Comparative Investigation of Thermal and Structural Behavior in Renewably Sourced Composite Films of Even-Even Nylons (610 and 1010) with Silk Fibroin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
2.2. Material Synthesis
2.3. SEM Characterization
2.4. Fourier-Transform Infrared (FTIR)Spectrometry
2.5. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.6. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Surface Morphology
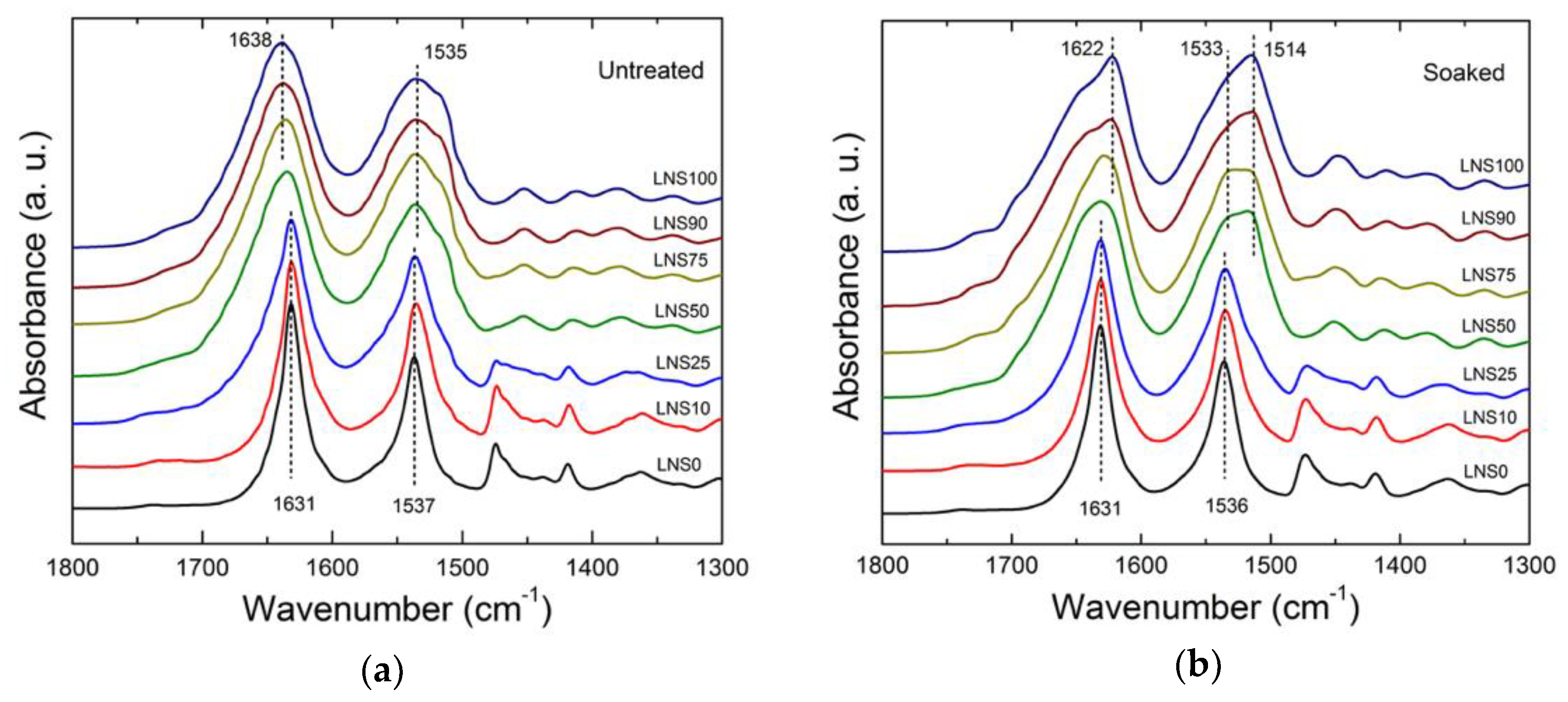
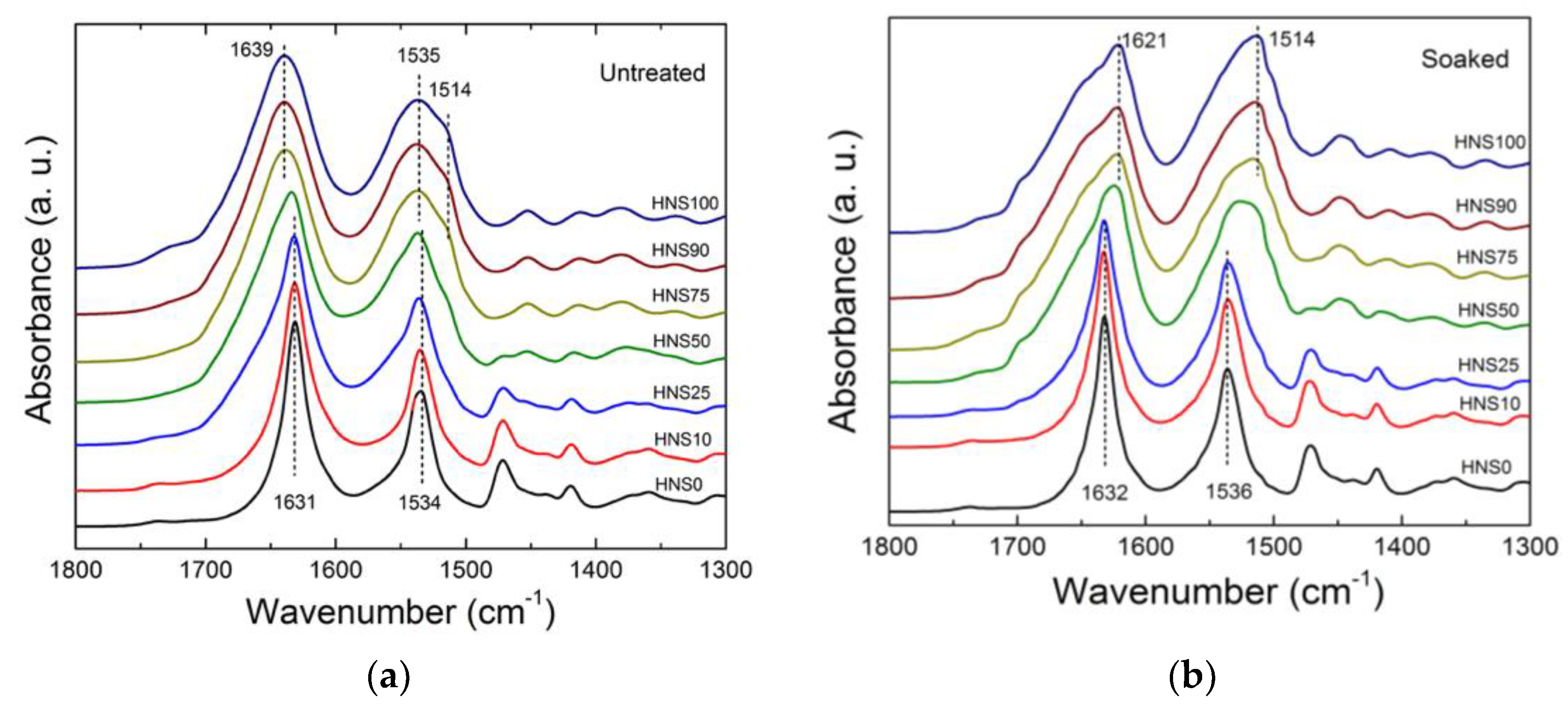
3.2. Structural Analysis
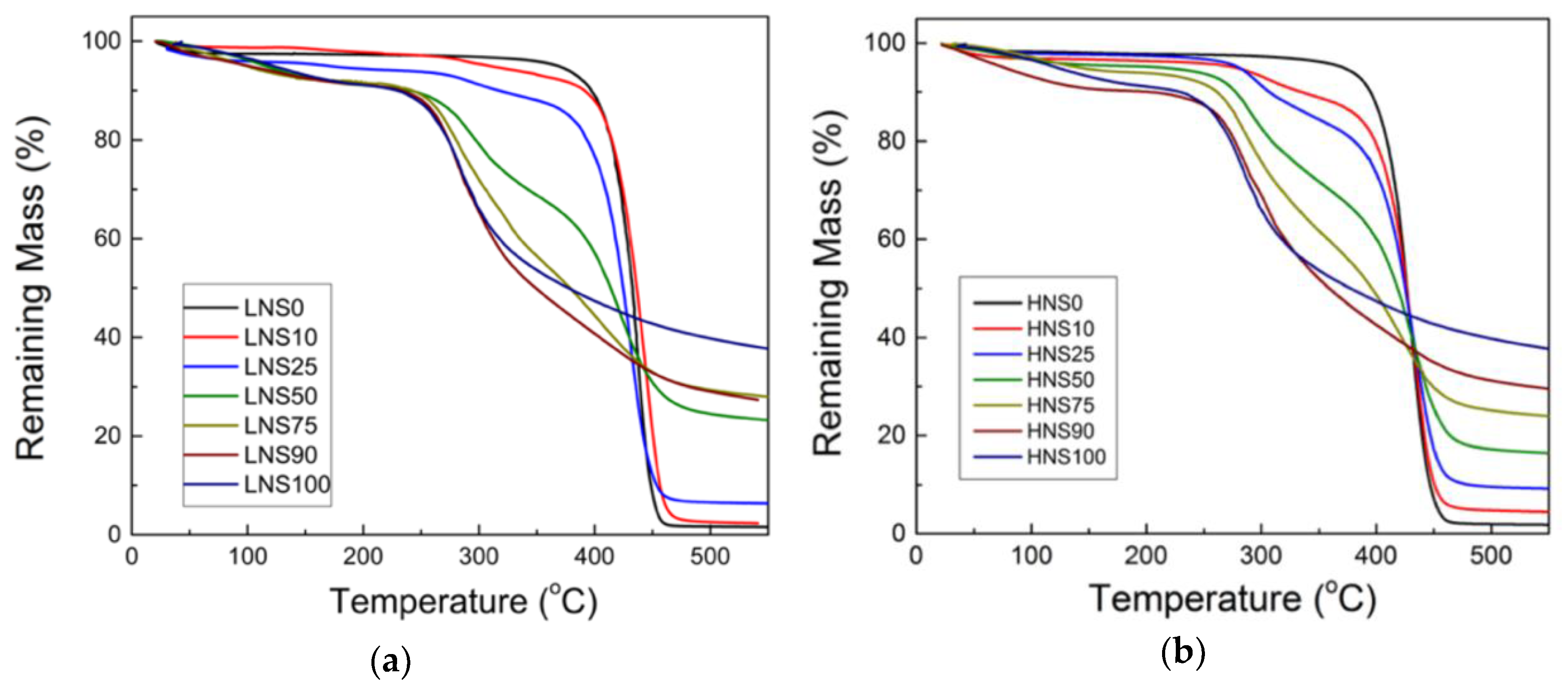
3.3. Thermogravimetric Analysis
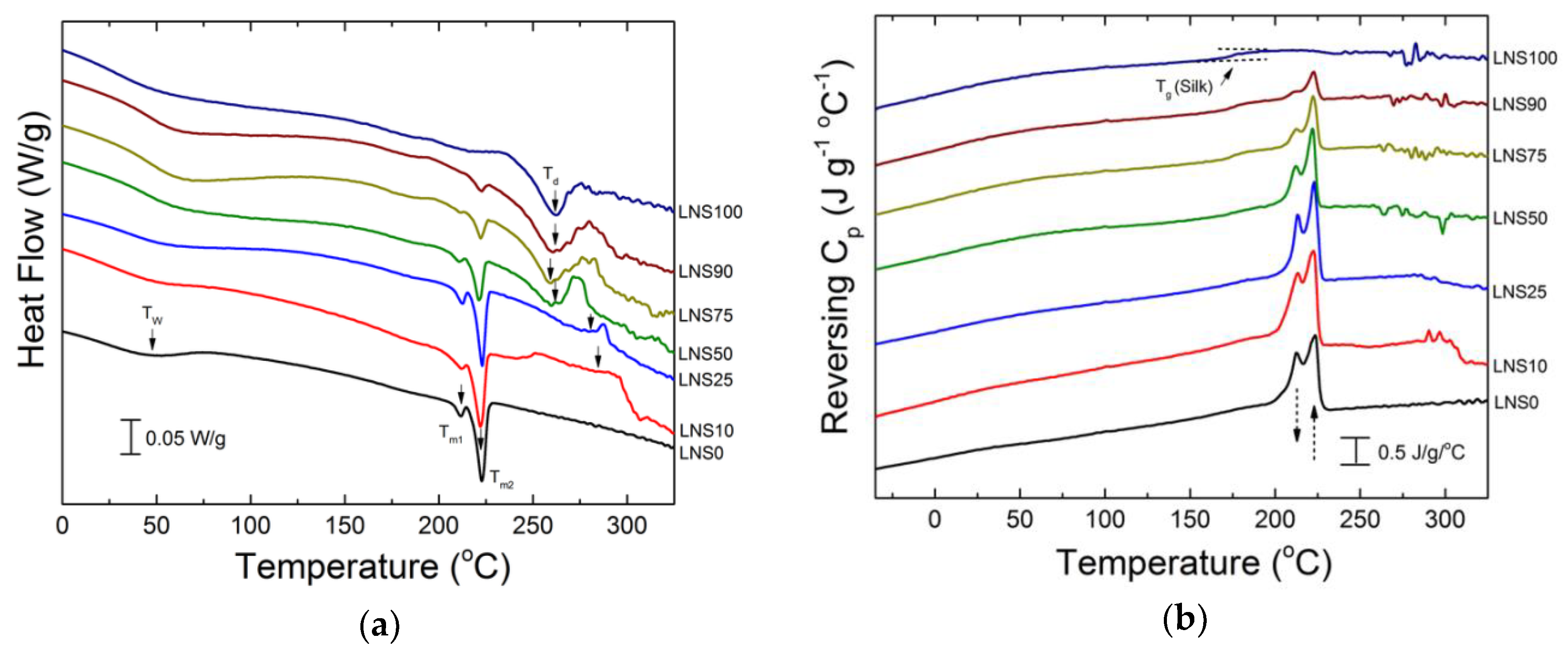
3.4. DSC Analysis
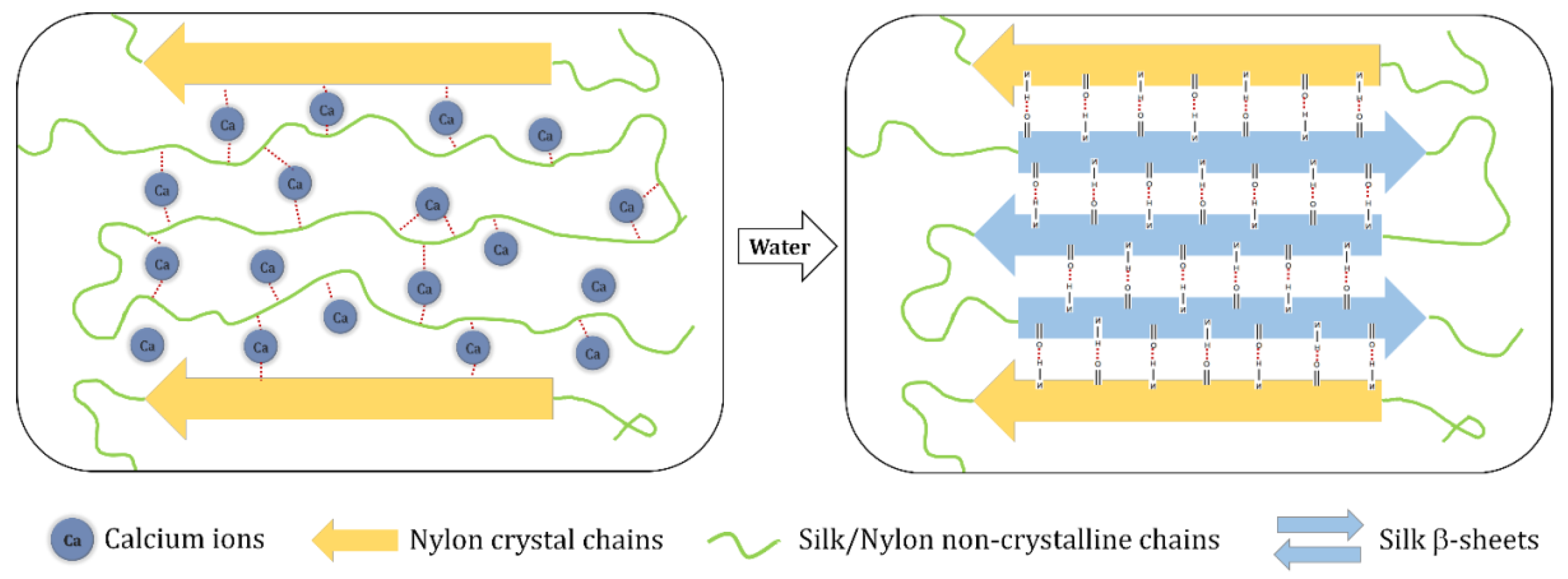
3.5. Mechanism
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aramwit, P.; Ratanavaraporn, J.; Siritientong, T. Improvement of physical and wound adhesion properties of silk sericin and polyvinyl alcohol dressing using glycerin. Adv. Skin Wound Care 2015, 28, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lammel, A.S.; Hu, X.; Park, S.-H.; Kaplan, D.L.; Scheibel, T.R. Controlling silk fibroin particle features for drug delivery. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 4583–4591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.Z.; Confalonieri, F.; Jacquet, M.; Perasso, R.; Li, Z.G.; Janin, J. Silk fibroin: Structural implications of a remarkable amino acid sequence. Protein Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2001, 44, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omenetto, F.G.; Kaplan, D.L. New opportunities for an ancient material. Science 2010, 329, 528–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vepari, C.; Kaplan, D.L. Silk as a biomaterial. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2007, 32, 991–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, U.-J.; Park, J.; Li, C.; Jin, H.-J.; Valluzzi, R.; Kaplan, D.L. Structure and properties of silk hydrogels. Biomacromolecules 2004, 5, 786–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wongpinyochit, T. Manufacture and drug delivery applications of silk nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2016, 71, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Q.; Zhang, B.; He, Y.; Lu, Q.; Kaplan, D.L. Silk nanofibers as robust and versatile emulsifiers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interface 2017, 9, 35693–35700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeFrates, K.; Markiewicz, T.; Callaway, K.; Xue, Y.; Stanton, J.; Salas-de la Cruz, D.; Hu, X. Structure-property relationships of thai silk-microcrystalline cellulose biocomposite materials fabricated from ionic liquid. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 104, 919–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil, E.S.; Frankowski, D.J.; Bowman, M.K.; Gozen, A.O.; Hudson, S.M.; Spontak, R.J. Mixed protein blends composed of gelatin and bombyx m ori silk fibroin: Effects of solvent-induced crystallization and composition. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 728–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardy, J.G.; Scheibel, T.R. Composite materials based on silk proteins. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2010, 35, 1093–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Naby, W.; Cole, B.; Liu, A.; Liu, J.; Wan, P.; Guaiquil, V.H.; Schreiner, R.; Infanger, D.; Lawrence, B.D.; Rosenblatt, M.I. Silk-derived protein enhances corneal epithelial migration, adhesion, and proliferation. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2017, 58, 1425–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, B.D.; Marchant, J.K.; Pindrus, M.A.; Omenetto, F.G.; Kaplan, D.L. Silk film biomaterials for cornea tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 1299–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kundu, B.; Rajkhowa, R.; Kundu, S.C.; Wang, X. Silk fibroin biomaterials for tissue regenerations. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.-Z.; Confalonieri, F.; Medina, N.; Zivanovic, Y.; Esnault, C.; Yang, T.; Jacquet, M.; Janin, J.; Duguet, M.; Perasso, R. Fine organization of bombyx mori fibroin heavy chain gene. Nucleic Acid. Res. 2000, 28, 2413–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitropoulos, A.N.; Marelli, B.; Ghezzi, C.E.; Applegate, M.B.; Partlow, B.P.; Kaplan, D.L.; Omenetto, F.G. Transparent, nanostructured silk fibroin hydrogels with tunable mechanical properties. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2015, 1, 964–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockwood, D.N.; Preda, R.C.; Yücel, T.; Wang, X.; Lovett, M.L.; Kaplan, D.L. Materials fabrication from bombyx mori silk fibroin. Nat. Protoc. 2011, 6, 1612–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanton, J.; Xue, Y.; Pandher, P.; Malek, L.; Brown, T.; Hu, X.; Salas-de la Cruz, D. Impact of ionic liquid type on the structure, morphology and properties of silk-cellulose biocomposite materials. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 108, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Knight, D.P.; Shao, Z.; Vollrath, F. Regenerated bombyx silk solutions studied with rheometry and ftir. Polymer 2001, 42, 09969–09974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Yu, H.-Y.; Gu, Z.-G.; Si, L.; Liu, Q.-C.; Hu, X. Impact of calcium chloride concentration on structure and thermal property of thai silk fibroin films. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2017, 130, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thitiwuthikiat, P.; Ii, M.; Saito, T.; Asahi, M.; Kanokpanont, S.; Tabata, Y. A vascular patch prepared from thai silk fibroin and gelatin hydrogel incorporating simvastatin-micelles to recruit endothelial progenitor cells. Tissue Eng. Part A 2015, 21, 1309–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Yucel, T.; Lu, Q.; Hu, X.; Kaplan, D.L. Silk nanospheres and microspheres from silk/pva blend films for drug delivery. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 1025–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, T.; Tanigami, T.; Yamaura, K. Phase separation structure in poly (vinyl alcohol)/silk fibroin blend films. Polym. Int. 1998, 45, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, J.S.; Lee, K.H.; Bae, D.G.; Um, I.C. Miscibility, structural characteristics, and thermal behavior of wet spun regenerated silk fibroin/nylon 6 blend filaments. Fiber Polym. 2010, 11, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, S.; Hammond, W.B.; Goddard, W.A. Crystal structures and properties of nylon polymers from theory. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 12291–12301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohan, M.I. Nylon Plastics; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Q.; Vitchuli, N.; Nowak, J.; Noar, J.; Caldwell, J.M.; Breidt, F.; Bourham, M.; McCord, M.; Zhang, X. One-step synthesis of silver nanoparticle-filled nylon 6 nanofibers and their antibacterial properties. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 10330–10335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, E.; Wilson, F. Physical structure of nylons. In Nylon Plastic; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Hu, X.; Cebe, P. Thermal properties and phase transitions in blends of nylon-6 with silk fibroin. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2008, 93, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Shao, Z.; Zhou, P.; Chen, X. Thermal and crystalline behaviour of silk fiborin/nylon 66 blend films. Polymer 2004, 45, 7705–7710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Jao, D.; Hu, W.; Hu, X. Silk-silk blend materials. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2017, 127, 915–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Kaplan, D.; Cebe, P. Determining beta-sheet crystallinity in fibrous proteins by thermal analysis and infrared spectroscopy. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 6161–6170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotter, G.; Ishida, H. Ftir separation of nylon-6 chain conformations: Clarification of the mesomorphous and γ-crystalline phases. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 1992, 30, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilezikian, J.P.; Rubin, M.R. Chapter 38-monitoring anabolic treatment. In Dynamics of Bone and Cartilage Metabolism, 2nd ed.; Bilezikian, M.J.S.P.R.P., Ed.; Academic Press: Burlington, MA, USA, 2006; pp. 629–647. [Google Scholar]
- Paquet-Mercier, F.; Lefèvre, T.; Auger, M.; Pézolet, M. Evidence by infrared spectroscopy of the presence of two types of β-sheets in major ampullate spider silk and silkworm silk. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Lu, Q.; Yue, X.; Zuo, B.; Qin, M.; Li, F.; Kaplan, D.L.; Zhang, X. Regeneration of high-quality silk fibroin fiber by wet spinning from CaCl2-formic acid solvent. Acta Biomater. 2015, 12, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murase, R. Physicochemical studies on silk. V. Salt contraction of nitrated silk fibroin. J. Soc. Text. Cellul. Ind. 1950, 6, 385–387. [Google Scholar]


| Sample | Silk/% | Measured M500 °C/% | Expected M500 °C/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| LNS0 | 0% | 1.7% | 1.7% |
| LNS10 | 10% | 2.6% | 5.5% |
| LNS25 | 25% | 6.6% | 11.3% |
| LNS50 | 50% | 24.5% | 20.9% |
| LNS75 | 75% | 29.4% | 30.4% |
| LNS90 | 90% | 29.0% | 36.2% |
| LNS100 | 100% | 40.0% | 40.0% |
| HNS0 | 0% | 2.0% | 2.0% |
| HNS10 | 10% | 4.8% | 5.8% |
| HNS25 | 25% | 9.6% | 11.5% |
| HNS50 | 50% | 17.2% | 20.9% |
| HNS75 | 75% | 25.1% | 30.4% |
| HNS90 | 90% | 31.2% | 36.0% |
| HNS100 | 100% | 39.8% | 39.8% |
| Sample | Silk Composition | Tc1 | Tc2 | Tm1 | Tm2 | Td (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HNS0 | 0% | 189.5 | 197.3 | 189.0 | 197.5 | - |
