On the Deactivation Analysis of IM-5 Zeolite in Pseudocumene Methylation with Methanol
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials, Method of Preparation of Protonic-Form Zeolites, and Catalyst Testing
2.2. The Characterization Methods of Deactivated and Fresh Zeolites
2.3. Comprehensive Analytical Method for the Composition and Properties of Coke Deposition on Deactivated IM-5 Zeolite
- Sample Pretreatment: Proton-form zeolite samples, previously calcined at 550 °C to remove organic and ammonia molecules, and deactivated zeolites were irradiated with an infrared heating lamp (Shanghai Thermal Lighting Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China) for 3 min to desorb adsorbed moisture before pellet preparation. Particularly, before performing FT-IR, the zeolite powder should be thoroughly mixed with chromatographic-grade KBr. Subsequently, the samples were pressed into pellets using a 769YP-24B manual hydraulic press (Tianjin Keqi High-Tech Co., Ltd., Tianjin, China) at 20 MPa (12 tf) for 2 min. The pellet thickness (l) in the Lambert–Beer law was maintained constant at 0.5 mm by ensuring consistent mold dimensions and zeolite powder mass.
- Py-IR: Pellets were sealed in an in situ cell within the IR spectrometer, evacuated to 10−3 Pa at 400 °C for 60 min, then cooled to room temperature. A background spectrum was collected (32 scans, resolution 32 cm−1, absorbance format, and wavenumber range 1700–1300 cm−1 with automatic atmospheric background subtraction). After closing the evacuation valve, pyridine was introduced into the cell at 2.67 Pa for 3 min, followed by 17 min of equilibrium adsorption. The cell was then evacuated again to 1 × 10−3 Pa, heated to 200 °C for 90 min, cooled to room temperature, and scanned using the background file. Spectra were recorded at 350 °C (60 min hold time for higher temperatures). The pyridine adsorption quantities were calculated using the Lambert–Beer law as follows:
- FT-IR: Pellets were evacuated to 10−3 Pa at room temperature. Background spectra were collected (32 scans, resolution 32 cm−1, absorbance format, and wavenumber range 4000–400 cm−1 with automatic atmospheric background subtraction). The full spectrum was recorded under identical conditions using the background file.
- OH-IR: Pellets were evacuated to 10−3 Pa at 400 °C for 60 min, cooled to room temperature, and the background spectra were collected (32 scans, resolution 32 cm−1, absorbance format, and wavenumber range 4000–3000 cm−1 with automatic atmospheric background subtraction). The hydroxyl spectra were recorded using the same parameters with the background file.
2.4. The Analytic Methods of Deactivated IM-5 Zeolite’s External Surface, Internal Surface, and Insoluble Coke
- (1)
