Application of Melt-Blown Poly(lactic acid) Fibres in Self-Reinforced Composites
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Melt-Blowing
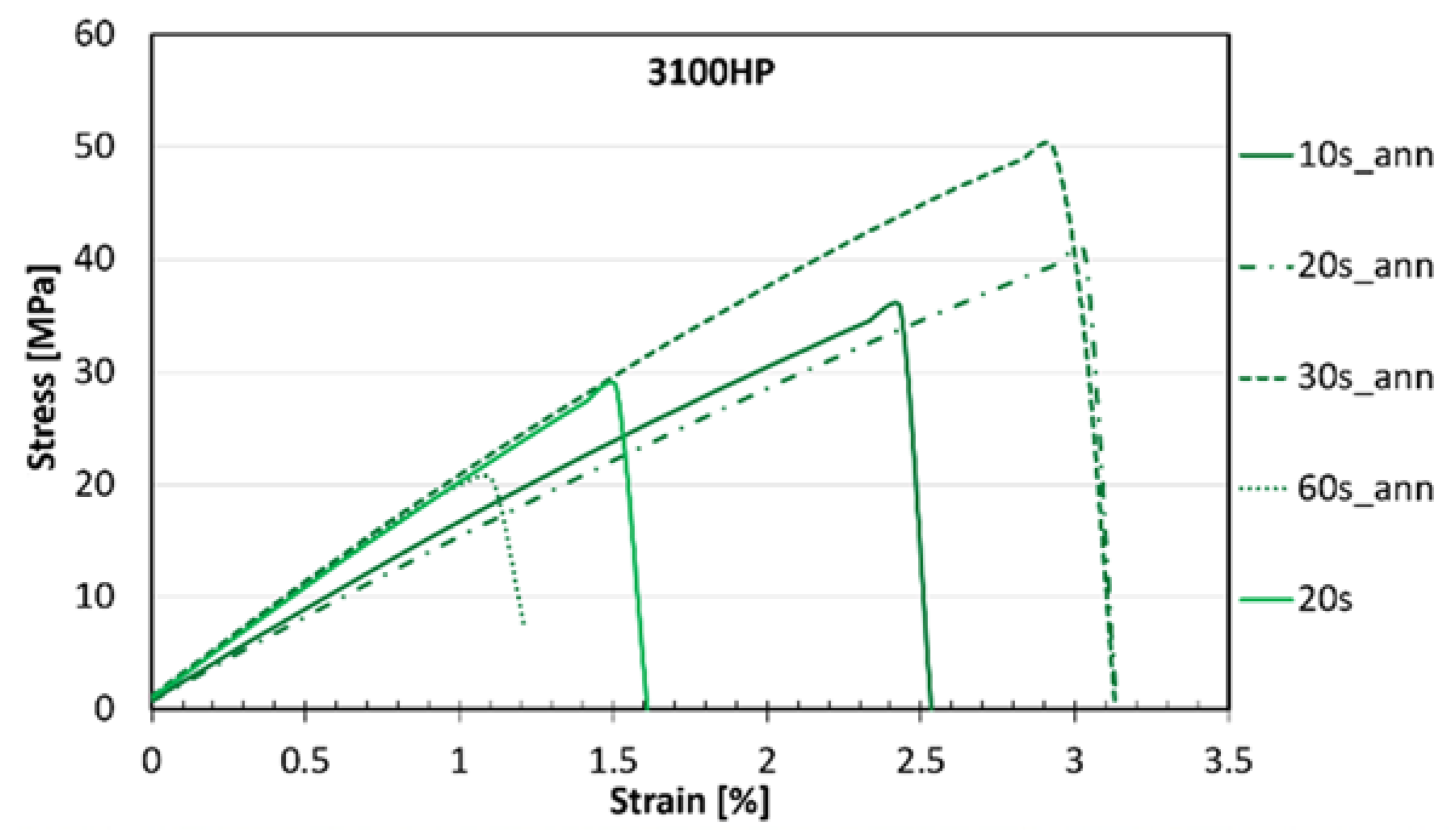
2.3. Thermal Annealing
