Abstract
We present a model of a Cr2+-doped saturable absorber (SA), which is employed in passively Q-switched (PQS) Tm:CaF2 lasers. The overall round-trip loss, the time evolution of the intracavity photon density, and the effective population inversion density can all be obtained through numerical solutions. Under the mode-matching condition, this model can be used to easily determine the PQS laser’s main output parameters, including the average output power, repetition frequency, peak power, pulse energy, and pulse width. This concept is also applicable to a range of thulium-doped solid-state lasers (SSLs) operating on the transition from the 3F4 level to the 3H6 level, which are Q-switched by a Cr2+-doped SA. This model is helpful for the design and optimization of this kind of laser.
1. Introduction
High peak power or high energy nonlinear frequency conversion in the mid-infrared wavelength region, lidar, laser communication, medicine, and other fields all make extensive use of 2 μm pulse lasers [1,2,3,4,5]. In recent years, with the emergence of new saturable absorbers, the use of passive Q-switching technology to obtain pulsed lasers has been widely reported [6,7,8,9,10]. Furthermore, PQS lasers are more advantageous than active Q-switched lasers in pulsed laser shrinking due to their low cost and simple, compact designs [11,12]. The right SA and gain medium selection are essential for obtaining high energy or high peak power in a PQS laser.
Bulk materials doped with Cr2+ (such as Cr:ZnS and Cr:ZnSe) and two-dimensional layered materials are the primary sources of SA for the 2 μm wavelength range. Compared with two-dimensional materials, the SA with bulk structure can utilize more doped ions, and, thus, obtain a higher initial population inversion density [6,7,8,9,10]. Moreover, Cr2+-doped bulk materials also have the characteristics of a high damage threshold, wide absorption spectrum, and large absorption cross-section [13,14]. These characteristics facilitate the production of high peak power or high energy 2 μm pulsed lasers using Cr2+-doped SA Q-switched lasers.
Within the wavelength range of 2 μm, Tm3+-doped gain media can be directly pumped by commercial semiconductor lasers, while Ho3+-doped gain media typically use a two-stage pumping structure (LD → Tm3+ → Ho3+). Therefore, compared to SSLs doped with Ho3+, SSLs doped with Tm3+ can have lower production costs and greatly reduce the complexity of the laser system. Apart from the exceptional physical and chemical characteristics of CaF2 crystals, including their wide transmittance spectrum, increased heat conductivity, low coefficient of thermal expansion, and high damage threshold, their low phonon energy (≤495 cm−1) can also lessen the likelihood of a non-radiative transition [15]. Moreover, Tm3+ tends to form cluster structures within the CaF2 crystal, which can enhance the cross-relaxation effects [16]. These advantages help improve the efficiency of optical-to-optical conversion of Tm:CaF2 lasers, thereby increasing peak power or output energy. For the first time, in 2013, A. A. Lyapin et al. employed LD as a pumping source for Tm:CaF2 crystals to produce a continuous-wave laser with a slope efficiency of 26.7% and a wavelength of 1890 nm [17]. In 2018, it was initially shown that a Tm:CaF2 laser may operate PQS by employing silver nanorods as a SA [18]. With a maximum output power of 385 mW and a minimum pulse width of 3.1 µs, a wavelength of 1935.4 nm was achieved. The associated pulse energy was 41.4 µJ, and the corresponding repetition frequency was 9.3 kHz. In the same year, this research team developed a continuous-wave laser with an output power of 2.71 W and a center wavelength of 1917.0 nm in an LD-pumped Tm:CaF2 laser, achieving the highest slope efficiency of this class of lasers to date. The associated slope efficiency was 70.3% [19]. Using a 1610 nm fiber laser as the pump source for the Tm:CaF2 laser, R. Thouroude et al. created a continuous-wave laser in 2020 with a maximum power of 1.25 W at around 1880 nm and a slope efficiency of 55% [20]. Moreover, CaF2 lasers co-doped with Tm3+ and other ions, like Y3+ or La3+, have been researched to improve the laser’s performance [21,22,23,24,25].
So far, the research of Tm:CaF2 lasers has mainly focused on continuous-wave operation, and there are few researches on PQS operation, especially since there have been no reports on Tm:CaF2 lasers which are Q-switched by Cr2+-doped saturable absorbers. A model of PQS Tm:CaF2 lasers with saturable absorbers doped with Cr2+ is established in this work. The main output parameters of the PQS laser can be calculated numerically using this model. Furthermore, the effect of resonator parameters on the output characteristics of the PQS laser is investigated. This paper’s paradigm can also be used for various kinds of thulium-doped SSLs (3F4 → 3H6) that are Q-switched by saturable absorbers doped with Cr2+. This study, in our opinion, has significant reference value for the development and improvement of such lasers.
