Breathable and Flexible Piezoelectric ZnO@PVDF Fibrous Nanogenerator for Wearable Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of PVDF Nanofiber Mats
2.2. Hydrothermal Growth of ZnO Nanorods
2.2.1. Preparation of ZnO Seed Solution
2.2.2. Preparation of ZnO Growth Solution
2.2.3. Growth of ZnO Nanorods
2.3. Piezoelectric Response Measurements
2.4. Characterization Methods
3. Results
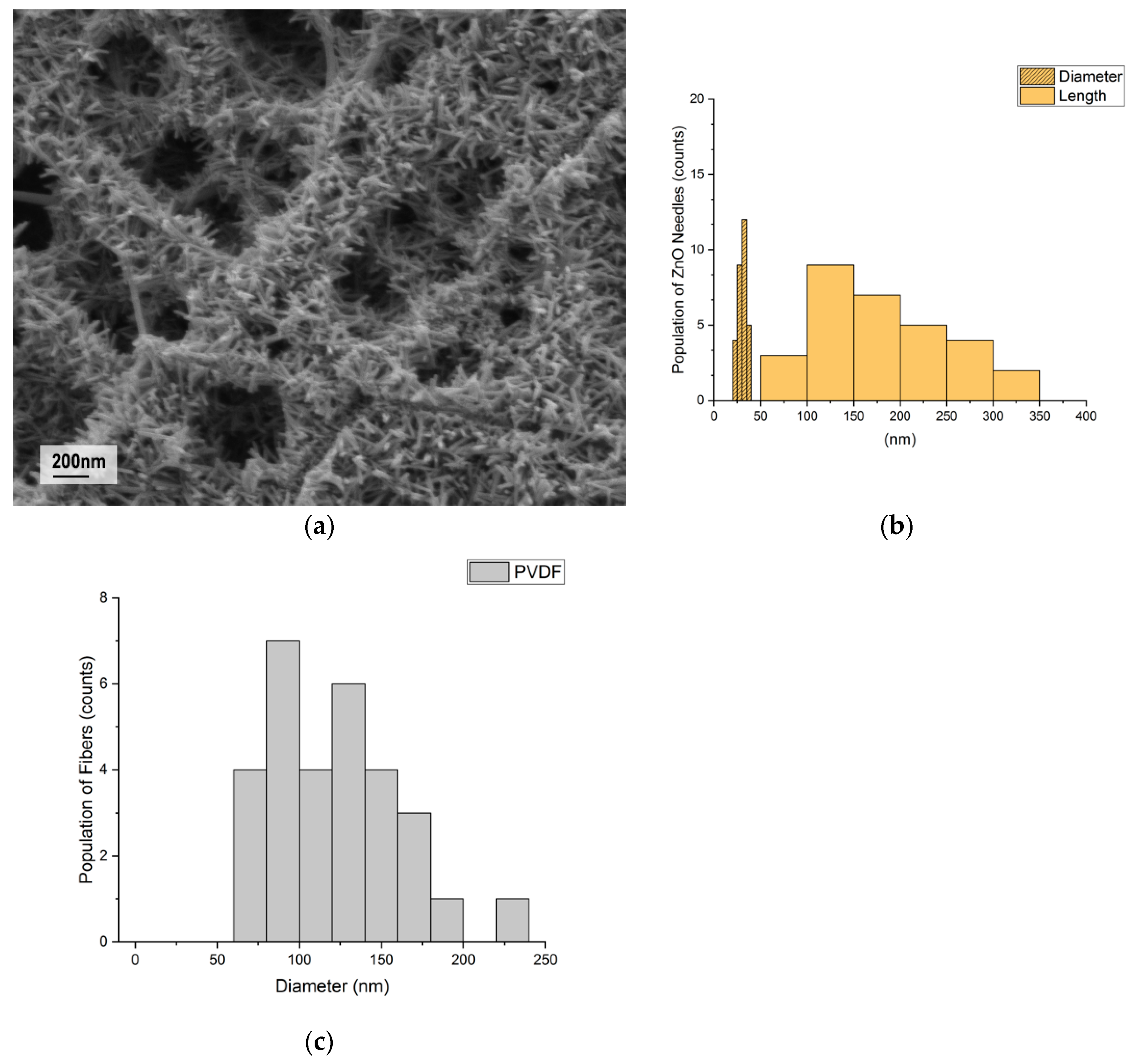
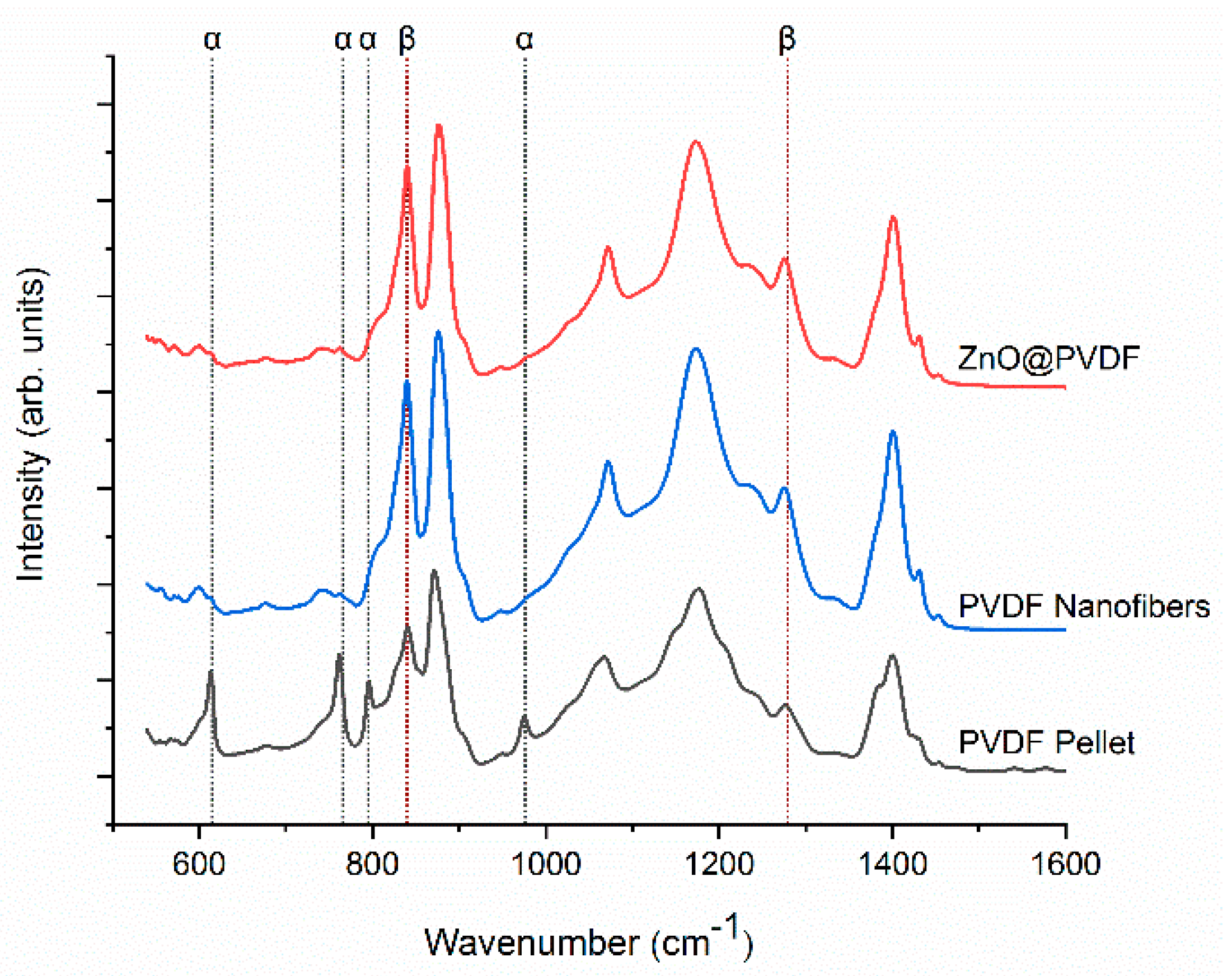
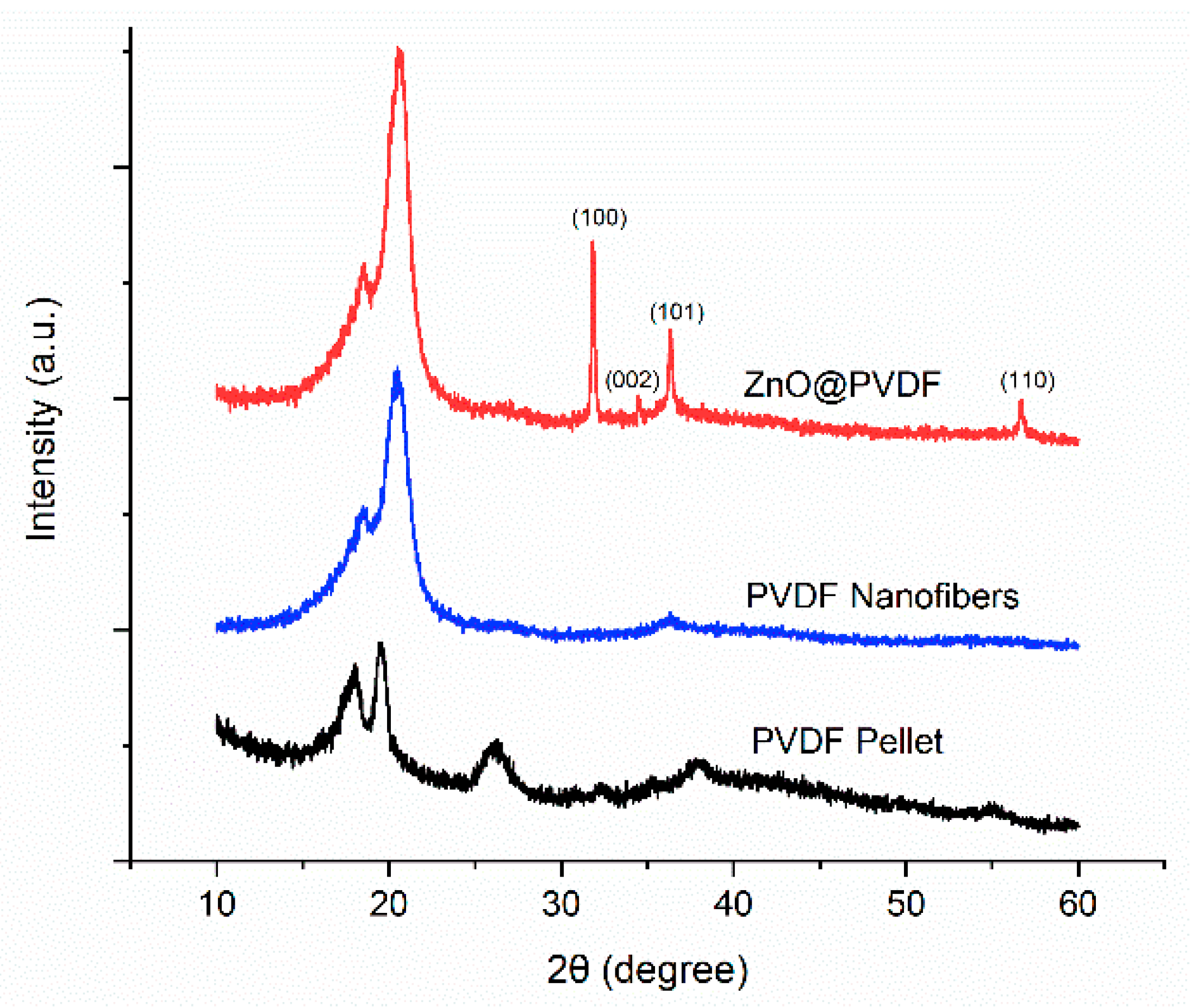
3.1. ZnO Growth on PVDF Nanofibers
3.2. Piezoelectric Measurements
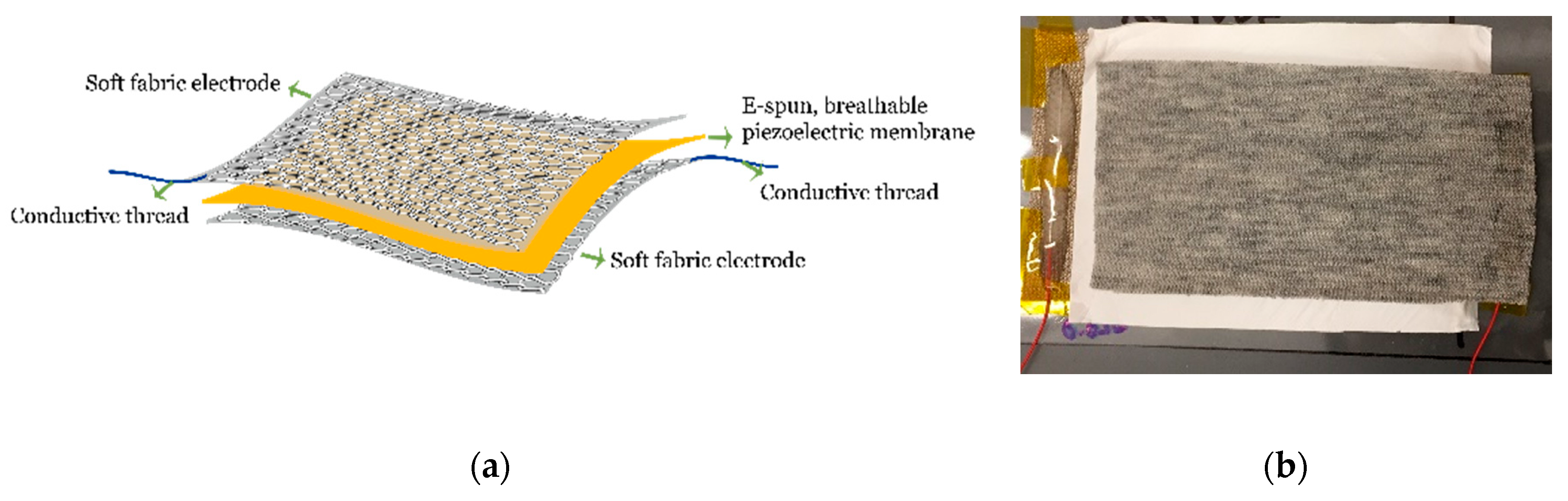
3.2.1. Comparison of Aluminum Foil and Conductive Knitted Fabric as Electrodes
3.2.2. Improvement of Piezoelectric Property after Growing ZnO Nanorods on PVDF Fibers
3.3. Material Breathability
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anton, S.R.; Sodano, H.A. A review of power harvesting using piezoelectric materials (2003–2006). Smart Mater. Struct. 2007, 16, R1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Recent progress in piezoelectric nanogenerators as a sustainable power source in self-powered systems and active sensors. Nano Energy 2015, 14, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, X. Smart Fibres, Fabrics and Clothing: Fundamentals and Applications; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2001; ISBN 978-1-85573-760-0. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, W.; Shu, L.; Li, Q.; Chen, S.; Wang, F.; Tao, X.-M. Fiber-Based Wearable Electronics: A Review of Materials, Fabrication, Devices, and Applications. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 5310–5336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Gao, T.; Wang, J.; Liao, J.; Qiu, Y.; Yang, Q.; Xue, H.; Shi, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Xiong, Z.; et al. A hybrid fibers based wearable fabric piezoelectric nanogenerator for energy harvesting application. Nano Energy 2015, 13, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Wang, C.; Yu, H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, M. Human walking-driven wearable all-fiber triboelectric nanogenerator containing electrospun polyvinylidene fluoride piezoelectric nanofibers. Nano Energy 2015, 14, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoppa, M.; Chiolerio, A. Wearable Electronics and Smart Textiles: A