Investigation of the Flammability and Thermal Stability of Halogen-Free Intumescent System in Biopolymer Composites Containing Biobased Carbonization Agent and Mechanism of Their Char Formation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of PLA/IFR Composites
2.3. Mechanism of Char Formation
2.4. Limiting Oxygen Index and UL-94 Vertical Burning Test
2.5. Cone Calorimetry Test
2.6. Thermogravimetric Analysis
2.7. Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.8. Mechanical Testing
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. LOI and UL-94 Vertical Burning Test
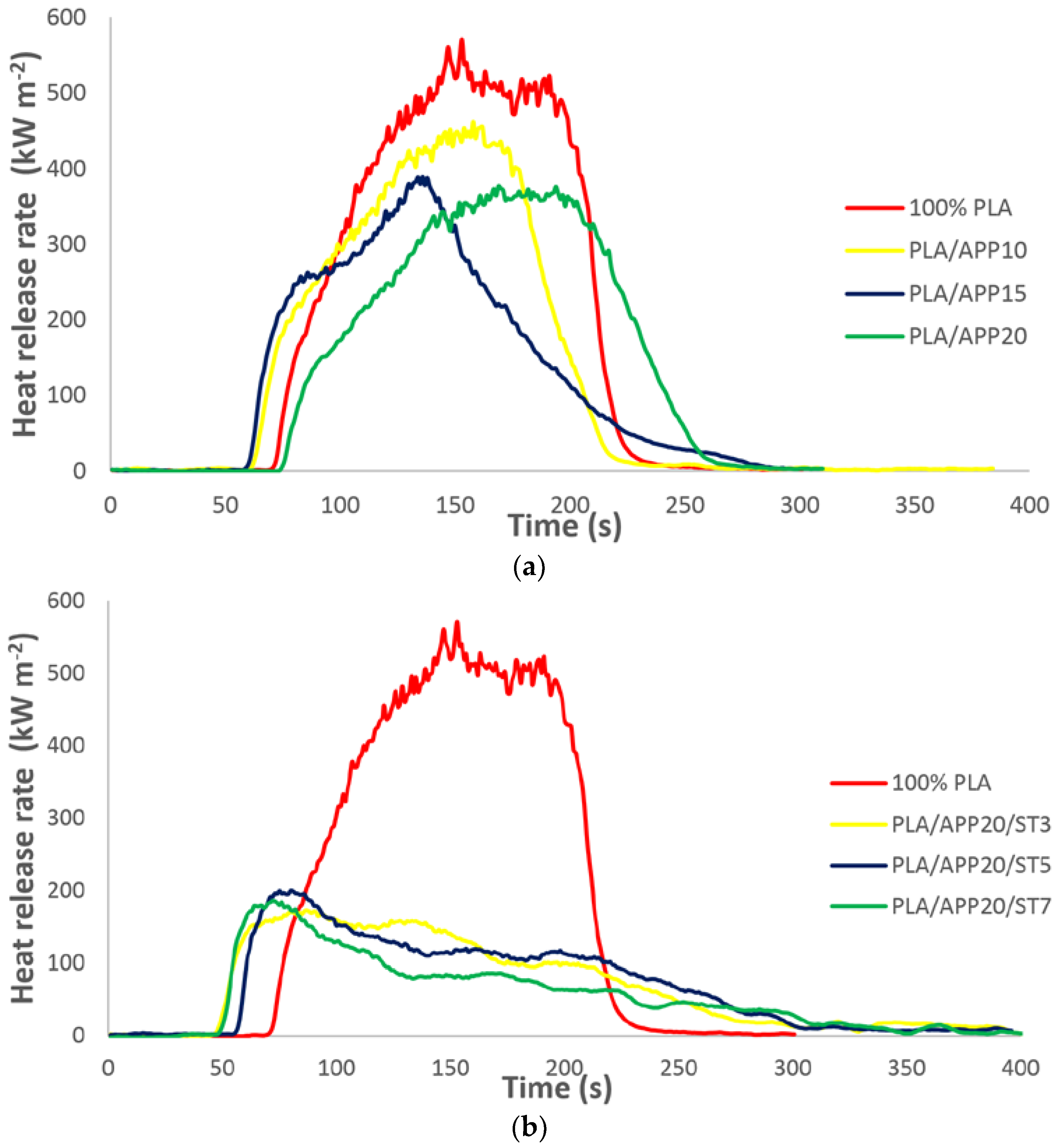
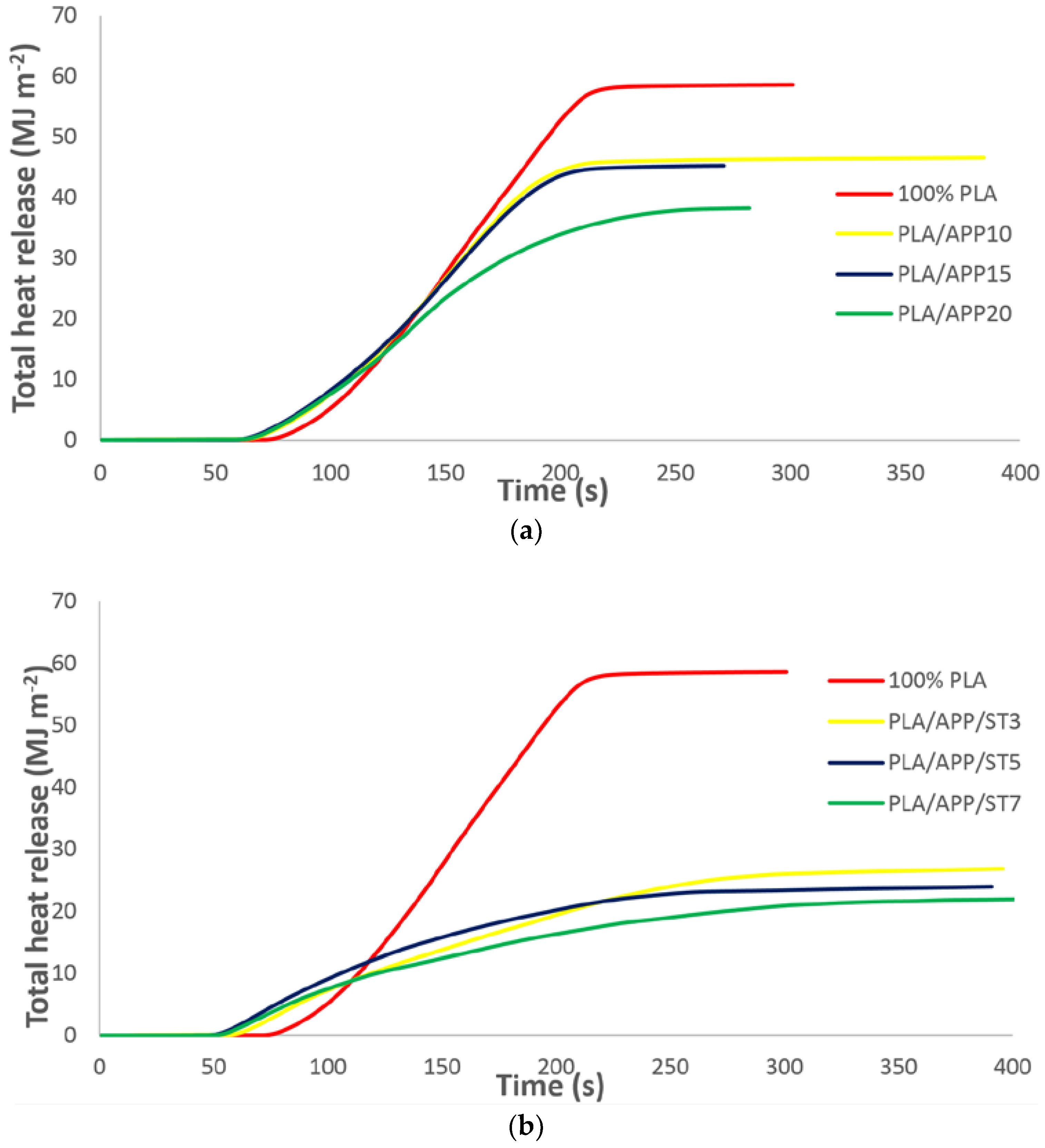
3.2. Cone Calorimetry
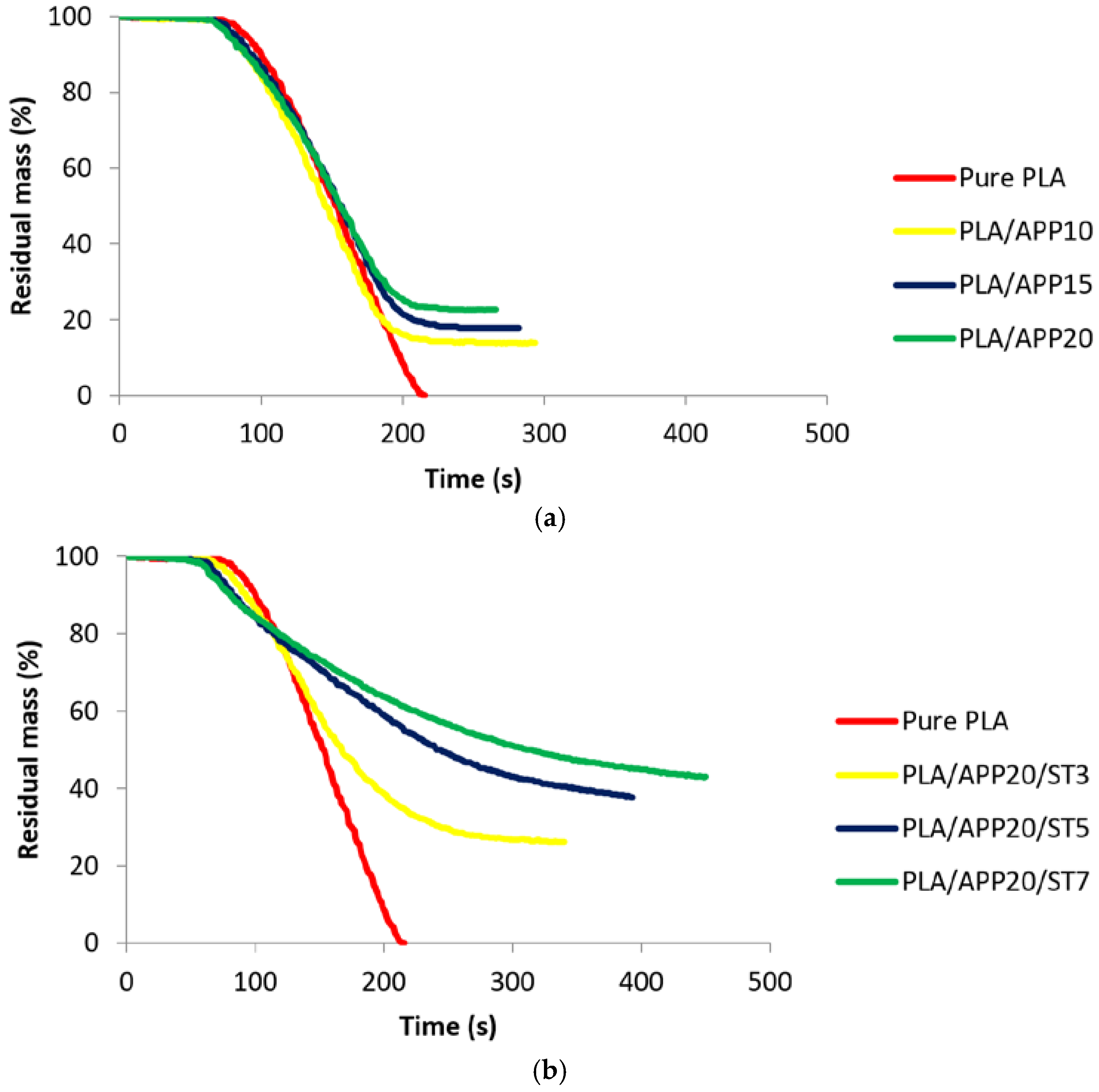
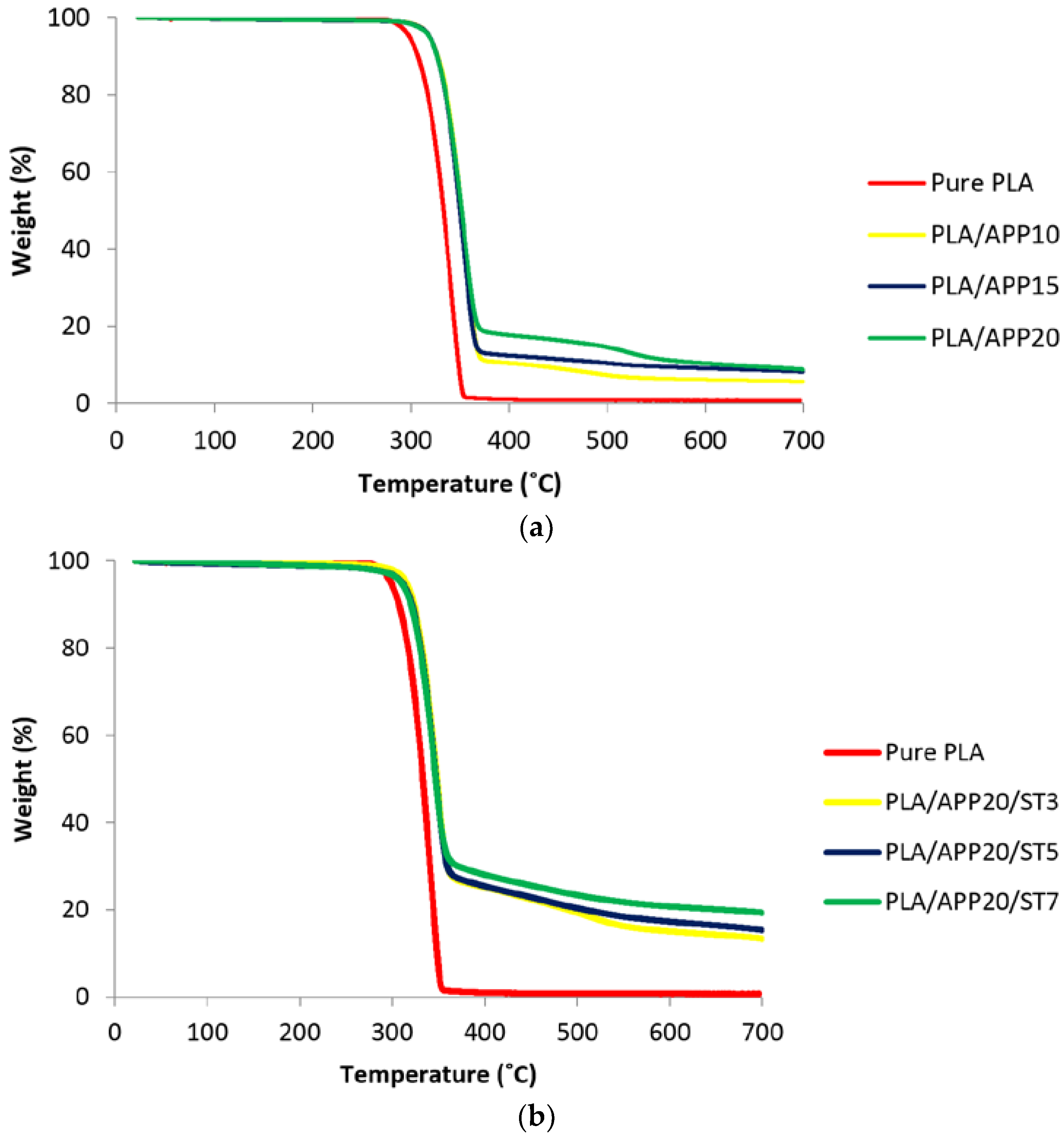
3.3. Thermogravimetric Analysis
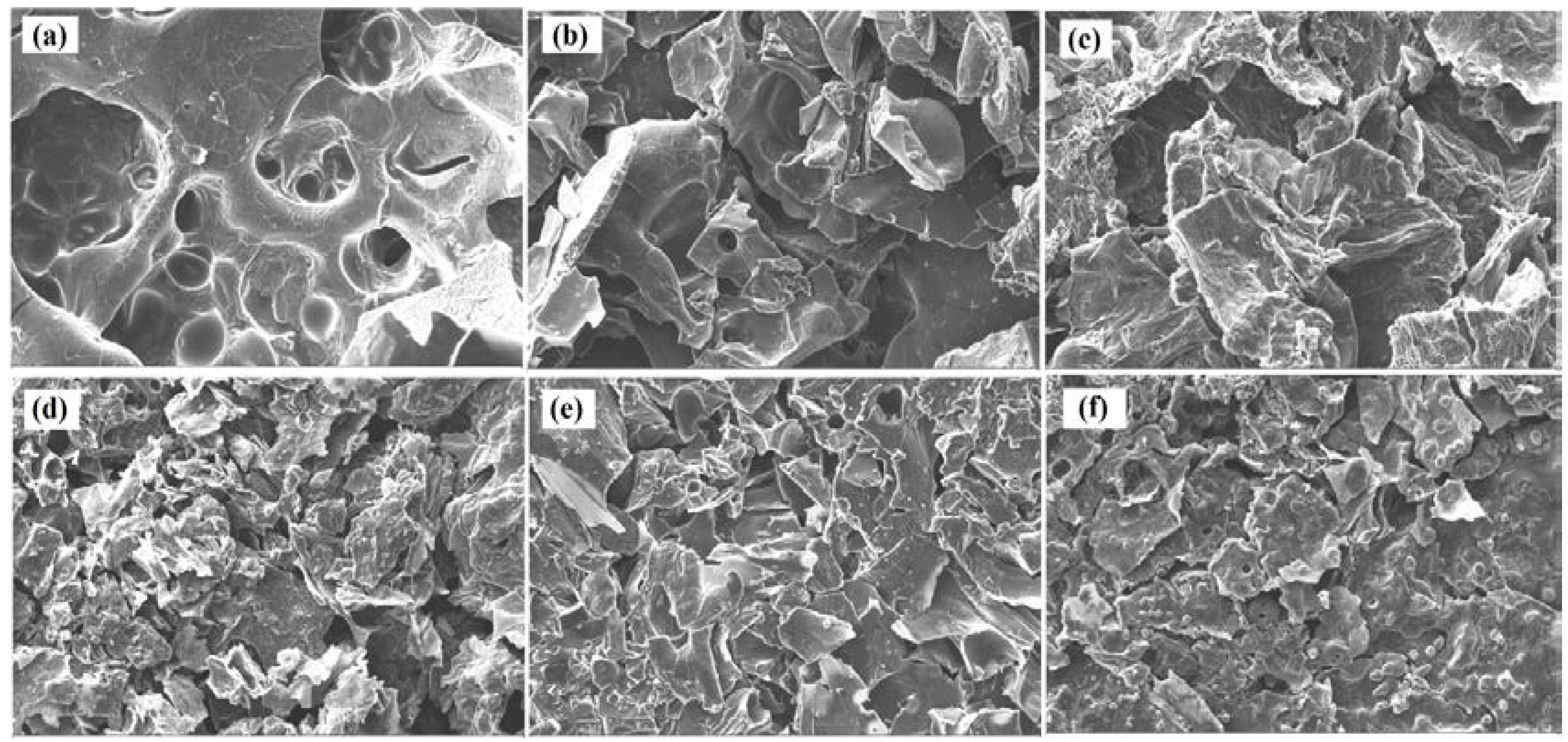
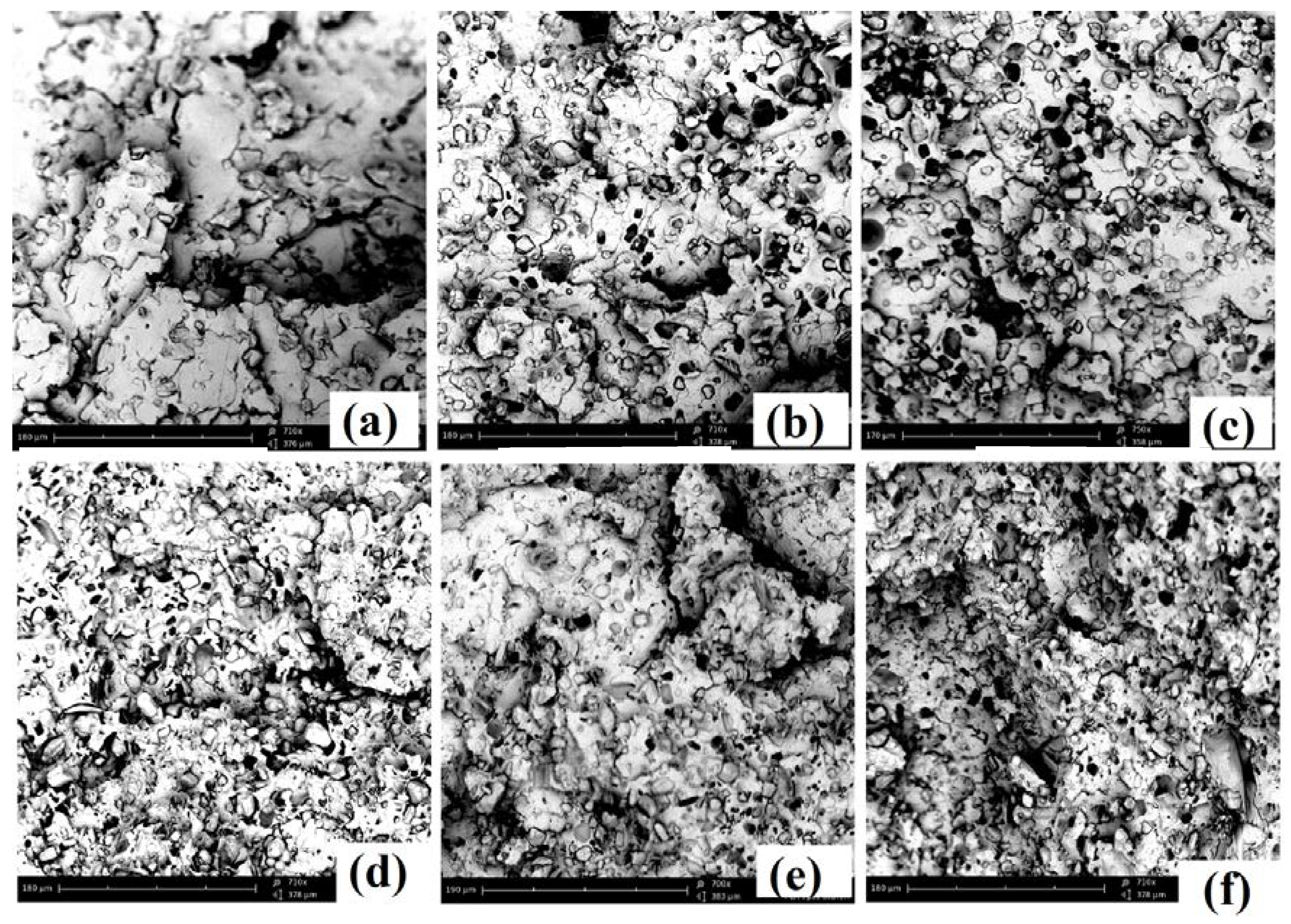
3.4. SEM Analysis
3.5. Mechanical Testing
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cayla, A.; Rault, F.; Giraud, S.; Salaün, F.; Fierro, V.; Celzard, A. PLA with intumescent system containing lignin and ammonium polyphosphate for flame retardant textile. Polymers 2016, 8, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.C. Flammability and tensile properties of polylactide nanocomposites with short carbon fibers. J. Mater. Sci. 2015, 50, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Guan, J.; Tang, R.; Liu, K. Improvement of flame retardancy of poly (lactic acid) nonwoven fabric with a phosphorus- containing flame retardant. J. Ind. Text. 2015, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idumah, C.I.; Hassan, A. Emerging