Influence of Ethylene Glycol Methacrylate to the Hydration and Transition Behaviors of Thermo-Responsive Interpenetrating Polymeric Network Hydrogels
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
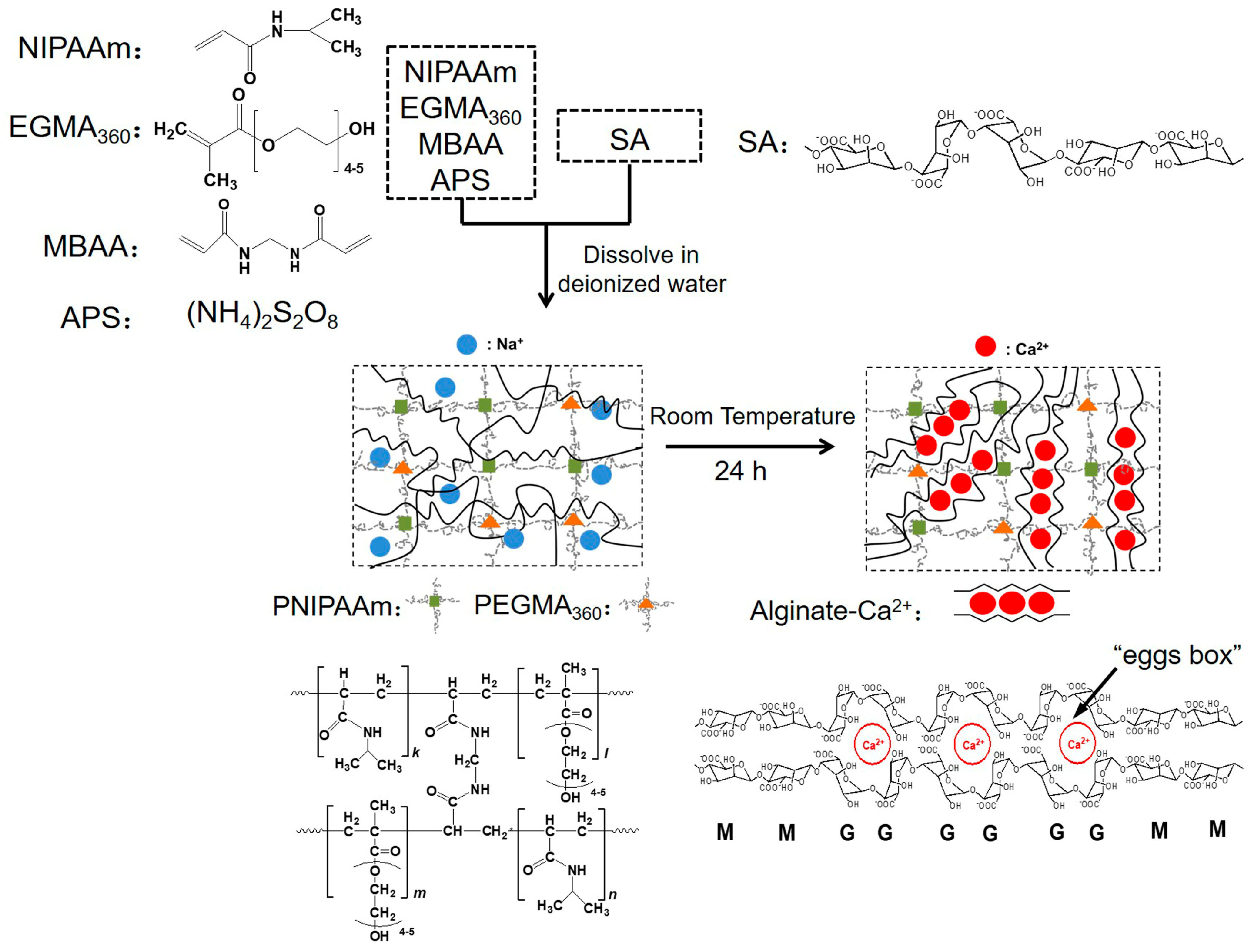
2.1. Materials
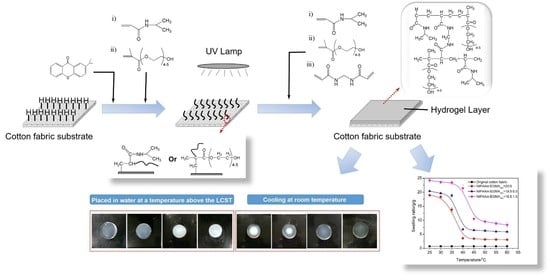
2.2. Preparation of Hydrogels
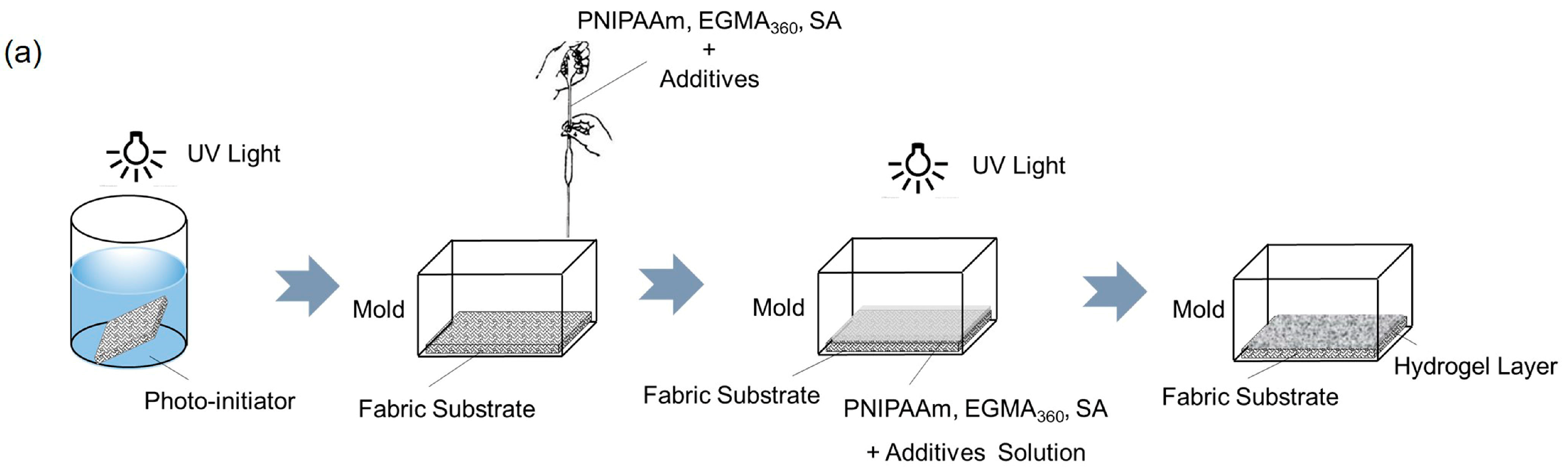
2.3. Preparation of Cotton Fabric Grafted Hydrogels
2.4. Characterizations
2.4.1. ATR-FTIR Analysis
2.4.2. Thermogravimetric Analysis
2.4.3. DSC Thermal Analysis
2.4.4. Surface Morphology
2.4.5. Determination of Swelling Behavior
2.4.6. Hand Evaluation
3. Results and Discussion
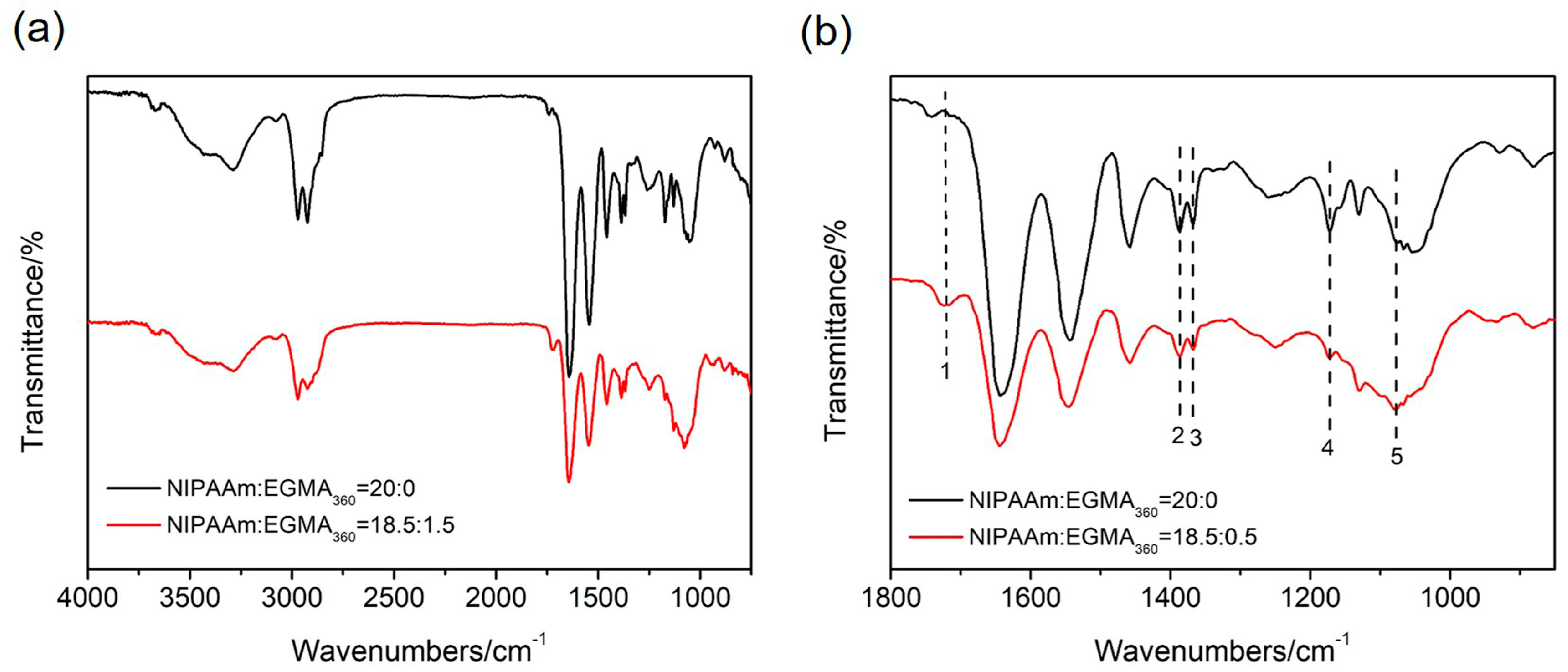
3.1. ATR-FTIR Analysis of Hydrogels
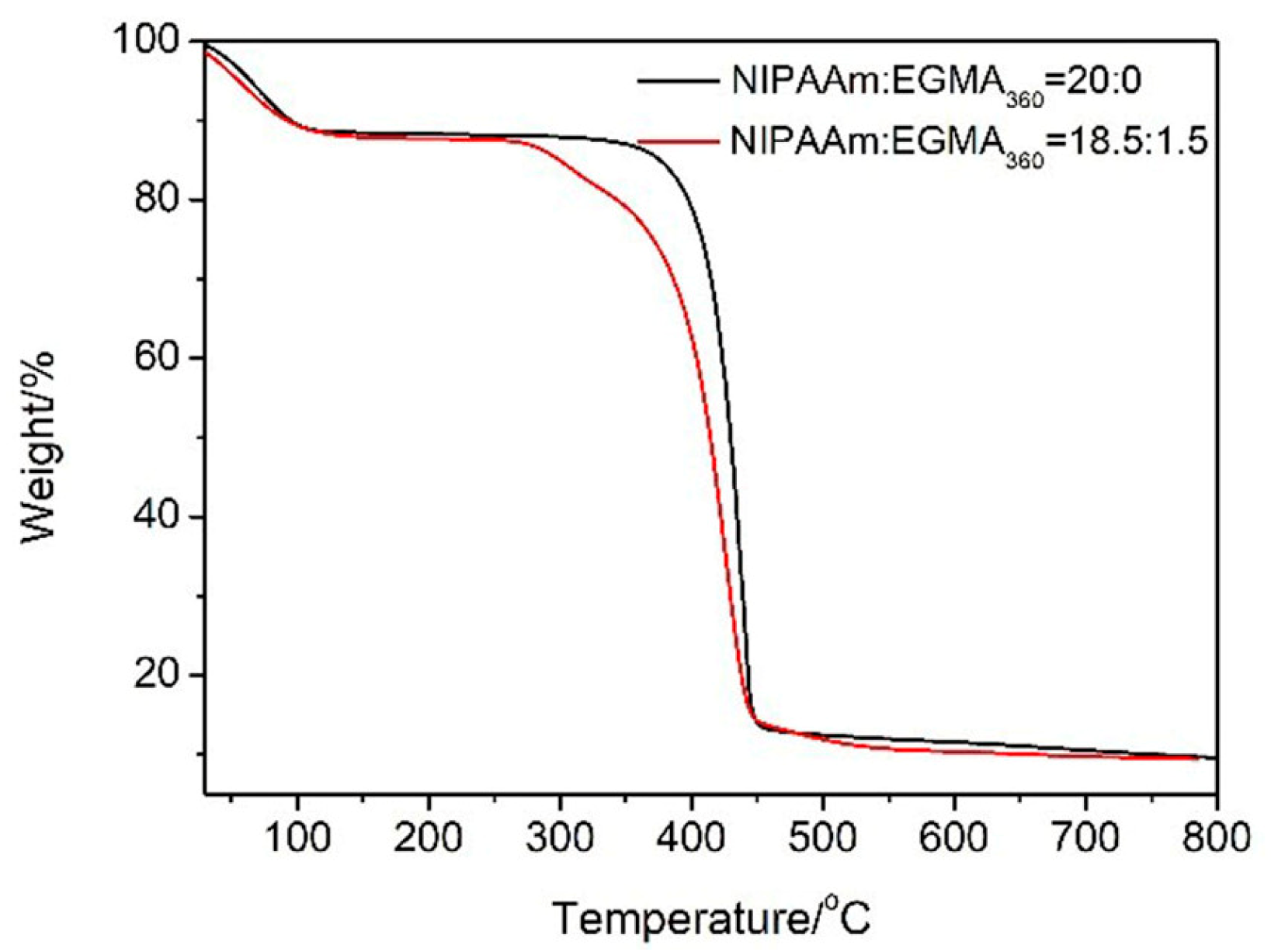
3.2. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
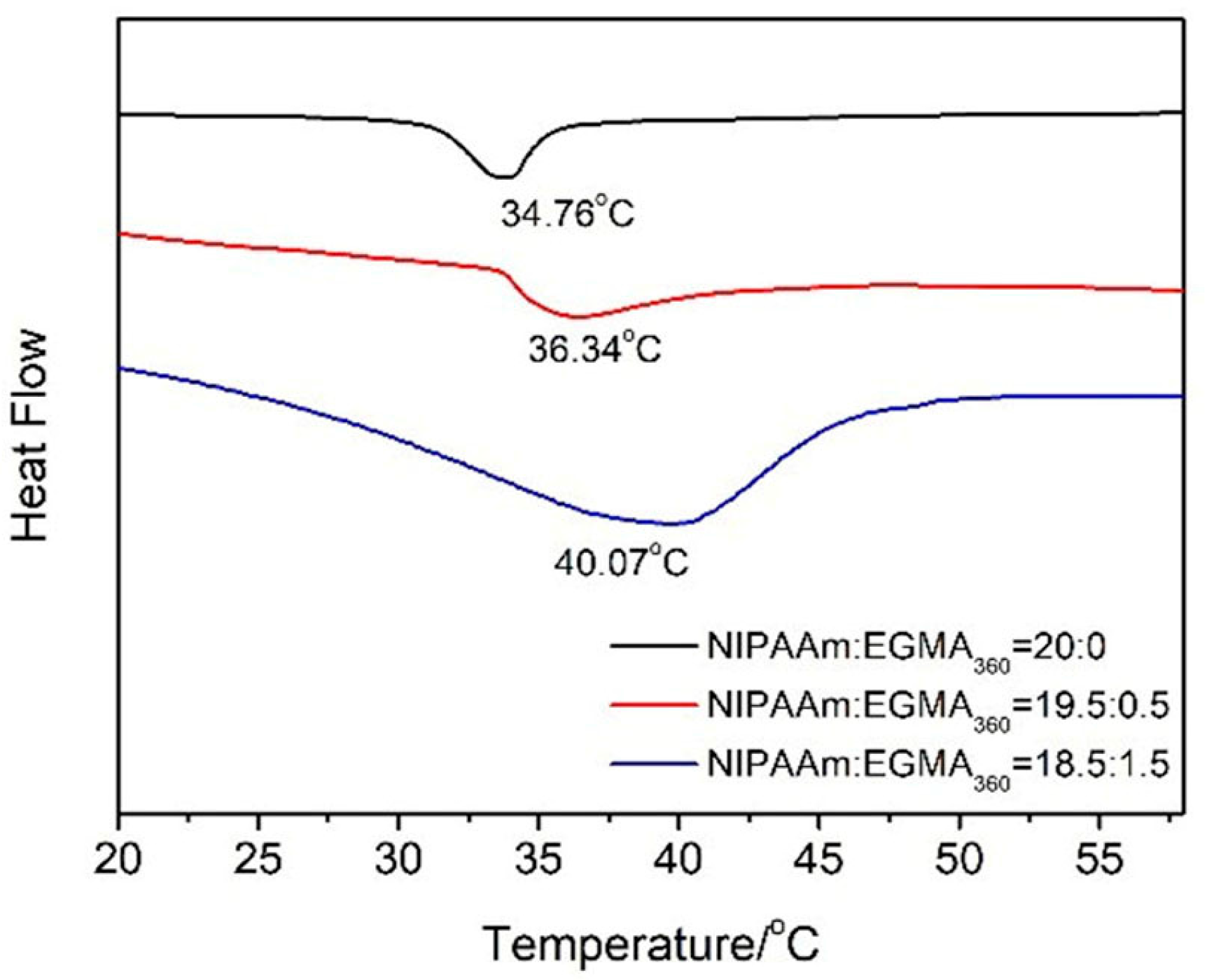
3.3. Phase Transition of Hydrogels
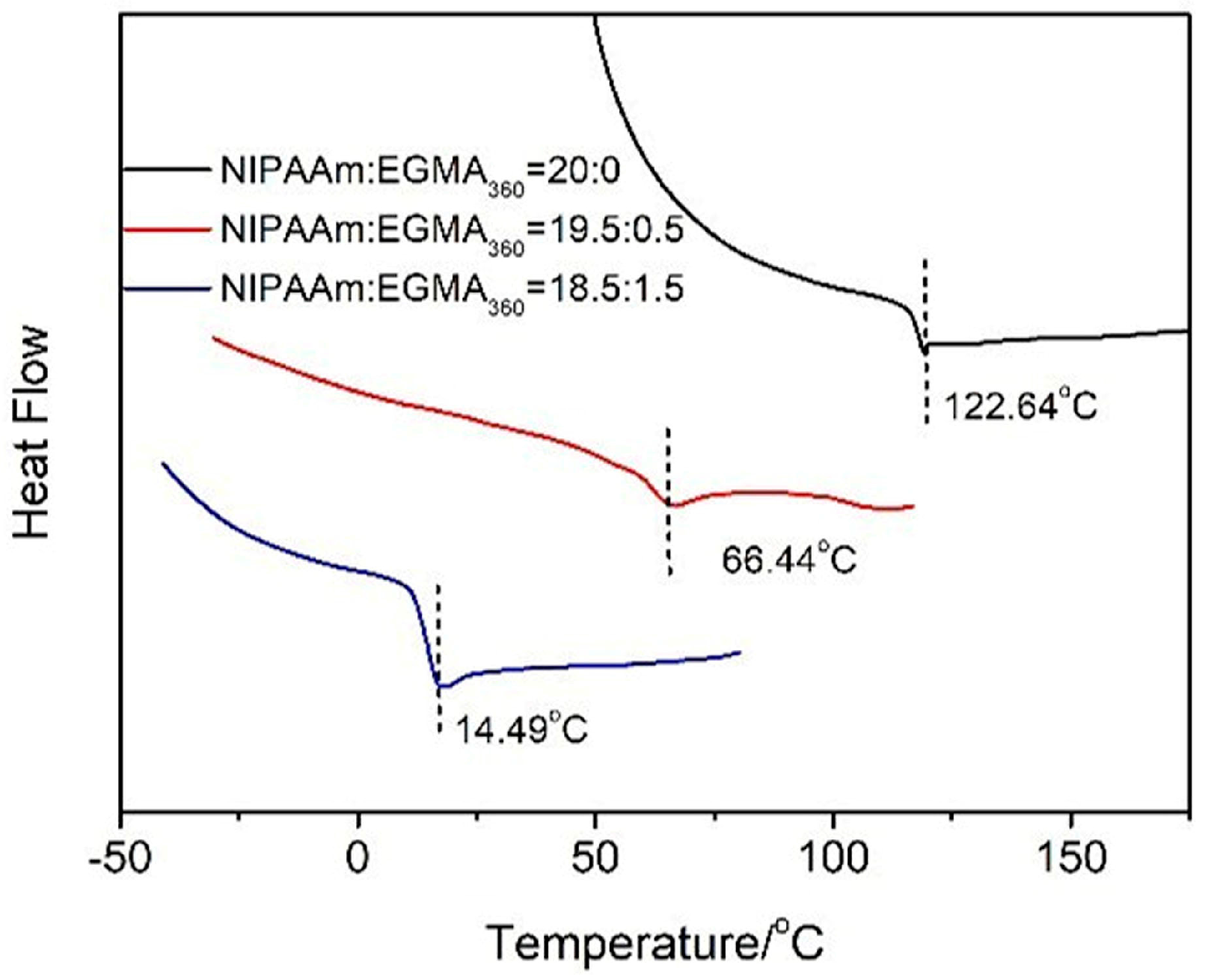
3.4. Glass Transition Temperature of Hydrogels
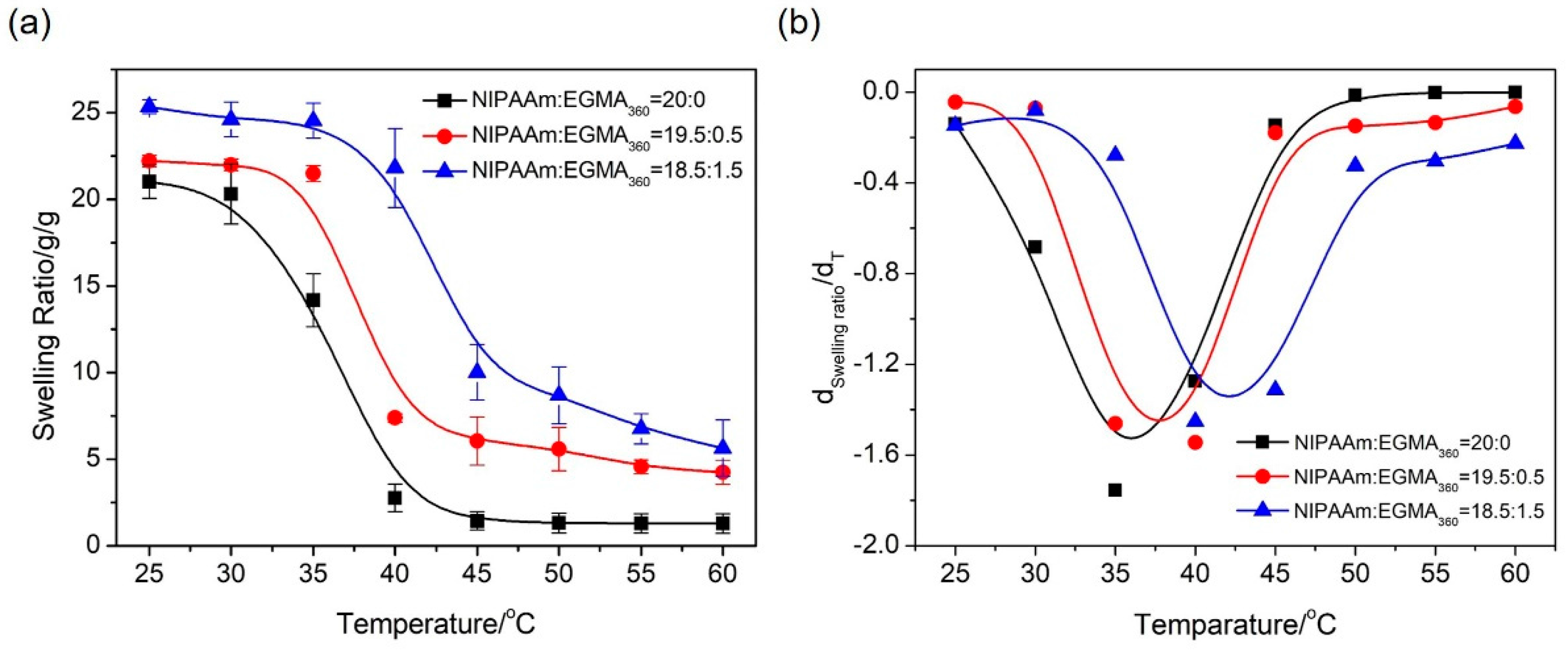
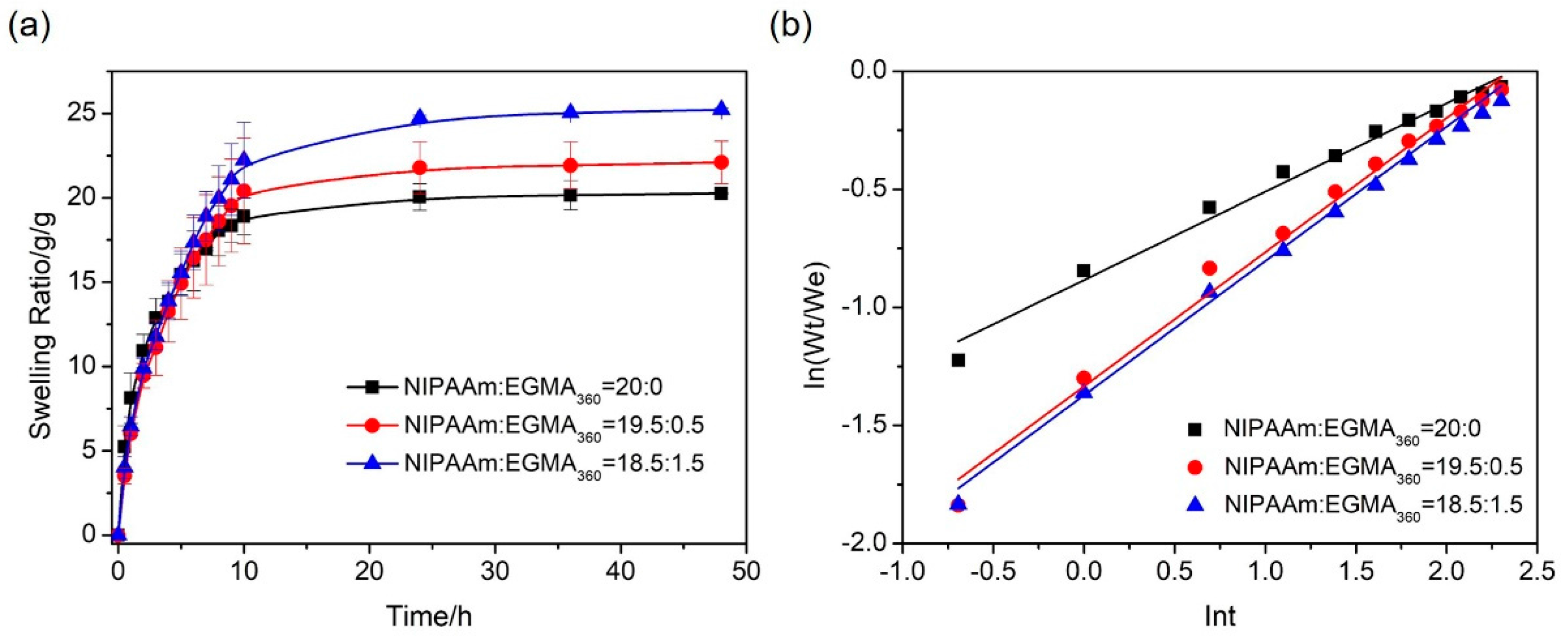
3.5. Swelling of Hydrogels
3.5.1. Swelling Kinetics
3.5.2. Deswelling Kinetics
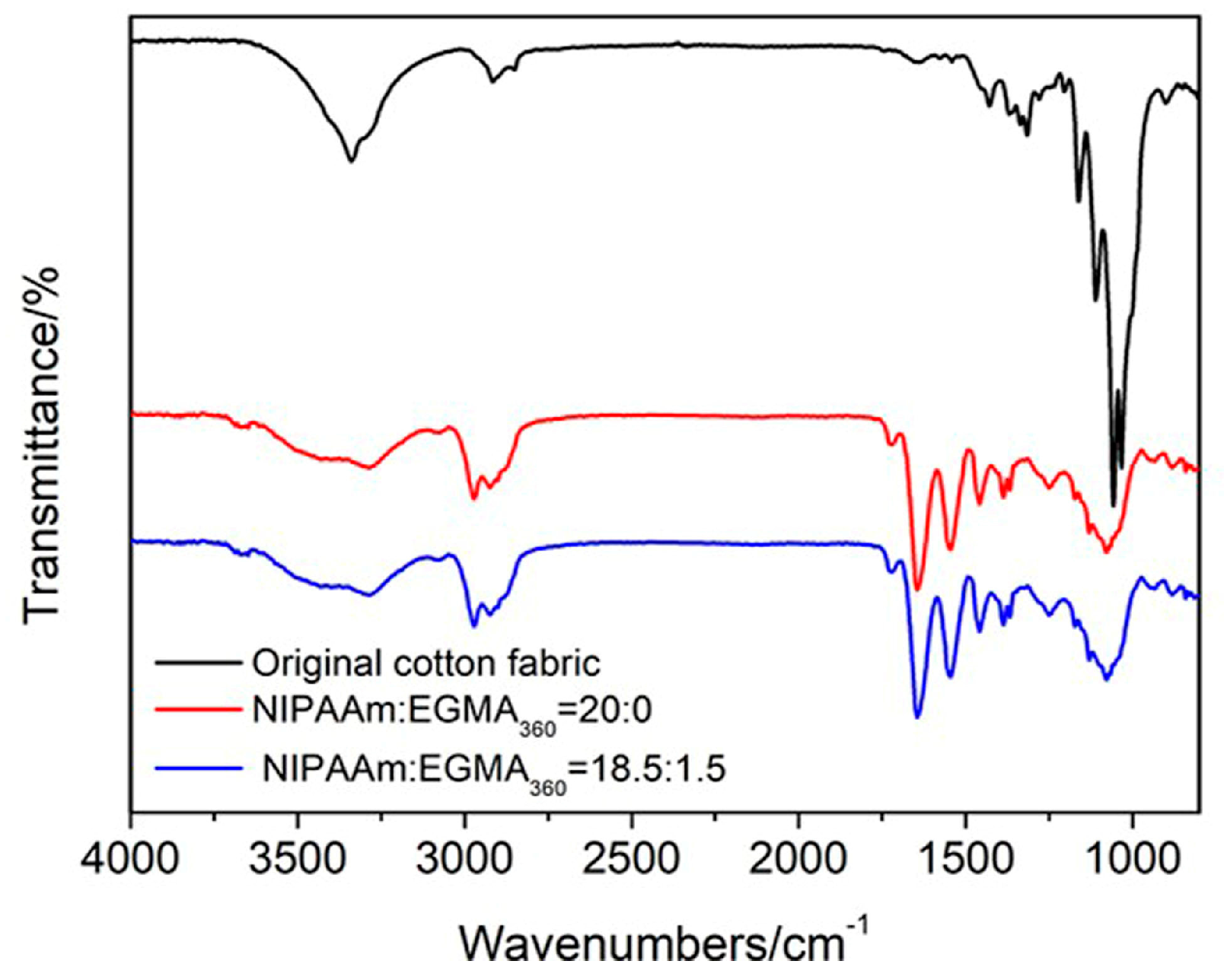
3.6. ATR-FTIR Analysis of Cotton Fabric Grafted Hydrogels
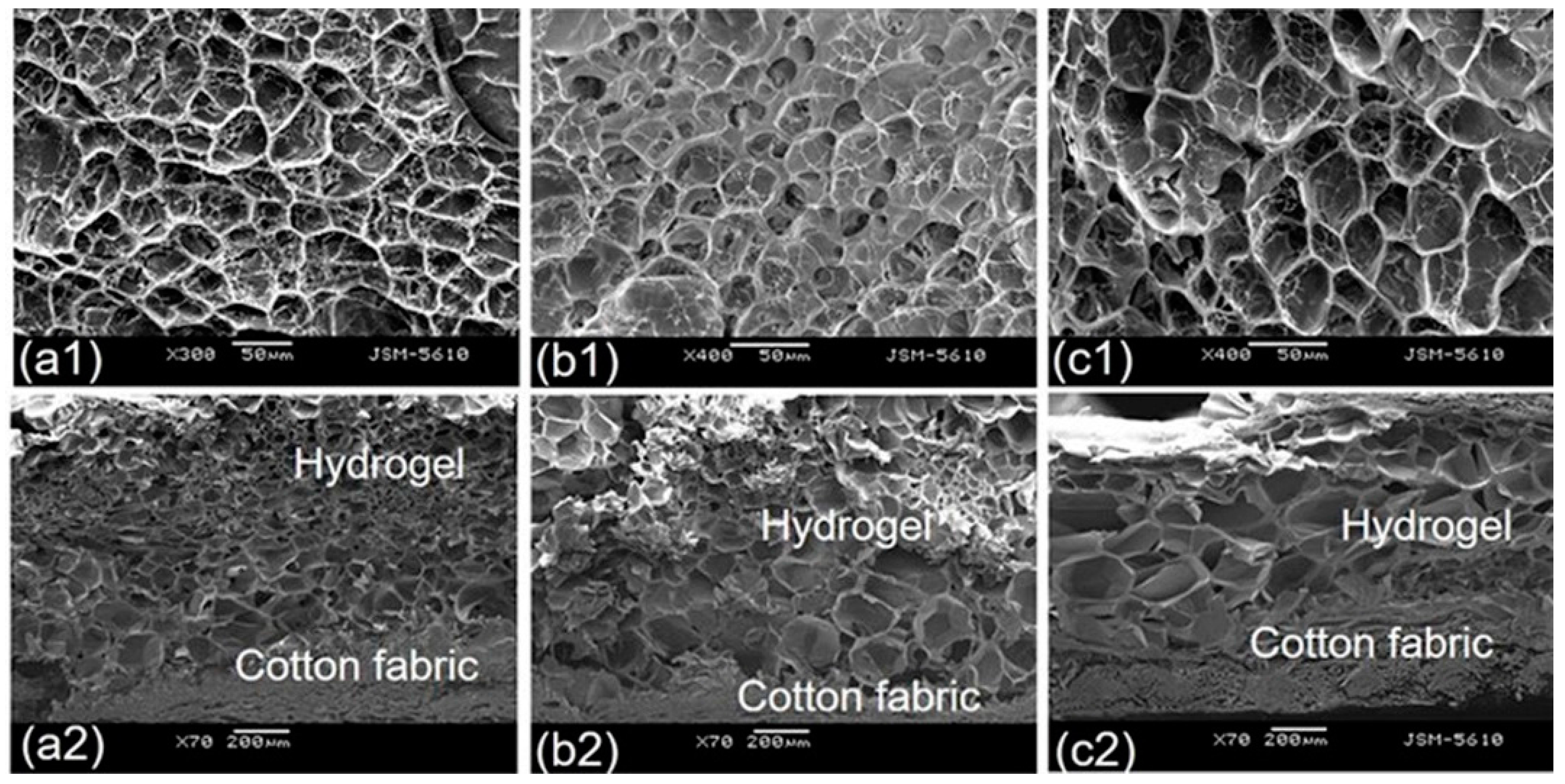
3.7. Morphological Observation
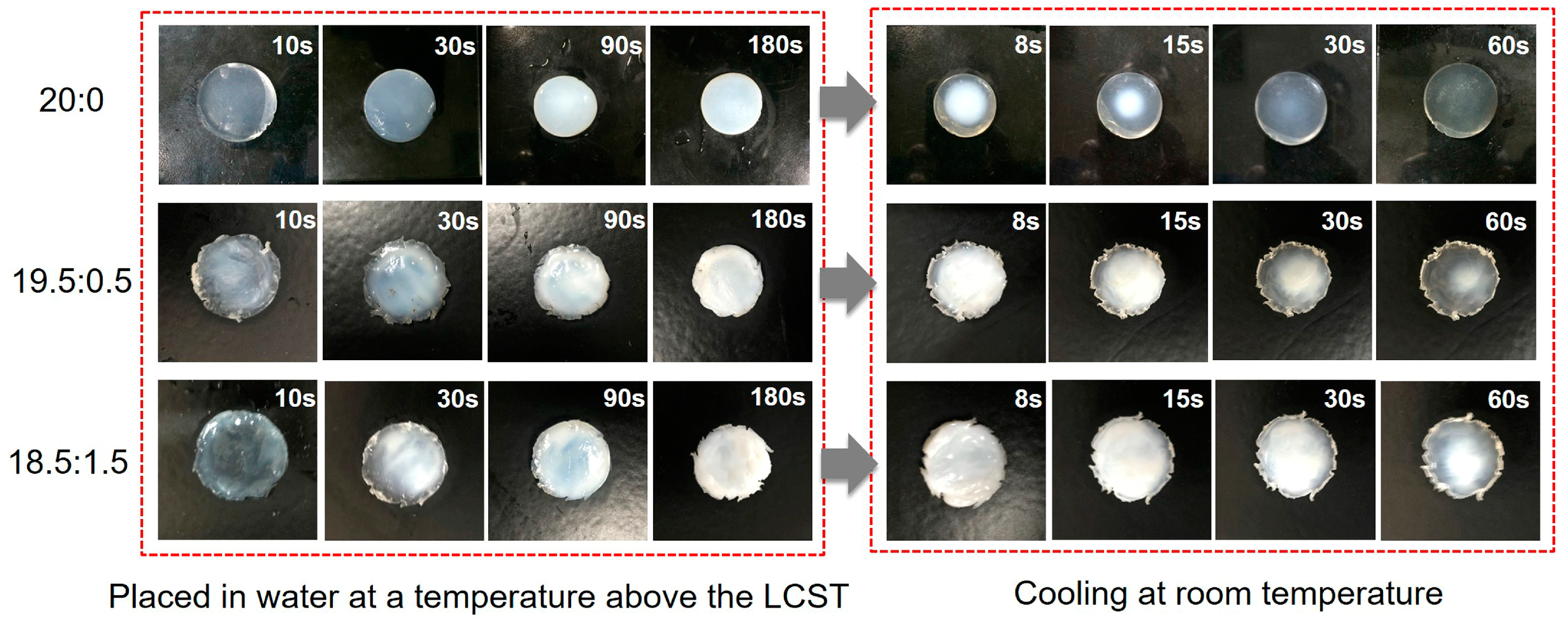
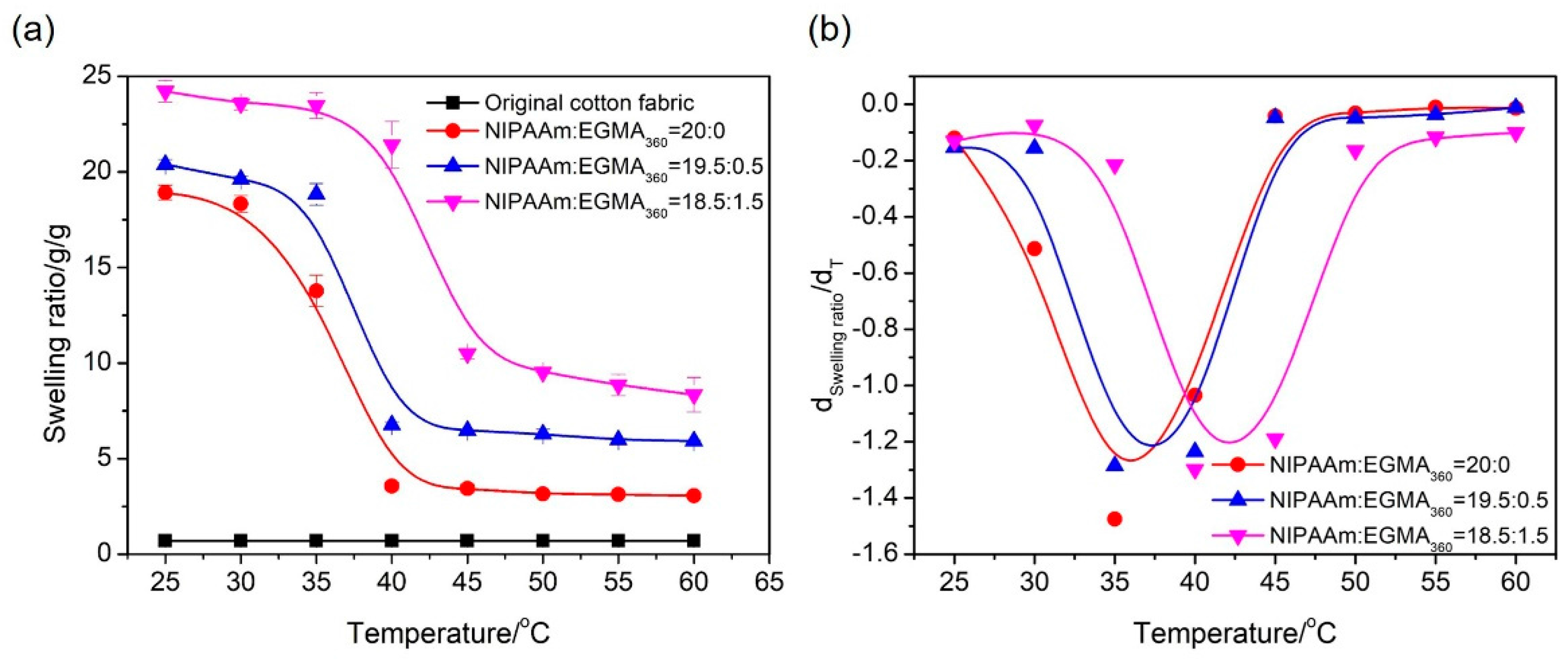
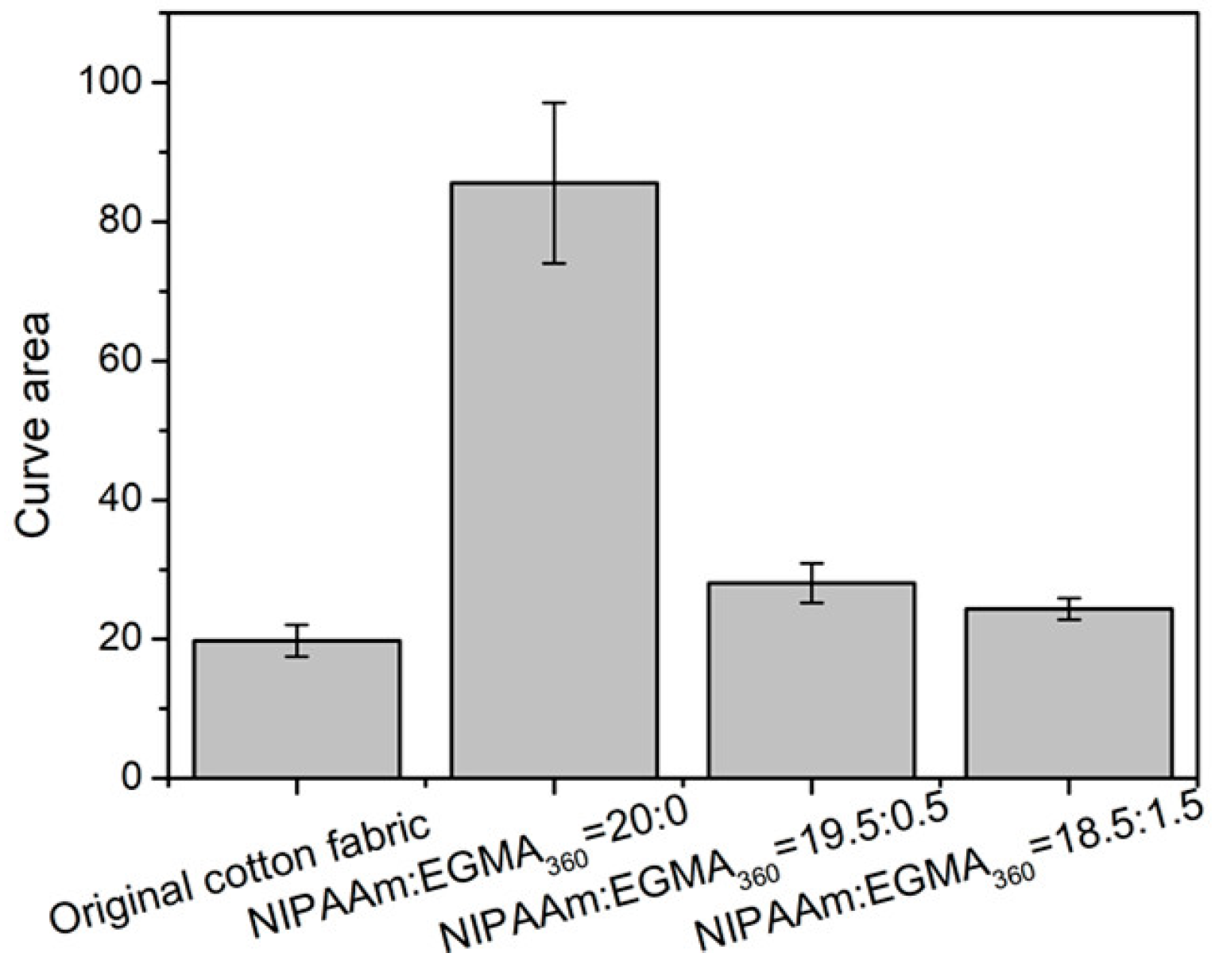
3.8. Temperature Dependence of Fabric Grafted Hydrogels
3.9. Hand Feeling of Cotton Fabric Grafted Hydrogels