Critical Review. Sensors 2014, 14, 11957–11992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovinger, A.J. Ferroelectric Polymers. Science 1983, 220, 1115–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Shi, J. Piezoelectric Nanogenerators for Self-powered Nanodevices. In Piezoelectric Nanomaterials for Biomedical Applications; Nanomedicine and Nanotoxicology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 135–172. ISBN 978-3-642-28043-6. [Google Scholar]
- Kochervinskii, V.V.; Kozlova, N.V.; Khnykov, A.Y.; Shcherbina, M.A.; Sulyanov, S.N.; Dembo, K.A. Features of structure formation and electrophysical properties of poly(vinylidene fluoride) crystalline ferroelectric polymers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 116, 695–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tichý, P.J.; Erhart, D.J.; Kittinger, P.D.E.; Přívratská, P.J. Piezoelectric Materials. In Fundamentals of Piezoelectric Sensorics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 119–185. ISBN 978-3-540-43966-0. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, J.S.; Ounaies, Z. Piezoelectric Polymers. In Encyclopedia of Polymer Science and Technology; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002; ISBN 978-0-471-44026-0. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, H.B.; Han, C.S.; Pyun, J.C.; Ryu, W.H.; Kang, C.-Y.; Cho, Y.S. (Na,K)NbO3 nanoparticle-embedded piezoelectric nanofiber composites for flexible nanogenerators. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2015, 111, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes-Pereira, J.; Sencadas, V.; Correia, V.; Rocha, J.G.; Lanceros-Méndez, S. Energy harvesting performance of piezoelectric electrospun polymer fibers and polymer/ceramic composites. Sens. Actuators Phys. 2013, 196, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; Tao, X.-M.; Chen, S.; Shang, S.; Chan, H.L.W.; Choy, S.H. Highly durable all-fiber nanogenerator for mechanical energy harvesting. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 2631–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Chen, C.-Y.; Wang, S.; Cha, S.N.; Park, Y.J.; Kim, J.M.; Chou, L.-J.; Wang, Z.L. A Hybrid Piezoelectric Structure for Wearable Nanogenerators. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 1759–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, J.; Niu, H.; Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Lin, T. Enhanced mechanical energy harvesting using needleless electrospun poly(vinylidene fluoride) nanofibre webs. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 2196–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Dommer, M.; Chang, C.; Lin, L. Piezoelectric nanofibers for energy scavenging applications. Nano Energy 2012, 1, 356–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bafqi, M.S.S.; Bagherzadeh, R.; Latifi, M. Fabrication of composite PVDF-ZnO nanofiber mats by electrospinning for energy scavenging application with enhanced efficiency. J. Polym. Res. 2015, 22, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirinov, A.V.; Schomburg, W.K. Pressure sensor from a PVDF film. Sens. Actuators Phys. 2008, 142, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Hashim, N.A.; Liu, Y.; Abed, M.R.M.; Li, K. Progress in the production and modification of PVDF membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 375, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, P.K. Review: Environmental friendly lead-free piezoelectric materials. J. Mater. Sci. 2009, 44, 5049–5062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeder, M.D.; Damjanovic, D.; Setter, N. Lead Free Piezoelectric Materials. J. Electroceramics 2014, 13, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Min Kim, S.; Son, H.; Kim, H.; Park, B.; Ku, J.; Inn Sohn, J.; Im, K.; Eun Jang, J.; Park, J.-J.; et al. Enhancement of piezoelectricity via electrostatic effects on a textile platform. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 8932–8936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsubara, M.; Yamaguchi, T.; Sakamoto, W.; Kikuta, K.; Yogo, T.; Hirano, S. Processing and Piezoelectric Properties of Lead-Free (K,Na) (Nb,Ta) O3 Ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2005, 88, 1190–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilling, K.; Bradford, B.; Castelli, D.; Dufour, E.; Frank Nash, J.; Pape, W.; Schulte, S.; Tooley, I.; Bosch, J.; Schellauf, F. Human safety review of “nano” titanium dioxide and zinc oxide. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2010, 9, 495–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteiro-Riviere, N.A.; Wiench, K.; Landsiedel, R.; Schulte, S.; Inman, A.O.; Riviere, J.E. Safety Evaluation of Sunscreen Formulations Containing Titanium Dioxide and Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles in UVB Sunburned Skin: An In Vitro and In Vivo Study. Toxicol. Sci. 2011, 123, 264–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, M.D.; Stotland, M.; Ellis, J.I. The safety of nanosized particles in titanium dioxide– and zinc oxide–based sunscreens. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2009, 61, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smijs, T.G.; Pavel, S. Titanium dioxide and zinc oxide nanoparticles in sunscreens: Focus on their safety and effectiveness. Nanotechnol. Sci. Appl. 2011, 4, 95–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Athauda, T.J.; Ozer, R.R. Nylon Fibers as Template for the Controlled Growth of Highly Oriented Single Crystalline ZnO Nanowires. Cryst. Growth Des. 2013, 13, 2680–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koka, A.; Zhou, Z.; Sodano, H.A. Vertically aligned BaTiO3 nanowire arrays for energy harvesting. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 7, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magrez, A.; Vasco, E.; Seo, J.W.; Dieker, C.; Setter, N.; Forró, L. Growth of Single-Crystalline KNbO3 Nanostructures. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, J.H.; Lee, M.; Hong, J.-I.; Ding, Y.; Chen, C.-Y.; Chou, L.-J.; Wang, Z.L. Lead-Free NaNbO3 Nanowires for a High Output Piezoelectric Nanogenerator. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 10041–10046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, G.; Wang, A.C.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Functional Electrical Stimulation by Nanogenerator with 58 V Output Voltage. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 3086–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saravanakumar, B.; Mohan, R.; Thiyagarajan, K.; Kim, S.-J. Fabrication of a ZnO nanogenerator for eco-friendly biomechanical energy harvesting. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 16646–16656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.-I.; Wuu, D.-S.; Shen, K.-C.; Horng, R.-H. Fabrication of an Ultra-Flexible ZnO Nanogenerator for Harvesting Energy from Respiration. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 2013, 2, P400–P404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yu, A.; Peng, M.; Song, M.; Liu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhai, J. Improvement in the Piezoelectric Performance of a ZnO Nanogenerator by a Combination of Chemical Doping and Interfacial Modification. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 6971–6977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.; Tran, V.H.; Wang, J.; Fuh, Y.-K.; Lin, L. Direct-Write Piezoelectric Polymeric Nanogenerator with High Energy Conversion Efficiency. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 726–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanik, M.; Aktas, O.; Sen, H.S.; Durgun, E.; Bayindir, M. Spontaneous High Piezoelectricity in Poly(vinylidene fluoride) Nanoribbons Produced by Iterative Thermal Size Reduction Technique. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 9311–9323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Athauda, T.J.; Neff, J.G.; Sutherlin, L.; Butt, U.; Ozer, R.R. Systematic Study of the Structure–Property Relationships of Branched Hierarchical TiO2/ZnO Nanostructures. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 6917–6926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Wang, Z.L. One-dimensional ZnO nanostructures: Solution growth and functional properties. Nano Res. 2011, 4, 1013–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baruah, S.; Thanachayanont, C.; Dutta, J. Growth of ZnO nanowires on nonwoven polyethylene fibers. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2008, 9, 025009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolbeck, A.G. Aging of piezoelectricity in poly(vinylidene fluoride). J. Polym. Sci. Polym. Phys. Ed. 1982, 20, 1987–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugunan, A.; Warad, H.C.; Boman, M.; Dutta, J. Zinc oxide nanowires in chemical bath on seeded substrates: Role of hexamine. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2006, 39, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lord, M. Foot pressure measurement: A review of methodology. J. Biomed. Eng. 1981, 3, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urry, S. Plantar pressure-measurement sensors. Meas. Sci. Technol. 1999, 10, R16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duckworth, T.; Betts, R.P.; Franks, C.I.; Burke, J. The Measurement of Pressures under the Foot. Foot Ankle 1982, 3, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ImageJ. Available online: https://imagej.nih.gov/ij/ (accessed on 31 May 2018).
