Preferential Adsorption of Single-Stranded DNA on Graphene Oxide with Hydroxyl and Epoxy Groups
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Method and Model
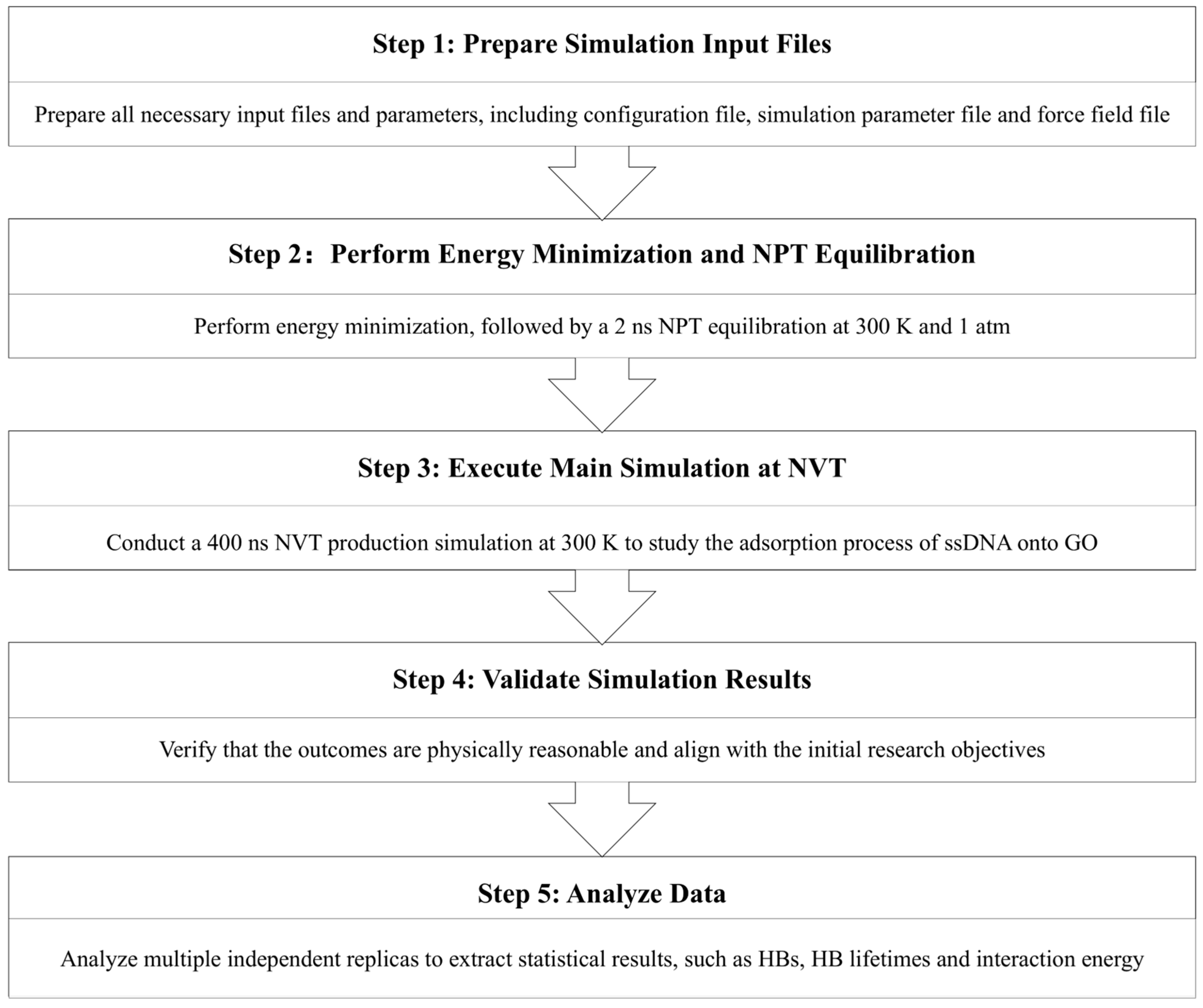
2.1. Simulation Workflow
- (a)
- All essential input files and parameters were prepared, including the configuration file, simulation parameter file, and force field file.
