Abstract
Aiming to enhance the surface properties of low-carbon steel, NiCrBSi coatings containing 10 wt.% Nb were fabricated via pulsed laser cladding. Samples were realized with laser power ranging from 2800 to 3200 W. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM), coupled with energy-dispersive X-ray (EDX) analysis, was used to examine the microstructure and chemical composition. X-ray diffraction (XRD) was employed to evaluate the new phases formed within the coatings compared to the initial powder composition. Hardness measurements and corrosion resistance in a 3.5% NaCl solution were conducted to evaluate the effect of the Nb alloying on the properties of the cladded layers. In all cases, good metallurgical bonds were formed between the coatings and the substrate. However, the coatings produced at low laser power were thinner, and the substrate experienced more intense thermal exposure, resulting in increased dissolution of iron from the substrate. Increasing the laser power significantly enhanced the hardness of the coating compared to coatings produced using lower power. These phenomena can be the result of improved powder cladding efficiency, which can lead to thicker coatings with enhanced corrosion resistance. The results suggest that Nb addition can lead to improved mechanical behavior and corrosion resistance, but the process is highly dependent on the parameters and mainly on the laser power.
1. Introduction
Nowadays, laser cladding is widely used as a surface modification method to improve the physical and chemical properties of surfaces of various parts for industrial applications [1]. It has several advantages, such as the potential to produce coatings with low dilution [2]; a strong bond with the substrate [3]; and the possibility to manufacture thick coatings, from micrometers to several millimeters [4]. Despite these advantages, cracking is one of the most common defects encountered in coatings, and Ni-based coatings are susceptible to hot cracking during cladding. Moreover, deposition parameters such as laser power and scanning speed significantly influence the area of the alloying zone, as well as the depth and width of the heat-affected zone (HAZ) [5]. Therefore, these parameters need to be kept under control to ensure quality coatings. In addition, to reduce the risk of failure and extend the service life of coated components, so far, laser cladding technology has often incorporated reinforcement within the coatings [6]. In the field of cladding, one of the highly versatile Ni-based cladding materials is NiCrBSi due to its relatively low cost and high corrosion resistance. To further improve the performance of NiCr-based coatings, numerous studies investigated the addition of hard ceramic particles, such as ZrB2 [7], Al2O3 [8] and WC [9], WC-Co [10], WC-Co(Ti) [11], and TiC [12] within the feedstock powder to enhance the performance of the coatings. Besides the ceramic particles, the addition of refractory metals has gained attention due to their high meting points and high-temperature strength. Among them, Nb is the lightest refractory metal; has the lowest melting temperature; and presents unique properties, such as very good conductivity, high ductility, and high-temperature stability. Nb is used to alloy steel and nickel-based superalloys, providing a significant strengthening effect [13]. Moreover, it is a strong carbide former since it reacts easily with C to form NbC. According to Funch and Proust, Nb alloys are more effectively produced using electron beam or arc melting techniques to achieve improved high-temperature strength and oxidation resistance [14]. However, few studies faced the challenge of depositing coatings with Nb addition using laser cladding. Zhang et al. studied the effects of Nb addition on the laser energy efficiency and properties of (NiCrCoFe)100-xNbx HEA manufactured underwater using laser cladding [15]. They determined that the presence of the Nb in the underwater wet laser cladding process reduces the coating width, increases the cladding depth, and improves the utilization efficiency of underwater laser energy. Chen et al. studied the effect of Nb content on FeCo0.5CrNi1.5B0.5Nbx coatings on ductile iron, and they observed an increased hardness due to Nb addition and increased corrosion resistance due to the synergic effect of solid solution strengthening, precipitation strengthening, and fine-grain strengthening [16]. Zehuan Chen et al. found that the addition of Nb promoted the formation of the Laves phase in the CrFeNi Medium-Entropy Alloy, which effectively improved the wear resistance of coatings deposited via laser-cladding [17]. Xiulin Ji, as well, demonstrated that the addition of Nb to laser-clad AlCr2FeCoNi HEA improves the corrosion and wear resistance of coatings [18]. This study aims to investigate the effect Nb addition on the NiCrBSi alloy via pulsed laser cladding. In previous studies, the authors investigated laser cladding of NiCrBSi with the addition of WC-Co, using a continuous laser [19], and WC-Co/NiCrBSi(Ti) [20], using a pulsed laser, and also developed dual coatings consisting of a buffer layer of Inconel 718 with a top layer of NiCrBSi [21] to reduce cracking and to increase the coating’s performance. Moreover, Khorram et al. [22] demonstrated the potential of pulsed laser cladding to produce defect-free coatings using IN625 and C263 filler metals for the repair of turbine vanes.
Considering the lack of results about the impact of Nb addition on the mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of Ni-based coatings, this study aims to address this gap. Since Nb has a high melting temperature, pulsed laser is of interest because it operates at a higher power output than continuous-wave laser cladding. Additionally, the pulsed laser offers better control over the melt pool, as described by Kumar et al. [23].