2. Materials and Methods
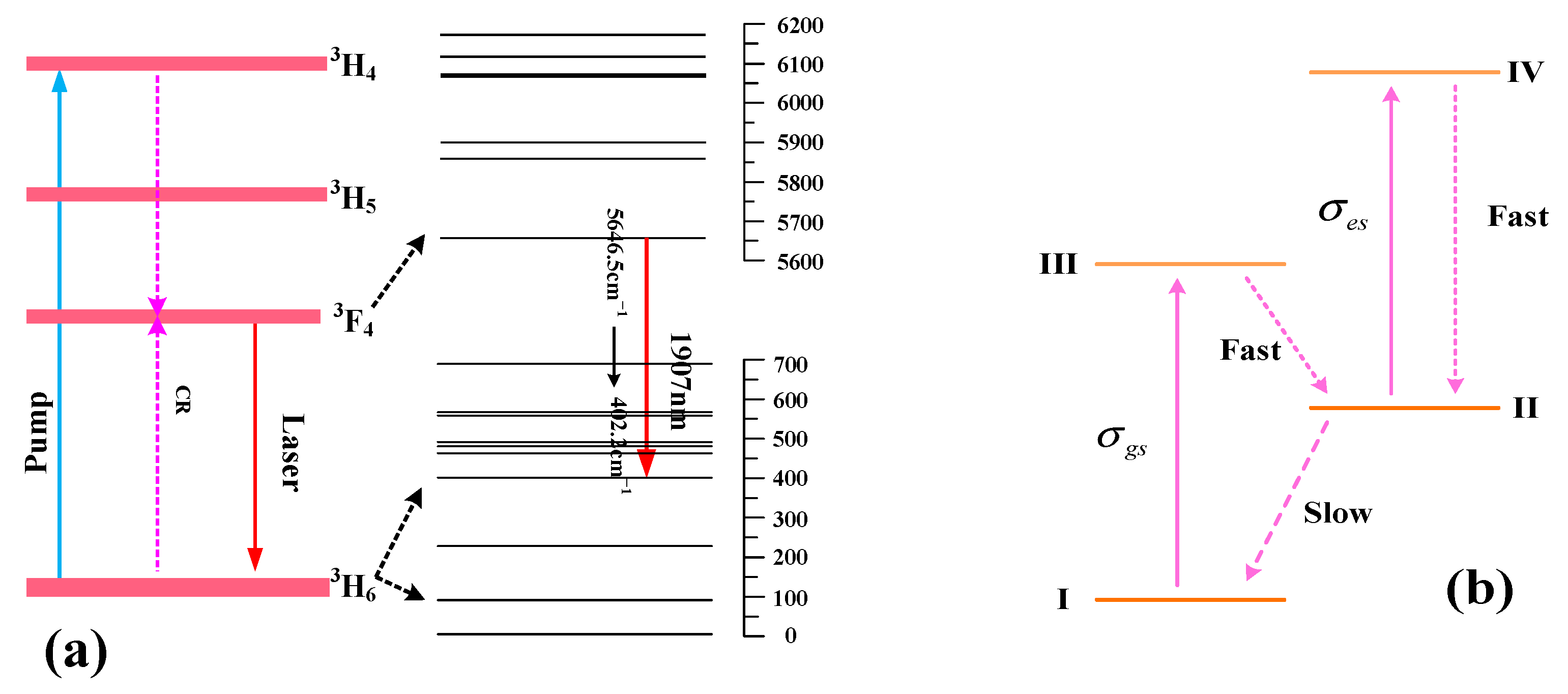
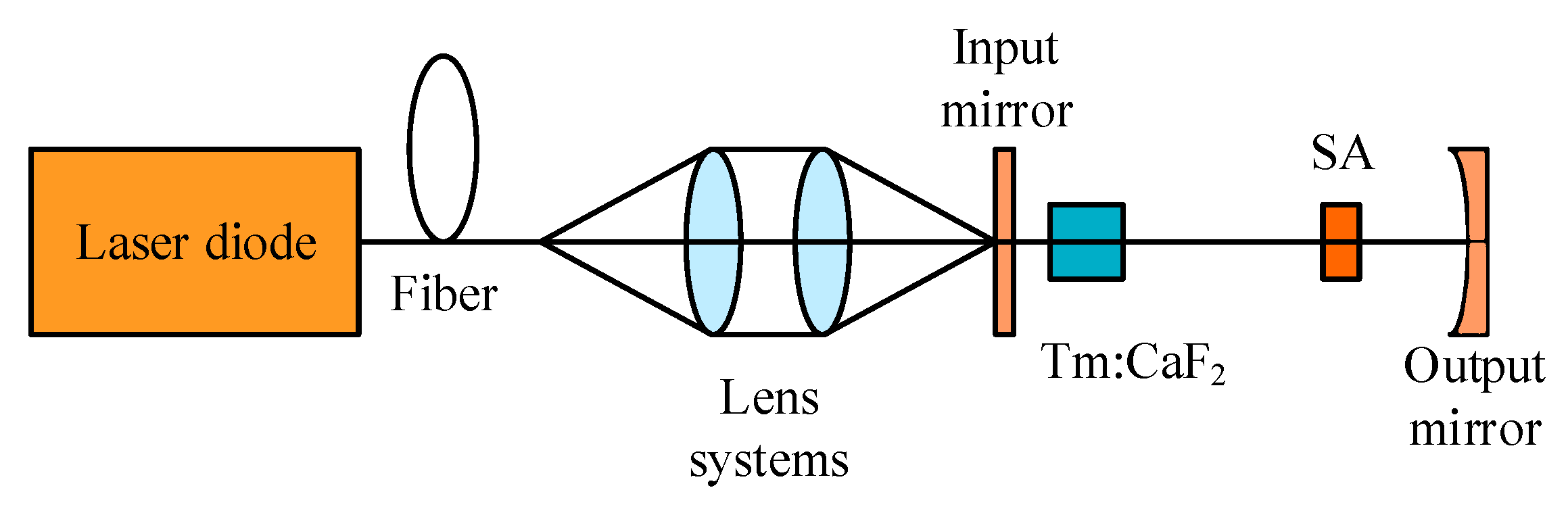
The laser-generating process in a Tm3+-doped gain medium is shown in Figure 1a [26]. The 3H6 → 3H4 transition is where the pump light is absorbed. The Tm3+ system contains a potent cross-relaxation (CR) mechanism between two neighboring ions, 3H4 + 3H6→3F4 + 3F4. By generating two photons at approximately 1.9 μm from a single pump photon at around 0.8 μm, this method achieves a 200% quantum efficiency. Laser action occurs between one sublevel, 5646.5 cm−1, of the 3F4 level and one sublevel, 402.2 cm−1, of the 3H6 level, and the corresponding wavelength is ~1907 nm [27,28]. Figure 1b shows the Cr2+ energy level diagram in the Cr2+-doped SA. The II→I transition is slow, but the III→II and IV→II transitions are quick. The I→III and II→IV transitions can both be absorbed at the laser wavelength, with absorption cross-sections of σgs and σes, respectively. Therefore, it can be considered only levels I and II are appreciably populated. Furthermore, Cr2+-doped crystals show broad absorption bandwidths and a wide range of spectral transparency. These crystals’ wide absorption spectra allow them to modulate lasers across a remarkably wide wavelength range. The emission cross-section of Tm3+ is two orders of magnitude lower than the peak absorption and emission cross-sections of Cr2+, which are on the scale of 10−18 cm2. Consequently, Cr2+-doped crystals are appropriate for usage as passive Q-switches in Tm3+-doped laser systems in addition to being gain media for widely tunable mid-infrared lasers [13,14]. The common structure of a PQS Tm:CaF2 laser employing an SA doped with Cr2+ is depicted in Figure 2.
