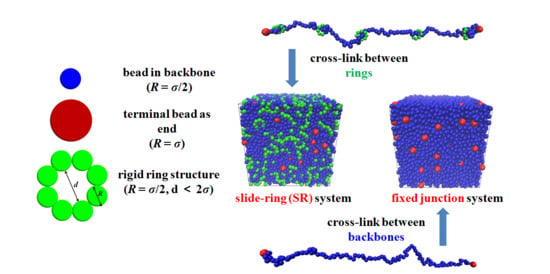
Designing the Slide-Ring Polymer Network with both Good Mechanical and Damping Properties via Molecular Dynamics Simulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Simulation and Method
2.1. Model and Force Field
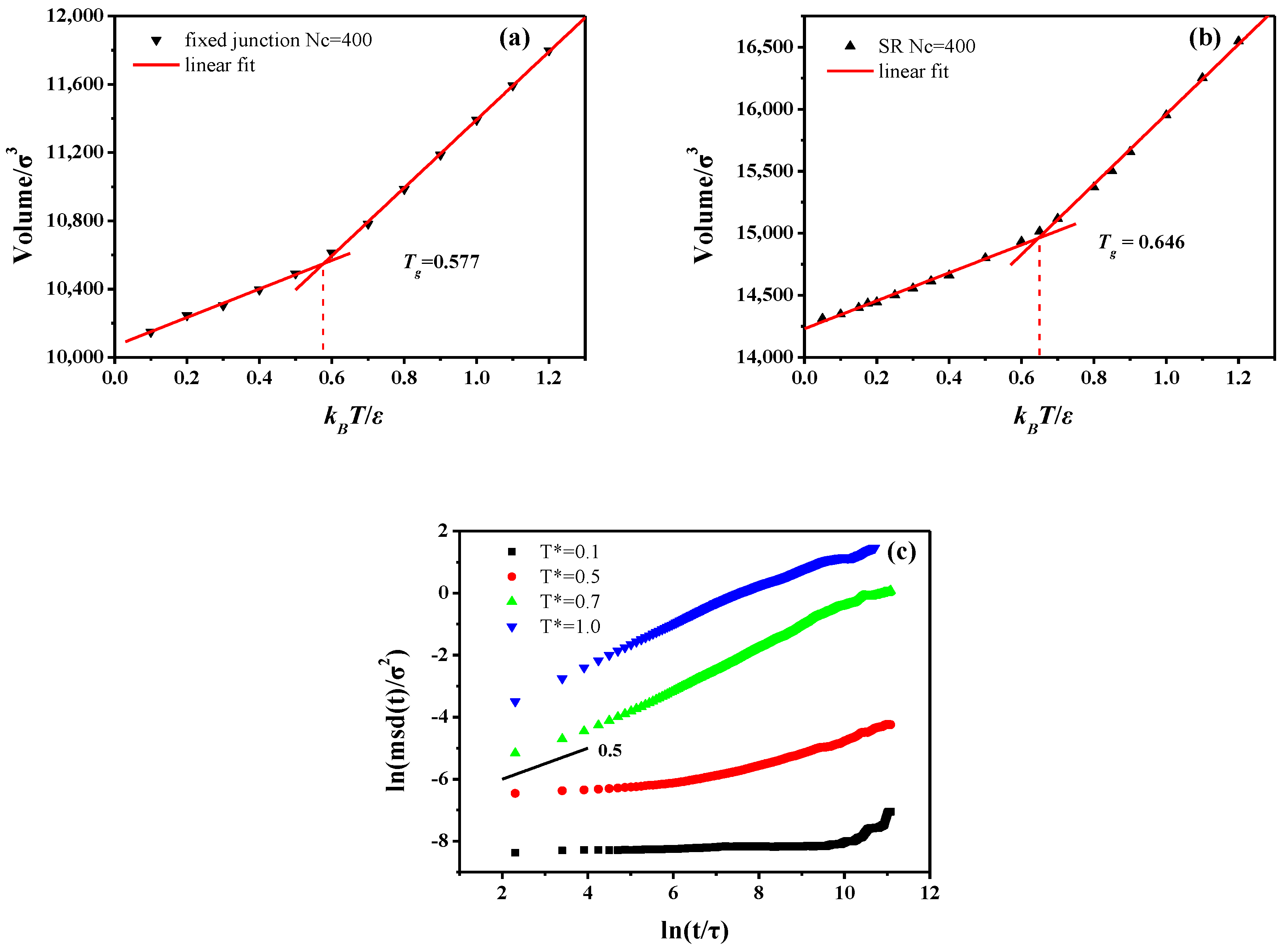
2.2. Equilibrium Simulation
2.3. Non-Equilibrium Simulation
3. Results and Discussion
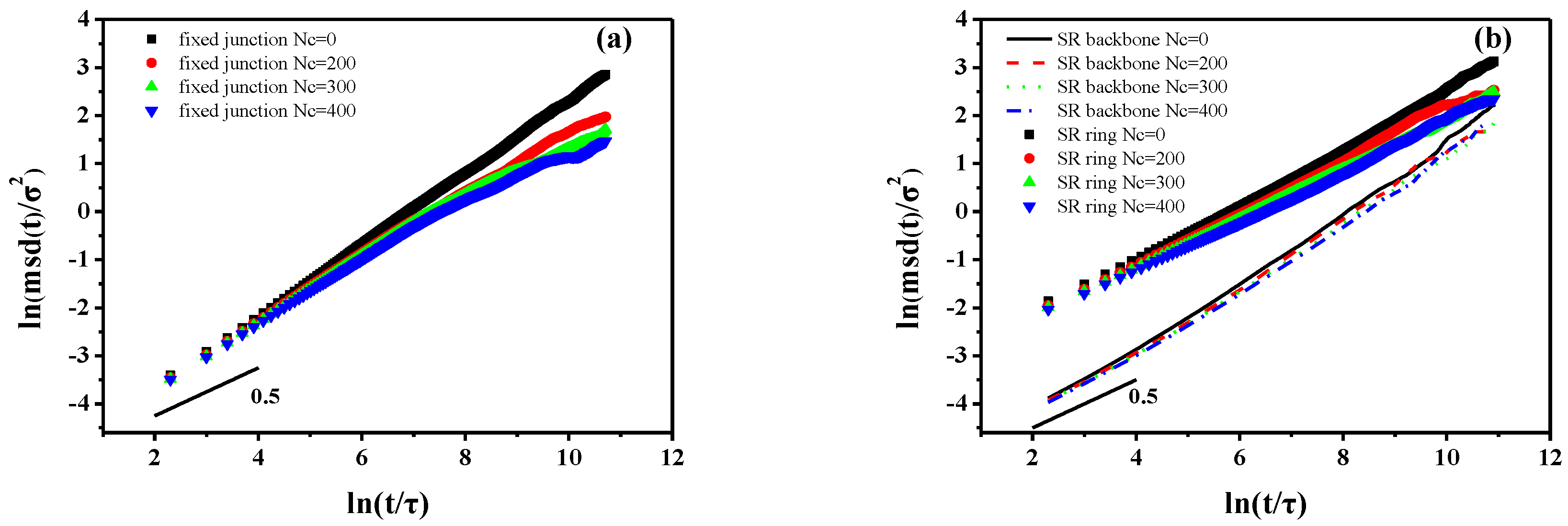
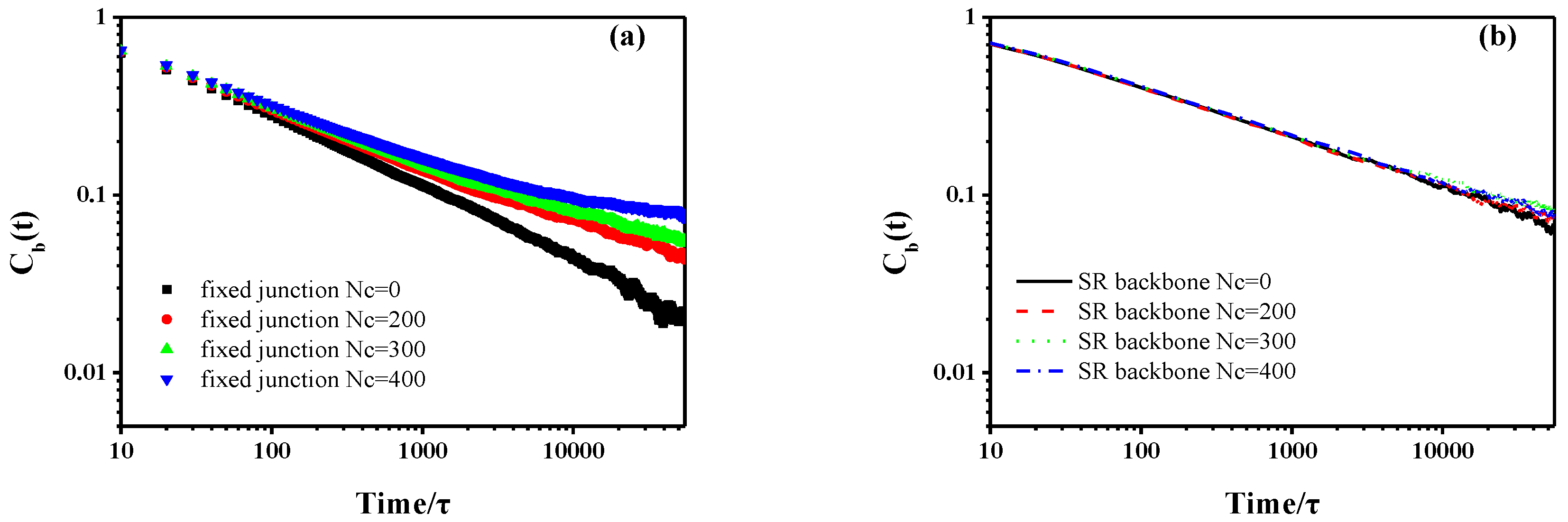
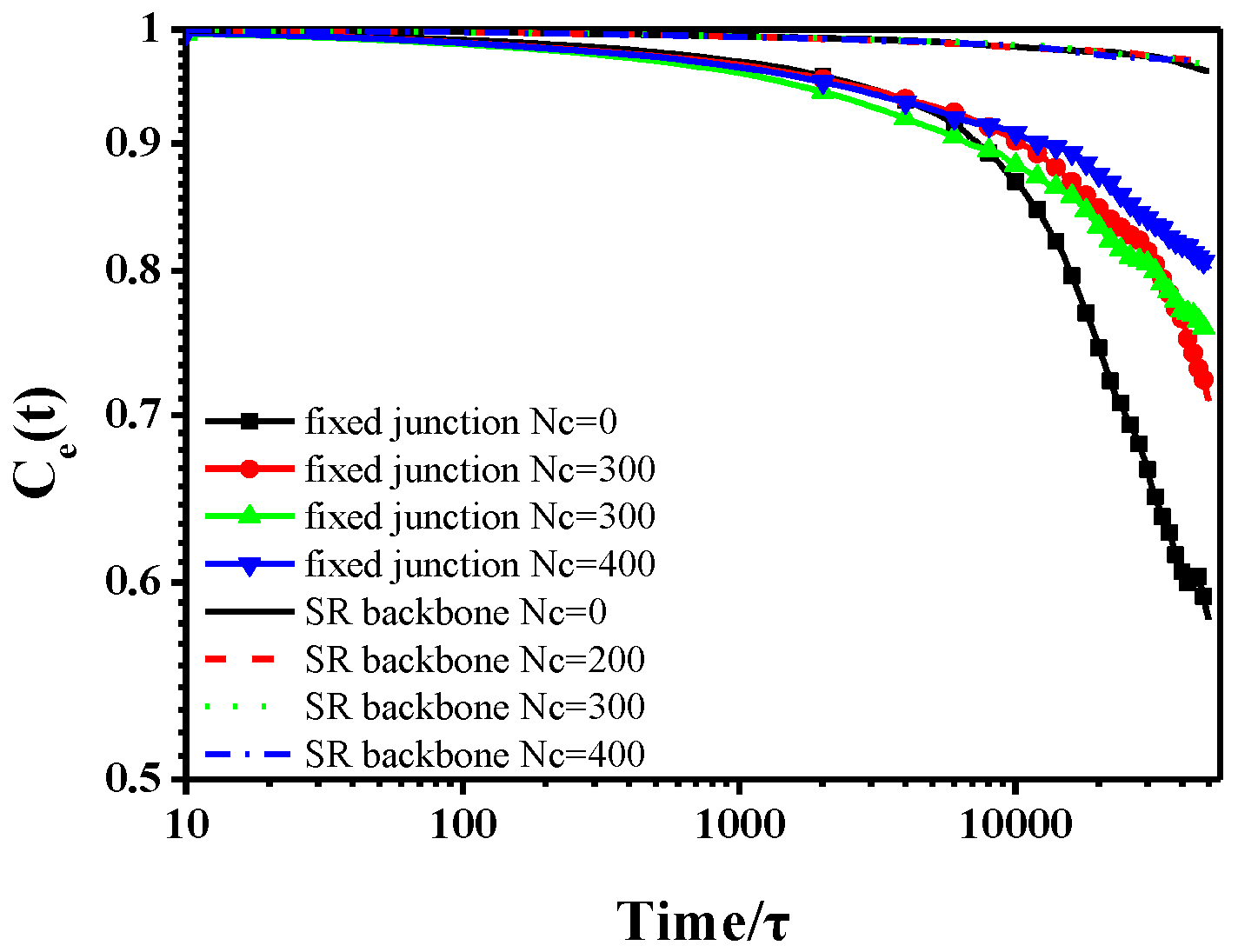
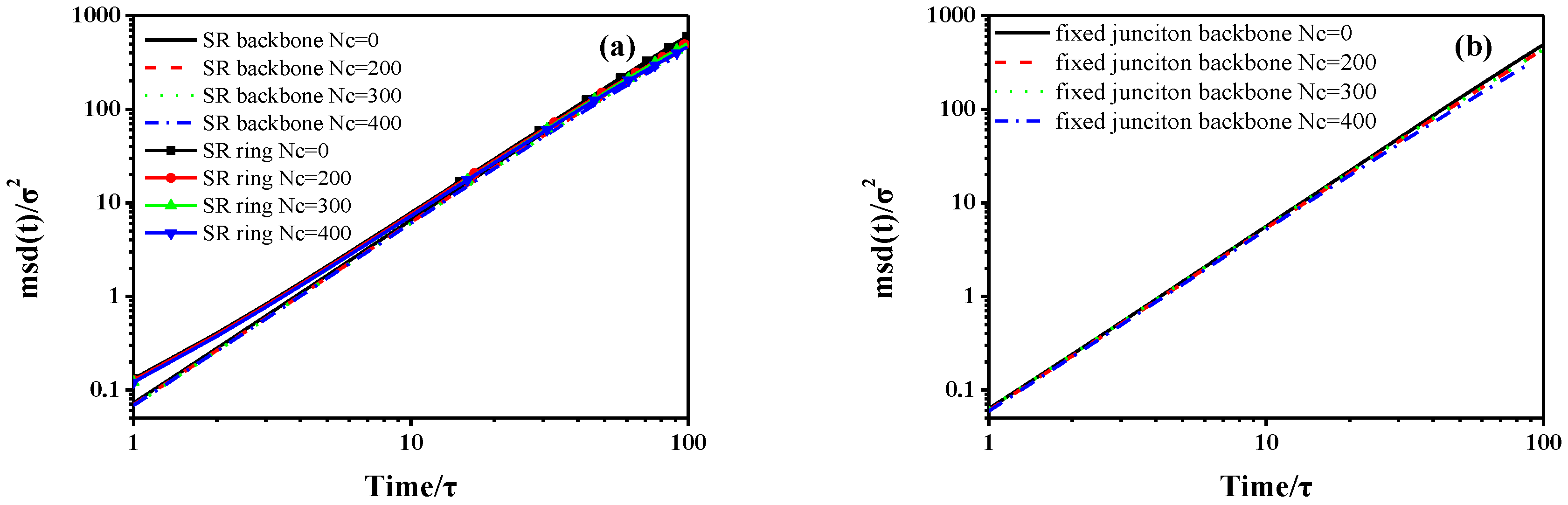
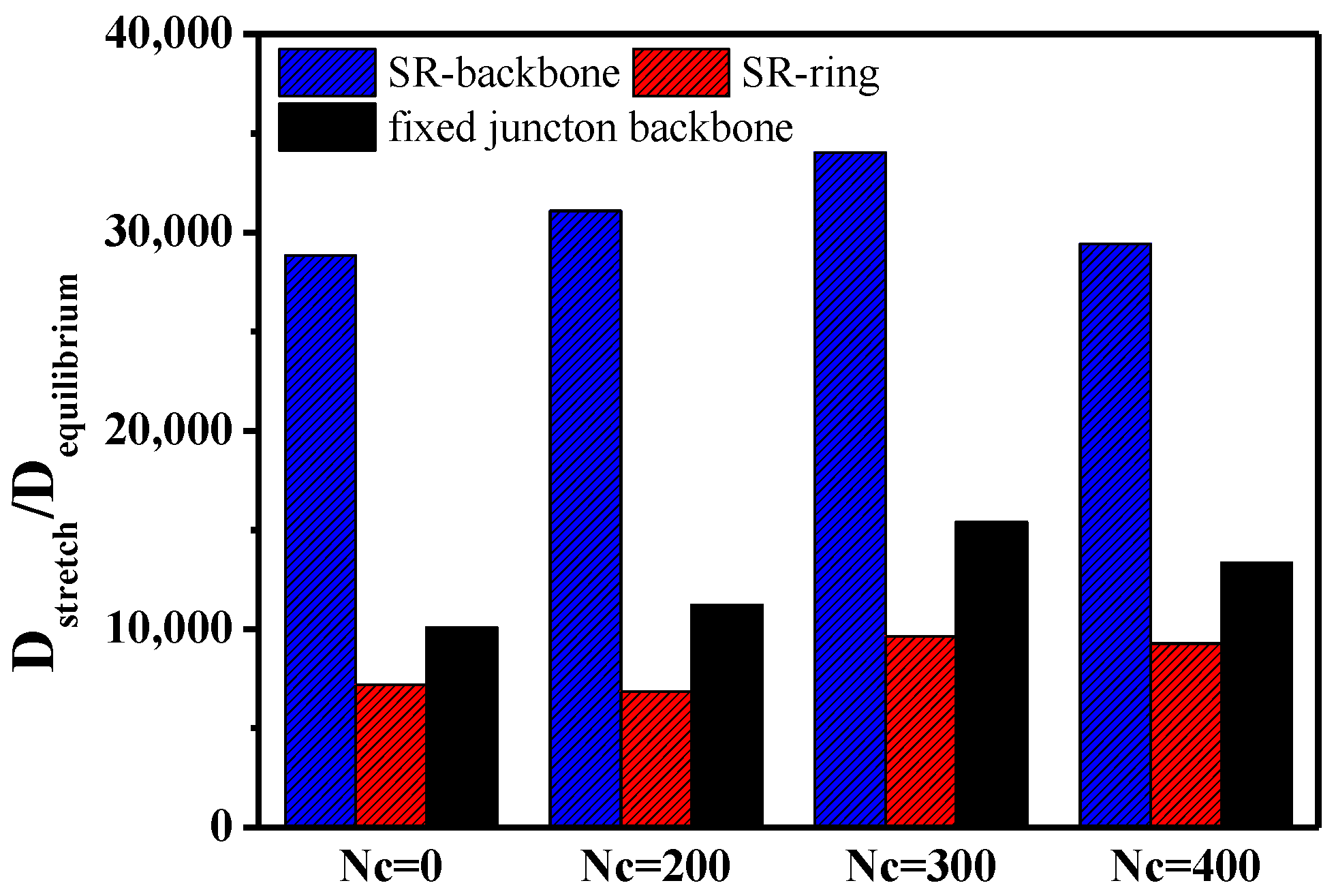
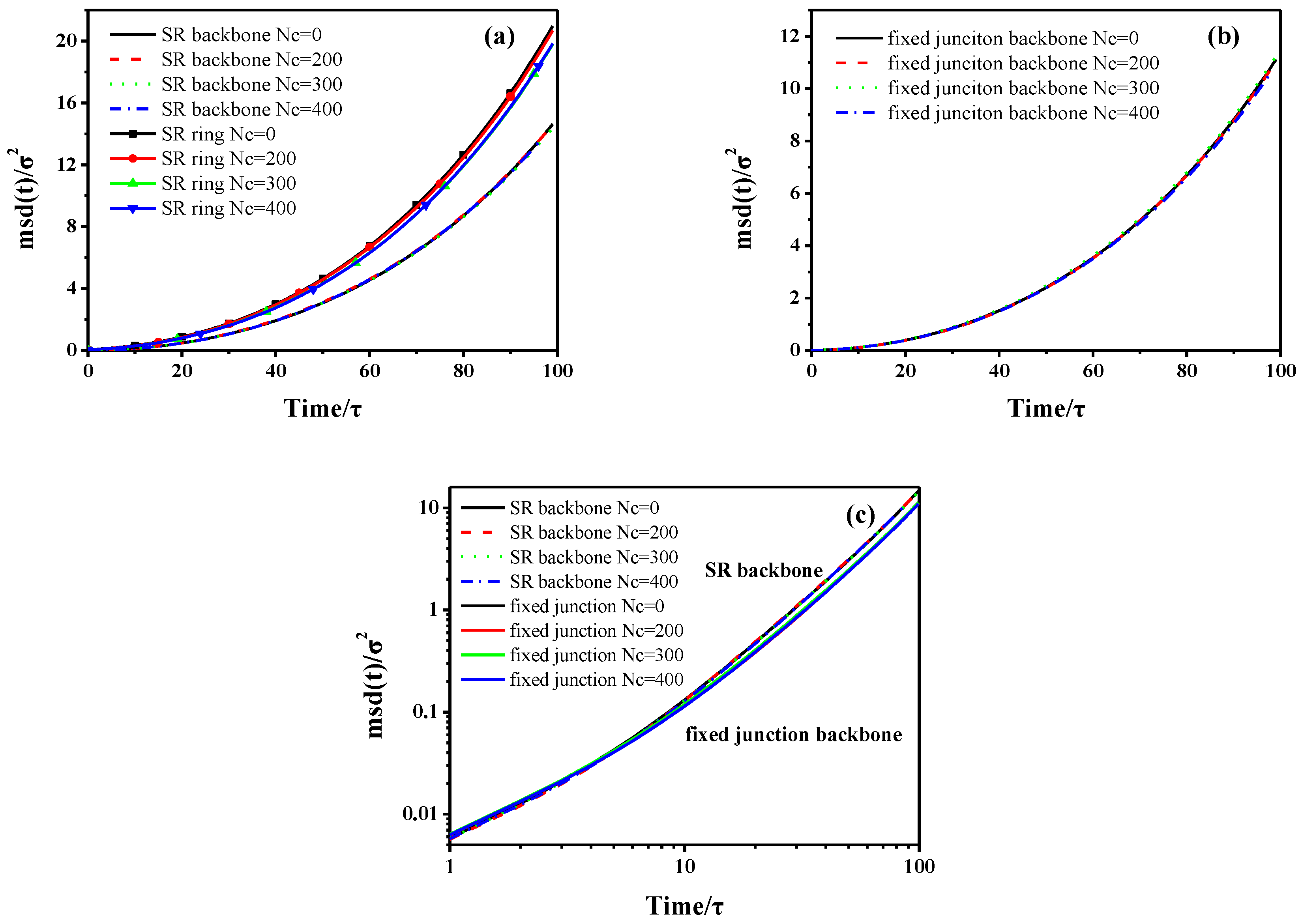
3.1 Dynamic Properties
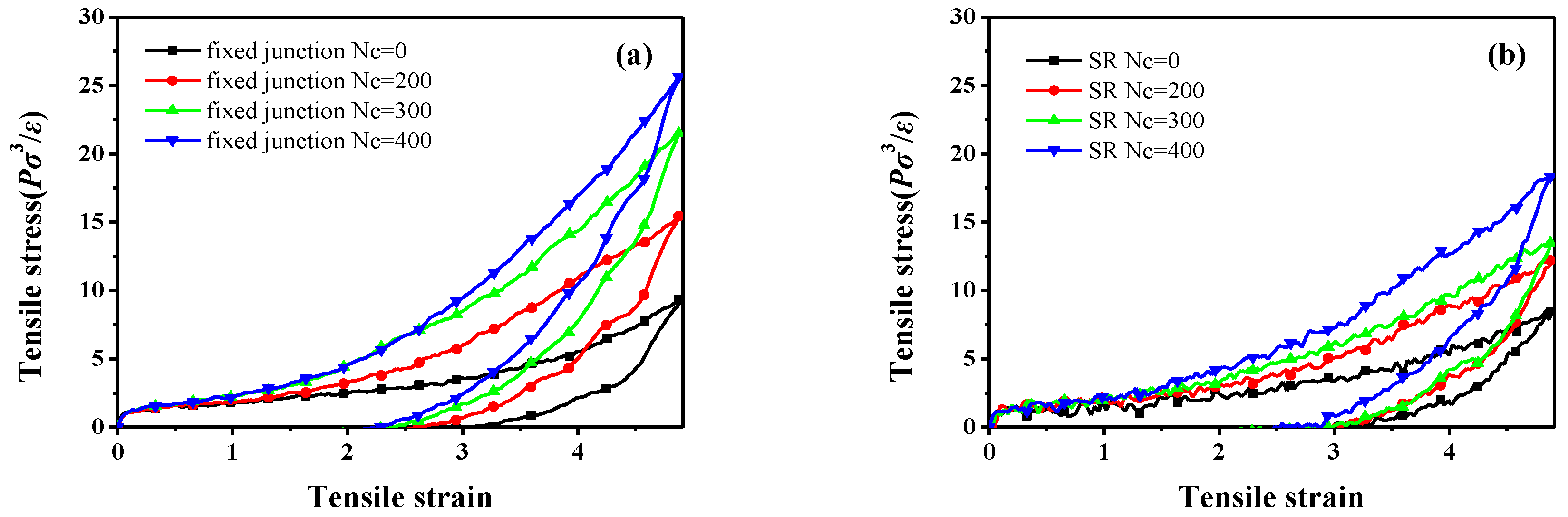
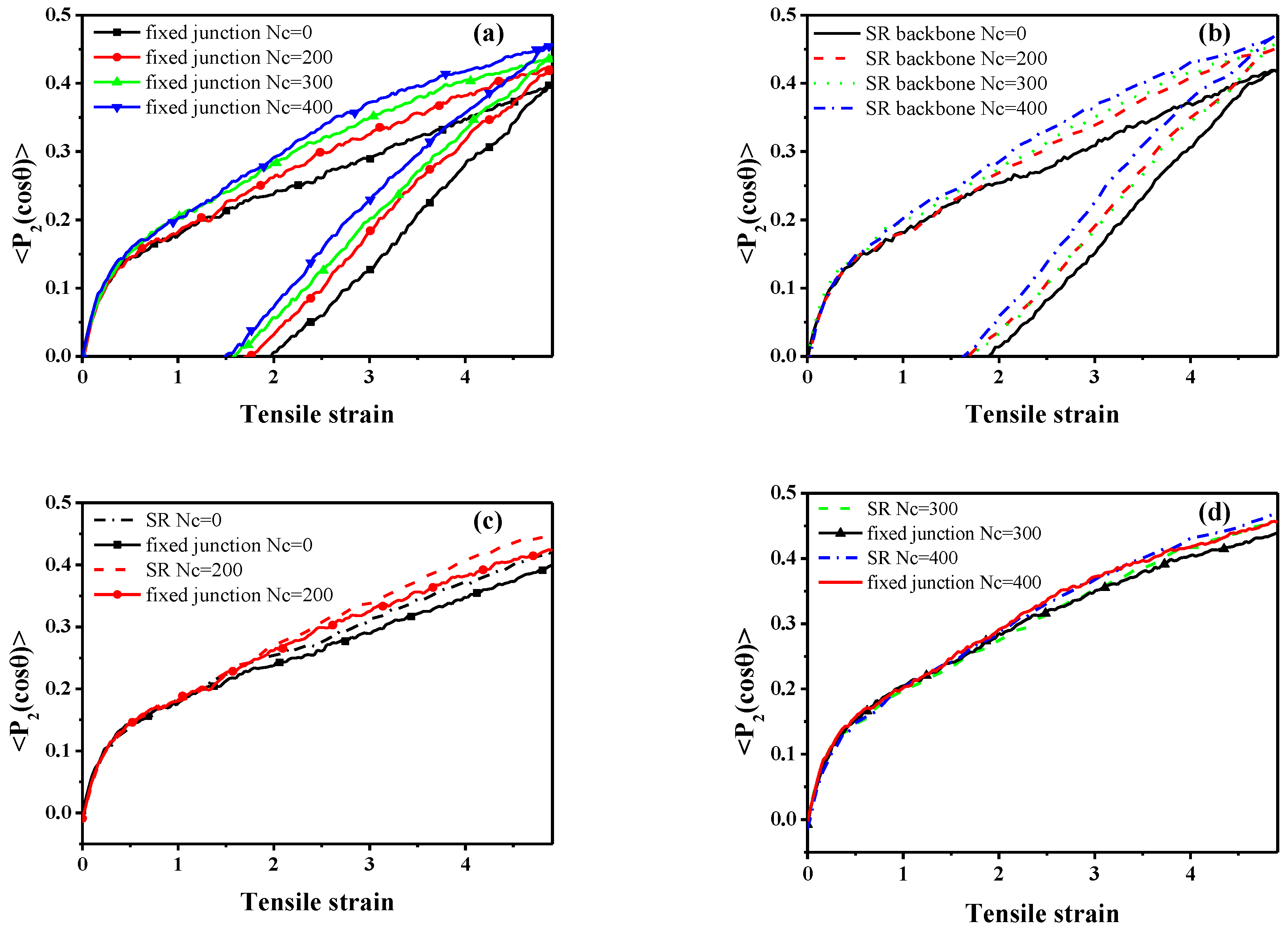
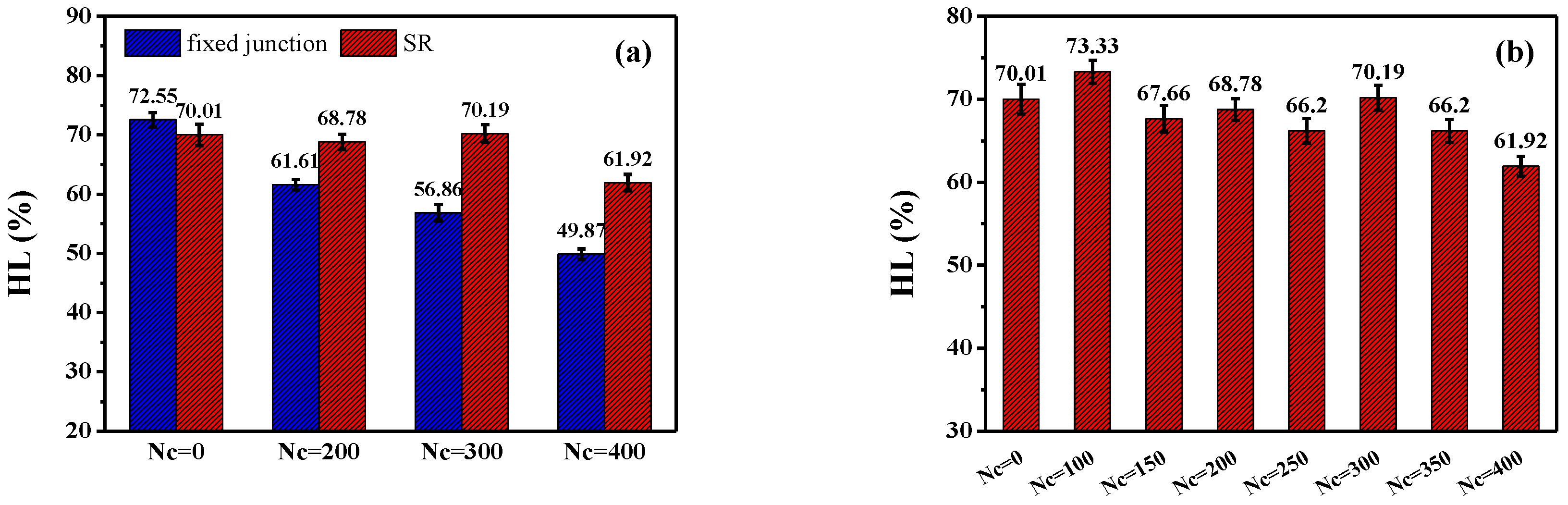
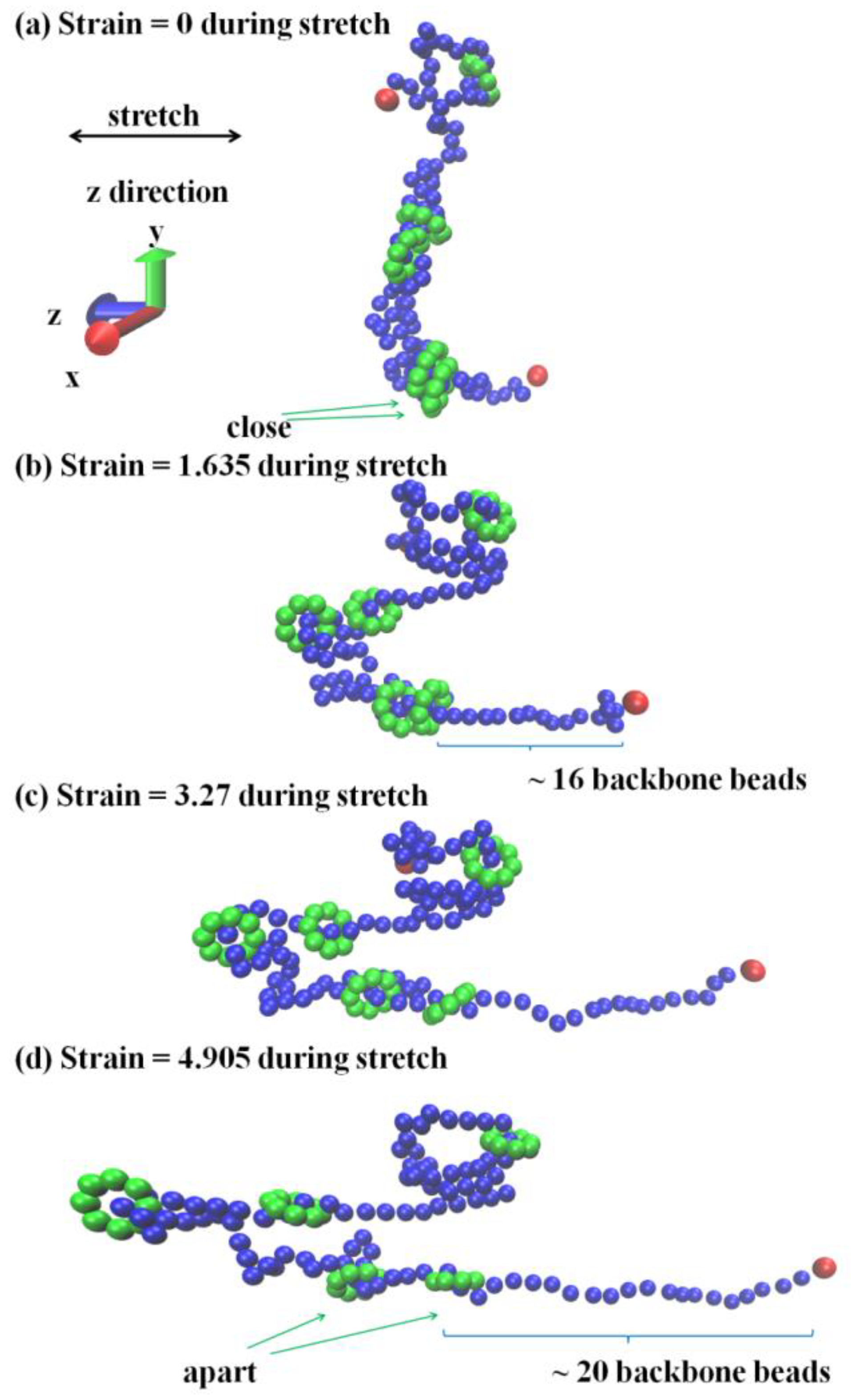
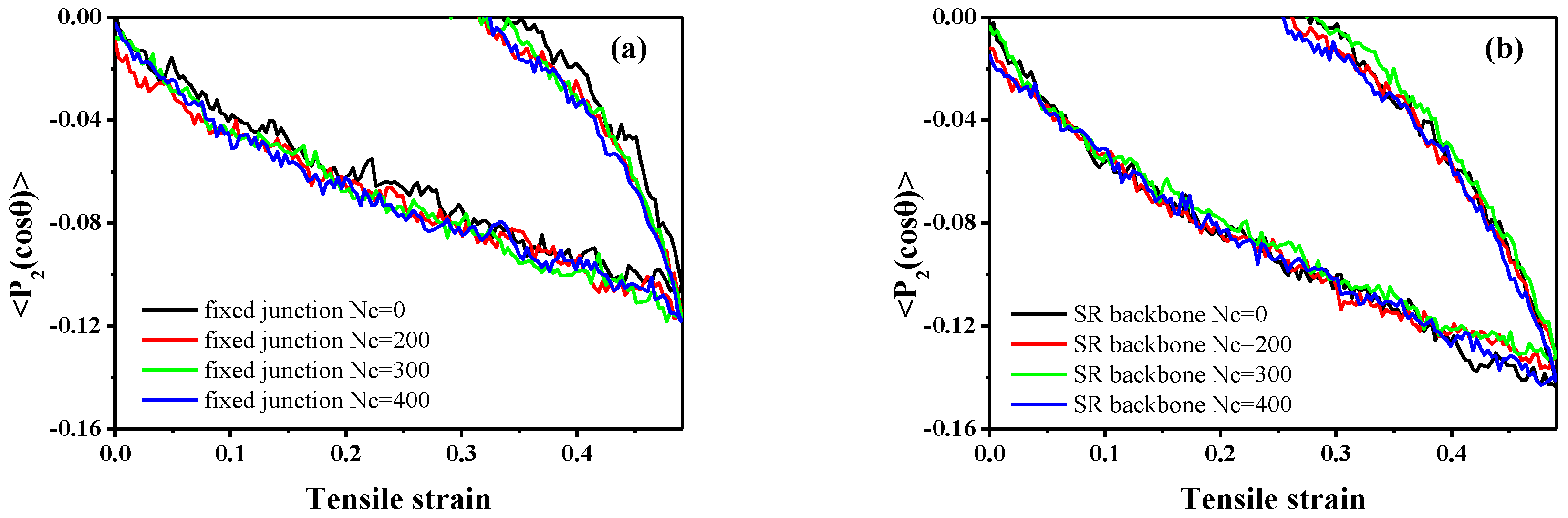
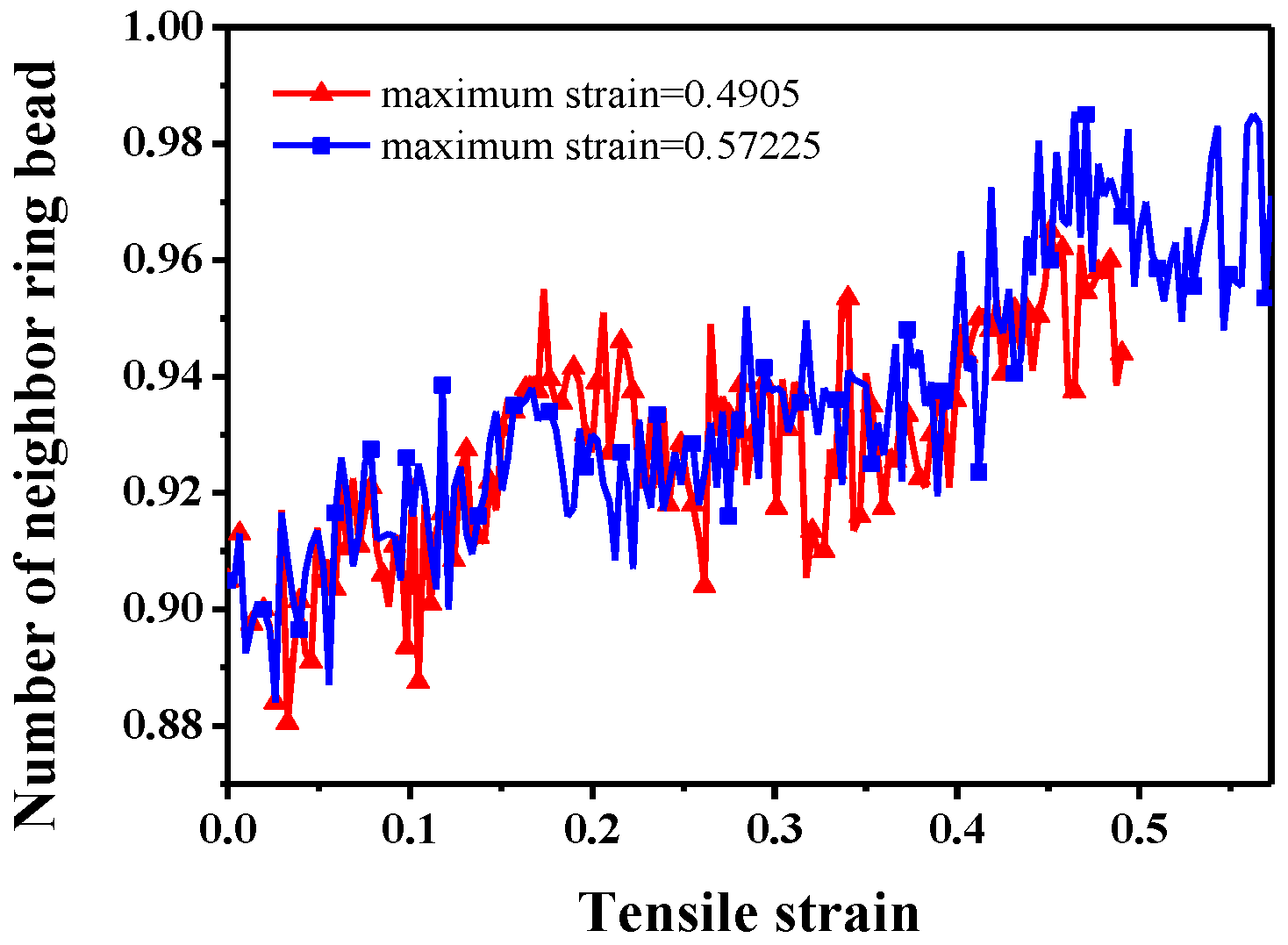
3.2. Stretch-Recovery Behavior
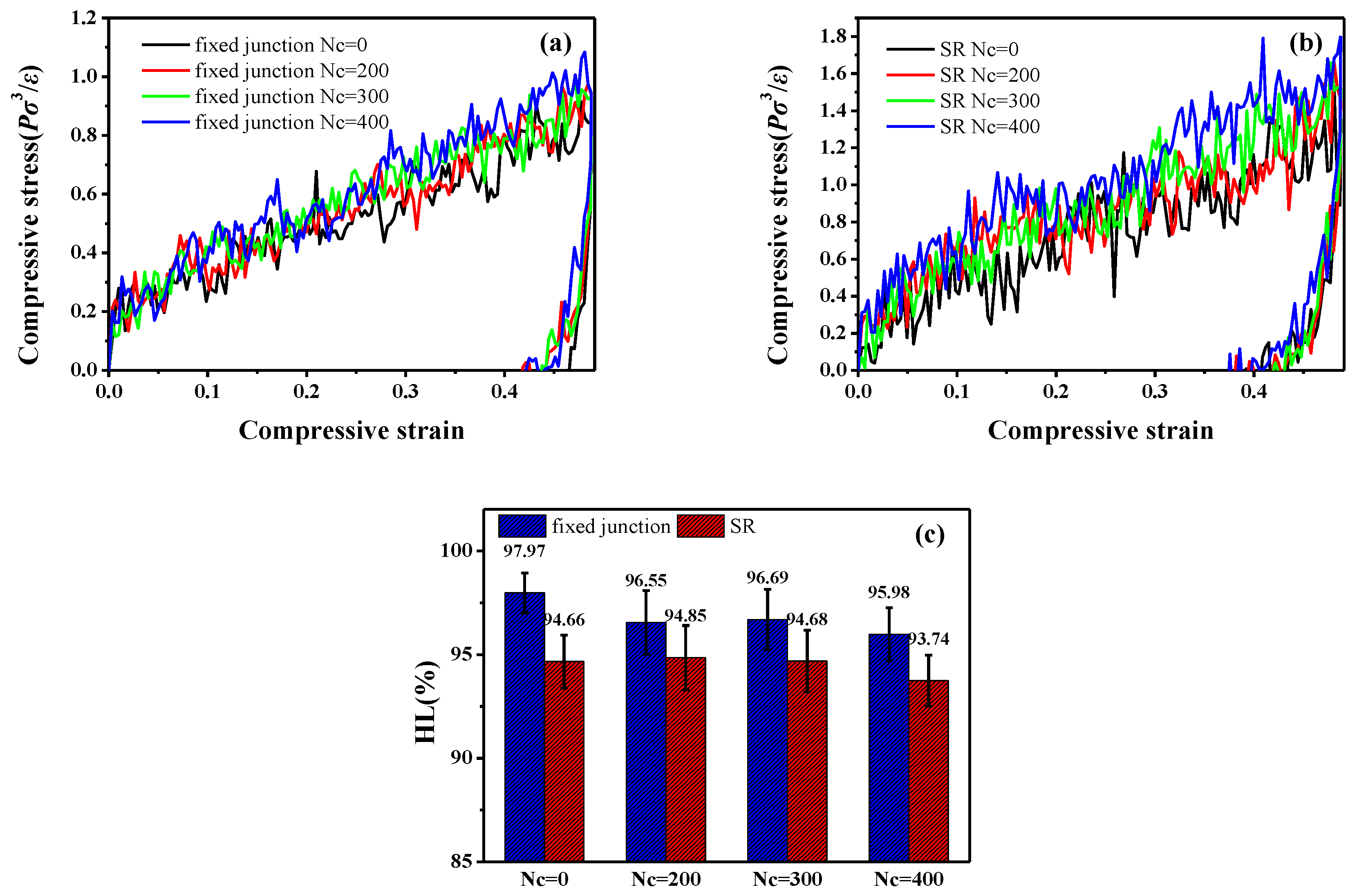
3.3. Compression-Recovery Behavior
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| length parameter | |
| Well depth in LJ interaction | |
| reduced time | |
| reduced temperature | |
| reduced density | |
| reduced pressure | |
| reduced energy | |
| reduced volume | reduced volume |
References
- Dai, L.; Zhang, L.; Wang, B.; Yang, B.; Khan, I.; Khan, A.; Ni, Y. Multifunctional self-assembling hydrogel from guar gum. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 330, 1044–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.-S.; Park, W.; Park, H.; Lee, D.-K.; Na, K. Thermo-sensitive injectable hydrogel based on the physical mixing of hyaluronic acid and pluronic f-127 for sustained nsaid delivery. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 156, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Yuk, H.; Zhang, T.; Parada, G.A.; Koo, H.; Yu, C.; Zhao, X. Stretchable hydrogel electronics and devices. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 4497–4505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maulvi, F.A.; Lakdawala, D.H.; Shaikh, A.A.; Desai, A.R.; Choksi, H.H.; Vaidya, R.J.; Ranch, K.M.; Koli, A.R.; Vyas, B.A.; Shah, D.O. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of novel implantation technology in hydrogel contact lenses for controlled drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2016, 226, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peppas, N.A.; Hilt, J.Z.; Khademhosseini, A.; Langer, R. Hydrogels in biology and medicine: From molecular principles to bionanotechnology. Adv. Mater. 2006, 18, 1345–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuk, H.; Lin, S.; Ma, C.; Takaffoli, M.; Fang, N.X.; Zhao, X. Hydraulic hydrogel actuators and robots optically and sonically camouflaged in water. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yashin, V.V.; Balazs, A.C. Pattern formation and shape changes in self-oscillating polymer gels. Science 2006, 314, 798–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, W.R.; Wu, J.H.; Shim, B.S.; Kuan, W.F.; Mastroianni, S.E.; Young, W.S.; Kuo, C.C.; Epps, T.H.; Martin, D.C. Synthesis and characterization of bicontinuous cubic poly(3,4-ethylene dioxythiophene) gyroid (pedot gyr) gels. Phys. Chem. Phys. Chem. 2015, 17, 5115–5123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veschgini, M.; Habe, T.; Mielke, S.; Inoue, S.; Liu, X.H.; Krafft, M.P.; Tanaka, M. Existence of two-dimensional physical gels even at zero surface pressure at the air/water interface: Rheology of self-assembled domains of small molecules. Angew. Chem. 2017, 59, 12603–12607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flory, P.J. Principles of Polymer Chemistry; Cornell University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1953. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, A.J. Non-covalent polymer assembly using arrays of hydrogen-bonds. Soft Matter 2007, 3, 409–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukao, K.; Nonoyama, T.; Kiyama, R.; Furusawa, K.; Kurokawa, T.; Nakajima, T.; Gong, J.P. Anisotropic growth of hydroxyapatite in stretched double network hydrogel. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 12103–12110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.Y.; Liu, J.; Shen, J.X.; Cao, D.P.; Zhang, L.Q. Molecular dynamics simulation of the rupture mechanism in nanorod filled polymer nanocomposites. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 18483–18492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, K. Slide-ring materials using topological supramolecular architecture. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2010, 14, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhao, D.; Yang, J.; Nishi, T.; Ito, K.