Abstract
Crystal structures of five hexaethylguanidinium salts (PF6− 1, FeCl4− 2, CuCl42−·H2O 3, CoBr42−/Br−·H2O 4, bistriflimide 5) were determined. Short interionic contacts were identified. Cyclic voltammetry of 2 revealed an electrochemical window from +1.0 to −1.5 V with a single Fe(III)/Fe(II) redox event at −0.27 V on a gold electrode versus Ag/AgCl.
1. Introduction
The advent of phase-transfer catalysis has opened a very large new chapter in synthetic chemistry [1,2]. A number of catalysts are commercially available. There is, however, some confusion about their exact composition [3]. This is particularly true in the special case of Aliquat® HTA-1 (trademark of BASF) which is available from Sigma-Aldrich (Steinheim, Germany) as an aqueous solution (pH 9) of “a unique high temperature and caustic resistant phase transfer catalyst” [4]. What is Aliquat® HTA-1? Although it has a CAS Registry Number [1166837-27-9], the chemical structure is declared as unspecified [5]. To chemists who want to use this catalyst, this situation of course is unsatisfactory, if not unacceptable. Specification sheets for Aliquat® HTA-1 are available online from BASF [6] and from Cognis [7], the company which had been acquired by BASF in 2010. According to this specification, the solution contains 10%–15% NaCl and 30%–36% HTA-1, “a quaternary ammonium salt of unique structure”. In order to elucidate this secret structure, a crystalline salt (the hexafluorophosphate 1) was precipitated from the commercial solution and subjected to X-ray analysis. The organic cation was found to be N,N,N',N',N'',N''-hexaethylguanidinium (HEG). Compounds of this type have been pioneered by W. Kantlehner [8,9,10]. Their use as phase-transfer catalysts is well documented [11,12,13,14]. They have also been proposed as components of electrolytes in ultracapacitors [15]. Some hexaalkylguanidinium salts, which are liquid at room temperature, have been considered as novel reaction media for organic syntheses [16,17,18]. Thus far, only the crystal structure of HEG chloride has been reported [19], although crystal structures of several other hexaalkylguanidinium salts have been described in recent years [20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29].
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthetic Considerations
After our initial success with the hexafluorophosphate 1, further attempts to obtain other salts (oxalate, lactate, tartrate, citrate, azotetrazolate, sulfate, acetate) were not successful. Crystallization gave, if at all, only sodium salts of these anions, confirming the presence of sodium in the commercial solution. Chloride was also detected. As we had noticed on other occasions [30], tetrachloroferrate(III) gives well-crystallizing salts with organic cations commonly used in the field of Ionic Liquids (ILs). Therefore, we turned to these complex halometallates and a series of salts was prepared by metathesis, such as tetrachloroferrate(III) 2, tetrachlorocuprate(II) 3, and tetrabromocobaltate(II) 4. Finally, the low-melting bistriflimide 5 was precipitated. The crystal structures of these new compounds were determined by single-crystal X-ray diffraction. The known chloride 6 [19] is included for comparison.
2.2. Crystal Structures
Crystal data and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 1. Hydrogen bond parameters are shown in Table 2. In the hexaethylguanidinium cations of 1–6, the central carbon atom is surrounded by the three nitrogen atoms in an approximately trigonal planar fashion. The central C atom deviates from the N–N–N plane by only 0.001 Å in 1, 0.003 Å in 2, 0.001 Å in 3, 0.001 Å in 4, and 0.000 Å in 5. The central C–N bond lengths are 1.342–1.344 Å in 1, 1.342–1.344 Å in 2, 1.331–1.350 Å in 3, 1.320–1.325 Å in 4, and 1.336–1.343 Å in 5. The pertinent N–C–N angles are 119.2°–120.6° in 1, 119.8°–120.1° in 2, 119.1°–120.7° in 3, 119.6°–120.8° in 4, and 119.9°–120.2° in 5. Additionally, the cations of 4–6 are located on a two-fold rotation axis. Figure 1a illustrates the different geometries adopted by the hexaethylguanidinium moiety. Differences in the conformation of the six ethyl groups are described by the six corresponding torsion angles C–C–N–C1. The diagram in Figure 1b indicates a general preference for geometries where these angles are near to 120°. The hexaethylguanidinium geometries of 1, 2 and 6 are closely related to one another in that all their C–C–N–C1 torsion angles lie between 110° and 130°. A similar geometry is also observed in 3, except for the conformation of one ethyl group (91.2°). In contrast, two ethyl groups of 4 exhibit a torsion angle of 92.4°, and two ethyl groups of 6 are gauche (63.1°). The remaining C–C–N–C1 angles of each of these two structures again are in the range between 110° and 130°.