trends in flame retardancy of biofibers, biopolymers, biocomposites, and bionanocomposites. Rev. Chem. Eng. 2016, 32, 115–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atabek Savas, L.; Mutlu, A.; Dike, A.S.; Tayfun, U.; Dogan, M. Effect of carbon fiber amount and length on flame retardant and mechanical properties of intumescent polypropylene composites. J. Compos. Mater. 2017, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depeng, L.; Chixiang, L.; Xiulei, J.; Tao, L.; Ling, Z. Synergistic effects of intumescent flame retardant and nano-CaCO3 on foamability and flame-retardant property of polypropylene composites foams. J. Cell. Plast. 2017, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duquesne, S.; Samyn, F.; Ouagne, P.; Bourbigot, S. Flame retardancy and mechanical properties of flax reinforced woven for composite applications. J. Ind. Text. 2015, 44, 665–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.Y.; Leuteritz, A.; Wang, Y.Z.; Wagenknecht, U.; Heinrich, G. Preparation and burning behaviors of flame retarding biodegradable poly(lactic acid) nanocomposite based on zinc aluminum layered double hydroxide. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2010, 95, 2474–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourbigot, S.; Duquesne, S.; Fontaine, G.; Bellayer, S.; Turf, T.; Samyn, F. Characterization and Reaction to Fire of Polymer Nanocomposites with and without Conventional Flame Retardants. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2008, 486, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.Y.; Song, Y.P.; Lin, L.; Wang, X.L.; Wang, Y.Z. A novel phosphorus-containing poly(lactic acid) toward its flame retardation. Polymer 2011, 52, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Wei, P.; Jiang, P.; Li, Z.; Yan, Y.; Ji, K. Aluminated mesoporous silica as novel high-effective flame retardant in polylactide. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2013, 82, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solarski, S.; Mahjoubi, F.; Ferreira, M.; Devaux, E.; Bachelet, P.; Bourbigot, S.; Delobel, R.; Coszach, P.; Murariu, M.; Da Silva Ferreira, A.; et al. Designing Polylactide/Clay nanocomposites for textile applications: Effect of processing conditions, spinning, and characterization. Polym. Polym. Compos. 2013, 21, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thunga, M.; Chen, K.; Grewell, D.; Kessler, M.R. Bio-renewable precursor fibers from lignin/polylactide blends for conversion to carbon fibers. Carbon 2014, 68, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsoulis, C.; Kandare, E.; Kandola, B.K. The combined effect of epoxy nanocomposites and phosphorus flame retardant additives on thermal and fire reaction properties of fiber-reinforced composites. J. Fire Sci. 2011, 29, 361–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Manley, R.S.J.; Feldman, D. Synthetic polymer-lignin copolymers and blends. Prog. Polym. Sci. 1992, 17, 611–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wang, J.; Zhao, D.; Zhai, W. Preparation of microcellular poly(lactic acid) composites foams with improved flame retardancy. J. Cell. Plast. 