2.4. Composite Preparation
2.5. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.6. Differential Scanning Calorimetry
2.7. Tensile Testing
3. Results and Discussion
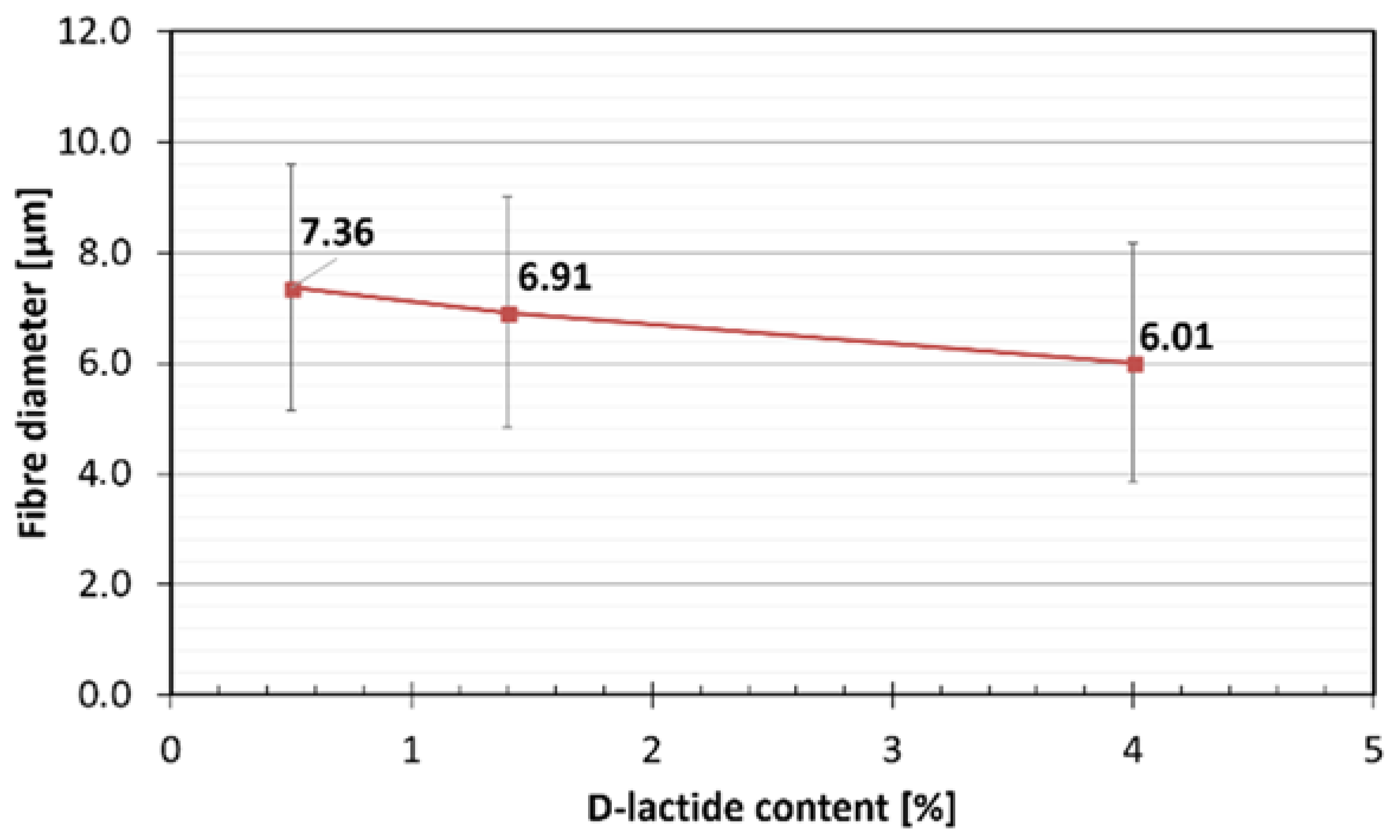
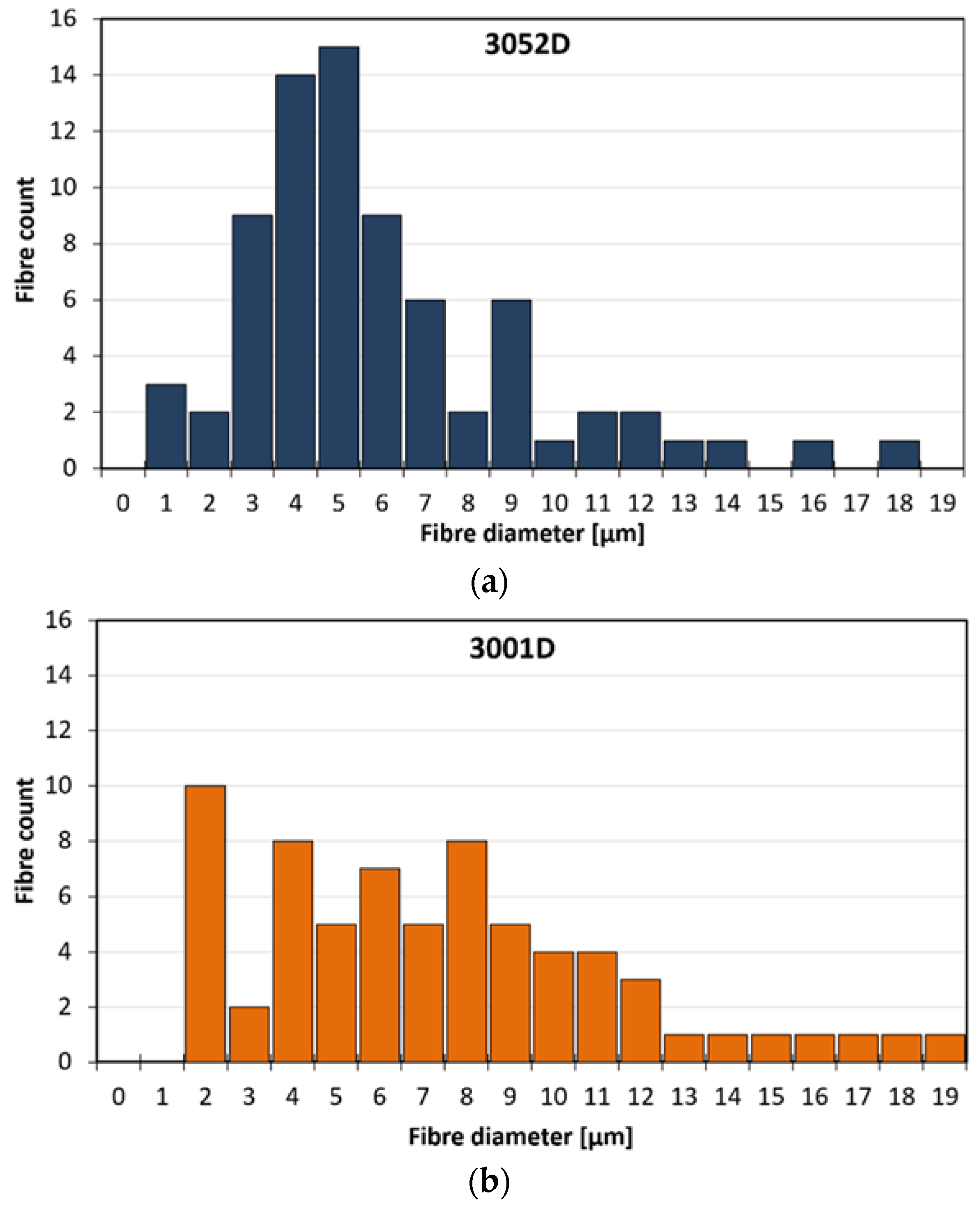
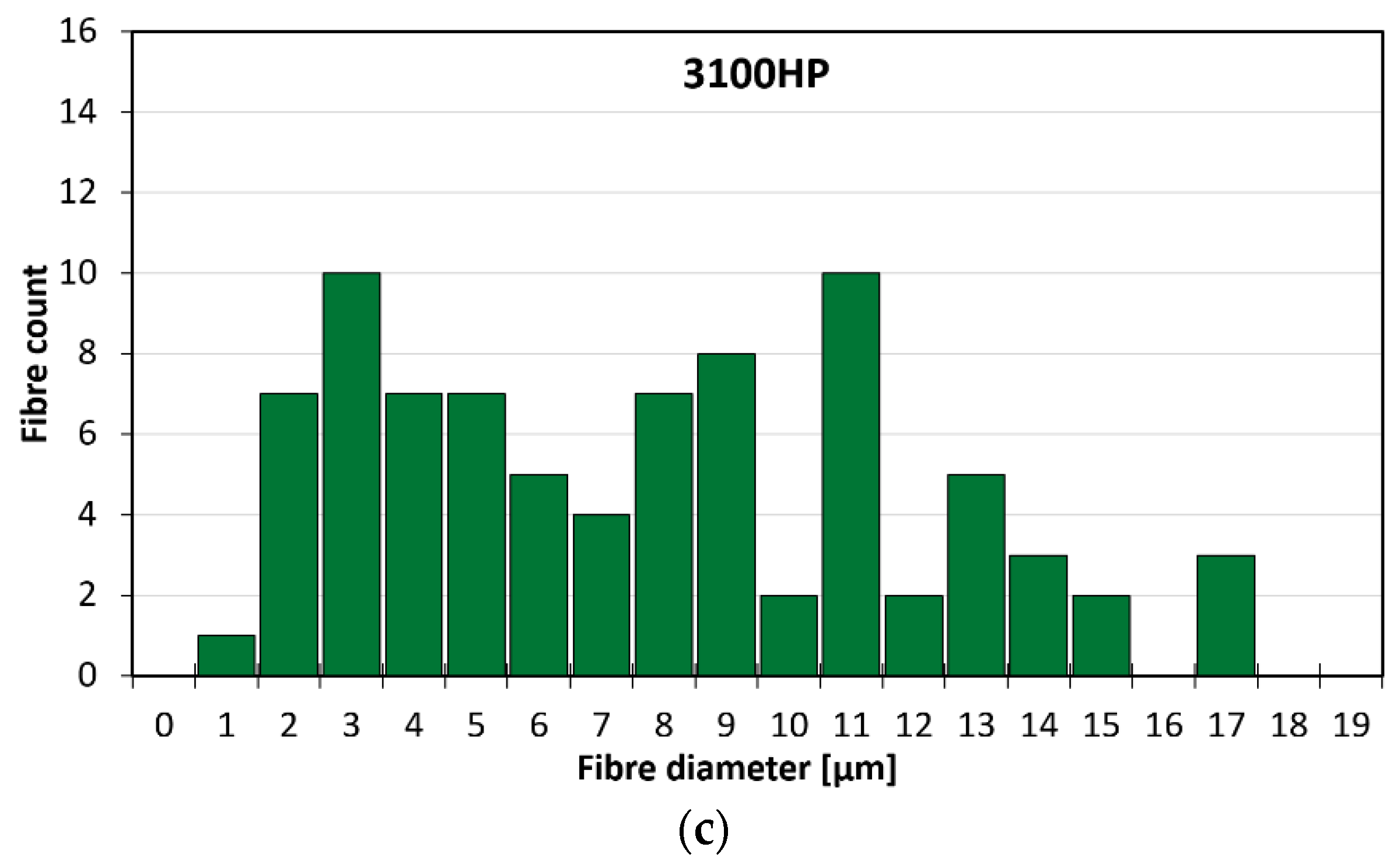
3.1. Fibre Morphology
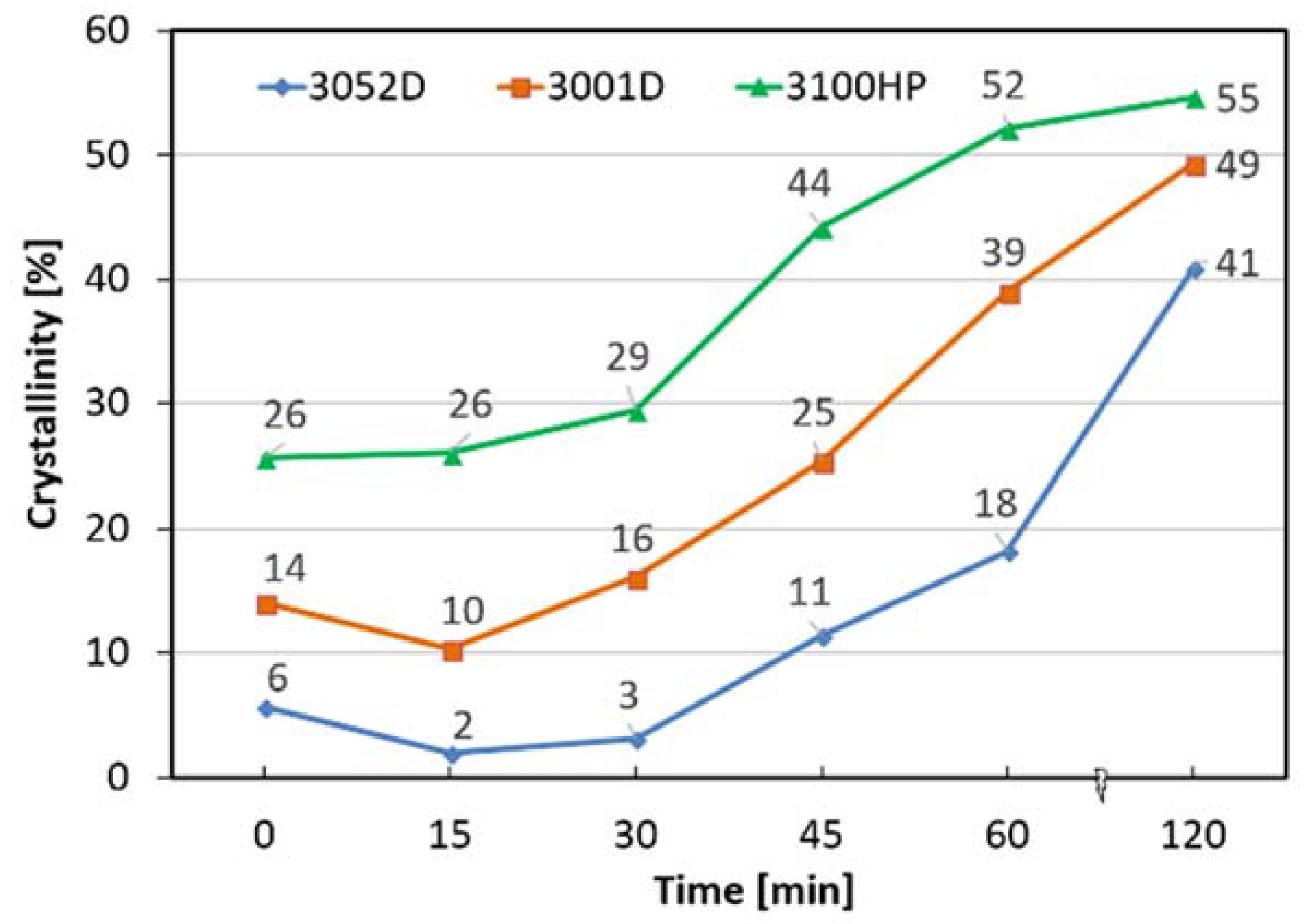
3.2. Thermal Properties—Crystallinity
