Mono- and Bimetalic Amidoboranes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
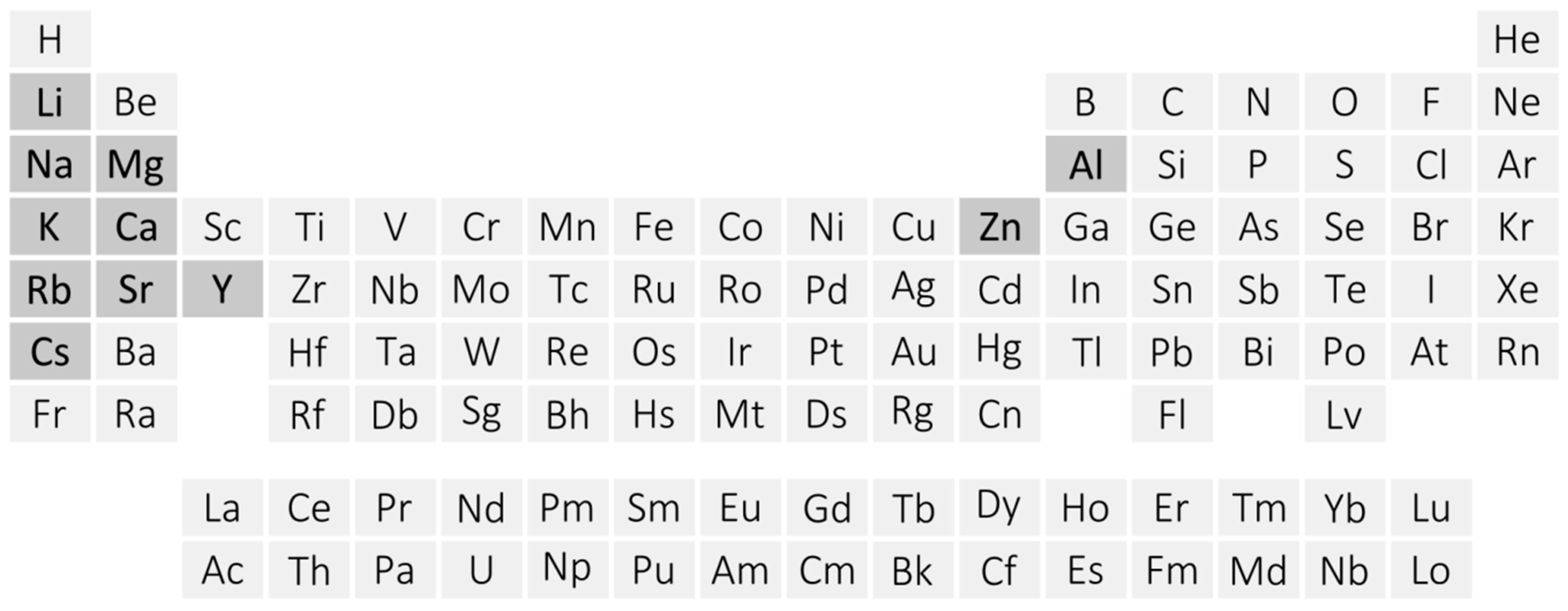
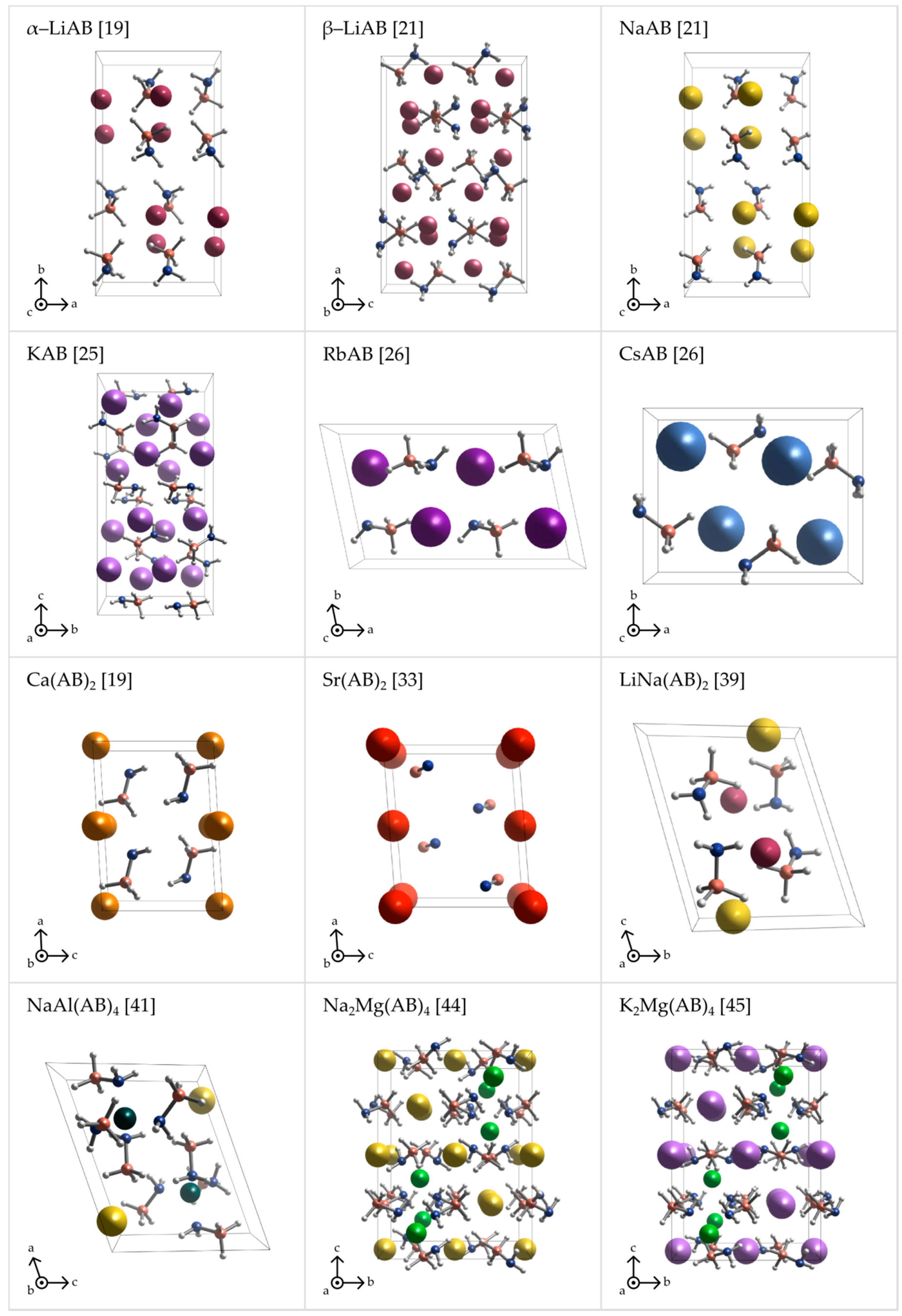
2. Crystal Structures of Metal Amidoboranes
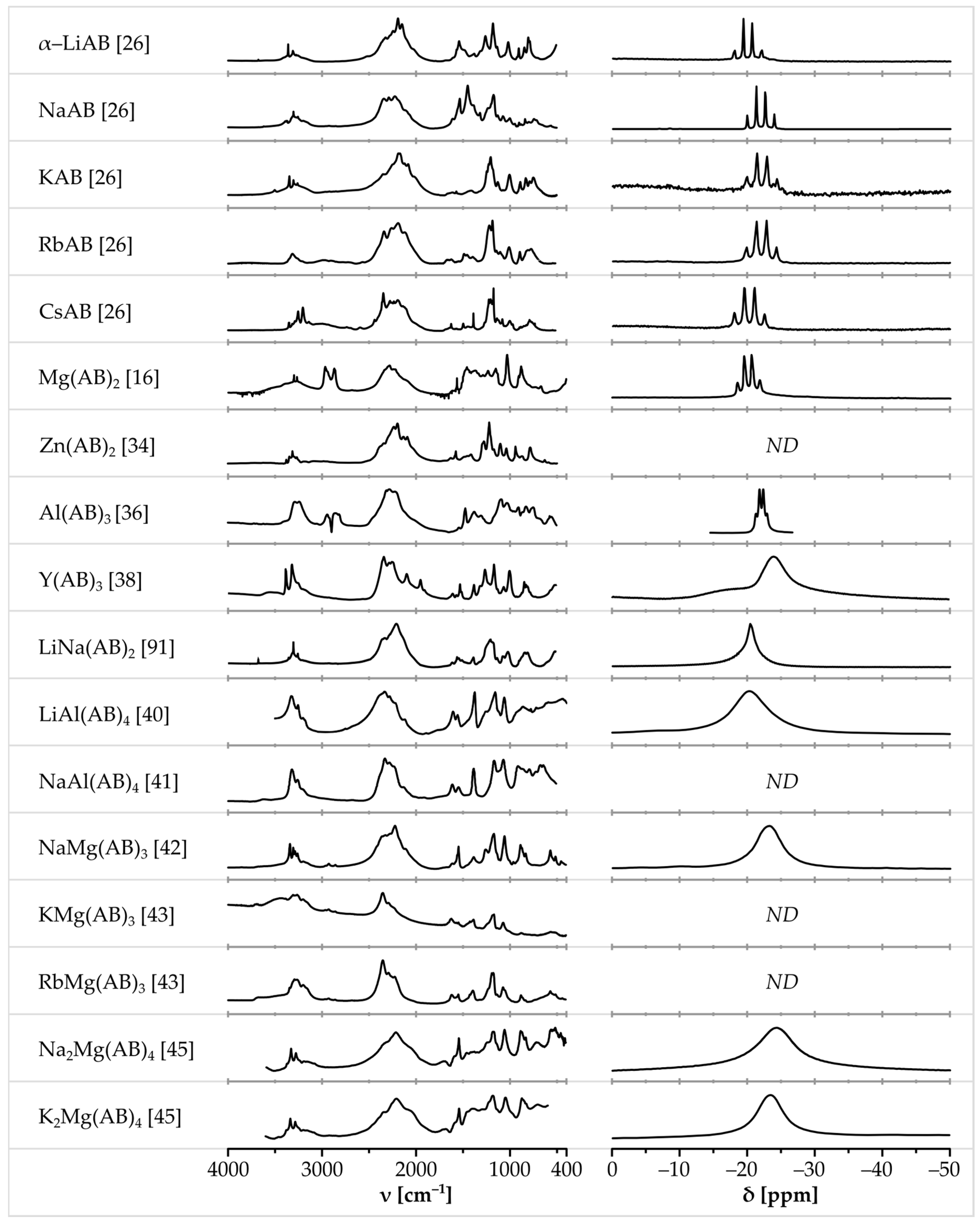
3. NMR, IR and Raman Spectra of Metal Amidoboranes
4. Thermal Decomposition of Metal Amidoboranes
5. Synthesis, Reactivity and Selected Properties of Metal Amidoboranes
5.1. Alkali Metal Amidoboranes
5.1.1. Alpha-Lithium Amidoborane, α-LiNH2BH3 [α-LiAB]
5.1.2. Beta-Lithium Amidoborane, β-LiNH2BH3 [β-LiAB]
5.1.3. Sodium Amidoborane, NaNH2BH3 [NaAB]
5.1.4. Potassium Amidoborane, KNH2BH3 [KAB]
5.1.5. Rubidium Amidoborane, RbNH2BH3 [RbAB]
5.1.6. Cesium Amidoborane, CsNH2BH3 [CsAB]
5.2. Alkaline Earth Metal Amidoboranes
5.2.1. Magnesium Amidoborane Mg(NH2BH3)2 [Mg(AB)2]
5.2.2. Calcium Amidoborane Ca(NH2BH3)2 [Ca(AB)2]
5.2.3. Strontium Amidoborane Sr(NH2BH3)2 [Sr(AB)2]
5.3. Other Metal and Mixed Metal Amidoboranes
5.3.1. Zinc amidoborane Zn(NH2BH3)2 [Zn(AB)2]
5.3.2. Aluminum Amidoborane Al(NH2BH3)3 [Al(AB)3]
5.3.3. Yttrium Amidoborane Y(NH2BH3)3 [Y(AB)3]
5.3.4. Lithium–Sodium Amidoborane, LiNa(NH2BH3)2 [LiNa(AB)2]
5.3.5. Lithium–Aluminum Amidoborane, LiAl(NH2BH3)4 [LiAl(AB)4]
5.3.6. Sodium–Aluminum Amidoborane Composite, NaAl(NH2BH3)4 [NaAl(AB)4]
5.3.7. Sodium–Magnesium Amidoborane, NaMg(NH2BH3)3 [NaMg(AB)3]
5.3.8. Potassium–Magnesium Amidoborane, KMg(NH2BH3)3 [KMg(AB)3]
5.3.9. Rubidium–Magnesium Amidoborane, RbMg(NH2BH3)3 [RbMg(AB)3]
5.3.10. Disodium–Magnesium Amidoborane, Na2Mg(NH2BH3)4 [Na2Mg(AB)4]
5.3.11. Dipotassium–Magnesium Amidoborane, K2Mg(NH2BH3)4 [K2Mg(AB)4]
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shore, S.G.; Parry, R.W. The crystalline compound ammonia borane, H3NBH3. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1955, 77, 6084–6085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, J.; Baitalow, F.; Wolf, G. Thermal decomposition of polymeric aminoborane (H2BNH2)x under hydrogen release. Thermochim. Acta 2005, 430, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, M.E.; Gainsford, G.J.; Robinson, W.T. Room-Temperature Structure of Ammonia Borane. Aust. J. Chem. 2007, 60, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klooster, W.T.; Koetzle, T.F.; Siegbahn, P.E.M.; Richardson, T.B.; Crabtree, R.H. Study of the N–H∙∙∙H–B Dihydrogen Bond Including the Crystal Structure of BH3NH3 by Neutron Diffraction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 6337–6343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, Y.S.; Chen, P.; Wu, G.; Xiong, Z. Development of amidoboranes for hydrogen storage. Chem. Comm. 2011, 47, 5116–5129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, B.L.; Dixon, D.A.; Garner, E.B.; Gordon, J.C.; Matus, M.H.; Scott, B.; Stephens, F.H. Efficient Regeneration of Partially Spent Ammonia Borane Fuel. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 6812–6816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, M.G.; Geanangel, R.A.; Wendlandt, W.W. The thermal decomposition of ammonia borane. Thermochim. Acta 1978, 23, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frueh, S.; Kellett, R.; Mallery, C.; Molter, T.; Willis, W.S.; King’ondu, C.; Suib, S.L. Pyrolytic Decomposition of Ammonia Borane to Boron Nitride. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 50, 783–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hess, N.J.; Schenter, G.K.; Hartman, M.R.; Daemen, L.L.; Proffen, T.; Kathmann, S.M.; Mundy, C.J.; Hartl, M.; Heldebrant, D.J.; Stowe, A.C.; et al. Neutron Powder Diffraction and Molecular Simulation Study of the Structural Evolution of Ammonia Borane from 15 to 340 K. J. Phys. Chem. A 2009, 113, 5723–5735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephens, F.H.; Pons, V.; Baker, R.T. Ammonia-borane: The hydrogen source par excellence? Dalton Trans. 2007, 25, 2613–2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staubitz, A.; Robertson, A.P.M.; Manners, I. Ammonia-Borane and Related Compounds as Dihydrogen Sources. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 4079–4124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grochala, W.; Edwards, P.P. Thermal Decomposition of the Non-Interstitial Hydrides for the Storage and Production of Hydrogen. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 1283–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlesinger, H.I.; Burg, A.B. Hydrides of Boron. VIII. The Structure of the Diammoniate of Diborane and its Relation to the Structure of Diborane. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1938, 60, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niedenzu, P.M. Studies on Polyboron Hydride Anions and Ammine-Borane. Ph.D. Thesis, The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Salupo, T. Preparations of Ytterbium and Europium Borides from Yb(II) and Eu(II) Boron Hydride Precursors. Ph.D. Thesis, The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- DeGraffenreid, A.L. Studies on Boron—Nitrogen and Boron—Gadolinium Compounds. Ph.D. Thesis, The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Myers, A.G.; Yang, B.H.; Kopecky, D.J. Lithium Amidotrihydroborate, a Powerful New Reductant. Transformation of Tertiary Amides to Primary Alcohols. Tetrahedron Lett. 1996, 37, 3623–3626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Z.; Yong, C.K.; Wu, G.; Chen, P.; Shaw, W.; Karkamkar, A.; Autrey, T.; Jones, M.O.; Johnson, S.R.; Edwards, P.P.; et al. High-capacity hydrogen storage in lithium and sodium amidoboranes. Nat. Mater. 2008, 7, 138–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Zhou, W.; Ylidirim, T. Alkali and Alkaline-Earth Metal Amidoboranes: Structure, Crystal Chemistry and Hydrogen Storage Properties. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 14834–14839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Wu, G.; Xiong, Z.; David, W.I.F.; Ryan, K.R.; Jones, M.O.; Edwards, P.P.; Chu, H.; Chen, P. Stepwise Phase Transition in the Formation of Lithium Amidoborane. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 49, 4319–4323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, K.R. A Study of Ammonia Borane and its Derivatives. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Oxford, Oxford, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, Z.; Wu, G.; Chua, Y.S.; Hu, J.; He, T.; Xu, W.; Chen, P. Synthesis of sodium amidoborane (NaNH2BH3) for hydrogen production. Energy Environ. Sci. 2008, 1, 360–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fijalkowski, K.J.; Grochala, W. Substantial emission of NH3 during thermal decomposition of sodium amidoborane, NaNH2BH3. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 2043–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fijalkowski, K.J.; Jurczakowski, R.; Kozminski, W.; Grochala, W. Insights from impedance spectroscopy into the mechanism of thermal decomposition of M(NH2BH3), M = H, Li, Na, Li0.5Na0.5, hydrogen stores. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2012, 14, 5778–5784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diyabalanage, H.V.K.; Nakagawa, T.; Shrestha, R.P.; Semelsberger, T.A.; Davis, B.L.; Scott, B.L.; Burrell, A.K.; David, W.I.F.; Ryan, K.R.; Jones, M.O.; et al. Potassium(I) Amidotrihydroborate: Structure and Hydrogen Release. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 11836–11837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owarzany, R.; Fijalkowski, K.J.; Palasyuk, T.; Jaroń, T.; Grochala, W. Heavy alkali metal amidoboranes: RbNH2BH3 and CsNH2BH3. Unpublished work. 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Haider, S. Borazane (H3BNH3) Based Hydrogen Storage Materials. Ph.D. Thesis, Queen Mary, University of London, London, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, X.; Ma, L.; Fang, Z.; Gao, L.; Luo, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, P. Promoted hydrogen release from ammonia borane by mechanically milling with magnesium hydride: A new destabilizing approach. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2009, 11, 2507–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Kang, X.; Wang, P. Synthesis, formation mechanism, and dehydrogenation properties of the long-sought Mg(NH2BH3)2 compound. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 1018–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wolverton, C. Crystal Structures, Phase Stabilities, and Hydrogen Storage Properties of Metal Amidoboranes. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 14224–14231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diyabalanage, H.V.K.; Shrestha, R.P.; Semelsberger, T.A.; Scott, B.L.; Bowden, M.E.; Davis, B.L.; Burrell, A.K. Calcium Amidotrihydroborate: A Hydrogen Storage Material. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 8995–8997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spielmann, J.; Jansen, G.; Bandmann, H.; Harder, S. Calcium Amidoborane Hydrogen Storage Materials: Crystal Structures of Decomposition Products. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 6290–6391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Tang, C.; Fang, C.; Fang, F.; Sun, D.; Ouyang, L.; Zhu, M. Synthesis, Crystal Structure, and Thermal Decomposition of Strontium Amidoborane. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 1709–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owarzany, R. Synthesis and Characterisation of Zinc Amidoborane. Bachelor’s Thesis, University of Warsaw, Warsaw, Poland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hawthorne, M.F.; Jalisatgi, S.S.; Safronov, A.V.; Lee, H.B.; Wu, J. Chemical Hydrogen Storage Using Polyhedral Borane Anions and Aluminum-Ammonia-Borane Complexes; Final Report; University of Missouri. 2010. Available online: http://www.osti.gov/scitech//servlets/purl/990217-xUxbgx/ (accessed on 20 April 2016). [Google Scholar]