2017, 53, 45–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, J.; Song, L.; Nie, S.; Hu, Y. Combustion properties and thermal degradation behavior of polylactide with an effective intumescent flame retardant. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2009, 94, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Xiao, X.; Tai, Q.; Huang, H.; Yang, J.; Hu, Y. Preparation of lignin-silica hybrids and its application in intumescent flame-retardant poly(lactic acid) system. High Perform. Polym. 2012, 24, 738–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.W.; Guan, J.P.; Tang, R.C.; Liu, K.Q. Phytic acid as a bio-based phosphorus flame retardant for poly(lactic acid) nonwoven fabric. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 124, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Yan, H.; Shen, L.; Fang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, B. Chitosan/phytic acid polyelectrolyte complex: A green and renewable intumescent flame retardant system for ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 19199–19207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.X.; Su, S.P.; Zhu, J. An intumescent flame retardant system using β-cyclodextrin as a carbon source in polylactic acid (PLA). Polym. Adv. Technol. 2011, 22, 1115–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laufer, G.; Kirkland, C.; Cain, A.A.; Grunlan, J.C. Clay-chitosan nanobrick walls: Completely renewable gas barrier and flame-retardant nanocoatings. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 1643–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Ren, Q.; Zheng, W.; Zhai, W. Improved flame-retardant properties of poly(lactic acid) foams using starch as a natural charring agent. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 1422–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reti, C.; Casetta, M.; Duquesne, S.; Bourbigot, S.; Delobel, R. Flammability properties of intumescent PLA including starch and lignin. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2006, 17, 395–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocz, K.; Szolnoki, B.; Marosi, A.; Tábi, T.; Wladyka-Przybylak, M.; Marosi, G. Flax fibre reinforced PLA/TPS biocomposites flame retarded with multifunctional additive system. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2014, 106, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pack, S.; Bobo, E.; Muir, N.; Yang, K.; Swaraj, S.; Ade, H.; Cao, C.; Korach, C.S.; Kashiwagi, T.; Rafailovich, M.H. Engineering biodegradable polymer blends containing flame retardant-coated starch/nanoparticles. Polymer 2012, 53, 4787–4799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teoh, E.L.; Mariatti, M.; Chow, W.S. Thermal and Flame Resistant Properties of Poly (Lactic Acid)/Poly (Methyl Methacrylate) Blends Containing Halogen-free Flame Retardant. Procedia Chem. 2016, 19, 795–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushima, K.; Murariu, M.; Camino, G.; Dubois, P. Effect of expanded graphite/layered-silicate clay on thermal, mechanical and fire retardant properties of poly(lactic acid). Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2010, 95, 1063–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.J.; Liu, S.R.; Han, L.J.; Wang, X.M.; Bian, Y.J.; Dong, L.S. Effect of a phosphorus-containing oligomer on flame-retardant, rheological and mechanical properties of poly (lactic acid). Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2013, 98, 1389–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murariu, M.; Bonnaud, L.; Yoann, P.; Fontaine, G.; Bourbigot, S.; Dubois, P. New trends in polylactide (PLA)-based materials: “Green” PLA-Calcium sulfate (nano)composites tailored with flame retardant properties. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2010, 95, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.L.; Wang, D.Y.; Chen, H.B.; Chen, L.; Wang, X.L.; Wang, Y.Z. Effect of a phosphorus-containing flame retardant on the thermal properties and ease of ignition of poly(lactic acid). Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2011, 96, 1557–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, D.M.; Lee, J.; Citro, C.J.; Novy, M. Flame retarded poly(lactic acid) using POSS-modified cellulose. 1. Thermal and combustion properties of intumescing composites. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2013, 98, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabanian, M.; Kang, N.J.; Wang, D.Y.; Wagenknecht, U.; Heinrich, G. Synthesis of aromatic-aliphatic polyamide acting as adjuvant in polylactic acid (PLA)/ammonium polyphosphate (APP) system. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2013, 98, 1036–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
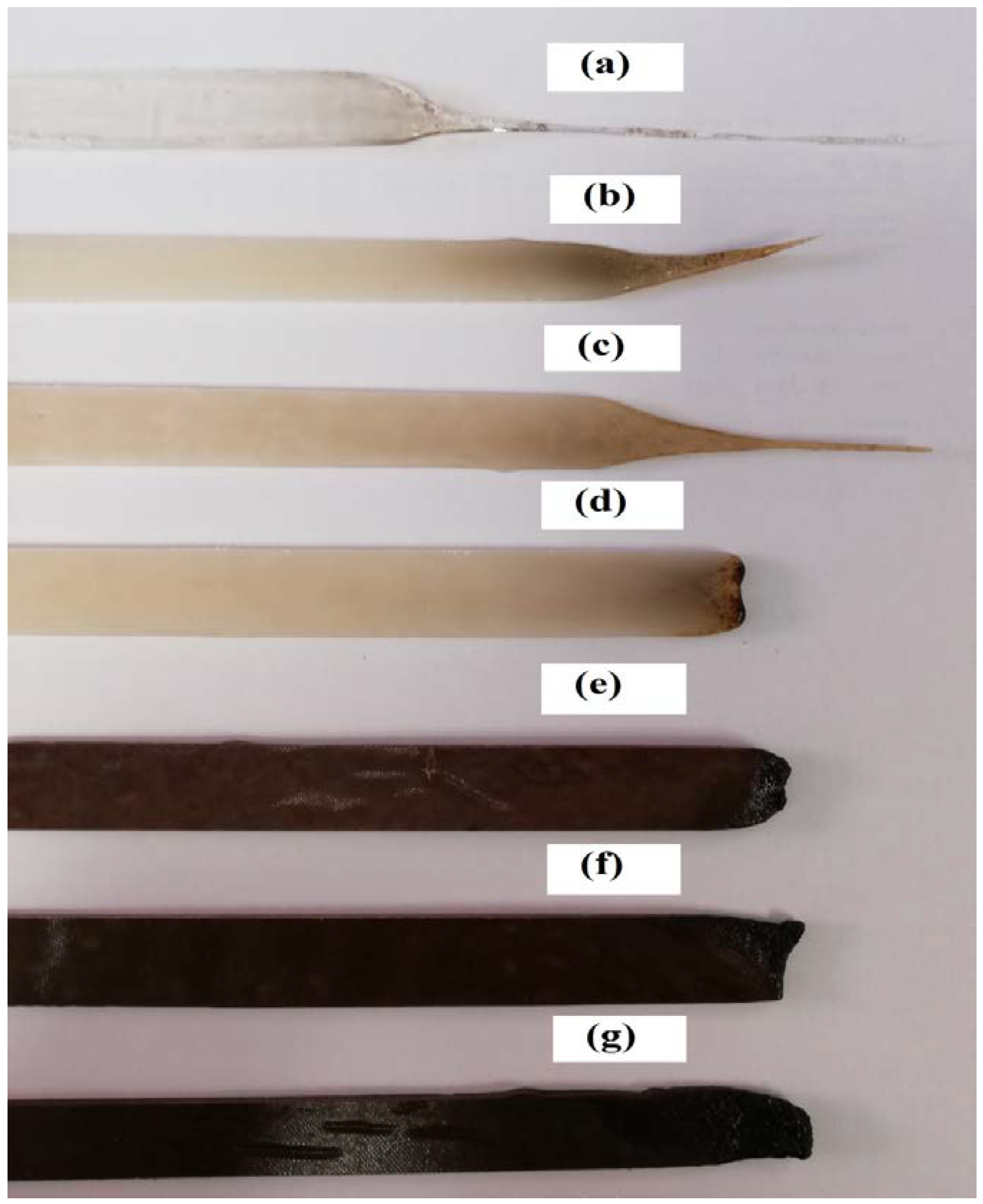
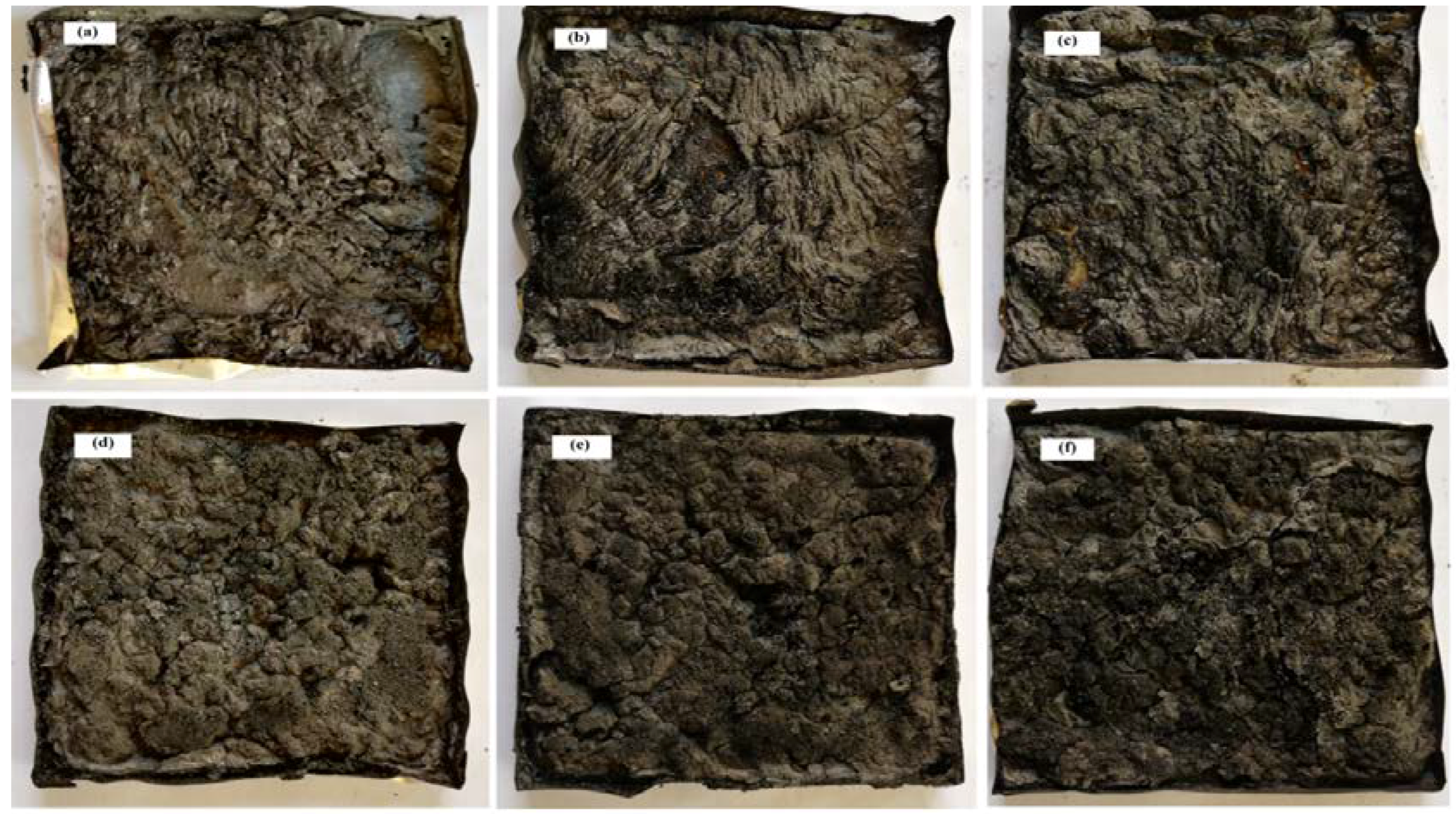
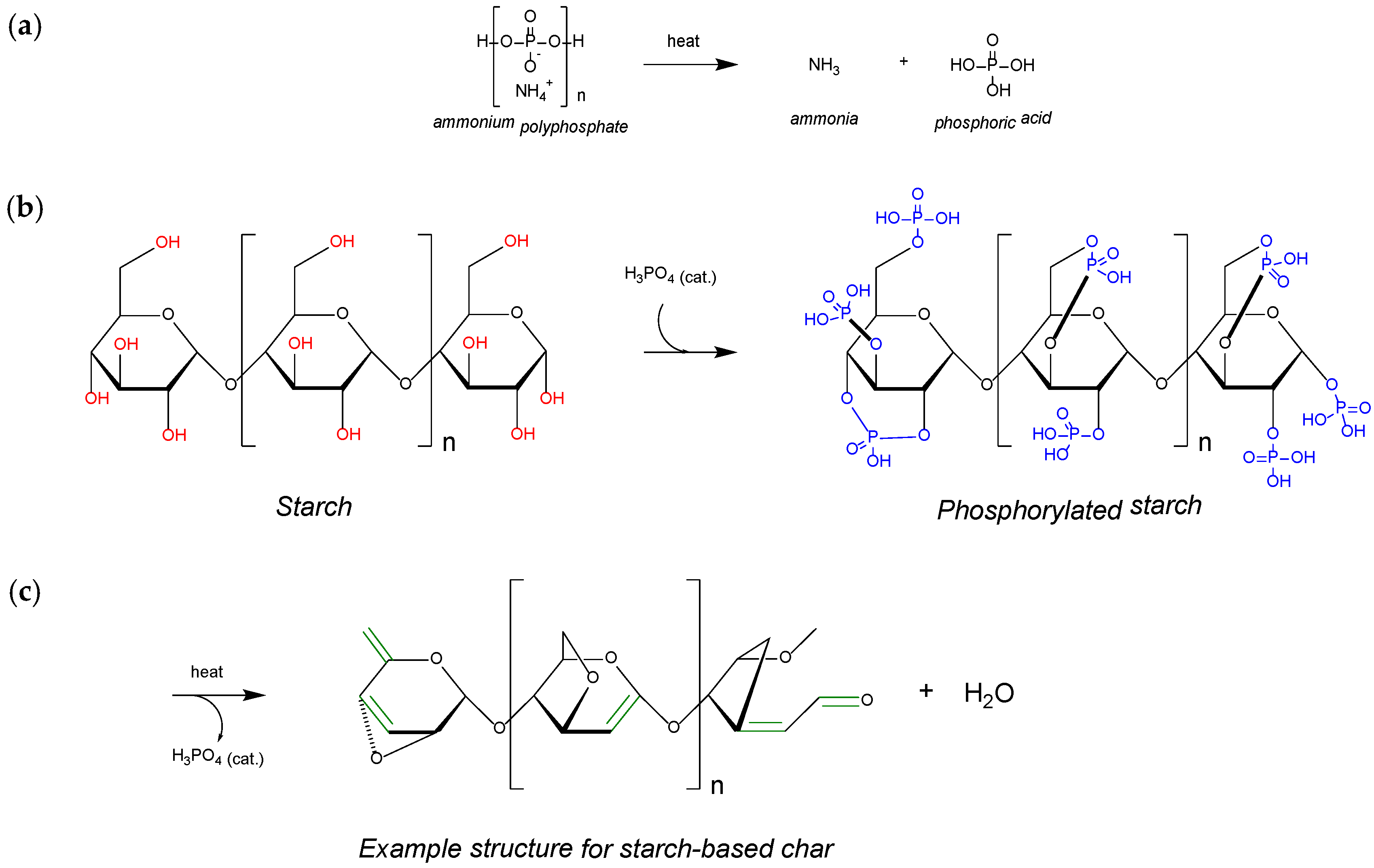


| No | Formulations | PLA wt % | APP % | ST % | LOI % | UL-94 | Dripping |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | PLA | 100 | 0 | 0 | 19.5 | Failed | Y/Y |