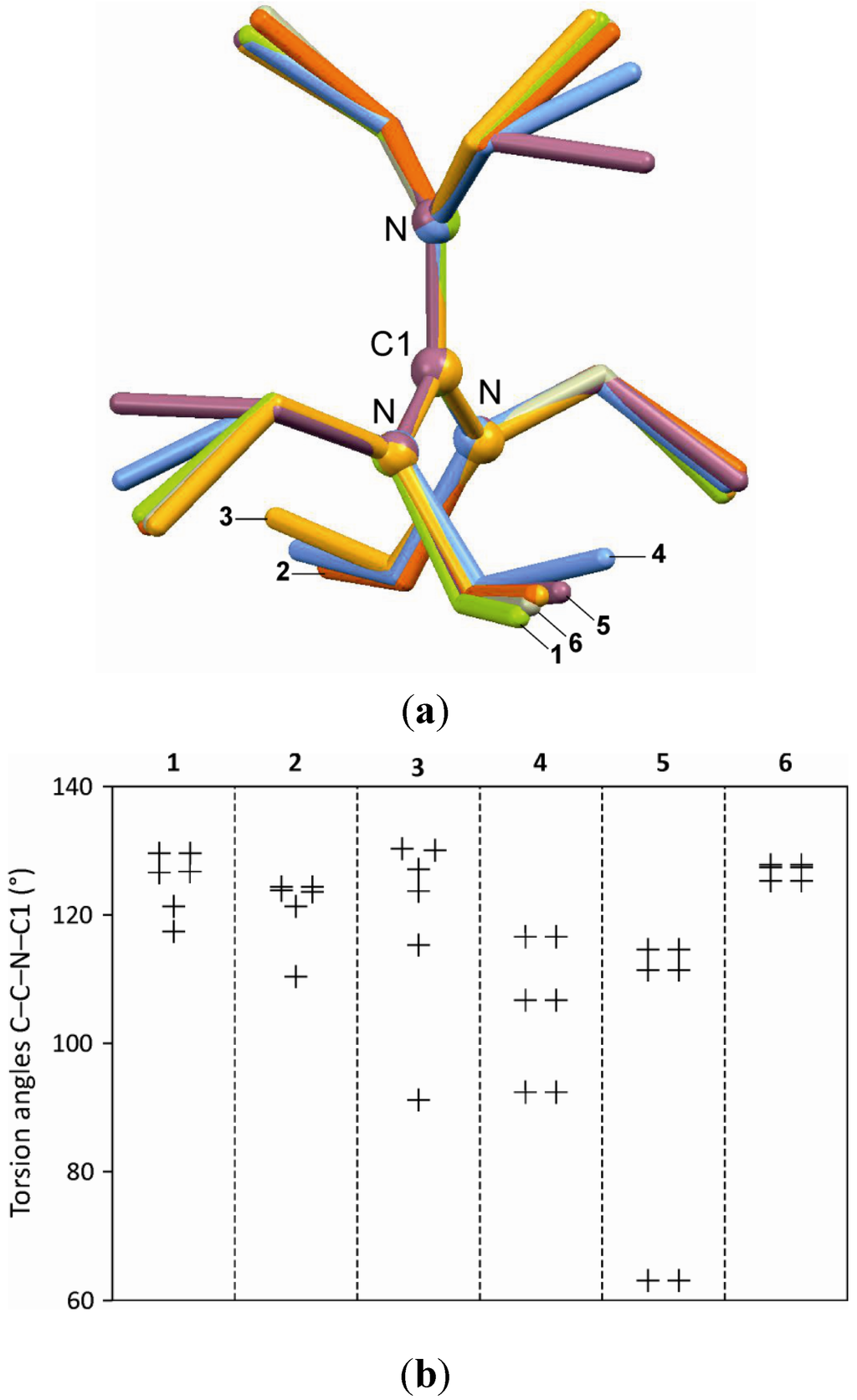
Figure 1.
(a) Overlay of the hexaethylguanidinium cations (least-squares fits of the central C7N3 fragments of 1 = green, 2 = orange, 3 = yellow, 4 = blue, 5 = purple, 6 = grey); (b) Torsion angles C–C–N–C1 describing the conformation of the six ethyl groups in the cations of 1–6.
In the crystal structure of 1, the ions are linked by C–H···F contacts. The hexafluorophosphate ion exhibits 0.85:0.15 orientational disorder (Figure 2). In the structure of 2, Fe–Cl bond lengths range from 2.188 to 2.198 Å and Cl–Fe–Cl angles from 108.4° to 111.3°, indicating a regular tetrahedral geometry of the FeCl4− anion. The two types of ions are alternately arranged in chains by C–H···Cl contacts (Figure 3a). In monohydrate 3, the Cu atom is located on a two-fold rotation axis in the direction of the b axis. Cu–Cl bond lengths range from 2.248 to 2.274 Å, and Cl–Cu–Cl angles from 97.7° to 135.0°. Thus, the CuCl42− ion displays a distorted tetrahedral geometry. A three-dimensional network of C–H···Cl, C–H···O and O–H···Cl interactions is observed (Figure 3b).

Table 1.
Crystal data and structure refinement details.
| Compound | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CCDC No. | 976081 | 976082 | 976083 | 976084 | 976085 | |||||
| Chemical formula | C13H30N3·F6P | C13H30N3·Cl4Fe | (C13H30N3)2·Cl4Cu·(OH2)0.67 | C13H30N3·(Br4Co)0.42·Br0.16·OH2 | C13H30N3·C2F6NO4S2 | |||||
| Mr | 373.37 | 426.05 | 674.16 | 418.20 | 508.55 | |||||
| Crystal size/mm3 | 0.15 × 0.15 × 0.10 | 0.26 × 0.18 × 0.14 | 0.20 × 0.15 × 0.15 | 0.20 × 0.15 × 0.15 | 0.26 × 0.20 × 0.03 | |||||
| Crystal system | Monoclinic | Monoclinic | Monoclinic | Trigonal | Tetragonal | |||||
| Space group | P21/n | P21/n | C2/c | R3c | P43212 | |||||
| a/Å | 9.6283(4) | 13.1905(4) | 16.2803(9) | 17.4600(2) | 9.05490(17) | |||||
| b/Å | 12.9449(4) | 10.3657(3) | 14.6412(7) | – | – | |||||
| c/Å | 15.5960(6) | 15.9222(5) | 17.1885(11) | 34.5190(3) | 29.3944(13) | |||||
| β/° | 105.511(4) | 102.698(3) | 117.797(8) | – | – | |||||
| V/Å3 | 1873.05(12) | 2123.78(11) | 3624.4(4) | 9113.33(17) | 2410.08(12) | |||||
| Z | 4 | 4 | 4 | 18 | 4 | |||||
| Dx/g·cm−3 | 1.32 | 1.33 | 1.24 | 1.37 | 1.40 | |||||
| μ/mm−1 | 1.83 | 1.21 | 0.92 | 4.02 | 2.69 | |||||
| F(000)/e | 792 | 892 | 1477 | 3865 | 1064 | |||||
| Diffractometer | Gemini-R Ultra | Gemini-R Ultra | Gemini-R Ultra | Nonius KappaCCD | Gemini-R Ultra | |||||
| Radiation | CuKα | MoKα | MoKα | MoKα | CuKα | |||||
