Corrosion Study and Intermetallics Formation in Gold and Copper Wire Bonding in Microelectronics Packaging
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Bonding Parameters and Material Properties of Au and Cu wires
| Property | Au | Cu |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | 99.99% Au | 99.99% Cu |
| Diameter (μm) | 25 | 25 |
| Specified Breaking Load (g) | 9.7~17.4 | 6.8~14.5 |
| Elongation (%) | 2~7 | 6~18 |
| Parameter | Au | Cu |
|---|---|---|
| Bonding Time (ms) | 10.0 | 9.0 |
| Bonding Force (gf) | 26.0 | 9.0 |
| Ultrasonic Power (mW) | 256 | 306 |
2.2. Corrosion Studies in Halide Environment
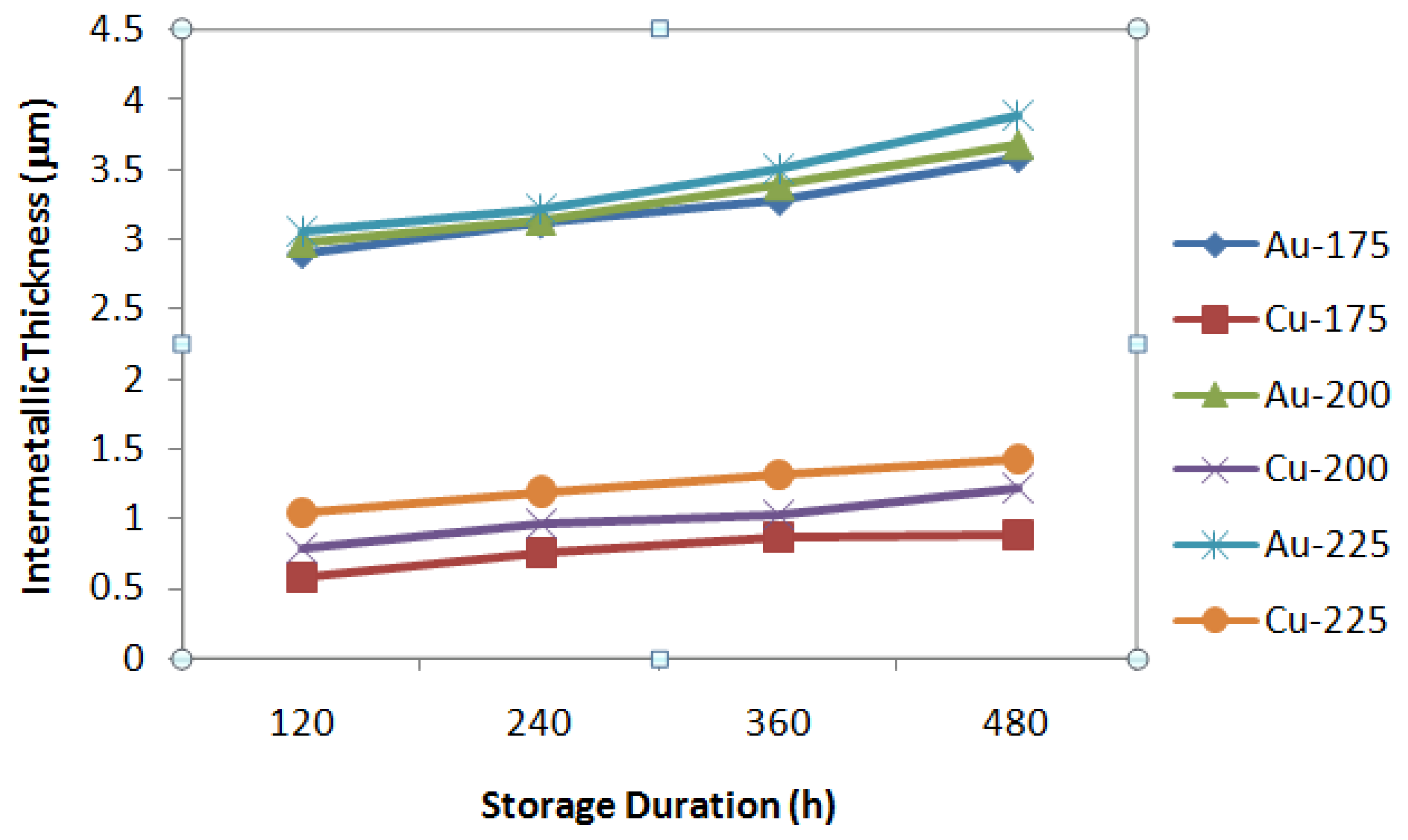
2.3. Intermetallic Growth Rate Evaluation in Au/Al and Cu/Al Wire Bonding
| Condition | Temperature (°C) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 175 | 200 | 225 | |
| Duration (h) | 120 | 120 | 120 |
| 240 | 240 | 240 | |
| 360 | 360 | 360 | |
| 480 | 480 | 480 | |
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Corrosion Studies in Halide Environment
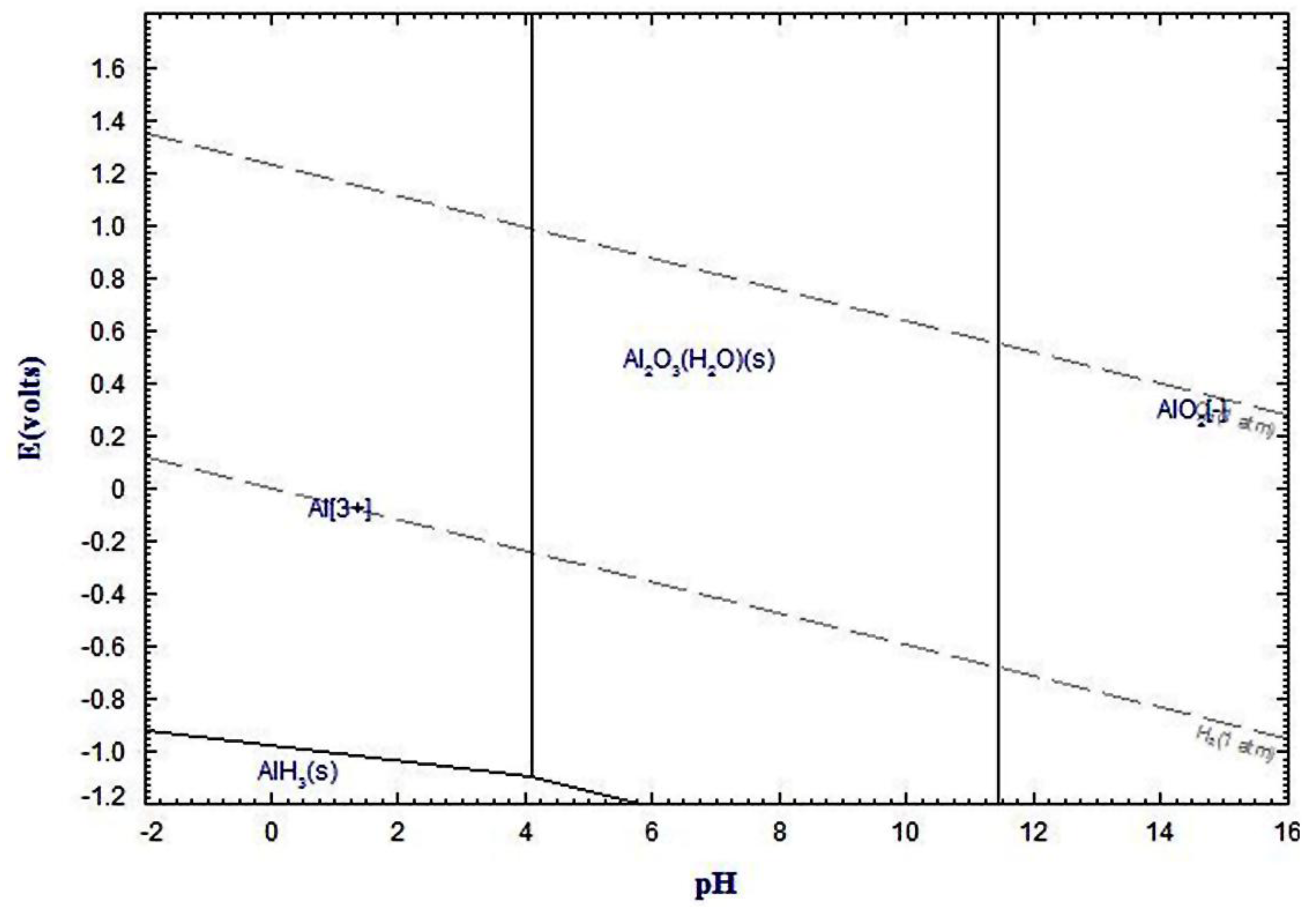
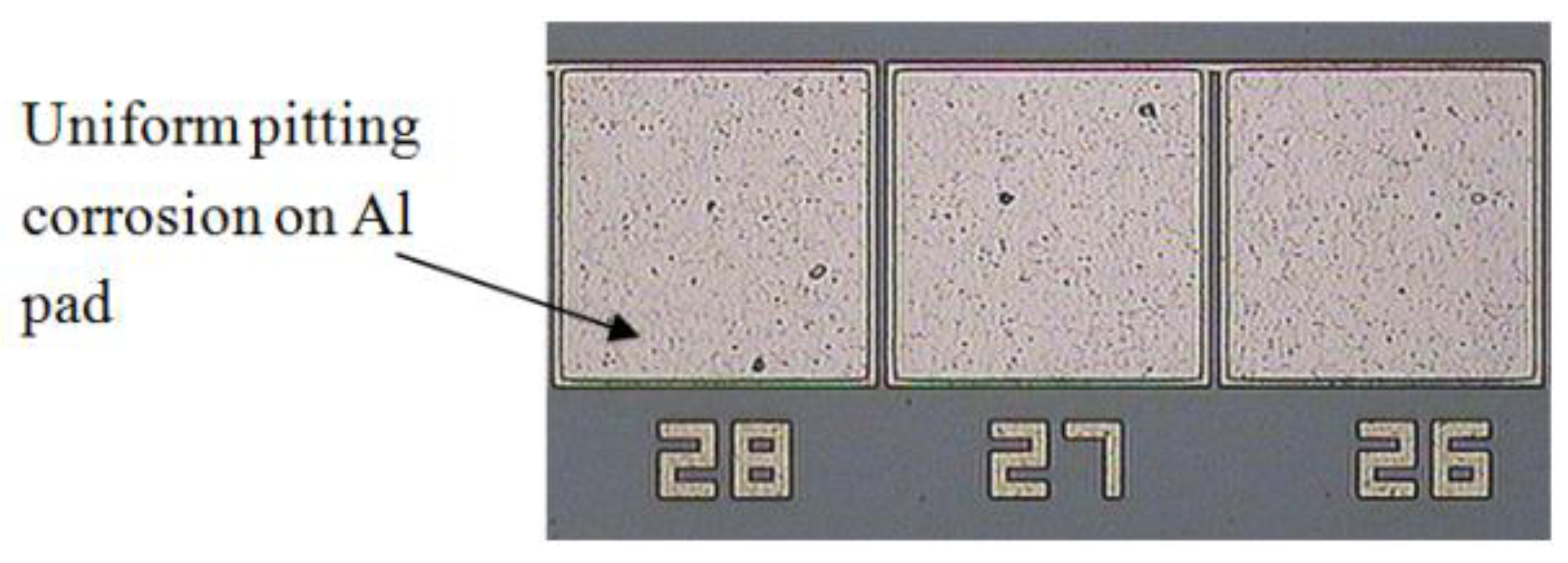
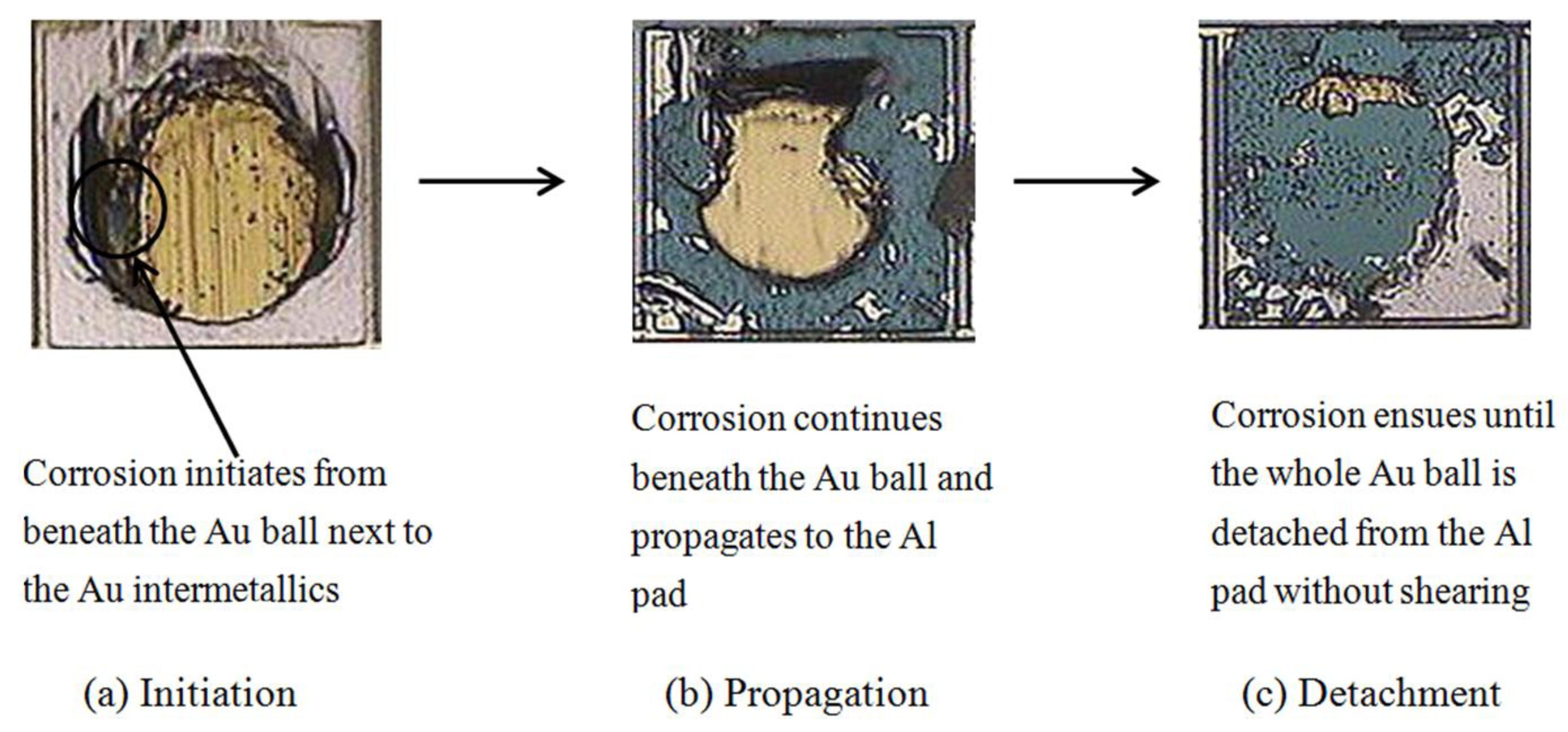