- Extraction of External Surface Organic Adsorbates (Ultrasonic Extraction Method): The deactivated catalyst sample was immersed in toluene (extraction solvent) for 30 min, then transferred to a CREST 230D ultrasonic generator (Crest Ultrasonics, Ewing Township, NJ, USA) for 60 min of oscillatory extraction. The mixture of the extracted sample and solvent was filtered, and the filtrate was concentrated using an IKA rotary evaporator (IKA-Werke GmbH & Co. KG, Staufen im Breisgau, Germany);
- (2)
- Extraction of Internal Surface Organic Adsorbates (Within Zeolite Pores): A total of 10 g of the deactivated catalyst, pre-extracted for external surface adsorbates, was placed in a PTFE beaker. Then, 15–20 mL of hydrofluoric acid was added to dissolve the catalyst framework, releasing the carbon deposits within the pores. The acid solution was neutralized with sodium carbonate until gas evolution ceased. The resulting mixture was washed and filtered and the collected filter cake was dried at a low temperature. The dried cake was transferred to a conical flask, 20 mL of toluene was added, and ultrasonic extraction was performed. The extract was filtered to remove residues, and the filtrate was concentrated to 1–2 mL using the IKA rotary evaporator;
- (3)
- Insoluble Carbon Deposits: The filter cake remaining after internal surface extraction was dried at a low temperature (120 °C) to obtain the insoluble carbon deposits.
3. Results
3.1. Catalytic Test
3.2. Chracterization of the Fresh and Deactivated Zeolites
3.2.1. Phase
3.2.2. Chemical Composition
3.2.3. Morphology
3.2.4. Textural Properties
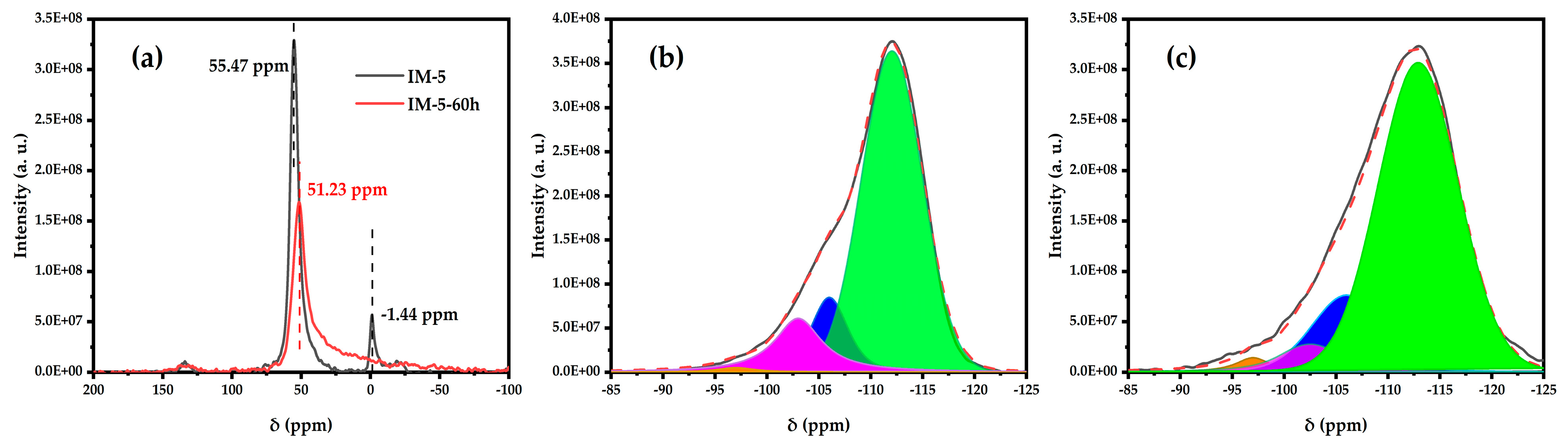
3.2.5. 27Al MAS NMR and 29Si MAS NMR
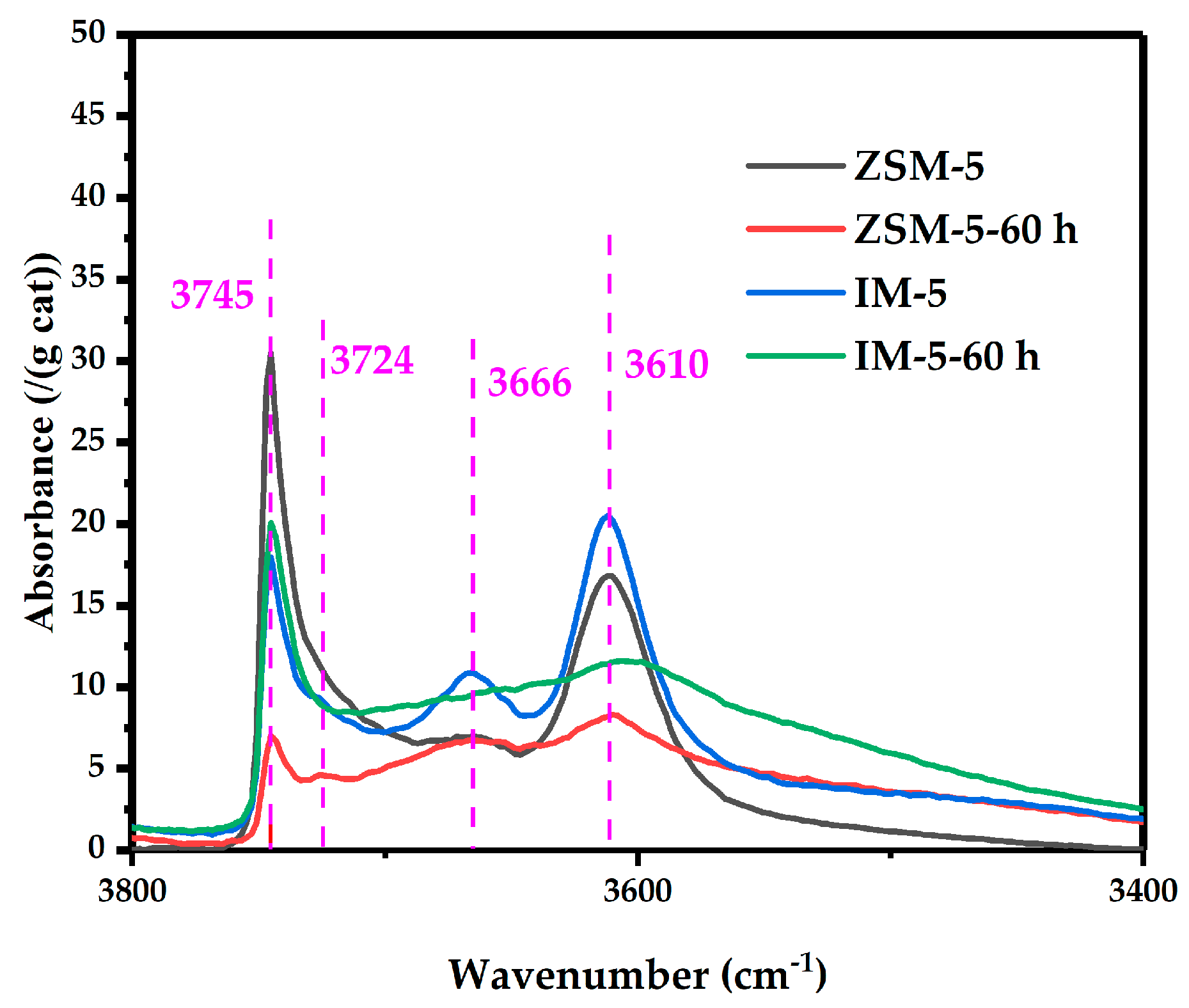
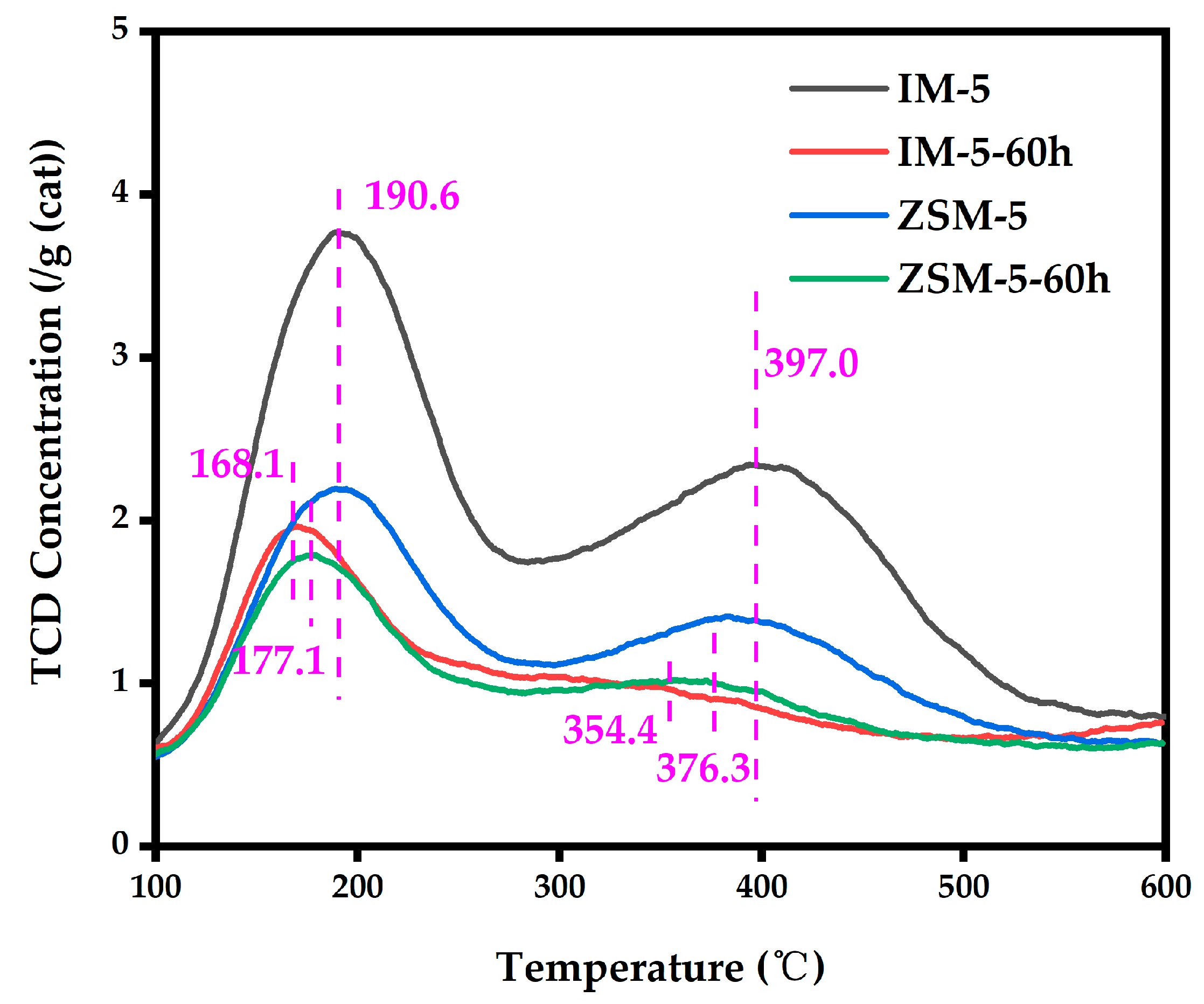
3.2.6. Acidity
3.3. Comprehensive Analysis of Coke Properties and Composition on Deactivated IM-5 Zeolite
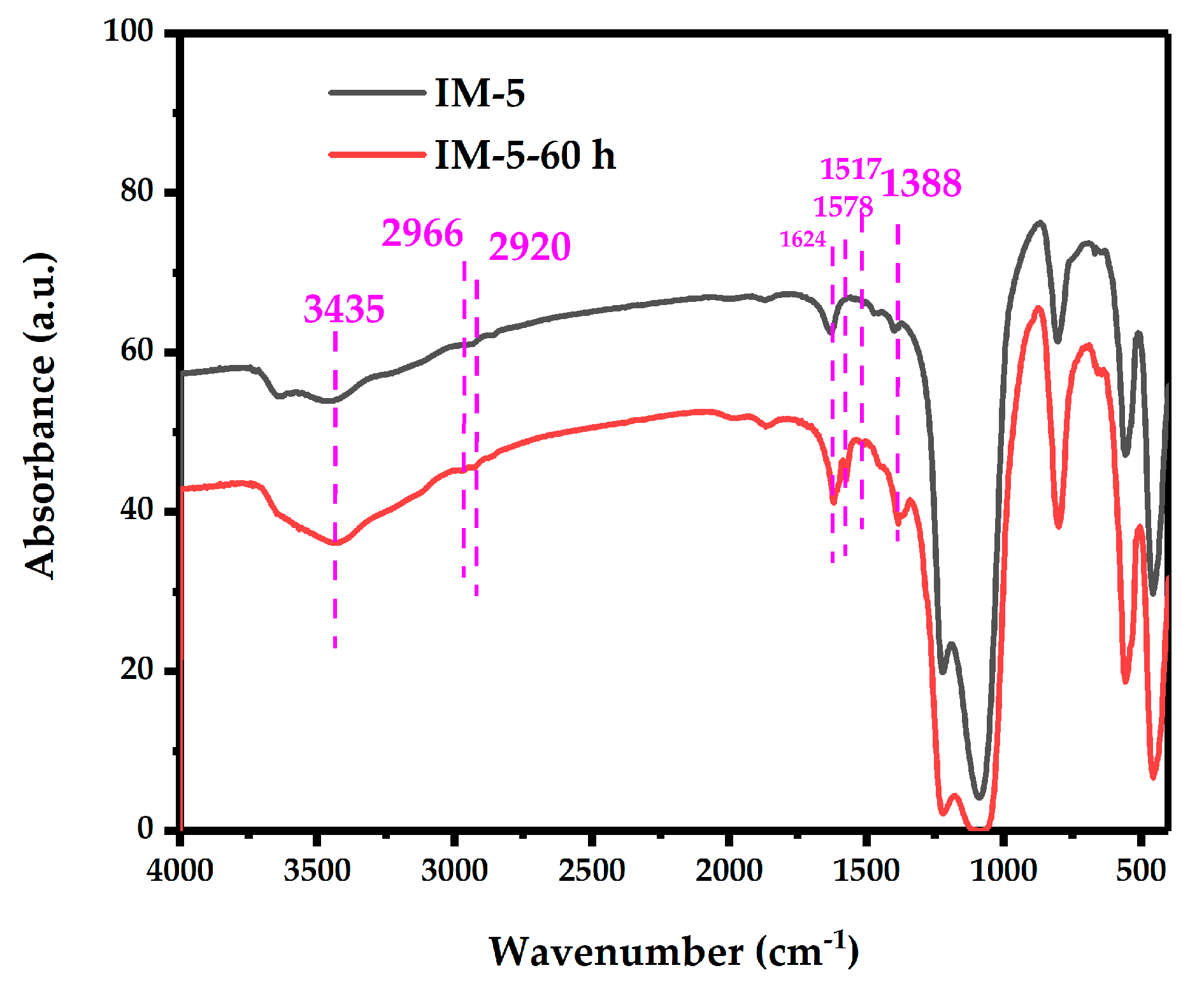
3.3.1. FT-IR Analysis
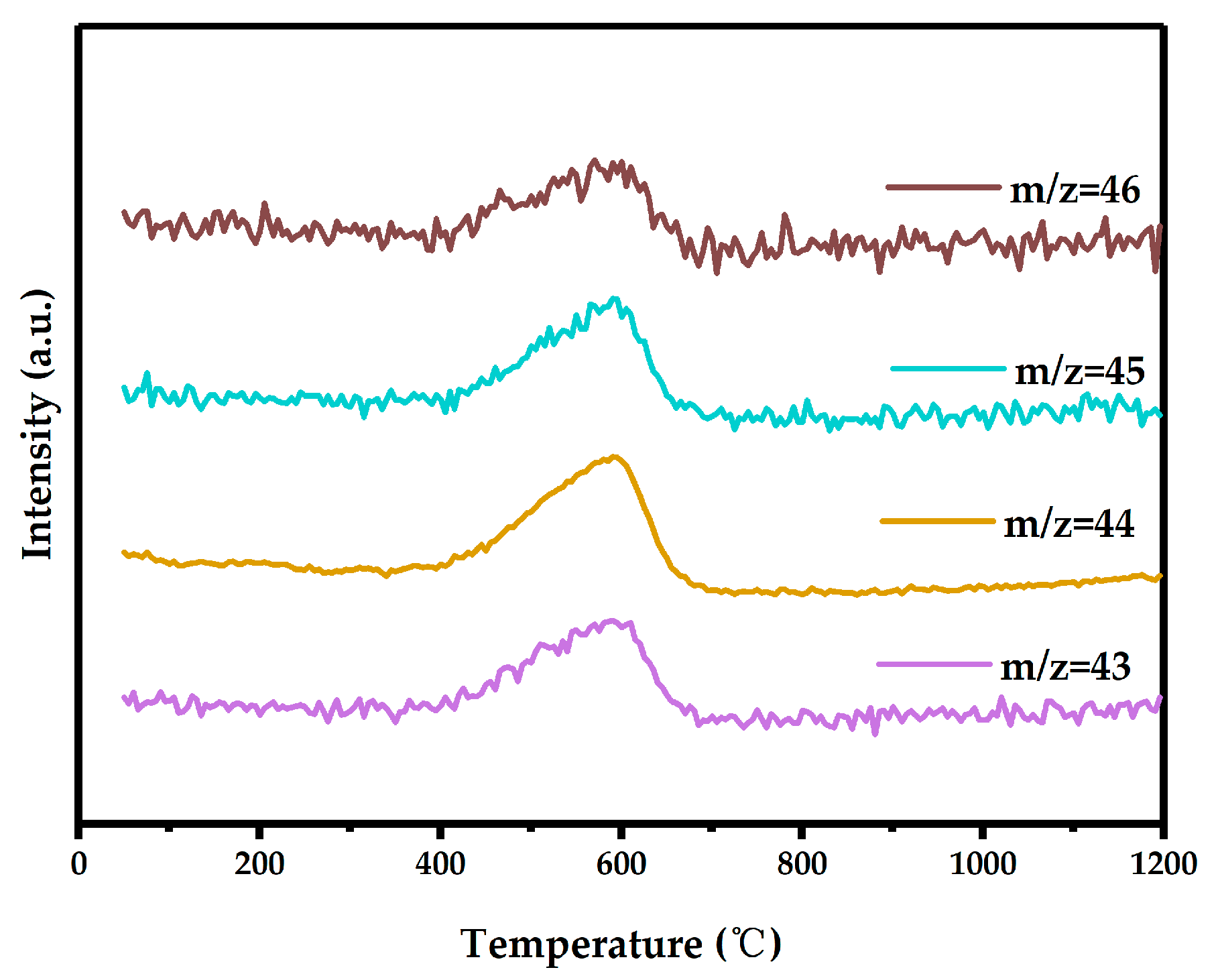
3.3.2. TG-MS Analysis
3.4. The Analysis of Deactivated IM-5 Zeolite’s External Surface, Internal Surface, and Insoluble Coke
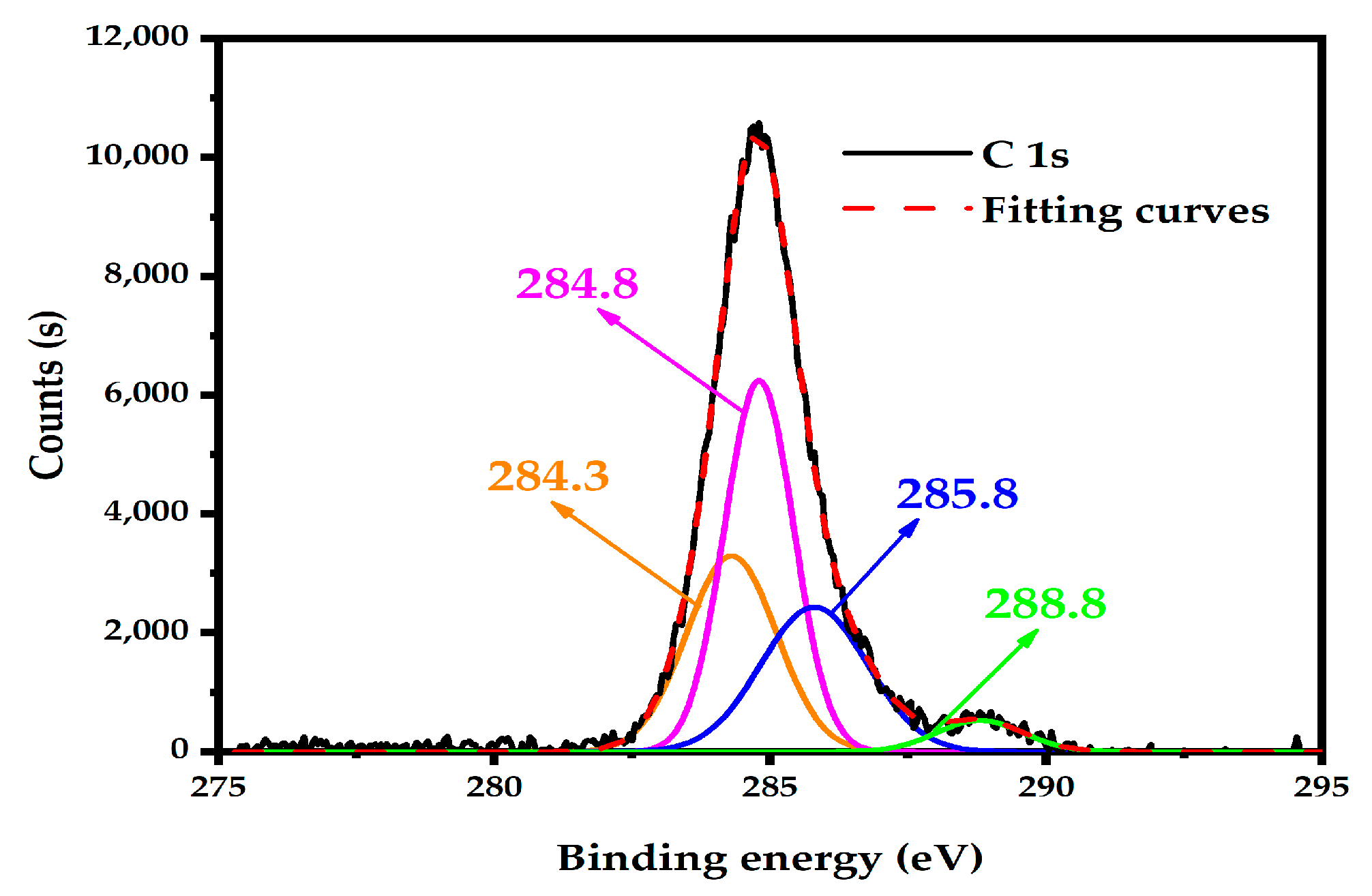
3.4.1. XPS Analysis of Coke on the External Surface
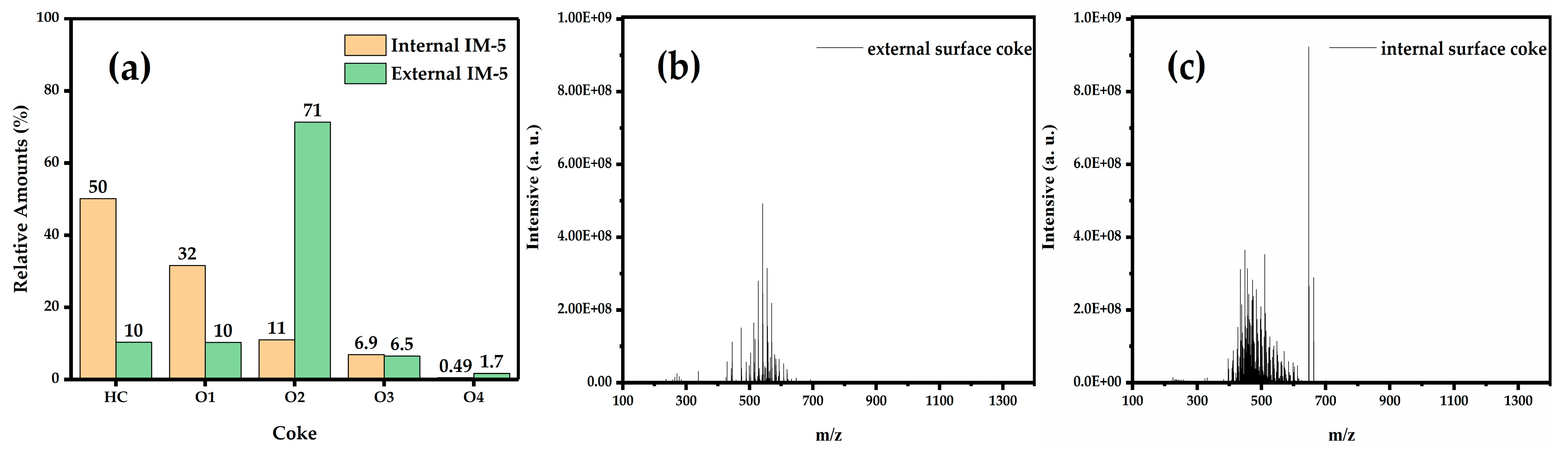
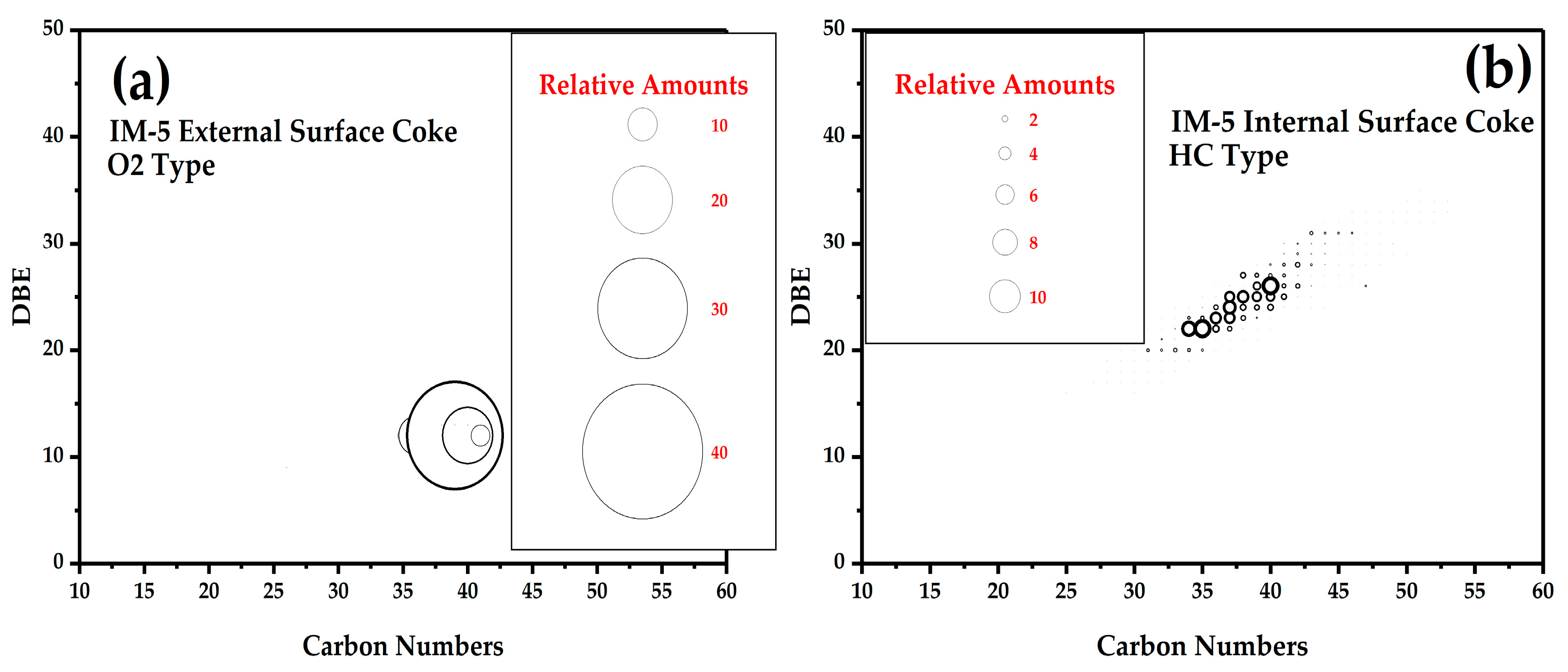
3.4.2. FT ICR MS Analysis of Coke on the External Surface and Internal Surface
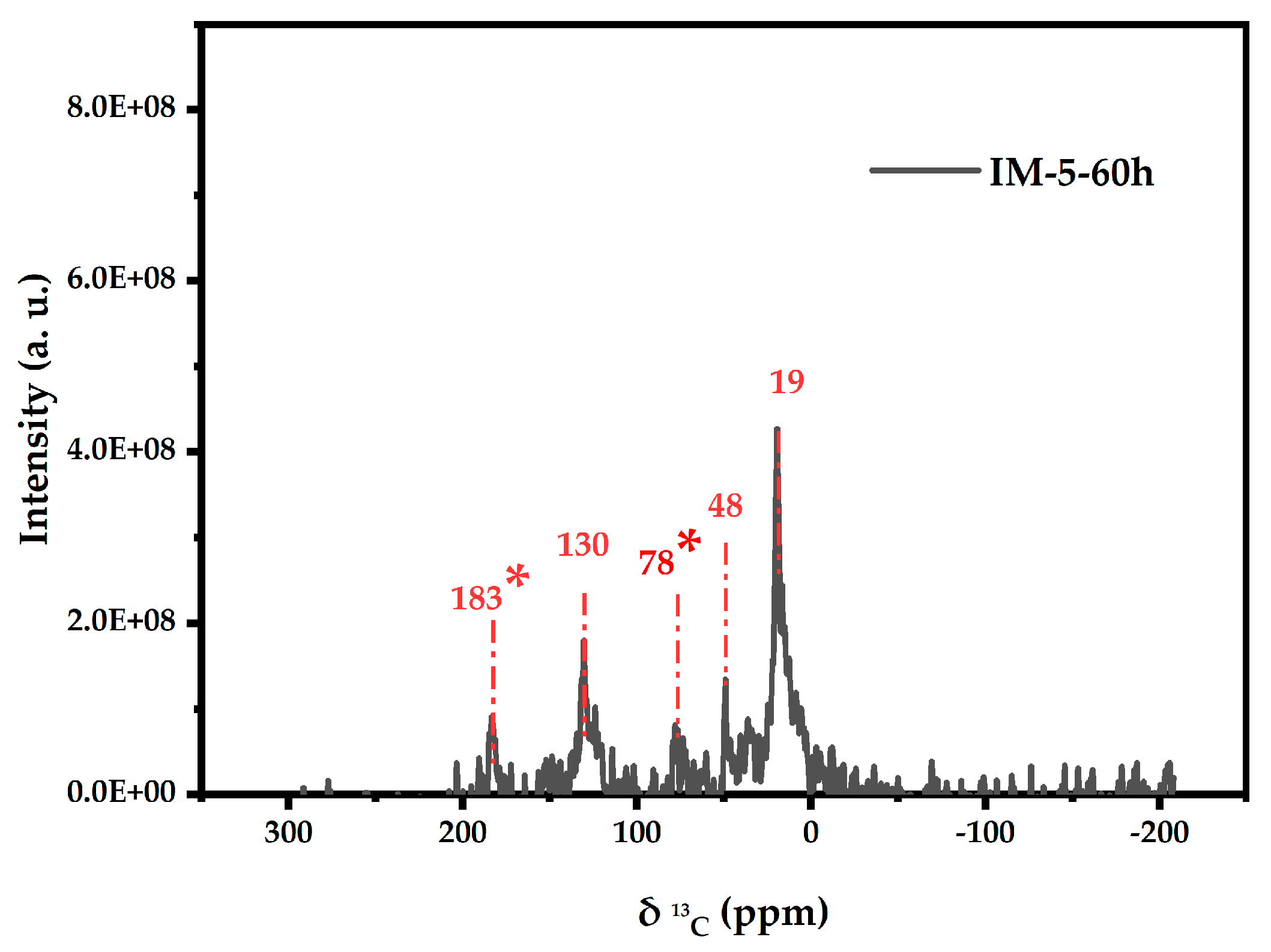
3.4.3. 13C (CP) MAS NMR Analysis of the Insoluble Carbon Deposits