| Data collection method | ω scans | ω scans | ω scans | φ and ω scans | ω scans | |||||
| T/K | 223 | 173 | 173 | 233 | 173 | |||||
| θmax/° | 67.5 | 25.4 | 25.1 | 25.0 | 67.0 | |||||
| h, k, l range | −11 ≤ h ≤ 10 −14 ≤ k ≤ 15 −18 ≤ l ≤ 16 | −15 ≤ h ≤ 13 −12 ≤ k ≤ 11 −19 ≤ l ≤ 19 | −19 ≤ h ≤ 19 −17 ≤ k ≤ 17 −20 ≤ l ≤ 20 | −20 ≤ h ≤ 20 −20 ≤ k ≤ 20 −40 ≤ l ≤ 40 | −9 ≤ h ≤ 10 −10 ≤ k ≤ 10 −31 ≤ l ≤ 35 | |||||
| Absorption correction | multi-scan | multi-scan | multi-scan | none | analytical | |||||
| Measured reflections | 18889 | 17064 | 49168 | 18293 | 9170 | |||||
| Independent reflections (Rint) | 3338 (0.040) | 3889 (0.032) | 3195 (0.065) | 1771 (0.038) | 2139 (0.040) | |||||
| Observed reflections [I ≥ 2σ(I)] | 2616 | 3263 | 2502 | 1580 | 1884 | |||||
| Restraints/parameters | 54/300 | 0/196 | 2/213 | 0/98 | 9/151 | |||||
| R1/wR2 [I ≥ 2σ(I)] | 0.049/0.085 | 0.031/0.076 | 0.060/0.108 | 0.052/0.138 | 0.048/0.123 | |||||
| R1/wR2 (all data) | 0.064/0.090 | 0.042/0.083 | 0.075/0.114 | 0.057/0.141 | 0.054/0.130 | |||||
| Goodness of fit | 1.02 | 1.02 | 0.93 | 1.07 | 1.05 | |||||
| Flack parameter x | – | – | – | – | 0.04(4) | |||||
| ∆ρmax/min/e Å−3 | 0.24/−0.21 | 0.42/−0.23 | 0.64/−0.92 | 1.19/−0.68 | 0.31/−0.19 | |||||

Table 2.
Hydrogen bond parameters (Å, °).
| Compound | Interaction | H···A | D···A | <D–H···A | Symmetry A |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | C34–H···F5 | 2.589 | 3.455(5) | 148.6 | x,y,z |
| C14–H···F5 | 2.612 | 3.439(4) | 143.2 | −1 + x,y,z | |
| C14–H···F2 | 2.631 | 3.578(4) | 165.2 | −1/2 + x,1/2 − y,1/2 + z | |
| 2 | C2–H···Cl1 | 2.9110 | 3.699(2) | 137.3 | x,y,z |
| C11–H···Cl3 | 2.9164 | 3.697(2) | 136.4 | −1/2 + x,3/2 − y,1/2 + z | |
| 3 | O1–H···Cl2 | 2.18(3) | 2.996(7) | 156(7) | x,y,z |
| C14–H···O1 | 2.526 | 3.235(9) | 130.7 | 1 − x,−y,1 − z | |
| C13–H···O1 | 2.683 | 3.182(8) | 112.4 | 1 − x,−y,1 − z | |
| C11–H···Cl1 | 2.928 | 3.858(3) | 161.0 | 1/2 − x,1/2 − y,1 − z | |
| 4 | O2–H···Br1 | – | 2.76(2) | – | x − y,−y,1/2 − z |
| C5–H···O2 | 2.50 | 3.41(4) | 156.6 | x − y,−y,1/2 − z | |
| O2–H···Br1 | – | 3.19(3) | – | y,x,1/2 − z | |
| O1–H···Br1 | – | 3.30(1) | – | x − y,−y,1/2 − z | |
| C2–H···Br1 | 3.001 | 3.913(6) | 154.9 | −1/3 + x − y,1/3 + x,1/3 − z | |
| C5–H···O1 | 2.70 | 3.66(2) | 168.0 | x,y,z | |
| 5 | C7–H···O2 | 2.515 | 3.356(5) | 142.6 | y,−1 + x,−z |
| C2–H···N3 | 2.62 | 3.582(7) | 170 | x,y,z | |
| C8–H···O1 | 2.707 | 3.657(5) | 163.5 | −1 + y,−1 + x,−z |
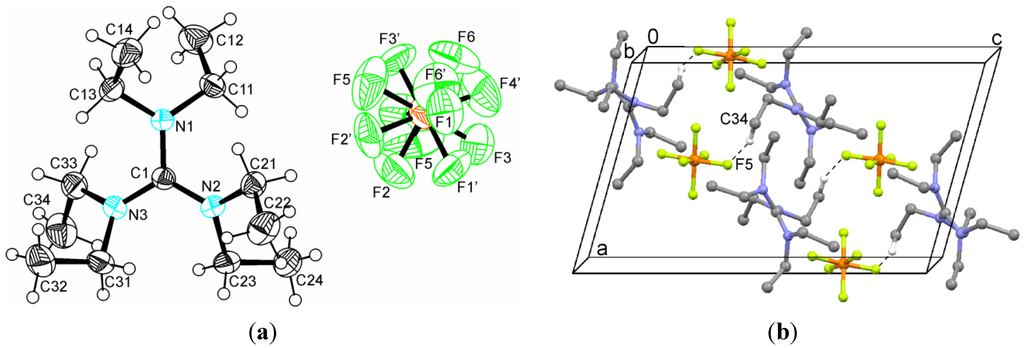
Figure 2.