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, L. Novel slide-ring material/natural rubber composites with high damping property. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Niu, K.; Xu, Y.; Peng, Z.; Jia, L.; Hui, D.; Zhang, L. Morphology and performance of nr/nbr/enr ternary rubber composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2016, 107, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, I.R.; Li, C.; Colella, N.S.; Ito, K.; Watkins, J.J. Strain-tunable one dimensional photonic crystals based on zirconium dioxide/slide-ring elastomer nanocomposites for mechanochromic sensing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 3641–3646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Ge, F.; Tian, M.; Ning, N.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, C.; Ito, K.; Nishi, T.; Wang, H.; Luan, Y. Dielectric elastomer actuator with excellent electromechanical performance using slide-ring materials/barium titanate composites. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 9468–9479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, A.; Li, J.; Kamachi, M. The molecular necklace: A rotaxane containing many threaded α-cyclodextrins. Nature 1992, 356, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okumura, Y. Topological gel: A third kind of gel consisting of linear polymer chains and figure-of-eight cross-links. Kobunshi Ronbunshu 2005, 62, 380–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murayama, H.; Bin Imran, A.; Nagano, S.; Seki, T.; Kidowaki, M.; Ito, K.; Takeoka, Y. Chromic slide-ring gel based on reflection from photonic bandgap. Macromolecules 2008, 41, 1808–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karino, T.; Okumura, Y.; Ito, K.; Shibayama, M. Sans studies on spatial inhomogeneities of slide-ring gels. Macromolecules 2004, 37, 6177–6182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, K. Novel cross-linking concept of polymer network: Synthesis, structure, and properties of slide-ring gels with freely movable junctions. Polym. J. 2007, 39, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, K.; Yasuda, T.; Ito, K. Peculiar elasticity and strain hardening attributable to counteracting entropy of chain and ring in slide-ring gels. Polymer 2014, 55, 2614–2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, K.; Ito, K. Polymer networks characterized by slidable crosslinks and the asynchronous dynamics of interlocked components. React. Funct. Polym. 