| 2 | PLA/APP10 | 90 | 10 | 0 | 24.4 | V-2 | Y/Y |
| 3 | PLA/APP15 | 85 | 15 | 0 | 28.5 | V-1 | N/Y |
| 4 | PLA/APP20 | 80 | 20 | 0 | 31.9 | V-0 | N/Y |
| 5 | PLA/APP20/ST3 | 77 | 20 | 3 | 34.5 | V-0 | N/N |
| 6 | PLA/APP20/ST5 | 75 | 20 | 5 | 36.2 | V-0 | N/N |
| 7 | PLA/APP20/ST7 | 73 | 20 | 7 | 37.3 | V-0 | N/N |
| No. | Formulation | TTI (s) | PHRR (kW m−2) | THR (MJ m−2) | Residual Mass (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | PLA | 41 ± 1.3 | 570 ± 4 | 58 ± 0.11 | 0 ± 0.00 |
| 2 | PLA/APP10 | 48 ± 1.7 | 461 ± 6 | 46 ± 0.18 | 14 ± 0.03 |
| 3 | PLA/APP15 | 53 ± 2.2 | 378 ± 7 | 44 ± 0.32 | 17 ± 0.06 |
| 4 | PLA/APP20 | 58 ± 1.5 | 337 ± 4 | 38 ± 0.23 | 22 ± 0.08 |
| 5 | PLA/APP20/ST3 | 63 ± 2.1 | 212 ± 6 | 28 ± 0.19 | 26 ± 0.05 |
| 6 | PLA/APP20/ST5 | 67 ± 1.4 | 200 ± 5 | 26 ± 0.13 | 37 ± 0.04 |
| 7 | PLA/APP20/ST7 | 77 ± 1.8 | 192 ± 3 | 24 ± 0.28 | 43 ± 0.06 |
| No | Formulations | T5 (°C) | T50 (°C) | Tmax (°C) | Residue at 700 °C (wt %) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | PLA | 325 | 372 | 377 | 0.00 |
| 2 | PLA/APP10 | 320 | 374 | 379 | 5.90 |
| 3 | PLA/APP15 | 346 | 376 | 378 | 8.16 |
| 4 | PLA/APP20 | 358 | 376 | 378 | 9.21 |
| 5 | PLA/APP20/ST3 | 365 | 380 | 379 | 13.34 |
| 6 | PLA/APP20/ST5 | 371 | 381 | 380 | 15.32 |
| 7 | PLA/APP20/ST7 | 373 | 383 | 380 | 19.30 |
| Formulations | Tensile Strength ± (MPa) | Elongation at Break ± (%) | Young’s Modulus ± (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PLA | 69.19 ± 3 | 2.49 ± 0.2 | 4695.43 ± 21 |
| PLA/APP10 | 47.86 ± 1 | 2.35 ± 0.4 | 4146.65 ± 18 |