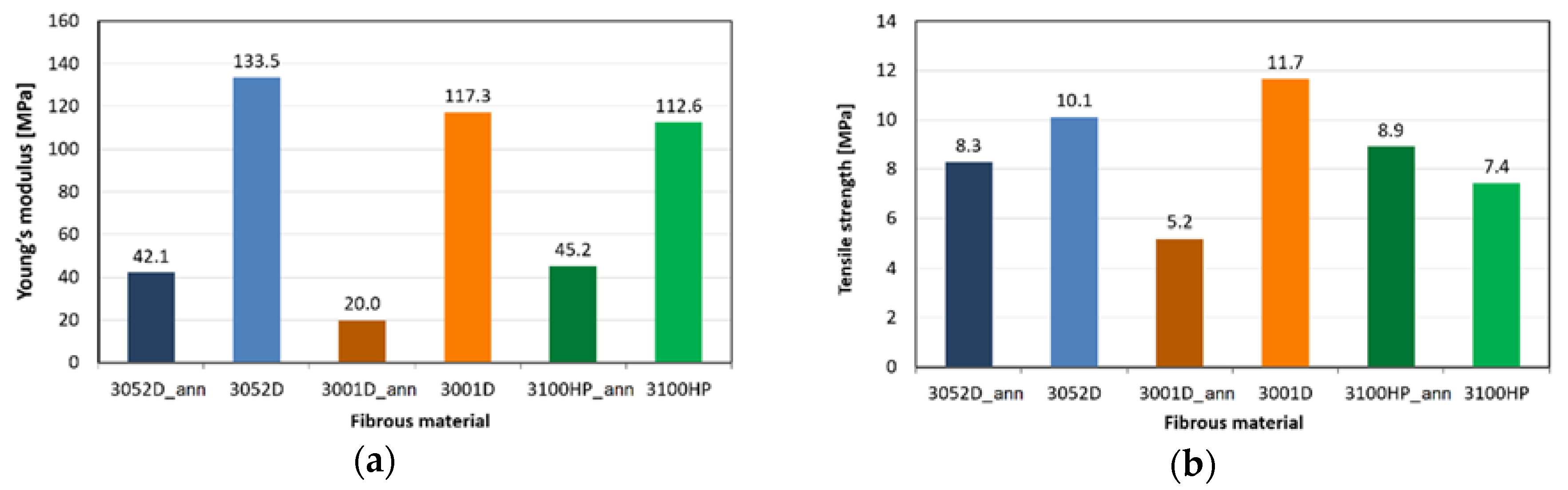
3.3. Mechanical Properties of the Microfibrous Mats
3.4. Mechanical Properties of SR Composites
3.5. Morphology of the SR–PLA Composites
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- European Bioplastics: Facts and Figures. Available online: http://docs.european-bioplastics.org/publications/EUBP_Facts_and_figures.pdf (accessed on 11 June 2018).
