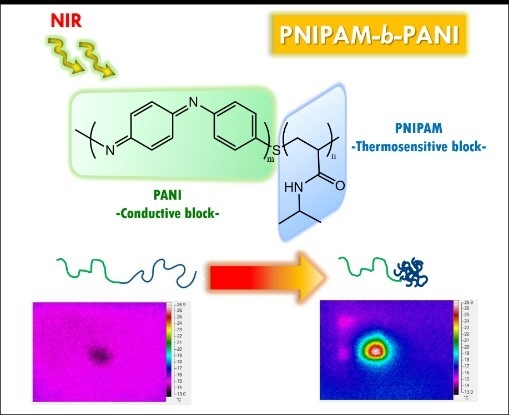
Synthesis of a Smart Conductive Block Copolymer Responsive to Heat and Near Infrared Light
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
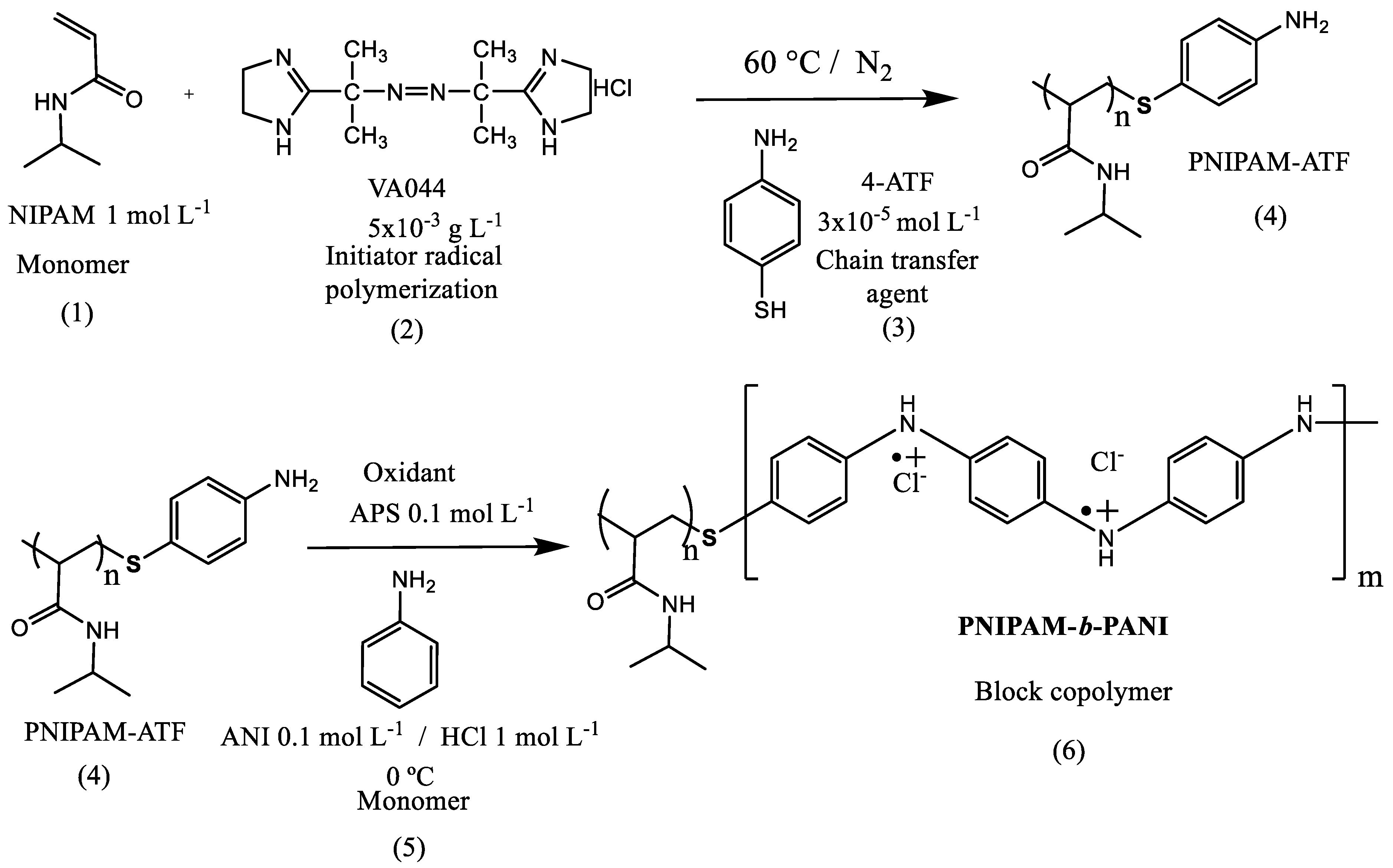
2.2. Synthesis of PNIPAM-b-PANI
2.3. Solubility
2.4. Characterization Techniques
2.4.1. Molecular Weight (Mw) Determination
2.4.2. Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (1H NMR)
2.4.3. Fourier Transformed Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR)
2.4.4. UV-Visible Spectroscopy and Turbidimetry Measurements
2.4.5. Conductivity Test
2.4.6. Photothermal Effect
2.4.7. Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM)
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ansari, M.O.; Ansari, S.A.; Cho, M.H.; Ansari, S.P.; Abdel-wahab, M.S.; Alshahrie, A. Conducting Polymer Nanocomposites as Gas Sensors. In Functional Polymers; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2019; pp. 911–940. [Google Scholar]
- Zarrintaj, P.; Khalili, R.; Vahabi, H.; Saeb, M.R.; Ganjali, M.R.; Mozafari, M. Polyaniline/metal oxides nanocomposites. In Fundamentals and Emerging Applications of Polyaniline; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 131–141. [Google Scholar]
- Kašpárková, V.; Humpolíček, P.; Stejskal, J.; Capáková, Z.; Bober, P.; Skopalová, K.; Lehocký, M. Exploring the Critical Factors Limiting Polyaniline Biocompatibility. Polymers 2019, 11, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vines, J.B.; Lim, D.-J.; Park, H. Contemporary Polymer-Based Nanoparticle Systems for Photothermal Therapy. Polymers 2018, 10, 1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Cheng, L.; Wang, C.; Peng, R.; Liu, Z. Conjugated polymers for photothermal therapy of cancer. Polym. Chem. 2014, 5, 1573–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongiovanni Abel, S.; Gallarato, L.A.; Dardanelli, M.S.; Barbero, C.A.; Rivarola, C.R.; Yslas, E.I. Photothermal lysis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by polyaniline nanoparticles under near infrared irradiation. Biomed. Phys. Eng. Express 2018, 4, 045037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ibarra, L.; Yslas, E.; Molina, M.; Rivarola, C.; Romanini, S.; Barbero, C.; Rivarola, V.; Bertuzzi, M. Near-infrared mediated tumor destruction by photothermal effect of PANI-Np in vivo. Laser Phys. 2013, 23, 066004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongiovanni Abel, S.; Yslas, E.I.; Rivarola, C.R.; Barbero, C.A. Synthesis of polyaniline (PANI) and functionalized polyaniline (F-PANI) nanoparticles with controlled size by solvent displacement method. Application in fluorescence detection and bacteria killing by photothermal effect. Nanotechnology 2018, 29, 125604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarrintaj, P.; Vahabi, H.; Saeb, M.R.; Mozafari, M. Application of polyaniline and its derivatives. In Fundamentals and Emerging Applications of Polyaniline; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 259–272. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, G.; Li, Q.; Xu, Z. The chemical modification of polyaniline with enhanced properties: A review. Prog. Org. Coat. 2019, 126, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acevedo, D.F.; Rivarola, C.R.; Miras, M.C.; Barbero, C.A. Effect of chemical functionalization on the electrochemical properties of conducting polymers. Modification of polyaniline by diazonium ion coupling and subsequent reductive degradation. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 56, 3468–3473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrin, A.; Ngamna, O.; O’Malley, E.; Kent, N.; Moulton, S.E.; Wallace, G.G.; Smyth, M.R.; Killard, A.J. The fabrication and characterization of inkjet-printed polyaniline nanoparticle films. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 53, 5092–5099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Liu, P. Conducting polyaniline nanoparticles and their dispersion for waterborne corrosion protection coatings. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 2694–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Peñas, A.; Biswas, C.S.; Liang, W.; Wang, Y.; Yang, P.; Stadler, F.J. Effect of Hydrophobic Interactions on Lower Critical Solution Temperature for Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-dopamine Methacrylamide) Copolymers. Polymers 2019, 11, 991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongiovanni Abel, S.; Molina, M.A.; Rivarola, C.R.; Kogan, M.J.; Barbero, C.A. Smart polyaniline nanoparticles with thermal and photothermal sensitivity. Nanotechnology 2014, 25, 495602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivero, R.E.; Molina, M.A.; Rivarola, C.R.; Barbero, C.A. Pressure and microwave sensors/actuators based on smart hydrogel/conductive polymer nanocomposite. Sens. Actuators B 2014, 190, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, M.V.; Bongiovanni Abel, S.; Rivero, R.; Miras, M.; Rivarola, C.; Barbero, C. Polymeric nanocomposites made of a conductive polymer and a thermosensitive hydrogel: Strong effect of the preparation procedure on the properties. Polymer 2015, 78, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, M.; Rivarola, C.; Miras, M.; Lescano, D.; Barbero, C. Nanocomposite synthesis by absorption of nanoparticles into macroporous hydrogels. Building a chemomechanical actuator driven by electromagnetic radiation. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 245504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, X.; Meng, C.; Liu, Z.; Sun, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, M.; Wei, H. Synthesis and phase transition of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-based thermo-sensitive cyclic brush polymer. Polymers 2017, 9, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, L.; Fan, X.; Wang, F.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z. Multi-Responsive Behaviors of Copolymers Bearing N-Isopropylacrylamide with or without Phenylboronic Acid in Aqueous Solution. Polymers 2018, 10, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rwei, S.P.; Chiang, W.Y.; Way, T.F.; Tuan, H.; Chang, Y.C. Study of theThermo-/pH-Sensitivity of Stereo-Controlled Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-IAM) Copolymers via RAFT Polymerization. Polymers 2018, 10, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimm, O.; Schacher, F. Dual Stimuli-Responsive P (NIPAAm-co-SPA) Copolymers: Synthesis and Response in Solution and in Films. Polymers 2018, 10, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoneoka, S.; Park, K.; Nakagawa, Y.; Ebara, M.; Tsukahara, T. Synthesis and Evaluation of Thermoresponsive Boron-Containing Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) Diblock Copolymers for Self-Assembling Nanomicellar Boron Carriers. Polymers 2019, 11, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, C.-W.; Chen, H.-L.; Liao, Z.-X.; Sureshbabu, R.; Hsiao, H.-C.; Lin, S.-J.; Chang, Y.; Sung, H.-W. Effective Photothermal Killing of Pathogenic Bacteria by Using Spatially Tunable Colloidal Gels with Nano-Localized Heating Sources. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 721–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdebenito, A.; Encinas, M.V. Thiophenols as chain transfer agents in the polymerization of vinyl monomers. Polymer 2005, 46, 10658–10662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, M.A.; Rivarola, C.R.; Barbero, C.A. Effect of copolymerization and semi-interpenetration with conducting polyanilines on the physicochemical properties of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) based thermosensitive hydrogels. Eur. Polym. J. 2011, 47, 1977–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmont, A.; Leclère, P.; Doneux, C.; Lambin, G.; Tong, J.D.; Jérôme, R.; Lazzaroni, R. Microphase separation at the surface of block copolymers, as studied with atomic force microscopy. Colloids Surf. B 2000, 19, 381–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leclère, P.; Lazzaroni, R.; Brédas, J.L.; Yu, J.M.; Dubois, P.; Jérôme, R. Microdomain morphology analysis of block copolymers by atomic force microscopy with phase detection imaging. Langmuir 1996, 12, 4317–4320. [Google Scholar]
- Raybin, J.; Ren, J.; Chen, X.; Gronheid, R.; Nealey, P.F.; Sibener, S.J. Real-time atomic force microscopy imaging of block copolymer directed self assembly. Nano Lett. 2017, 17, 7717–7723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Douglas, J.F.; Jones, R.L. Influence of film casting method on block copolymer ordering in thin films. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 4980–4987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.H.; Musavi, S.M. Preparation and Characterization of Conducting Polystyrene Graft Polyaniline. Life Sci. J. 2012, 9, 4912–4925. [Google Scholar]
- Rubinstein, I.; Rishpon, J.; Sabatani, E.; Redondo, A.; Gottesfeld, S. Morphology control in electrochemically grown conducting polymer films. Precoating the metal substrate with an organic monolayer. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1990, 112, 6135–6136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, H.; Ando, I.; Fujishige, S.; Kubota, K. A 13C PST/MAS NMR study of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) in solution and in the gel phase. J. Mol. Struct. 1991, 245, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nechtschein, M.; Santier, C.; Travers, J.P.; Chroboczek, J.; Alix, A.; Ripert, M. Water effects in polyaniline: NMR and transport properties. Synth. Met. 1987, 18, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, P.C.; Cantão, M.P.; Janissek, P.; Scarpa, P.C.; Mathias, A.L.; Ramos, L.P.; Gomes, M.A. Polyaniline/lignin blends: FTIR, MEV and electrochemical characterization. Eur. Polym. J. 2002, 38, 2213–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trchová, M.; Šeděnková, I.; Stejskal, J. In-situ polymerized polyaniline films. FTIR spectroscopic study of aniline polymerisation. Synth. Met. 2005, 154, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broglia, M.F.; Balmaceda, I.; Carrizo, F.; Barbero, C.; Rivarola, C.R. Acid hydrogel matrixes as reducing/stabilizing agent for the in-situ synthesis of Ag-nanocomposites by UV irradiation: pH effect. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 055021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.S.; MacDiarmid, A.G. Optical properties of polyaniline. Polymer 1993, 34, 1833–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stejskal, J.; Trchová, M.; Bober, P.; Humpolíček, P.; Kašpárková, V.; Sapurina, I.; Shishov, M.A.; Varga, M. Conducting Polymers: Polyaniline. In Encyclopedia of Polymer Science and Technology; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, L.; Zhang, F.; Wang, S.; Pan, X.; Han, S.; Liu, S.; Yuan, Q. Activation of Prodrugs by NIR-Triggered Release of Exogenous Enzymes for Locoregional Chemo-photothermal Therapy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 7728–7732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Tang, D.; Wang, N.; Jia, S.; Sun, Z.; Yang, X.; Peng, J. Polyethylene glycol–modified molybdenum oxide as NIR photothermal agent and its ablation ability for HeLa cells. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2019, 297, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, S.; Li, J.; Wei, J.; Müllen, K.; Yin, M. A Water-Soluble, NIR-Absorbing Quaterrylenediimide Chromophore for Photoacoustic Imaging and Efficient Photothermal Cancer Therapy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 1638–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Sun, Y.; Wei, Y. Molecular weight of chemically polymerized polyaniline. Die Makromol. Chem. Rapid Commun. 1988, 9, 829–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Kaner, R.B. A general chemical route to polyaniline nanofibers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 851–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongiovanni Abel, S.; Olejník, R.; Rivarola, C.R.; Slobodian, P.; Sáha, P.; Acevedo, D.F.; Barbero, C.A. Resistive sensors for organic vapors based on nanostructured and chemically modified polyanilines. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 18, 6510–6516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razak, S.I.A.; Rahman, W.A.W.A.; Hashim, S.; Yahya, M.Y. Polyaniline and their conductive polymer blends: A short review. Malays. J. Fundam. Appl. Sci. 2013, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, P.; Biswas, S.; Ghosh, M.; De, S.K.; Chatterjee, S. The dc and ac conductivity of polyaniline–polyvinyl alcohol blends. Synth. Met. 2001, 122, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Kim, K.; Lee, S.J. Nature-inspired thermo-responsive multifunctional membrane adaptively hybridized with PNIPAm and PPy. NPG Asia Mater. 2017, 9, e445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, M.A.; Rivarola, C.R.; Broglia, M.F.; Acevedo, D.F.; Barbero, C.A. Smart surfaces: Reversible switching of a polymeric hydrogel topography. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salavagione, H.J.; Acevedo, D.F.; Miras, M.C.; Motheo, A.J.; Barbero, C.A. Comparative study of 2-amino and 3-aminobenzoic acid copolymerization with aniline synthesis and copolymer properties. J. Polym. Sci. Part A 2004, 42, 5587–5599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luützenkirchen, J.; van Male, J.; Leermakers, F.; Sjoöberg, S. Comparison of Various Models to Describe the Charge− pH Dependence of Poly(acrylic acid). J. Chem. Eng. Data 2011, 56, 1602–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Solvent | Solubility |
|---|---|
| 1-octanol | Insoluble |
| Acetone | Soluble |
| Acetonitrile | Soluble |
| Carbon tetrachloride | Insoluble |
| Chloroform | Insoluble |
| Cyclohexane | Insoluble |
| Cyclohexanol | Slightly soluble |
| Dichloromethane | Insoluble |
| Dimethyl sulfoxide | Soluble |
| Ethanol | Soluble |
| Formic acid # | Soluble |
| Isopropyl alcohol | Soluble |
| N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone # | Soluble |
| Pyridine | Soluble |
| Tetrahydrofuran | Slightly Soluble |
| Water | Soluble |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bongiovanni Abel, S.; Riberi, K.; Rivarola, C.R.; Molina, M.; Barbero, C.A. Synthesis of a Smart Conductive Block Copolymer Responsive to Heat and Near Infrared Light. Polymers 2019, 11, 1744. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11111744
Bongiovanni Abel S, Riberi K, Rivarola CR, Molina M, Barbero CA. Synthesis of a Smart Conductive Block Copolymer Responsive to Heat and Near Infrared Light. Polymers. 2019; 11(11):1744. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11111744
Chicago/Turabian StyleBongiovanni Abel, Silvestre, Kevin Riberi, Claudia R. Rivarola, Maria Molina, and Cesar A. Barbero. 2019. "Synthesis of a Smart Conductive Block Copolymer Responsive to Heat and Near Infrared Light" Polymers 11, no. 11: 1744. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11111744
APA StyleBongiovanni Abel, S., Riberi, K., Rivarola, C. R., Molina, M., & Barbero, C. A. (2019). Synthesis of a Smart Conductive Block Copolymer Responsive to Heat and Near Infrared Light. Polymers, 11(11), 1744. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11111744