- (b)
- Energy minimization was carried out to eliminate unfavorable atomic contacts, followed by a 2 ns isothermal-isobaric (NPT) equilibration at 300 K and 1 atm to stabilize the system density.
- (c)
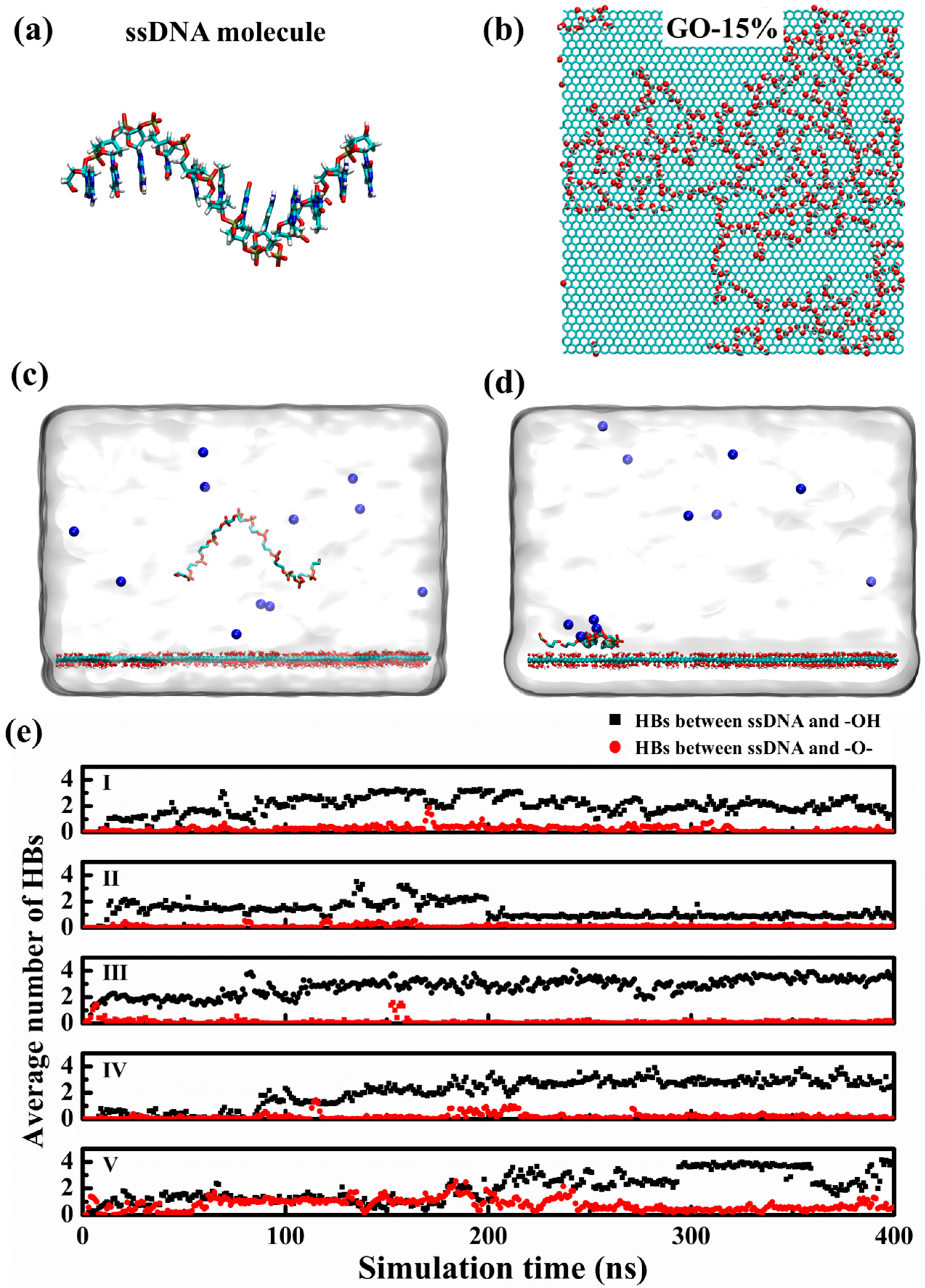
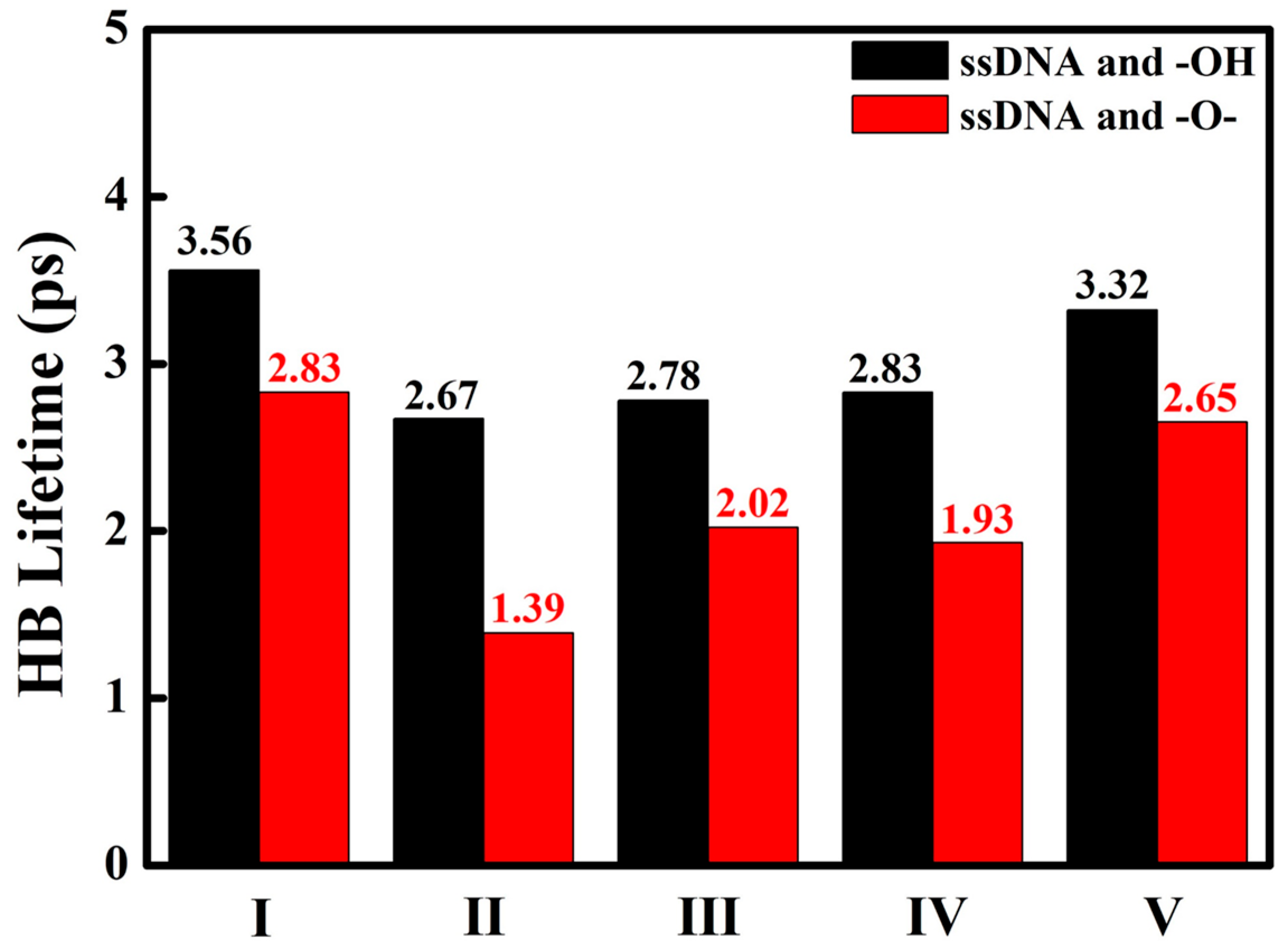
- The production phase consisted of a 400 ns canonical ensemble (NVT) simulation at 300 K to investigate the adsorption mechanism of ssDNA onto GO. The carbon atoms of GO were frozen at their initial positions while the other atoms were free to move. Five independent simulation replicates with identical initial configurations were performed to obtain statistically averaged results.
- (d)
- The simulation outcomes were then validated to ensure physical plausibility and consistency with the initial research objectives.