2013, 73, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, K. Novel entropic elasticity of polymeric materials: Why is slide-ring gel so soft? Polym. J. 2011, 44, 38–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bando, A.; Kasahara, R.; Kayashima, K.; Okumura, Y.; Kato, K.; Sakai, Y.; Yokoyama, H.; Shinohara, Y.; Amemiya, Y.; Ito, K. Volume phase transitions of slide-ring gels. Polymers 2016, 8, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karino, T.; Okumura, Y.; Zhao, C.M.; Kataoka, T.; Ito, K.; Shibayama, M. Sans studies on deformation mechanism of slide-ring gel. Macromolecules 2005, 38, 6161–6167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koga, T.; Tanaka, F. Elastic properties of polymer networks with sliding junctions. Eur. Phys. J. E 2005, 17, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sevick, E.M.; Williams, D.R.M. Piston-rotaxanes as molecular shock absorbers. Langmuir 2010, 26, 5864–5868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habasaki, J.; Ishikawa, M. Molecular dynamics study of coagulation in silica-nanocolloid-water-nacl systems based on the atomistic model. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 24000–24017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, Y.D.; Xu, X.Q.; Wang, Q.; Wu, P.; Zhang, H.; Cai, C.X. Electrochemical probing of the solution ph-induced structural alterations around the heme group in myoglobin. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 16941–16948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frankland, S.J.V.; Harik, V.M.; Odegard, G.M.; Brenner, D.W.; Gates, T.S. The stress-strain behavior of polymer-nanotube composites from molecular dynamics simulation. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2003, 63, 1655–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Liu, J.; Li, H.; Gao, Y.; Li, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, L. Molecular dynamics simulations of the structural, mechanical and visco-elastic properties of polymer nanocomposites filled with grafted nanoparticles. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 7196–7207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vemparala, S.; Karki, B.B.; Kalia, R.K.; Nakano, A.; Vashishta, P. Large-scale molecular dynamics simulations of alkanethiol self-assembled monolayers. J. Chem. Phys. 2004, 121, 4323–4330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Lu, Y.-L.; Tian, M.; Li, F.; Shen, J.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, L. The interesting influence of nanosprings on the viscoelasticity of elastomeric polymer materials: Simulation and experiment. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 1156–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlov, A.S.; Khalatur, P.G. Filler reinforcement in cross-linked elastomer nanocomposites: Insights from fully atomistic molecular dynamics simulation. Soft Matter 2016, 12, 5402–5419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.D.; Huang, J.C.; Zhao, D.; Ding, B.B.; Zhang, L.; Cai, J. High-flexibility, high-toughness double-cross-linked chitin hydrogels by sequential chemical and physical cross-linkings (vol 28, pg 5844, 2016). Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 9667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonpheng, B.; Yu, J.C.; Andersson, O. Effects of cross-links, pressure and temperature on the thermal properties and glass transition behaviour of polybutadiene. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 15047–15054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kremer, K.; Grest, G.S. Dynamics of entangled linear polymer melts: A molecular-dynamics simulation. J. Chem. Phys. 1990, 92, 5057–5086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Shen, J.; Liu, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, W. Tuning the visco-elasticity of elastomeric polymer materials via flexible nanoparticles: Insights from molecular dynamics simulation. Rsc Adv. 2016, 6, 28666–28678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, M.P.; Tildesley, D.J. Computer Simulation of Liquids; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Hagita, K.; Morita, H.; Doi, M.; Takano, H. Coarse-grained molecular dynamics simulation of filled polymer nanocomposites under uniaxial elongation. Macromolecules 2016, 49, 1972–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, G.; Tao, W.; Liu, J.