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, M.; Jiao, L.; Nawaz, M.A.; Cheng, L.; Meng, C.; Yang, T.; Tariq, M.; Liu, D. A one-step synthesis method of durene directly from syngas using integrated catalyst of Cu/ZnO/Al2O3 and Co-Nb/HZSM-5. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2019, 200, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.; Hong, B.; Zhou, W.; Wen, D.; Xie, Y.; Luo, F.; Ye, L.; Zuo, J.; Yuan, Y. Upgrading Trimethylbenzene to Durene by CO2-Mediated Methylation over Cu-Boosted ZnZrOx Integrated with HZSM-5. ACS Catal. 2024, 14, 11780–11793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Qu, Y.; Feng, Z.; Chen, S.; Xu, T.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Li, C. Synthesis of tetramethylbenzene from CO2 hydrogenation over ZnZrO/ZSM-11 tandem catalyst. Appl. Catal. A-Gen. 2023, 666, 119410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H. Outlook of aromatics production technology. Pet. Process. Petrochem. 2013, 1, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, F.-Y.; Wang, J.-H.; Qi, S.-L.; Tian, G.-F.; Wu, D.-Z. Structures and Properties of Polyimide with Different Pre-imidization Degrees. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2020, 38, 840–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, D.; Wang, M.; Ruan, J.; Chen, X.; Zhou, S. Efficient, continuous oxidation of durene to pyromellitic dianhydride mediated by a V-Ti-P ternary catalyst: The remarkable doping effect. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2023, 55, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yashima, T.; Inaka, A.; Namba, S. Selective Formation of 1, 2, 4, 5-Tetra methyl benzene by the Alkylation of 1, 2, 4-Trimethylbenzene with Methanol on HZSM-5 Type Zeolite Catalysts. J. Jpn. Petrol. Inst. 1985, 28, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yashima, T. Shape selective alkylation of methylbenzenes with methanol on ZSM-5 type zeolite catalysts. J. Jpn. Petrol. Inst. 1988, 31, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernykh, S.P.; Ione, K.G.; Chekrii, P.S.; Bitman, G.L.; Loktev, A.S.; Romannikov, V.N.; Makhlis, L.A.; Snytnikova, G.P.; Porollo, V.A.; Spektor, A.N. Preparation of alkylaromatic hydrocarbons on high-silicon zeolite-containing catalysts. Chem. Technol. Fuels Oil+ 1992, 28, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLuca, M.; Hibbitts, D. Predicting diffusion barriers and diffusivities of C6–C12 methylbenzenes in MFI zeolites. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2022, 333, 111705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, D.; Zuo, J.; Han, X.; Liu, J.; Ye, L.; Yuan, Y. Synthesis of durene by methylation of 1,2,4-tri-methylbenzene with syngas over bifunctional CuZnZrOx–HZSM-5 catalysts. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2022, 12, 2555–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, K.; Zang, Y.; Jia, T.; Liu, R.; Li, H. Alkylation of 1,2,4-trimethylbenzene with methanol on HZSM-5 zeolite catalysts to form 1,2,4,5-tetramethylbezene. Acta Pet. Sin. Pet. Process. Sect. 1989, 5, 33–38. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.-H.; Lee, J.-H.; Rhee, H.