- Jalisatgi, S.S.; Wu, J.; Hawthorne, M.F. Chemical Hydrogen Storage Using Aluminum Ammonia-borane Complexes; Report, University of Missouri. 2009. Available online: https://www.hydrogen.energy.gov/pdfs/review09/stp_20_hawthorne.pdf/ (accessed on 28 April 2016). [Google Scholar]
- Hoy, J.M. Syntheses of Aluminum Amidotrihydroborate Compounds and Ammonia Triborane as Potential Hydrogen Storage Materials. M.Sc. Thesis, The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Genova, R.V.; Fijalkowski, K.J.; Budzianowski, A.; Grochala, W. Towards Y(NH2BH3)3: Probing hydrogen storage properties of YX3/MNH2BH3 (X = F, Cl; M= Li, Na) and YHx∼3/NH3BH3 composites. J. Alloys. Comp. 2010, 499, 144–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fijalkowski, K.J.; Genova, R.V.; Filnchuk, Y.; Budzianowski, A.; Derzsi, M.; Jaron, T.; Leszczynski, P.J.; Grochala, W. Na[Li(NH2BH3)2]—The first mixed-cation amidoborane with unusual crystal structure. Dalton Trans. 2010, 40, 4407–4413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, G.; Tan, Y.; Chen, X.; Guo, Z.; Liu, H.; Yu, X. Mixed-metal (Li, Al) amidoborane: synthesis and enhanced hydrogen storage properties. J. Mater. Chem. A. 2013, 1, 1810–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dovgaliuk, I.; Jepsen, L.H.; Safin, D.A.; Łodziana, Z.; Dyadkin, V.; Jensen, T.R.; Devillers, M.; Filinchuk, Y. A Composite of Complex and Chemical Hydrides Yields the First Al-Based Amidoborane with Improved Hydrogen Storage Properties. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 14562–14570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, X.; Luo, J.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, P. Combined formation and decomposition of dual-metal amidoborane NaMg(NH2BH3)3 for high-performance hydrogen storage. Dalton Trans. 2011, 40, 3799–3801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, X.-D.; Luo, J.-H.; Wang, P. Efficient and highly rapid hydrogen release from ball-milled 3NH3BH3/MMgH3 (M [Na, K, Rb]) mixtures at low temperatures. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2012, 37, 4259–4266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhou, W.; Pinkerton, F.E.; Meyer, M.S.; Yao, Q.; Gadipelli, S.; Udovic, T.J.; Yildirim, T.; Rush, J.J. Sodium magnesium amidoborane: the first mixed-metal amidoborane. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 4102–4104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chua, Y.S.; Li, W.; Wu, G.; Xiong, Z.; Chen, P. From Exothermic to Endothermic Dehydrogenation—Interaction of Monoammoniate of Magnesium Amidoborane and Metal Hydrides. Chem. Mater. 2012, 24, 3574–3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Wang, J.; Chen, Z.; Wu, A.; Wu, G.; Yin, J.; Chu, H.; Xiong, Z.; Zhang, T.; Chen, P. Metathesis of alkali-metal amidoborane and FeCl3 in THF. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 7478–7483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, G.; Yu, X.; Guo, Y.; Wu, Z.; Yang, C.; Liu, H.; Dou, S. Amminelithium Amidoborane Li(NH3)NH2BH3: A New Coordination Compound with Favorable Dehydrogenation Characteristics. Chem. Eur. J. 2010, 16, 3763–3769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chua, Y.S.; Wu, G.; Xiong, Z.; Karkamkar, A.; Guo, J.; Jian, M.; Wong, M.W.; Autrey, T.; Chen, P. Synthesis, structure and dehydrogenation of magnesium amidoborane monoammoniate. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 5752–5754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Kang, X.; Fang, Z.; Wang, P. Promotion of hydrogen release from ammonia borane with magnesium nitride. Dalton Trans. 2011, 40, 6469–6474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chua, Y.S.; Wu, H.; Zhou, W.; Udovic, T.J.; Wu, G.; Xiong, Z.; Wong, M.W.; Chen, P. Monoammoniate of Calcium Amidoborane: Synthesis, Structure, and Hydrogen-Storage Properties. Inorg. Chem. 2012, 51, 1599–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chua, Y.S.; Wu, G.; Xiong, Z.; He, T.; Chen, P. Calcium Amidoborane Ammoniate; Synthesis, Structure, and Hydrogen Storage Properties. Chem. Mater. 2009, 21, 4899–4904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Beaumont, P.R.; Humphries, T.D.; Jensen, C.M.; Li, X. Efficient Synthesis of an Aluminum Amidoborane Ammoniate. Energies 2015, 8, 9107–9116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Wu, H.; Wu, G.; Li, Z.; Zhou, W.; Juz, X.; Xie, D.; Chen, P. Lithium amidoborane hydrazinates: synthesis, structure and hydrogen storage properties. J. Chem. Mater. A 2015, 3, 10100–10106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; He, T.; Wu, G.; Chen, W.; Chua, Y.S.; Guo, J.; Xie, D.; Ju, X.; Chen, P. Synthesis, structure and the dehydrogenation mechanism of calcium amidoborane hydrazinates. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Wu, G.; Xiong, Z.; Han, X.; Chu, H.; He, T.; Chen, P. LiNH2BH3∙NH3BH3: Structure and Hydrogen Storage Properties. Chem. Mater. 2010, 22, 3–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nöth, H.; Thomas, S.; Schmidt, M. Solvates of Lithium (Dimethylamino)trihydroborate. Chem. Ber. 1996, 129, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, P.C. Reactions of Lithium Dimethylamide with Some Borane Derivatives. Evidence for the Displacement of Lithium Hydride. Inorg. Chem. 1975, 14, 438–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mountford, A.J.; Clegg, W.; Coles, S.J.; Harrington, R.W.; Horton, P.N.; Humphrey, S.M.; Hursthouse, M.B.; Wright, J.A.; Lancaster, S.J. The Synthesis, Structure and Reactivity of B(C6F5)3-Stabilised Amide (M-NH2) Complexes of the Group 4 Metals. Chem. Eur. J. 2007, 13, 4535–4547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Blacque, O.; Fox, T.; Frech, C.M.; Berke, H. Development of Rhenium Catalysts for Amine Borane Dehydrocoupling and Transfer Hydrogenation of Olefins. Organometallics 2009, 28, 5493–5504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolstenholme, D.J.; Flogeras, J.; Che, F.N.; Decken, A.; McGrady, G.S. Homopolar Dihydrogen Bonding in Alkali Metal Amidoboranes: Crystal Engineering of Low-Dimensional Molecular Materials. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 2439–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellham, P.; Hill, M.S.; Kociok-Köhn, G. Alkali metal-mediated dehydrocoupling of Me2NH·BH3. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 12078–12081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stennett, T.E.; Harder, S. s-Block amidoboranes: Syntheses, structures, reactivity and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 1112–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spielmann, J.; Bolte, M.; Harder, S. Synthesis and structure of a magnesium-amidoborane complex and its role in catalytic formation of a new bis-aminoborane ligand. Chem. Commun. 2009, 45, 6934–6936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spielmann, J.; Piesik, D.F.-J.; Harder, S. Thermal Decomposition of Mono- and Bimetallic Magnesium Amidoborane Complexes. Chem. Eur. J. 2010, 16, 8307–8318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spielmann, J.; Harder, S. Hydrogen Elimination in Bulky Calcium Amidoborane Complexes: Isolation of a Calcium Borylamide Complex. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 5064–5065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spielmann, J.; Piesik, D.; Wittkamp, B.; Jansen, G.; Harder, S. Convenient synthesis and crystal structure of a monomeric zinc hydride complex with a three-coordinate metal center. Chem. Commun. 2009, 23, 3455–3456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forster, T.D.; Tuononen, H.M.; Parvez, M.; Roesler, R. Characterization of β-B-Agostic Isomers in Zirconocene Amidoborane Complexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 6689–6691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torgersen, A.N.; Jorgensen, S.W. Scaffolded Borazane-Lithium Hydride Hydrogen Storage Materials. U.S. Patent US 7166150 B2 (appl. 2005), 23 January 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Burrell, A.K.; Davis, B.J.; Thorn, D.L.; Gordon, J.C.; Baker, R.T.; Semelsberger, T.A.; Tumas, W.; Diyabalanage, H.V.K.; Shrestha, R.P. Metal Aminoboranes. U.S. Patent US 7713506 B2 (appl. 2008), 11 May 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Balema, V.; Josyula, K.; Xu, G.; Wallock, N.; Batcheller, S.; Gao, P.; Jasty, S. Metal Amidoborane Compositions and Processes for Their Preparation. U.S. Patent US 8920760 B2 (appl. 2010), 30 December 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.Y.; Singh, N.J.; Lee, H.M.; Kim, K.S. Hydrogen-Release Mechanisms in Lithium Amidoboranes. Chem. Eur. J. 2009, 15, 5598–5604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.L.; McKee, M.L. Mechanistic Study of LiNH2BH3 Formation from (LiH)4 + NH3BH3 and Subsequent Dehydrogenation. Inorg. Chem. 2009, 48, 7564–7575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swinnen, S.; Nguyen, V.S.; Nguyen, M.T. Potential hydrogen storage of lithium amidoboranes and derivatives. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2010, 489, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chittari, B.L.; Tewari, S.P. First principles calculations of LiNH2BH3, LiNH3BH4, and NaNH2BH3. Phys. Status Solidi B 2014, 251, 898–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, T. Crystal and electronic structures of solid M(NH2BH3)n (M = Li, Na, K) and the decomposition mechanisms. Int. J. Hydrog. Energ. 