| PLA/APP15 | 46.12 ± 2 | 2.03 ± 0.3 | 4087.90 ± 17 |
| PLA/APP20 | 45.62 ± 2 | 1.98 ± 0.1 | 3822.11 ± 15 |
| PLA/APP20/ST3 | 43.93 ± 2 | 1.94 ± 0.1 | 3750.73 ± 13 |
| PLA/APP20/ST5 | 39.30 ± 1 | 1.87 ± 0.1 | 2870.04 ± 14 |
| PLA/APP20/ST7 | 38.41 ± 1 | 1.66 ± 0.1 | 2522.32 ± 11 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maqsood, M.; Seide, G. Investigation of the Flammability and Thermal Stability of Halogen-Free Intumescent System in Biopolymer Composites Containing Biobased Carbonization Agent and Mechanism of Their Char Formation. Polymers 2019, 11, 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11010048
Maqsood M, Seide G. Investigation of the Flammability and Thermal Stability of Halogen-Free Intumescent System in Biopolymer Composites Containing Biobased Carbonization Agent and Mechanism of Their Char Formation. Polymers. 2019; 11(1):48. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11010048
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaqsood, Muhammad, and Gunnar Seide. 2019. "Investigation of the Flammability and Thermal Stability of Halogen-Free Intumescent System in Biopolymer Composites Containing Biobased Carbonization Agent and Mechanism of Their Char Formation" Polymers 11, no. 1: 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11010048
APA StyleMaqsood, M., & Seide, G. (2019). Investigation of the Flammability and Thermal Stability of Halogen-Free Intumescent System in Biopolymer Composites Containing Biobased Carbonization Agent and Mechanism of Their Char Formation. Polymers, 11(1), 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11010048