- Haniffa, M.A.C.M.; Ching, Y.C.; Abdullah, L.C.; Poh, S.C.; Chuah, C.H. Review of bionanocomposite coating films and their applications. Polymers 2016, 8, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, V.G.L.; Pires, J.R.A.; Vieira, É.T.; Coelhoso, I.M.; Duarte, M.P.; Fernando, A.L. Shelf life assessment of fresh poultry meat packaged in novel bionanocomposite of chitosan/montmorillonite incorporated with ginger essential oil. Coatings 2018, 8, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistretta, M.C.; Botta, L.; Morreale, M.; Rifici, S.; Ceraulo, M.; Mantia, F.P.L. Injection molding and mechanical properties of bio-based polymer nanocomposites. Materials 2018, 11, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertolino, V.; Cavallaro, G.; Lazzara, G.; Merli, M.; Milioto, S.; Parisi, F.; Sciascia, L. Effect of the biopolymer charge and the nanoclay morphology on nanocomposite materials. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 7373–7380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolino, V.; Cavallaro, G.; Lazzara, G.; Milioto, S.; Parisi, F. Halloysite nanotubes sandwiched between chitosan layers: A novel bionanocomposite with multilayer structure. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 8384–8390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allied Market Research: Polylactic Acid (PLA) Market—Global Opportunity Analysis and Industry Forecast, 2012–2020. Available online: https://www.alliedmarketresearch.com/polylactic-acid-market (accessed on 11 June 2018).
- Grand View Research: Lactic Acid Market Size Worth $9.8Bn by 2025 & PLA to Reach $6.5Bn. Available online: https://www.grandviewresearch.com/press-release/global-lactic-acid-and-poly-lactic-acid-market (accessed on 11 June 2018).
- Södergard, A.; Stolt, M. Properties of lactic acid based polymers and their correlation with composition. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2002, 27, 1123–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajioka, I.; Enomoto, K.; Suzuki, K.; Yamaguchi, A. The basic properties of poly(lactic acid) produced by the direct condensation polymerization of lactic acid. J. Environ. Polym. Degr. 1995, 3, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocz, K.; Domonkos, M.; Igricz, T.; Kmetty, Á.; Bárány, T.; Marosi, G. Flame retarded self-reinforced poly(lactic acid) composites of outstanding impact resistance. Compos. Part A 2015, 70, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, F.; Tu, W.; Bilotti, E.; Peijs, T. Preparation and properties of self-reinforced poly(lactic acid) composites based on oriented tapes. Compos. Part A 2015, 76, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Gong, R.H.; Hogg, P.J. Poly (lactic acid) fibre reinforced biodegradable composites. Compos. Part B 2014, 62, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somord, K.; Suwantong, O.; Tawichai, N.; Peijs, T.; Soykeabkaew, N. Self-reinforced poly(lactic acid) nanocomposites of high toughness. Polymer 2016, 103, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kriel, H.; Sanderson, R.D.; Smit, E. Single polymer composite yarns and films prepared from heat bondable poly(lactic acid) core-shell fibres with submicron fibre diameters. Fibres Text. East Eur. 2013, 21, 44–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bognitzki, M.; Czado, W.; Frese, T.; Schaper, A.; Hellwig, M.; Steinhart, M.; Greiner, A.; Wendorff, J.H. Nanostructured Fibers via Electrospinning. Adv. Mater. 2001, 13, 70–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dicastillo, C.L.; Roa, K.; Garrido, L.; Pereira, A.; Galotto, M.J. Novel Polyvinyl Alcohol/Starch Electrospun Fibers as a Strategy to Disperse Cellulose Nanocrystals into Poly(lactic acid). Polymers 2017, 9, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkas, B.; Balogh, A.; Farkas, A.; Domokos, A.; Borbás, E.; Marosi, G.; Nagy, Z.K. Medicated Straws Based on Electrospun Solid Dispersions. Periodica Polytechn. Chem. Eng. 2018, 62, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liang, X.; Wang, S.; Qin, W.; Zhang, Q. Electrospun Antimicrobial Polylactic Acid/Tea Polyphenol Nanofibers for Food-Packaging Applications. Polymers 2018, 10, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borbás, E.; Sinkó, B.; Tsinman, O.; Tsinman, K.; Kiserdei, É.; Démuth, B.; Balogh, A.; Bodák, B.; Domokos, A.; Dargó, G.; et al. Investigation and mathematical description of the real driving force of passive transport of drug molecules from supersaturated solutions. Mol. Pharm. 