2014, 39, 21372–21379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhang, J.G.; He, P. Theoretical study on the structure and dehydrogenation mechanism of mixed metal amidoborane, Na[Li(NH2BH3)]2. J. Alloys Comp. 2013, 581, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhang, J.G. Structural study and dehydrogenation mechanisms of a novel mixed metal amidoborane: Sodium magnesium amidoborane. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2013, 590, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chittari, B.L.; Tewari, S.P. Structural, bonding and elastic properties of Mg(NH2BH3)2, Ca(NH2BH3)2 and Sr(NH2BH3)2. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2014, 148, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, K.R.; Ramirez-Cuesta, A.J.; Refson, K.; Jones, M.O.; Edwards, P.P.; David, W.I.F. A combined experimental inelastic neutron scattering, Raman and ab initio lattice dynamics study of a-lithium amidoborane. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 12249–12253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolstenholme, D.J.; Titah, J.T.; Che, F.N.; Traboulsee, K.T.; Flogeras, J.; McGrady, G.S. Homopolar Dihydrogen Bonding in Alkali-Metal Amidoboranes and Its Implications for Hydrogen Storage. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 16598–16604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leardini, F.; Ares, J.R.; Bodega, J.; Valero-Pedraza, M.J.; Bañares, M.A.; Fernández, J.F.; Sánchez, C. Hydrogen Desorption Behavior of Calcium Amidoborane Obtained by Reactive Milling of Calcium Hydride and Ammonia Borane. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 24430–24435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banu, T.; Debnath, T.; Ash, T.; Das, A.K. Hydrolysis of ammonia borane and metal amidoboranes: A comparative study. J. Chem. Phys. 2015, 143, 194305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrahams, S.C.; Kalnajs, J. The Lattice Constants of the Alkali Borohydrides and the Low-Temperature Phase of Sodium Borohydride. J. Chem Phys. 1954, 22, 434–436. [Google Scholar]
- Juza, R.; Jacobs, H.; Klose, W. Die Kristallstrukturen der Tieftemperaturmodifikationen von Kalium- und Rubidiumamid. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 1965, 338, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juza, R.; Mehne, A. Zur Kristallstruktur der Alkalimetallamide. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 1965, 299, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luedtke, A.T.; Autrey, T. Hydrogen Release Studies of Alkali Metal Amidoboranes. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 49, 3905–3910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fijalkowski, K.J.; Jaron, T.; Leszczynski, P.J.; Magos-Palasyuk, E.; Palasyuk, T.; Cyranski, M.K.; Grochala, W. M(BH3NH2BH2NH2BH3)—The missing link in the mechanism of the thermal decomposition of light alkali metal amidoboranes. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 23340–23346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimoda, K.; Zhang, Y.; Ichikawa, T.; Miyaoka, H.; Kojima, Y. Solid state NMR study on the thermal decomposition pathway of sodium amidoborane NaNH2BH3. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 2609–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimoda, K.; Doi, K.; Nakagawa, T.; Zhang, Y.; Miyaoka, H.; Ichikawa, T.; Tansho, M.; Shimizu, T.; Burrel, A.K.; Kojima, Y. Comparative Study of Structural Changes in NH3BH3, LiNH2BH3, and KNH2BH3 During Dehydrogenation Process. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 5957–5964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.; Fang, Z.; Kong, L.; Cheng, H.; Yao, X.; Lu, G.; Wang, P. Ammonia Borane Destabilized by Lithium Hydride: An Advanced On-Board Hydrogen Storage Material. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 2756–2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fijalkowski, K.J. Synthesis and Characterization of Amidoboranes of Selected Elements in a Context of Their Ability of Hydrogen Storage. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Warsaw, Warsaw, Poland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Owarzany, R.; Fijalkowski, K.J.; Jaron, T.; Leszczynski, P.; Dobrzycki, Ł.; Cyranski, M.K.; Grochala, W. Complete Series of Alkali-Metal M(BH3NH2BH2NH2BH3) Hydrogen-Storage Salts Accessed via Metathesis in Organic Solvents. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 55, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Target Explanation Document: Onboard Hydrogen Storage for Light-Duty Fuel Cell Vehicles, U.S. Department of Energy. 2015. Available online: http://energy.gov/sites/prod/files/2015/05/f22/fcto_targets_onboard_hydro_storage_explanation.pdf/ (accessed on 28 April 2016).
