Electrospun Polycaprolactone Nanofibers as a Reaction Membrane for Lateral Flow Assay
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
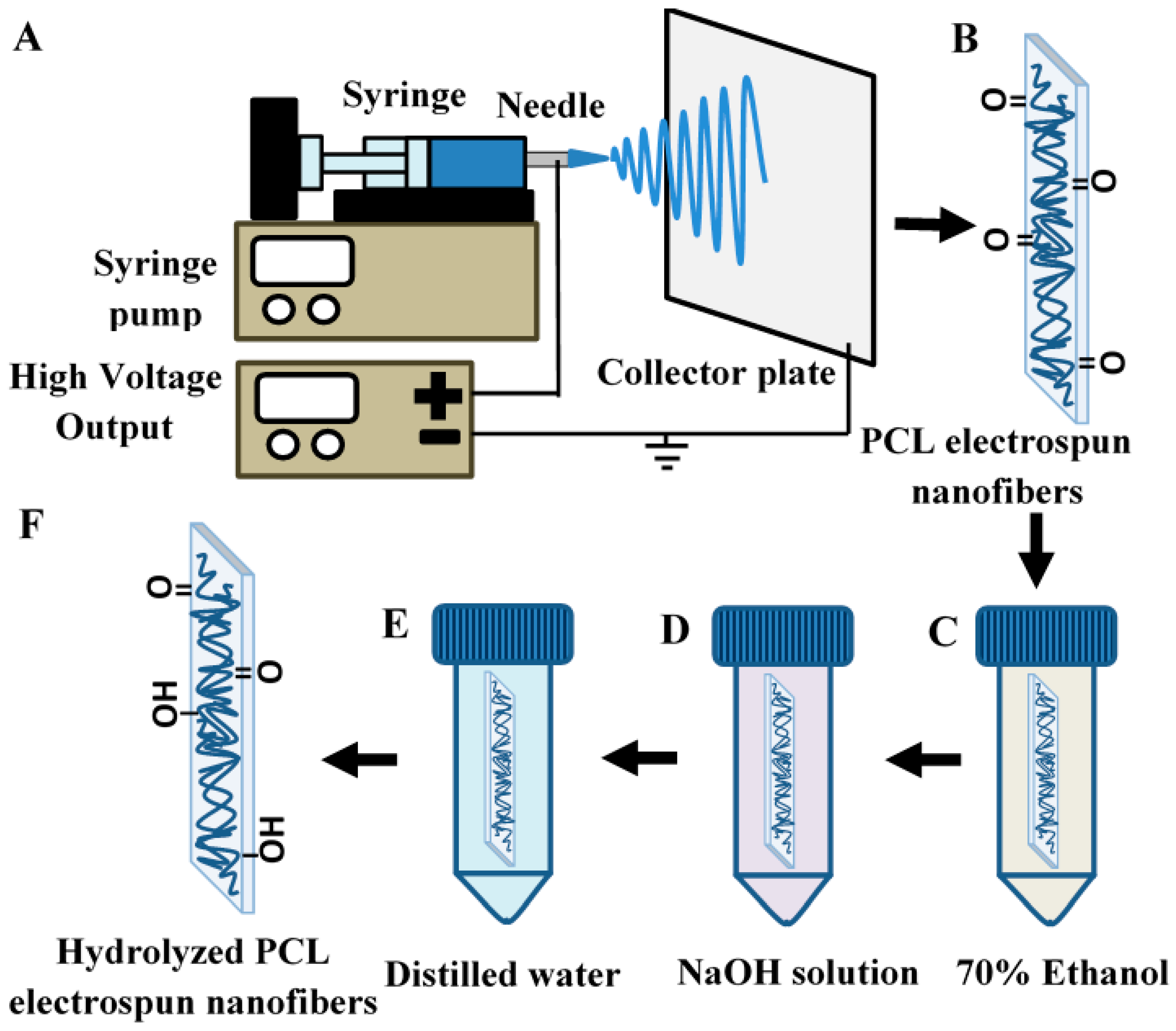
2.1. Fabrication of Electrospun Polycaprolactone (PCL) Nanofibers
2.2. Alkaline Hydrolysis of Electrospun PCL Nanofibers
2.3. Morphology Characterization
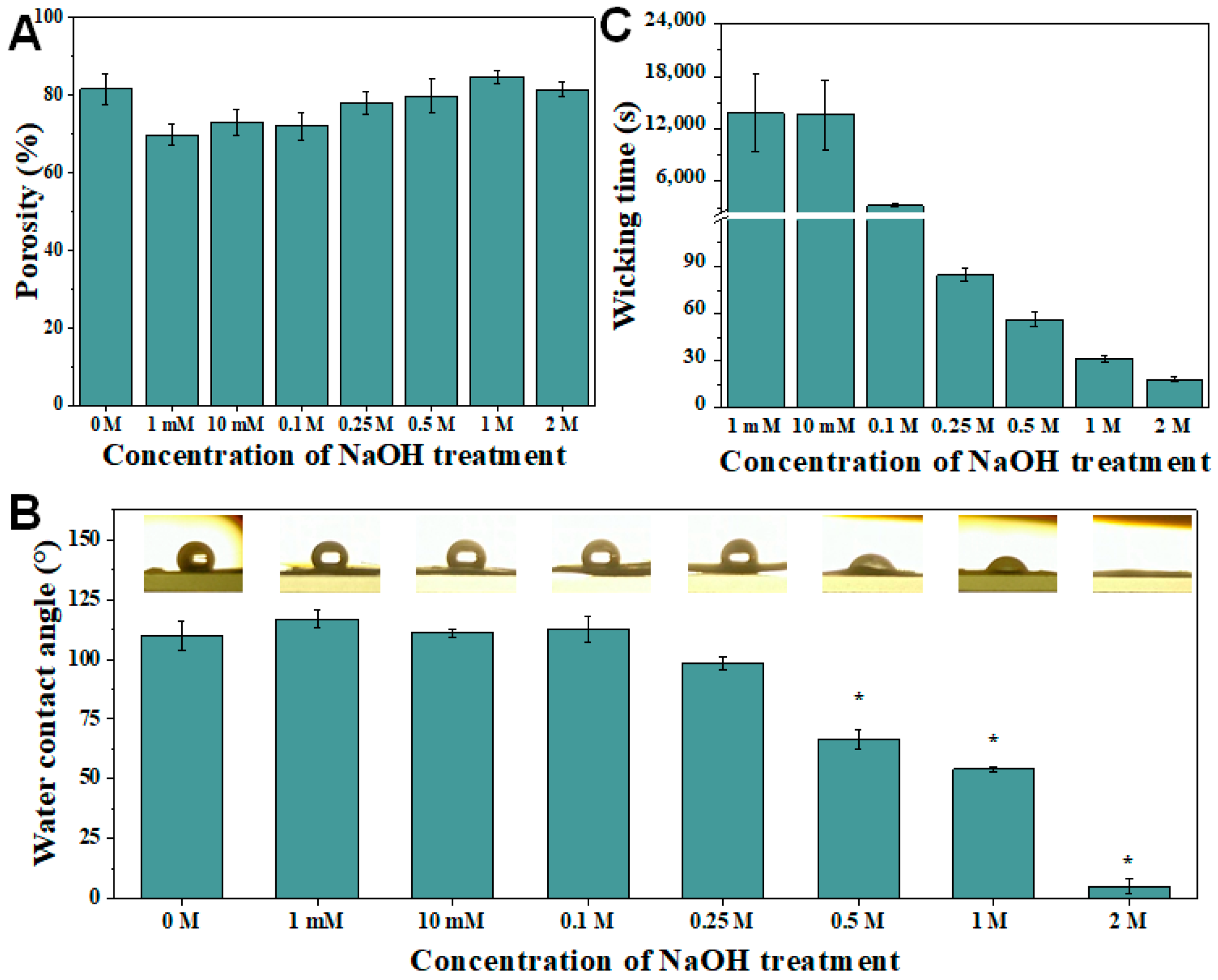
2.4. Porosity Estimation
2.5. Water Contact Angle
2.6. Preparation of Gold Nanoparticles (AuNPs) and AuNP-Detecting Probe Conjugates (AuNP–DPs)
2.7. Fabrication of Lateral Flow Assay (LFA) Strip
2.8. Wicking Time Measurement
2.9. Colorimetric Analysis of LFA
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Hydrolysis of Electrospun PCL Nanofibers as Reaction Membrane
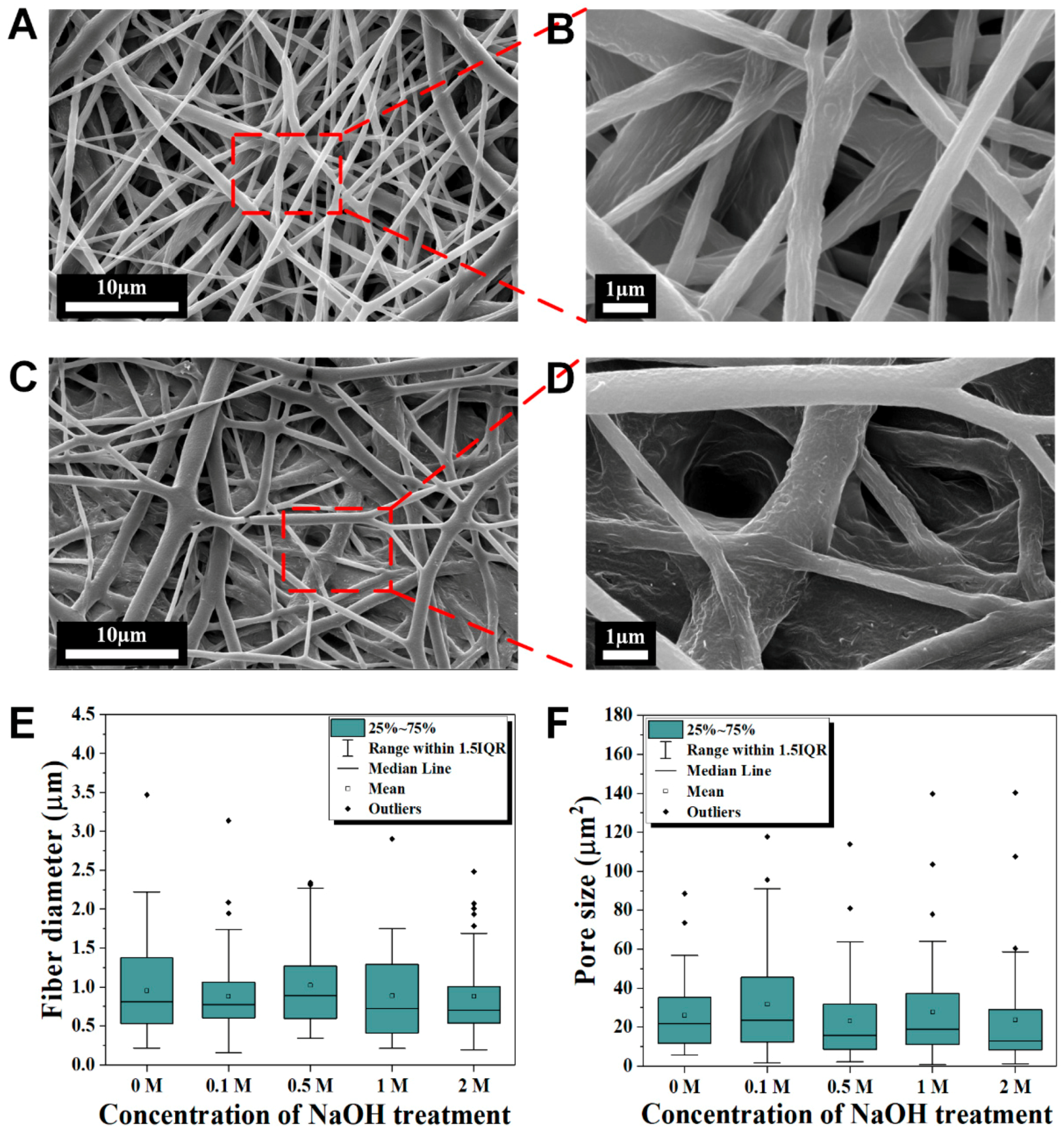
3.2. Surface Morphology
3.3. Wettability and Wickability Analysis of PCL and Hydrolyzed Electrospun PCL Nanofibrous Membrane
3.4. Detection of Nucleic Acid in LFA
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Choi, J.R.; Hu, J.; Tang, R.; Gong, Y.; Feng, S.; Ren, H.; Wen, T.; Li, X.; Wan Abas, W.A.; Pingguan-Murphy, B.; et al. An integrated paper-based sample-to-answer biosensor for nucleic acid testing at the point of care. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 611–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.R.; Liu, Z.; Hu, J.; Tang, R.; Gong, Y.; Feng, S.; Ren, H.; Wen, T.; Yang, H.; Qu, Z.; et al. Polydimethylsiloxane-Paper Hybrid Lateral Flow Assay for Highly Sensitive Point-of-Care Nucleic Acid Testing. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 6254–6264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.R.; Yong, K.W.; Tang, R.; Gong, Y.; Wen, T.; Yang, H.; Li, A.; Chia, Y.C.; Pingguan-Murphy, B.; Xu, F. Lateral Flow Assay Based on Paper-Hydrogel Hybrid Material for Sensitive Point-of-Care Detection of Dengue Virus. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2017, 6, 1600920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Shen, Z.; Xiang, Y.; Lu, Y. Integration of Solution-Based Assays onto Lateral Flow Device for One-Step Quantitative Point-of-Care Diagnostics Using Personal Glucose Meter. ACS Sens. 2016, 1, 1091–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walper, S.A.; Lasarte