Abstract
Unreinforced and reinforced semi-rigid polyurethane (PU) foams were prepared and their compressive behavior was investigated. Aluminum microfibers (AMs) were added to the formulations to investigate their effect on mechanical properties and crush performances of closed-cell semi-rigid PU foams. Physical and mechanical properties of foams, including foam density, quasi-elastic gradient, compressive strength, densification strain, and energy absorption capability, were determined. The quasi-static compression tests were carried out at room temperature on cubic samples with a loading speed of 10 mm/min. Experimental results showed that the elastic properties and compressive strengths of reinforced semi-rigid PU foams were increased by addition of AMs into the foams. This increase in properties (61.81%-compressive strength and 71.29%-energy absorption) was obtained by adding up to 1.5% (of the foam liquid mass) aluminum microfibers. Above this upper limit of 1.5% AMs (e.g., 2% AMs), the compressive behavior changes and the energy absorption increases only by 12.68%; while the strength properties decreases by about 14.58% compared to unreinforced semi-rigid PU foam. The energy absorption performances of AMs reinforced semi-rigid PU foams were also found to be dependent on the percentage of microfiber in the same manner as the elastic and strength properties.
1. Introduction
Porous materials (PMs), such as polymeric [1,2,3], metallic [4,5,6], and ceramic [7,8] foams, have been widely spread in recent years to a variety of engineering applications due to their exceptional mechanical, physical, thermal, and acoustic properties. The main properties of the foam materials (FMs) have a direct connection with the size (cell-wall thickness and cell length), shape (from regular to the most irregular shapes), and topology (connections between cells) of the cells that constitute the PMs. Regardless of the matrix constituent (polymeric, metallic, or ceramic material), cellular materials (CMs) are ideal energy absorbers. This feature of the FMs is highlighted by the appearance of a large flat/hardening plateau region (up to 70% strain) at almost constant stress [9,10,11].
Polymeric foams (PFs) are a promising category of CMs because they can be obtained at a relatively low cost compared to the other kind of FMs. The PFs show many engineering applications depending on their physical properties. Because of their very low thermal conductivity, one of the main uses of PFs is like a thermal insulator for modern buildings, refrigerated trucks/railway cars, ships designed to carry liquid natural gas, pipes, etc. [12,13]. Contrary to fully dense solid materials [14,15], the PFs are non-corrosive in a damp salt-water environment, so they are widely used in marine applications (rafts and floatation devices) [16,17,18]. In addition, open-cell FMs are used as filters at many different levels, as water-repellent membranes that allow air to permeate whatever is underneath the membrane, or even as a hydrophobic barrier in some high-quality sporting and leisurewear [16,17,19]. PFs, especially polyurethane (PU) foams, are used in the sport, automotive, and medical industries to absorb energy, and to reduce sound/noise and vibrations [20,21].
In recent years, different techniques have been developed for manufacturing flexible [22,23] and rigid [24,25,26] PMs with closed, open, or mixed (partly open and partly closed) cells. Also, the effect of different reinforcements (particles, fibers, etc.) on the mechanical and physical properties of PFs was studied in previous works. Soto and co-workers [27] presented a route for the production of more environmentally friendly filled flexible PU foams through the replacement of part of the synthetic polyol by biobased ones, and by the addition of waste tire particles. Good acoustic absorption properties were found by the authors in a wide range of frequencies. Short glass-fibers, glass micro-spheres, and chopped glass-fiber strands were used by Khanna and Gopalan [16] to reinforce polyurethane flexible foam. The authors observed that short glass fibers are more effective in improving the tensile and flexural deformation response of the foam compared to other reinforcing fillers. All types of the reinforced foams show degradation in compressive strength compared to the unfilled polyurethane foams. Gama and co-workers [28] evaluated the sound absorption properties of rigid polyurethane foams produced from crude glycerol (CG) and/or liquefied coffee grounds derived polyol (POL). The POL derived foam has slightly higher sound absorption coefficient values at lower frequencies, while the CG foam has higher sound absorption coefficient values at higher frequencies. The influence of potato protein (PP) on the rigid polyurethane foams’ morphology and on physical and mechanical properties were explored by Członka and co-workers [29]. The authors show that an addition of 0.1 wt % PP improves the compressive behavior, while the addition of PP over a certain optimal level has a negative effect on the physico-mechanical properties. Rigid polyurethane foams reinforced with buffing dust (BD) were characterized by Członka and co-workers [30] by means of mechanical and thermal methods. Depending on the amount of BD in polymer mixture, resulting composites exhibit improvement or deterioration of abovementioned properties. Patricio and co-workers [31] studied the effect of poly lactic acid (PLA) addition into poly (e-caprolactone) (PCL) matrices on the morphological, thermal, chemical, mechanical and biological performance of the 3D constructs produced with a novel biomanufacturing device. Their results show that the addition of PLA to PCL scaffolds strongly improves the biomechanical performance of the constructs, compared to blends prepared by melt blending.