The present study aims to investigate the NiCrBSi composition further alloyed by 10 wt.% high-purity Nb powder to fabricate NiCrBSi/Nb coatings using a coaxial laser cladding system. The goal is to enhance hardness and corrosion resistance by finding optimal process parameters, and to reduce the cracking susceptibility of the cladded layers.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Base Materials
A mixture of commercially available powders was used as feedstock material, consisting of Metco 14E (Oerlikon Metco, Westbury, NY, USA) and 10 wt.% high-purity AMtrinsic powder (TANIOBIS GmbH, Im Schleeke, Goslar, Germany). The two powders were blended by a planetary ball mill machine for one hour in order to ensure a uniform distribution of the particles. In the present study, the resulting mixture will be referred to as NiCrBSiNb powder. Metco 14E is a gas-atomized self-fluxing alloy with Ni 11Cr 3.7Si 2.75Fe 2.2B 0.5C nominal chemistry and a particle size distribution in the range of 45–125 µm (according to the manufacturer). The high-purity Nb powder was produced via atomization, with a particle size distribution of 63–105 µm. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM, TESCAN VEGA, TESCAN Group, Brno, Czech Republic) was used to analyze the powders’ morphology, while their chemical composition was assessed through elemental analysis, using energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX). As shown in Figure 1a, the Nb powder particles generally have an atomized microstructure with high sphericity, including satellite particles. Compared to the Metco 14E powder (grey color in Figure 1b), which displays a spheroidal microstructure and smooth surface in the Nb powder, some particles show agglomeration with satellites smaller than 20 microns. According to Gobber et al. [24], the formation of satellites and increased roughness of powder particles are attributed to the use of higher gas pressure during fabrication. After mixing, it was observed that some Nb particles exhibited deformation due to contact with the NiCr-based powder, which is designed for wear and corrosion resistance and possesses significantly higher hardness. The elemental composition of the powder particles was analyzed using EDX, and the characteristic spectra are depicted in Figure 1c. Generally, the powder particles contain the elements specified by the manufacturer. However, some contamination occurred during the mixing process, as Ni and C were detected on the Nb particles. Additionally, surface oxides were identified, likely due to surface oxidation, as traces of oxygen were also detected.
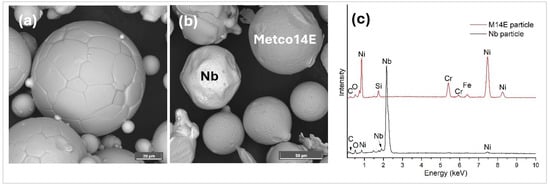
Figure 1.
Morphology of the Nb powder prior to mixing (a), NiCrBSiNb mixed powder (b), and EDX microanalysis of individual NiCr-Nb powder particles (c).
2.2. Laser Cladding
The cladding was carried out with a Trumpf TruPulse 556 (Trumpf, Ditzingen, Germany) near-infrared pulsed laser and a Precitec YW50 (Precitec GmbH, Gaggenau, Germany) laser head, which was manipulated by a six-axis Cloos robot arm. High-purity argon was used as transport and protective gas. The coatings were fabricated using the process parameters presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Cladding process parameters.
As base material, low-carbon steel plates measuring 60 × 80 × 8 mm were used, and a preheating temperature of 120 °C was applied. The laser cladding head was perpendicular on the cladding direction, and a 12 mm standoff distance was used between the cladding nozzle and substrate.
2.3. Characterization and Testing Methods
The cross-section morphology of the NiCrBSi-Nb coatings was analyzed by SEM (TESCAN VEGA LMU, TESCAN Group, Brno, Czech Republic) equipped with an energy-dispersive X-ray (EDX) spectrometer for local compositional analyses. Prior to metallography investigations, the samples were sectioned using a liquid-cooled precision cutting machine to prevent local heating and microstructural changes, followed by hot-mounting and grinding using abrasive paper of various grit sizes, ranging from P200 to P2000.