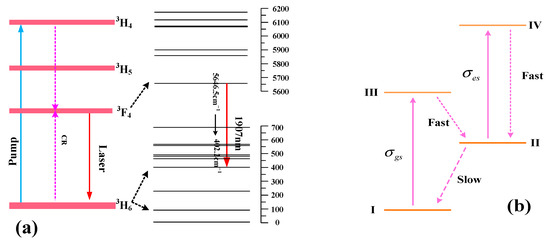
Figure 1.
Tm3+ ion (a) and Cr2+ ion (b) energy level diagrams.
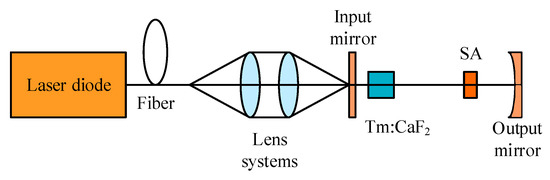
Figure 2.
A typical configuration of a Cr2+-doped saturable absorber Q-switched Tm:CaF2 laser.
Here, we assume immediate thermalization of the laser manifolds and create the rate equations using the effective population inversion density, effective absorption cross-section, and effective emission cross-section, which are more suited for the quasi-three-level system, thus, (1) through (3) provide the rate equations.
Ag is the effective cross-sectional area of the laser beam inside the gain medium, while N1 and N2 stand for the lower and higher laser manifold population densities, respectively. Additionally, the equations state that ϕ is the intracavity photon density, l is the gain medium’s length, c is the vacuum speed of light, σeff is the gain medium’s effective emission cross-section, and L is the cavity optical length. The Boltzmann factors for the lower and upper laser intensities are denoted by f1 and f2, respectively. The effective absorption cross-sections of the ground and excited states are denoted by σgs and σes, respectively, and ls is the SA’s length. Ngs and Nes represent the SA ground and excited state population densities, respectively, whereas τc represents the cavity photon lifetime and ΔN represents the effective population inversion density. Wp is the pump rate in addition to the effective cross-sectional areas of the SA. The excited-state lifetimes of the SA and the gain metal are denoted by τs and τ2, respectively.