- Huang, J.; Qian, X. Comparison of Test Methods for Measuring Water Vapor Permeability of Fabrics. Text. Res. J. 2008, 78, 342–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indushekar, R.; Awasthi, P.; Gupta, R.K.; Kotresh, T.M. Studies on Test Methods used to Measure Water Vapor Transmission of Fabrics by DSC and Conventional Dish Techniques. J. Ind. Text. 2005, 34, 223–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagherzadeh, R.; Latifi, M.; Najar, S.S.; Tehran, M.A.; Gorji, M.; Kong, L. Transport properties of multi-layer fabric based on electrospun nanofiber mats as a breathable barrier textile material. Text. Res. J. 2012, 82, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, P.; Lopes, A.C.; Lanceros-Mendez, S. Electroactive phases of poly(vinylidene fluoride): Determination, processing and applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 683–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soin, N.; Shah, T.H.; Anand, S.C.; Geng, J.; Pornwannachai, W.; Mandal, P.; Reid, D.; Sharma, S.; Hadimani, R.L.; Vatansever Bayramol, D.; et al. Novel “3-D spacer” all fibre piezoelectric textiles for energy harvesting applications. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 1670–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Wang, X.; Lin, T. Electrical power generator from randomly oriented electrospun poly(vinylidene fluoride) nanofibre membranes. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 11088–11091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.H.; Pan, C.T.; Lin, L.W.; Huang, J.C.; Ou, Z.Y. Direct-write PVDF nonwoven fiber fabric energy harvesters via the hollow cylindrical near-field electrospinning process. Smart Mater. Struct. 2014, 23, 025003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.-A.; Kim, M.-J.; Chen, S.-M.; Wu, Y.-S.; Lam, K.-H.; Chan, H.L.-W.; Fan, J.-T. Tough and porous piezoelectric P(VDF-TrFE)/organosilicate composite membrane. High Perform. Polym. 2017, 29, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Sarkar, M.; Lau, S.; Fan, J.; Chan, L.H. Preparation and characterization of porous poly(vinylidene fluoride-trifluoroethylene) copolymer membranes via electrospinning and further hot pressing. Polym. Test. 2011, 30, 436–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-K.; Wang, L.; Fan, J.; Shou, W.; Zhou, B.