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, J.; Tan, H. Alginate-based biomaterials for regenerative medicine applications. Materials 2013, 6, 1285–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, A.S. Hydrogels for biomedical applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Gao, W.; Hu, H.; Ma, K.; He, B.; Dai, W.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Q. Novel thermo-sensitive hydrogel system with paclitaxel nanocrystals: High drug-loading, sustained drug release and extended local retention guaranteeing better efficacy and lower toxicity. J. Control. Release 2014, 174, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Chen, L.; Shen, T.; Wu, D. Preparation and properties of a novel thermo-sensitive hydrogel based on chitosan/hydroxypropyl methylcellulose/glycerol. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 93, 775–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omidi, M.; Yadegari, A.; Tayebi, L. Wound dressing application of pH-sensitive carbon dots/chitosan hydrogel. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 10638–10649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagonis, K.; Bokias, G. Temperature- and solvent-sensitive hydrogels based on N-isopropylacrylamide and N,N-dimethylacrylamide. Polym. Bull. 2007, 58, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pour, Z.S.; Ghaemy, M. Removal of dyes and heavy metal ions from water by magnetic hydrogel beads based on poly(vinyl alcohol)/carboxymethyl starch-g-poly(vinyl imidazole). RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 64106–64118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Park, S.; Kim, I.Y.; Shin, M.S.; Kim, S.I. Electric stimuli responses to poly(vinyl alcohol)/chitosan interpenetrating polymer network hydrogel in NaCl solutions. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2002, 86, 2285–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heskins, M.; Guillet, J.E. Solution properties of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide). J. Macromol. Sci. Part A Chem. 1968, 2, 1441–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.T.; Bhat, R.; Jandt, K.D. Temperature-sensitive PVA/PNIPAAm semi-IPN hydrogels with enhanced responsive properties. Acta Biomater. 2009, 5, 488–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Qi, W.; Li, G.; Cao, S. Biomimetic self-assembly of calcium phosphate templated by PNIPAAm nanogels for sustained smart drug delivery. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2012, 32, 1299–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navaei, A.; Truong, D.; Heffernan, J.; Cutts, J.; Brafman, D.; Sirianni, R.W.; Vernon, B.; Nikkhah, M. PNIPAAm-based biohybrid injectable hydrogel for cardiac tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2016, 32, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, T.; Chen, H.; Zheng, J.; Yu, Q.; Wu, Z.; Yuan, L. Inhibition of protein adsorption and cell adhesion on PNIPAAm-grafted polyurethane surface: Effect of graft molecular weight. Colloid Surf. B Biointerfaces 2011, 85, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burkert, S.; Bittrich, E.; Kuntzsch, M.; Müller, M.; Eichhorn, K.J.; Bellmann, C.; Uhlmann, P.; Stamm, M. Protein resistance of PNIPAAm brushes: Application to switchable protein adsorption. Langmuir 2010, 26, 1786–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Alves, N.M.; Mano, J.F. Chitosan coated alginate beads containing poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) for dual-stimuli-responsive drug release. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B: Appl. Biomater. 2008, 84, 595–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rani, P.; Mishra, S.; Sen, G. Microwave based synthesis of polymethyl methacrylate grafted sodium alginate: Its application as flocculant. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 91, 686–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawar, S.N.; Edgar, K.J. Alginate derivatization: A review of chemistry, properties and applications. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 3279–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Han, Z.; Ma, L.; Sun, S.; Zhao, C. A highly hemo-compatible, mechanically strong, and conductive dual cross-linked polymer hydrogel. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 8016–8024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Han, Z.; Zhao, C. Super anti-coagulant dual-network hydrogels with controllable conductivity, tunable swelling and mechanically strong properties. In Proceedings of the 4th Symposium on Innovative Polymers for Controlled Delivery, Suzhou, China, 23–26 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J.; Alves, N.M.; Mano, J.F. Drug release of pH/temperature-responsive calcium alginate/poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) semi-IPN beads. Macromol. Biosci. 2006, 6, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Zha, L.; Zhou, M.; Ma, J.; Liang, B. Rapid deswelling of sodium alginate/poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) semi-interpenetrating polymer network hydrogels in response to temperature and pH changes. Polym. Sci. Polym. Sci. 2005, 283, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumitriu, R.P.; Mitchell, G.R.; Vasile, C. Multi-responsive hydrogels based on N-isopropylacrylamide and sodium alginate. Polym. Int. 2011, 60, 222–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durme, K.V.; And, G.V.A.; Mele, B.V. Kinetics of demixing and remixing in poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)/water studied by modulated temperature DSC. Macromolecules 2015, 37, 9596–9605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Q.; Wang, W.; Adelsberger, J.; Golosova, A.; Bivigou, A.; Golosova, A.; Funari, S.S.; Perlich, J.; Roth, S.V.; Papadakis, C.M.; et al. Collapse transition in thin films of poly(methoxydiethylenglycol acrylate). Colloid Polym. Sci. 2011, 289, 569–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yenice, Z.; Schön, S.; Bildirir, H.; Genzer, J.; Klitzing, R.V. Thermoresponsive PDMAEMA brushes: Effect of gold nanoparticle deposition. J. Phys. Chem. B 2015, 119, 10348–10358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Z.; Mao, J.; Wang, D.; Yang, M.; Ji, X. Synthesis and multi-stimuli-responsive behavior of poly(N,N-dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate) spherical brushes under different modes of confinement in solution. Langmuir ACS J. Surf. Colloids 2015, 31, 8930–8939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Q.; Chen, Y.; Guan, S.; Fang, Q.; Chen, T.; Buschbaum, P.M.; Wang, J.P. Smart cleaning cotton fabrics cross-linked with thermo-responsive