Equation (1) states that the reason for reabsorption in a quasi-three-level laser is “(f1/f2) N1ϕ,” or stimulated absorption of the laser in the lower energy level. A four-level laser inhibits reabsorption since the bottom laser level has no population. The expression “1/LAg” in Equation (1) denotes spontaneous emission from the upper laser level, which is a prerequisite to producing passive Q-switched pulses. Equation (4) is also satisfied by N1 and N2.
where N0 is the dopant concentration in the gain medium. Ngs and Nes satisfy Equation (5)
where Nso is the saturable absorber’s doping concentration. One way to express the effective population inversion density is as
Equation (7) provides Nso, where T0 is the saturable absorber’s initial transmittance.
Equation (8) can be used to obtain the cavity photon lifetime, where R stands for the output coupler reflectivity, the whole travel time is tr, and δ is the round-trip internal resonator loss.
The pump beam’s effective cross-sectional area is 0.5πwp2, where wp is the pump beam’s radius in the gain medium. This is because the pump strength has a Gaussian spatial distribution when the LD end-pumped regime is used. The pump rate can be expressed using Equation (9).
Due to the presence of cross-relaxation in the Tm3+-doped gain medium, the upper laser level will increase by two particles when the gain medium absorbs one pump photon, so the numerator of formula (9) contains the integer 4. In Equation (9), Pp is the pump power, hvp is the energy of a pump photon, and σp is the effective absorption cross-section at the pump wavelength.
