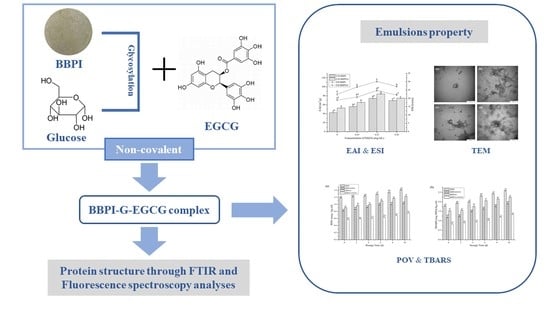
The Effect of (−)-Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Non-Covalent Interaction with the Glycosylated Protein on the Emulsion Property
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation and Characterization of Maillard Reaction Products
2.3. Incubation of BBPI and BBPI-G with EGCG
2.4. Fluorescence Spectroscopy
2.5. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.6. Emulsifying Properties
2.7. Emulsion Preparation
2.8. Mean Particle Size and Zeta Potential of Emulsions
2.9. Determination of the Percentage of the Interfacial Protein Adsorption (AP%)
2.10. Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM) Observation
2.11. Oxidative Stability
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Maillard reaction Products
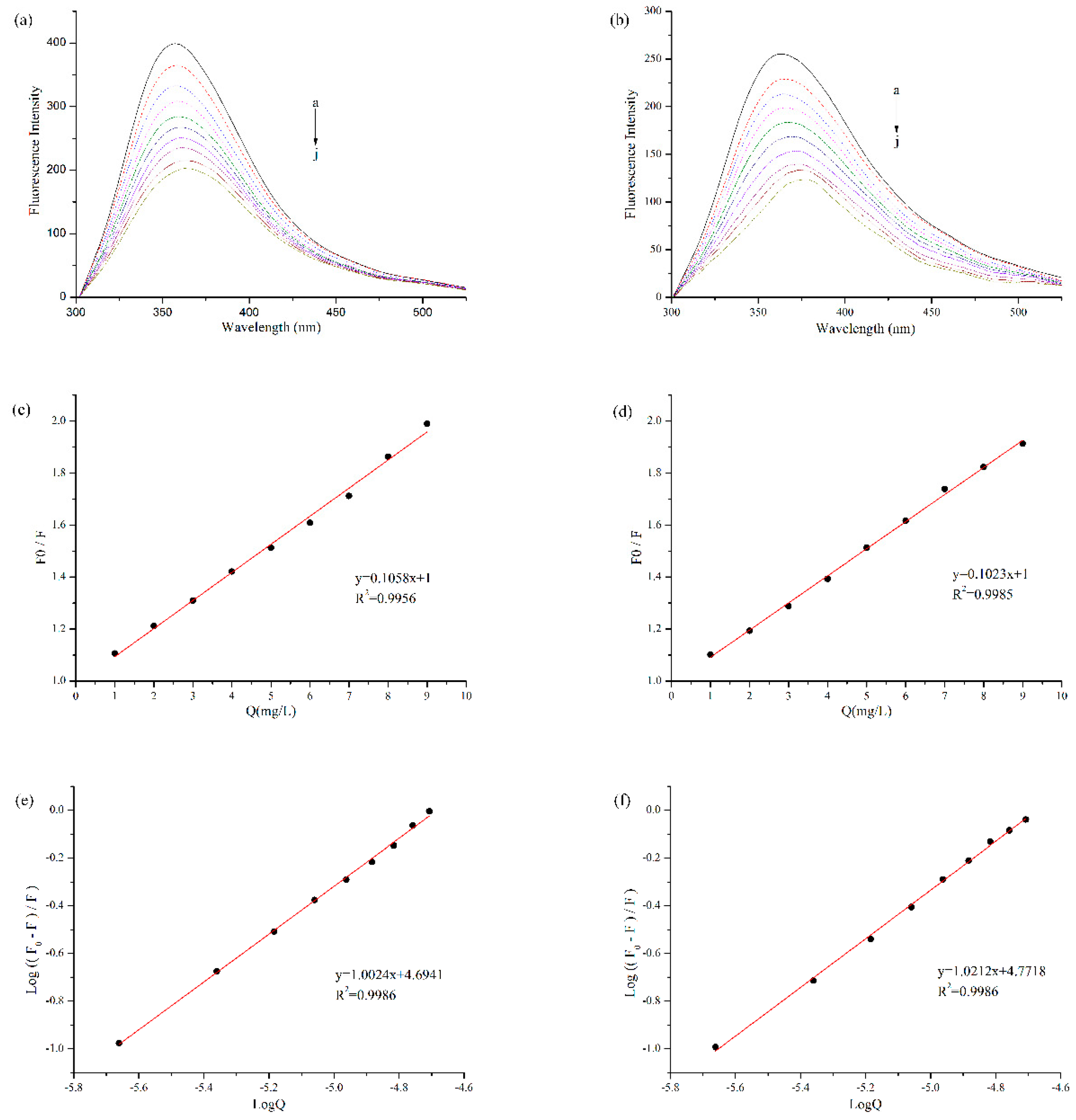
3.2. Fluorescence Quenching Analysis
3.3. Secondary Structure Changes of BBPI-EGCG/BBPI-G-EGCG
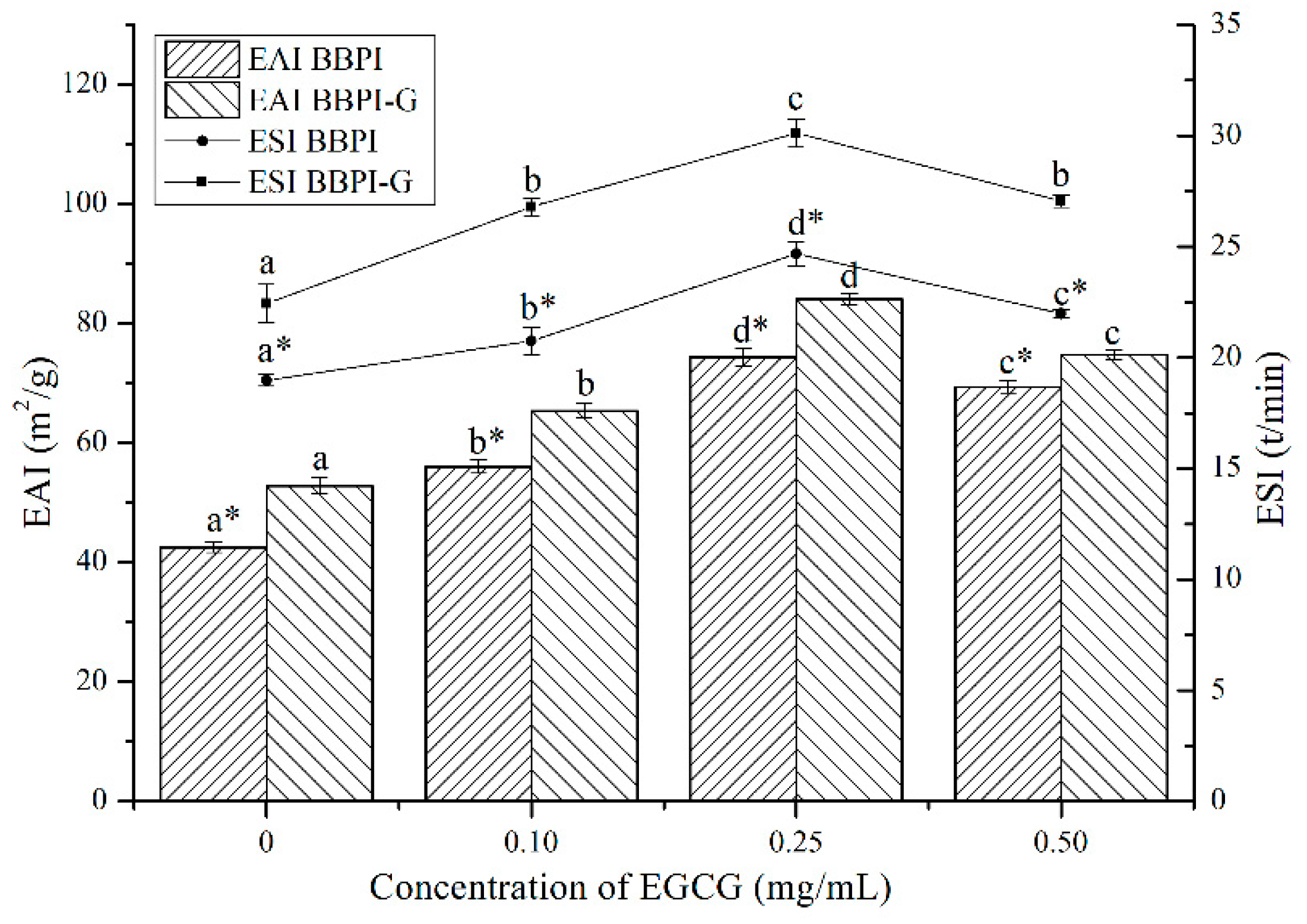
3.4. Emulsifying Properties of BBPI-EGCG/BBPI-G-EGCG
3.5. Mean Particle Size and Zeta-Potential of Emulsions
3.6. Interfacial Protein Adsorption Fraction of Emulsions
3.7. Transmission Electron Microscope Observation of Emulsions
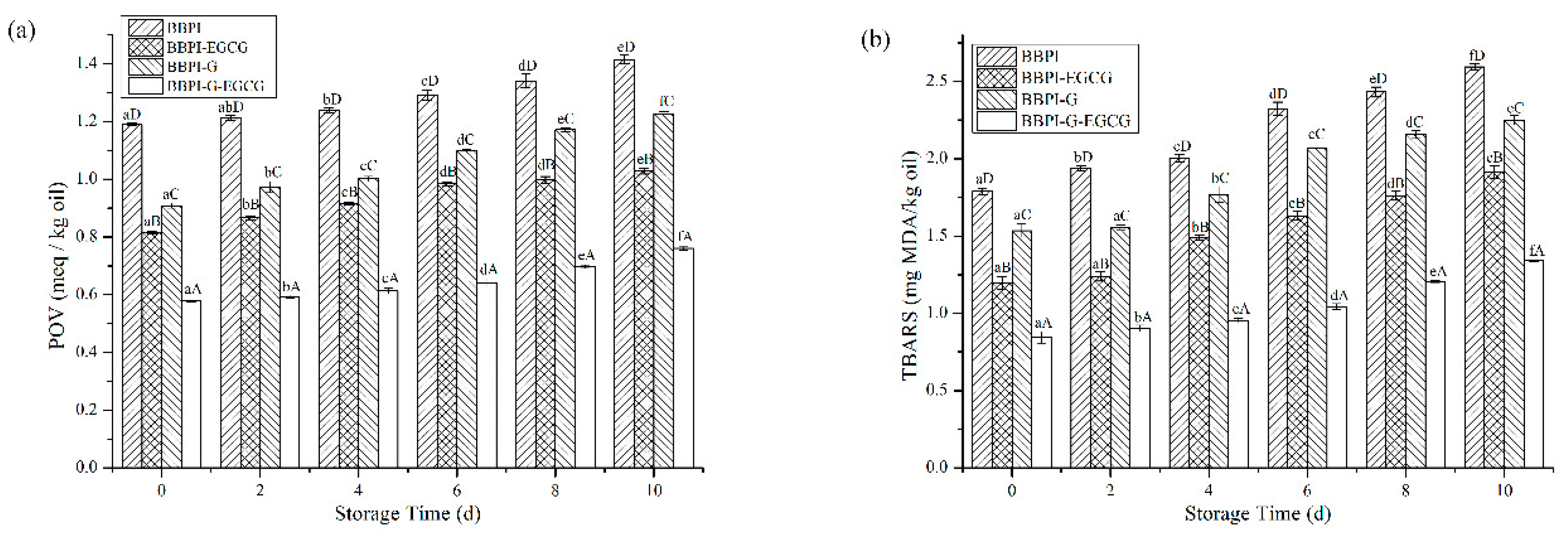
3.8. Oxidative Stability of Emulsions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McClements, D.J. Protein-stabilized emulsions. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 9, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Guo, X.; Zhu, K.; Peng, W.; Zhou, H. Improvement of emulsifying properties of oat protein isolate-dextran conjugates by glycation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 127, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhtar, M.; Dickinson, E. Emulsifying properties of whey protein-dextran conjugates at low pH and different salt concentrations. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2003, 31, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Cui, S.W.; Gong, J.; Guo, Q.; Wang, Q.; Hua, Y. A soy protein-polysaccharides Maillard reaction product enhanced the physical stability of oil-in-water emulsions containing citral. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 48, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Gao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yi, J. Oxidative stability and in vitro digestion of menhaden oil emulsions with whey protein: Effects of EGCG conjugation and interfacial cross-linking. Food Chem. 2018, 265, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Han, G.