(a) Ionic structure of hexaethylguanidinium hexafluorophosphate (1) showing the disordered anion; (b) C–H···F interactions in the crystal structure of 1. Hydrogen atoms have been omitted for clarity, except for those engaged in contacts.
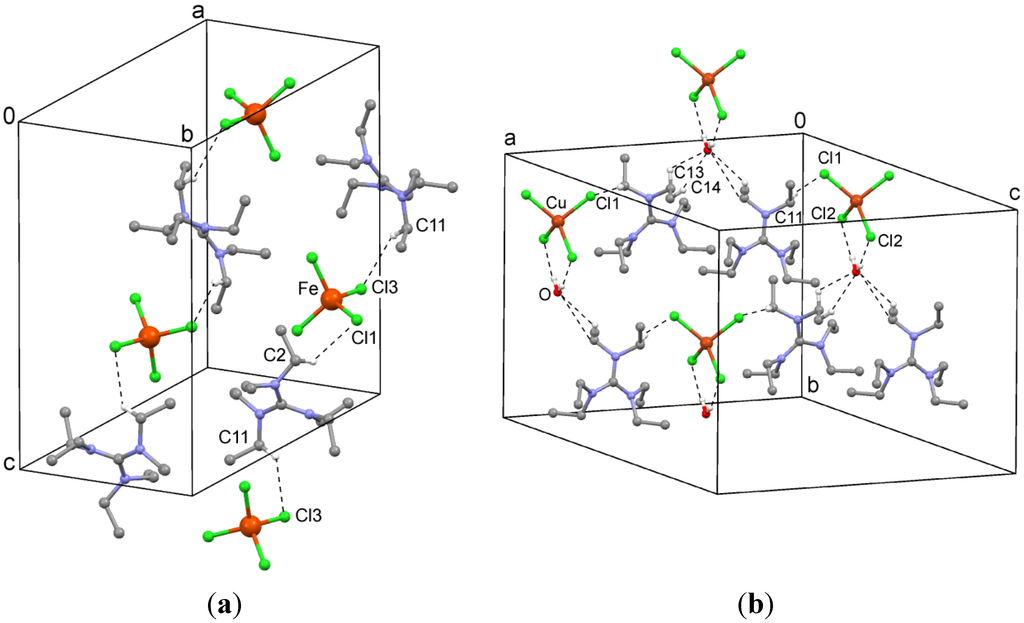
Figure 3.
(a) C–H···Cl interactions in the crystal structure of hexaethylguanidinium tetrachloroferrate(III) (2); (b) C–H···Cl interactions in the crystal structure of hexaethylguanidinium tetrachlorocuprate(II) hydrate (3). Hydrogen atoms have been omitted for clarity, except for those engaged in contacts.
In the crystal structure of monohydrate 4 (Figure 4a), there is half a molecule of the guanidinum cation in the asymmetric unit, and C1 and N1 occupy special positions on the two-fold rotation axis parallel to the b axis. The lattice contains two kinds of anions: first, the divalent anion Co(II)Br42− and second, the monovalent bromide Br−, which are distributed in a disordered manner. The Co atom and Br2 are located on a three-fold rotation axis parallel to the c axis with an occupancy of 0.21 (instead of 0.333), whereas Br1 is found in general position with occupancy of 0.63 (instead of 1.0). The bromide Br3 lies between the atoms Co1 and Br2 on the three-fold rotation axis with an occupancy of 0.08. This indicates an occupational disorder of the two anions, and charge neutrality requires that 0.043 of these positions remain vacant. Close to the CoBr42− anion, there is a water molecule, which is also split over two positions (O1 and O2 in the ratio 0.21:0.29). The disordered O positions of this water molecule were refined isotropically, while the positions of its H atoms could not be determined. The oxygen atoms obviously donate hydrogen bonds to Br1 of the anion (Figure 4b). The occupancies 0.21 for CoBr42− and 0.08 for Br− were first confirmed by free refinement of occupancy factors and then optimized by varying the occupancy factors manually to improve the R value.
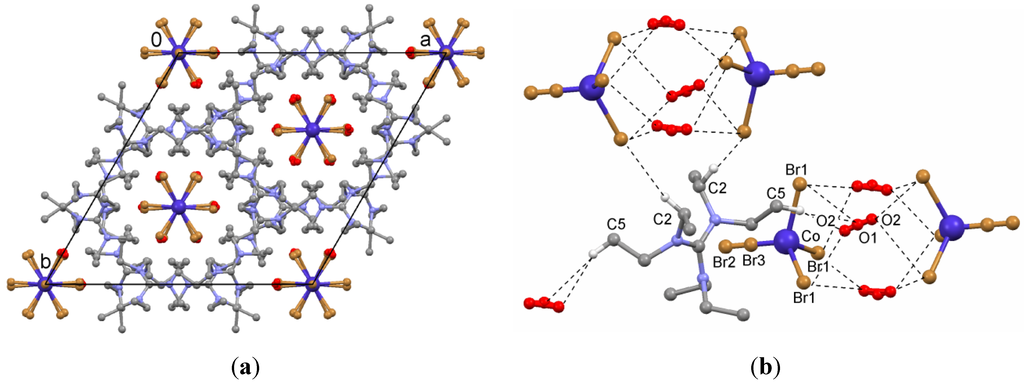
Figure 4.
(a) Packing diagram of hexaethylguanidinium tetrabromocobaltate(II)/bromide hydrate (4); (b) Short contacts in the crystal structure of 4. Hydrogen atoms have been omitted for clarity, except for those engaged in contacts.
The geometry of the CoBr42− anion is that of an almost regularly shaped tetrahedron with a Co–Br1 bond length of 2.380 Å and Co–Br2 of 2.386 Å. The Br–Co–Br angles are 109.2° and 109.8°.
