Synthesis and Properties of Low-Molecular-Weight PEI-Based Lipopolymers for Delivery of DNA
Abstract
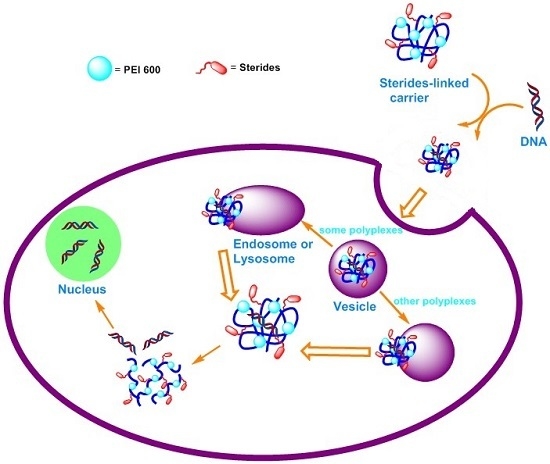
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis and Characterization of 6a–6c
2.3. Synthesis and Characterization of 7a–7c
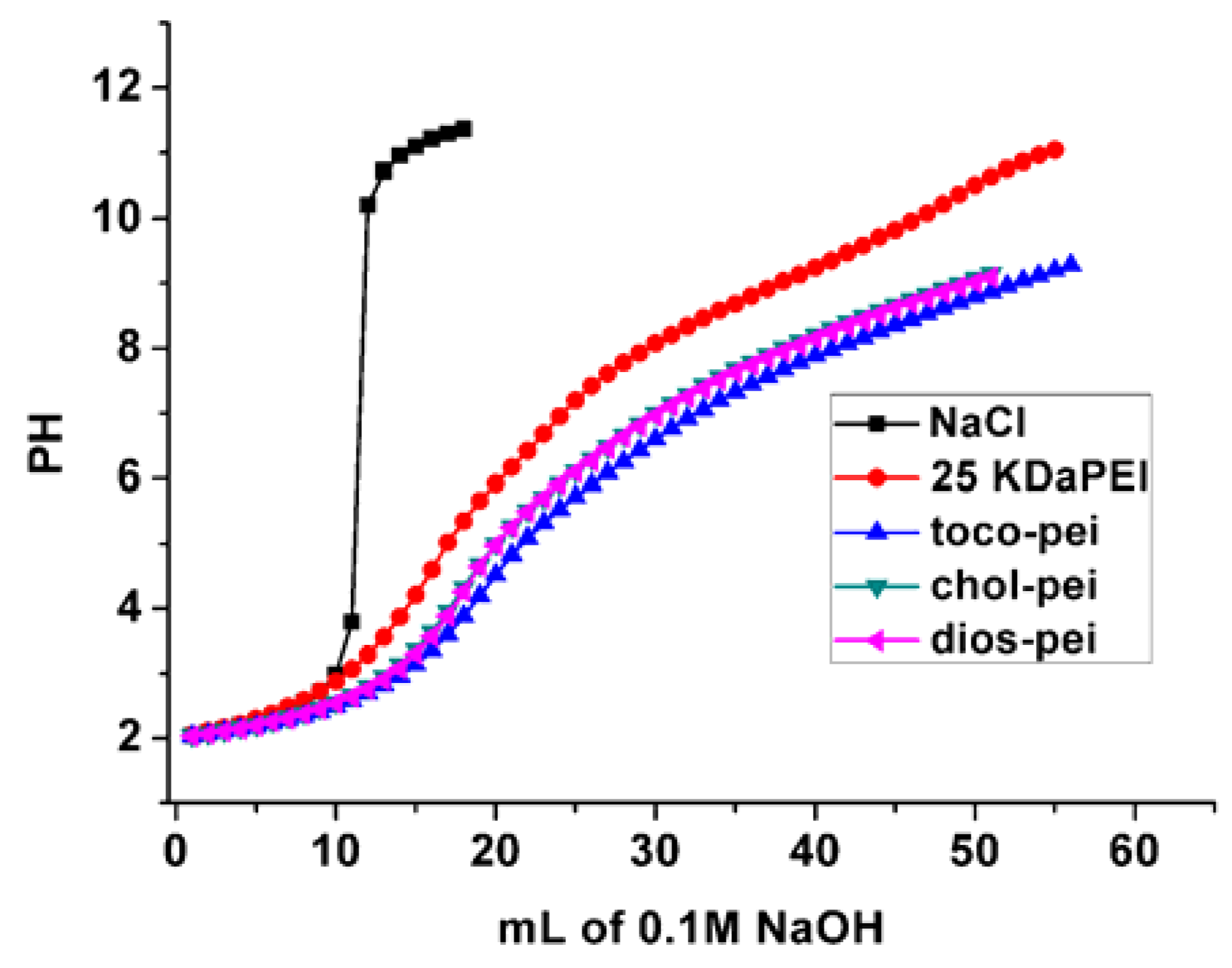
2.4. Buffer Capacity Test
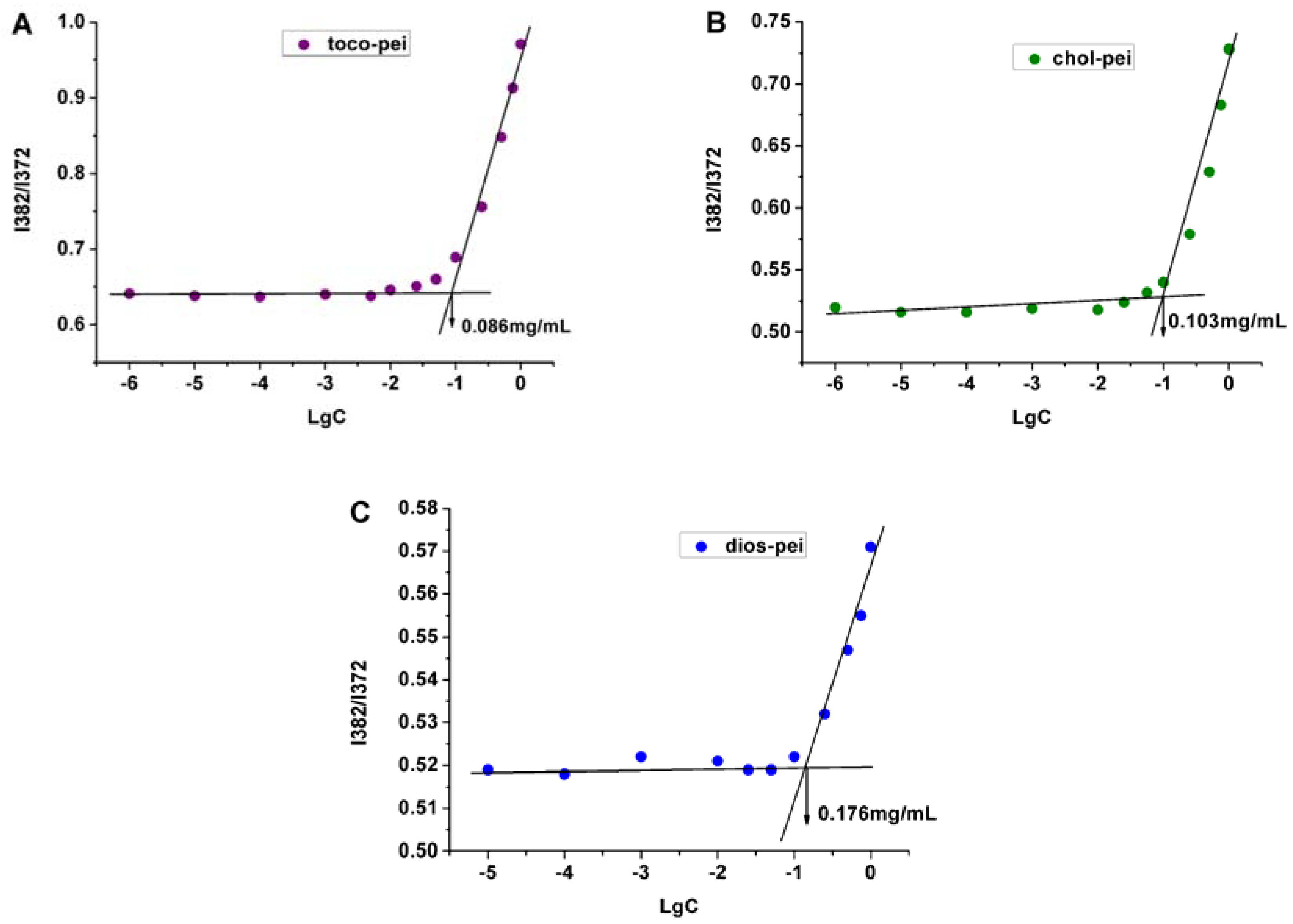
2.5. Measurement of Critical Micelle Concentration
2.6. Cell Culture
2.7. Amplification and Purification of pEGFP-N1 and pGL-3 Plasmids
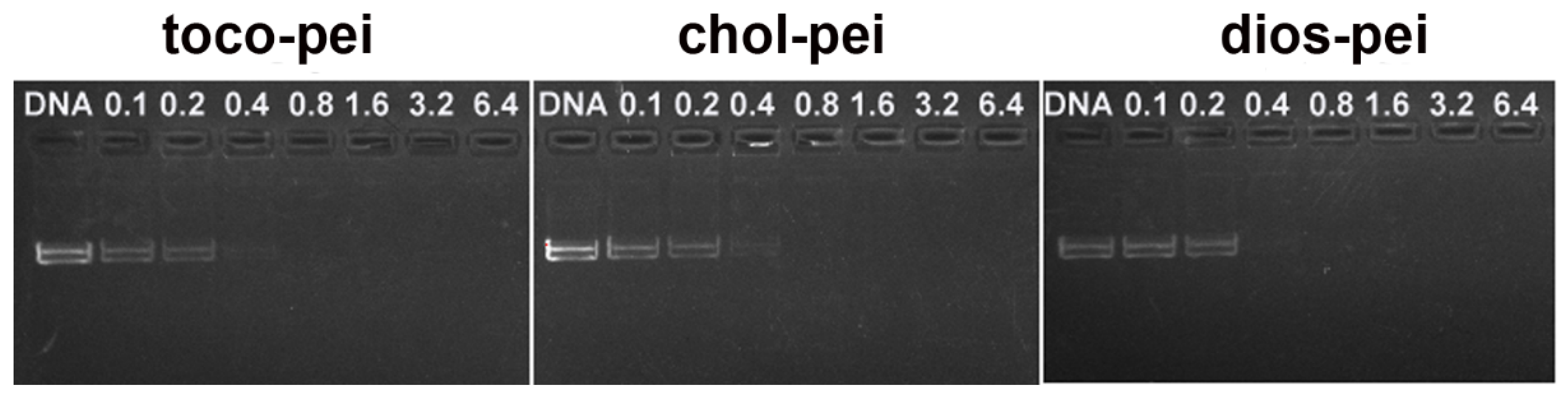
2.8. Agarose Gel Electrophoresis
2.9. Ethidium Bromide Displacement
2.10. Measurements of Particle Size and Zeta Potential in Water
2.11. Cell Viability
2.12. Transfection Assay
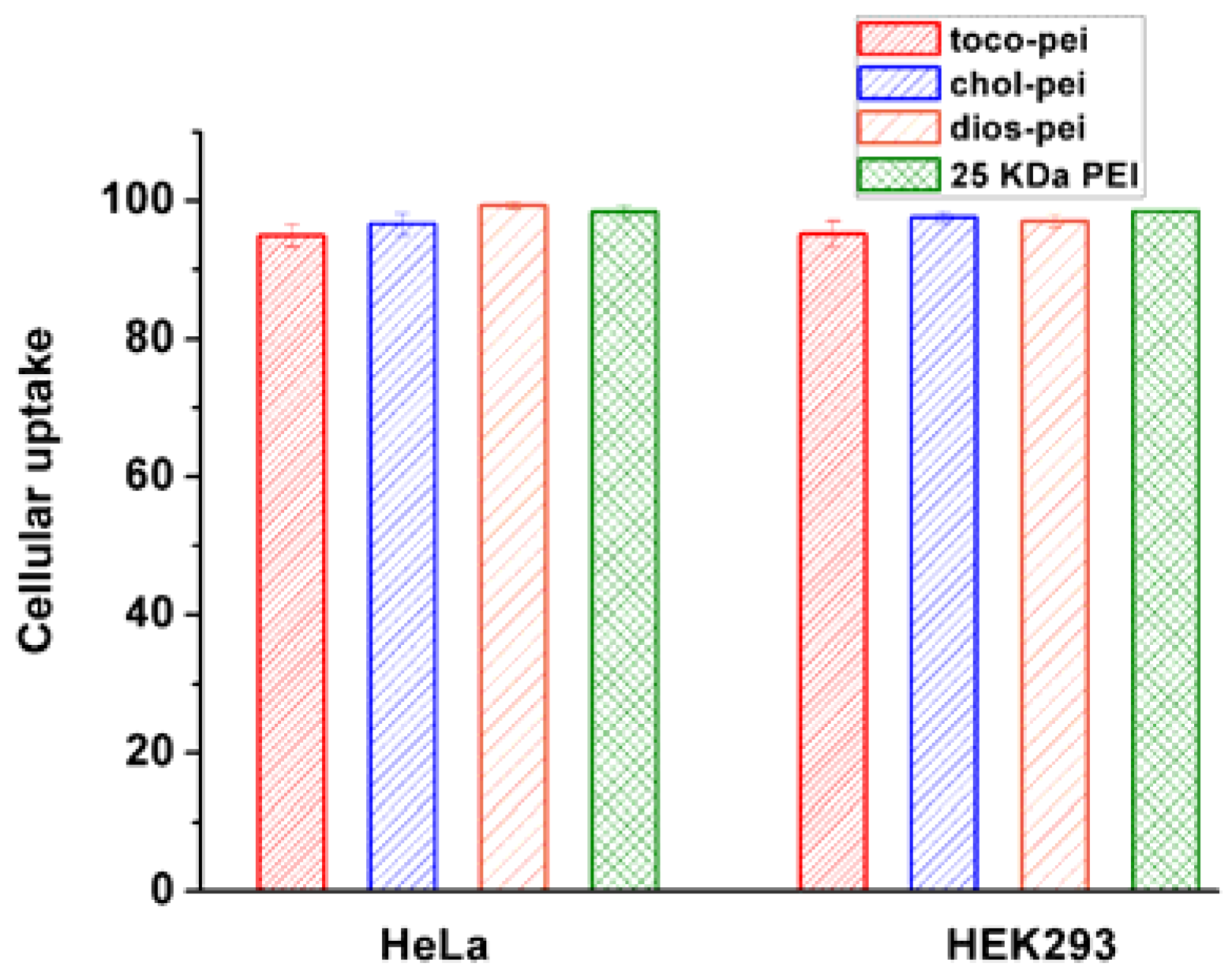
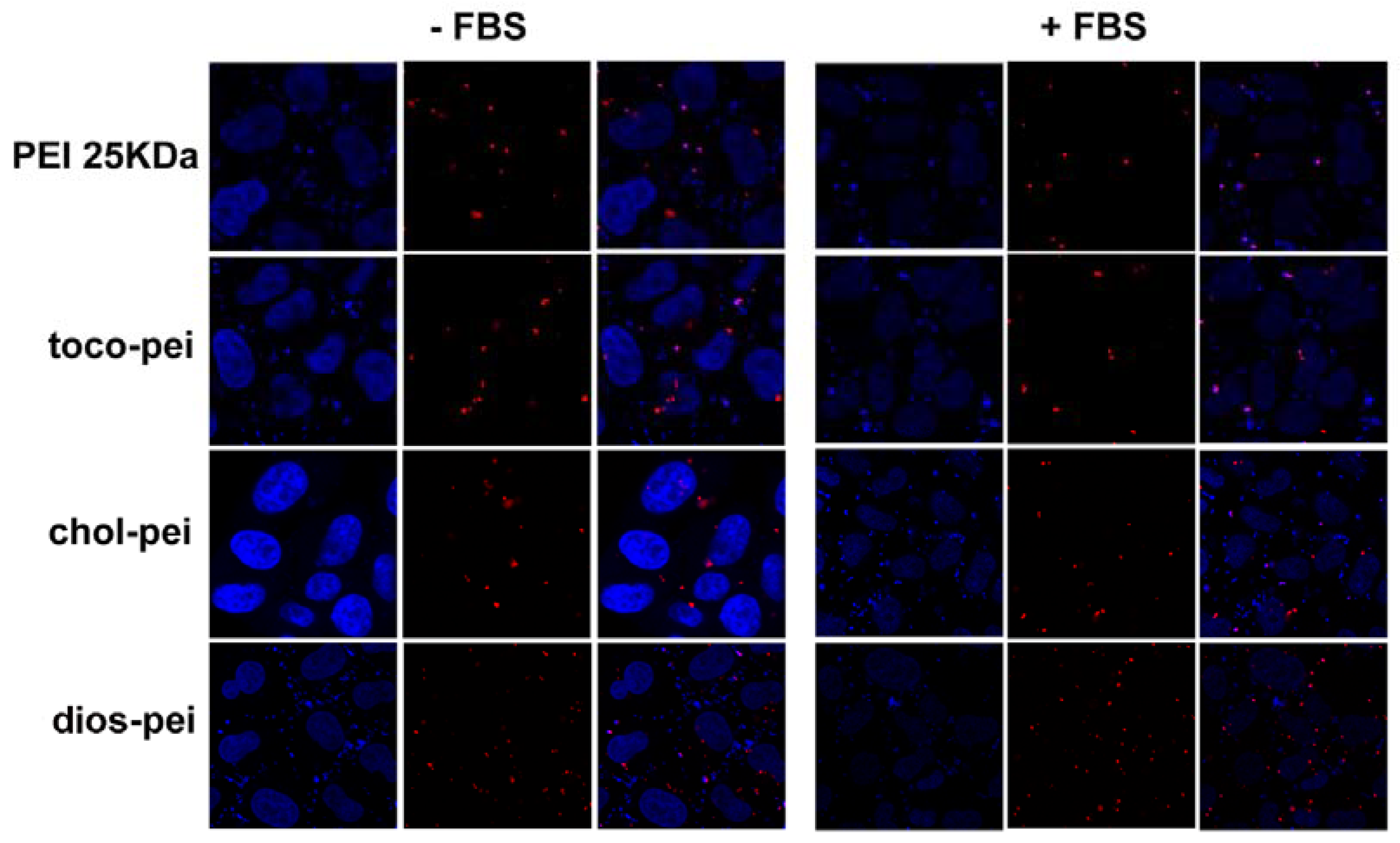
2.13. Cellular Uptake
2.14. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis and Chemical Properties of Target Lipopolymers
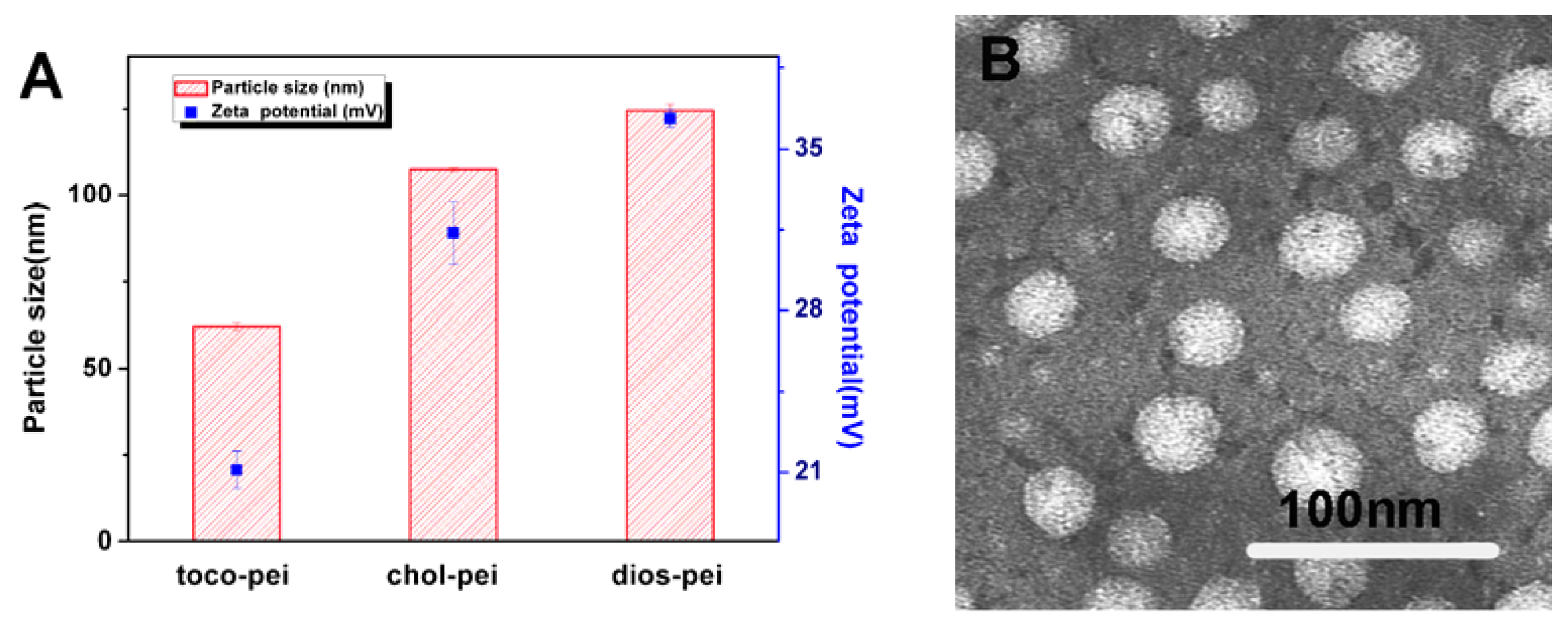
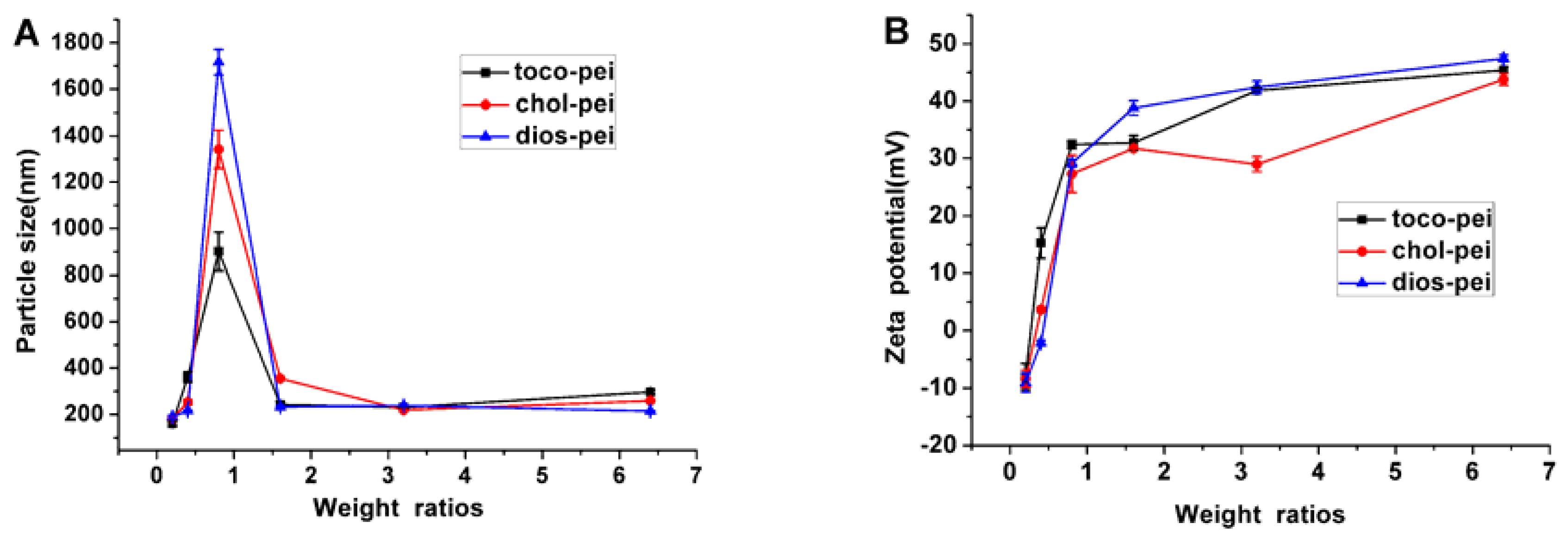
3.2. Properties of Lipopolymer/DNA Polyplexes
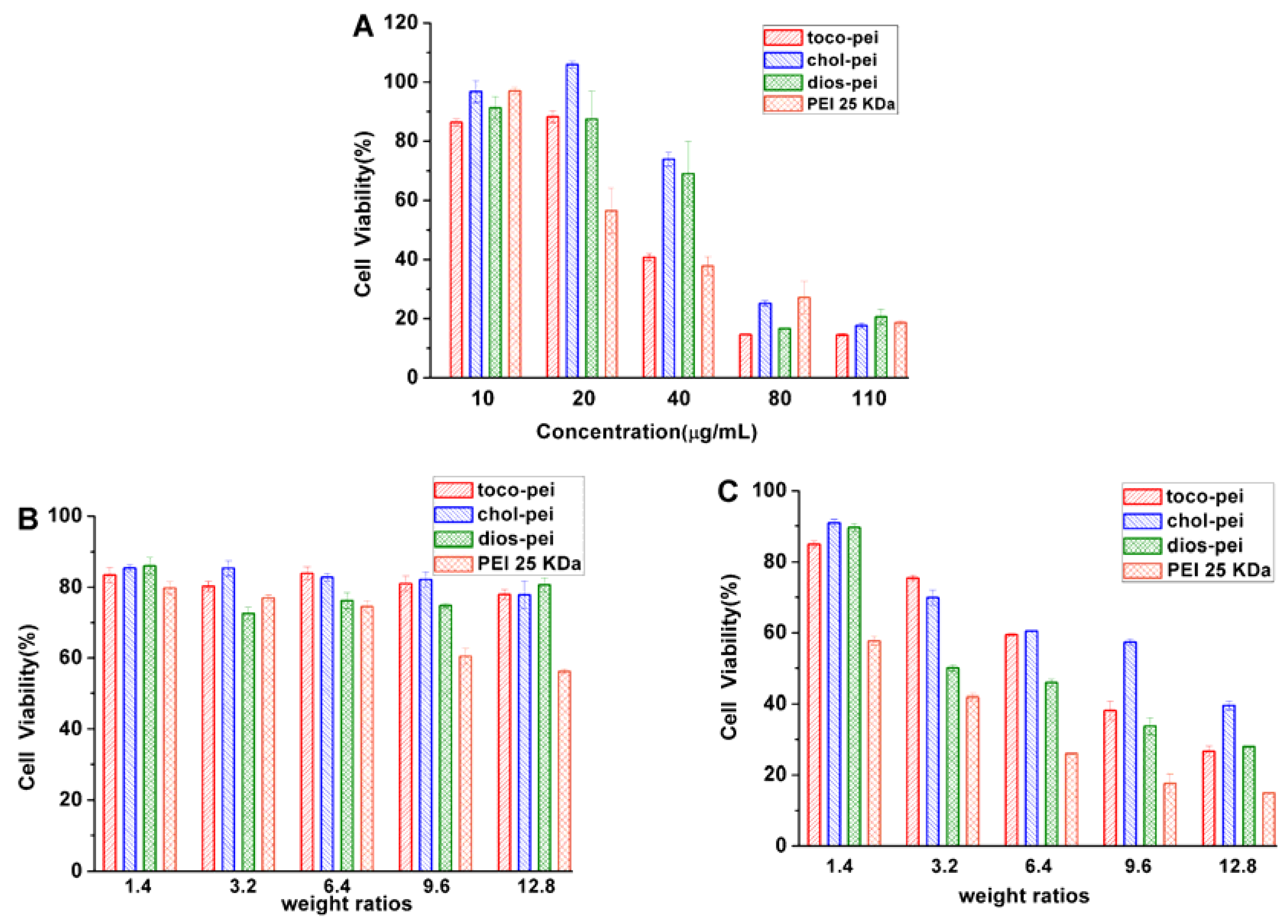
3.3. Cytotoxicity
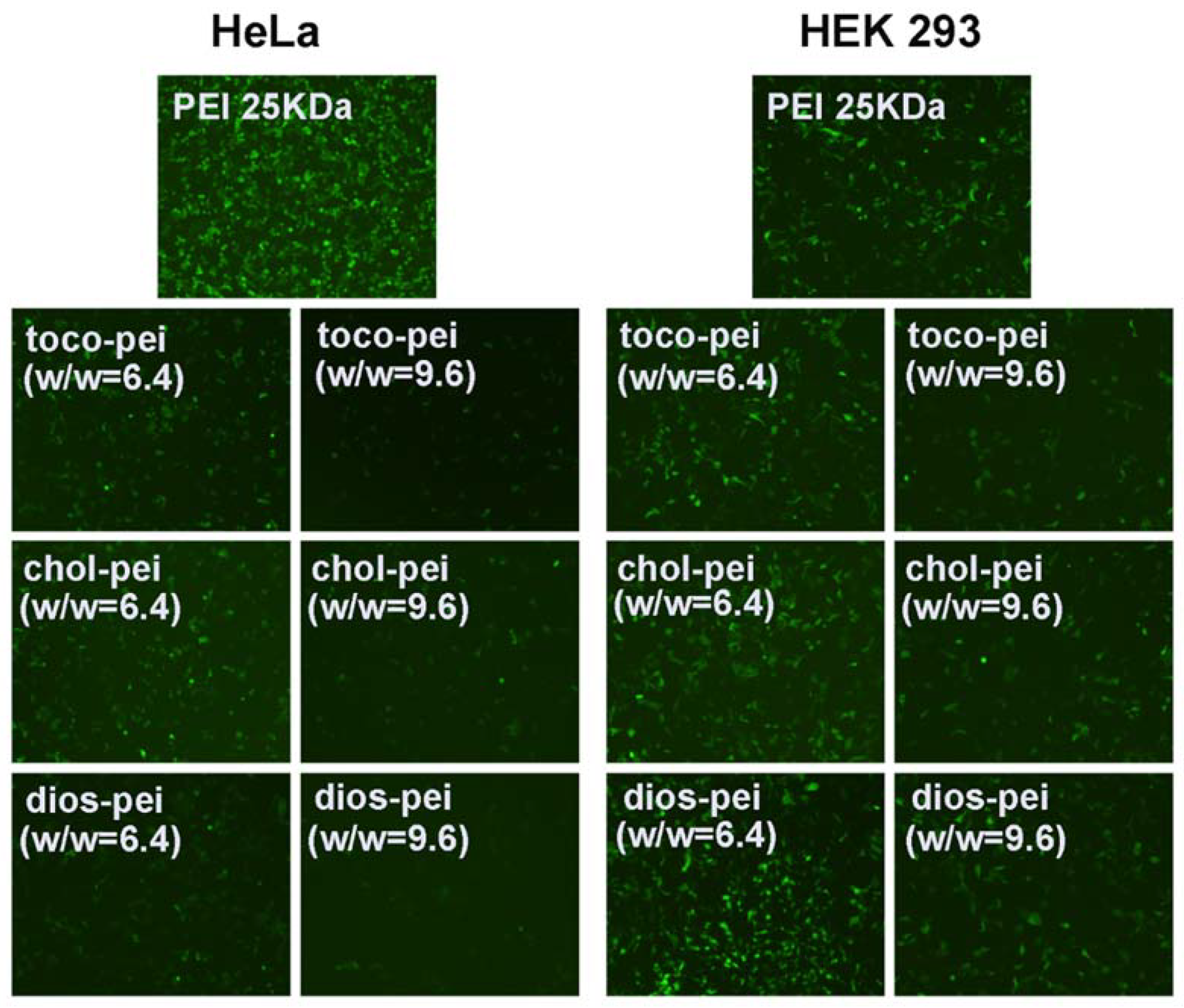
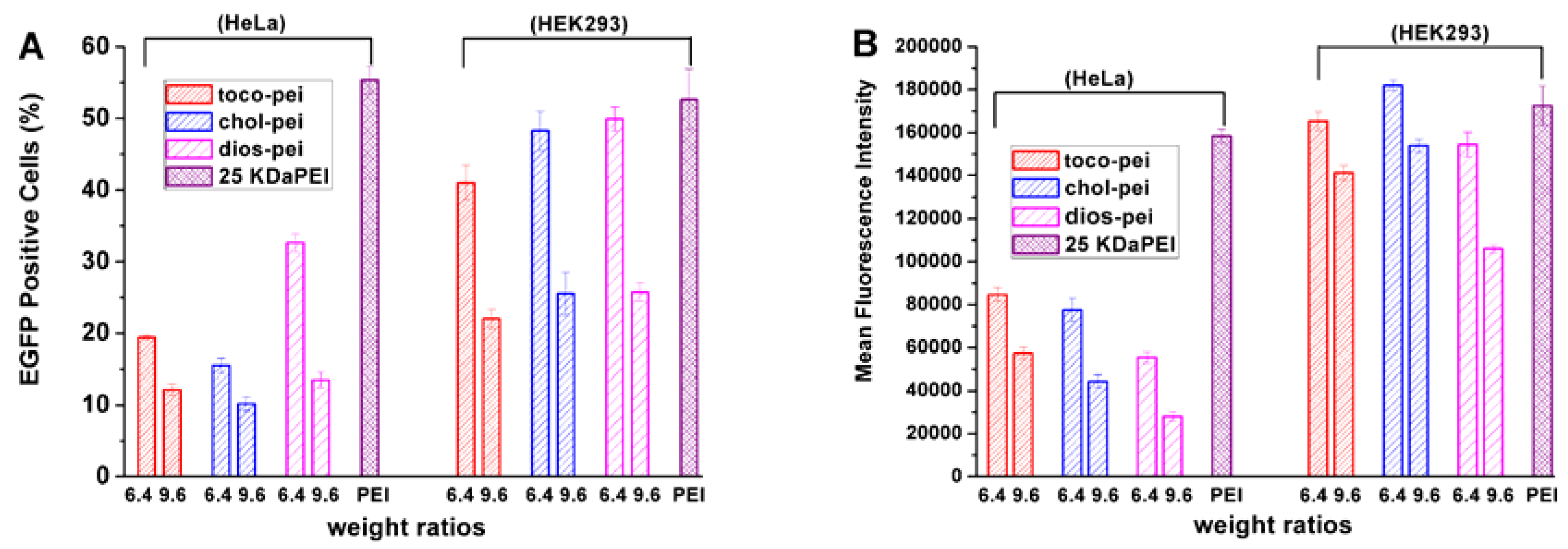
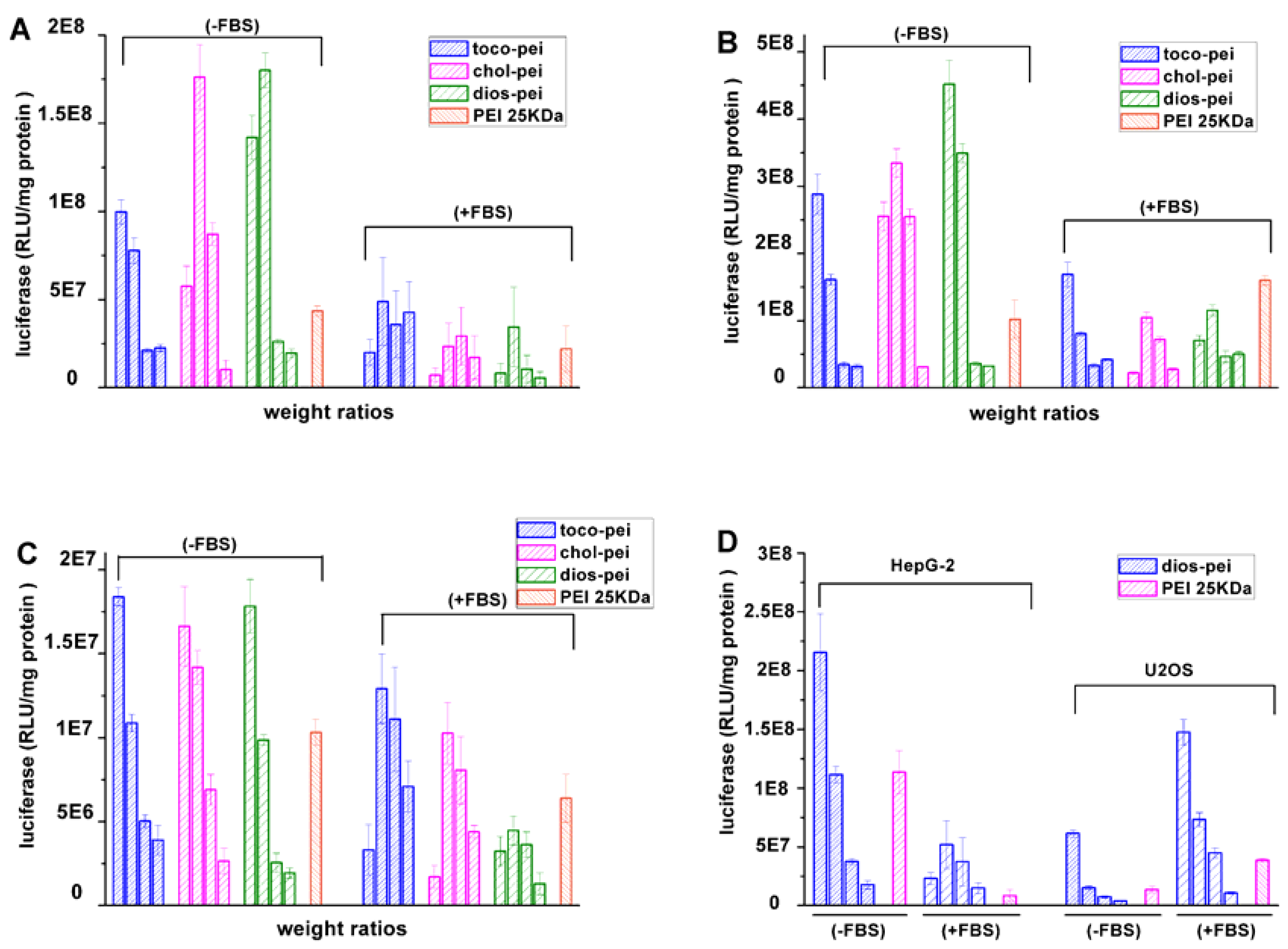
3.4. Gene Transfection In Vitro
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yao, X.; Chen, L.; Chen, X.; He, C.; Zheng, H.; Chen, X. Intercellular pH-responsive histidine modified dextran-g-cholesterol micelle for anticancer drug delivery. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 121, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Schmaltz, R.M.; Bozeman, T.C.; Paul, R.; Rishel, M.J.; Tsosie, K.S.; Hecht, S.M. Selective tumor cell targeting by the disaccharide moiety of bleomycin. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 2883–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Wu, H.; Wang, J.; Yang, Y.; Wu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Yang, S. Graphene oxide-BaGdF5 nanocomposites for multi-modal imaging and photothermal therapy. Biomaterials 2015, 42, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akita, H.; Ishiba, R.; Togashi, R.; Tange, K.; Nakai, Y.; Hatakeyama, H.; Harashima, H. A neutral lipid envelope-type nanoparticle composed of a pH-activated and vitamin E-scaffold lipid-like material as a platform for a gene carrier targeting renal cell carcinoma. J. Control. Release 2015, 200, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guan, X.W.; Li, Y.H.; Jiao, Z.X.; Lin, L.; Chen, J.; Guo, Z.P.; Tian, H.Y.; Chen, X.S. Codelivery of antitumor drug and gene by a pH-sensitive charge-conversion system. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 3207–3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginn, S.L.; Alexander, I.E.; Edelstein, M.L.; Abedi, M.R.; Wixon, J. Gene therapy clinical trials worldwide to 2012—An update. J. Gene Med. 2013, 15, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, G.; Clima, L.; Calin, M.; Constantinescu, C.A.; Balan-Porcarasu, M.; Uritu, C.M.; Simionescu, B.C. Simionescu, Squalene/polyethylenimine based non-viral vectors: Synthesis and use in systems for sustained gene release. Polym. Chem. 2018, 9, 1072–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Kanasty, R.L.; Eltoukhy, A.A.; Vegas, A.J.; Dorkin, J.R.; Anderson, D.G. Non-viral vectors for gene-based therapy. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2014, 15, 541–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, K.; Vulugundam, G.; Kondaiah, P.; Bhattacharya, S. Co-liposomes of redox-active alkyl-ferrocene modified low MW branched PEI and DOPE for efficacious gene delivery in serum. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 2318–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Ding, A.-X.; Zhang, K.-X.; Gong, B.; Lu, Z.-L.; He, L. Degradable polyesters via ring-opening polymerization of functional valerolactones for efficient gene delivery. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2017, 15, 6567–6574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, D.; Yan, H.; Zhou, Z.; Tang, J.; Liu, X.; Hartmann, R.; Parak, W.J.; Feliu, N.; Shen, Y. Detailed investigation on how the protein corona modulates the physicochemical properties and gene delivery of polyethylenimine (PEI) polyplexes. Biomater. Sci. 2018, 6, 1800–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zintchenko, A.; Philipp, A.; Dehshahri, A.; Wagner, E. Simple modifications of branched PEI lead to highly efficient siRNA carriers with low toxicity. Bioconjug. Chem. 2008, 19, 1448–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bonetta, L. The inside scoopdevaluating gene delivery methods. Nat. Methods 2005, 2, 875–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lungwitz, U.; Breunig, M.; Blunk, T.; Gopferich, A. Polyethylenimine-based nonviral gene delivery systems. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2005, 60, 247–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moghimi, S.M.; Symonds, P.; Murray, J.C.; Hunter, A.C.; Debska, G.; Szewczyk, A. A two-stage poly(ethylenimine)-mediated cytotoxicity: Implications for gene transfer/therapy. Mol. Ther. 2005, 11, 990–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- RB, K.C.; Kucharski, C.; Uludag, H. Additive nanocomplexes of cationic lipopolymers for improved non-viral gene delivery to mesenchymal stem cells. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 3972–3982. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Zheng, M.; Meng, F.; Zhong, Z. Non-viral gene transfection in vitro using endosomal pH-sensitive reversibly hydrophobilized polyethylenimine. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 9109–9119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, T.; Yoshihara, C.; Hamada, K.; Koyama, Y. DNA/polyethyleneimine/hyaluronic acid small complex particles and tumor suppression in mice. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 2912–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, J.-Z.; Sun, Y.-X.; Wang, H.-Y.; Li, C.; Huang, F.-W.; Cheng, S.-X.; Zhuo, R.-X.; Zhang, X.-Z. Poly(β-amino amine) cross-linked PEIs as highly efficient gene vectors. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 2200–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forrest, M.L.; Koerber, J.T.; Pack, D.W. A degradable polyethylenimine derivativewith low toxicity for highly efficient gene delivery. Bioconjug. Chem. 2003, 14, 934–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xun, M.-M.; Xiao, Y.-P.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.-H.; Peng, Q.; Guo, Q.; Wu, W.-X.; Xu, Y.; Yu, X.-Q. Low molecular weight PEI-based polycationic gene vectors via Michael addition polymerization with improved serum-tolerance. Polymer 2015, 65, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloeckner, J.; Wagner, E.; Ogris, M. Degradable gene carriers based on oligomerized polyamines. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2006, 29, 414–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.H.; Cook, S.E.; Arote, R.B.; Cho, M.H.; Nah, J.W.; Choi, Y.J.; Cho, C.S. A degradable hyperbranched poly(ester amine) based on poloxamer diacrylate and polyethylenimine as a gene carrier. Macromol. Biosci. 2007, 7, 611–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arote, R.; Kim, T.H.; Kim, Y.K.; Hwang, S.K.; Jiang, H.L.; Song, H.H.; Nah, J.W.; Cho, M.H.; Cho, C.S. A biodegradable poly(ester amine) based on polycaprolactone and polyethylenimine as a gene carrier. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 735–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, C.; Jiao, Y. Hydrophobic modifications of cationic polymers for gene delivery. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2010, 35, 1144–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, A.; Kondaiah, P.; Bhattacharya, S. Synthesis and gene transfection efficacies of PEI-cholesterol-based lipopolymers. Bioconjug. Chem. 2008, 19, 1640–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Chen, J.; Ying, J.; Xu, Y.; Sheng, R. Hydrophobic chain modified low molecular weight polyethylenimine for efficient antigen delivery. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 13636–13643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Wang, H.; Ling-hu, Y.; Lv, J.; Chang, H.; Cheng, Y. Screening of efficient polymers for siRNA delivery in a library of hydrophobically modified polyethyleneimines. J. Mater. Chem. B. 2016, 4, 6468–6474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xun, M.-M.; Zhang, X.-C.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, Q.-Q.; Yi, W.