-K. Disproportionation of 1,2,4-Trimethylbenzene over Zeolite NU-87. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2000, 17, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-H.; Rhee, H.-K. Shape selective conversion of 1,2,4-trimethylbenzene over zeolite NU-87. Catal. Today 2000, 63, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benazzi, E.; Guth, J.L.; Roulean, L. IM-5 Zeolite, a Process for Its Preparation and Catalytic Applications Thereof. U.S. Patent US6136290A, 24 October 2000. [Google Scholar]
- He, N.; Xie, H.-B.; Ding, Y.-H. Computational study on IM-5 zeolite: What is its preferential location of Al and proton siting? Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2008, 111, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Huang, Z.; Sun, H.; Li, L.; Zhu, X.; Ren, S.; Shen, B. Investigation on n-Alkane Hydroisomerization, a Comparison of IM-5 to ZSM-5 Zeolites. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 14448–14459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, D.; Meng, X.; Liu, N.; Shi, L. Catalytic performance of a phosphorus-modified H-IM-5@meso-SiO2 composite in the alkylation of toluene with methanol. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 11758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corma, A.; Chica, A.; Guil, J.M.; Llopis, F.J.; Mabilon, G.; Perdigón-Melón, J.A.; Valencia, S. Determination of the Pore Topology of Zeolite IM-5 by Means of Catalytic Test Reactions and Hydrocarbon Adsorption Measurements. J. Catal. 2000, 189, 382–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corma, A.; Martínez-Triguero, J.; Valencia, S.; Benazzi, E.; Lacombe, S. IM-5: A Highly Thermal and Hydrothermal Shape-Selective Cracking Zeolite. J. Catal. 2002, 206, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-H.; Lee, D.-K.; Shin, C.-H.; Park, Y.-K.; Wright, P.A.; Lee, W.M.; Hong, S.B. Synthesis, characterization, and catalytic properties of zeolites IM-5 and NU-88. J. Catal. 2003, 215, 151–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zones, S.I.; Chen, C.Y.; Corma, A.; Cheng, M.T.; Kibby, C.L.; Chan, I.Y.; Burton, A.W. Indirect assessment of unknown zeolite structures through inference from zeolite synthesis comparisons coupled with adsorption and catalytic selectivity studies. J. Catal. 2007, 250, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Yi, D.; Shi, L.; Liu, N. Catalytic performance of IM-5 zeolite with high xylene selectivity in benzene alkylation with methanol. An alternative to ZSM-5 zeolite. Petrol. Sci. Technol. 2020, 38, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarach, K.A.; Martinez-Triguero, J.; Valencia, S.; Wojciechowska, K.; Rey, F.; Góra-Marek, K. Hierarchical zeolites TNU-9 and IM-5 as the catalysts for cracking processes. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. Energy 2023, 338, 123066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Ren, S.; Ji, X.; Song, W.; Guo, Q.; Shen, B. Doping Fe and Zn to modulate Ni nanoparticles on IM-5 for methane decomposition to form hydrogen and CNTs. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 13081–13096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, Z.; Cui, J.; Yang, C.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, R.; Zhao, J. Uncovering the roles of Ce and Mn for NH3-SCR over Mn-Ce/IM-5 with extraordinarily superior wide-temperature performance. J. Mol. Struct. 2025, 1321, 139727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, S.; Wang, Y.; Xing, E.; Mu, X. Improved Catalytic Performance of IM-5 Zeolite in Pseudocumene Methylation with Methanol Superior to ZSM-5 Zeolite. Micropor Mesopor Mat. 2025; submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, S.; Wang, Y.; Xing, E.; Mu, X. Understanding the Effect of IM-5 Zeolite Treated with Hexafluorosilicic Acid for the Methanol Alkylation of Pseudocumene. Materials 2025, 18, 2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baerlocher, C.; Gramm, F.; Massüger, L.; McCusker, L.B.; He, Z.; Hovmöller, S.; Zou, X. Structure of the Polycrystalline Zeolite Catalyst IM-5 Solved by Enhanced Charge Flipping. Science 2007, 315, 1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corma, A.; Mengual, J.; Miguel, P.J. IM-5 zeolite for steam catalytic cracking of naphtha to produce propene and ethene. An alternative to ZSM-5 zeolite. Appl. Catal. A-Gen. 2013, 460–461, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Q.; Wei, L.; Hou, R.; Zhang, L.; Hao, K.; Hu, C.; Wen, X.; Xiang, H.; Tao, Z.; Yang, Y.; et al. Insight into performance over IM-5, ZSM-5 and ZSM-11 zeolites for n-heptane cracking to light olefins in the absence & presence of steam. Fuel 2023, 353, 129255. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, H.; Lin, T.; Shi, L.; Meng, X. Acetylene carbonylation over Ni-containing catalysts: Role of surface structure and active site distribution. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 97285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Trenco, A.; Valencia, S.; Martínez, A. The impact of zeolite pore structure on the catalytic behavior of CuZnAl/zeolite hybrid catalysts for the direct DME synthesis. Appl. Catal. A-Gen. 2013, 468, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gołąbek, K.; Tarach, K.A.; Filek, U.; Góra-Marek, K. Ethylene formation by dehydration of ethanol over medium pore zeolites. Spectrochim. Acta A 2018, 192, 464–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojo-Gama, D.; Etemadi, S.; Kirby, E.; Lillerud, K.P.; Beato, P.; Svelle, S.; Olsbye, U. Time- and space-resolved study of the methanol to hydrocarbons (MTH) reaction—Influence of zeolite topology on axial deactivation patterns. Faraday Discuss. 