- (e)
- Finally, statistical analyses were performed using multiple independent replicas to extract reliable metrics, including HBs, HB lifetimes, and interaction energies, and so on.
2.2. System Settings
2.3. Simulation Parameters
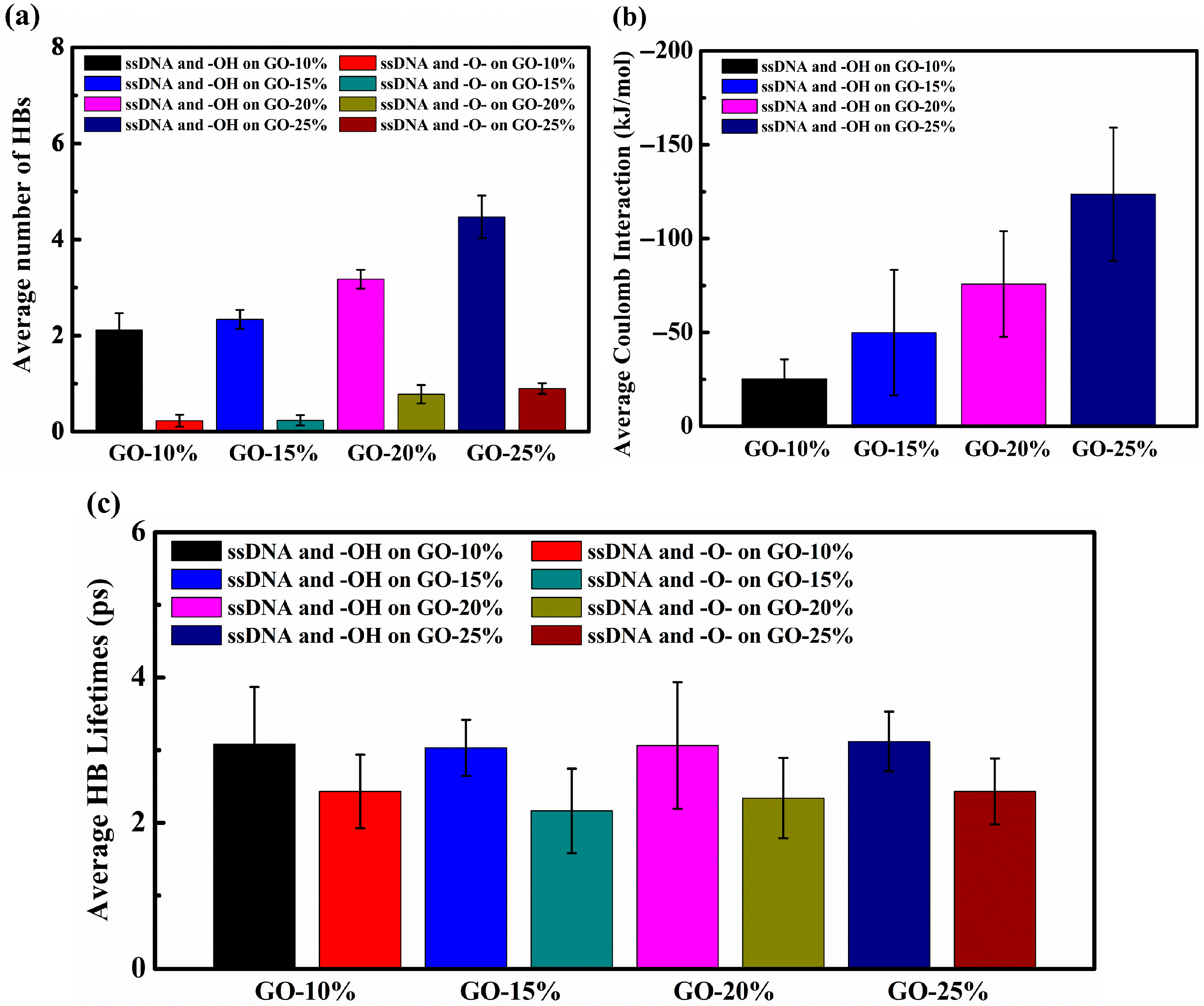
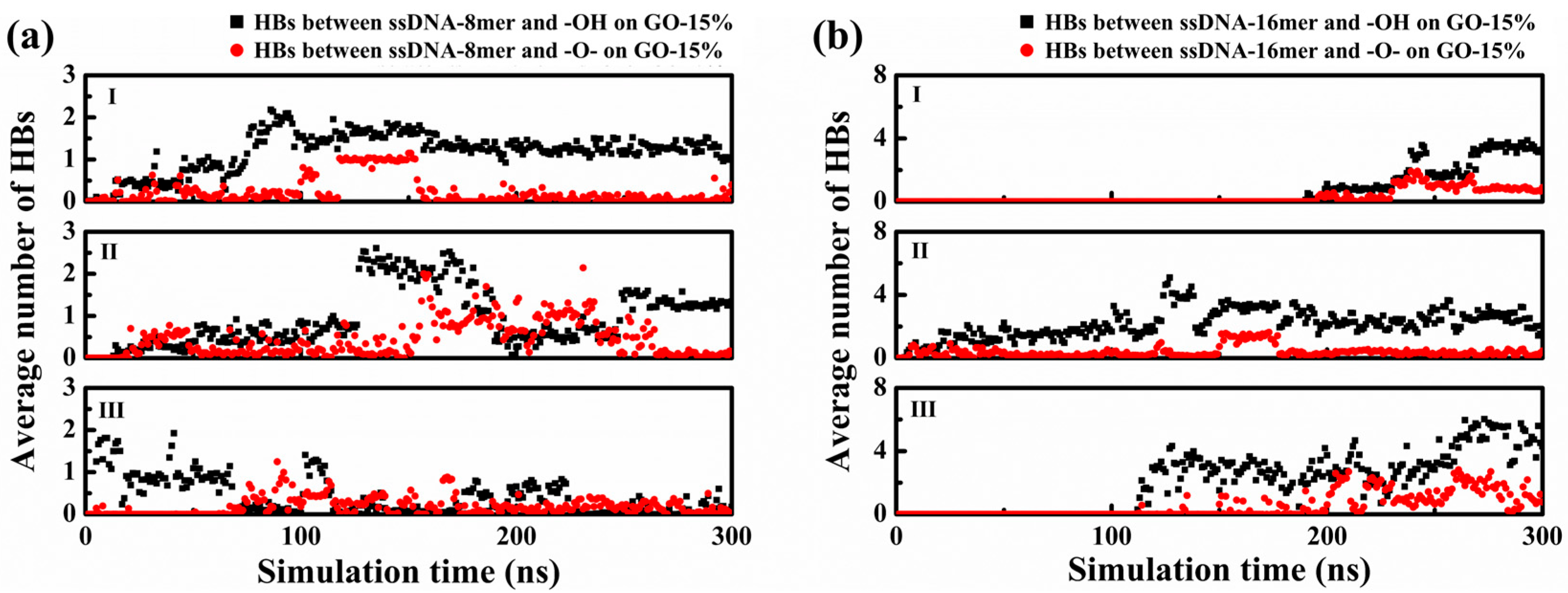
3. Result and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- An, H.; Jin, B. Prospects of nanoparticle–DNA binding and its implications in medical biotechnology. Biotechnol. Adv. 2012, 30, 1721–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glick, B.R.; Patten, C.L. Molecular Biotechnology: Principles and Applications of Recombinant DNA; John Wiley & Sons: Washington DC, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Hirao, I. Unnatural base pair systems for DNA/RNA-based biotechnology. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2006, 10, 622–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Hartman, M.R.; Derrien, T.L.; Hamada, S.; An, D.; Yancey, K.G.; Cheng, R.; Ma, M.; Luo, D. DNA materials: Bridging nanotechnology and biotechnology. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 1902–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Vasquez, K.M. Dynamic alternative DNA structures in biology and disease. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2023, 24, 211–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Mao, X.; Wang, F.; Zuo, X.; Fan, C. Data storage using DNA. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2307499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladabaum, M.; Tikhomirov, G. Growing moiré with DNA. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Tabatabaei, S.K.; Tabatabaei Yazdi, S.H.; Hernandez, A.G.; Schroeder, C.M.; Milenkovic, O. Rewritable two-dimensional DNA-based data storage with machine learning reconstruction. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crane-Robinson, C. Role of water in defining the structure and properties of B-Form DNA. Crystals 2022, 12, 818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Yadav, P.; Barati Farimani, A. Which 2D material is better for DNA detection: Graphene, MoS2, or MXene? Nano Lett. 2022, 22, 7874–7881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Situ, B.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, L.; Tu, Y. Graphene oxide-based large-area dynamic covalent interfaces. Nanoscale 2023, 15, 17739–17750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Feng, Z.; Xie, Y.; Wang, H.; Ji, Q.; Wang, J.; Xu, C. Surface modification of graphene oxide and its strengthening and toughening mechanism for alumina-based ceramic materials. Crystals 2024, 14, 949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Shi, G.; Shen, J.; Peng, B.; Zhang, B.; Wang, Y.; Bian, F.; Wang, J.; Li, D.; Qian, Z. Ion sieving in graphene oxide membranes via cationic control of interlayer spacing. Nature 2017, 550, 380–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, C.; Kim, Y.K.; Shin, D.; Ryoo, S.R.; Hong, B.H.; Min, D.H. Biomedical applications of graphene and graphene oxide. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 2211–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimiev, A.M.; Tour, J.M. Mechanism of graphene oxide formation. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 3060–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreyer, D.R.; Park, S.; Bielawski, C.W.; Ruoff, R.S. The chemistry of graphene oxide. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 228–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eigler, S.; Hirsch, A. Chemistry with graphene and graphene oxide—Challenges for synthetic chemists. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 7720–7738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; Loh, K.P. Carbocatalysts: Graphene oxide and its derivatives. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 2275–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; James, D.K.; Tour, J.M. New routes to graphene, graphene oxide and their related applications. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 4924–4955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutapea, J.A.A.; Manik, Y.G.O.; Ndruru, S.T.C.L.; Huang, J.; Goei, R.; Tok, A.I.Y.; Siburian, R. Comprehensive review of graphene synthesis techniques: Advancements, challenges, and future directions. Micro 2025, 5, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakchaure, M.B.; Menezes, P.L. Advances in the tribological performance of graphene oxide and its composites. Materials 2025, 18, 3587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Lee, C.J.M.; Tan, G.S.X.; Ng, P.R.; Zhang, P.; Zhao, J.; Novoselov, K.S.; Andreeva, D.V. Ultra-tough graphene oxide/DNA 2D hydrogel with intrinsic sensing and actuation functions. Macromol. Rapid. Commun. 2025, 46, 2400518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Jia, S.; Lv, M.; Shi, J.; Zuo, X.; Su, S.; Wang, L.; Huang, W.; Fan, C.; Huang, Q. Size-dependent programming of the dynamic range of graphene oxide–DNA interaction-based ion sensors. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 4047–4051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Lian, C.; Zhou, Y.; Yan, L.; Li, Q.; Zhang, C.; Chen, L.; Chen, K. Graphene oxide–DNA based sensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 60, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Salgado, S.; Maheshwari, V.; Liu, J. DNA adsorbed on graphene and graphene oxide: Fundamental interactions, desorption and applications. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 26, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, R.; Jiang, T.; Sun, W.; Gu, Z. ATP-responsive DNA-graphene hybrid nanoaggregates for anticancer drug delivery. Biomaterials 2015, 50, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, J. DNA-directed self-assembly of graphene oxide with applications to ultrasensitive oligonucleotide assay. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 3817–3822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, T.; Cui, X.; Guan, W.; Wang, Q.; Liu, C.; Wang, H.; Qi, K.; Singh, D.J.; Zheng, W. Surface plasmon resonance technique for directly probing the interaction of DNA and graphene oxide and ultra-sensitive biosensing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 58, 374–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiticaru, E.A.; Damian, C.M.; Pilan, L.; Ioniță, M. Label-free DNA biosensor based on reduced graphene oxide and gold nanoparticles. Biosensors 2023, 13, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Bytesnikova, Z.; Ashrafi, A.M.; Adam, V.; Richtera, L. Graphene oxide as a nanocarrier for biochemical molecules: Current understanding and trends. Processes 2020, 8, 1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wang, Q.; Yang, X.; Wang, K.; Zhang, H.; Nie, W. High sensitivity surface plasmon resonance biosensor for detection of microRNA and small molecule based on graphene oxide-gold nanoparticles composites. Talanta 2017, 174, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Lin, Y.; Song, M.; Gui, C.; Leesirisan, S. Enhancing the electrical conductivity of polymer composites. Eur. Polym. J. 2013, 49, 1066–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J. Mechanisms of DNA sensing on graphene oxide. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 7987–7993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Yim, Y.; Kim, S.; Choi, M.H.; Choi, B.S.; Lee, Y.; Min, D.H. In-depth investigation of the interaction between DNA and nano-sized graphene oxide. Carbon 2016, 97, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, S.; Chen, L.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J. Exploration on the mechanism of DNA adsorption on graphene and graphene oxide via molecular simulations. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2015, 48, 275402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balapanuru, J.; Yang, J.X.; Xiao, S.; Bao, Q.; Jahan, M.; Polavarapu, L.; Wei, J.; Xu, Q.H.; Loh, K.P. A graphene oxide–organic dye ionic complex with DNA-sensing and optical-limiting properties. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 6549–6553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.S.; Goo, N.I.; Kim, D.E. Mechanism of DNA adsorption and desorption on graphene oxide. Langmuir 2014, 30, 12587–12595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Chang, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, J. Duplex DNA/graphene oxide biointerface: From fundamental understanding to specific enzymatic effects. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 3083–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Zhang, H.