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Q.; Kong, B. Improving the physical and oxidative stability of emulsions based on the interfacial electrostatic effects between porcine bone protein hydrolysates and porcine bone protein hydrolysate-rutin conjugates. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 94, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Ma, C.; McClements, D.J.; Gao, Y. Development of polyphenol-protein-polysaccharide ternary complexes as emulsifiers for nutraceutical emulsions: Impact on formation, stability, and bioaccessibility of β-carotene emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 61, 578–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wang, D.; Xu, H.; Sun, C.; Gao, Y. Physicochemical properties of β-carotene emulsions stabilized by chlorogenic acid-lactoferrin-glucose/polydextrose conjugates. Food Chem. 2016, 196, 338–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroyo-Maya, I.J.; Campos-Terán, J.; Hernández-Arana, A.; McClements, D.J. Characterization of flavonoid-protein interactions using fluorescence spectroscopy: Binding of pelargonidin to dairy proteins. Food Chem. 2016, 213, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Fan, F.; Xu, X.; Liang, Y. Interactions of black and green tea polyphenols with whole milk. Food Res. Int. 2013, 53, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Liu, Y. The effect of non-covalent interaction of chlorogenic acid with whey protein and casein on physicochemical and radical-scavenging activity of in vitro protein digests. Food Chem. 2018, 268, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karefyllakis, D.; Altunkaya, S.; Berton-Carabin, C.C.; Goot, A.J.V.D.; Nikiforidis, C.V. Physical bonding between sunflower proteins and phenols: Impact on interfacial properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 73, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staszewski, M.V.; Ruiz-Henestrosa, V.M.P.; Pilosof, A.M.R. Green tea polyphenols-β-lactoglobulin nanocomplexes: Interfacial behavior, emulsification and oxidation stability of fish oil. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 35, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Zhao, Q.; Feng, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Han, D.; Xu, J. Changes on the structural and physicochemical properties of conjugates prepared by the Maillard reaction of black bean protein isolates and glucose with ultrasound pretreatment. Polymers 2019, 11, 848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferraro, V.; Madureira, A.R.; Sarmento, B.; Gomes, A.; Pintado, M.E. Study of the