Effect of Al–Mg Alloy Infiltration on Mechanical and Electrical Properties for Carbon/Carbon Composites
Abstract
:1. Introduction
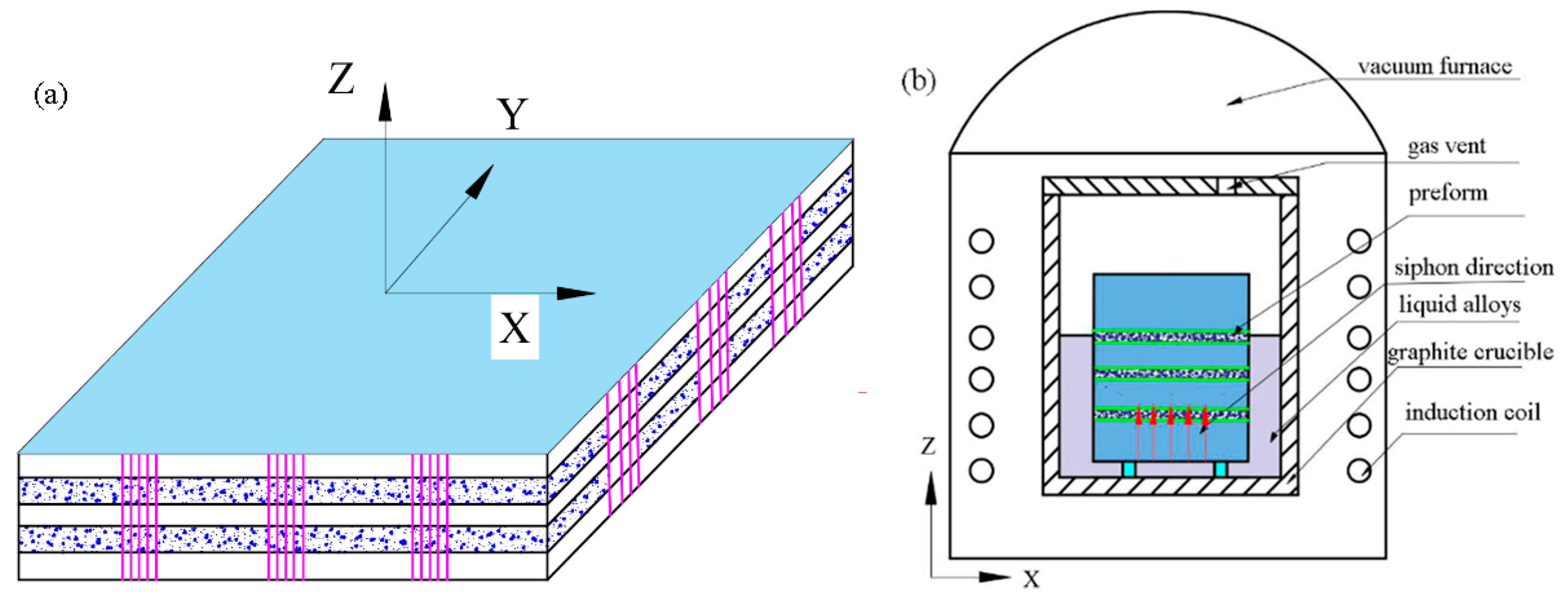
2. Experimental Procedure
2.1. Preparation of Materials
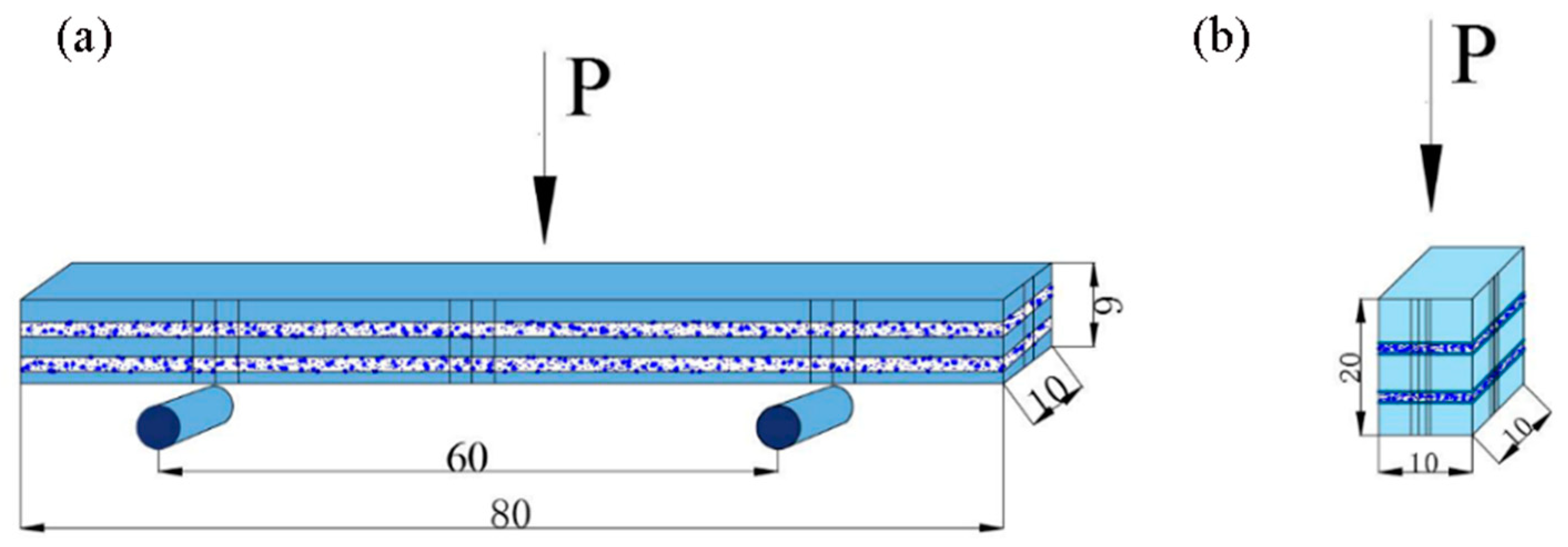
