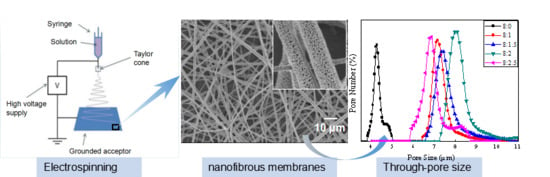
Nanoporous PLA/(Chitosan Nanoparticle) Composite Fibrous Membranes with Excellent Air Filtration and Antibacterial Performance
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Solutions
2.3. Electrospinning
2.4. Characterisation
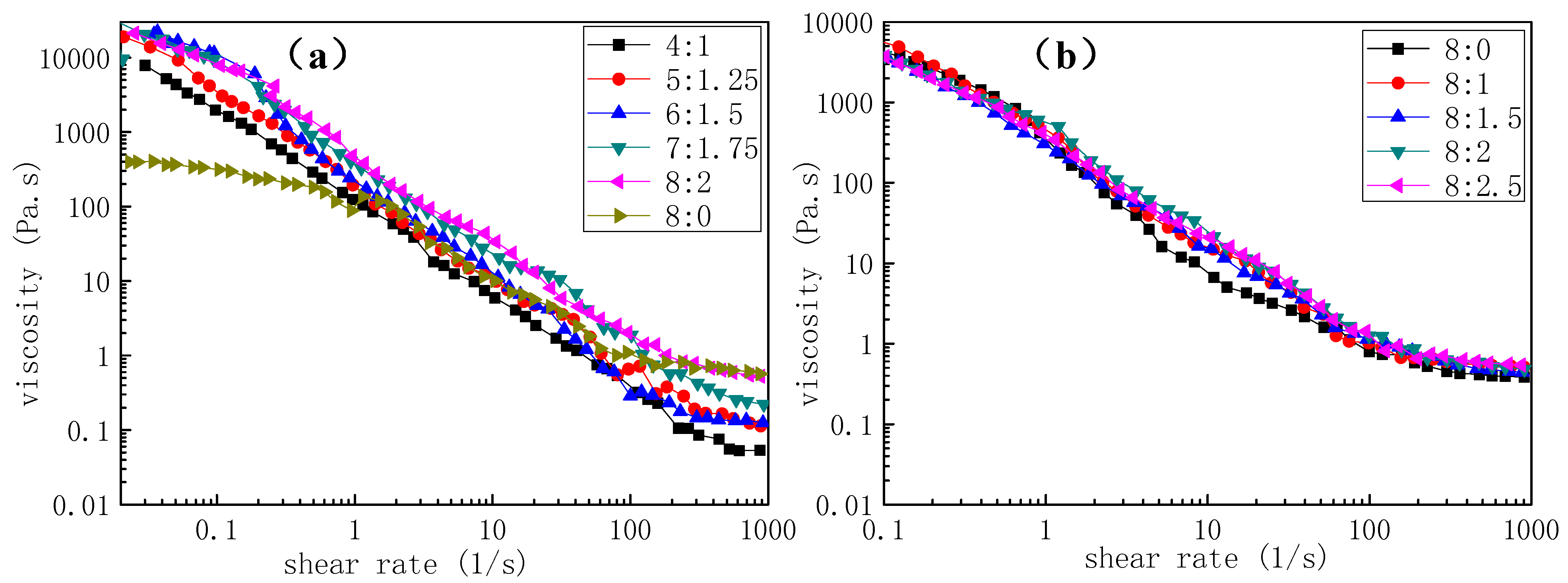
2.4.1. Solution Viscosity
2.4.2. Fibre Morphology
2.4.3. Elemental Detection
2.4.4. Through-Pore Size and Distribution
2.4.5. Filtration Performance
2.4.6. Antibacterial Activity
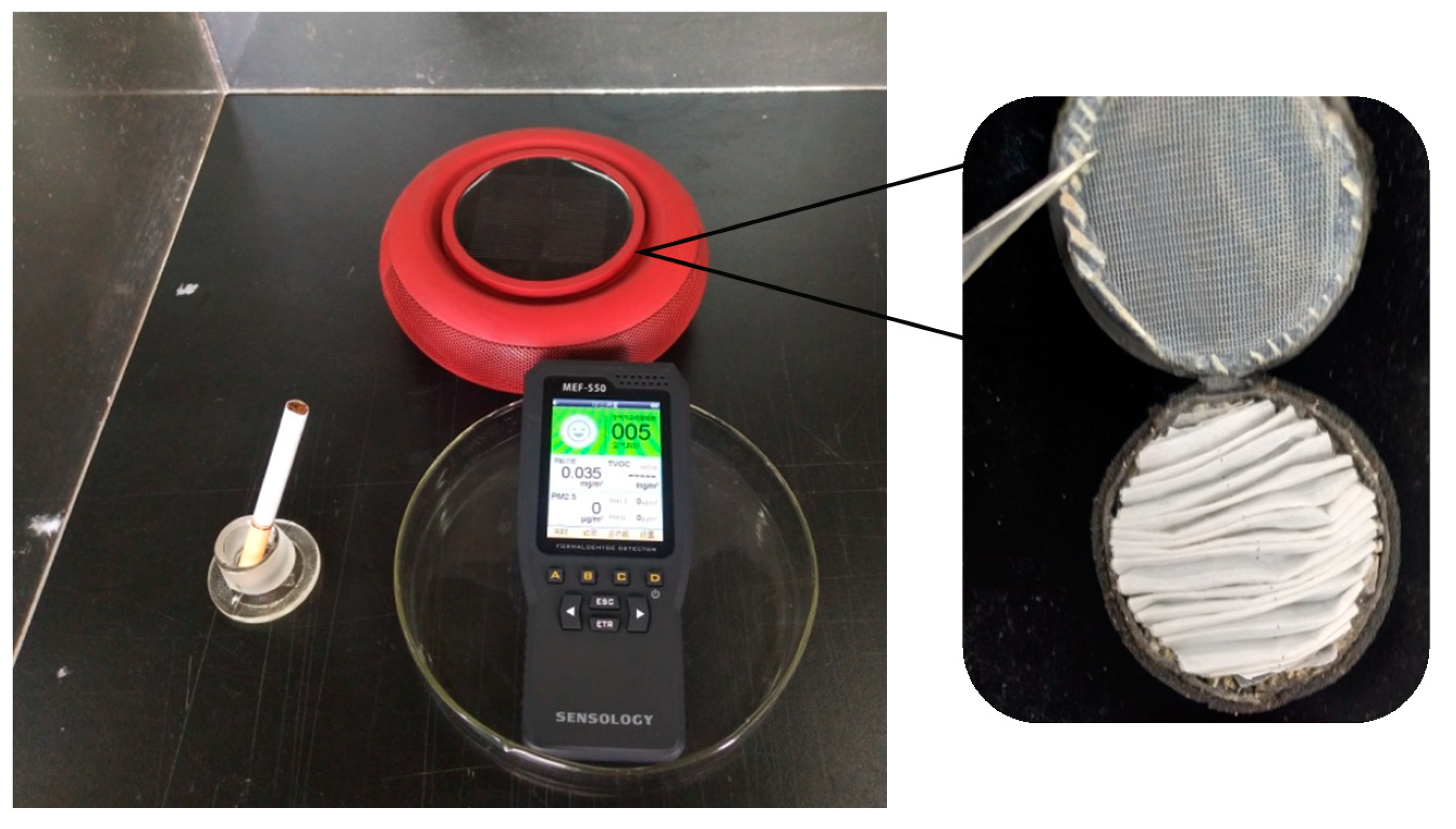
2.4.7. Air Purification Performance
3. Results and Discussion
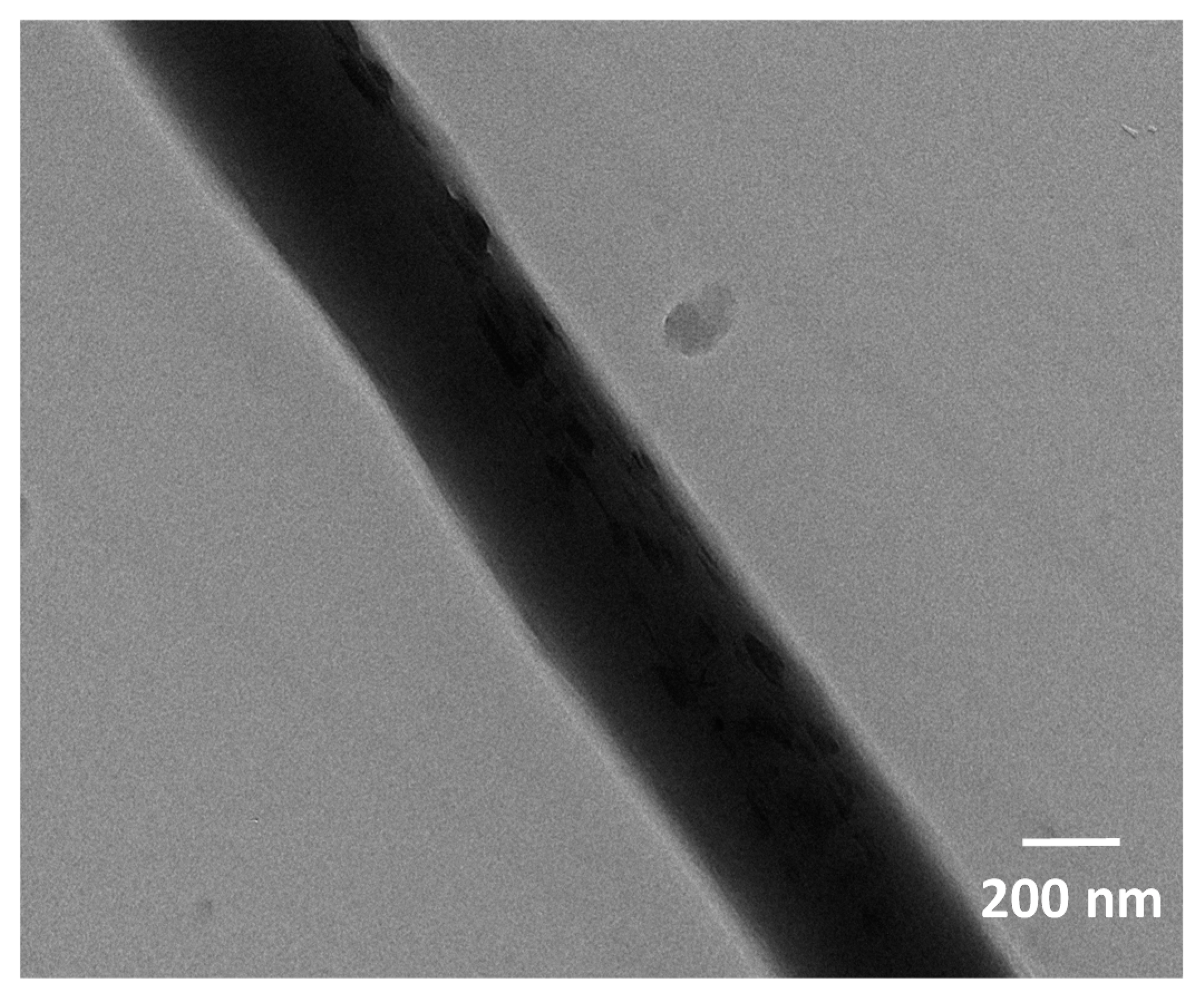
3.1. Morphologies of PLA/Chitosan Porous Nanofibres
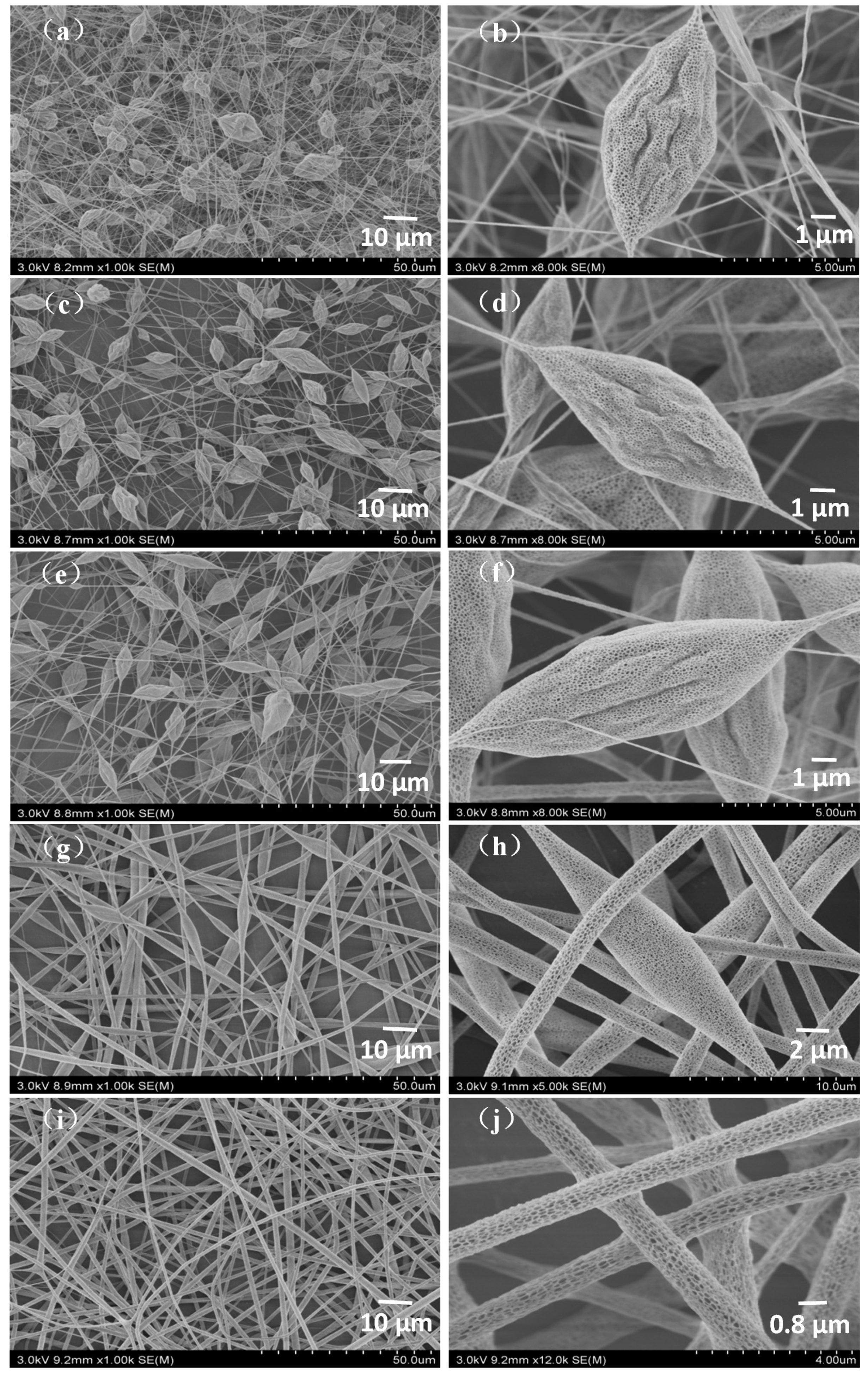
3.1.1. Effect of Concentration on Morphology of PLA/Chitosan Fibres
3.1.2. Effect of Humidity on Morphology of PLA/Chitosan Fibres
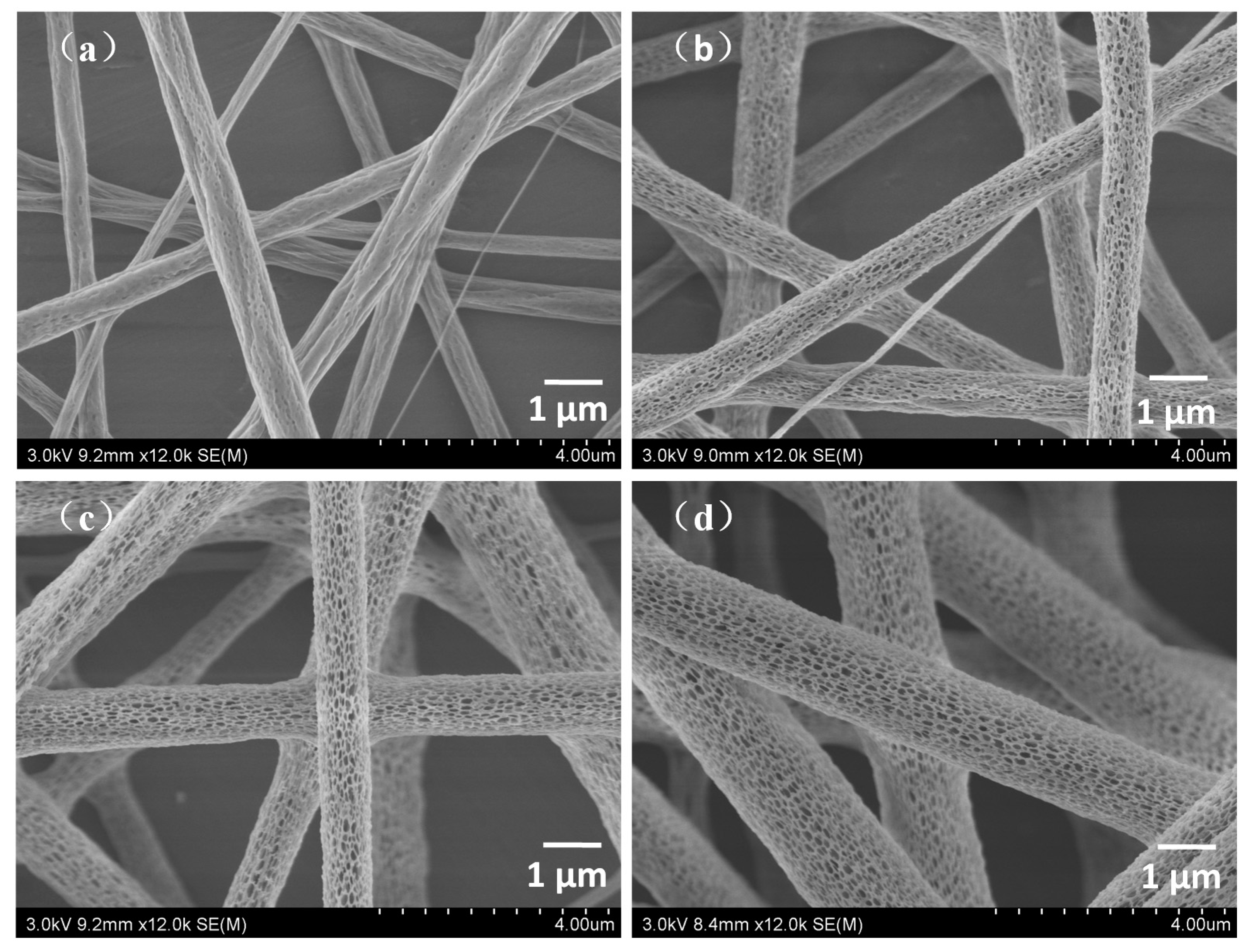
3.1.3. Effect of Mass Ratios of PLA and Chitosan on Morphology of Fibres
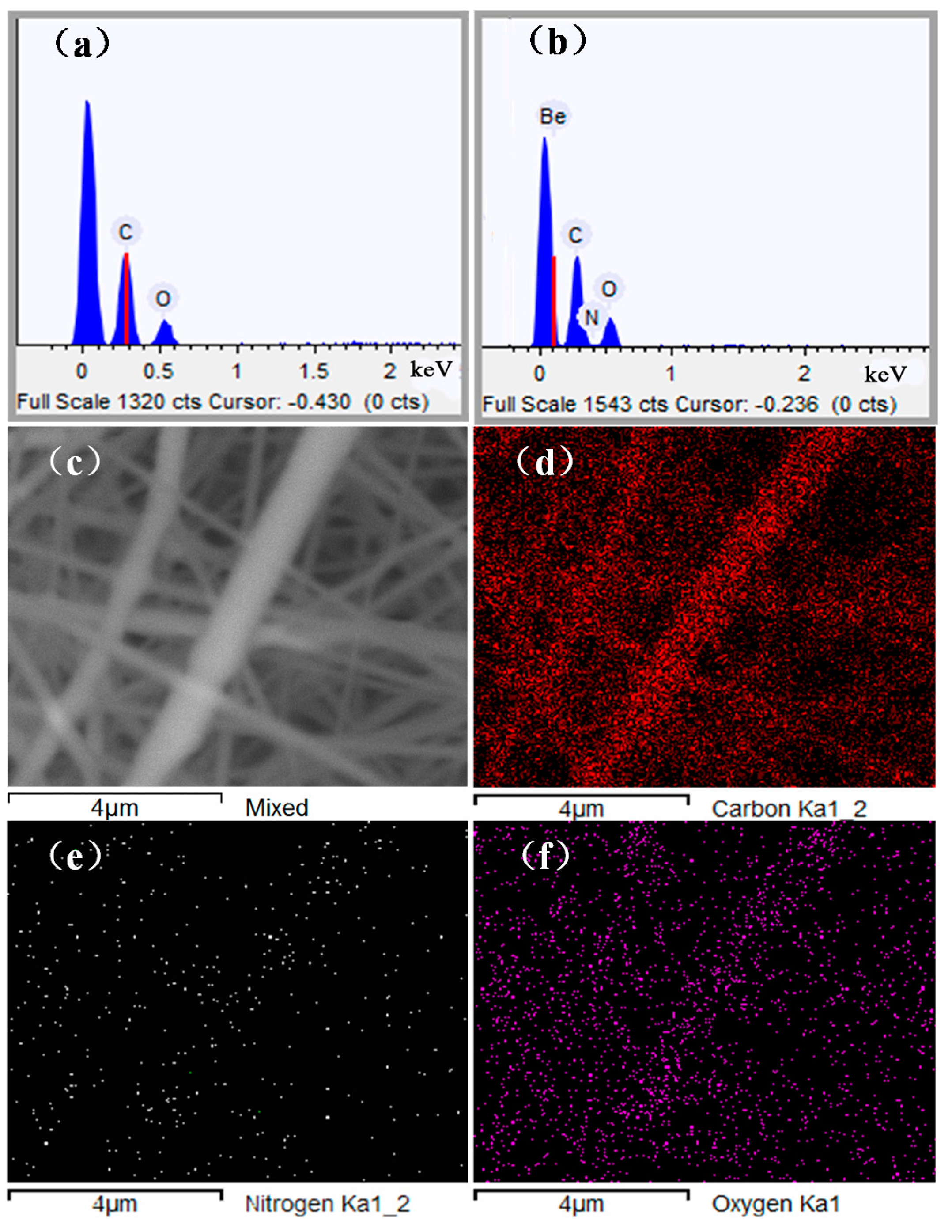
3.2. Dispersion of Chitosan NPs and Element Contents
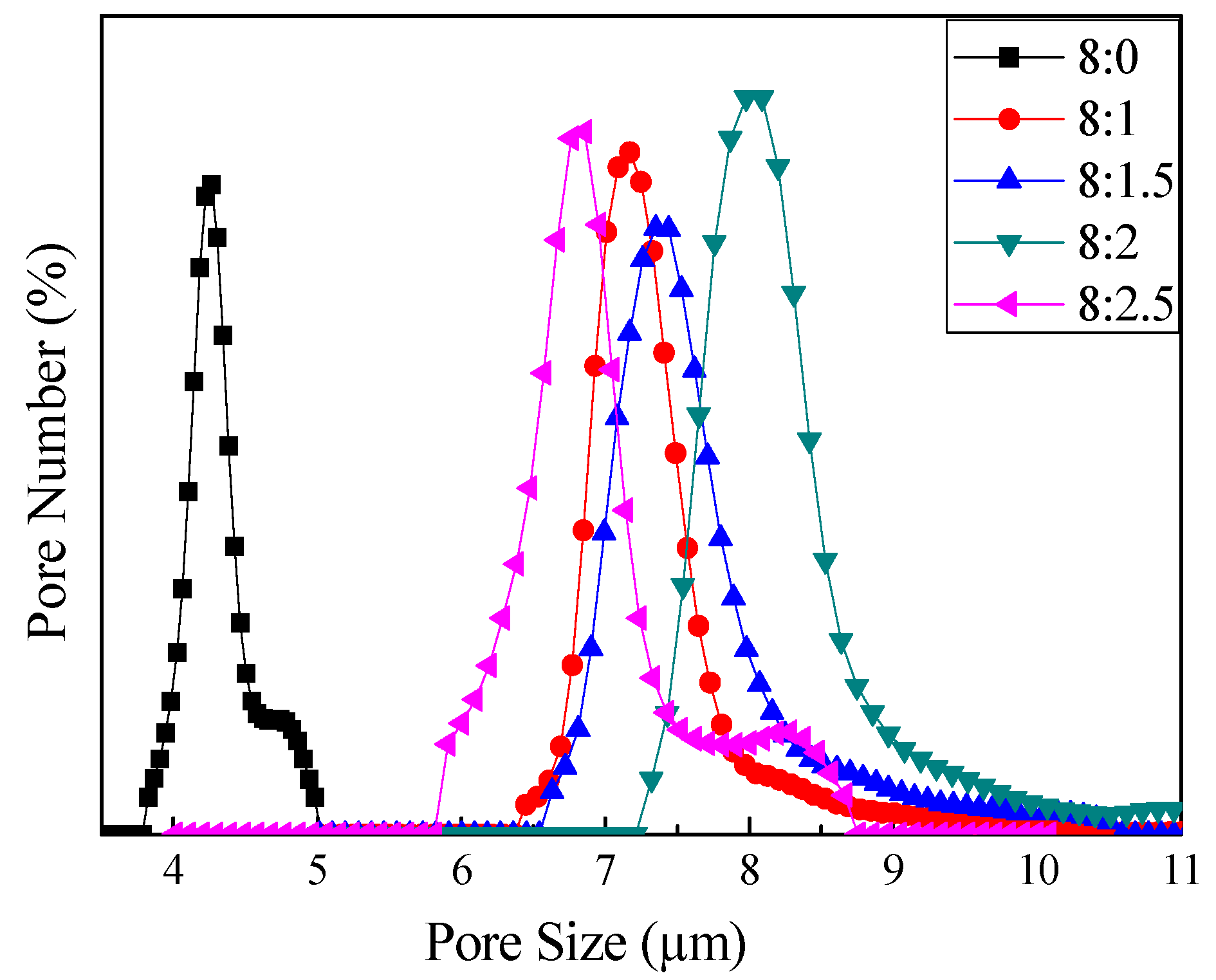
3.3. Through-Pore Size and Distribution
3.4. Filtration Efficiency
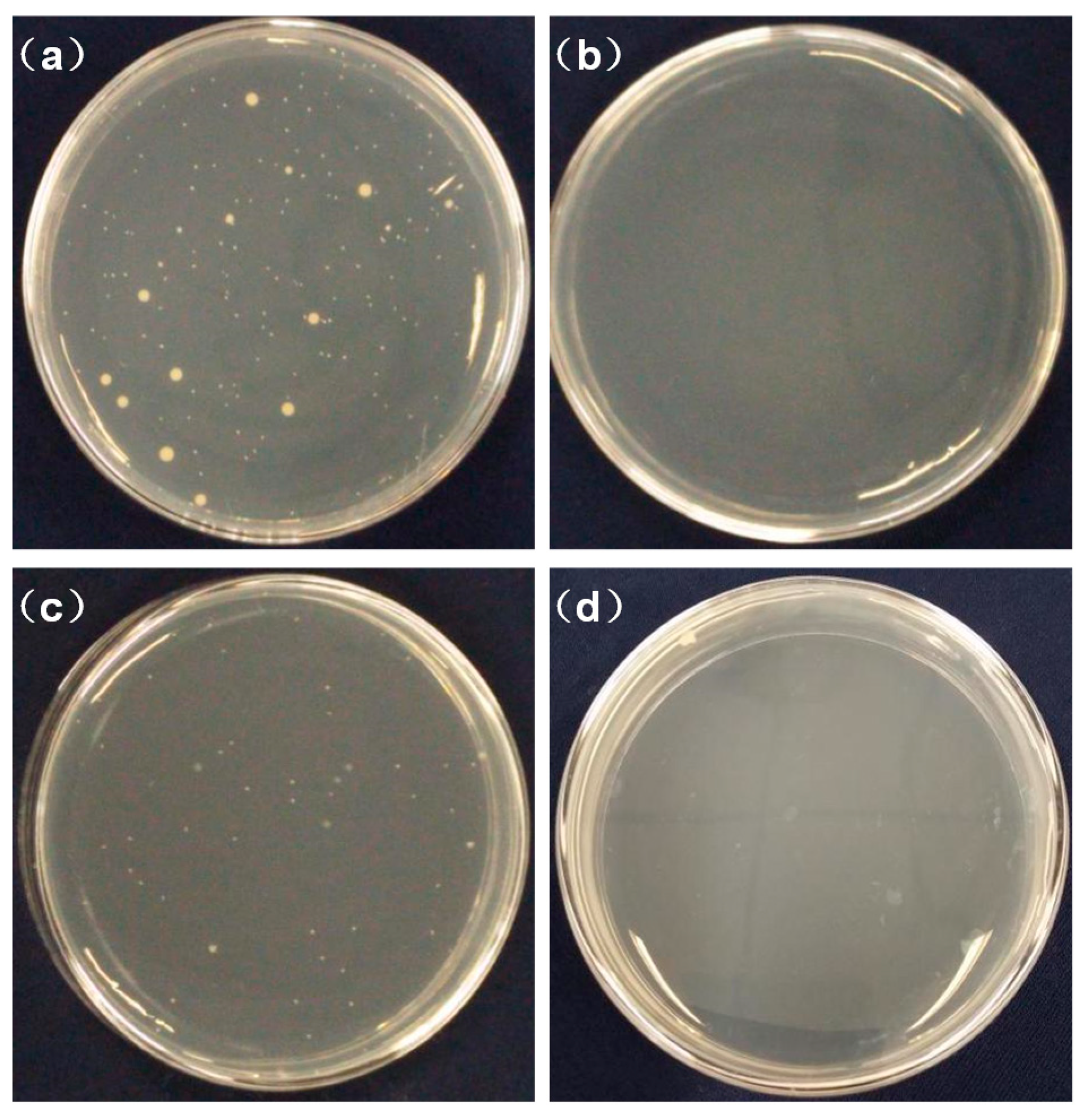
3.5. Antibacterial Activity
3.6. Air Purification Performance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nel, A. Atmosphere. Air pollution-related illness: Effects of particles. Science 2005, 308, 804–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yildiz, O.; Bradford, P.D. Aligned carbon nanotube sheet high efficiency particulate air filters. Carbon 2013, 64, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, K.; Hsiao, B.S.; Chu, B. Functional nanofibers for environmental applications. J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 5326–5334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, D.E.; Skinner, C.B.; Singh, D.; Diffenbaugh, N.S. Occurrence and persistence of future atmospheric stagnation events. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2014, 4, 698–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Harrison, R.M.; Yin, J.X. Particulate matter in the atmosphere: Which particle properties are important for its effects on health? Sci. Total Environ. 