-J.; Zhu, W.; Yu, X.-Q. Low molecular weight PEI-based biodegradable lipopolymers as gene delivery vectors. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2013, 11, 1242–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behr, J.P. The proton sponge: A trick to enter cells the viruses did not exploit. Chimia 1997, 51, 34–36. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Ni, P.; He, J.; Liu, C. Novel fluoroalkyl end-capped amphiphilic diblock copolymers with pH/temperature response and self-assembly behavior. Langmuir 2008, 24, 4647–4654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.L.; Winnik, M.A.; Riess, G.; Croucher, M.D. Fluorescence probe techniques used to study micelle formation in water-soluble block copolymers. Langmuir 1990, 6, 514–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Shi, C.; Wang, J.; Di, S.; Zhou, S. pH-triggered intracellular release from actively targeting polymer micelles. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 4544–4554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Tian, Q.; Huang, Z.; Fan, D.; She, Z.; Liu, X.; Cheng, X.; Yu, B.; Deng, Y. Self-assembled micelles of novel amphiphilic copolymer cholesterol-coupled F68 containing cabazitaxel as a drug delivery system. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 2307–2317. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, L.; Li, Z.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, Q.; Shen, J.; Guo, H.; Tian, X.; Liu, G.; Zheng, D.; Qi, L. Redox-responsive catiomer based on PEG-ss-chitosan oligosaccharide-ss-polyethylenimine copolymer for effective gene delivery. Polym. Chem. 2013, 4, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.-K.; Seu, Y.-B.; Bae, Y.-U.; Kwak, T.