and flexible poly(2-(2-methoxyethoxy) ethoxyethyl methacrylate-co-ethylene glycol methacrylate). RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 38382–38390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhuo, R. Synthesis of Temperature-sensitive poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) hydrogel with improved surface property. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2000, 223, 311–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Jia, J.; Guo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, P. Preparation and characterization of IPN hydrogels composed of chitosan and gelatin cross-linked by genipin. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 99, 31–38. [Google Scholar]
- Karthik, R.; Meenakshi, S. Removal of Cr(VI) ions by adsorption onto sodium alginate-polyaniline nanofibers. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 72, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Wang, K.; Yang, D.; Nie, J. Photopolymerization of methacrylated chitosan/PNIPAAm hybrid dual-sensitive hydrogels as carrier for drug delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2009, 44, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Q.; Wu, J.; Lin, J.; Li, Q.; Fan, S. Two-step synthesis of polyacrylamide/polyacrylate interpenetrating network hydrogels and its swelling/deswelling properties. J. Mater. Sci. 2008, 43, 5884–5890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; La Flamme, K.; Peppas, N.A. Dynamic swelling behavior of pH-sensitive anionic hydrogels used for protein delivery. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 89, 1606–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khare, A.R.; Peppas, N.A. Swelling/deswelling of anionic copolymer gels. Biomaterials 1995, 16, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, C.M.; Peppas, N.A. Solute and penetrant diffusion in swellable polymers: X. Swelling of multiethylene glycol dimethacrylate copolymers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1990, 39, 2043–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shieh, L.Y.; Peppas, N.A. Solute and penetrant diffusion in swellable polymers. XI. The dynamic swelling behavior of hydrophilic copolymers containing multiethylene glycol dimethacrylates. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 42, 1579–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.T.; Keller, T.F.; Bhat, R.; Garipcan, B.; Jandt, K.D. A novel two-level microstructured poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) hydrogel for controlled release. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 3890–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritger, P.L.; Peppas, N.A. A simple equation for description of solute release II. Fickian and anomalous release from swellable devices. J. Control. Release 1987, 5, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Su, H.; Tan, T. Synthesis and properties of thermo- and pH-sensitive poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)/polyaspartic acid IPN hydrogels. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 87, 2425–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample Code | SA/g | NIPAAm/EGMA360/mol/mol | MBAA/NIPAAm/%(mol/mol) | APS/mg | TEMED/μL | DI Water/mL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.2 | 20:0 | 1.0 | 20 | 6 | 20 |