2016, 13, 3816–3826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wehmann, M.; McCulloch, W.J.G. Melt blowing technology. In Polypropylene: An A–Z Reference; Krager-Kocsis, J., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1999; Volume 2, pp. 415–420. ISBN 978-94-011-4421-6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammonds, R.L.; Gazzola, W.H.; Benson, R.S. Physical and thermal characterization of polylactic acid meltblown nonwovens. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131, 40593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Cheng, B.; Cheng, G. Development and filtration performance of polylactic acid meltblowns. Text. Res. J. 2010, 80, 771–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhao, M.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, Q.; Shen, Y.; Gong, R.H.; Zhou, F.; Li, Y.; Deng, B. Polylactide single-polymer composites with a wide melt-processing window based on core-sheath PLA fibers. Mater. Des. 2018, 139, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puchalski, M.; Kwolek, S.; Szparaga, G.; Chrzanowski, M.; Krucinska, I. Investigation of the Influence of PLA Molecular Structure on the Crystalline Forms (α’ and α) and Mechanical Properties of Wet Spinning Fibres. Polymers 2017, 9, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, E.W.; Sterzel, H.J.; Wegner, G. Investigation of the structure of solution grown crystals of lactide copolymers by means of chemical reactions. Colloid Polym. Sci. 1973, 251, 980–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tábi, T.; Hajba, S.; Kovács, J.G. Effect of crystalline forms (α’ and α) of poly(lactic acid) on its mechanical, thermo-mechanical, heat deflection temperature and creep properties. Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 82, 232–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gualandi, C.; Govoni, M.; Foroni, L.; Valente, S.; Bianchi, M.; Giordano, E.; Pasquinelli, G.; Biscarini, F.; Focarete, M.L. Ethanol disinfection affects physical properties and cell response of electrospun poly(l-lactic acid) scaffolds. Eur. Polym. J. 2012, 48, 2008–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flood, J.E.; Nulf, S.A. How molecular weight distribution and drawing temperature affect polypropylene physical properties and morphology. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1990, 30, 1504–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Type | 3052D | 3001D | 3100HP |
|---|---|---|---|
| Density (g/cm3) | 1.24 | 1.24 | 1.24 |
| MFI (g/10 perc) (210 °C, 2.16 kg) | 14 | 22 | 24 |
| d-lactide content (%) | 4.0 | 1.4 | 0.5 |
| Crystalline melt temperature (Tm) (°C) | 145–160 | 160–175 * | 165–180 * |
| Glass transition temperature (Tg) (°C) | 55–60 | 55–60 * | 55–60 * |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vadas, D.; Kmetykó, D.; Marosi, G.; Bocz, K. Application of Melt-Blown Poly(lactic acid) Fibres in Self-Reinforced Composites. Polymers 2018, 10, 766. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10070766
Vadas D, Kmetykó D, Marosi G, Bocz K. Application of Melt-Blown Poly(lactic acid) Fibres in Self-Reinforced Composites. Polymers. 2018; 10(7):766. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10070766
Chicago/Turabian StyleVadas, Dániel, Dávid Kmetykó, György Marosi, and Katalin Bocz. 2018. "Application of Melt-Blown Poly(lactic acid) Fibres in Self-Reinforced Composites" Polymers 10, no. 7: 766. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10070766
APA StyleVadas, D., Kmetykó, D., Marosi, G., & Bocz, K. (2018). Application of Melt-Blown Poly(lactic acid) Fibres in Self-Reinforced Composites. Polymers, 10(7), 766. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10070766