Flexible and rigid polyurethane foams have found limited applications in the transport industry for design of vehicle lightweight composite structures in terms of increased crash energy resistance [32]. On the one hand, flexible PU foams are used on a large scale for cushioning and vibration damping, but they are worse in terms of impact energy absorption performances [33]. On the other hand, rigid PU foams shows good energy absorption capabilities, but they are too rigid and present plastic collapse from a much earlier stage of deformation [34]. The most useful foam would be one that presents a combination of the best properties of the two mentioned PU foams. Therefore, this paper proposes a methodology for obtaining reinforced semi-rigid polyurethane foams using aluminum microfibers in a polymeric matrix. The effect of aluminum microfibers on the main mechanical properties and energy absorption capability is investigated. The obtained semi-rigid PU foams highlight a higher load bearing capacity with appropriate energy absorption performances, elastic properties, and compression strength.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Unreinforced and reinforced closed-cell semi-rigid polyurethane (PU) foams with a density of 0.15 g/cm3 were prepared in the laboratories of the National Institute of Research for Electrochemistry and Condensed Matter (Timisoara, Romania). The polymer matrix was made up of polyol (200 mL) and isocyanate (180 mL), while aluminum solid wastes (referred to in the paper as aluminum microfibers) were reinforcements. The aluminum microfibers (AMs) shows a repetitive geometric shape and the foam manufacturing acting as the recycling process. Figure 1 presents the optical and SEM images of used AMs.
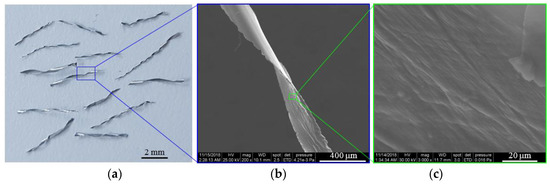
Figure 1.
Optical (a) and SEM images (b, c) of AMs.
The used AMs had a length of 4–6 mm and a cross section of 270 ± 40 μm (width) × 37 ± 3 μm (thickness). The chemical composition of the commercially available AMs is shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Chemical composition of AMs.
The collection and insertion of the AMs into the foam matrix material was done following a well-established procedure. Semi-rigid PU foams with different contents of the aluminum microfibers (0, 0.5, 1, 1.5, and 2% AMs of the foam liquid mass) were prepared using a two-step method. Firstly, the AM were added half to the isocyanate solution and half to the polyol solution, followed by an individual mechanically stirred process for 3 min to ensure their complete homogenization. Before being added to the individual components, the AMs were dried at 80 °C for about 60 min. Secondly, after the individual stirring process, the two components (isocyanate and polyol together with the corresponding percentage of reinforcements) were mixed and mechanically stirred together for 30 s. The obtained reinforced PU foam was dried in a controlled environment, at room temperature (25 °C), for 24 h [35]. After the drying and hardening process, large semi-rigid PU foam blocks were obtained (see Figure 2). The same procedure (less reinforcement) was followed to obtain unreinforced PU foams. The foam density was measured using both mass and sample dimensions. The average resulting foam density was 0.15 g/cm3 and the samples with a density above or below the 10% range were excluded [36].

Figure 2.
Semi-rigid PU foam blocks obtained depending on the percentage of AMs.
The reaction parameters (percentage of foam components, time, temperature, etc.) were optimized in order to produce the most economical and functional reinforced semi-rigid PU foam [37]. The resulting PU foams were marked as U-PU foam (unreinforced semi-rigid PU foam) and R-PU foam (reinforced semi-rigid PU foam).