-M.; Liu, Y. Multi-Jet Electrospinning with Auxiliary Electrode: The Influence of Solution Properties. Polymers 2018, 10, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bormashenko, Y.; Pogreb, R.; Stanevsky, O.; Bormashenko, E. Vibrational spectrum of PVDF and its interpretation. Polym. Test. 2004, 23, 791–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salimi, A.; Yousefi, A.A. Analysis Method: FTIR studies of β-phase crystal formation in stretched PVDF films. Polym. Test. 2003, 22, 699–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregorio, R.; Cestari, M. Effect of crystallization temperature on the crystalline phase content and morphology of poly(vinylidene fluoride). J. Polym. Sci. Part B 1994, 32, 859–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zeng, H.C. Hydrothermal Synthesis of ZnO Nanorods in the Diameter Regime of 50 nm. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 4430–4431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, C.; Jiang, Y.; Yao, Y.; Meng, X.; Zapien, J.A.; Lee, C.S.; Lifshitz, Y.; Lee, S.T. Well-Aligned ZnO Nanowire Arrays Fabricated on Silicon Substrates. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2004, 14, 589–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athauda, T.J.; Butt, U.; Ozer, R.R. One-dimensional hierarchical composite materials based on ZnO nanowires and electrospun blend nanofibers. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 21431–21438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Kelder, E.M.; Schoonman, J. Functional Ceramic Films with Reticular Structures Prepared by Electrostatic Spray Deposition Technique. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1997, 144, L289–L291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjiri, M.; El Mir, L.; Leonardi, S.G.; Pistone, A.; Mavilia, L.; Neri, G. Al-doped ZnO for highly sensitive CO gas sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 196, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jedda, H.; Ghith, A.; Sakli, F. Prediction of fabric drape using the FAST system. J. Text. Inst. 2007, 98, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shou, D.; Ye, L.; Fan, J. Gas transport properties of electrospun polymer nanofibers. Polymer 2014, 55, 3149–3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shou, D.; Fan, J.; Mei, M.; Ding, F. An analytical model for gas diffusion though nanoscale and microscale fibrous media. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2014, 16, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

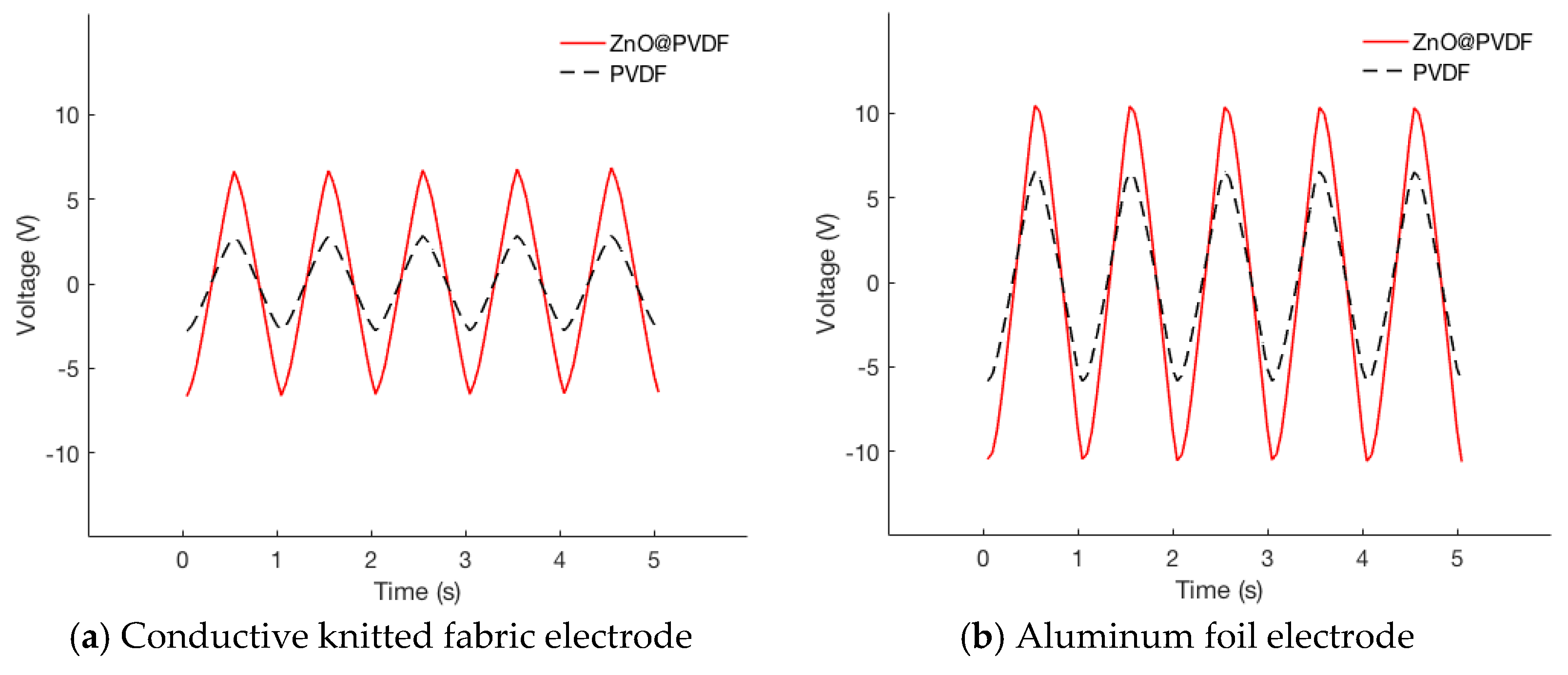
| Materials | Conductive knit electrode | Aluminum foil electrode | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average (V) | Standard deviation σ (V) | Coefficient of variation | Average (V) | Standard deviation σ (V) | Coefficient of variation | |
| PVDF | 2.76 | 0.22 | 0.08 | 6.26 | 3.51 | 0.56 |
| ZnO @PVDF | 6.36 | 1.89 | 0.30 | 10.84 | 6.12 | 0.56 |
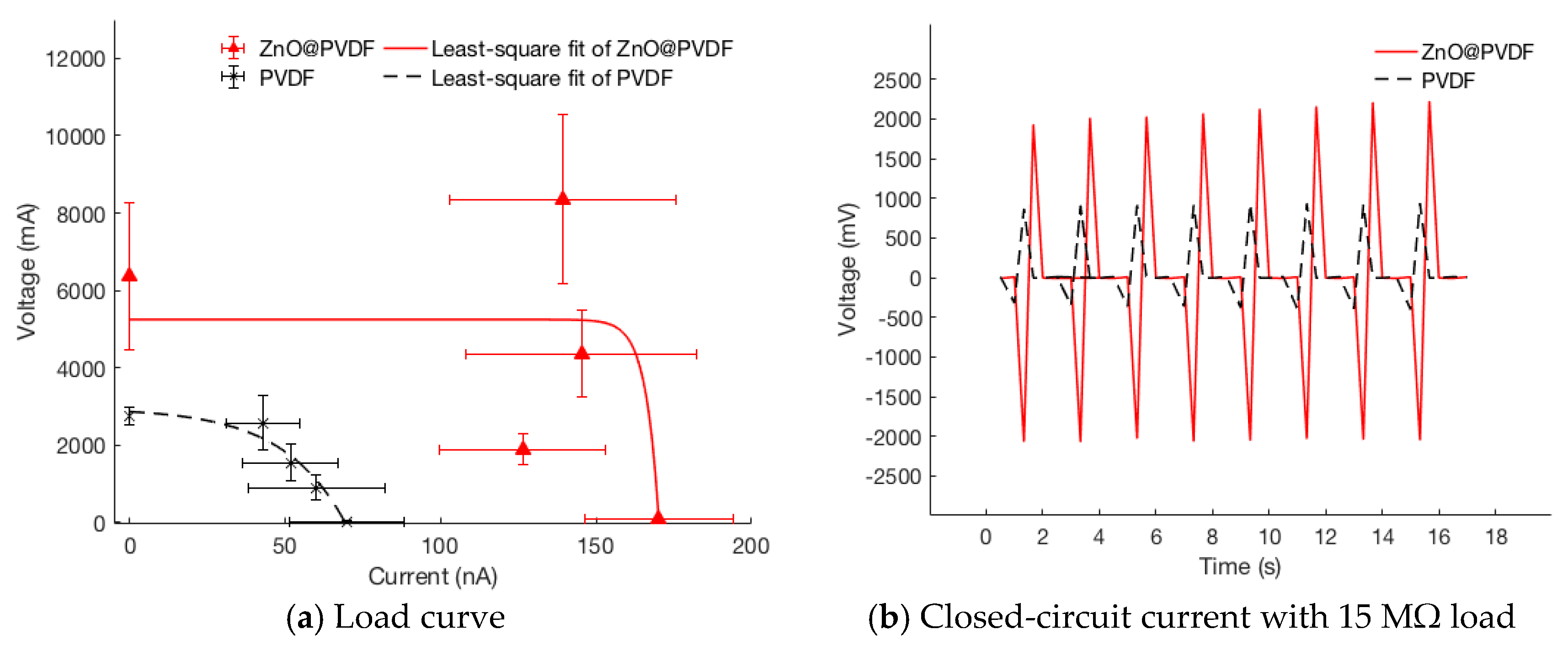