In bistriflimide ions two major conformations (cisoid/transoid; syn/anti) are known to occur [31,32,33,34,35]. In the crystal structure of 5, the bistriflimide clearly adopts an almost ideal anti conformation with a torsion angle of 179.2°.
A typical, weak coordination via the O atoms is observed, but the N atom is also involved in bifurcated, short contacts (Figure 5). The only hydrogen donors in this ion pair are, of course, of the C–H type.
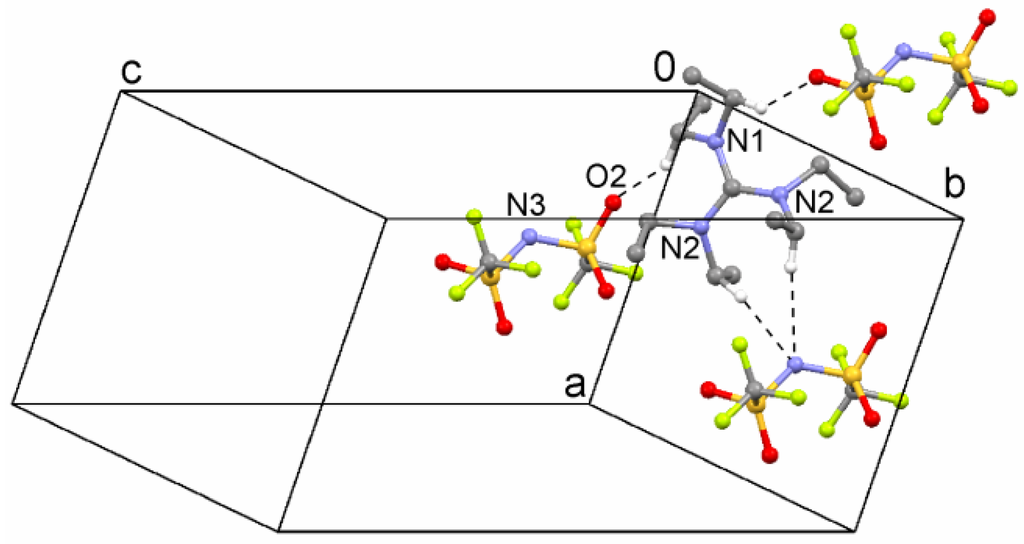
Figure 5.
Short contacts in the crystal structure of hexaethylguanidinium bistriflimide (5). Hydrogen atoms have been omitted for clarity, except for those engaged in contacts.
2.3. Cyclic Voltammetry of Hexaethylguanidinium Tetrachloroferrate(III) (2)
As previously reported, a hexaalkylguanidinium-based IL showed a broad electrochemical window [36]. Thus, our HEG FeCl4 exhibited the expected wide window from +1.0 to −1.5 V with a single reversible Fe(III)/Fe(II) redox event at half-wave potential of −0.27 V (Figure 6). This compound could be of interest as a component in batteries [37,38].
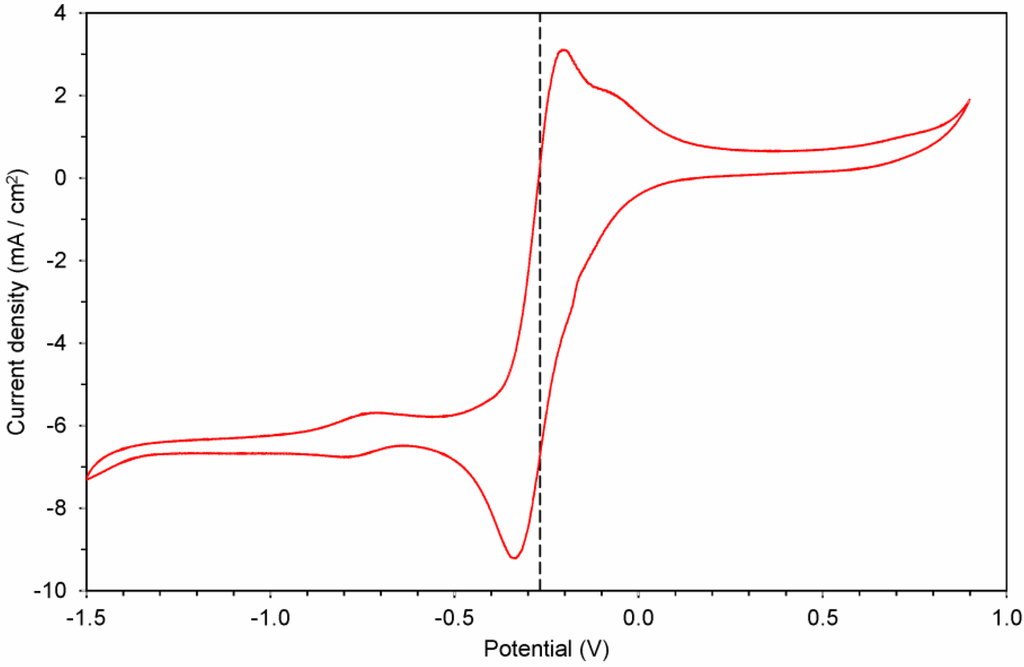
Figure 6.
Cyclic voltammogram of 2 (0.02 M in CH3CN) on a gold electrode vs. Ag/AgCl.
3. Experimental Section
Aliquat® HTA-1 (High-Temperature Phase Transfer Catalyst, 30%–35% in H2O) was purchased from Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA (European affiliate Steinheim, Germany). NMR spectra were recorded with a Bruker Avance DPX 300 spectrometer (Billerica, MA, USA). IR spectra were obtained with a Nicolet 5700 FT instrument (Thermo Electron Scientific Instruments Corp., Madison, WI, USA). Cyclic voltammograms were measured on a Radiometer analytical Voltalab PGZ 402 instrument (Villeurbanne, France) at a scan rate of 50 mV·s−1. X-ray diffraction data were collected with an Oxford Diffraction Gemini-R Ultra (Oxford Diffraction Ltd., Abingdon, Oxfordshire, UK) or Nonius KappaCCD (Bruker, Billerica, MA, USA) diffractometer using MoKα (λ = 0.7107 Å) or CuKα radiation (λ = 1.5418 Å). CCDC reference numbers: 976081–976085. These data can be obtained free of charge from The Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre.