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Yan, G. ssDNA-QDs/GO multicolor fluorescence system for synchronous screening of hepatitis virus DNA. Arabian J. Chem. 2023, 16, 104582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Lei, X.; Tu, Y.; Tan, Z.J.; Song, B.; Fang, H. Dynamic cooperation of hydrogen binding and π stacking in ssDNA adsorption on graphene oxide. Chem. Eur. J. 2017, 23, 13100–13104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Shi, G.; Tu, Y.; Fang, H. High correlation between oxidation loci on graphene oxide. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 126, 10354–10358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.; Wang, G.; Yuan, H.; Li, J.; Ni, K.; Pan, F.; Guo, M.; Wu, Y.; Ji, H.; Zhang, F.; et al. Microfluidic oxidation of graphite in two minutes with capability of real-time monitoring. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2107083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, S.; Huang, W.; Shen, F.; Li, T.; Li, S.; Xu, W.; Lv, C.; Luo, Q.; Liu, J. Graphene oxide-based colorimetric detection of organophosphorus pesticides via a multi-enzyme cascade reaction. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 5829–5833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liou, T.H.; Tseng, Y.K.; Zhang, T.Y.; Liu, Z.S.; Chen, J.Y. Rice husk char as a sustainable material for the preparation of graphene oxide-supported biocarbons with mesoporous structure: A characterization and adsorption study. Fuel 2023, 344, 128042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Chen, J.; Fang, H.; Lei, X. Oxidation degree dependent adsorption of ssDNA onto graphene-based surface. Chin. Phys. B 2021, 30, 106806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Xu, Z.; Fang, H.; Lei, X. Unexpected sequence adsorption features of polynucleotide ssDNA on graphene oxide. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2020, 22, 11740–11746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, H.; Huang, X.; Wang, S.; Wu, M.; Wang, H.; Shao, G.; Zhao, L.; Lei, X. Preferential Adsorption of Single-Stranded DNA on Graphene Oxide with Hydroxyl and Epoxy Groups. Crystals 2025, 15, 800. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15090800
Ma H, Huang X, Wang S, Wu M, Wang H, Shao G, Zhao L, Lei X. Preferential Adsorption of Single-Stranded DNA on Graphene Oxide with Hydroxyl and Epoxy Groups. Crystals. 2025; 15(9):800. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15090800
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Huishu, Xiaodan Huang, Shijun Wang, Mei Wu, Hanbing Wang, Guowei Shao, Liang Zhao, and Xiaoling Lei. 2025. "Preferential Adsorption of Single-Stranded DNA on Graphene Oxide with Hydroxyl and Epoxy Groups" Crystals 15, no. 9: 800. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15090800
APA StyleMa, H., Huang, X., Wang, S., Wu, M., Wang, H., Shao, G., Zhao, L., & Lei, X. (2025). Preferential Adsorption of Single-Stranded DNA on Graphene Oxide with Hydroxyl and Epoxy Groups. Crystals, 15(9), 800. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15090800