2017, 197, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bleken, F.; Skistad, W.; Barbera, K.; Kustova, M.; Bordiga, S.; Beato, P.; Lillerud, K.P.; Svelle, S.; Olsbye, U. Conversion of methanol over 10-ring zeolites with differing volumes at channel intersections: Comparison of TNU-9, IM-5, ZSM-11 and ZSM-5. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 2539–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmar, D.; Cha, S.H.; Huang, C.; Chiang, H.; Washburn, S.; Grabow, L.C.; Rimer, J.D. Impact of medium-pore zeolite topology on para-xylene production from toluene alkylation with methanol. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2023, 13, 5227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Lin, S.; Wei, Y.; Tian, P.; Ye, M.; Liu, Z. Cavity-controlled methanol conversion over zeolite catalysts. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2023, 10, nwad120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Wang, W.; Sun, W.; Yang, Z.; Cao, Y.; Chen, W.; Ge, X.; Qian, G.; Feng, X.; Duan, X.; et al. Poisoning effect of polyvinyl chloride on the catalytic pyrolysis of mixed plastics over zeolites. Sci. China Chem. 2024, 67, 2265–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolopoulos, N.; van Veenhuizen, O.; Weckhuysen, B.M. Effect of Steaming on Waste-Derived Zeolite ZSM-5 as Methanol-To-Hydrocarbons Catalyst. Chemcatchem 2022, 14, e202201021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, M.; Chen, J.; Xing, E.; Luo, Y.; Shu, X. Effects of Modification of Acidity and Pore Structure of IM-5 Zeolite on the Catalytic Performance in Methanol to Propylene Reaction. Acta Pet. Sin. Pet. Process. Sect. 2020, 36, 17–27. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Yang, W.Y.; Ling, F.X.; Shen, Z.Q.; Yang, R.C.; Sun, W.F.; Fang, X.C.; Ji, H.H. A facile method for the fabrication of IM-5 hollow zeolite sphere in emulsion system. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2012, 163, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ma, B.; Yang, W.Y.; Ling, F.X.; Shen, Z.Q.; Hou, Y.X. Green Synthesis and Characterization of IM -5 Zeolite. Petro Chem. Technol. 2014, 43, 897–902. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, Y.; Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Luo, Y.; Shu, X. Effect of H2SiF6 modification of IM-5 on catalytic performance in benzene alkylation with ethylene. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 18288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Liu, C. Hierarchical Porous ZSM-5 Zeolite Synthesized by in situ Zeolitization and Its Coke Deposition Resistance in Aromatization Reaction. Chin. J. Chem. 2012, 30, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.; Yang, L.; Dai, W.; Wang, C.; Wu, G.; Guan, N.; Hunger, M.; Li, L. On the deactivation mechanism of zeolite catalyst in ethanol to butadiene conversion. J. Catal. 