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y. Tailoring the dispersion of nanoparticles and the mechanical behavior of polymer nanocomposites by designing the chain architecture. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 32024–32037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plimpton, S. Fast parallel algorithms for short-range molecular dynamics. J. Comput. Phys. 1995, 117, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Liu, J.; Gao, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, L. Elucidating and tuning the strain-induced non-linear behavior of polymer nanocomposites: A detailed molecular dynamics simulation study. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 5099–5113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, J.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, L.; Lyulin, A.V. Self-assembly of block copolymer chains to promote the dispersion of nanoparticles in polymer nanocomposites. J. Phys. Chem. B 2017, 121, 9311–9318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Hou, G.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, L.; Liu, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Lyulin, A.V. Designing polymer nanocomposites with a semi-interpenetrating or interpenetrating network structure: Toward enhanced mechanical properties. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 15808–15820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Cao, D.; Zhang, L. Molecular dynamics study on nanoparticle diffusion in polymer melts: A test of the stokes—Einstein law. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 6653–6661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremer, K.; Grest, G.S.; Carmesin, I. Crossover from rouse to reptation dynamics: A molecular-dynamics simulation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1988, 61, 566–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, C.; Srivastava, D.; Cho, K. Thermal expansion and diffusion coefficients of carbon nanotube-polymer composites. Nano Lett. 2002, 2, 647–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batchelor, G.K. An Introduction to Fluid Dynamics; Cambridge University Press: Cambrige, UK, 1990; p. 635. [Google Scholar]