The final preparation step involved polishing using pads with a grit of up to 1 micron, followed by etching. Aqua regia (HNO3: HCl/1:3) was employed as the etchant, with an etching time of 5 s. To observe the phases within the coatings and compare them to the feedstock powder, XRD was performed using a D8 ADVANCE diffractometer (BRUKER AXS, Karlsruhe, Germany) with Cu-Kα radiation (λ = 1.5418 Å) and scanning width of 2θ in the range of 30–100°, with a step size of 0.02° and counting time of 0.2 s/step. The X-ray tube was operated at 40 kV and 40 mA at room temperature. The microhardness of the coating was measured using the Vickers method with a FALCON 600G2 hardness tester (INNOVATEST Europe BV, Maastricht, The Netherlands). Microhardness indentations were performed on the cross-section of each sample using a load of 200 gf and a dwell time of 15 s. In order to evaluate the corrosion performance of the coatings, an SP-150 potentiostat/galvanostat (Biologic, Seyssinet-Pariset, France) was used. A conventional three-electrode electrochemical cell was used, with the analyzed sample acting as the working electrode (WE). The 1 cm2 testing area was immersed in a 3.5 wt.% NaCl solution at room temperature. The working electrode’s potential was determined relative to an Ag/AgCl saturated calomel electrode (SCE) immersed in potassium chloride (KCl) solution that acted as a reference electrode (RE). Platinum gauze served as the counter-electrode (CE). The time evolution of the open-circuit potential (OCP) was recorded to obtain the first observations of the processes occurring at the electrode/electrolyte interface. The method involves measuring the equilibrium potential between the working electrode and the electrolyte with the use of RE. The equilibrium potential is measured under OCP conditions, i.e., in the absence of current flow. The time evolution of the OCP for the NiCrBSiNi coatings was monitored over a period of one hour. Potentiodynamic polarization was recorded by applying a potential sweep of ±250 mV relative to the open circuit potential at a scan rate of 1 mV/s.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Microstructural Characterization of Coatings
The effect of laser power on the NiCrBSi-Nb coatings was investigated by using SEM and a back-scattered (BSE) combo detector. The cross-sectional views of the samples are presented in Figure 2 at 500× magnification. As shown, the coatings are metallurgically bonded to the substrate without major defects, such as pores or cracks. Samples 1 and 2 show partially melted particles sticking on both sample surfaces probably due to insufficient laser energy. Similar observations have been reported by Wang et al. [25]. Furthermore, Pal et al. [26] concluded that the quantity of adherent powder particles on the surface decreases with increasing laser power and scanning speed. In the present case, the scanning speed is a parameter that was kept constant. Using lower laser power, fewer particles absorb enough energy to reach their melting point, resulting in less melted feedstock powder and thinner coatings being deposited. Another reason might be that not all powder particles fall directly into the center of the laser beam; thus, they are partially melted and projected in various directions. As shown in Figure 2, the coating thickness increases as laser power rises from 2800 W to 3200 W. With an input of less than 3000 W, a smaller melt pool was generated, resulting in a thinner coating of approximately 315 µm for Sample 1. The intermediate sample, deposited at 3000 W, was approximately 6% thicker (~334 µm) than Sample 1, while Sample 3 (~545 µm) was around 73% thicker than Sample 1. This is because higher laser power creates a larger and deeper melt pool, resulting in increased coating thickness and more extensive melting of the substrate [27]. This indicates that the laser power has a strong influence on the penetration depth, which is affected by the capacity of the feedstock material to absorb the laser’s thermal energy.
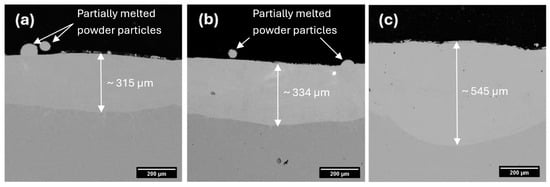
Figure 2.
Cross-sectional SEM micrographs of the coatings: (a) Sample 1, (b) Sample 2, and (c) Sample 3.
Planar and cellular crystals characterize the microstructure present at the coating–substrate interface in all samples, with similar structures reported by Qian et al. [28]. This is a common feature of laser-clad coatings and is caused by the high thermal gradient encountered during the solidification process. The planar crystals grow on the flat interface and form a grey band above the substrate, as can be seen in Figure 3 and as has been described by Wang et al. [25]. As the temperature decreased during solidification, cellular crystals formed next to the planar crystals with preferred orientation, resulting in the growth of coarse columnar crystals, which are tilted along the heat flow direction [29]. Changes in the ratio of the temperature gradient (G) to the growth rate (R) influence the solidification mode, which influence the microstructure and grain size. Planar crystals are formed at a high G/R ratio, whereas cellular crystals develop at lower G/R ratios. As can be seen in Figure 3, the coarser grains dominate at the interface in Sample 1, and grain refinement occurs in Sample 3 as the power increases.
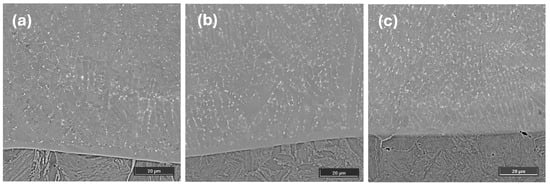
Figure 3.
Cross-sectional SEM micrographs of the coatings at the coating–substrate interface: Sample 1 (a), Sample 2 (b), and Sample 3 (c).
As presented in Figure 4, it was observed that Ni, Cr, and Nb diffused into the base material at grain boundaries in Sample 1. Ni-Cr diffusion is possible since the pulsed laser produces intense localized heating, which melts the substrate in the heat-affected zone (HAZ). The diffusion of γ-[Ni, Cr, Fe] solid solution and Nb as carbide and borides (within the γ-[Ni, Cr, Fe] phase) at the grain boundaries of the low-carbon substrate within the heat-affected zone can have a significant impact on the performance of the layer. Similar observations were reported by Kharanzhevskiy et al. [30] when depositing chromium oxide on the surface of low-carbon steel using pulsed laser cladding. This can potentially lead to stress concentrations and subsequent coating failure.