Because the SA’s ground and excited state populations change over time when the pulse is established, the total loss also varies with time and it can be expressed as [29].
Through the output mirror, the cavity’s instantaneous power coupling output can be expressed as [30]:
where hvl is the oscillating light’s photon energy and LAg is the resonator’s volume that the oscillating light occupies.
Under the influence of the lattice field, the Tm3+-doped gain medium’s excited state (3F4) and ground state (3H6) will split into several sub-levels. The population of each manifold’s sub-levels satisfies the Boltzmann distribution when the thermal equilibrium is present. Let fi represent the Boltzmann Fraction (Bolt. Frac.) of the ith level within a given manifold and it can be expressed as:
where T represents the temperature, kb the Boltzmann constant, Ei the ith level’s energy, and Zi is the manifold’s partition function, which can be written as:
The “m” represents the thermally populated stark level in the manifold. By using Equations (12) and (13) and considering the energy levels in [28], the Bolt. Frac. for each sublevel of the 3H6 and 3F4 manifolds can be calculated, as shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Bolt. Frac. in the Stark energy levels of the Tm:CaF2 at 280 K.
3. Results and Discussions
Here, the numerical solution approach can be used to determine the intracavity photon density, effective population inversion density, and total round-trip loss. By using these data further, the PQS laser’s main output parameters—peak power, pulse width, pulse energy, repetition frequency, and average output power—can be determined. This research examines in depth how the resonator parameters affect the laser’s output parameters. Here, the SA was chosen to be Cr:ZnS, and a Tm:CaF2 crystal with a 3at.