| 2 | 0.2 | 19.5:0.5 | 1.0 | 20 | 6 | 20 |
| 3 | 0.2 | 18.5:1.5 | 1.0 | 20 | 6 | 20 |
| Sample | Characteristic Index (n) | Fitting Coefficient |
|---|---|---|
| NIPAAm:EGMA360 = 20:0 | 0.37 | 0.99 |
| NIPAAm:EGMA360 = 19.5:0.5 | 0.57 | 0.99 |
| NIPAAm:EGMA360 = 18.5:1.5 | 0.56 | 0.99 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, B.; Zhong, Q.; Li, D.; Xu, K.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J. Influence of Ethylene Glycol Methacrylate to the Hydration and Transition Behaviors of Thermo-Responsive Interpenetrating Polymeric Network Hydrogels. Polymers 2018, 10, 128. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10020128
Li B, Zhong Q, Li D, Xu K, Zhang L, Wang J. Influence of Ethylene Glycol Methacrylate to the Hydration and Transition Behaviors of Thermo-Responsive Interpenetrating Polymeric Network Hydrogels. Polymers. 2018; 10(2):128. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10020128
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Bing, Qi Zhong, Dapeng Li, Ke Xu, Lu Zhang, and Jiping Wang. 2018. "Influence of Ethylene Glycol Methacrylate to the Hydration and Transition Behaviors of Thermo-Responsive Interpenetrating Polymeric Network Hydrogels" Polymers 10, no. 2: 128. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10020128
APA StyleLi, B., Zhong, Q., Li, D., Xu, K., Zhang, L., & Wang, J. (2018). Influence of Ethylene Glycol Methacrylate to the Hydration and Transition Behaviors of Thermo-Responsive Interpenetrating Polymeric Network Hydrogels. Polymers, 10(2), 128. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10020128