Aragones, G.; Sapsford, K.E.; Brown Iii, C.W.; Rowland, C.E.; Breger, J.C.; Medintz, I.L. Detecting Biothreat Agents: From Current Diagnostics to Developing Sensor Technologies. ACS Sens. 2018, 3, 1894–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Puig, H.; Bosch, I.; Gehrke, L.; Hamad-Schifferli, K. Challenges of the Nano-Bio Interface in Lateral Flow and Dipstick Immunoassays. Trends Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 1169–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thenmozhi, S.; Dharmaraj, N.; Kadirvelu, K.; Kim, H.Y. Electrospun nanofibers: New generation materials for advanced applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2017, 217, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varesano, A.; Rombaldoni, F.; Mazzuchetti, G.; Tonin, C.; Comotto, R. Multi-jet nozzle electrospinning on textile substrates: Observations on process and nanofibre mat deposition. Polym. Int. 2010, 59, 1606–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Niu, H.; Lin, T.; Wang, X. Needleless electrospinning of nanofibers with a conical wire coil. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2009, 49, 1582–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.J.; Yang, Y.Y.; Yu, D.G.; Du, Q.; Yang, X.L. Fast dissolving drug delivery membrane based on the ultra-thin shell of electrospun core-shell nanofibers. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 122, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 1Yu, D.G.; Li, J.J.; Williams, G.R.; Zhao, M. Electrospun amorphous solid dispersions of poorly water-soluble drugs: A review. J. Control. Release 2018, 292, 91–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, W.; Yu, D.G.; Wang, G.; Williams, G.R.; Zhang, Z. Tunable drug release from nanofibers coated with blank cellulose acetate layers fabricated using tri-axial electrospinning. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 203, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Yang, Y.; Yu, D.-G.; Zhu, M.-J.; Zhao, M.; Williams, G.R. Tunable zero-order drug delivery systems created by modified triaxial electrospinning. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 356, 886–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarino, V.; Gloria, A.; Raucci, M.G.; De Santis, R.; Ambrosio, L. Bio-inspired composite and cell instructive platforms for bone regeneration. Int. Mater. Rev. 2012, 57, 256–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai, T.; Wan, X.; Yu, D.-G.; Wang, K.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Z.-P. Electrospun lipid-coated medicated nanocomposites for an improved drug sustained-release profile. Mater. Des. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akram, H.; Azari, P.; Wan Abas, W.A.B.; Zain, N.M.; Gan, S.N.; Yahya, R.; Wong, C.S.; Pingguan-Murphy, B. An in-vitro study on the proliferative potential of rat bone marrow stem cells on electrospun fibrous polycaprolactone scaffolds containing micro-hydroxyapatite particles. Mater. Res. Innov. 2014, 18, S6–S520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azari, P.; Luan, N.S.; Gan, S.N.; Yahya, R.; Wong, C.S.; Chua, K.H.; Pingguan-Murphy, B. Electrospun Biopolyesters as Drug Screening Platforms for Corneal Keratocytes. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2015, 64, 785–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ding, B.; Li, B. Biomimetic electrospun nanofibrous structures for tissue engineering. Mater. Today 2013, 16, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.-Y.; Lung, Y.-C.; Kuo, C.-C.; Liang, F.-C.; Tsai, T.-L.; Jiang, D.-H.; Satoh, T.; Jeng, R.-J. Novel Multifunctional Luminescent Electrospun Fluorescent Nanofiber Chemosensor-Filters and Their Versatile Sensing of pH, Temperature, and Metal Ions. Polymers 2018, 10, 1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Nartker, S.; Wiederoder, M.; Miller, H.; Hochhalter, D.; Drzal, L.T.; Alocilja, E.C. Novel Biosensor Based on Electrospun Nanofiber and Magnetic Nanoparticles for the Detection of E. coli O157:H7. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 2012, 11, 676–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinholt, S.J.; Sonnenfeldt, A.; Naik, A.; Frey, M.W.; Baeumner, A.J. Developing new materials for paper-based diagnostics using electrospun nanofibers. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 3297–3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worsley, G.J.; Attree, S.L.; Noble, J.E.; Horgan, A.M. Rapid duplex immunoassay for wound biomarkers at the point-of-care. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 34, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guler, Z.; Erkoc, P.; Sarac, A.S. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopic study of single-stranded DNA-immobilized electroactive polypyrrole-coated electrospun poly(ε-caprolactone) nanofibers. Mater. Express 2015, 5, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Song, K.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Shi, F.; Nie, Y.; Liu, T. Design and Biophysical Characterization of Poly (l-Lactic) Acid Microcarriers with and without Modification of Chitosan and Nanohydroxyapatite. Polymers 2018, 10, 1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.-C.; Yeh, I.-T.; Niyama, E.; Huang, W.-R.; Ebara, M.; Wu, C.-S. Electrospun Poly(ε-caprolactone) Nanofibrous Mesh for Imiquimod Delivery in Melanoma Therapy. Polymers 2018, 10, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manavitehrani, I.; Fathi, A.; Badr, H.; Daly, S.; Negahi Shirazi, A.; Dehghani, F. Biomedical Applications of Biodegradable Polyesters. Polymers 2016, 8, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duque Sanchez, L.; Brack, N.; Postma, A.; Pigram, P.J.; Meagher, L. Surface modification of electrospun fibres for biomedical applications: A focus on radical polymerization methods. Biomaterials 2016, 106, 24–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, W.; Yoo, H.S. Pluronic-Induced Surface Etching of Biodegradable Nanofibers for Enhanced Adsorption of Serum Protein. Macromol. Biosci. 2017, 17, 1700057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahmoradi, S.; Yazdian, F.; Tabandeh, F.; Soheili, Z.S.; Hatamian Zarami, A.S.; Navaei-Nigjeh, M. Controlled surface morphology and hydrophilicity of polycaprolactone toward human retinal pigment epithelium cells. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 73, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadian, M.; Rashidi, A.; Majidi, M.; Mehrjoo, M.; Emami, B.A.; Tavassoli, H.; Asl, M.P.; Bonakdar, S. Nanofiber protein adsorption affected by electrospinning physical processing parameters. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2015, 12, 1089–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Wan, Y.; Dalai, S.; Zhang, R. Response of rat osteoblasts to polycaprolactone/chitosan blend porous scaffolds. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2010, 92, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stalder, A.F.; Melchior, T.; Müller, M.; Sage, D.; Blu, T.; Unser, M. Low-bond axisymmetric drop shape analysis for surface tension and contact angle measurements of sessile drops. Colloids Surf. A 2010, 364, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.Y.; Wang, C.R.; Xie, C.M.; Wang, X.G.; Liang, R.L.; Xu, W.W. Rapid and Sensitive Lateral Flow Immunoassay Method for Procalcitonin (PCT) Based on Time-Resolved Immunochromatography. Sensors 2017, 17, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouxhet, L.; Duhoux, F.; Borecky, O.; Legras, R.; Schneider, Y.-J. Adsorption of albumin, collagen, and fibronectin on the surface of poly(hydroxybutyrate-hydroxyvalerate) (PHB/HV) and of poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL) films modified by an alkaline hydrolysis and of poly(ethylene terephtalate) (PET) track-etched membranes. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 1998, 9, 1279–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosorn, W.; Thavornyutikarn, B.; Janvikul, W. Effects of Surface Treatments of Polycaprolactone Scaffolds on their Properties. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 747, 178–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donelli, I.; Taddei, P.; Smet, P.F.; Poelman, D.; Nierstrasz, V.A.; Freddi, G. Enzymatic surface modification and functionalization of PET: A water contact angle, FTIR, and fluorescence spectroscopy study. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2009, 103, 845–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alisch-Mark, M.; Herrmann, A.; Zimmermann, W. Increase of the hydrophilicity of polyethylene terephthalate fibres by hydrolases from Thermomonospora fusca and Fusarium solani f. sp. pisi. Biotechnol. Lett. 2006, 28, 681–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Washburn, E.W. The Dynamics of Capillary Flow. Phys. Rev. 1921, 17, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Frey, M.W.; Baeumner, A.J. Electrospun polylactic acid nanofiber membranes as substrates for biosensor assemblies. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 279, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Nartker, S.; Miller, H.; Hochhalter, D.; Wiederoder, M.; Wiederoder, S.; Setterington, E.; Drzal, L.T.; Alocilja, E.C. Surface functionalization of electrospun nanofibers for detecting E. coli O157:H7 and BVDV cells in a direct-charge transfer biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 26, 1612–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Material | Characteristics | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Electrospun polylactic acid nanofiber infused with biotin |
| [40] |
| Plasma-treated electrospun nitrocellulose |
| [41] |
| Co-electrospun nanofibers of poly(lactic acid), poly(ethylene glycol) and polystyrene8K-block-poly(ethyleneran-butylene)25K-block-polyisoprene10K-Brij76 |
| [21] |
| NaOH-hydrolyzed electrospun polycaprolactone nanofibers |
| This work |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yew, C.H.T.; Azari, P.; Choi, J.R.; Muhamad, F.; Pingguan-Murphy, B. Electrospun Polycaprolactone Nanofibers as a Reaction Membrane for Lateral Flow Assay. Polymers 2018, 10, 1387. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10121387
Yew CHT, Azari P, Choi JR, Muhamad F, Pingguan-Murphy B. Electrospun Polycaprolactone Nanofibers as a Reaction Membrane for Lateral Flow Assay. Polymers. 2018; 10(12):1387. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10121387
Chicago/Turabian StyleYew, Chee Hong Takahiro, Pedram Azari, Jane Ru Choi, Farina Muhamad, and Belinda Pingguan-Murphy. 2018. "Electrospun Polycaprolactone Nanofibers as a Reaction Membrane for Lateral Flow Assay" Polymers 10, no. 12: 1387. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10121387
APA StyleYew, C. H. T., Azari, P., Choi, J. R., Muhamad, F., & Pingguan-Murphy, B. (2018). Electrospun Polycaprolactone Nanofibers as a Reaction Membrane for Lateral Flow Assay. Polymers, 10(12), 1387. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10121387