2.2. Property Test and Morphological Analysis
2.3. Electrical Resistivity Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
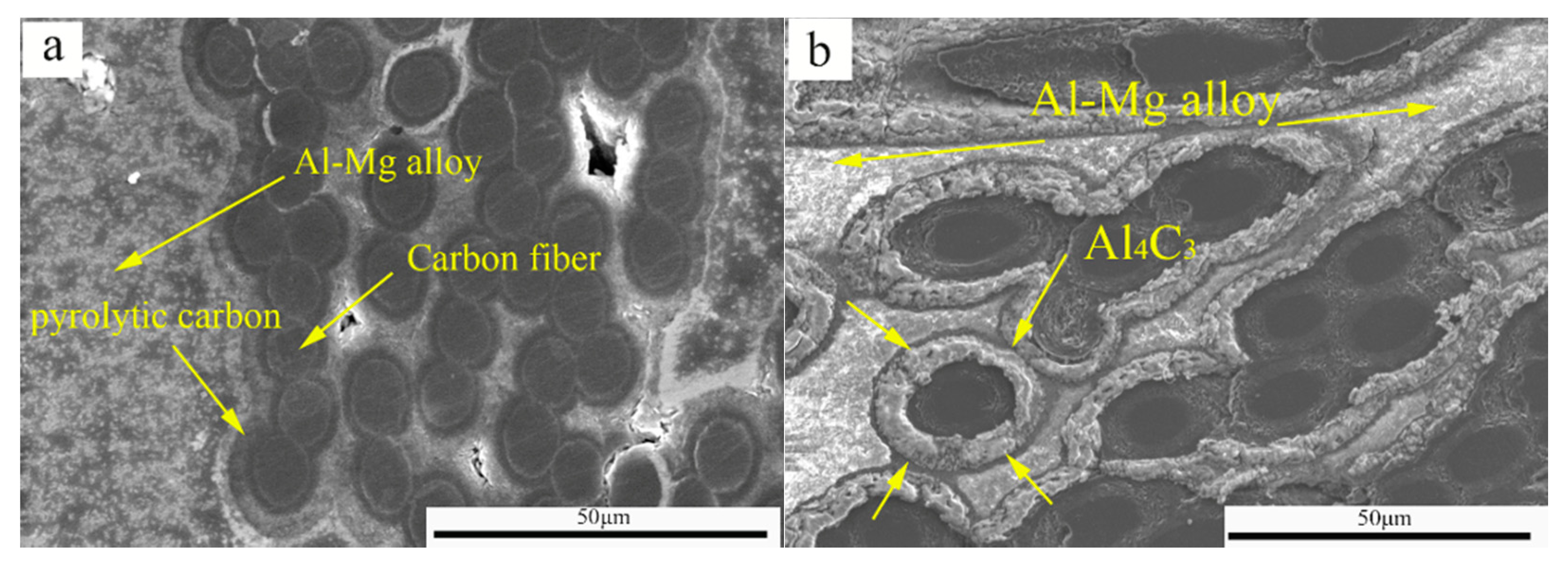
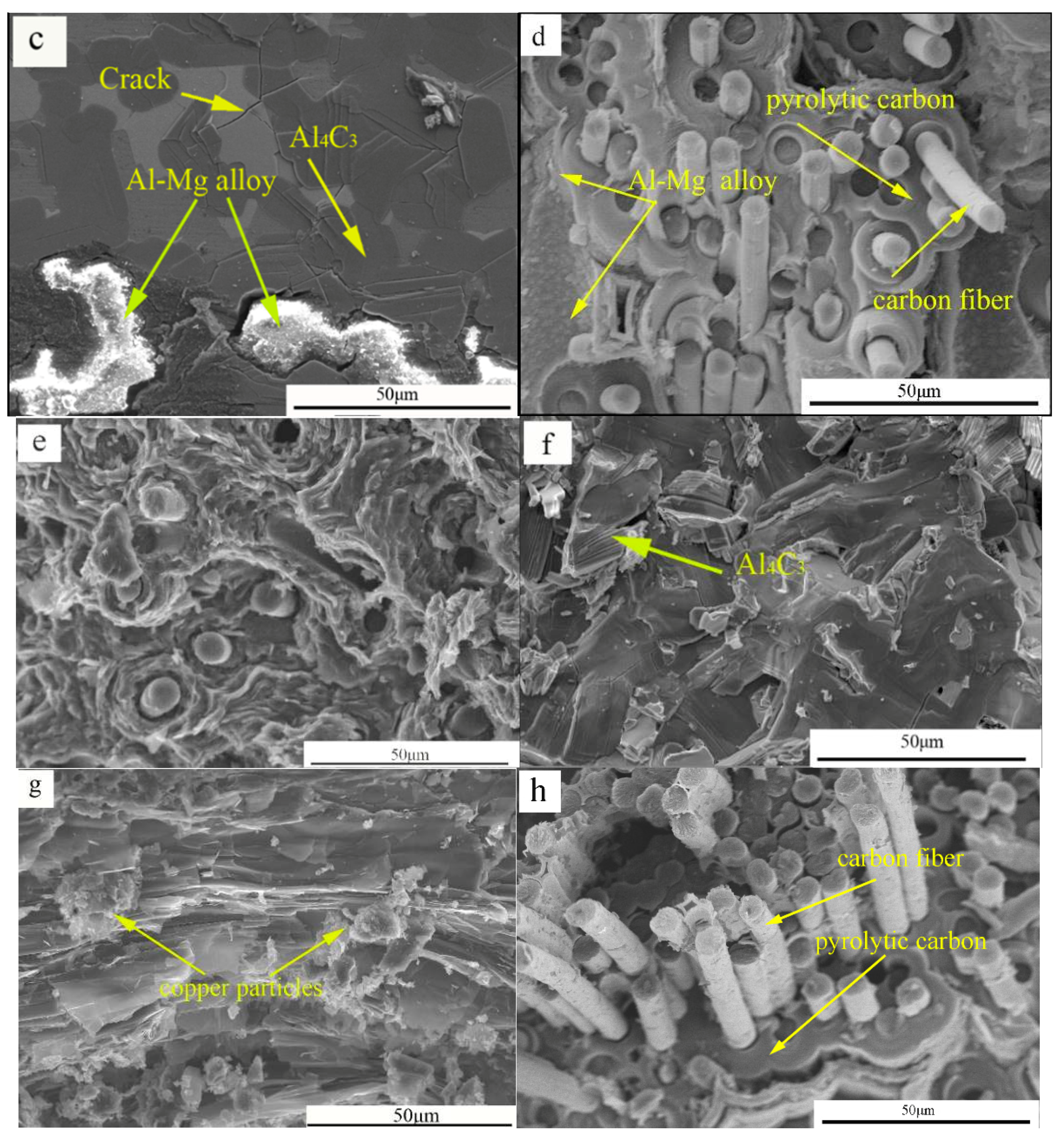
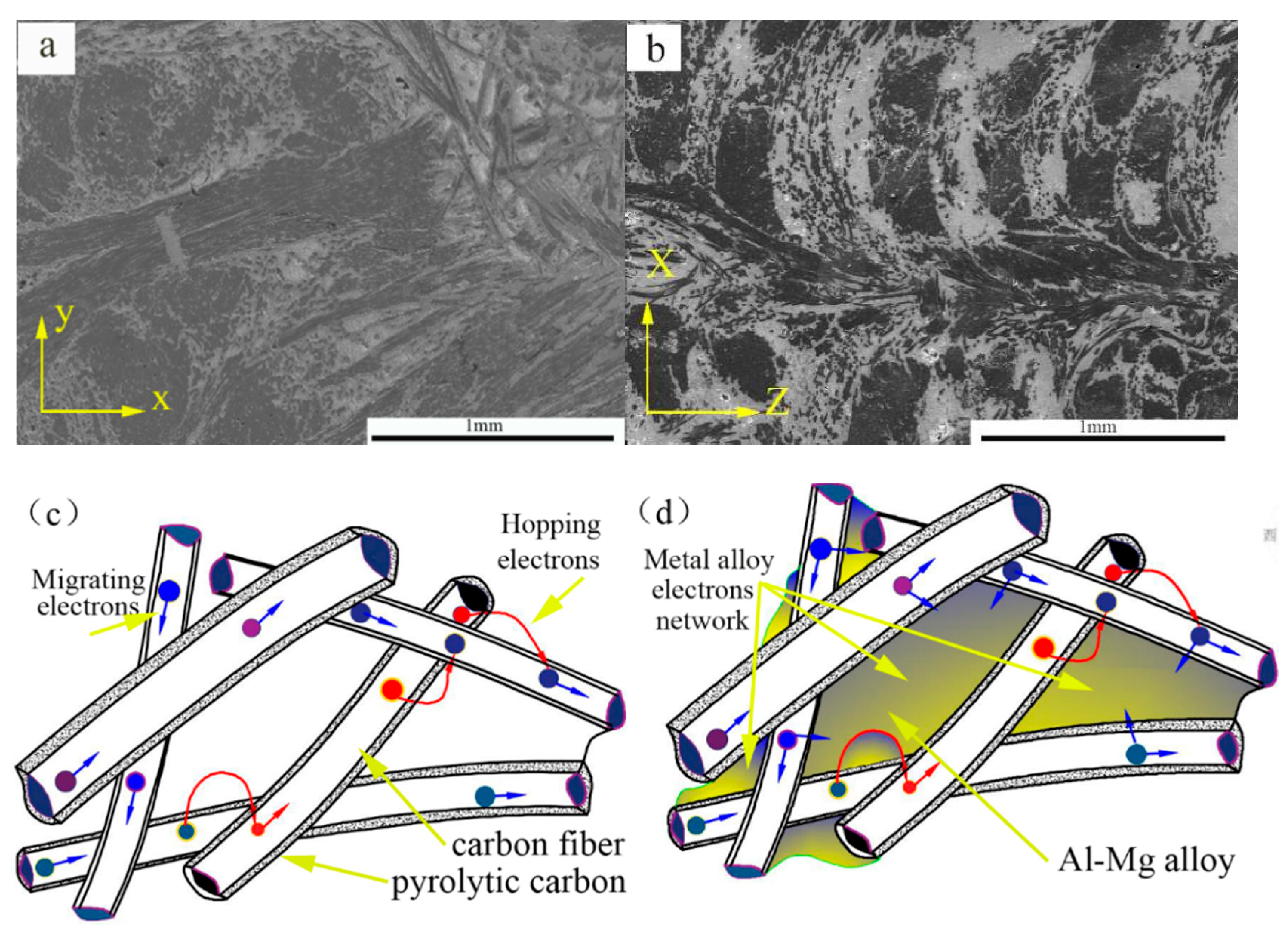
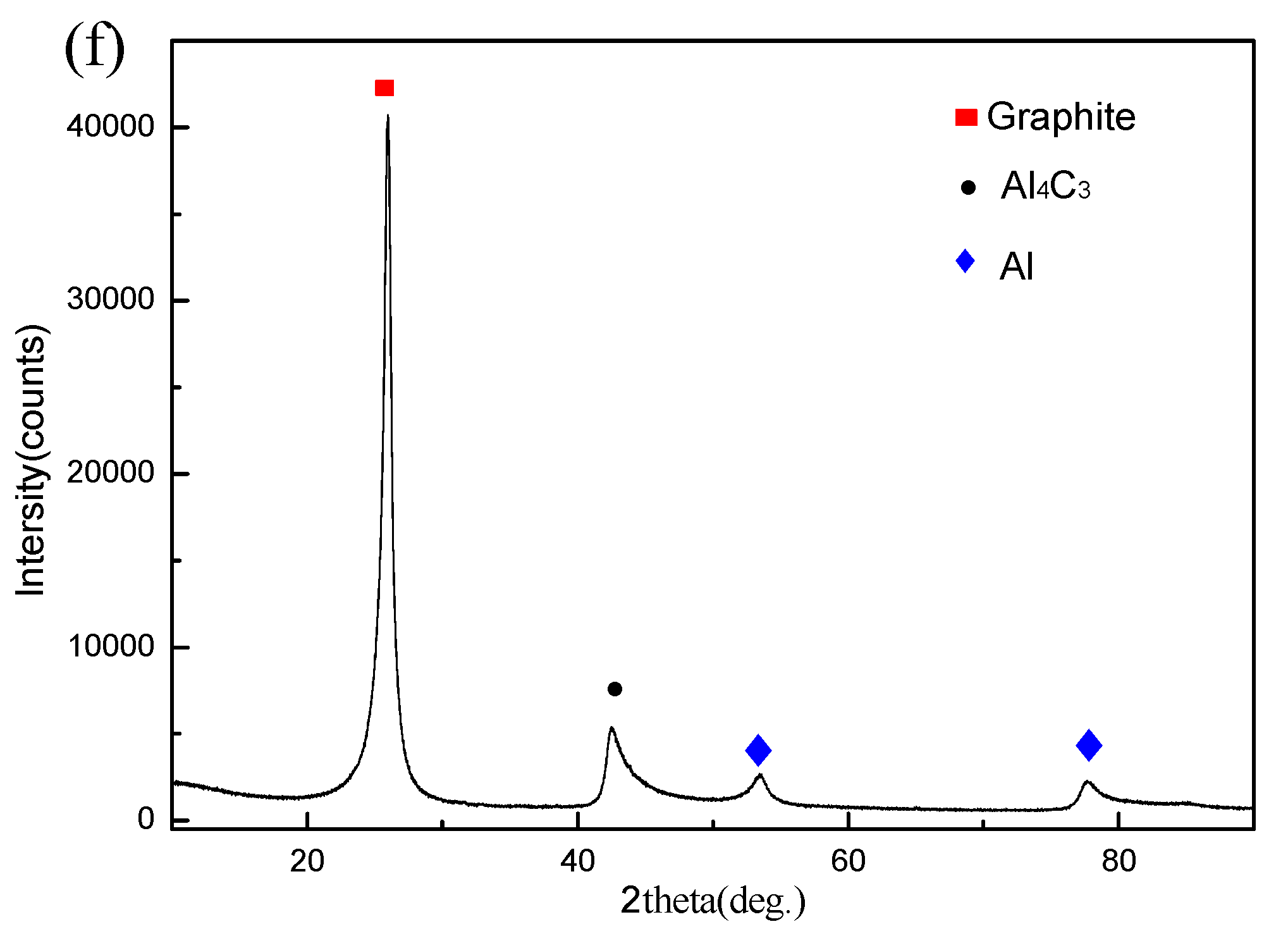