% thulium doping concentration was used as the gain medium. Table 2 lists the parameters utilized in the rate equation modeling unless otherwise noted.

Table 2.
Values for the rate equation modeling parameters.
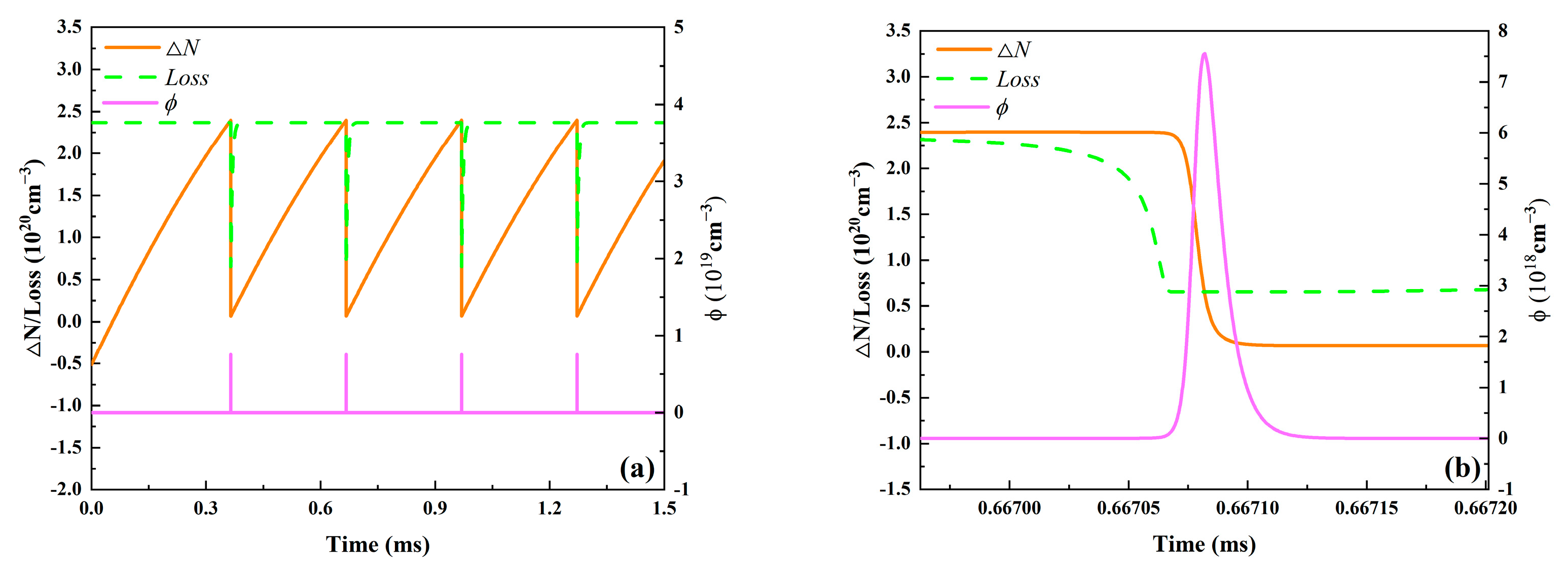
Additionally, the PQS laser’s output parameters were acquired with mode matching, or wp = wl. Naturally, the laser spot size in the gain medium should be the same as the Ag = As laser spot size in the SA. The intracavity photon density, effective population inversion density, and total round-trip loss change curves over time were created using the values from Table 2, as illustrated in Figure 3. Figure 3b displays a partial enlargement of Figure 3a. As seen in Figure 3a, the building time of the first Q-switched pulse is substantially longer than that of the subsequent pulses. This is because the first pulse’s initial population inversion density (negative value) is significantly lower than that of the subsequent pulses. The pulse buildup process is illustrated in Figure 3b. With the increase of intracavity photon density, both total round-trip loss and effective population inversion density gradually decrease, until the effective population inversion density equals the total round-trip loss, the intracavity photon density reaches its maximum value, and then the intracavity photon density rapidly drops to zero.
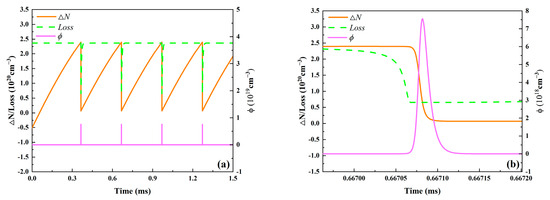
Figure 3.