-W.; Kang, H.; Moon, I.-J.; Hwang, G.-B.; Park, S.-Y.; Doh, K.-O. Efficient delivery of plasmid DNA using cholesterol-based cationic lipids containing polyamines and ether linkages. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 7293–7312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xun, M.-M.; Liu, Y.-H.; Guo, Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Q.-F.; Wu, W.-X.; Yu, X.-Q. Low molecular weight PEI-appended polyesters as non-viral gene delivery vectors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 78, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cha, C.; Kim, E.-S.; Kim, I.W.; Kong, H. Integrative design of a poly(ethylene glycol)-poly(propylene glycol)-alginate hydrogel to control three dimensional biomineralization. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 2695–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Y.; Pan, S.; Luo, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, W.; Feng, M. A biodegradable low molecular weight polyethylenimine derivative as low toxicity and efficient gene vector. Bioconjug. Chem. 2009, 20, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, R.; Luo, T.; Li, H.; Sun, J.; Wang, Z.; Cao, A. Cholesterol-based cationic lipids for gene delivery: Contribution of molecular structure factors to physico-chemical and biological properties. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 116, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Yuan, W.; Zhao, N.-N.; Ma, J.; Yang, W.-T.; Xu, F.-J. Supramolecular pseudo-block gene carriers based on bioreducible star polycations. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 5411–5422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kedika, B.; Patri, S.V. Synthesis and gene transfer activities of novel serum compatible reducible tocopherol-based cationic lipids. Mol. Pharm. 2012, 9, 1146–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