- Riggleman, R.A.; Lee, H.-N.; Ediger, M.D.; De Pablo, J.J. Free volume and finite-size effects in a polymer glass under stress. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 99, 215501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Shen, J.; Gao, Y.; Zhou, H.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, L. Detailed simulation of the role of functionalized polymer chains on the structural, dynamic and mechanical properties of polymer nanocomposites. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 8971–8984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murat, M.; Grest, G.S. Structure of a grafted polymer brush: A molecular dynamics simulation. Macromolecules 1989, 22, 4054–4059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilgis, T.A.; Heinrich, G. Dynamics of heterogeneous polymer networks. Phys. Rev. E 1994, 49, 2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.-H.; Khare, R. Local chain dynamics and dynamic heterogeneity in cross-linked epoxy in the vicinity of glass transition. Macromolecules 2010, 43, 6505–6510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenkare, N.R.; Smith, S.W.; Hall, C.K.; Khan, S.A. Discontinuous molecular dynamics studies of end-linked polymer networks. Macromolecules 1998, 31, 5861–5879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, H.; Green, P.F. Polymer chain dynamics and glass transition in athermal polymer/nanoparticle mixtures. Nat. Mater. 2009, 8, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Kröger, M.; Liu, W.K. Nanoparticle geometrical effect on structure, dynamics and anisotropic viscosity of polyethylene nanocomposites. Macromolecules 2012, 45, 2099–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinstein, M.; Colby, R.H. Polymer Physics; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2003; Volume 23. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, X.J.; Liu, Z.P.; Cao, D.P. Improved classical united-atom force field for imidazolium-based ionic liquids: Tetrafluoroborate, hexafluorophosphate, methylsulfate, trifluoromethylsulfonate, acetate, trifluoroacetate, and bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)amide. J. Phys. Chem. B 2011, 115, 10027–10040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Gao, Y.G.; Cao, D.P.; Zhang, L.Q.; Guo, Z.H. Nanoparticle dispersion and aggregation in polymer nanocomposites: Insights from molecular dynamics simulation. Langmuir 2011, 27, 7926–7933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Wu, Y.; Shen, J.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Cao, D. Polymer-nanoparticle interfacial behavior revisited: A molecular dynamics study. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 13058–13069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