The overall round-trip loss (Loss), the effective population inversion density (ΔN), and the intracavity photon density (ϕ) as a function of time. Figure (b) is an enlarged detail of a specific region in Figure (a).
3.1. The Effect of Incident Pump Power on Laser Characteristics
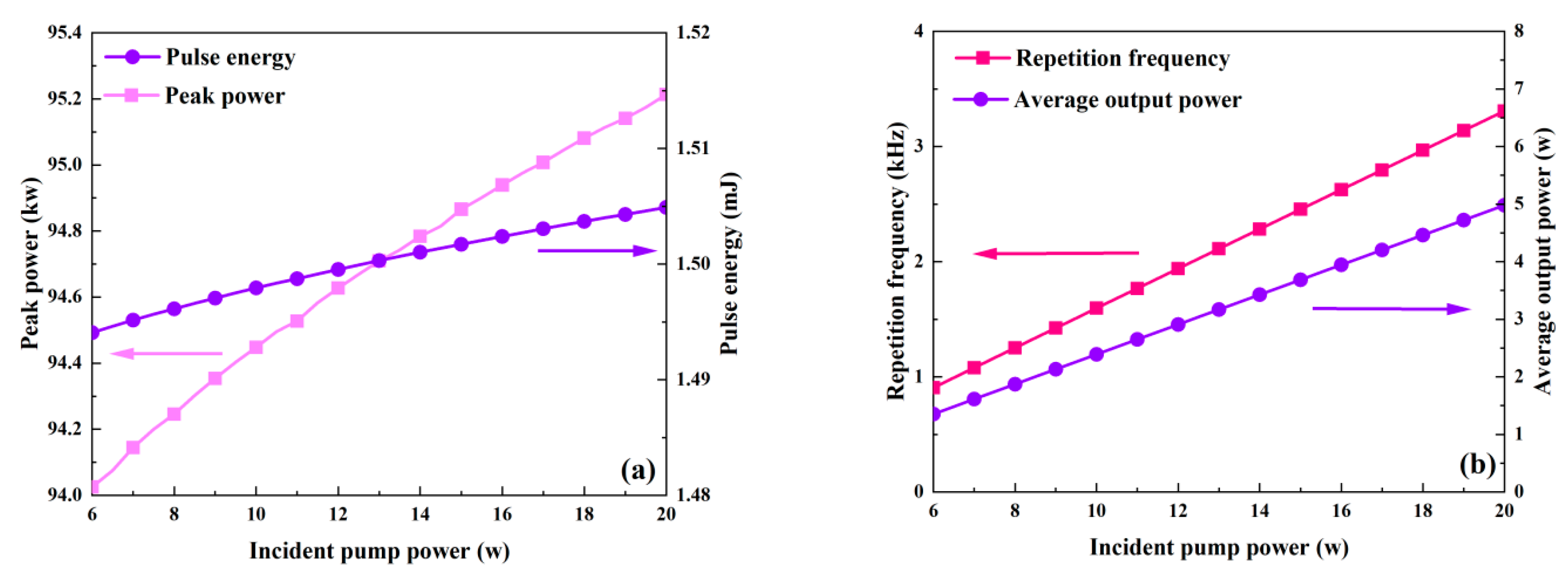
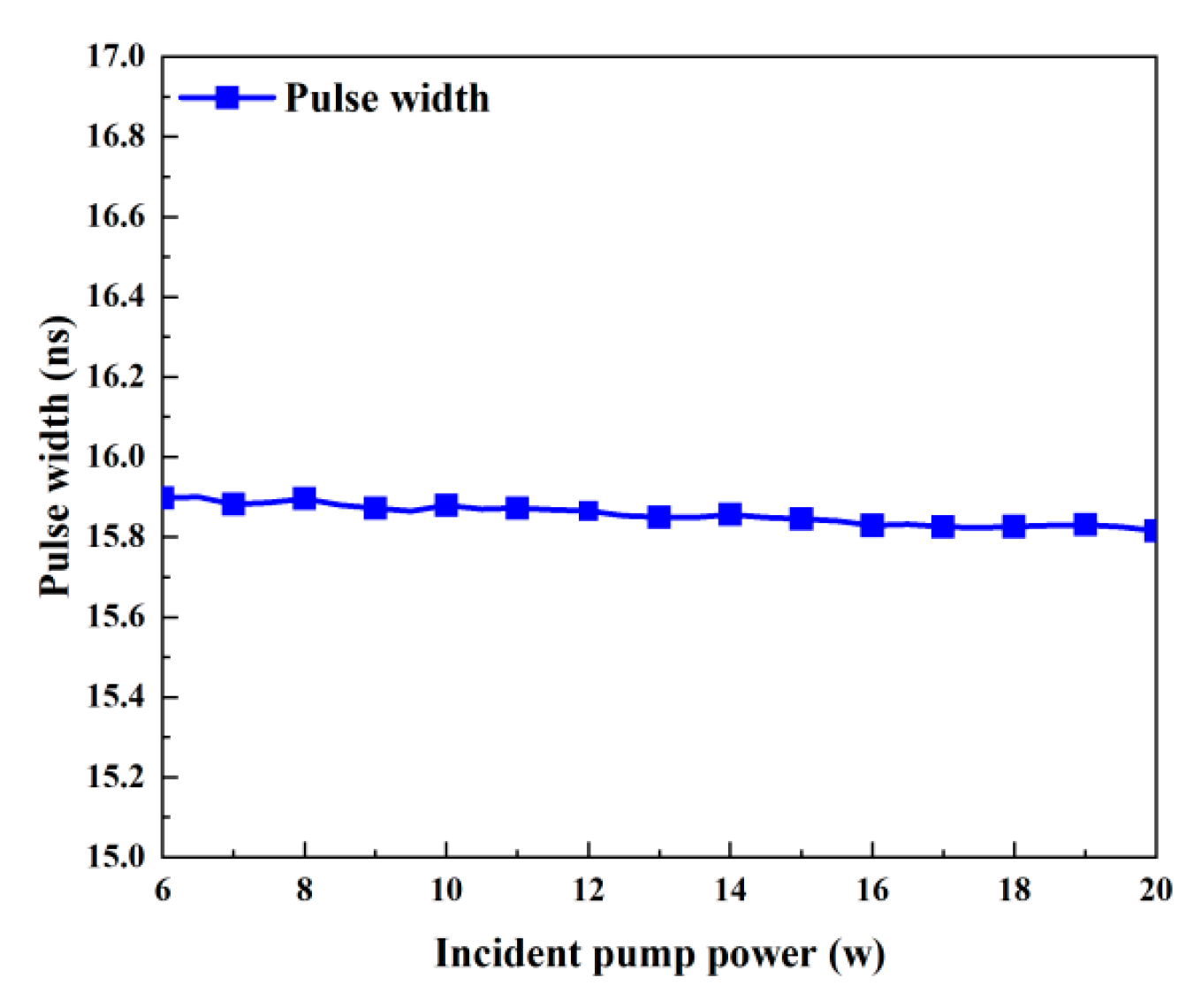
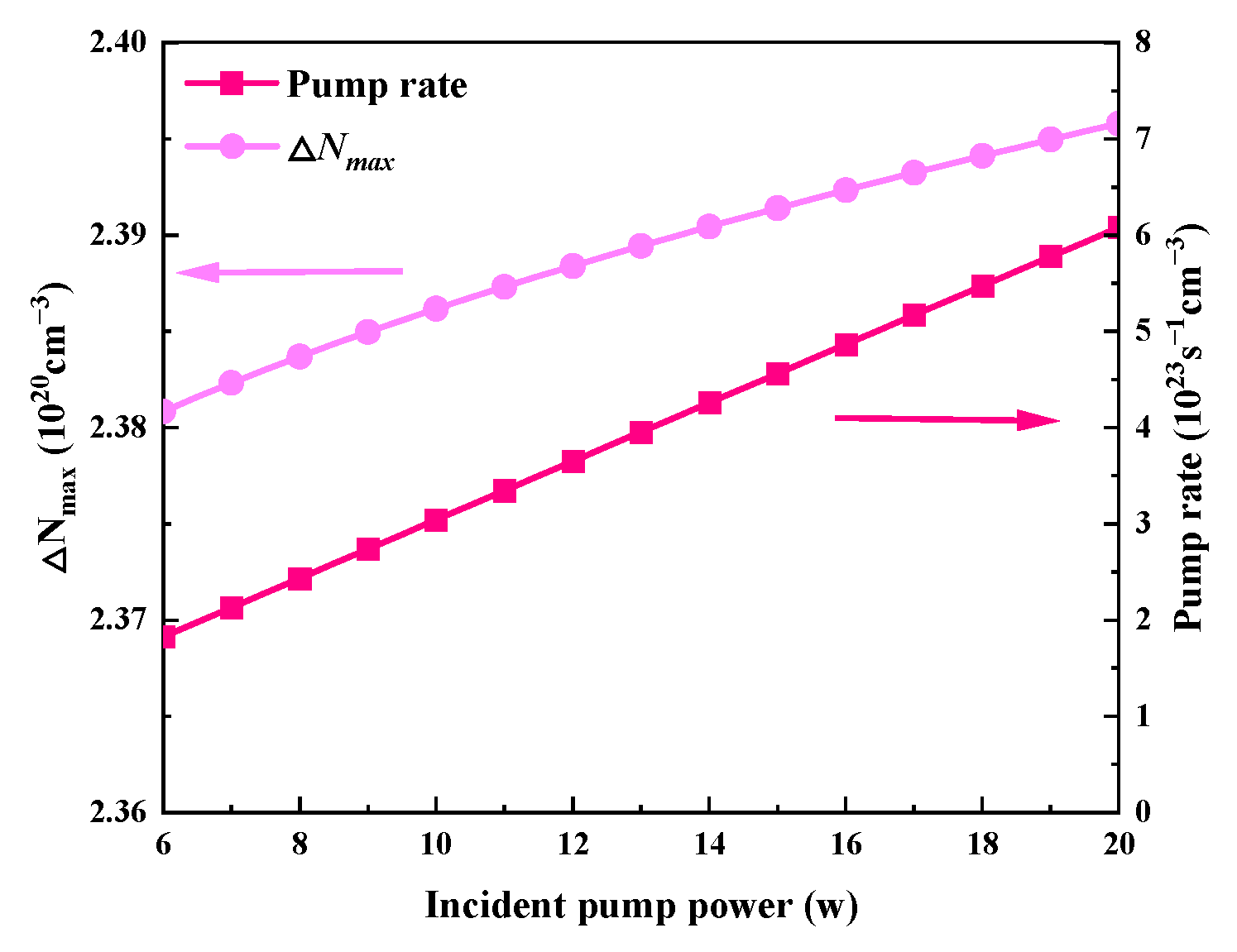
While Table 2 uses the values of other parameters, Figure 4 and Figure 5 illustrate how the output characteristics change as the incident pump power varies between 6 W and 20 W. As the pump power increases, the pulse width stays almost constant, but the peak power and pulse energy slightly increase, as shown in Figure 4a and Figure 5. This is because the effective population inversion density still somewhat grows under the pump’s excitation during the laser pulse’s creation. The maximum effective population inversion that may be achieved rises with incident pump power, as shown in Figure 6. Approximately 0.6% more effective population inversion occurs at a 20 W pump power than at a 6 W pump power. Both the average output power and the repetition frequency grow monotonically as the incident pump power increases, as seen in Figure 4b. As the incident pump power rises, the pump rate rises as well, increasing the average output power (Figure 6). This raises the frequency of repetition and decreases the time it takes for a pulse to develop.
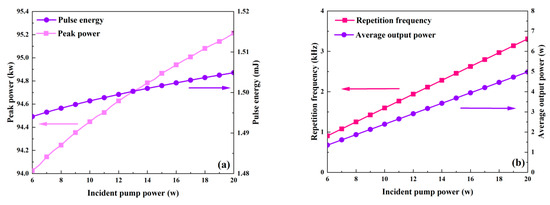
Figure 4.
The dependence of peak power, pulse energy (a), and repetition frequency and average output power (b) on the incident pump power.
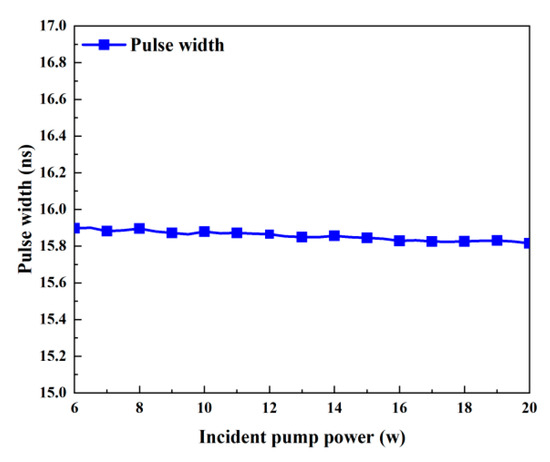
Figure 5.