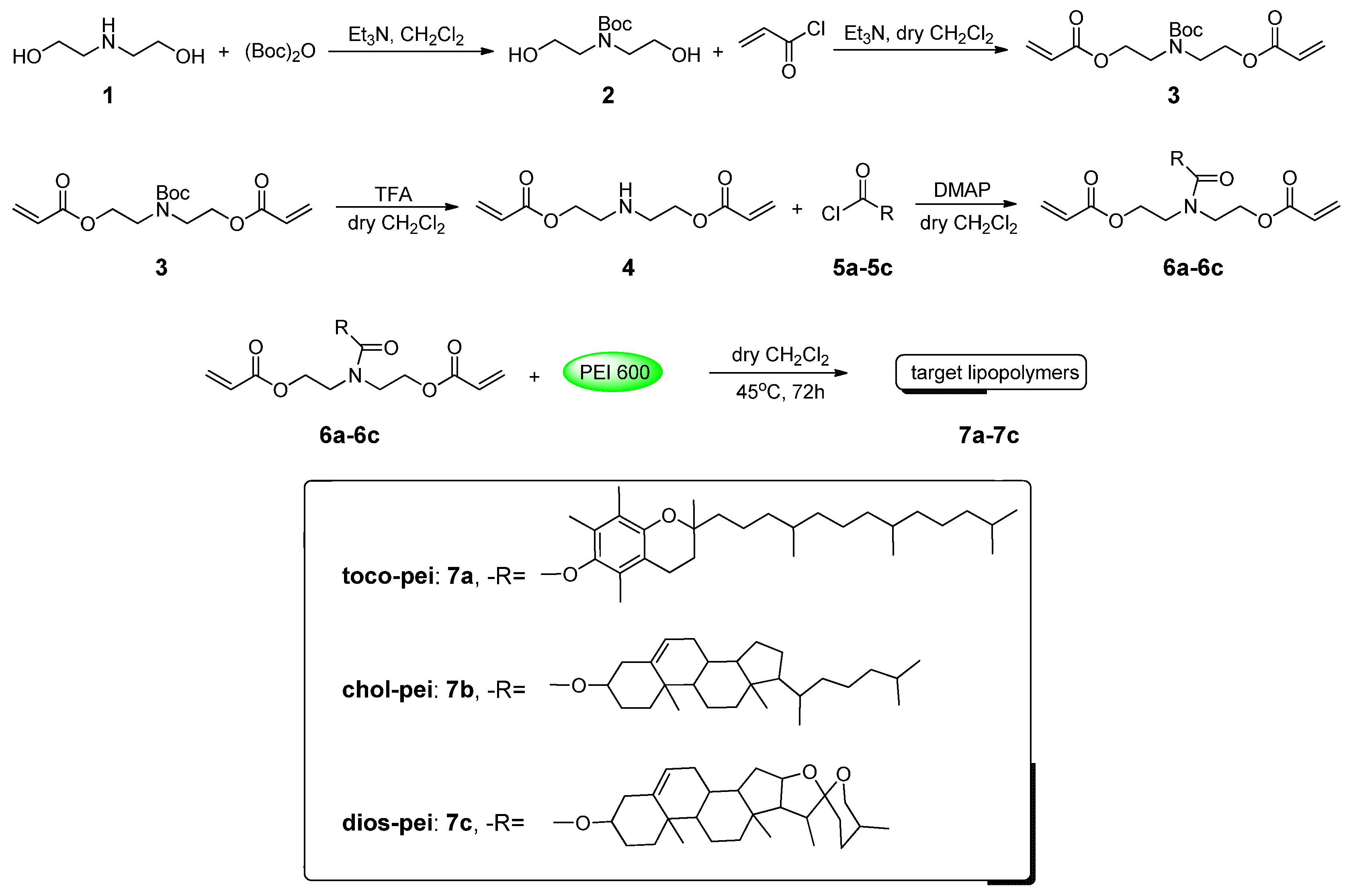

| Compounds | Mw | PDI |
|---|---|---|
| Tocopherol–PEI (toco-pei) | 7880 | 1.68 |
| Cholesterol–PEI (chol-pei) | 8974 | 1.79 |
| Diosgenin–PEI (dios-pei) | 10,985 | 1.95 |
| Sample | toco-pei | chol-pei | dios-pei | 25-kDa PEI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer capacity (%) | 26.0 | 24.0 | 26.0 | 16.0 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xun, M.-M.; Huang, Z.; Xiao, Y.-P.; Liu, Y.-H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.-H.; Yu, X.-Q. Synthesis and Properties of Low-Molecular-Weight PEI-Based Lipopolymers for Delivery of DNA. Polymers 2018, 10, 1060. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10101060
Xun M-M, Huang Z, Xiao Y-P, Liu Y-H, Zhang J, Zhang J-H, Yu X-Q. Synthesis and Properties of Low-Molecular-Weight PEI-Based Lipopolymers for Delivery of DNA. Polymers. 2018; 10(10):1060. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10101060
Chicago/Turabian StyleXun, Miao-Miao, Zheng Huang, Ya-Ping Xiao, Yan-Hong Liu, Ji Zhang, Ju-Hui Zhang, and Xiao-Qi Yu. 2018. "Synthesis and Properties of Low-Molecular-Weight PEI-Based Lipopolymers for Delivery of DNA" Polymers 10, no. 10: 1060. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10101060
APA StyleXun, M.-M., Huang, Z., Xiao, Y.-P., Liu, Y.-H., Zhang, J., Zhang, J.-H., & Yu, X.-Q. (2018). Synthesis and Properties of Low-Molecular-Weight PEI-Based Lipopolymers for Delivery of DNA. Polymers, 10(10), 1060. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10101060