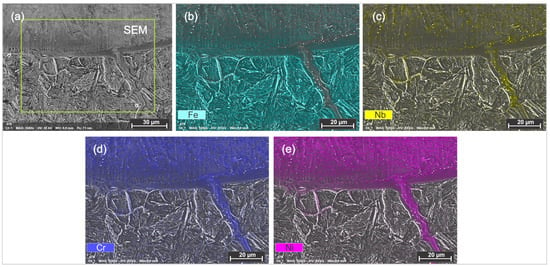
Figure 4.
EDX map of Sample 1 at the coating–substrate interface, (a) Secondary electron micrograph with indication area of EDX mapping, (b) Fe distribution, (c) Nb distribution, (d) Cr distribution and (e) the Ni distribution.
At higher laser power, the heat-affected zone (HAZ) on the surface of the substrate becomes larger, and cracks exist inside.
Comparing the samples (Figure 5), it was determined that, as the temperature increased, a more obvious grain refinement effect was observed in Sample 3. Similar observations were reported by Diao et al. [31] when investigating the influence of laser power on the grain refinement of a Ti5321G alloy manufactured using laser technology. Their results show that the microstructure refinement is promoted and the equiaxed grains region is expanded with increasing laser power. The grain morphology in this sample changed significantly from columnar to equiaxed crystals. Increasing the laser power, the heat accumulation increases, leading to a lower G/R ratio and the formation of equiaxed crystals [32,33]. In Sample 3, fine black particles can be seen, suggesting that intermetallic compounds have formed. Furthermore, the white phase, which is likely to be carbide-based, exhibits a higher volume fraction compared to the other samples and is more uniformly distributed along the grain boundaries (Figure 5c). The increase in carbides and secondary phases within the coating, in combination with the grain refinement caused by the Hall–Petch effect, leads to an enhanced hardness [34]. In contrast, the carbides (white areas on the micrographs) precipitated in Sample 1 are significantly larger than those in Samples 2 and 3, and they are randomly distributed both within the matrix and along the grain boundaries.
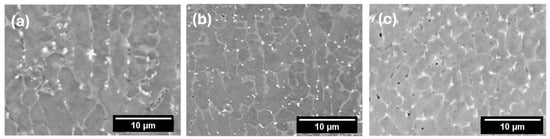
Figure 5.
Cross-sectional SEM micrographs of the coatings in the central area: Sample 1 (a), Sample 2 (b), and Sample 3 (c).
To evaluate the microstructure of the layers, the distribution of the main elements, including Ni, Cr, Fe, Si, C, and Nb, in the areas of interest was analyzed using EDX point scanning. As the composition of the layers was similar, only the microstructure and EDX results for Sample 1 are presented. Five major areas were identified within the samples according to the microstructure and EDX investigations, as shown in Figure 6. The main phase, labelled Area 1, is the main gamma phase. As the coatings solidify, they form a γ-[Ni, Cr, Fe] solid solution as the matrix. Since Area 2 is rich in Fe and Ni, it is considered to be NiFe eutectic enriched in Nb. The white, blocky, cross-shaped particles labelled Area 3 are enriched in Nb and C, so according to the EDX spectra, they are more likely to correspond to NbC. Moreover, the atomic number of Nb is the highest among the investigated elements, and it appears brighter in the BSD micrograph. Analysis of the dark-colored precipitates labelled Area 4 shows that they are rich in Cr, Fe, and C, indicating that they are complex carbides, such as (Cr, Fe)23C6. Although B was present in low amounts in the feedstock powder composition, it was not detected by point scanning due to the limited sensitivity of EDX to light elements.
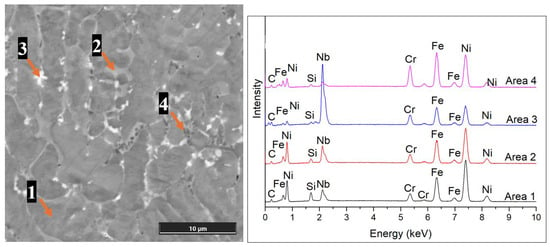
Figure 6.
High-magnification SEM and EDX spectra for Sample 1 collected at the center of the coating.
Figure 7 shows that the Nb-rich areas are located not only in the matrix, but also at grain boundaries. As the laser power increased, the NbC transformed from blocky, cross-shaped particles to fine particles that were more evenly distributed at the fine-grain boundaries and triple junctions in Sample 3 (see Figure 7c). The formation of NbC is of interest since it possesses an increased hardness, elevated melting point, and high elastic modulus [35]. It can also be observed that Nb enriched the surrounding area of carbides through its dissolution within the solid solution matrix.