| HNS10 | 10% | 191.4 | 198.4 | 190.6 | 198.8 | 290 |
| HNS25 | 25% | 192.4 | 199.4 | 192.0 | 200.3 | 287 |
| HNS50 | 50% | 194.5 | 200.8 | 193.5 | 201.5 | 272 |
| HNS75 | 75% | 192.1 | 200.7 | 191.1 | 201.2 | 270 |
| HNS90 | 90% | 190.3 | 200.5 | 189.1 | 200.1 | 269 |
| HNS100 | 100% | - | - | - | - | 267 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Callaway, K.A.; Xue, Y.; Altimari, V.; Jiang, G.; Hu, X. Comparative Investigation of Thermal and Structural Behavior in Renewably Sourced Composite Films of Even-Even Nylons (610 and 1010) with Silk Fibroin. Polymers 2018, 10, 1029. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10091029
Callaway KA, Xue Y, Altimari V, Jiang G, Hu X. Comparative Investigation of Thermal and Structural Behavior in Renewably Sourced Composite Films of Even-Even Nylons (610 and 1010) with Silk Fibroin. Polymers. 2018; 10(9):1029. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10091029
Chicago/Turabian StyleCallaway, Kayla A., Ye Xue, Vincent Altimari, Guoxiang Jiang, and Xiao Hu. 2018. "Comparative Investigation of Thermal and Structural Behavior in Renewably Sourced Composite Films of Even-Even Nylons (610 and 1010) with Silk Fibroin" Polymers 10, no. 9: 1029. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10091029
APA StyleCallaway, K. A., Xue, Y., Altimari, V., Jiang, G., & Hu, X. (2018). Comparative Investigation of Thermal and Structural Behavior in Renewably Sourced Composite Films of Even-Even Nylons (610 and 1010) with Silk Fibroin. Polymers, 10(9), 1029. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10091029