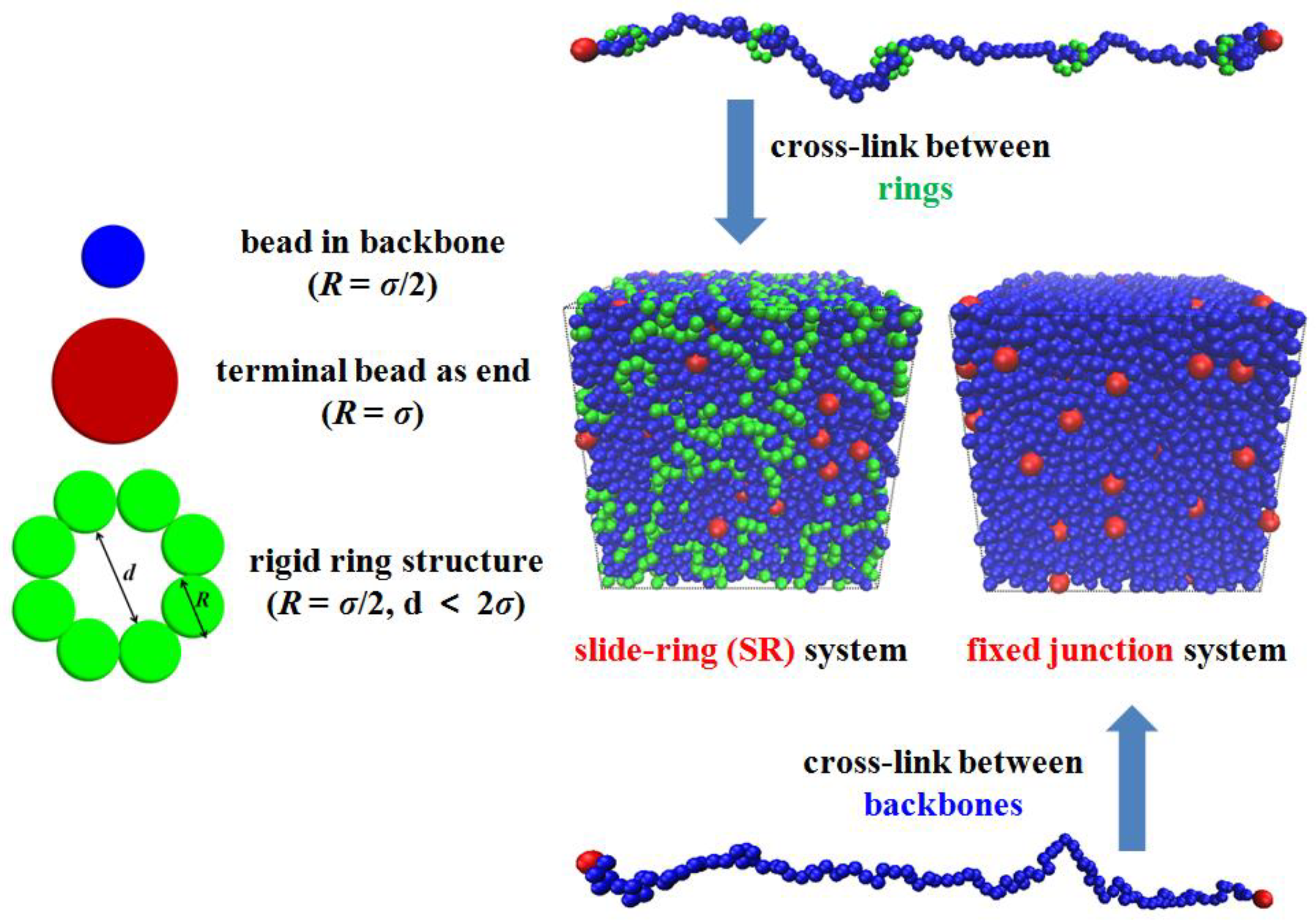
| Non-Bonding Pair | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| backbone | backbone | 1.0 | 1.0 | 0 | 2.5 |
| backbone | end | 5.0 | 1.0 | 0.5 | 2.24 |
| backbone | ring | 1.0 | 1.0 | 0 | 2.24 |
| end | end | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.12 |
| end | ring | 1.0 | 1.0 | 0.5 | 1.12 |
| ring | ring | 1.0 | 1.0 | 0 | 1.12 |
| Bond Stretching | ||
|---|---|---|
| backbone–backbone | 100 | 1.0 |
| cross-linking bond inter-backbone | 100 | 1.0 |
| backbone–end | 180 | 1.5 |
| cross-linking bond inter-ring | 100 | 1.0 |
| Permanent Set after Stretch-Recovery Deformation | ||
|---|---|---|
| Fixed Junction | SR | |
| 0 | 3.10 | 3.01 |
| 200 | 2.61 | 3.01 |
| 300 | 2.42 | 2.97 |
| 400 | 2.29 | 2.65 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Z.; Hou, G.; Shen, J.; Liu, J.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, L. Designing the Slide-Ring Polymer Network with both Good Mechanical and Damping Properties via Molecular Dynamics Simulation. Polymers 2018, 10, 964. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10090964
Zhang Z, Hou G, Shen J, Liu J, Gao Y, Zhao X, Zhang L. Designing the Slide-Ring Polymer Network with both Good Mechanical and Damping Properties via Molecular Dynamics Simulation. Polymers. 2018; 10(9):964. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10090964
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Zhiyu, Guanyi Hou, Jianxiang Shen, Jun Liu, Yangyang Gao, Xiuying Zhao, and Liqun Zhang. 2018. "Designing the Slide-Ring Polymer Network with both Good Mechanical and Damping Properties via Molecular Dynamics Simulation" Polymers 10, no. 9: 964. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10090964
APA StyleZhang, Z., Hou, G., Shen, J., Liu, J., Gao, Y., Zhao, X., & Zhang, L. (2018). Designing the Slide-Ring Polymer Network with both Good Mechanical and Damping Properties via Molecular Dynamics Simulation. Polymers, 10(9), 964. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10090964