interactions between rosmarinic acid and bovine milk whey protein α-lactalbumin, β-lactoglobulin and lactoferrin. Food Res. Int. 2015, 77, 450–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Gao, X.; Hao, M.; Tang, L. Comparison of binding interaction between ß-lactoglobulin and three common polyphenols using multi-spectroscopy and modeling methods. Food Chem. 2017, 228, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perusko, M.; Al-Hanish, A.; Mihailovic, J.; Minic, S.; Trifunovic, S.; Prodic, I.; Velickovic, T.C. Antioxidative capacity and binding affinity of the complex of green tea catechin and beta-lactoglobulin glycated by the Maillard reaction. Food Chem. 2017, 232, 744–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, K.N.; Kinsella, J.E. Emulsifying properties of proteins: Evaluation of a turbidimetric technique. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1978, 26, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Wang, X.; Chen, Z.; Li, Y.; Liu, C.; Xu, J. Fabrication of β-conglycinin-stabilized nanoemulsions via ultrasound process and influence of SDS and peg 10000 co-emulsifiers on the physicochemical properties of nanoemulsions. Food Res. Int. 2018, 106, 800–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Lu, J.; Liu, F.; Nsor-Atindana, J.; Xu, F.; Goff, H.D.; Ma, J.; Zhong, F. Study on the emulsifying stability and interfacial adsorption of pea proteins. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 88, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R.J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chaiyasit, W.; Silvestre, M.P.; McClements, D.J.; Decker, E.A. Ability of surfactant hydrophobic tail group size to alter lipid oxidation in oil-in-water emulsions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 3077–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, L.; McClements, D.J.; Wu, J.; Decker, E.A. Iron-catalyzed lipid oxidation in emulsions as affected by surfactant, pH and NaCl. Food Chem. 1998, 61, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, L.; Su, P.; Han, K.; Chen, J.; Cao, A.; Zhang, Z.; Jin, Y.; Ma, M. Synthesis and structural characterization of lysozyme-pullulan conjugates obtained by the Maillard reaction. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 71, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Ma, N.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, L.; Ma, G.; Pei, F.; Hu, Q. Characterization and functional evaluation of oat protein isolate-Pleurotus ostreatus β-glucan conjugates formed via Maillard reaction. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 87, 459–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, A.; Kasoju, N.; Bora, U. Fluorescence study of the curcumin-casein micelle complexation and its application as a drug nanocarrier to cancer cells. Biomacromolecules 2008, 9, 2905–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, D.C.; Kothari, R.; Patel, R.C.; Patel, S.C. Retinol and retinoic acid bind to a surface cleft in bovine β-lactoglobulin: A method of binding site determination using fluorescence resonance energy transfer. Biophys. Chem. 1998, 74, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.; Niu, F.; Li, J.; Su, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y. Interactions between tea polyphenol and two kinds of typical egg white proteins-ovalbumin and lysozyme: Effect on the gastrointestinal digestion of both proteins in vitro. Food Res. Int. 2014, 59, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.J.; Han, F.F.; Sui, B.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, H. Effect of ultrasound treatment on the wet heating Maillard reaction between mung bean [Vigna radiate (L.)] protein isolates and glucose and on structural and physico-chemical properties of conjugates. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 1532–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Yang, W.; Fan, R.; Yuan, F.; Gao, Y. Evaluation of structural and functional properties of protein–EGCG complexes and their ability of stabilizing a model β-carotene emulsion. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 45, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, J.J.; Yong, K.Y. Fourier-based classification of protein secondary structures. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 485, 731–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berezovsky, I.N.; Guarnera, E.; Zheng, Z. Basic units of protein structure, folding, and function. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2017, 128, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yakimets, I.; Wellner, N.; Smith, A.C.; Wilson, R.H.; Farhat, I.; Mitchell, J. Mechanical properties with respect to water content of gelatin films in glassy state. Polymer 2005, 46, 12577–12585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattia, C.D.D.; Sacchetti, G.; Mastrocola, D.; Sarker, D.K.; Pittia, P. Surface properties of phenolic compounds and their influence on the dispersion degree and oxidative stability of olive oil O/W emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2010, 24, 652–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Liu, Q.; Kong, B.; Diao, X. Effects