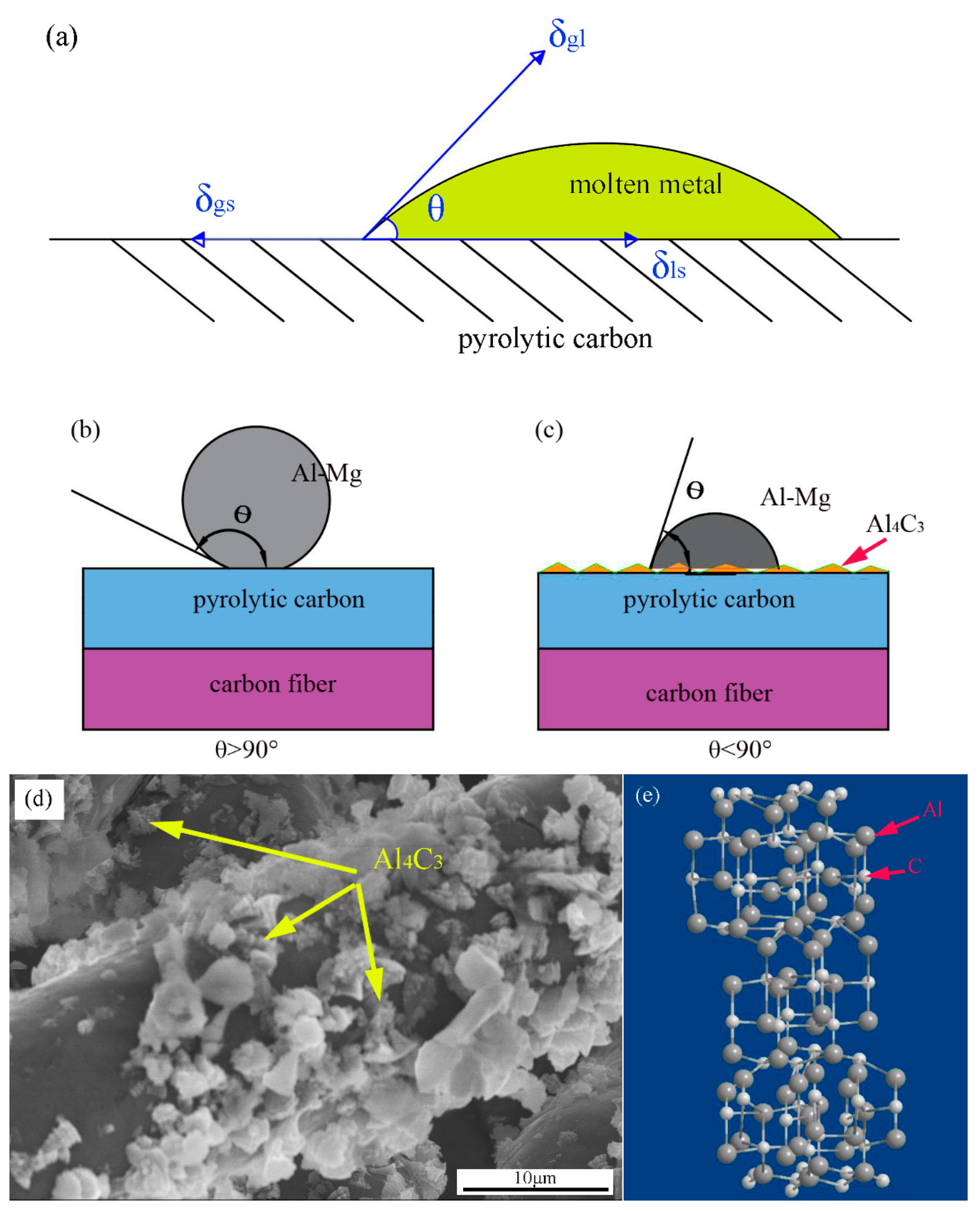
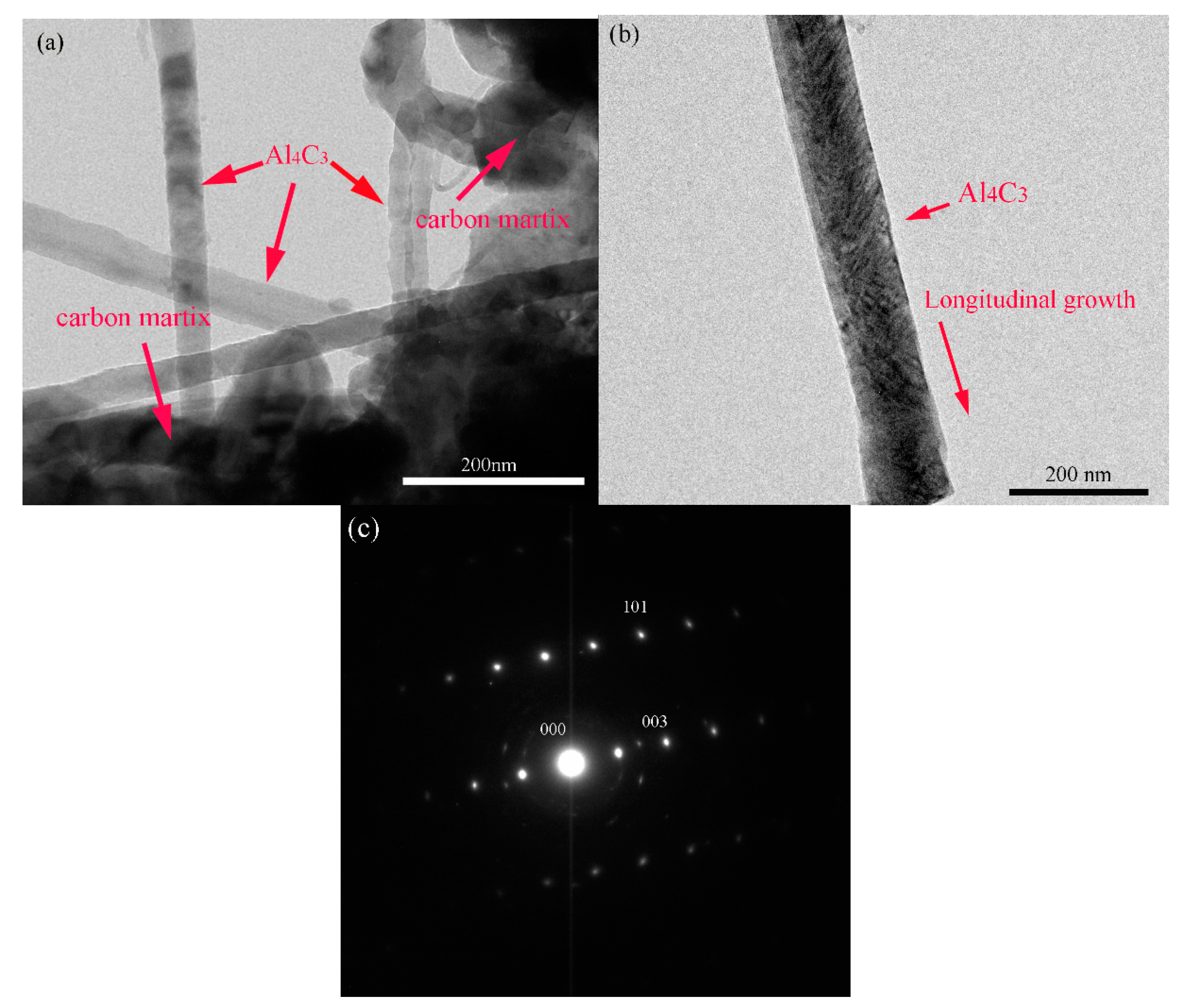
3.1. Microstructure
3.2. Mechanical Properties and Fracture Behavior of Composites
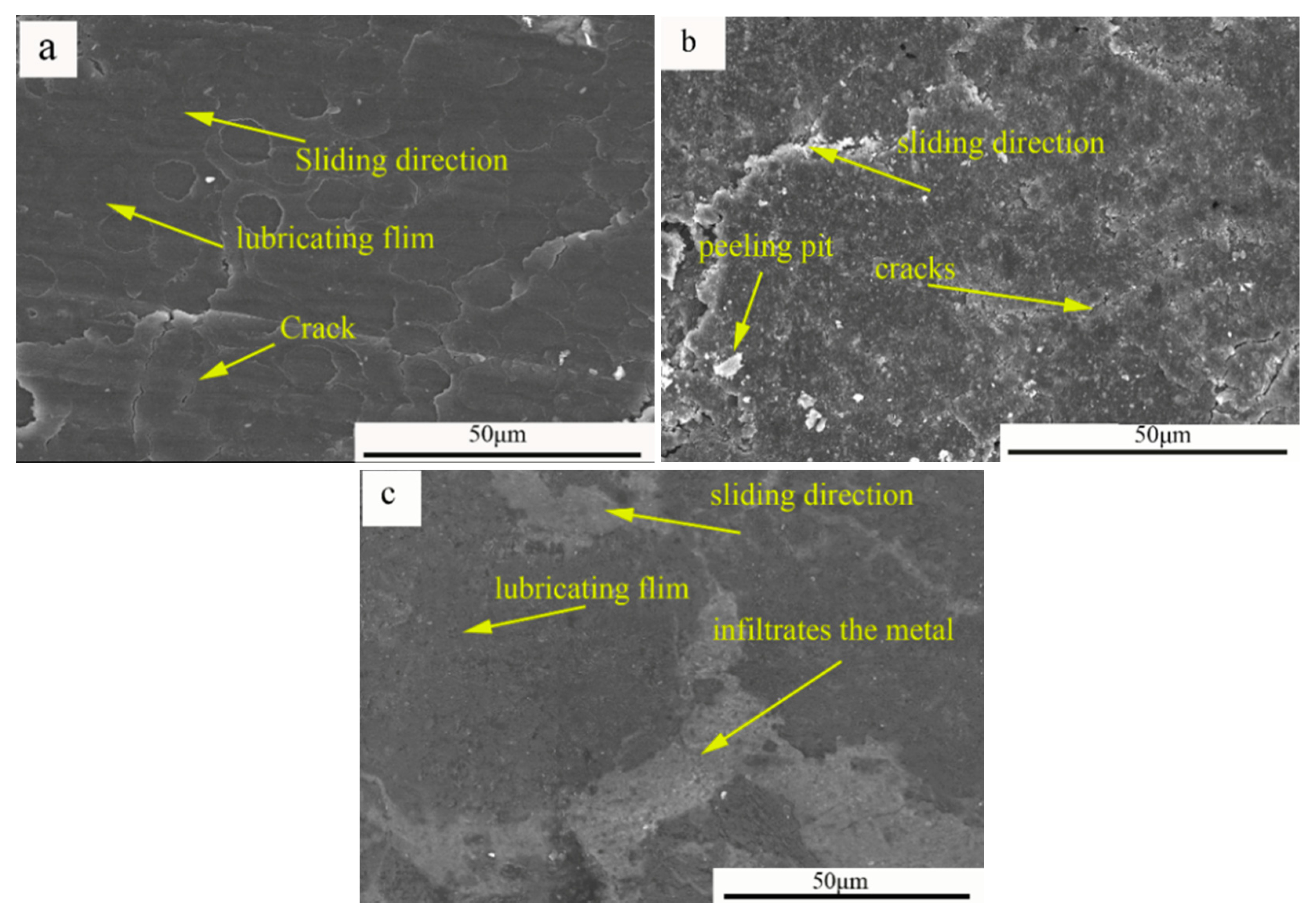
3.3. Friction Coefficient and Frictional Behavior of the Composites
3.4. Electrical Performance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The results showed that flexural strength of C/C–Al–Mg composites was 183 MPa, whereas the bending property of C/C composites reached 165 MPa. The compressive strengths of C/C–Al–Mg and C/C composites measured 206 and 142 MPa, respectively. The flexural strength and compressive strength of the steeped metal slider material reached 121 and 104 MPa, respectively. Compared with industry standards, the flexural strength of the powder metallurgy of the pantograph was higher than 80 MPa, whereas C/C–Al–Mg met the requirements of pantograph materials.
- (2)
- The resistivities of C/C–Al–Mg and C/C composites were 1.63 and 3.56 µΩm, respectively. C/C–Al–Mg had a good electrical conductivity, which was considerably less than the 12 µΩm industry standard of pantograph conductivity materials.