3.1. Hexaethylguanidinium Hexafluorophosphate (1)
Aliquat® (30%–35% aqueous solution, 5.8 g) was diluted with H2O (10 mL), and addition of NH4PF6 (1.3 g) resulted in a white precipitate, which was filtered off and washed with cold H2O (35 mL). Vacuum-drying for 5 h gave a fine white powder (2.4 g). Single crystals were grown by slow evaporation of a solution in CH2Cl2. M.p. > 260 °C. 1H NMR (CD3OD, 300 MHz): δ 1.32 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 18H), 3.41 (m, 12H) ppm. 13C NMR (CD3OD, 75 MHz): δ 13.0 (6C), 44.8 (6C), 164.9 ppm. IR (neat): ν 2998 (w), 2947 (w), 1540 (m), 1464 (m), 1440 (m), 1386 (m), 1296 (m), 1212 (w), 1189 (w), 1152 (w), 1127 (w), 1080 (w), 1056 (w), 1009 (m), 874 (w), 828 (s), 791 (m), 555 (m), 463 (m) cm−1.
3.2. Hexaethylguanidinium Tetrachloroferrate(III) (2)
Aliquat® (30%–35% aqueous solution, 5.8 g), HCl (37%, 0.6 mL), iron(III) chloride hexahydrate (2.1 g) and H2O (100 mL) were mixed and stirred to give an orange solution. The solvent was removed under reduced pressure to give an orange residue which was resuspended in CH3CN (50 mL) and filtered off. Evaporation of the solvent and vacuum-drying for 5 h at room temperature yielded yellow crystalline hexaethylguanidinium tetrachloroferrate (3.0 g). Onset of decomposition: 300 °C. Single crystals were grown by slow evaporation of a solution in acetone or CH2Cl2. IR (neat): ν 2978 (m), 2937 (w), 1539 (s), 1440 (m), 1383 (m), 1296 (m), 1210 (m), 1185 (m), 1148 (m), 1116 (m), 1074 (m), 1053 (m), 1004 (m), 944 (w), 793 (m), 467 (m) cm−1.
3.3. Bis(Hexaethylguanidinium) Tetrachlorocuprate(II) Hydrate (3)
Aliquat® (30%–35% aqueous solution, 5.8 g), H2O (10 mL) and ammonium tetrachlorocuprate dihydrate (1.1 g) were mixed to give a green-blue solution. Evaporation of the solvent by means of a rotary evaporator gave a brown residue, which was resuspended in CH3CN (50 mL) and filtered off. Evaporation of the solvent and vacuum-drying for 5 h at room temperature yielded an orange solid (2.3 g). Single crystals were grown by diffusion of Et2O into a CH2Cl2 solution at −27 °C. Onset of decomposition: 85 °C, final melting: 150 °C. 1H NMR (CD3OD, 300 MHz): δ 0.91 (br s, 18H), 3.00 (m, 12H) ppm. 13C NMR (CD3OD, 75 MHz): δ 13.9 (6C), 45.6 (6C), 164.9 ppm. IR (neat): ν 2970 (m), 2938 (w), 2877 (w), 1551 (s), 1530 (s), 1448 (s), 1385 (m), 1294 (m), 1209 (m), 1186 (m); 1146 (w), 1112 (m), 1077 (m), 1053 (m), 1007 (m), 941 (w), 799 (m), 487 (m), 463 (m) cm−1.
3.4. Bis(Hexaethylguanidinium) Tetrabromocobaltate(II)/Bromide Hydrate (4)
Aliquat® (30%–35% aqueous solution, 5.0 g), HBr (48%, 0.8 mL) and cobalt bromide (16% water content, 0.9 g) were mixed to give a purple solution. Evaporation of the solvent under reduced pressure gave a dark blue residue which was resuspended in CH3CN (50 mL) and filtered off. Evaporation of the solvent and vacuum-drying for 5 h at room temperature yielded a blue crystalline solid (2.7 g). Single crystals were grown by slow evaporation of an acetone solution. Onset of decomposition: 70 °C, final melting: 170 °C. IR (neat): ν 2972 (m), 2931 (w), 1537 (s), 1437 (m), 1379 (m), 1298 (m), 1209 (w), 1184 (m), 1144 (w), 1103 (m), 1073 (m), 1052 (m), 1004 (m), 944 (w), 795 (m), 467 (m) cm−1.
3.5. Hexaethylguanidinium Bis(Trifluoromethanesulfonyl)Imide (5)
To Aliquat® (30%–35% aqueous solution, 5.8 g), CH2Cl2 (10 mL) and LiNTf2 (2.2 g) were added. The resulting aqueous phase was extracted with CH2Cl2 (2 × 10 mL) and the combined organic phases dried with Na2SO4. Removal of the solvent by means of a rotary evaporator and vacuum drying for 5 h at room temperature yielded a white solid (3.1 g). Single crystals were grown by slow evaporation of an EtOH solution. M.p. 75 °C. 1H NMR (CD3OD, 300 MHz): δ 1.22 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 18H), 3.30 (m, 12H) ppm. 13C NMR (CD3OD, 75 MHz): δ 13.2 (6C), 45.0 (6C), 121.4 (q, J = 321 Hz), 165.0 ppm. IR (neat): ν 2985 (w), 2945 (w); 1540 (m), 1464 (w), 1444 (w), 1383 (w), 1339 (m), 1326 (m), 1302 (m), 1227 (w), 1173 (s), 1132 (s), 1053 (m), 1006 (m), 947 (w), 800 (w), 785 (m), 761 (w), 740 (w), 655 (m), 597 (m), 568 (m), 504 (m), 464 (m) cm−1.