of zein hydrolysates coupled with sage (salvia officinalis) extract on the emulsifying and oxidative stability of myofibrillar protein prepared oil-in-water emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 87, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Liang, R.; Chen, L.; Liu, H.; Goff, H.D.; Ma, J.; Zhong, F. The antioxidant mechanism of Maillard reaction products in oil-in-water emulsion system. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 87, 582–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, F.; Dong, S.; Rao, J.; Chen, B. Pea protein isolate-gum Arabic Maillard conjugates improves physical and oxidative stability of oil-in-water emulsions. Food Chem. 2019, 285, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabouri, S.; Geng, J.; Corredig, M. Tea polyphenols association to caseinate-stabilized oil-water interfaces. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 51, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.H.; Wan, Z.L.; Yang, X.Q.; Wang, J.M.; Guo, J.; Lin, Y. Colloidal complexation of zein hydrolysate with tannic acid: Constructing peptides-based nanoemulsions for alga oil delivery. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 54, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Kong, B.; Liu, Q.; Xia, X.; Chen, H. Improvement of the emulsifying and oxidative stability of myofibrillar protein prepared oil-in-water emulsions by addition of zein hydrolysates. Process Biochem. 2017, 53, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xiong, Y.L.; Chen, J.; Zhou, L. Synergy of licorice extract and pea protein hydrolysate for oxidative stability of soybean oil-in-water emulsions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 8204–8213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Xiong, Y.L. Role of interfacial protein membrane in oxidative stability of vegetable oil substitution emulsions applicable to nutritionally modified sausage. Meat Sci. 2015, 109, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, S.; Panya, A.; Zeng, M.; Chen, B.; McClements, D.J.; Decker, E.A. Characteristics and antioxidant activity of hydrolyzed β-lactoglobulin-glucose Maillard reaction products. Food Res. Int. 2012, 46, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, B.F.; Walch, S.G.; Tinzoh, L.N.; Stühlinger, W.; Lachenmeier, D.W. Rapid UHPLC determination of polyphenols in aqueous infusions of Salvia officinalis L. (sage tea). J. Chromatogr. B 2011, 879, 2459–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| 0 | 0.10 mg/mL | 0.25 mg/mL | 0.50 mg/mL | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BPPI | α-Helix (%) | 16.84 ± 0.12 d | 15.96 ± 0.07 c | 15.41 ± 0.14 b | 15.10 ± 0.05 a |