2.2. Methods
Uniaxial quasi-static compression tests were carried out on a 5 kN Zwick Roell 005 testing machine (ZwickRoell LP, Kennesaw, GA, USA). The experimental tests were performed on cubic samples (22.5 mm × 22.5 mm × 22.5 mm); using a constant crosshead speed of 10 mm/min. Ten samples were provided for each test condition and the properties of the semi-rigid PU foams were determined according to ASTM D1621-16 standard [38] (see Figure 3).

Figure 3.
Semi-rigid PU foam blocks obtained depending on the percentage of AMs.
The compressive properties were investigated in a direction parallel to the free direction of the foam rise at a maximum load of about 300 N. The material properties were assessed in the controlled room temperature and humidity conditions on samples taken from the center of the foam blocks.
3. Results and Discussions
Quasi-static compressive tests were carried out to investigate the main mechanical properties of the semi-rigid PU foams, since they also play an important role in the energy absorption performances and can be of high interest for possible applications in automotive, sport, and building construction industries [39,40,41]. Figure 4 presents the compressive engineering stress (σ)–engineering strain (ε) and energy absorption (W)-strain (ε) curves for unreinforced and AMs reinforced semi-rigid PU foams.
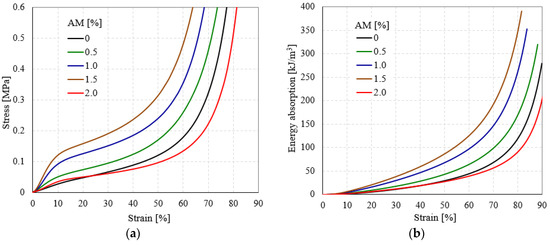
Figure 4.
Compressive engineering stress-engineering strain (a) and energy absorption-engineering strain (b) curves of semi-rigid PU foams.
Regardless of semi-rigid PU foam type (unreinforced or reinforced), each foam sample is characterized by similar quasi-static compression behavior, exhibiting three different regions: A narrow linear-elastic region (< 5% strain), followed by a stress-plateau region (around 10–40%), and ending with a densification region (over 40% strain) [42,43,44].
As is well known, the limited slope of the linear elastic area from the stress-strain curves is directly related to the foam compression modulus [45,46,47]. The σ-ε curve of unreinforced and reinforced semi-rigid PU foams exhibit a smooth transition from the linear to the plateau region. In this case, there is no well-defined yield point corresponding to the compressive yield strength because there is no drop stress [48,49,50]. This behavior is typical of semi-rigid and flexible PU foams, which differ significantly from that of rigid foams [51,52]. After the elastic-plateau transition area, the σ-ε curves exhibit an extended strain hardening plateau region outstanding in the field of energy absorption. In this region, the main foam collapse mechanisms occur [53,54]. With an increasing content of AMs of the foam liquid mass, the investigated foams exhibit a shorter range of elongation (measured up to a predetermined stress) because of the gradual loss of PU matrix flexibility. In terms of the densification strain, R-PU foams show lower values than unreinforced ones, indicating that the samples can sustain slightly lower deformation without collapsing.
The main quasi-static compressive mechanical properties (quasi-elastic gradient, 0.2% offset yield stress, 1% offset yield stress, plateau stress, densification strain, and energy absorption at densification strain) of the unreinforced and reinforced semi-rigid PU foams modified with aluminum microfibers are reported in Table 2. The investigation of elastic properties was based only on compression loading tests, while unloading tests were not considered [55]. Densification strain is defined as the strain at which the slope of the curve in a plot of energy efficiency versus strain is zero. The densification strain of cellular materials represents the start of the cell-wall interactions, which enhance the compressive resistance of a cellular solid [56].

Table 2.
The main compressive mechanical properties of investigated semi-rigid PU foams.
The volumetric energy absorption capacity, W, of investigated PU foams is defined by Equation (1), and by using variable integration limits, it can be interpreted as the area under the engineering stress-engineering strain curves [57,58].
The energy absorption values at different strains (10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, and 80% engineering strain) of investigated foams are presented in Table 3.

Table 3.
The mean energy absorption values of investigated PUF foams at different strains (kJ/m3).
