; Kim, Y.J.; Jeon, I.S.; Jho, J.Y.; Chung, D.J. Novel PEEK Copolymer Synthesis and Biosafety—I: Cytotoxicity Evaluation for Clinical Application. Polymers 2019, 11, 1803. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11111803
Chon JW, Yang X, Lee SM, Kim YJ, Jeon IS, Jho JY, Chung DJ. Novel PEEK Copolymer Synthesis and Biosafety—I: Cytotoxicity Evaluation for Clinical Application. Polymers. 2019; 11(11):1803. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11111803
Chicago/Turabian StyleChon, Joon Woo, Xin Yang, Seung Mook Lee, Young Jun Kim, In Sung Jeon, Jae Young Jho, and Dong June Chung. 2019. "Novel PEEK Copolymer Synthesis and Biosafety—I: Cytotoxicity Evaluation for Clinical Application" Polymers 11, no. 11: 1803. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11111803
APA StyleChon, J. W., Yang, X., Lee, S. M., Kim, Y. J., Jeon, I. S., Jho, J. Y., & Chung, D. J. (2019). Novel PEEK Copolymer Synthesis and Biosafety—I: Cytotoxicity Evaluation for Clinical Application. Polymers, 11(11), 1803. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11111803