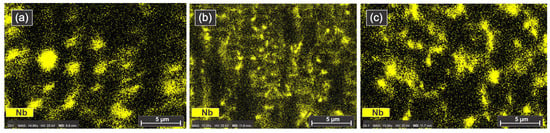
Figure 7.
EDX maps revealing the Nb distribution in Sample 1 (a), Sample 2 (b), and Sample 3 (c).
3.2. Phase Composition
X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis was conducted to investigate the phase composition of the NiCrBSiNb powder and cladding layers, with the results presented in Figure 8. The γ-[Ni, Cr, Fe] phase was identified as the primary phase within the coatings. Various carbides and borides, such as M7C3, Cr23C6, NbC, and CrB, were also detected, in addition to this primary phase. Similar findings were reported by Huang et al. when investigating NiCrBSi coatings deposited via laser induction cladding [36]. Increasing the laser power was found to lead to a slight increase in the number of carbides in Samples 2 and 3 compared to the feedstock powder and Sample 1. Furthermore, the volume fraction of M7C3, Cr23C6, NbC, and CrB, identified at the 2θ peak at about 49°, increased with the laser power employed during cladding. The absence of broad halo peaks indicates that no amorphous structures were detected.
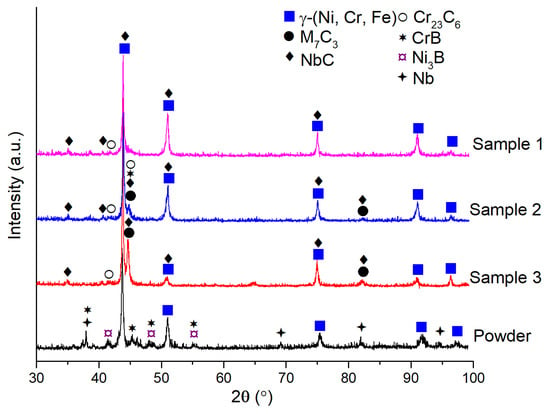
Figure 8.
XRD pattern for the initial powder and the claddings.
3.3. Microhardness
Microhardness was measured across the cladded coatings, from the surface down to the substrate, and the results are presented in Figure 9. In all coatings, the hardness is high at the top of the coating and decreases towards the substrate. Sample 3 has a significantly higher hardness, through the dispersion of carbides at grain boundaries, lower Fe content, and grain refinement, thus improving the mechanical properties due to the Hall–Petch effect. In general, hardness increases as laser power increases. As the laser energy increases, so does dilution, resulting in better wetting of the substrate and spreading of the feedstock material, but this leads to decreased carbide content [37]. However, this does not appear to be the case in the present study. The lower energy input, combined with the same powder feed rate and scanning speed, appears to be insufficient to melt the powder completely. Consequently, more of the laser energy is absorbed by the substrate than by the powder, leading to lower hardness due to the Fe content from the substrate. In contrast, Sample 3 appears to require an increased laser power of 3200 W, applied using a pulsed laser system, for more efficient cladded layers. This higher power enables the powder to melt more efficiently. This results in more of the laser energy being absorbed, leading to the formation of a greater volume of precipitates and secondary phases that enhance the performance of the coatings. The hardness of the heat-affected zone (HAZ) in Samples 1 and 2 is somewhat higher compared to the HAZ in Sample 3. This increase is likely due to metallurgical changes resulting from rapid heating and cooling, which are strongly influenced by the laser beam interacting with less powder during the cladding process. At 2800–3000 W, the powder feed rate is high in relation to the laser energy input, and the beam cannot melt all of the incoming powder. This decreases cladding efficiency, leading to thinner, lower-quality coatings with unmelted particles on the surface. When using other types of laser processes, this could also increase porosity. Thus, a higher laser power ensures more complete melting of the powder particles [38]. Another possible explanation is the intergranular diffusion of the γ-[Ni, Cr, Fe] phase along grain boundaries, as observed in the microstructural analysis of Sample 1.
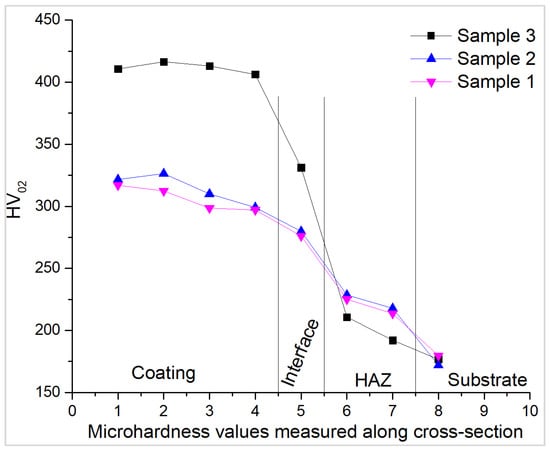
Figure 9.
Microhardness distribution at the cross-section of the investigated samples.