2000, 249, 85–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, S.; Querol, X.; Alastuey, A.; Viana, M.M.; Alarcon, M.; Mantilla, E.; Ruiz, C.R. Comparative PM10-PM2.5 source contribution study at rural, urban and industrial sites during PM episodes in Eastern Spain. Sci. Total Environ. 2004, 328, 95–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thavasi, V.; Singh, G.; Ramakrishna, S. Electrospun nanofibers in energy and environmental applications. Energy Environ. Sci. 2008, 1, 205–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Hsu, P.C.; Lee, H.W.; Ye, M.; Zheng, G.; Liu, N.; Li, W.; Cui, Y. Transparent air filter for high-efficiency PM2.5 capture. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pope, C.A.; Dockery, D.W. Health Effects of Fine Particulate Air Pollution: Lines that Connect. J. Air Waste Manag. 2012, 56, 709–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.W.; Arena, J.T.; Manickam, S.S.; Jiang, X.Q.; Willis, B.G.; McCutcheon, J.R. Improved mechanical properties and hydrophilicity of electrospun nanofiber membranes for filtration applications by dopamine modification. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 460, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Liu, C.; Hsu, P.C.; Zhang, C.; Liu, N.; Zhang, J.; Lee, H.R.; Lu, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Chu, S.; et al. Nanofiber Air Filters with High-Temperature Stability for Efficient PM2.5 Removal from the Pollution Sources. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 3642–3649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, K.M.; Hogan, C.J.; Mastubayashi, Y.; Kawabe, M.; Iskandar, F.; Okuyama, K. Nanoparticle filtration by electrospun polymer fibers. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2007, 62, 4751–4759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balogh, A.; Domokos, A.; Farkas, B.; Farkas, A.; Rapi, Z.; Kiss, D.; Nyiri, Z.; Eke, Z.; Szarka, G.; Orkenyi, R.; et al. Continuous end-to-end production of solid drug dosage forms: Coupling flow synthesis and formulation by electrospinning. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 350, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardiansyah, A.; Tanadi, H.; Yang, M.C.; Liu, T.Y. Electrospinning and antibacterial activity of chitosan-blended poly(lactic acid) nanofibers. J. Polym. Res. 2015, 22, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Yin, X.Q.; Zeng, Q.H.; Dong, W.Y.; Liu, H.F.; Zhu, L. Preparation of carboxymethyl chitosan nanofibers through electrospinning the ball-milled nanopowders with poly (lactic acid) and the blood compatibility of the electrospun NCMC/PLA mats. J. Polym. Res. 2017, 24, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.J.; Li, F.T.; Wang, H.T.; Fu, L.; Zhang, B.R.; Li, G.T. Effects of poly (vinyl alcohol) (PVA) content on preparation of novel thiol-functionalized mesoporous PVA/SiO2 composite nanofiber membranes and their application for adsorption of heavy metal ions from aqueous solution. Polymer 2010, 51, 6203–6211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Shim, W.S.; Kim, J. Design of ultra-fine nonwovens via electrospinning of Nylon 6: Spinning parameters and filtration efficiency. Mater. Des. 2009, 30, 3659–3666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, L.; Shim, K.; Toe, C.Y.; Fang, T.; Zhao, C.; Amal, R.; Sun, K.N.; Kim, J.H.; Ng, Y.H. Electrospun Polyacrylonitrile-Ionic Liquid Nanofibers for Superior PM2.5 Capture Capacity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 7030–7036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Z.W.; Li, D.N.; Qi, J.Q.; Chen, X.D.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, L.; Gao, B.; Cui, Y.; Duan, Q. Effect of the phenyl ring substituent on stereoselectivity in the ring-opening polymerization of the rac-lactide initiated by salen aluminum complexes. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2015, 293, 3449–3457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramot, Y.; Haim-Zada, M.; Domb, A.J.; Nyska, A. Biocompatibility and safety of PLA and its copolymers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 107, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva, D.; Kaduri, M.; Poley, M.; Adir, O.; Krinsky, N.; Shainsky-Roitman, J.; Schroeder, A. Biocompatibility, biodegradation and excretion of polylactic acid (PLA) in medical implants and theranostic systems. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 340, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bognitzki, M.; Czado, W.; Frese, T.; Schaper, A.; Hellwig, M.; Steinhart, M.; Greiner, A.; Wendorff, J.H. Nanostructured fibers via electrospinning. Adv. Mater. 2001, 13, 70–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Pan, Z.J. Preparation of hierarchical structured nano-sized/porous poly(lactic acid) composite fibrous membranes for air filtration. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 356, 1168–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, C.; Pan, Z. Porous bead-on-string poly(lactic acid) fibrous membranes for air filtration. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 441, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Vimal, A.; Kumar, A. Why Chitosan? From properties to perspective of mucosal drug delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 91, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamari, A.; Pulford, I.D.; Hargreaves, J.S. Chitosan as a potential amendment to remediate metal contaminated soil—A characterisation study. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2011, 82, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabea, E.I.; Badawy, M.E.T.; Stevens, C.V.; Smagghe, G.; Steurbaut, W. Chitosan as antimicrobial agent: Applications and mode of action. Biomacromolecules 2003, 4, 1457–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, P.; Wang, C.J.; Yang, X.Y.; Chen, X.Y.; Gao, C.Y.; Feng, X.X.; Chen, J.Y.; Ye, J.A.; Gou, Z.R. Electrospinning of chitosan nanofibers: The favorable effect of metal ions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 84, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homayoni, H.; Ravandi, S.A.H.; Valizadeh, M. Electrospinning of chitosan nanofibers: Processing optimization. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 77, 656–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klossner, R.R.; Queen, H.A.; Coughlin, A.J.; Krause, W.E. Correlation of chitosan’s rheological properties and its ability to electrospin. Biomacromolecules 2008, 9, 2947–2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Huang, X.B.; Duan, B.; Wu, L.L.; Li, S.; Yuan, X.Y. Preparation of electrospun chitosan/poly(vinyl alcohol) membranes. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2007, 285, 855–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuy, T.T.N.; Chung, O.H.; Park, J.S. Coaxial electrospun poly(lactic acid)/chitosan (core/shell) composite nanofibers and their antibacterial activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 86, 1799–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, X.Q.; Li, F.Q.; Liu, C.S.; Gao, Q. Electrospinning of Chitosan/Poly(lactic acid) Nanofibers: The Favorable Effect of Nonionic Surfactant. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.J.; Chen, F.; Nie, J.; Yang, D.Z. Electrospun poly(lactic acid)/chitosan core-shell structure nanofibers from homogeneous solution. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 90, 1445–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tighzert, W.; Habi, A.; Ajji, A.; Sadoun, T.; Daoud, F.B.O. Fabrication and Characterization of Nanofibers Based on Poly(lactic acid)/Chitosan Blends by Electrospinning and Their Functionalization with Phospholipase A1. Fiber Polym. 2017, 18, 514–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, H.T.; Pham, L.N.; Thu, H.T.V.; Park, J.S. Fabrication of an antibacterial non-woven mat of a poly(lactic acid)/chitosan blend by electrospinning. Macromol. Res. 2012, 20, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.Y.; Zeng, Q.H.; Yin, X.Q.; Liu, H.F.; Lv, J.; Zhu, L. Preparation and blood compatibility of electrospun nanofibrous CTS/PLA mats from chitosan nanopowders and poly(lactic acid). Polym. Compos. 