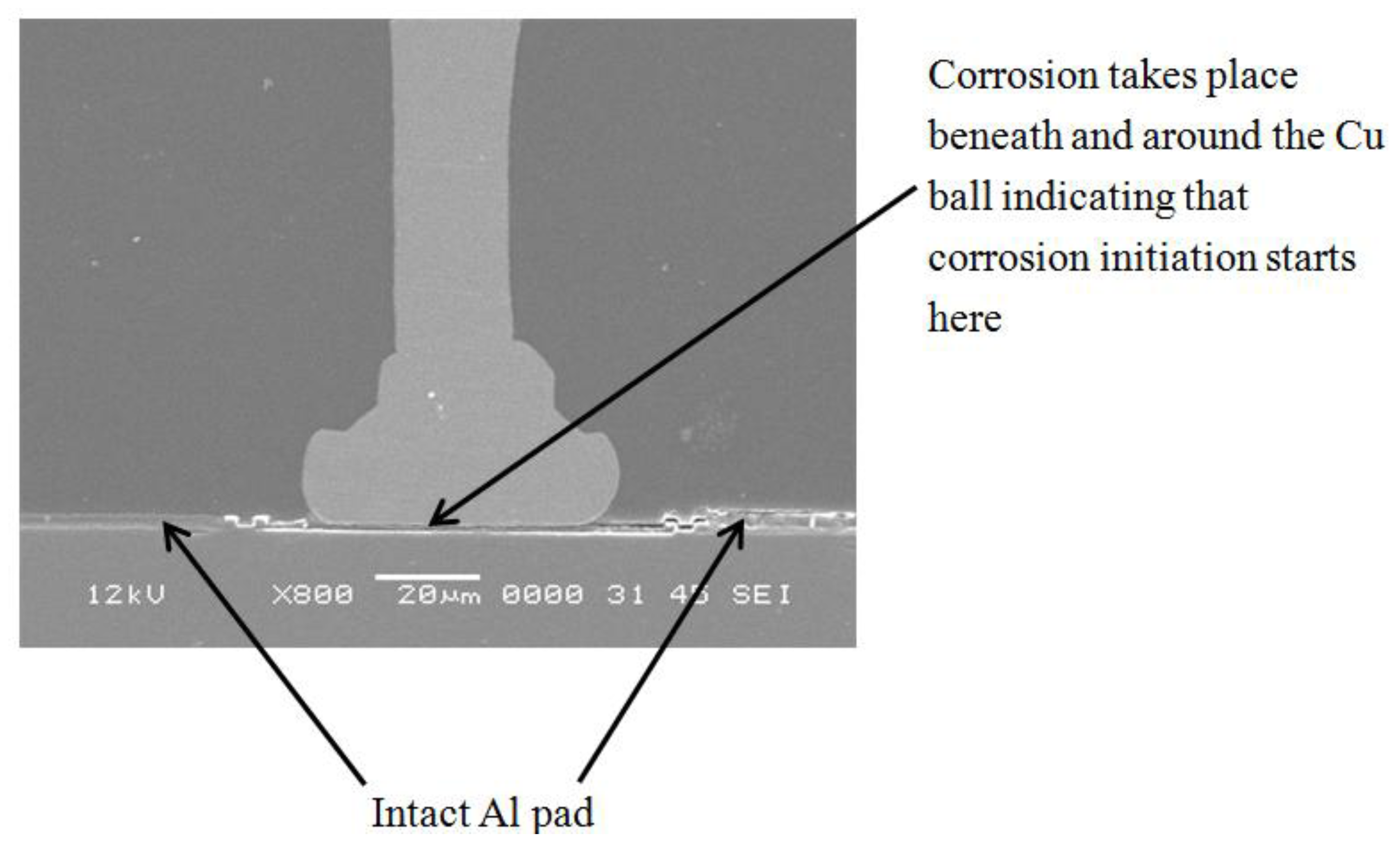

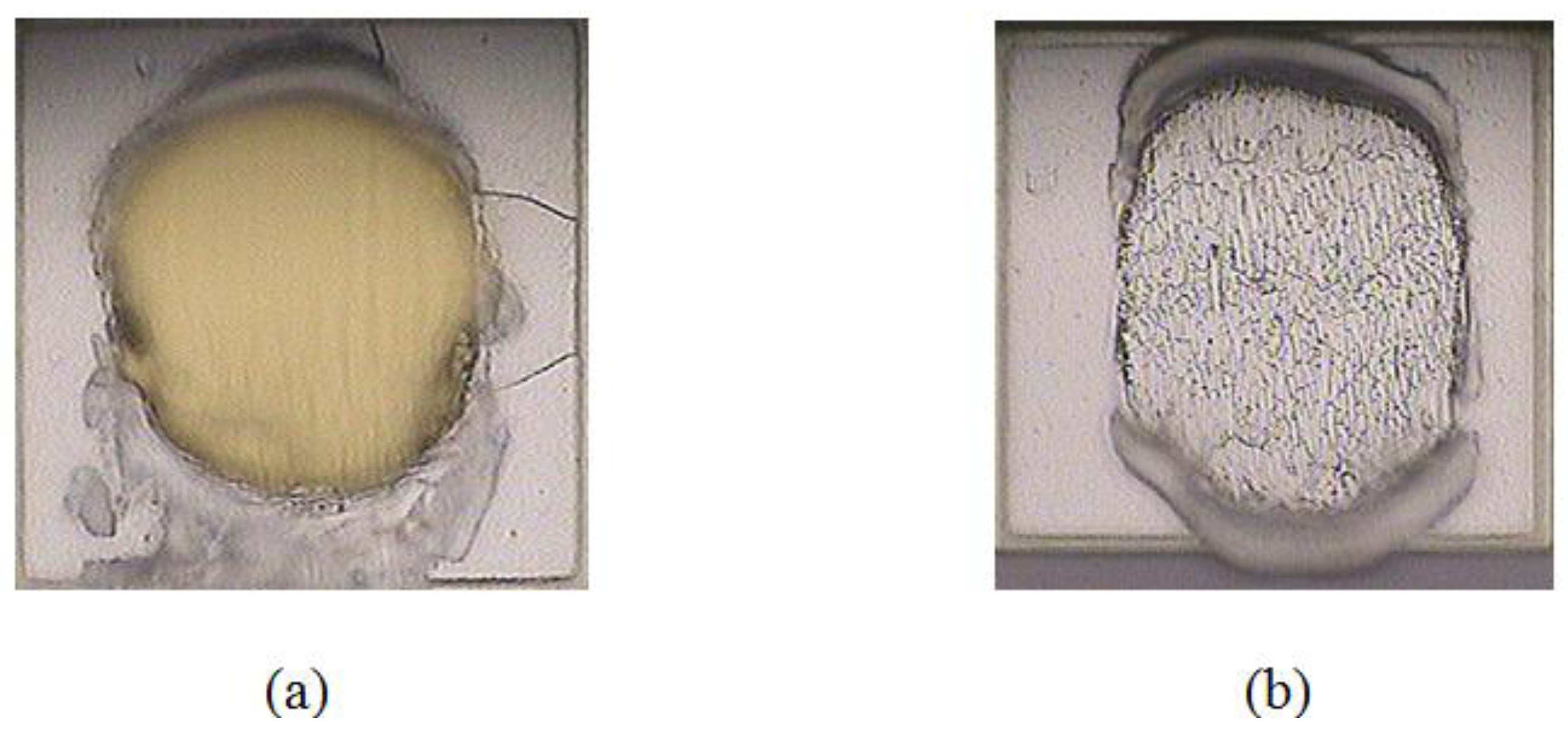
3.2. Intermetallic Growth Rate Evaluation in Au/Al and Cu/Al Wire Bonding
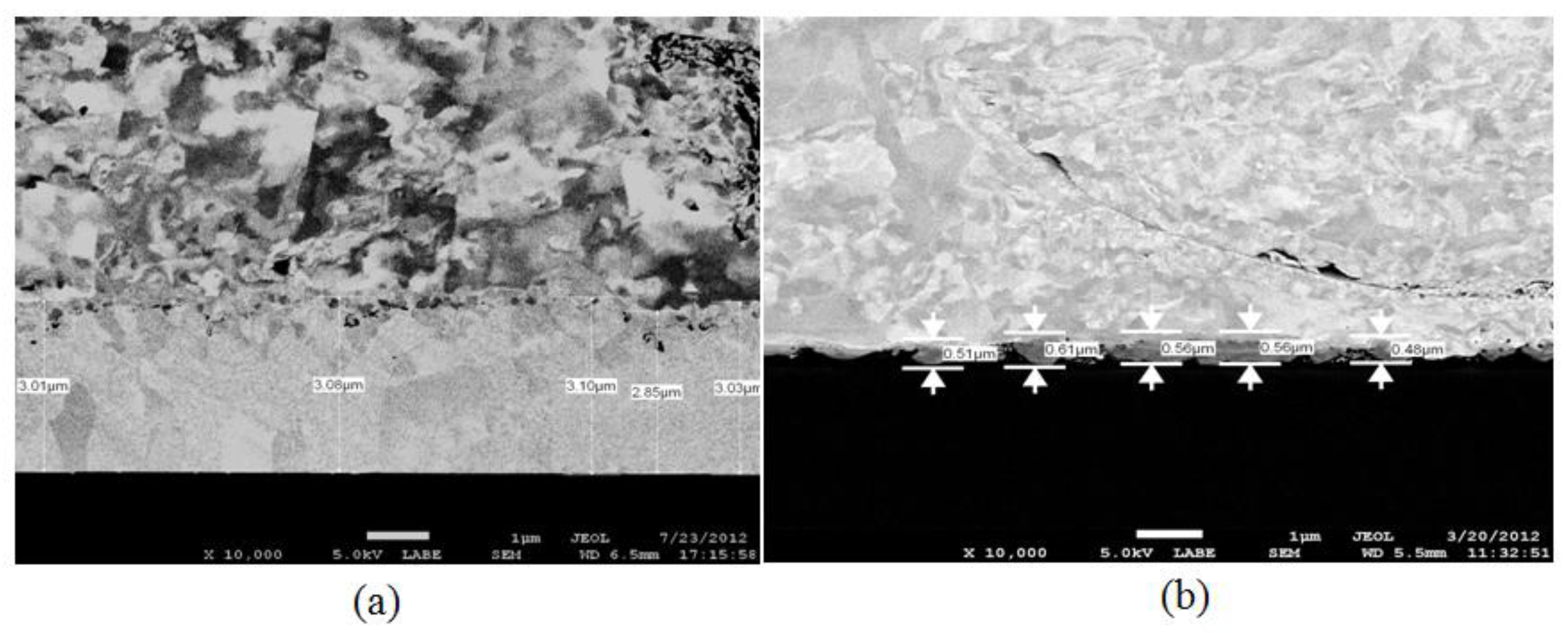

- t = Annealing time (s)
- K = Reaction rate of IMC formation (μm2/s)
- K1 = Constant related to initial IMC thickness (μm2)

- R = Gas constant (1.99 cal/mol K)
- T = Annealing Temperature (K)
- Ko = Pre-exponential Factor (μm2/s)
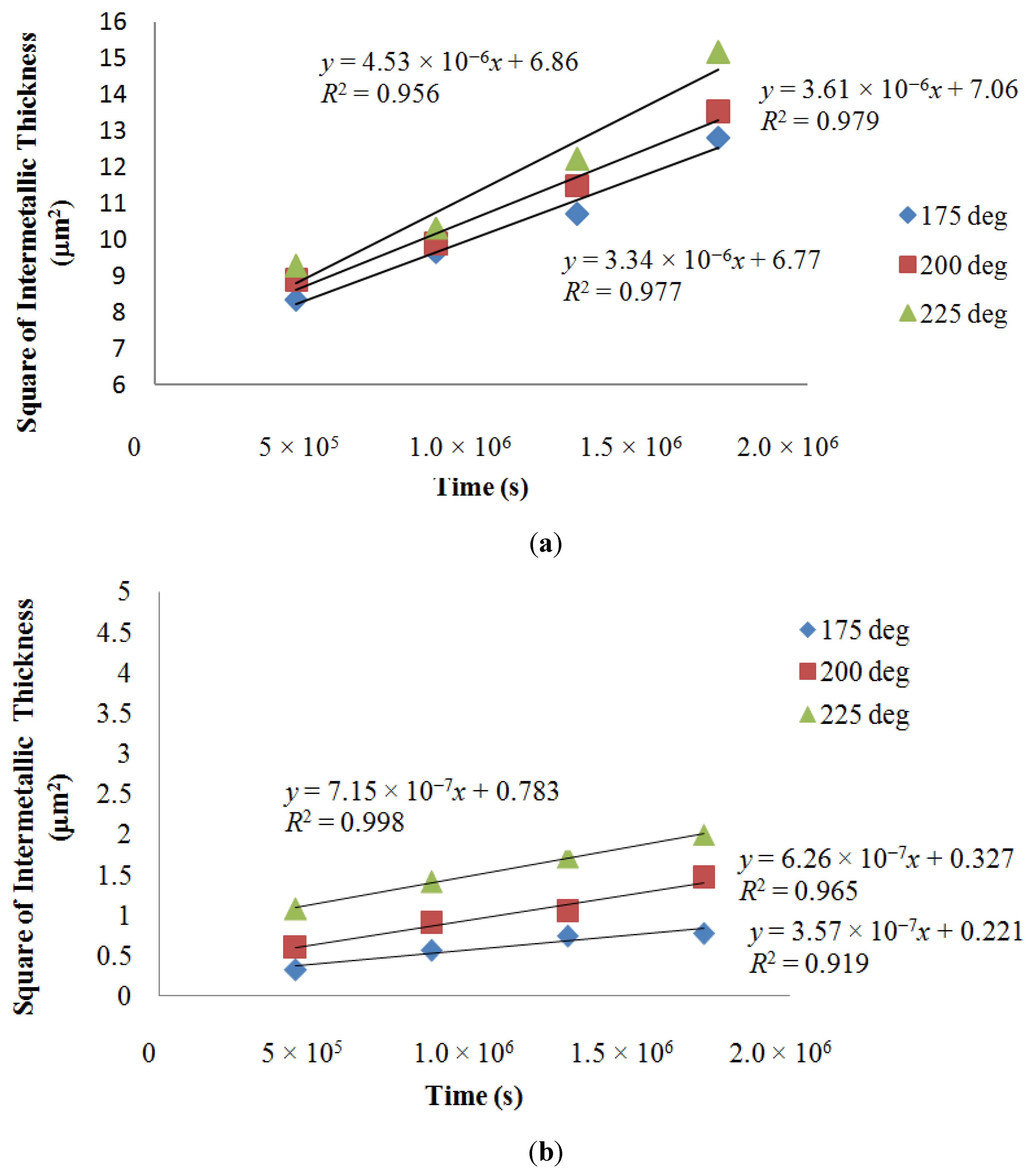

| Sample | Author | Time (h) | Temperature (°C) | Rate (μm2/s) | ΔQ (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Au | Current | 120, 240, 360, 480 | 175 | 3.34 × 10−6 | 2.5 |