- Baitalow, F.; Baumann, J.; Wolf, G.; Jaenicke-Roessler, K.; Leitner, G. Thermal decomposition of B–N–H compounds investigated by using combined thermoanalytical methods. Termochim. Acta 2002, 391, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, M.; Autrey, T.; Brown, I.; Ryan, M. The thermal decomposition of ammonia borane: A potential hydrogen storage material. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2008, 8, 498–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutowska, A.; Li, L.; Shin, Y.; Wang, C.M.; Li, X.S.; Linehan, J.C.; Smith, R.S.; Kay, B.D.; Schmid, B.; Shaw, W.; et al. Nanoscaffold Mediates Hydrogen Release and the Reactivity of Ammonia Borane. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 3578–3582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, H.-B.; Gao, L.-L.; Liang, Y.; Kang, X.-D.; Wang, P. Promoted hydrogen generation from ammonia borane aqueous solution using cobalt-molybdenum-boron/nickel foam catalyst. J. Power Sources 2010, 195, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandra, F.P.R.; Demirci, U.B.; Chiriac, R.; Moury, R.; Miele, P. A simple preparation method of sodium amidoborane, highly efficient derivative of ammonia borane dehydrogenating at low temperature. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2011, 36, 7423–7430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stowe, A.C.; Shaw, W.J.; Linehan, J.C.; Schmid, B.; Autrey, T. In situ solid state 11B MAS-NMR studies of the thermal decomposition of ammonia borane: mechanistic studies of the hydrogen release pathways from a solid state hydrogen storage material. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2007, 9, 1831–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, I.C. Metallated Derivatives of Ammonia Borane with a View to Their Potential as Hydrogen Storage Materials. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Birmingham, Birmingham, West Midlands, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wan, L.; Huang, Z.; Liu, H.; Guo, Z.; Yu, X. Regeneration of alkaline metal amidoboranes with high purity. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2016, 41, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najiba, S.; Chen, J. High-pressure study of lithium amidoborane using Raman spectroscopy and insight into dihydrogen bonding absence. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 19140–149144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magos-Palasyuk, E.; Fijalkowski, K.J.; Palasyuk, T. Chemically driven strong negative linear compressibility in sodium amidoborane, Na(NH2BH3). Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magos-Palasyuk, E.; Palasyuk, T.; Zaleski-Ejgierd, P.; Fijalkowski, K.J. Hydrogen-mediated affinity of ions found in compressed potassium amidoborane, K[NH2BH3]. CrystEngComm 2014, 16, 10367–10370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shimoda, K.; Ichikawa, T.; Kojima, Y. Activation of Ammonia Borane Hybridized with Alkaline-Metal Hydrides: A Low-Temperature and High-Purity Hydrogen Generation Material. J. Phys. Chem. 2010, 114, 14662–14664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Miao, L.; Scheicher, R.H.; Xiong, Z.; Wu, G.; Araújo, C.M.; Blomqvist, A.; Ahuja, R.; Feng, Y.P.; Chen, P. Li-Na Ternary Amidoborane for Hydrogen Storage: Experimental and First-Principles Study. Dalton Tran. 2012, 41, 4754–4764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


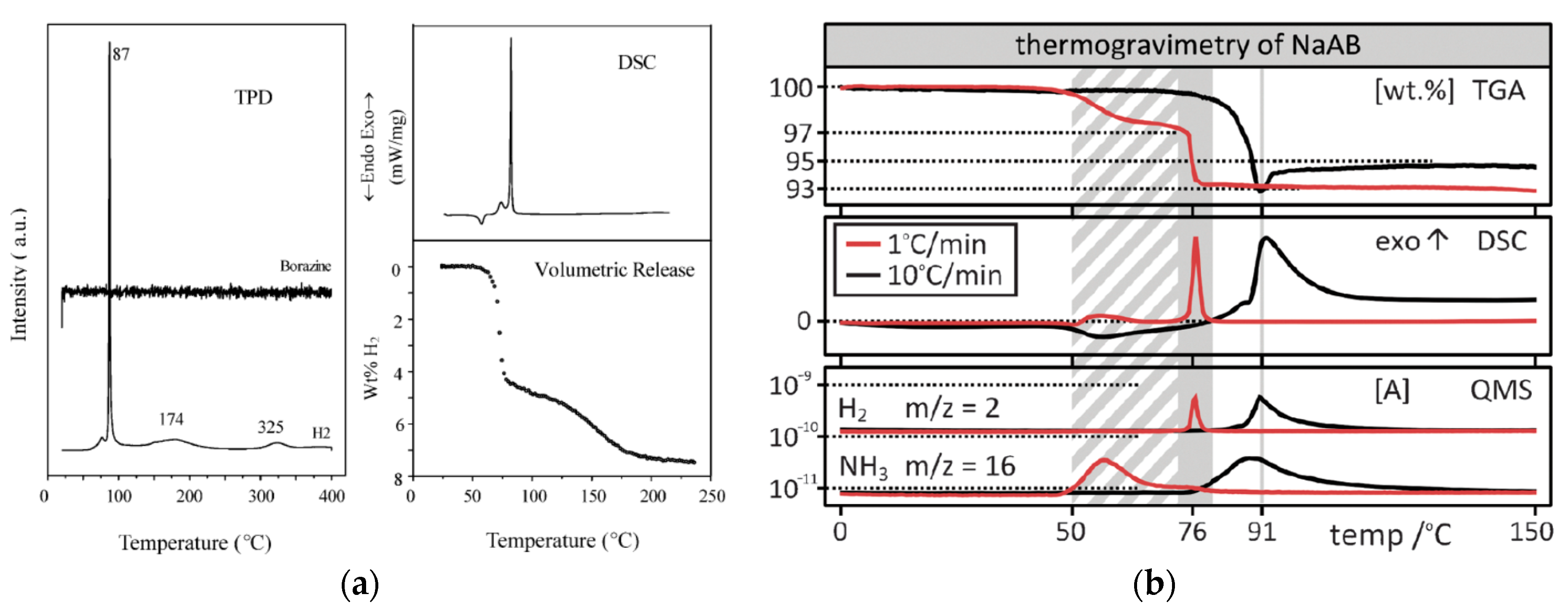
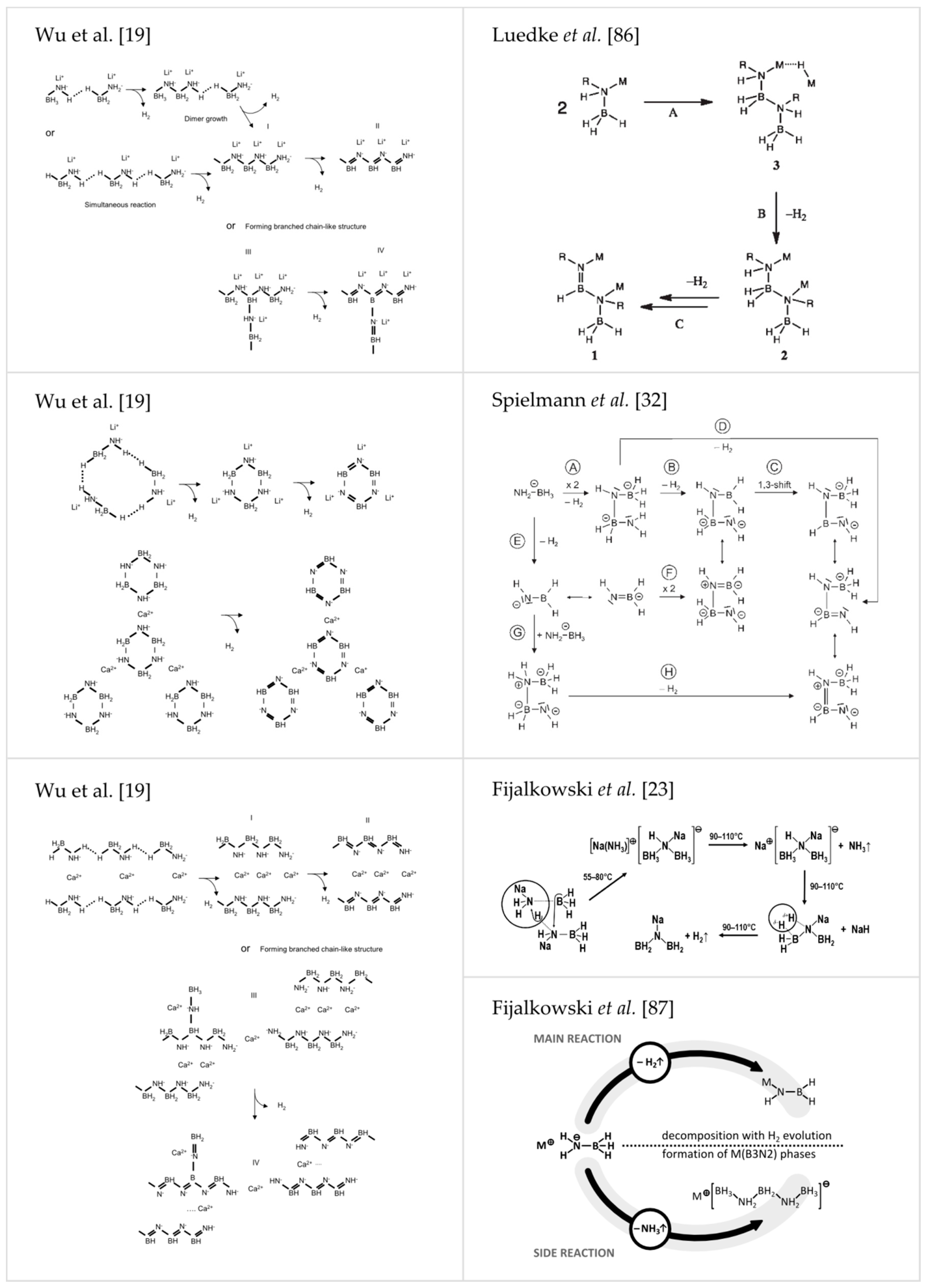
| Compound | Sp. Gr. | a [Å] | b [Å] | c [Å] | α [°] | β [°] | γ [°] | V [Å3] | FU [Å3] | Z | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α-LiAB | Pbca | 7.11 | 13.93 | 5.15 | 90 | 90 | 90 | 509.5 | 63.7 | 8 | [19] |
| β-LiAB | Pbca | 15.15 | 7.72 | 9.27 | 90 | 90 | 90 | 1083.8 | 67.7 | 16 | [21] |