| β-Sheet (%) | 38.29 ± 0.08 a | 38.63 ± 0.07 b | 39.02 ± 0.04 c | 39.17 ± 0.06 d | |
| β-Turn (%) | 28.74 ± 0.10 a,* | 29.14 ± 0.10 b,* | 29.22 ± 0.07 b,* | 29.46 ± 0.08 c,* | |
| Random coil (%) | 16.13 ± 0.04 a | 16.26 ± 0.06 a,b | 16.35 ± 0.16 b | 16.26 ± 0.07 a,b | |
| BBPI-G | α-Helix (%) | 15.94 ± 0.08 c,* | 15.02 ± 0.10 b,* | 14.85 ± 0.09 b,* | 14.46 ± 0.11 a,* |
| β-Sheet (%) | 35.99 ± 0.06 a,* | 36.60 ± 0.08 b,* | 36.51 ± 0.08 b,* | 36.80 ± 0.08 c,* | |
| β-Turn (%) | 33.77 ± 0.08 a | 33.98 ± 0.07 b | 34.04 ± 0.06 b | 34.19 ± 0.05 c | |
| Random coil (%) | 14.30 ± 0.10 a,* | 14.41 ± 0.10 a,b,* | 14.60 ± 0.11 c,* | 14.54 ± 0.04 b,c,* |
| Mean Particle Size (nm) | PDI | Zeta-Potential (mV) | AP (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BBPI | 291.30 ± 0.56 d | 0.220 ± 0.007 c | −24.47 ± 0.23b | 9.52 ± 0.29 a |
| BBPI-EGCG | 267.47 ± 0.38 b | 0.173 ± 0.004 a | −28.30 ± 0.11 d | 12.41 ± 0.19 c |
| BBPI-G | 282.73 ± 0.35 c | 0.187 ± 0.009 b | −23.20 ± 0.17 a | 10.53 ± 0.38 b |
| BBPI-G-EGCG | 245.59 ± 0.71 a | 0.172 ± 0.007 a | −26.30 ± 0.26 c | 17.54 ± 0.29 d |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, H.; Jin, H.; Gao, Y.; Zhu, X.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, C.; Xu, J. The Effect of (−)-Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Non-Covalent Interaction with the Glycosylated Protein on the Emulsion Property. Polymers 2019, 11, 1688. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11101688
Feng H, Jin H, Gao Y, Zhu X, Zhao Q, Liu C, Xu J. The Effect of (−)-Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Non-Covalent Interaction with the Glycosylated Protein on the Emulsion Property. Polymers. 2019; 11(10):1688. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11101688
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Haiying, Hua Jin, Yu Gao, Xiuqing Zhu, Qingshan Zhao, Chunhong Liu, and Jing Xu. 2019. "The Effect of (−)-Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Non-Covalent Interaction with the Glycosylated Protein on the Emulsion Property" Polymers 11, no. 10: 1688. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11101688
APA StyleFeng, H., Jin, H., Gao, Y., Zhu, X., Zhao, Q., Liu, C., & Xu, J. (2019). The Effect of (−)-Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Non-Covalent Interaction with the Glycosylated Protein on the Emulsion Property. Polymers, 11(10), 1688. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11101688