2018, 367, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, R.; Liu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Dong, M.; Wang, S.; Fan, W.; Wang, J.; Qin, Z. Evolution of carbon deposits during ethylene aromatization over Zn/ZSM-5. Fuel 2024, 358, 130078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Xu, J.; Deng, F. Recent advances in solid-state NMR of zeolite catalysts. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2022, 9, nwad155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Tan, X.; Zhang, T.; Han, Z.; Jiang, H. The deactivation of a ZnO doped ZrO2–SiO2 catalyst in the conversion of ethanol/acetaldehyde to 1,3-butadiene. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 34069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Hu, Y.; Bao, Q.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Ge, J.; Xu, M. The study of ferrierite zeolite synthesized by using silica sol modified by HCl as silica source for the skeletal isomerization reaction of 1-butene. React. Kinet. Mech. Catal. 2021, 133, 309–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Li, F.; Shan, C.; Han, D.; Zhang, Q.; Niu, L.; Ivaska, A. Covalent functionalization of chemically converted graphene sheets viasilane and its reinforcement. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 4632–4638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pylypenko, S.; Olson, T.S.; Carroll, N.J.; Petsev, D.N.; Atanassov, P. Templated Platinum/Carbon Oxygen Reduction Fuel Cell Electrocatalysts. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 4200–4207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Rui, P.; Cai, X.; Xie, X.; Liao, W.; Luo, Y.; Shu, X. Insights into the methanol to olefins (MTO) performance of SAPO-34 under the stripper conditions of fluid catalytic cracking (FCC). Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2022, 345, 112244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.-D.; Schimmelmann, A.; Mastalerz, M.; Hatcher, P.G.; Li, Y. Structural Features of a Bituminous Coal and Their Changes during Low-Temperature Oxidation and Loss of Volatiles Investigated by Advanced Solid-State NMR Spectroscopy. Energy Fuels 2010, 24, 2536–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lashchinskaya, Z.N.; Gabrienko, A.A.; Prosvirin, I.P.; Toktarev, A.V.; Stepanov, A.G. Effect of Silver Cations on Propene Aromatization on H-ZSM-5 Zeolite Investigated by 13C MAS NMR and FTIR Spectroscopy. ACS Catal. 2023, 13, 10248–10260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLuca, M.; Kravchenko, P.; Hoffman, A.; Hibbitts, D. Mechanism and Kinetics of Methylating C6–C12 Methylbenzenes with Methanol and Dimethyl Ether in H-MFI Zeolites. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 6444–6460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhe, W.; Fei, C.; Jia-Bao, L.; Bing, X. Shape-Selective Alkylation of Toluene with Dimethyl Carbonate into p-Xylene Over MgO/MCM-22 Prepared by a Novel Pre-impregnation Method. Catal. Lett. 2024, 154, 170–180. [Google Scholar]