| 0.47 MΩ | 15 MΩ | 30 MΩ | 60 MΩ | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVDF | Current (nA) | 69.78 | 60.06 | 51.79 | 42.77 |
| Power Density (nW/cm2) | 0.15 | 3.61 | 5.36 | 7.32 | |
| Voltage (mV) | 32.80 | 900.96 | 1553.63 | 2566.49 | |
| Standard Deviation σ (mV) | 8.59 | 328.30 | 460.01 | 704.94 | |
| Coefficient of Variation | 0.26 | 0.36 | 0.30 | 0.27 | |
| ZnO@PVDF | Current (nA) | 170.10 | 126.33 | 145.30 | 139.36 |
| Power Density (nW/cm2) | 0.91 | 15.96 | 42.22 | 77.69 | |
| Voltage (mV) | 79.95 | 1894.88 | 4359.03 | 8361.61 | |
| Standard Deviation σ (mV) | 11.20 | 399.01 | 1116.67 | 2176.22 | |
| Coefficient of Variation | 0.14 | 0.21 | 0.26 | 0.026 |
| WVP (g·m−2·day−1) | PVDF | ZnO@PVDF | Conductive knit | Nanogenerator assembly by PVDF | Cotton |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average | 629.00 | 623.68 | 645.57 | 608.20 | 611.82 |
| Standard Deviation σ | 31.95 | 16.92 | 26.98 | 15.05 | 32.02 |
| Coefficient of Variation | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.05 |
| (units) | ZnO@PVDF | Lee et al. [16] | Zeng et al. [15] | Fang et al. [32] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Material | PVDF, ZnO | PVDF, ZnO | PVDF, NaNbO3 | PVDF | |
| Fabrication method | electrospinning | dip coating | electrospinning | needleless electrospinning | |
| Ceramic addition | growth | growth | filler | ||
| Pressure or strain | (MPa or %) | 0.1 MPa | <1% | 0.2 MPa | 0.05 MPa |
| Frequency | (Hz) | 1 | ~1 | 1 | 5 |
| Open-circuit voltage | (V) | 6.4 | 0.1 | 3.2 | 2.6 |
| Closed-circuit current | (μA) | 0.17 | - | 4.2 | 4.5 |
| Current density | (nA/cm2) | 11.34 | 10 | 672 | 2250 |
| Current resistive load | (kΩ) | 470 | - | 470 | - |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, M.; Wu, Y.S.; Kan, E.C.; Fan, J. Breathable and Flexible Piezoelectric ZnO@PVDF Fibrous Nanogenerator for Wearable Applications. Polymers 2018, 10, 745. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10070745
Kim M, Wu YS, Kan EC, Fan J. Breathable and Flexible Piezoelectric ZnO@PVDF Fibrous Nanogenerator for Wearable Applications. Polymers. 2018; 10(7):745. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10070745
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Minji, Yuen Shing Wu, Edwin C. Kan, and Jintu Fan. 2018. "Breathable and Flexible Piezoelectric ZnO@PVDF Fibrous Nanogenerator for Wearable Applications" Polymers 10, no. 7: 745. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10070745
APA StyleKim, M., Wu, Y. S., Kan, E. C., & Fan, J. (2018). Breathable and Flexible Piezoelectric ZnO@PVDF Fibrous Nanogenerator for Wearable Applications. Polymers, 10(7), 745. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10070745