- (3)
- The friction coefficient of the steeped metal slide composite was 0.068 whereas that of C/C composite was 0.152. When the Al–Mg alloy infiltrated the C/C composites, the friction coefficient increased from 0.152 to 0.189.
- (4)
- The final contact angle on the reaction product, Al4C3, was lower than the initial contact angle on the original substrate, graphite.
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Luo, R.Y.; Liu, T.; Li, J.S. Thermophysical properties of carbon/carbon composites and physical mechanism of thermal expansion and thermal conductivity. Carbon 2004, 42, 2887–2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheehan, J.E.; Buesking, K.W.; Sullivan, B.J. Carbon-carbon composites. Ann. Rev. Mater. Sci. 1994, 24, 19–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.L.; Li, Y.L.; Li, H.J.; Li, S.P.; Guo, L.J. Quasi-static and dynamic compressive fracture behavior of carbon/carbon composites. Carbon 2008, 46, 699–703. [Google Scholar]
- Fei, Y.B.; Lu, J.H.; Li, H.J.; Guo, L.J.; Chen, Z.S. Influence of heat treatment temperature on microstructure and thermal expansion properties of 2D carbon/carbon composites. Vacuum 2014, 2, 51–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.Y.; Liu, G.H.; Jin, H.B.; Chen, K.X. In situ synthesis of TiC reinforced metal matrix composite (MMC) coating by self-propagating high temperature synthesis (SHS). J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 30, 301–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.H.; Wang, H.Y.; Yang, Y.F.; Wang, Y.Y.; Jiang, Q.C. Evolution process of the synthesis of TiC in the Cu-Ti-C system. J. Alloys Compd. 2008, 452, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitai, C.A.; Suman, C.; Naresh, C.M.; Pranab, S.; Tapas, K. Effect of thermally reduced grapheme oxide on mechanical properties of woven carbon fiber/epoxy composite. Crystals 2018, 8, 111. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.C.; Cao, Y.; Yi, M.D.; Xie, L.H.; Huang, W.; Tang, N.J. Thermostability, photoluminescence, and electrical properties of reduced grapheme oxide-carbon nanotube hybrid materials. Crystals 2013, 3, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, S.; Kato, K. Effect of arc discharge on wear rate of Cu-impregnated carbon contact strip in unlubricated sliding against Cu trolley under electric current. Wear 1998, 216, 172–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuyama, S. Electric contact tribological behavior of pantograph. Toyo Denki Giho 1995, 91, 52–60. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.; Zhang, M.; Xu, Y. Effect of the electric current on the friction and wear properties of the CNT-Ag-G composites. Carbon 2005, 43, 2685–2692. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, M.Y.; Luo, R.Y.; Hou, Z.H.; Yang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, C.L. Effect of structure of of pyrocarbon on the static and dynamic mechanical properties of carbon/carbon composites. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 614, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.Y.; Zhong, Y.M.; Yun, H.B. Influence of lubrication on tribology properties of C/C composites. Chin. J. Nonferrous Met. 2004, 14, 1405–1409. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, L.H.; Ju, L.Y.; Zhou, J.M.; Li, S.L.; Zhang, T.; Tian, W.L. Tensile and fatigue behavior of carbon fiber reinforced magnesium composite fabricated by liquid-solid extrusion following vacuum pressure infiltration. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 721, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.G.; Zhu, X.Z.; Gao, T.; Liu, X.F. Revealing the roles of Al4C3 and Al8Mn5 during α-Mg nucleation in Mg-Al based alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 705, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.T.; Pinero, E.; Narciso, J.; Louis, E. Effects of temperature on pressure infiltration of liquid Al and Al-12wt. %Si alloy into packed Sic particles. Scr. Mater. 2005, 53, 1483–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narciso, J.; Alonso, A.; Pamies, A.; Garcia-Cordovvila, C.; Louis, E. Wettability of binary and ternary alloys of the system Al-Si-Mg with SiC. Scr. Metall. Mater. 1994, 31, 1495–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etter, T.; Schulz, P.; Weber, M.; Metz, J.; Wimmler, M.; Loffler, J.F.; Uggowitzer, P.J. Aluminium carbide formation in interpenetrating graphite/aluminium composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 448, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, A.A. Magnesium casting technology for structural applications. Magn. Alloy 2013, 1, 2–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.X.; Li, P.G.; Gu, M.Y.; Wu, R.J. Interface evolution and its relationship with fracture strength in C/Al, C/Al-Ti and C/Al-Cu composite materials. Compos. Interfaces 1993, 1, 75–86. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Barber, G.C.; Liu, J. Friction and wear in high speed sliding with and without electrical current. Wear 2001, 249, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.Z.; Yin, X.W.; Fan, S.W. Tribological behavior of three-dimensional needled ceramic modified carbon/carbon composites in seawater conditions. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2013, 87, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.W.; Luo, R.Y. Mechanical properties investigation of carbon/carbon composites fabricated by a fast densification process. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 2361–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, R.Y.; Cheng, J.W.; Wang, T.M. Oxidation behavior and protection of carbon/carbon composites prepared using rapid directional diffused CVI techniques. Carbon 2002, 40, 1965–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guellali, M.; Oberacker, R.; Hoffmann, M.J. Influence of the matrix microstructure on the mechanical properties of CVI-infiltrated carbon fiber felts. Carbon 2005, 43, 1954–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, K.; Talreja, R. Modeling of compressive failure in fiber reinforced composites. Int. Solids Struct. 