3.4. Corrosion Behavior of the NiCrBSiNb-Cladded Coatings
Potentiodynamic polarization was used to determine the corrosion rate based on the corrosion current density and Tafel slopes. After one hour, when the system had reached a quasi-stationary state, the linear polarization measurements were recorded. A potential sweep of ±250 mV relative to the open circuit potential was applied at a scan rate of 1 mV/s. This method enables the corrosion rate to be calculated by directly substituting anodic and cathodic slope values into the Butler–Volmer equation, as previously described [19]:
where E is the potential; icorr is the oxidation current, named the corrosion current; Ecorr is the corrosion potential; ba is the anodic Tafel slope; and bc is the cathodic Tafel slope.
i = icorr{exp[2.303(E − Ecorr)/ba] − exp[−2.303(E − Ecorr)/bc]}
The polarization curves were recorded for all the tested samples, and the results are presented in Figure 10. In all cases, the coatings demonstrated improved corrosion resistance compared to the low-carbon substrate. The results indicate that Sample 3 exhibited better corrosion resistance compared to Samples 1 and 2. The shift of the polarization curve toward lower current densities suggests that the increased coating thickness has enhanced corrosion resistance.
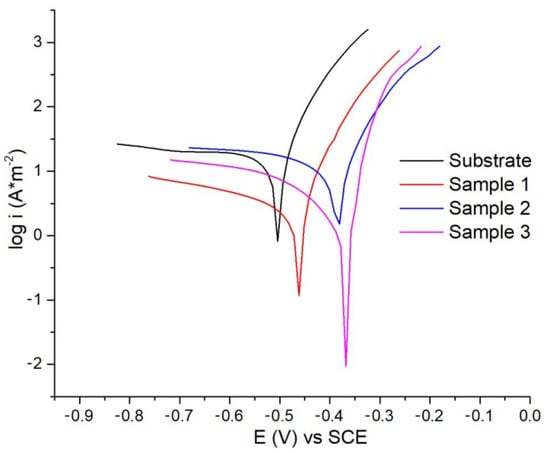
Figure 10.
Potentiodynamic polarization curves for laser-cladded NiCrBSiNb coatings in 3.5% NaCl solution at 22 °C.
Based on the polarization curves, and using the extrapolation method, icorr, Ecorr, and the corrosion rate were calculated, and the results are presented in Table 2. The results indicate that the substrate exhibits the highest current density, while the coated samples demonstrate improved corrosion resistance. Decreasing the laser power led to a reduction in current density and corrosion rate. Sample 3, which has the thickest coating, showed the most favorable corrosion performance. In addition to increased coating thickness and a reduced Fe content, which gradually decreases from the coating–substrate interface toward the surface [39], the presence of carbides and borides formed within the coatings plays a significant role in enhancing corrosion performance.

Table 2.
Corrosion test results.
It is well known that NbC is nobler than the matrix and is therefore less prone to anodic dissolution during electrochemical reactions. As a result, coatings with a higher NbC content are likely to show greater corrosion resistance and be less vulnerable to degradation in oxidative environments [32]. Based on microstructural analysis and XRD, the highest concentration of NbC was found in Sample 3, which also contributed, besides other carbides and phases, to improved corrosion resistance.
4. Conclusions
This study investigated pulsed laser cladding as an advanced manufacturing method for NiCrBSiNb coatings, using different laser power settings. Based on macro- and microstructural analyses, hardness measurements, and electrochemical testing in a 3.5% NaCl electrolyte, the following conclusions can be drawn:
- NiCrBSiNb coatings with reduced porosity and free of cracks were manufactured using pulsed laser cladding, exhibiting good metallurgical bonding to the base material.
- The power of the laser has a significant impact on the thickness, microstructure, hardness, and corrosion resistance of the coatings.
- Increasing the laser power from 2800 W to 3200 W significantly changes the morphology of the coating grains, promoting a transition from columnar to equiaxed crystals. This is due to greater heat accumulation at higher laser power, which reduces the G/R ratio, favoring the formation of equiaxed grains in Sample 3 deposited at 3200 W.
- If the laser power during pulsed laser cladding is too low, it leads to the preferential melting of the low-carbon steel substrate rather than the feedstock powder, as encountered for Sample 1, which was deposited using 2800W laser power. This results in the diffusion of the Ni-Cr solid solution with Nb-based carbides at the grain boundaries within the heat-affected zone, due to the intense localized heating generated by the pulsed laser.