4. Conclusions
Crystal structures of five salts derived from the commercial catalyst solution have been determined. Thus, the culprit has been identified and the mystery unraveled: Aliquat® HTA-1 is N,N,N',N',N'',N''-hexaethylguanidinium chloride in aqueous sodium hydroxide solution. It is certainly not a quaternary ammonium salt in a strict sense.
Author Contributions
Robert Salchner carried out experimental work (synthesis, crystallization and characterization). Volker Kahlenberg determined four crystal structures. Thomas Gelbrich discussed the conformations and contributed Figure 1. Klaus Wurst contributed one crystal structure, Martin Rauch contributed cyclic voltammetry measurements. Gerhard Laus prepared the manuscript. Herwig Schottenberger conceived and designed the study.
Appendix
Result of CAS Substance search [5]; specification sheets for Aliquat® HTA-1 [6,7].
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Starks, C.M. Phase-transfer catalysis. I. Heterogeneous reactions involving anion transfer by quaternary ammonium and phosphonium salts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1971, 93, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.A. Applications of phase-transfer catalysis in organic synthesis. Aldrichim. Acta 1976, 9, 35–45. [Google Scholar]
- Halpern, M. What is Aliquat® 336 and Adogen® 464 HF? Available online: http://phasetransfer.com/WhatisAliquat336andAdogen464.pdf (accessed on 10 July 2014).
- BASF Homepage. Available online: http://www.phasetransfer.com/suppliers/cognis.htm (accessed on 10 July 2014).
- CAS Substance search. Available online: https://scifinder.cas.org/scifinder/login (accessed on 10 July 2014).
- Aliquat HTA-1. Available online: http://www.mining-solutions.basf.com/ev/internet/mining-solutions/en/function/conversions:/publish/content/mining-solutions/download-center/technical-data-sheets/pdf/xAliquat_HTA-1_TI_EVH_0145.pdf (accessed on 10 July 2014).
- Aliquat HTA-1. Available online: http://e-applications.basf-ag.de/data/basf-pcan/pds2/pds2-web.nsf/6A7E9E7EEC8E167BC125757700445100/$File/Aliquat_r_HTA-1_E.pdf (accessed on 10 July 2014).
- Hagen, H.; Kantlehner, W.; Speh, P. Verfahren zur Herstellung von N,N',N''-hexasubstituierten Guanidiniumhalogeniden. Germany Patent DE2826011A1, 3 January 1980. (In German)[Google Scholar]
- Kantlehner, W.; Haug, E.; Mergen, W.W.; Speh, P.; Maier, T.; Kapassakalidis, J.J.; Bräuner, H.-J.; Hagen, H. Herstellung von 1,1,2,3,3-pentasubstituierten und 1,1,2,2,3,3-hexasubstituierten Guanidiniumsalzen sowie von 1,1,2,3,3-Pentaalkylguanidinen. Liebigs Ann. Chem. 1984, 1984, 108–126. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Kantlehner, W.; Haug, E.; Mergen, W.W.; Speh, P.; Maier, T.; Kapassakalidis, J.J.; Bräuner, H.-J.; Hagen, H. Ein Herstellungsverfahren für Hexaalkylguanidinium-chloride. Synthesis 1983, 15, 904–905. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Caringi, J.J.; Faler, G.R.; Phelps, P.D.; Guggenheim, T.L.; Flowers, L.I.; Brunelle, D.J.; Odle, R.R. Preparation of Aqueous Solutions of Hexasubstituted Guanidinium Chlorides from Secondary Amines and Phosgene and Their Use as Phase-Transfer Catalysts. Europa Patent EP0784051A1, 16 July 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Brunelle, D.J.; Haitko, D.A.; Barren, J.P.; Singh, S. Process for Reaction of a Highly Polar Compound with a Nonpolar Compound in the Presence of Hexaalkylguanidinium Salts as Phase-Transfer Catalysts. Canada Patent CA2034435A1, 6 August 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Brunelle, D.J.; Haitko, D.A.; Barren, J.P.; Singh, S. Method for Conducting Organic Reactions Using Guanidinium Salt as Phase Transfer Catalyst. Canada Patent CA2044470A1, 14 September 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Schlama, T.; Alcaraz, L.; Mioskowski, C. A convenient epoxidation of α,β-unsaturated ketones with sodium hypochlorite under phase transfer conditions catalyzed by hexaethylguanidinium chloride (HEGCl). Synlett 1996, 1996, 571–572. [Google Scholar]
- King, J.R.; Phelps, P.D. Hexasubstituted Guanidinium Salts and Ultracapacitors Employing Them as Electrolytes. U.S. Patent 5,726,856,10, 10 March 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Bogdanov, M.G.; Svinyarov, I.; Kunkel, H.; Steinle, C.; Arkhipova, M.; Kantlehner, W.; Maas, G. Empirical polarity parameters for hexaalkylguanidinium-based room-temperature ionic liquids. Z. Naturforsch. 2010, 65b, 791–797. [Google Scholar]
- Large, T.; Müller, T.; Kunkel, H.; Buck, S.; Maas, G. Ruthenium- and rhodium-catalyzed carbenoid reactions of diazoesters in hexaalkylguanidinium-based ionic liquids. Z. Naturforsch. 2012, 67b, 347–353. [Google Scholar]