Comparing the data from Table 2 and the variation of properties shown in Figure 5, it can be denoted that the investigated mechanical properties of the modified semi-rigid PU foams increase as aluminum microfibers content increases. This behavior is attributed to the rigidity of the aluminum microfibers’ structure, which introduced more cross-links in the PU foam network. Notice should be made that this increase in mechanical performances was obtained by adding up to a certain limit of AMs. Above this upper limit, the quasi-static compressive behavior changes and the mechanical properties decrease significantly, exhibiting values almost equal to U-PU foam. Furthermore, the W capabilities of R-PU foams were also found to be dependent on the percentage of AMs in the same manner as the elastic and strength mechanical properties (see Figure 4b and Table 3).
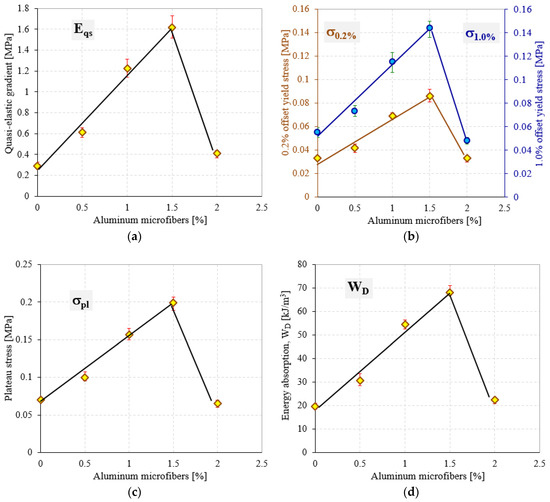
Figure 5.
Mechanical properties of investigated semi-rigid PU foams: (a) Quasi-elastic gradient; (b) 0.2% and 1.0% offset yield stress; (c) plateau stress; (d) energy absorption at densification strain.
An analysis of the elastic results presented in Figure 5a indicates that the quasi-elastic gradient (Eqe) of semi-rigid modified PU foams significantly increases with the increase in the percentage of AMs in their cellular structure. Therefore, considering the normalized data, the presence of aluminum microfibers results in an increase in foam stiffness up to about six times relative to U-PU foam. In addition, considerable increases in the case of strength properties (0.2 and 1% offset yield stresses and plateau stress) have also been observed. These increases in properties were obtained by adding in the liquid mass of the PU foam up to a maximum of 1.5% aluminum microfibers. In contrast, the addition of 2% AMs to the foam liquid mass leads to a decrease in mechanical properties up to 75% compared to 1.5% AMs reinforced foams, as shown in Table 2 and Figure 6. It seems that the effect of the AMs in the foams modified with 2 wt % is less significant, probably due to the kinetic reactions occurring between the liquid reactive mixture (isocyanate and polyol) and aluminum microfibers. This effect leads to a decrease of the growth rate of the foam formation (increased viscosity) and a less homogeneous foam structure, and at the same time, to more unstable failure mechanisms.
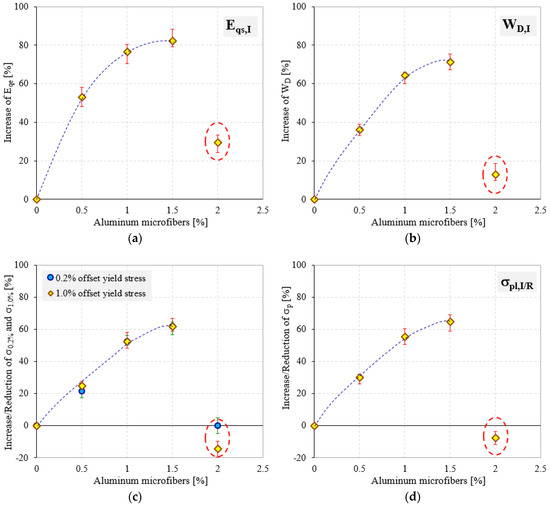
Figure 6.
Percentage increase/decrease of the quasi-elastic gradient (a); energy absorption (b); 0.2 and 1% offset yield stresses (c) and plateau stress (d) for modified semi-rigid PU foam samples normalized by reference PU foam (0% AMs).
Figure 6 shows the percentage increase/decrease values of mechanical properties of the modified semi-rigid PU foams (0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2% AMs) normalized by U-PU foam (0% AMs).