- Compared with the other samples, the coating deposited at a laser power of 3200 W exhibited enhanced hardness and improved corrosion resistance in a 3.5% NaCl solution. This can be attributed to several factors, such as increased coating thickness, grain refinement, and a more uniform distribution of carbides and secondary phases within the microstructure.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.H. and A.P.; methodology, I.H.; software, D.-C.C.; validation, A.P. and I.H.; formal analysis, A.P.; investigation, I.H. and D.-C.C.; resources, A.P.; writing—original draft preparation, I.H.; writing—review and editing, I.H. and A.P.; visualization, D.-C.C.; supervision, I.H. and A.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available upon request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Yu, T.; Chen, J.; Wen, Y.; Deng, Q. High Temperature Phase Stability and Wear Behavior of Laser Clad Ta Reinforced NiCrBSi Coating. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 547, 149171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zheng, Y.; Zheng, W.; Shen, Z.; Hu, M.; Wang, Y.; Feng, D.; Ma, Y.; Cai, Z.; Yang, J. Dilution Induced Variation of Microstructure and Mechanical Properties on Co-Cr-Fe-Ni High Entropy Alloy Coatings Prepared by Laser Cladding. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2024, 493, 131256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Bai, B.; Ke, H.; Cui, Z.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Xu, H.; Xiao, J.; Liu, Q.; Li, H. Effect of Metallurgical Behavior on Microstructure and Properties of FeCrMoMn Coatings Prepared by High-Speed Laser Cladding. Opt. Laser Technol. 2021, 144, 107431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santo, L. Laser Cladding of Metals: A Review. Int. J. Surf. Sci. Eng. 2008, 2, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alimohammadi, A.; Khorram, A.; Araee, A. Laser alloying of Hastelloy X with Metco 204 NS powder: Statistical modeling and optimization. Phys. Scr. 2025, 100, 085018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, S.; Liu, K.; Li, J.; Xu, C. A New Test for Evaluating the Cracking Susceptibility of Laser Cladding Coatings and Its Validity on Assessing the Effect of Laser Power. Opt. Laser Technol. 2025, 180, 111609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, K.; Liu, X.; Zhang, S. High-Temperature Oxidation Behavior and Tribological Performance of Nickel-Based Alloy Coatings Reinforced with ZrB 2 Ceramic. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2025, 38, 406–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochenek, K.; Węglewski, W.; Strojny-Nędza, A.; Pietrzak, K.; Chmielewski, T.; Chmielewski, M.; Basista, M. Microstructure, Mechanical, and Wear Properties of NiCr-Re-Al2O3 Coatings Deposited by HVOF, Atmospheric Plasma Spraying, and Laser Cladding. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2022, 31, 1609–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, A.; García, A.; Cadenas, M.; Fernández, M.R.; Cuetos, J.M. WC Particles Distribution Model in the Cross-Section of Laser Cladded NiCrBSi + WC Coatings, for Different Wt% WC. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 324, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Li, B.; Lu, C.; Zhou, Q.; Jia, J. Effect of WC–Co Content on the Microstructure and Properties of NiCrBSi Composite Coatings Fabricated by Supersonic Plasma Spraying. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 789, 966–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avram, D.N.; Davidescu, C.M.; Dan, M.L.; Mirza-Rosca, J.C.; Hulka, I.; Pascu, A.; Stanciu, E.M. Electrochemical Evaluation of Protective Coatings with Ti Additions on Mild Steel Substrate with Potential Application for PEM Fuel Cells. Materials 2022, 15, 5364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.L.; Lei, Y.W.; Niu, W. Laser Clad TiC Reinforced NiCrBSi Composite Coatings on Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Using a CW CO2 Laser. Surf. Coatings Technol. 2009, 203, 1395–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satya Prasad, V.V.; Baligidad, R.G.; Gokhale, A.A. Niobium and Other High Temperature Refractory Metals for Aerospace Applications. In Aerospace Materials and Material Technologies: Volume 1: Aerospace Materials; Springer: Singapore, 2017; pp. 267–288. [Google Scholar]
- Funch, C.V.; Proust, G. Laser-Based Additive Manufacturing of Refractory Metals and Their Alloys: A Review. Addit. Manuf. 2024, 94, 104464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Cui, X.; Wen, X.; Wang, J.; Zha, M.; Jin, G. Effects of Nb Addition on the Laser Energy Efficiency and Properties of (NiCrCoFe)100-XNbx HEA Underwater Wet Laser Cladding Coatings. Opt. Laser Technol. 2024, 178, 111234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Gao, L.; Song, X. Effect of Niobium Content on Microstructure and Wear and Corrosion Resistance of Laser-Clad FeCo0.5CrNi1.5B0.5Nbx Coatings on Ductile Iron. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2024, 476, 130210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Luo, F.; Jin, H.; Peng, Z.; Shi, W.; Huang, J. Effect of Nb on Laves Phase Formation and Wear Resistance in Laser-Cladding CrFeNi Medium-Entropy Alloy Coatings. Coatings 2025, 15, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Guan, K.; Bao, Y.; Mao, Z.; Wang, F.; Dai, H. Effect of Nb Addition on the Corrosion and Wear Resistance of Laser Clad AlCr2FeCoNi High-Entropy Alloy Coatings. Lubricants 2024, 12, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulka, I.; Uțu, I.D.; Avram, D.; Dan, M.L.; Pascu, A.; Stanciu, E.M.; Roată, I.C. Influence of the Laser Cladding Parameters on the Morphology, Wear and Corrosion Resistance of Wc-Co/Nicrbsi Composite Coatings. Materials 2021, 14, 5583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulka, I.; Utu, D.; Serban, V.A.; Negrea, P.; Lukáč, F.; Chráska, T. Effect of Ti Addition on Microstructure and Corrosion Properties of Laser Cladded WC-Co/NiCrBSi(Ti) Coatings. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 504, 144349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanciu, E.M.; Pascu, A.; Ţierean, M.H.; Voiculescu, I.; Roată, I.C.; Croitoru, C.; Hulka, I. Dual Coating Laser Cladding of NiCrBSi and Inconel 718. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2016, 31, 1556–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorram, A.; Meraji, H.; Dibaji, V. Microstructural evolution of laser repair welded rene 142 superalloy with IN625/C263 welding materials. Phys. Scr. 2025, 100, 075045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratheesh Kumar, S.; Elangovan, S.; Mohanraj, R.; Sathya Narayanan, V. Significance of Continuous Wave and Pulsed Wave Laser in Direct Metal Deposition. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 46, 8086–8096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobber, F.S.; Priarone, P.C.; Pennacchio, A.; Actis Grande, M. Effect of Inert Gas Pressure on the Properties and Carbon Footprint of UNS S32760 Powders Made from Waste Materials by Gas Atomization. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 33, 8814–8828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ren, X.; Xue, Y.; Luan, B. Investigation on Microstructure and High-Temperature Wear Properties of High-Speed Laser Cladding Inconel 625 Alloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 30, 626–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.; Lojen, G.; Hudakb, R.; Rajtukova, V.; Brajlih, T.; Kokol, V.; Drstvenšek, I. As-fabricated surface morphologies of Ti-6Al-4V samples fabricated by different laser processing parameters in selective laser melting. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 30, 101147. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, C.; Liu, Y.; Ni, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, H. Effects of Laser Energy Density on Microstructure, Texture and Tribological Property of CoCrFeMnNi High Entropy Alloy Coatings Fabricated by Laser Cladding. Surf. Interfaces 2025, 61, 106107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, S.; Dai, Y.; Guo, Y. Microstructure and Wear Resistance of Multi-Layer Ni-Based Alloy. Materials 2021, 14, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, S.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, G.; Jiang, E.; Wang, Y.; Guo, X.; Huang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Piao, Z. Preparation and corrosion resistance of Inconel 625 laser cladding coating for high temperature supercritical carbon dioxide environment. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2025, 38, 2751–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharanzhevskiy, E.; Reshetnikov, S. Chromium oxide dissolution in steels via short pulse laser processing. Appl. Phys. A 2014, 115, 1469–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, M.; Guo, C.; Wang, S.; Li, L.; Dong, T.; Xin, S.; Sun, Z.; Chen, Z.; Konovalov, S.; Jiang, F. Influence of Laser Power on Grain Refinement of Ti5321G Alloy Fabricated by Laser Powder Direct Energy Deposition Assisted with Ultrasonic Energy Field. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2025, 27, 2403002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Shu, X.; Xu, H.; Xu, S.; Zhang, S. Study on the Effect of Laser Power on the Microstructure and Properties of Cladding Stellite 12 Coatings on H13 Steel. Materials 2024, 17, 6098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Qian, M.; Brandt, M. Ultra-High-Speed Laser Cladding of Stellite 6 Alloy on Mild Steel. JOM 2020, 72, 4632–4638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Jiang, N.; Zhan, Y.; Luo, Y.; Ye, N.; Tang, J.; Zhuo, H. Preparation and Tribological Performance of Ni-SiC Composite Coating on 304 Stainless Steel through Brush Plating. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2024, 494, 131491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Wang, K.; Fu, H. Laser Cladding In Situ Carbide-Reinforced Iron-Based Alloy Coating: A Review. Metals 2024, 14, 1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zeng, X.; Hu, Q.; Zhou, S. Microstructure and Interface Interaction in Laser Induction Hybrid Cladding of Ni-Based Coating. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 255, 3940–3945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, L.; Samajdar, I.; Tak, M.; Doherty, R.D.; Gundakaram, R.C.; Prasad, K.S.; Joshi, S.V. Microstructure and Phase Evolution in Laser Clad Chromium Carbide-NiCrMoNb. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 357, 2391–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernsmann, J.S.L.; Hillebrandt, S.; Rommerskirchen, M.; Bold, S.; Schleifenbaum, J.H. On the Use of Metal Sinter Powder in Laser Powder Bed Fusion Processing. Materials 2023, 16, 5697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, R.N.; Searle, J.; Martin, T.L.; Walters, W.S.; Williams, G. The Role of Niobium Carbides in the Localised Corrosion Initiation of 20Cr-25Ni-Nb Advanced Gas-Cooled Reactor Fuel Cladding. Corros. Sci. 2020, 165, 108365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).