| 120, 240, 360, 480 | 200 | 3.61 × 10−6 | |||
| 120, 240, 360, 480 | 225 | 4.53 × 10−6 | |||
| [3] | 2, 25, 75, 100, 300 | 150 | 1.10 × 10−14 | – | |
| 2, 25, 75, 100, 300 | 280 | 2.40 × 10−11 | |||
| 2, 25, 75, 100, 300 | 350 | 3.90 × 10−10 | |||
| Cu | Current | 120, 240, 360, 480 | 175 | 3.57 × 10−7 | 6.1 |
| 120, 240, 360, 480 | 200 | 6.26 × 10−7 | |||
| 120, 240, 360, 480 | 225 | 7.15 × 10−7 | |||
| [3] | 2, 25, 75, 100, 300 | 150 | 1.88 × 10−16 | 26 | |
| 2, 25, 75, 100, 300 | 250 | 2.64 × 10−13 | |||
| 2, 25, 75, 100, 300 | 300 | 3.75 × 10−12 | |||
| [6] | 100, 250, 500, 1000 | 150 | 2.15 × 10−8 | 10.71 | |
| 100, 250, 500, 1000 | 200 | 2.56 × 10−8 | |||
| 100, 250, 500, 1000 | 250 | 1.08 × 10−7 |


4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Uniform pitting corrosion occurs on the Al pad in the absence of wire bonding.
- (2)
- The good Au coverage and intermetallic formation beneath the Au balls strengthens the bonding between Au and Al. Therefore, Cl− solution is not able to seep in easily to set up the corrosion cell, and the corrosion rate in Au/Al is much lower than Cu/Al.
- (3)
- The intermetallic thickness of Au/Al can range from 3 to 5 times higher than Cu/Al.
- (4)
- The thin Al metallization in previous works could be the rate-determining step in preventing faster intermetallic formation, and resulted in higher activation energy than what was observed in the current work.
Acknowledgments
Conflict of Interest
References
- Harmon, G. Wire Bonding in Microelectronics: Materials, Processes, Reliability and Yield, 2nd ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- England, L.; Jiang, T. Reliability of Cu Wire Bonding to Al Metallization. In Proceedings of IEEE Electronic Component Technology Conference, Reno, NV, USA, 29 May 2007; p. 1604.
- Kim, H.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Paik, K.W.; Koh, K.W.; Won, J.H.; Choe, S.; Lee, J.; Moon, J.T.; Park, Y.J. Effects of Cu/Al intermetallic compound (IMC) on copper wire and aluninum pad bondability. IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Technol. 2003, 26, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, J.; Cousens, D.; Dufour, M. Copper wire ball bonding. In Proceedings of the 34th Electron Component Conference, New Orleans, LA, USA, 14–16 May 1984; pp. 1–5.