- Branco, L.C.; Serbanovic, A.; Nunes da Ponte, M.; Afonso, C.A.M. Clean osmium-catalyzed asymmetric dihydroxylation of olefins in ionic liquids and supercritical CO2 product recovery. Chem. Commun. 2005, 107–109. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.-M.; Song, G.-L.; Wang, K.-L.; Heng, J.; Zhu, H.-J. Hexaethylguanidinium chloride. Acta Cryst. 2006, E62, o3519–o3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weller, F.; Petz, W. Concerning the reaction of Cp2TiCl2 with [C(NMe2)3][(CO)4FeC(O)NMe2]—Crystal structure of [C(NMe2)3]2[FeCl4]. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 1994, 620, 343–345. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Frey, W.; Vettel, M.; Edelmann, K.; Kantlehner, W. Crystal structure of N,N,N',N',N'',N''-hexamethylguanidinium tetraphenylborate, C31H38BN3. Z. Kristallogr. New Cryst. Struct. 1998, 213, 77–78. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, M.; Siehl, H.-U.; Viefhaus, T.; Frey, W.; Kantlehner, W. An ONIOM study of a guanidinium salt ionic liquid. Experimental and computational characterization of N,N,N',N',N''-pentabutyl-N''-benzylguanidinium bromide. Z. Naturforsch. 2009, 64b, 765–772. [Google Scholar]
- Frey, W.; Orbegozo, T.; Spitzner, D.; Jäger, V. Crystal structure of (R)-N,N',N',N'',N''-pentamethyl-N-(1-phenylethyl)guanidinium iodide, [C14H24N3]I. Z. Kristallogr. New Cryst. Struct. 2009, 224, 251–252. [Google Scholar]
- Oelkers, B.; Sundermeyer, J. Pentaalkylmethylguanidinium methylcarbonates—Versatile precursors for the preparation of halide-free and metal-free guanidinium-based ILs. Green Chem. 2011, 13, 608–618. [Google Scholar]
- Castiglia, A.; Sehrawi, H.M.E.; Orbegozo, T.; Spitzner, D.; Claasen, B.; Frey, W.; Kantlehner, W.; Jäger, V. Synthesis and characterization of chiral guanidines and guanidinium salts derived from 1-phenylethylamine. Z. Naturforsch. 2012, 67b, 337–346. [Google Scholar]
- Tiritiris, I.; Kantlehner, W. 1-Benzyl-2-dimethylamino-3-methyl-3,4,5,6-tetrahydropyrimidin-1-ium bromide. Acta Crystallogr. 2012, E68, o2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiritiris, I.; Kantlehner, W. 2-Dimethylamino-1-(2-ethoxy-2-oxo-ethyl)-3-methyl-3,4,5,6-tetrahydropyrimidin-1-ium tetraphenylborate. Acta Crystallogr. 2012, E68, o2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiritiris, I.; Kantlehner, W. N,N,N',N',N''-Pentamethyl-N''-[3-(1,3,3-trimethylureido)-propyl]guanidinium tetraphenylborate. Acta Crystallogr. 2012, E68, o2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, W.; Castiglia, A.; Jäger, V. Crystal structure of N,N',N''-trimethyl-N,N',N''-tris-(1-phenylethyl)guanidinium hexafluorophosphate, C28H36F6N3P. Z. Kristallogr. New Cryst. Struct. 2012, 227, 317–318. [Google Scholar]
- Froschauer, C.; Salchner, R.; Laus, G.; Weber, H.K.; Tessadri, R.; Griesser, U.; Wurst, K.; Kahlenberg, V.; Schottenberger, H. 1,3-di(alkoxy)imidazolium-based Ionic Liquids: Improved synthesis and crystal structures. Aust. J. Chem. 2013, 66, 391–395. [Google Scholar]
- Holbrey, J.D.; Reichert, W.M.; Rogers, R.D. Crystal structures of imidazolium bis(trifluoro-methanesulfonyl)imide “ionic liquid” salts: The first organic salt with a cis-TFSI anion conformation. Dalton Trans. 2004, 2267–2271. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, L.; DesMarteau, D.D.; Penningtn, W.T. Synthesis and structures of alkaline earth metal salts of bis[(trifluoromethyl)sulfonyl]imide. Solid State Sci. 2005, 7, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulechka, Y.U.; Kabo, G.J.; Blokhin, A.V.; Shaplov, A.S.; Lozinskaya, E.I.; Golovanov, D.G.; Lyssenko, K.A.; Korlyukov, A.A.; Vygodskii, Y.S. IR and X-ray study of polymorphism in 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imides. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 9538–9546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentivoglio, G.; Schwärzler, A.; Wurst, K.; Kahlenberg, V.; Nauer, G.; Bonn, G.; Schottenberger, H.; Laus, G. Hydrogen bonding in the crystal structures of new imidazolium triflimide protic ionic liquids. J. Chem. Crystallogr. 2009, 39, 662–668. [Google Scholar]
- Laus, G.; Hummel, M.; Többens, D.M.; Gelbrich, T.; Kahlenberg, V.; Wurst, K.; Griesser, U.J.; Schottenberger, H. The 1:1 and 1:2 salts of 1,4-diazabicyclo[2.2.2]octane and bis(trifluoro-methylsulfonyl)amine: Thermal behaviour and polymorphism. CrystEngComm 2011, 13, 5439–5446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnahm, M.; Berger, C.; Arkhipova, M.; Kunkel, H.; Pajkossy, T.; Maas, G.; Kolb, D.M. The interfaces of Au(111) and Au(100) in a hexaalkyl-substituted guanidinium ionic liquid: An electrochemical and in situ STM study. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2012, 14, 10647–10652. [Google Scholar]
- Hess, S.; Arkhipova, M.; Wohlfahrt-Mehrens, M.; Maas, G.; Wachtler, M. Synthesis and characterization of guanidinium-based ionic liquids as possible electrolytes in lithium-ion batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2014, 161, A753–A761. [Google Scholar]
- Bucher, N.; Hartung, S.; Arkhipova, M.; Yu, D.; Kratzer, P.; Maas, G.; Srinivasan, M.; Hoster, H.E. A novel ionic liquid for Li ion batteries—Uniting the advantages of guanidinium and piperidinium cations. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 1996–2003. [Google Scholar]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).