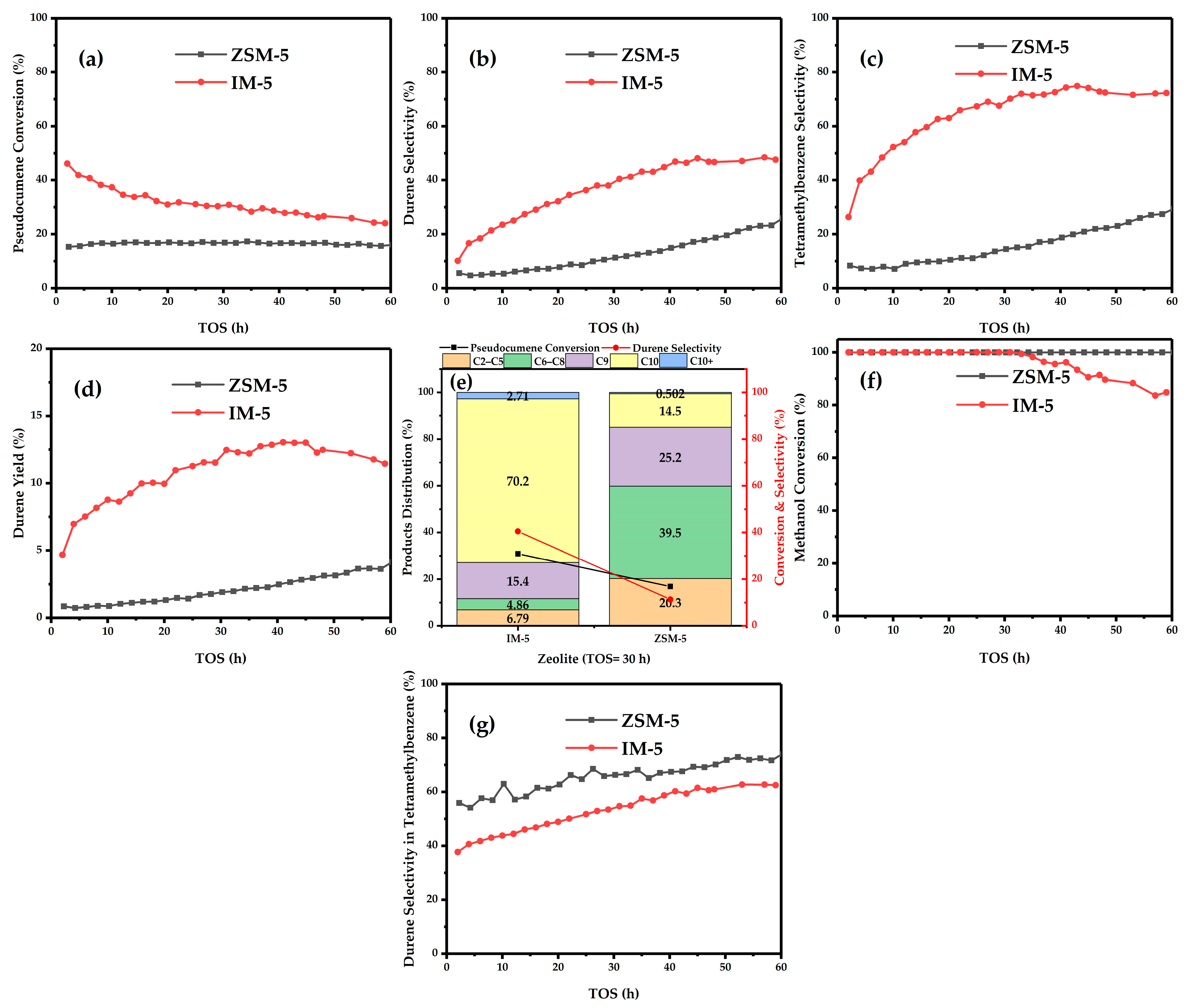
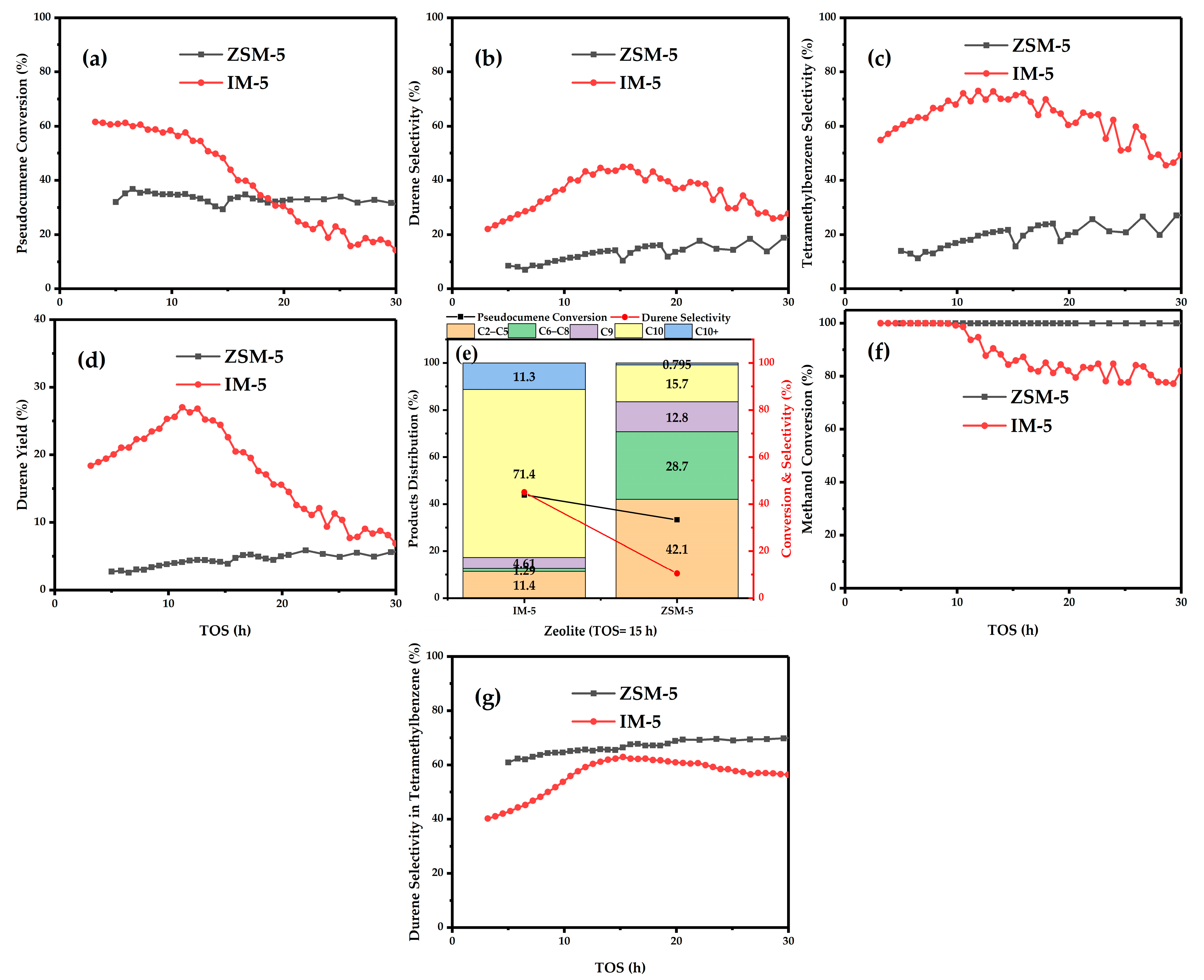
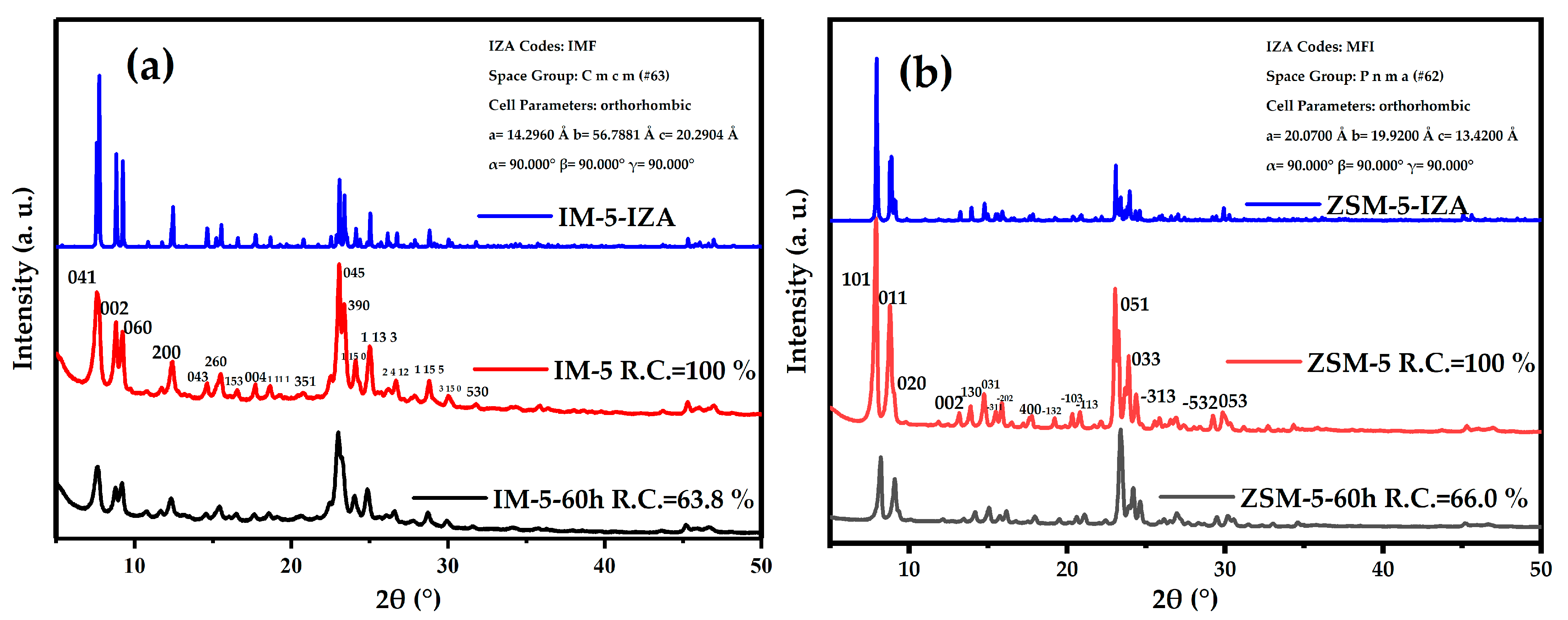

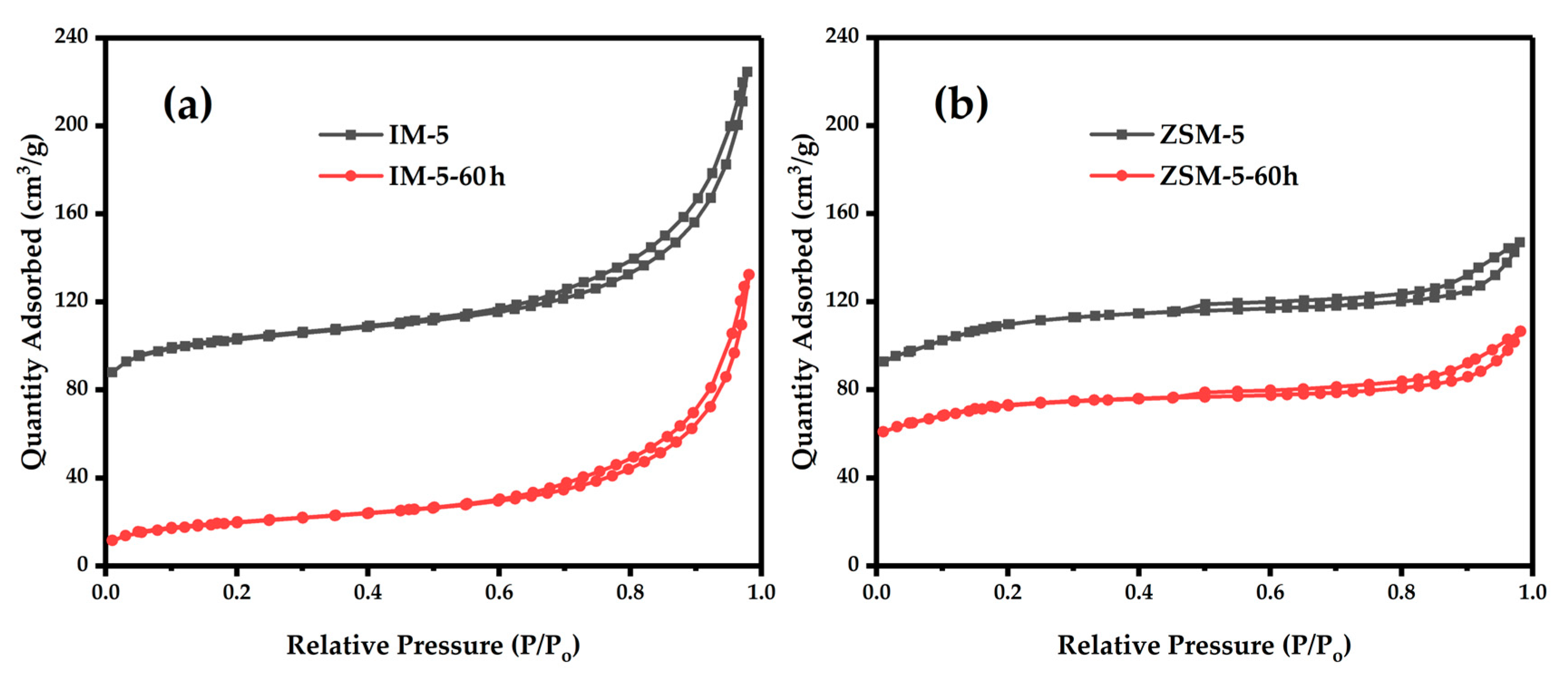
| Samples | SBET a/ (m2·g−1) | Smicro b/ (m2·g−1) | Sext b/ (m2·g−1) | Vtotal c/ (cm3·g−1) | Vmicro b/ (cm3·g−1) | Vmeso d/ (cm3·g−1) | D de e/ (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IM-5 | 372 | 332 | 40 | 0.32 | 0.15 | 0.17 | 3.4 |
| IM-5-60 h | 77 | 15 | 62 | 0.21 | 0.005 | 0.205 | 10.75 |
| ZSM-5 | 377 | 354 | 23 | 0.23 | 0.16 | 0.07 | 2.41 |
| ZSM-5-60 h | 250 | 234 | 16 | 0.16 | 0.11 | 0.05 | 2.63 |
| Samples | Si(4Si, 0Al)/% | Si(3Si, 1Al)/% | Si(2Si, 2Al)/% | Si(1Si, 3Al)/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IM-5 | 72.36 | 12.57 | 14.10 | 0.97 |
| IM-5-60 h | 77.05 | 15.02 | 6.71 | 1.21 |
| Samples | Acid Amounts/(μmol/g) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Weak | Strong | |
| IM-5 | 1462.6 | 793.5 | 669.1 |
| IM-5-60 h | 435.3 | 311.7 | 123.6 |
| ZSM-5 | 721.8 | 409.0 | 312.8 |
| ZSM-5-60 h | 433.9 | 286.0 | 147.9 |
| Samples | Brønsted Acid Amounts/(μmol/g) | Lewis Acid Amounts/ (μmol/g) | B/L | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 200 °C | 350 °C | 200 °C | 350 °C | 200 °C | 350 °C | |
| IM-5 | 151.30 | 115.20 | 43.90 | 23.80 | 3.40 | 4.83 |
| IM-5-60 h | 25.78 | 15.34 | 19.25 | 8.34 | 1.34 | 1.84 |
| ZSM-5 | 92.84 | 58.16 | 39.23 | 11.87 | 2.37 | 4.90 |
| ZSM-5-60 h | 28.67 | 13.86 | 19.05 | 6.66 | 1.51 | 2.08 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hao, S.; Wang, Y.; Xing, E.; Mu, X. On the Deactivation Analysis of IM-5 Zeolite in Pseudocumene Methylation with Methanol. Crystals 2025, 15, 598. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15070598
Hao S, Wang Y, Xing E, Mu X. On the Deactivation Analysis of IM-5 Zeolite in Pseudocumene Methylation with Methanol. Crystals. 2025; 15(7):598. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15070598
Chicago/Turabian StyleHao, Shumin, Yongrui Wang, Enhui Xing, and Xuhong Mu. 2025. "On the Deactivation Analysis of IM-5 Zeolite in Pseudocumene Methylation with Methanol" Crystals 15, no. 7: 598. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15070598
APA StyleHao, S., Wang, Y., Xing, E., & Mu, X. (2025). On the Deactivation Analysis of IM-5 Zeolite in Pseudocumene Methylation with Methanol. Crystals, 15(7), 598. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15070598