2018, 39, E416–E425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, J.H.; Gao, W.Q.; Liang, H.W.; Wang, H.Y.; Li, J.F. Preparation of chitosan/PLA blend micro/nanofibers by electrospinning. Mater. Lett. 2009, 63, 658–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinh, N.T.; Trang, N.T.T.; Thanh, D.T.M.; Hang, T.T.X.; Giang, N.V.; Quan, P.M.; Dung, N.T.; Hoang, T. Thermal property, morphology, and hydrolysis ability of poly(lactic acid)/chitosan nanocomposites using polyethylene oxide. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 41690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touny, A.H.; Bhaduri, S.B. A reactive electrospinning approach for nanoporous PLA/monetite nanocomposite fibers. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. 2010, 30, 1304–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, B.; Lin, J.Y.; Wang, X.F.; Yu, J.Y.; Yang, J.M.; Cai, Y. Investigation of silica nanoparticle distribution in nanoporous polystyrene fibers. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 8376–8383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Ding, B.; Yang, J.; Yu, J.; Sun, G. Subtle regulation of the micro- and nanostructures of electrospun polystyrene fibers and their application in oil absorption. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Si, Y.S.; Wang, N.; Sun, G.; El-Newehy, M.; Al-Deyab, S.S.; Ding, B. Multilevel structured polyacrylonitrile/silica nanofibrous membranes for high-performance air filtration. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 126, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casper, C.L.; Stephens, J.S.; Tassi, N.G.; Chase, D.B.; Rabolt, J.F. Controlling surface morphology of electrospun polystyrene fibers: Effect of humidity and molecular weight in the electrospinning process. Macromolecules 2004, 37, 573–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Tian, F.; Shang, Y.; Wang, F.; Ding, B.; Yu, J. Facile control of intra-fiber porosity and inter-fiber voids in electrospun fibers for selective adsorption. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 5316–5320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Pan, Z.J.; Wang, J.G.; Zhao, R.Z. A Novel Hierarchical Structured Poly(lactic acid)/Titania Fibrous Membrane with Excellent Antibacterial Activity and Air Filtration Performance. J. Nanomater. 2016, 2016, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrieta, M.P.; Lopez, J.; Lopez, D.; Kenny, J.M.; Peponi, L. Effect of chitosan and catechin addition on the structural, thermal, mechanical and disintegration properties of plasticized electrospun PLA-PHB biocomposites. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2016, 132, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.G.; Jou, C.H.; Yang, M.C. Surface grafting of polyester fiber with chitosan and the antibacterial activity of pathogenic bacteria. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2002, 86, 2977–2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Set | Sample | Chitosan/Solution wt % | PLA/Solution wt % | Mass Ratio of DCM/DMAC | Mass Ratio of Chitosan/PLA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | A1 | 1 | 4 | 10:1 | 1:4 |
| A2 | 1.25 | 5 | 10:1 | 1:4 | |
| A3 | 1.5 | 6 | 10:1 | 1:4 | |
| A4 | 1.75 | 7 | 10:1 | 1:4 | |
| A5 | 2 | 8 | 10:1 | 1:4 | |
| B | B1 | 0 | 8 | 10:1 | 0:8 |
| B2 | 1 | 8 | 10:1 | 1:8 | |
| B3 | 1.5 | 8 | 10:1 | 1.5:8 | |
| B4 | 2 | 8 | 10:1 | 2:8 | |
| B5 | 2.5 | 8 | 10:1 | 2.5:8 |
| Humidity/% | Diameter/µm | Coverage of Pores/% | Width of Pores/nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | 0.91 ± 0.14 | / | / |
| 30 | 1.15 ± 0.12 | 18.13 | 46.0 ± 12.8 |
| 45 | 1.34 ± 0.28 | 26.91 | 58.1 ± 14.8 |
| 60 | 1.50 ± 0.26 | 32.72 | 65.8 ± 15.9 |
| Samples | Diameter/µm | Width of Pores/nm | Coverage of Pores/% | Mean Flow through-Pore Size/µm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 wt % CS + 8 wt % PLA | 1.21 ± 0.21 | 58.52 ± 18.97 | 23.22 | 4.50 |
| 1 wt % CS + 8 wt % PLA | 1.34 ± 0.34 | 63.72 ± 18.02 | 23.85 | 7.25 |
| 1.5 wt % CS + 8 wt % PLA | 1.31 ± 0.26 | 64.97 ± 16.32 | 24.46 | 7.53 |
| 2 wt % CS + 8 wt % PLA | 1.35 ± 0.28 | 59.52 ± 20.57 | 23.81 | 7.92 |
| 2.5 wt % CS + 8 wt % PLA | 1.35 ± 0.26 | 53.19 ± 20.39 | 23.57 | 7.72 |