| NaAB | Pbca | 7.47 | 14.65 | 5.65 | 90 | 90 | 90 | 618.6 | 77.3 | 8 | [21] |
| KAB | Pbca | 9.35 | 8.21 | 17.19 | 90 | 90 | 90 | 1319.4 | 82.5 | 16 | [25] |
| RbAB | P21/c | 6.93 | 5.01 | 11.07 | 90 | 101.7 | 90 | 376.8 | 94.2 | 4 | [26] |
| CsAB | Pnam | 9.12 | 7.34 | 5.97 | 90 | 90 | 90 | 399.6 | 99.9 | 4 | [26] |
| Ca(AB)2 | C2 | 9.10 | 4.73 | 6.44 | 90 | 93.19 | 90 | 276.9 | 138.5 | 2 | [19] |
| Sr(AB)2 | C2 | 8.17 | 5.10 | 6.73 | 90 | 90 | 94.39 | 279.1 | 139.6 | 2 | [43] |
| Y(AB)3 | C2/c | 13.19 | 7.82 | 14.87 | 90 | 92.43 | 90 | 1533.2 | 191.7 | 8 | [38] |
| LiNa(AB)2 | P–1 | 5.02 | 7.12 | 8.92 | 103.0 | 102.1 | 103.6 | 290.0 | 145.0 | 2 | [39] |
| NaAl(AB)4 | P-1 | 9.44 | 7.72 | 7.63 | 97.2 | 109.2 | 89.7 | 519.9 | 259.9 | 2 | [41] |
| NaMg(AB)3 | P21|P21/m | 17.01 | 9.43 | 9.40 | 90 | 90 | 115.99 | 1355.3 | 169.4 | 8 | [42] |
| Na2Mg(AB)4 | I41/a | 9.41 | 9.41 | 12.72 | 90 | 90 | 90 | 1127.3 | 281.8 | 4 | [44] |
| K2Mg(AB)4 | I41/a | 9.60 | 9.60 | 13.58 | 90 | 90 | 90 | 1250.9 | 312.7 | 4 | [45] |
| AB (HT) | I4mm | 5.26 | 5.26 | 5.05 | 90 | 90 | 90 | 138.9 | 69.5 | 2 | [3] |
| AB (LT) | Pmn21 | 5.40 | 4.89 | 4.99 | 90 | 90 | 90 | 131.5 | 66.8 | 2 | [4] |
| Compound | N–H [Å] | B–H [Å] | B–N [Å] | M–B [Å] | M–N [Å] | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α-LiAB | 1.03 | 1.24–1.25 | 1.55 | 2.51–2.97 | 2.06 | [19] |
| β-LiAB | 0.99 | 1.18–1.22 | 1.58–1.59 | 2.50–2.93 | 1.93–2.04 | [21] |
| NaAB | 1.04–1.05 [21] | 1.29–1.32 [21] | 1.56 [18] | 2.68–2.93 [21] | 2.14 [21] | [18,21] |
| KAB | 0.78–1.05 | 1.08–1.26 | 1.53 | 3.28–3.59 | 2.91–3.36 | [25] |
| RbAB | 1.04 | 1.18–1.19 | 1.54 | 3.19–3.59 | 3.08–3.14 | [26] |
| CsAB | 1.05 | 1.19–1.20 | 1.53 | 3.68–3.85 | 3.34–3.54 | [26] |
| Ca(AB)2 | 1.04–1.10 | 1.25–1.32 | 1.55 | 3.00–3.18 | 2.47 | [19] |
| Sr(AB)2 | ND | ND | 1.528 | 3.11–3.19 | 2.68 | [43] |
| LiNa(AB)2 | 1.00–1.10 # | 1.22–1.32 # | 1.51–1.61 # | 2.86–3.11 # Na | 2.16–2.26 # Li | [39] |
| NaAl(AB)4 | 1.03 | 1.12–1.40 | 1.58–1.63 | 2.92–2.97 Na | 1.84–1.93 Al | [41] |
| Na2Mg(AB)4 | 1.03 | 1.24 | 1.56 | 2.96–3.03 Na | 2.11 Mg | [44] |
| K2Mg(AB)4 | 1.03 | 1.24 | 1.56 | 3.34–3.46 K | 2.21 Mg | [45] |
| AB (HT) | 0.85 | 1.11 | 1.58 | - | - | [3] |
| AB (LT) | 0.96–1.07 | 1.15–1.18 | 1.58 | - | - | [4] |
| Compound | σ [ppm] (THF-d8 Solution) | σ [ppm] (Solid State) |
|---|---|---|
| α-LiAB | −20.07 (q, J = 86 Hz) [87] | −19.7 [18]; −20.6 [24]; −22.8 [90] |
| NaAB | −21.5 (q, J = 83 Hz) [87]; −20.2 (q, J = 85 Hz, glyme) [35] | −22.9 [18]; −20.5 [39] |
| KAB | −19.62 (q, J = 84 Hz) [25]; −22.20 (q, J = 95 Hz) [87] | ND |
| RbAB | −22.20 (q, J = 94 Hz) [26] | ND |
| CsAB | −20.31 (q, J = 97 Hz) [26] | ND |
| Mg(AB)2 | −20.15 (q, J = 89 Hz) [16] | −22.8 [29] |
| Ca(AB)2 | −23.62 (q, J = 86 Hz) [31] | ND |
| Zn(AB)2 | −20.49 (q, J = 89 Hz) [16] | ND |
| Al(AB)3 | −22.2 (q, J = 90 Hz) (glyme) [35] | ND |
| Y(AB)3 | ND | −23.9 [38] |
| LiNa(AB)2 | ND | −20.7 [24] |
| LiAl(AB)4 | −22.7 (q, J = 92 Hz) [35] | −21.1 [40] |
| NaMg(AB)3 | ND | −23.3 [42]; −23 [43] |
| Na2Mg(AB)4 | ND | −24 [45] |
| K2Mg(AB)4 | ND | −23 [45] |
| AB (HT) | −20.4 (q, J = 95 Hz) [23]; −21.7 (q, J = 95 Hz, glyme) [35] | −22.8 [18] |
| Compound | ν-NH [cm−1] | ν-BH [cm−1] | δ-NH [cm−1] | δ-BH [cm−1] | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α-LiAB | 3360, 3319, 3251 | 2332, 2194, 2150 | 1607, 1545, 1505 | 1262, 1178, 1162 | [39] |
| NaAB | 3303, 3256, 3200 | 2340, 2289, 2224 | 1608, 1532 | 1232, 1189, 1173 | [23] |
| KAB | 3347, 3303, 3260 | 2187, 2170, 2121 | 1568 | 1243, 1223, 1202 | [25] |
| RbAB | 3444, 3290 | 2183, 2118 | 1601 | 1231, 1208, 1162 | [26] |
| CsAB | 3349, 3250, 3199 | 2338,2268,2187 | 1616, 1487 | 1213,1194,1163 | [26] |
| Mg(AB)2 | 3413, 3314, 3281 | 2285, 2245, 2226 | 1562 | 1242, 1160, 1038 | [16] |
| Ca(AB)2 | 2978, 2880 | 2197, 2146 | 1533, 1460 | 1261, 1168, 1042 | [31] |