- Mori, S.; Yoshida, H.; Uchiyama, N. The development of new copper ball bonding wire. In Proceedings of the 38th Elentron Component Conference, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 9–11 May 1988; pp. 539–545.
- Na, S.H.; Hwang, T.Y.; Park, J.S.; Kim, J.Y.; Yoo, H.Y.; Lee, C.H. Characterization of intermetallic compound (IMC) growth in Cu wire ball bonding on Al pad metallization. In Proceedings of the 61st Electronic Components and Technology Conference, Lake Buena Vista, FL, USA, 31 May–3 June 2011; pp. 1740–1745.
- Murali, S.; Srikanth, N.; Vath, C.J. Grains, deformation substructures and slip bands observed in thermosonic copper ball bonding. Mater. Charact. 2003, 50, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.T.; McDonald, D.; Danker, A.R.; Ng, P. Optimization of copper wire bonding on Al-Cu metallization. IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Manufact. Technol. Part A. 1995, 18, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.W.; Daud, A.R.; Yarmo, M.A. Corrosion study at the Cu-Al interface in microelectronics packaging. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2002, 191, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hang, C.J.; Wang, C.Q.; Mayer, M.; Tian, Y.H.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, H.H. Growth behaviour of Cu/Al intermetallic compounds and cracks in copper ball bonds during isothermal aging. Microelectron. Reliab. 2008, 48, 416–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.C.; Higgins, L.M. Challenges of Cu wire bonding on low-k/Cu wafers with BOA structures. In Proceedings of the 60th Electronic Components and Technology Conference, Las Vega, NV, USA, 1–4 June 2010; pp. 342–349.
- Boettcher, T.; Rother, M.; Liedtke, S.; Ulrich, M.; Bollmann, M.; Pinkernelle, A.; Gruber, D.; Funke, H.-J.; Kaiser, M.; Lee, K.; et al. On the intermetallic corrosion of Cu-Al wire bonds. In Proceedings of the 12th Electronics Packaging Technology Conference, Singapore, 8–10 December 2010; pp. 585–590.
- Facility for the Analysis of Chemical Thermodynamics. Available online: http://www.crct.polymtl.ca/factweb.php (accessed on 18 March 2013).
- Foley, R.T.; Hguyen, I.H. The chemical nature of Al corrosion—V. Energy transfer in Al dissolution. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1982, 192, 464–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beverskog, B.; Puigdomenech, I. SKI Rapport 98:19. Pourbaix diagrams for the system copper-chlorine at 5–100 °C. Available online: http://www.stralsakerhetsmyndigheten.se/global/ publikationer/ski_import/010803/04318226039/98-19.pdf (accessed on 18 March 2013).
- Lue, M.H.; Huang, C.T.; Huang, S.T.; Hsieh, K.C. Bromine and chlorine induced degradation of the Au–Al bonds. J. Electron. Mater. 2004, 33, 1111–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrapler, L.; Muller, T.; Knoll, H.; Petzold, M. Influence of intermetallic phases on bonding reliability in thermosonic Au–Al wire bonding. In Proceedings of the 1st Electronic System Integration Technology Conference, Dresden, Germany, 5–7 September 2006; pp. 1266–1273.
- Rajan, K.; Wallach, E.R. A transmission electron microscopy study of intermetallic formation in Al-Cu thin film couples. J. Cryst. Growth 1980, 49, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamou, Y.; Li, J.; Russell, S.W.; Mayer, J.W. Thermal and ion beam induced thin film reactions in Cu-Al bilayers. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. B 1992, 64, 130–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Goh, C.S.; Chong, W.L.E.; Lee, T.K.; Breach, C. Corrosion Study and Intermetallics Formation in Gold and Copper Wire Bonding in Microelectronics Packaging. Crystals 2013, 3, 391-404. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst3030391
Goh CS, Chong WLE, Lee TK, Breach C. Corrosion Study and Intermetallics Formation in Gold and Copper Wire Bonding in Microelectronics Packaging. Crystals. 2013; 3(3):391-404. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst3030391
Chicago/Turabian StyleGoh, Chwee Sim, Wee Ling Eddy Chong, Teck Kheng Lee, and Christopher Breach. 2013. "Corrosion Study and Intermetallics Formation in Gold and Copper Wire Bonding in Microelectronics Packaging" Crystals 3, no. 3: 391-404. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst3030391
APA StyleGoh, C. S., Chong, W. L. E., Lee, T. K., & Breach, C. (2013). Corrosion Study and Intermetallics Formation in Gold and Copper Wire Bonding in Microelectronics Packaging. Crystals, 3(3), 391-404. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst3030391