2000, 37, 2405–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narciso, J.; Garcia-Cordovilla, C.; Louis, E. Reactivity of thermally oxidized and unoxidized SiC particulates with aluminium-Silicon alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 1992, 15, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, A.; Narciso, J.; Pamies, C.; Garcia-Cordovvila, C.; Louis, E. Effect of K2ZrF6 coatings on pressure infiltration of packed SiC particulates by liquid aluminum. Scr. Metall. Mater. 1993, 29, 1559–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reznik, B.; Guellali, M.; Gerthsen, D.; Oberacker, R.; Hoffmann, M.J. Microstructure and mechanical properties of carbon/carbon composites with multilayered pyrocarbon matrix. Mater. Lett. 2002, 52, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.J.; Luo, R.Y. A novel bronze-impregnated carbon strip containing Al2O3 particles for subway current collectors. Wear 2011, 270, 675–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.J.; Luo, R.Y.; Han, S.; Li, M.D. Effect of the ratio of graphite/pitch coke on the mechanical and tribological properties of copper-carbon composites. Wear 2010, 11, 1337–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.J.; Luo, R.Y. Effect of coal tar pitch modified by sulfur as a binder on the mechanical and tribological properties of bronze-impregnated carbon-matrix composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 2011, 528, 2929–2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.L.; Qi, L.H.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, J.M.; Li, H.J. Interfacial microstructure and tensile properties of carbon fiber reinforced Mg-Al-RE matrix composites. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 663, 686–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagasawa, H.; Kato, K. Wear mechanism of copper alloy wire sliding against iron-base contact strip under electric current. Wear 1998, 216, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Luo, R.Y. A novel preparation and properties of in-situ grown carbon nanotube reinforced carbon/carbon composites. Vacuum 2016, 132, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.; Luo, R.Y. Effect of carbon nanotubes on the electron magnetic shielding properties of Sicf/Sic composites. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 745, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narciso, J.; Molina, J.M.; Rodríguez, A.; Rodríguez-Reinoso, F.; Louis, E. Effects of infiltration pressure on mechanical properties of Al-12Si/graphite composites for piston engines. Compos. Part B 2016, 91, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancin, M.; Marhic, C. TEM study of carbon fiber reinforced aluminium matrix composites: Influence of brittle phases and interface on mechanical properties. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2000, 20, 1493–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderon, N.R.; Voytovych, R.; Narciso, J.; Eustathopoulos, N. Wetting dynamics versus interfacial reactivity of Al-Si alloys on carbon. Mater. Sci. 2010, 45, 2150–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderon, N.R.; Voytovych, R.; Narciso, J.; Eustathopoulos, N. Pressureless infiltration versus wetting in AlSi/graphite system. Mater Sci. 2010, 45, 4345–4350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danilo, S.; Antonio, C.; Jose, M.M.; Alberto, O.; Javier, N. Surface growth for molten silicon infiltration into carbon millimeter-sized channels; Lattic-Boltzmann simulations, experiments and models. Mod. Phys. C 2016, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozcan, S.; Filip, P. Microstructure and wear mechanisms in C/C composites. Wear 2005, 259, 642–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.Y.; Lin, P.; Dong, G.N.; Zeng, Q.F. Mechanical and tribological properties of self-lubricating laminated composites with flexible design. Mater. Des. 2013, 50, 830–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasem, H.; Bonnamy, S.; Berthier, Y.; Dufrénocy, P.; Jacquemard, P. Tribological physicochemical and thermal study of the abrupt friction transition during carbon/carbon composites friction. Wear 2009, 267, 846–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Cordovilla, C.; Narciso, J.; Louis, E. Abrasive wear resistance of aluminium alloy/ceramic particulate composites. Wear 1996, 192, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, M.; Vragovic, I.; Molina, J.M.; Prieto, R.; Narciso, J.; Louis, E. 1/f Noise in sliding friction under wear conditions: The role of debris. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 102, 045501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Ran, L.; Yi, M.Z. Carbon fiber knitted fabric reinforced copper composite for sliding contact material. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 2365–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, C.C.; Zhang, Z.C.; Liang, P.; Shi, Y.H. Interfacial microstructure and grown mechanism of Al4C3 in Grf/Al composites fabricated by liquid pressure method. Micron 2014, 65, 10–14. [Google Scholar]
- Che, Z.F.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.W.; Zhang, H.L.; Wang, X.T.; Sun, C. Nucleation and growth mechanisms of interfacial Al4C3 in Al/diamond composites. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 65, 781–789. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, S.; Xu, E.Z.; Zhu, Z.F.; Liu, Q.; Yu, S.M.; Liu, J.W. Mechanical and wear performance of aluminum/sintered-carbon composites produced by pressure infiltration for pantograph slider. Powder Technol. 2018, 326, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cui, L.; Luo, R.; Cui, G. Effect of Al–Mg Alloy Infiltration on Mechanical and Electrical Properties for Carbon/Carbon Composites. Crystals 2018, 8, 196. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst8050196
Cui L, Luo R, Cui G. Effect of Al–Mg Alloy Infiltration on Mechanical and Electrical Properties for Carbon/Carbon Composites. Crystals. 2018; 8(5):196. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst8050196
Chicago/Turabian StyleCui, Lihui, Ruiying Luo, and Guangyuan Cui. 2018. "Effect of Al–Mg Alloy Infiltration on Mechanical and Electrical Properties for Carbon/Carbon Composites" Crystals 8, no. 5: 196. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst8050196
APA StyleCui, L., Luo, R., & Cui, G. (2018). Effect of Al–Mg Alloy Infiltration on Mechanical and Electrical Properties for Carbon/Carbon Composites. Crystals, 8(5), 196. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst8050196