| Zn(AB)2 | 3370, 3336, 3302 | 2209, 2172, 2107 | 1545 | 1240, 1198, 1184 | [34] |
| Al(AB)3 | 3302, 3258 | 2358, 2329, 2265 | 1548, 1454 | 1174, 1114 | [36] |
| Y(AB)3 | 3387, 3319, 3257 | 2341, 2098, 1951 | 1608, 1570, 1530 | 1264,1169, 1065 | [38] |
| LiNa(AB)2 | 3354, 3303, 3256 | 2328, 2202, 2140 | 1609, 1539, 1505 | 1245, 1199, 1177 | [39] |
| LiAlH2(AB)4 | 3150−3350 | 2200–2400 | ND | ND | [40] |
| NaAl(AB)4 | 3200–3430 | 2340–2420 | 1500–1650 | 1100–1150 | [41] |
| NaMg(AB)3 | 3250–3336 | 2220–2320 | 1300–1700 | 1000–1250 | [42] |
| KMg(AB)3 | 3150–3300 | 2200–2400 | 1300–1700 | 1000–1250 | [43] |
| RbMg(AB)3 | 3100–3300 | 2100–2400 | 1300–1700 | 1000–1250 | [43] |
| Na2Mg(AB)4 | 3285, 3300, 3330 | ND | ND | ND | [44] |
| AB (HT) | 3311,3253, 3196 | 2347, 2289, 2118 | 1611 | 1163, 1067 | [3] |
| Compound | ν-NH [cm−1] | ν-BH [cm−1] | δ-NH [cm−1] | δ-BH [cm−1] | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α-LiAB | 3361, 3303 | 2368, 2191, 2153 | 1650, 1613, 1524 | 1152, 1122, 1021 | [92] |
| NaAB | 3372, 3314 | 2376, 2183, 2103 | 1646, 1620, 1563 | 1242, 1202, 1172 | [92] |
| KAB | 3347, 3297 | 2359, 2182, 2078 | 1630 | 1240, 1190, 1179 | [26] |
| RbAB | 3347, 6292 | 2362, 2267, 2195 | 1619 | 1192, 1093, 1006 | [26] |
| CsAB | 3345, 3288 | 2344, 2250, 2173 | 1615 | 1221, 1197, 1175 | [26] |
| AB (HT) | 3314, 3253, 3177 | 2378, 2284 | 1598, 1583 | 1190, 1168, 1069 | [92] |
| Compound | H Content | 1st Step of Decomposition: Temp., Mass Loss | Contaminants of H2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| α-LiAB | 13.5 wt% | isothermal at 91 °C, 10.9 wt% [18]; | borazine-free [18] |
| isothermal at 91 °C, 8.8 wt% [20]; | NH3 [20] | ||
| 65–95 °C, 8.0 wt% [25] | NH3 [25] | ||
| β-LiAB | 13.5 wt% | RT-91 °C, 8.8 wt% [20] | NH3 [20] |
| NaAB | 9.4 wt% | isothermal at 89 °C, 7.4 wt% [18] | borazine-free [18] |
| 50–90 °C, 7.0 wt% [23,24] | NH3 [23,24] | ||
| 50–87 °C, 6.3 wt% [98] | NH3 [98] | ||
| KAB | 7.3 wt% | 65–100 °C, 4.0 wt% [25] | – |
| RbAB | 4.4 wt% | 65–90 °C, 9.0 wt% [26] | NH3 [26] |
| CsAB | 3.1 wt% | 55–85 °C, 7.0 wt% [26] | NH3 [26] |
| Mg(AB)2 | 12.0 wt% | 75–110 °C, 2.0 wt% [29] | – |
| Ca(AB)2 | 10.0 wt% | 80–130 °C, 4.0 wt% [19] | ND |
| 80–150 °C, 3.0 wt% [31] | NH3, N3B3H6 [31] | ||
| Sr(AB)2 | 6.8 wt% | 40–100 °C, 5.0 wt% [33] | NH3, B2H6 [33] |
| Zn(AB)2 | 8.1 wt% | below 0 °C, ND [16,34] | ND |
| Al(AB)3 | 12.8 wt% | 60–110 °C, 6.0 wt% [35] | N3B3H6 [35] |
| Y(AB)3 | 8.4 wt% | 80–200 °C, 6.0 wt% [38] | NH3 [38] |
| LiNa(AB)2 | 11.1 wt% | 75–100 °C, 6.0 wt% [39] | NH3, NBH5 [39] |
| LiAl(AB)4 | 13.2 wt% | 82–110 °C, 3.85 wt% [40] | - |
| NaAl(AB)4 | 11.9 wt% | 115–130 °C, 3.0 wt% [41] | NH3 [41] |
| NaMg(AB)3 | 11.0 wt% | 75–140 °C, 2.0 wt% [42] | NH3 [42] |
| KMg(AB)3 | 9.9 wt% | isothermal at 80 °C, 9.3 wt% [43] | NH3 [43] |
| RbMg(AB)3 | 7.6 wt% | isothermal at 80 °C, 6.2 wt% [43] | NH3 [43] |
| Na2Mg(AB)4 | 10.6 wt% | 65–150 °C, 2.0 wt% [44] | NH3, N3B3H6 [44] |
| AB (HT) | 19.6 wt% | 72–112 °C, 6.5 wt% | N3B3H6 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Owarzany, R.; Leszczyński, P.J.; Fijalkowski, K.J.; Grochala, W. Mono- and Bimetalic Amidoboranes. Crystals 2016, 6, 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst6080088
Owarzany R, Leszczyński PJ, Fijalkowski KJ, Grochala W. Mono- and Bimetalic Amidoboranes. Crystals. 2016; 6(8):88. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst6080088
Chicago/Turabian StyleOwarzany, Rafał, Piotr J. Leszczyński, Karol J. Fijalkowski, and Wojciech Grochala. 2016. "Mono- and Bimetalic Amidoboranes" Crystals 6, no. 8: 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst6080088
APA StyleOwarzany, R., Leszczyński, P. J., Fijalkowski, K. J., & Grochala, W. (2016). Mono- and Bimetalic Amidoboranes. Crystals, 6(8), 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst6080088