From Figure 6, it is obvious that the reinforcements have a significant and useful effect for increasing the mechanical properties of the semi-rigid PU foams. It has been found that reinforcing the foams with maximum 1.5% AMs leads to an increase in elastic properties of up to 82.20%. In addition, the increase percentage of energy absorption and strength properties is about 71.29% (for W) and 61.81% (for 1% offset yield stress). Compared with R-PU foams up to 1.5% AMs, the PU foams reinforced with 2% AMs do not show significant increases of their quasi-static compressive properties with respect to the U-PU foam. Quasi-elastic gradient shows a percentage increase of up to 29.41%, while energy absorption capacity increases by only 12.68% (Figure 6a,b). Furthermore, a negative effect on the strength properties (0.2 and 1% offset yield stresses and plateau stress) of 2% AMs reinforced foams was observed. In this case, the 1% offset yield stress showed a reduction percentage of 14.58% and a plateau stress of 7.69%.
4. Conclusions
In the present investigation, aluminum microfibers (AMs) and a polymer matrix (made up of polyol and isocyanate) were used to produce reinforced semi-rigid polyurethane (PU) foams. Therefore, a low-density closed-cell semi-rigid PU foam with a density of 0.15 g/cm3 was obtained. Quasi-static compressive tests were performed on cubic samples to investigate the mechanical properties of the produced foams. It has been observed that the presence of AMs has a direct effect on the main properties of the reinforced foams. The experimental results indicate that with increasing AMs content into the foam matrix, the PU foams are characterized by higher compressive strength (about 61.81%) and energy absorption performances (about 71.29%). However, larger AMs filler contents (2 wt %) do not lead to further changes in energy absorption capability (around 12.68%), highlighting even a negative effect on the strength properties (about 14.58%).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology, E.L. and P.-A.L.; investigation, writing—original draft preparation, E.L. and C.V.; writing—review and editing, E.L., C.V. and P.-A.L.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported (partial supported) by research grants PCD-TC-2017.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The founding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results
References
- Abbasi, H.; Antunes, M.; Velasco, J.I. Effects of carbon nanotubes/graphene nanoplatelets hybrid systems on the structure and properties of polyetherimide-based foams. Polymers 2018, 10, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voiconi, T.; Negru, R.; Linul, E.; Marsavina, L.; Filipescu, H. The notch effect on fracture of polyurethane materials. Frat. Ed Integrita Strutt. 2014, 30, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, M.; Velasco, J.I. Multifunctional polymer foams with carbon nanoparticles. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 486–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovácik, J.; Jerz, J.; Mináriková, N.; Marsavina, L.; Linul, E. Scaling of compression strength in disordered solids: Metallic foams. Frat. Ed Integrita Strutt. 2016, 36, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szlancsik, A.; Katona, B.; Májlinger, K.; Orbulov, I.N. Compressive behavior and microstructural characteristics of iron hollow sphere filled aluminum matrix syntactic foams. Materials 2015, 8, 7926–7937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovacik, J.; Marsavina, L.; Linul, E. Poisson’s ratio of closed-cell aluminium foams. Materials 2018, 11, 1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rugele, K.; Lehmhus, D.; Hussainova, I.; Peculevica, J.; Lisnanskis, M.; Shishkin, A. Effect of fly-ash cenospheres on properties of clay-ceramic syntactic foams. Materials 2017, 10, 828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linul, E.; Korniejenko, K.; Şerban, D.A.; Negru, R.; Marsavina, L.; Łach, M.; Mikuła, L. Quasi-static mechanical characterization of lightweight fly ash-based geopolymer foams. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 416, 012102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gedler, G.; Antunes, M.; Velasco, J.I. Effects of graphene nanoplatelets on the morphology of polycarbonate-graphene composite foams prepared by supercritical carbon dioxide two-step foaming. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2015, 100, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santo, L.; Bellisario, D.; Quadrini, F. Shape memory behavior of pet foams. Polymers 2018, 10, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linul, E.; Movahedi, N.; Marsavina, L. On the lateral compressive behavior of empty and ex-situ aluminum foam-filled tubes at high temperature. Materials 2018, 11, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbasi, H.; Antunes, M.; Velasco, J.I. Influence of polyamide-imide concentration on the cellular structure and thermo-mechanical properties of polyetherimide blend foams. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 69, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Realinho, V.; Antunes, M.; Velasco, J.I. Enhanced fire behavior of Casico-based foams. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2016, 128, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsavina, L.; Cernescu, A.; Linul, E.; Scurtu, D.; Chirita, C. Experimental determination and comparison of some mechanical properties of commercial polymers. Mater. Plast. 2010, 47, 85–89. [Google Scholar]