| Samples | C/wt % | N/wt % | O/wt % |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100% PLA | 70.13 | 0 | 29.87 |
| 100% chitosan | 51.97 | 8.86 | 39.17 |
| 80% PLA/20% chitosan | 60.45 | 2.75 | 36.50 |
| Samples | Thickness/mm | Filtration Efficiency/% | Pressure Drop/Pa | Quality Factor |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FY3107 | 1.152 | 89.18 | 71.67 | 0.0310 |
| 0 wt % CS + 8 wt % PLA | 0.215 | 99.90 | 335.90 | 0.0207 |
| 1 wt % CS + 8 wt % PLA | 0.196 | 98.10 | 167.05 | 0.0237 |
| 1.5 wt % CS + 8 wt % PLA | 0.198 | 98.78 | 162.35 | 0.0271 |
| 2 wt % CS + 8 wt % PLA | 0.206 | 98.26 | 147.00 | 0.0276 |
| 2.5 wt % CS + 8 wt % PLA | 0.202 | 98.99 | 147.60 | 0.0312 |
| Samples | Antibacterial Rate/% | |
|---|---|---|
| S. aureus | E. coli | |
| 0 wt % CS + 8 wt % PLA | 10.1 | 4.6 |
| 1 wt % CS + 8 wt % PLA | 79.0 | 57.8 |
| 1.5 wt % CS + 8 wt % PLA | 72.5 | 48.2 |
| 2 wt % CS + 8 wt % PLA | 87.5 | 92.8 |
| 2.5 wt % CS + 8 wt % PLA | 99.5 | 99.4 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Pan, Z. Nanoporous PLA/(Chitosan Nanoparticle) Composite Fibrous Membranes with Excellent Air Filtration and Antibacterial Performance. Polymers 2018, 10, 1085. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10101085
Li H, Wang Z, Zhang H, Pan Z. Nanoporous PLA/(Chitosan Nanoparticle) Composite Fibrous Membranes with Excellent Air Filtration and Antibacterial Performance. Polymers. 2018; 10(10):1085. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10101085
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Hui, Zhe Wang, Haiyan Zhang, and Zhijuan Pan. 2018. "Nanoporous PLA/(Chitosan Nanoparticle) Composite Fibrous Membranes with Excellent Air Filtration and Antibacterial Performance" Polymers 10, no. 10: 1085. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10101085
APA StyleLi, H., Wang, Z., Zhang, H., & Pan, Z. (2018). Nanoporous PLA/(Chitosan Nanoparticle) Composite Fibrous Membranes with Excellent Air Filtration and Antibacterial Performance. Polymers, 10(10), 1085. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10101085