- Nirmal, U. Friction performance of aged T-BFRP composite for bearing applications. Polymers 2018, 10, 1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, S.K.; Gopalan, S. Reinforced polyurethane flexible foams. In Compliant Structures in Nature and Engineering; WIT Press: Billerica, MA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Gibson, L.J.; Ashby, M.F. Cellular Solids-Structures and Properties, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Linul, E.; Marsavina, L. Prediction of fracture toughness for open cell polyurethane foams by finite element micromechanical analysis. Iran. Polym. J. 2011, 20, 736–746. [Google Scholar]
- Castejón, P.; Arencón, D.; Antunes, M.; Realinho, V.; Ignacio Velasco, J.; Martínez, A.B. Porous membranes based on polypropylene-ethylene copolymers. Polymers 2018, 10, 854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, M.; Gedler, G.; Abbasi, H.; Velasco, J.I. Graphene nanoplatelets as a multifunctional filler for polymer foams. Mater. Today Proc. 2016, 3, S233–S239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsavina, L.; Constantinescu, D.M.; Linul, E.; Stuparu, F.A.; Apostol, D.A. Experimental and numerical crack paths in PUR foams. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2016, 167, 68–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Yick, K.L.; Ng, S.; Sun, Y. Modeling of flexible polyurethane foam shrinkage for bra cup moulding process control. Polymers 2018, 10, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przystas, A.; Jovic, M.; Salmeia, K.A.; Rentsch, D.; Ferry, L.; Mispreuve, H.; Perler, H.; Gaan, S. Some key factors influencing the flame retardancy of EDA-DOPO containing flexible polyurethane foams. Polymers 2018, 10, 1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linul, E.; Marsavina, L.; Sadowski, T.; Kneć, M. Size effect on fracture toughness of rigid polyurethane foams. Solid State Phenom. 2012, 188, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Realinho, V.; Haurie, L.; Antunes, M.; Velasco, J.I. Thermal stability and fire behaviour of flame retardant high density rigid foams based on hydromagnesite-filled polypropylene composites. Compos. Part B-Eng. 2014, 58, 553–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voiconi, T.; Linul, E.; Marsavina, L.; Sadowski, T.; Kneć, M. Determination of flexural properties of rigid PUR foams using digital image correlation. Solid State Phenom. 2014, 216, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto, G.; Castro, A.; Vechiatti, N.; Iasi, F.; Armas, A.; Marcovich, N.E.; Mosiewicki, M. Biobased porous acoustical absorbers made from polyurethane and waste tire particles. Polym. Test. 2017, 57, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gama, N.; Silva, R.; Carvalho, A.P.O.; Ferreira, A.; Barros-Timmons, A. Sound absorption properties of polyurethane foams derived from crude glycerol and liquefied coffee grounds polyol. Polym. Test. 2017, 62, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Członka, S.; Bertino, M.F.; Strzelec, K. Rigid polyurethane foams reinforced with industrial potato protein. Polym. Test. 2018, 68, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Członka, S.; Bertino, M.F.; Strzelec, K.; Strąkowska, A.; Masłowski, M. Rigid polyurethane foams reinforced with solid waste generated in leather industry. Polym. Test. 2018, 69, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrício, T.; Domingos, M.; Gloria, A.; D’Amora, U.; Coelho, J.F.; Bártolo, P.J. Fabrication and characterisation of PCL and PCL/PLA scaffolds for tissue engineering. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2014, 20, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliha, M.R.M.; Linul, E.; Bahmani, A.; Marsavina, L. Experimental and theoretical fracture toughness investigation of PUR foams under mixed mode I + III loading. Polym. Test. 2018, 67, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, F.; You, F.; Yao, C. Structural design and sound absorption properties of nitrile butadiene rubber-polyurethane foam composites with stratified structure. Polymers 2018, 10, 946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linul, E.; Serban, D.A.; Marsavina, L. Influence of cell topology on mode I fracture toughness of cellular structures. Phys. Mesomech. 2018, 21, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linul, E.; Linul, P.A.; Valean, C.; Marsavina, L.; Silaghi-Perju, D. Manufacturing and compressive mechanical behavior of reinforced polyurethane flexible (PUF) foams. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 416, 012053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Movahedi, N.; Linul, E.; Marsavina, L. The temperature effect on the compressive behavior of closed-cell aluminum-alloy foams. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2018, 27, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcovich, N.E.; Kuranska, M.; Prociak, A.; Malewska, E.; Kulpa, K. Open cell semi-rigid polyurethane foams synthesized using palmoil-based bio-polyol. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2017, 102, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D1621. Standard test method for compressive properties of rigid cellular plastics. 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Linul, E.; Marsavina, L. Assesment of sandwich beams with rigid polyurethane foam core using failure-mode maps. Proc. Romanian Acad. A 2015, 16, 522–530. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.J.; Cho, M.Y.; Kim, B.H.; Lee, S. Development of eco-friendly polymer foam using overcoat technology of deodorant. Materials 2018, 11, 1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linul, E.; Serban, D.A.; Voiconi, T.; Marsavina, L. Energy-absorption and efficiency diagrams of rigid PUR foams. Key Eng. Mater. 2014, 601, 246–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kádár, C.; Máthis, K.; Orbulov, I.N.; Chmelík, F. Monitoring the failure mechanisms in metal matrix syntactic foams during compression by acoustic emission. Mater. Lett. 2016, 173, 31–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linul, E.; Şerban, D.A.; Marsavina, L.; Sadowski, T. Assessment of collapse diagrams of rigid polyurethane foams under dynamic loading conditions. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2017, 17, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katona, B.; Szebényi, G.; Orbulov, I.N. Fatigue properties of ceramic hollow sphere filled aluminium matrix syntactic foams. Mat. Sci. Eng. A-Struct. 2017, 679, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gama, N.V.; Ferreira, A. Polyurethane foams: Past, present, and future. Materials 2018, 11, 1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajak, D.K.; Mahajan, N.N.; Linul, E. Crashworthiness performance and microstructural characteristics of foam-filled thin-walled tubes under diverse strain rate. J. Alloy. Compd. 2019, 775, 675–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linul, E.; Marşavina, L.; Linul, P.A.; Kovacik, J. Cryogenic and high temperature compressive properties of Metal Foam Matrix Composites. Compos. Struct. 2019, 209, 490–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, W.; Li, J.; Cai, Z. Synthesis and characterization of cellulose nanofibril-reinforced polyurethane foam. Polymers 2017, 9, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Movahedi, N.; Linul, E. Quasi-static compressive behavior of the ex-situ aluminum-alloy foam-filled tubes under elevated temperature conditions. Mater. Lett. 2017, 206, 182–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, A.; Borreguero, A.M.; Garrido, I.; Rodríguez, J.F.; Carmona, M. The role of microstructure on the mechanical properties of polyurethane foams containing thermoregulating microcapsules. Polym. Test. 2017, 60, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Günther, M.; Lorenzetti, A. Fire phenomena of rigid polyurethane foams. Polymers 2018, 10, 1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linul, E.; Voiconi, T.; Marsavina, L.; Sadowski, T. Study of factors influencing the mechanical properties of polyurethane foams under dynamic compression. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2013, 451, 012002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, K.; Katona, B.; Cortes, P.; Orbulov, I.N. Quasi-static and high strain rate response of aluminum matrix syntactic foams under compression. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2015, 79, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linul, E.; Movahedi, N.; Marsavina, L. The temperature and anisotropy effect on compressive behavior of cylindrical closed-cell aluminum-alloy foams. J. Alloy. Compd. 2018, 740, 1172–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Amirrasouli, B.; Razavi, S.B.; Li, Q.M.; Lowe, T.; Withers, P.J. The variation in elastic modulus throughout the compression of foam materials. Acta Mater. 2016, 110, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.M.; Magkiriadis, I.; Harrigan, J.J. Compressive strain at the onset of the densification of cellular solids. J. Cell. Plast. 2016, 42, 371–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katona, B.; Szlancsik, A.; Tábi, T.; Orbulov, I.N. Compressive characteristics and low frequency damping of aluminium matrix syntactic foams. Mat. Sci. Eng. A-Struct. 2019, 739, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linul, E.; Movahedi, N.; Marsavina, L. The temperature effect on the axial quasi-static compressive behavior of ex-situ aluminum foam-filled tubes. Compos. Struct. 2017, 180, 709–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).