Pulse width versus incident pump power.
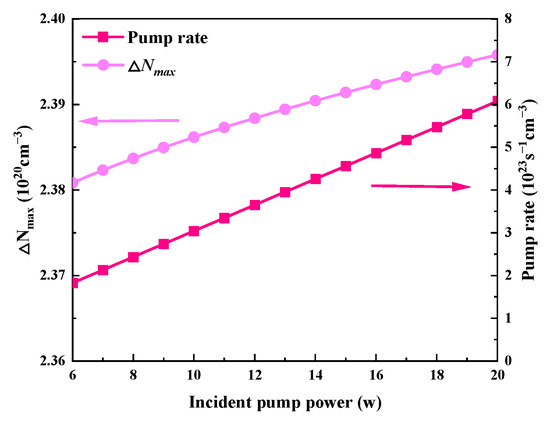
Figure 6.
The dependence of the maximum effective population inversion density (ΔNmax) and pump rate (around the threshold) on the incident pump power.
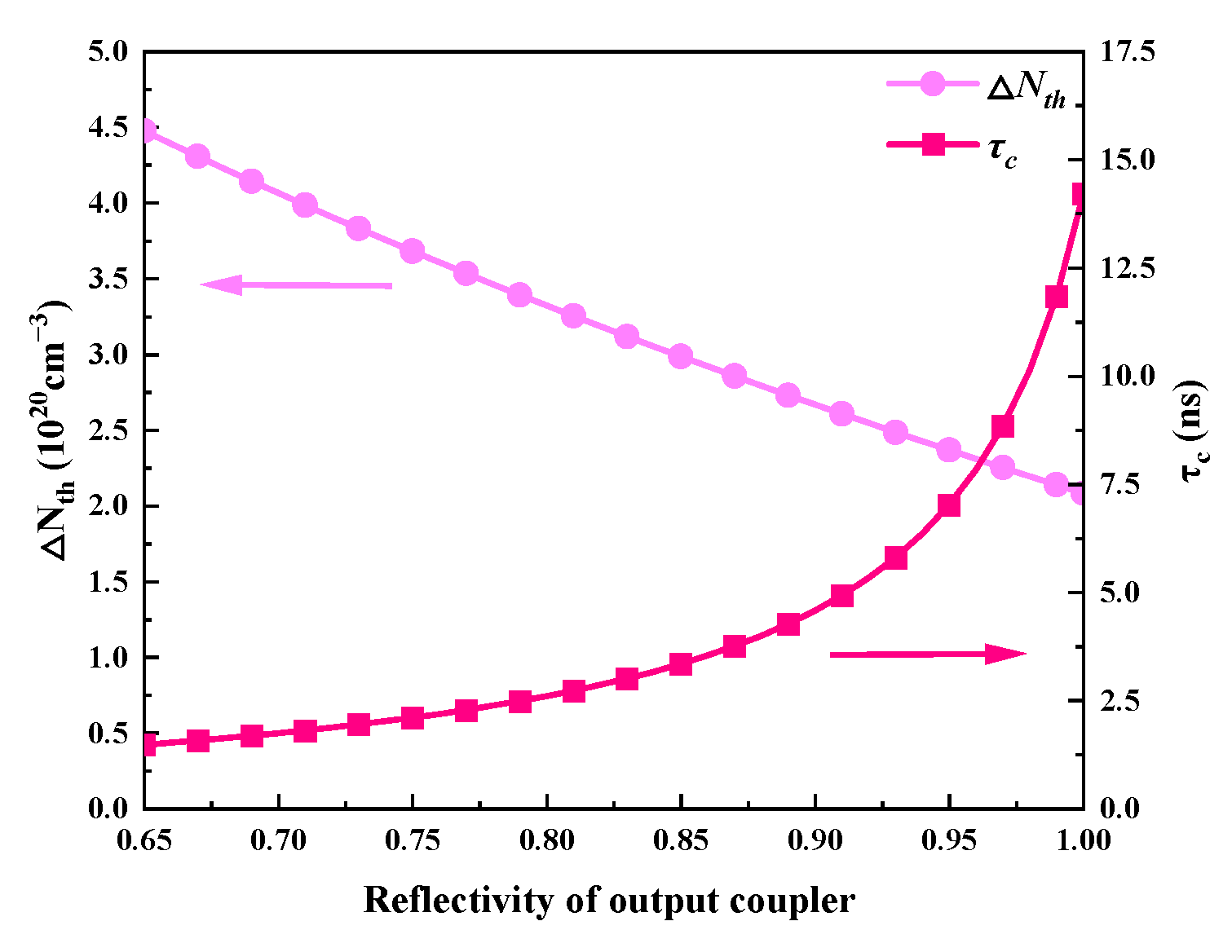
3.2. The Effect of Reflectivity of Output Coupler on Laser Characteristics
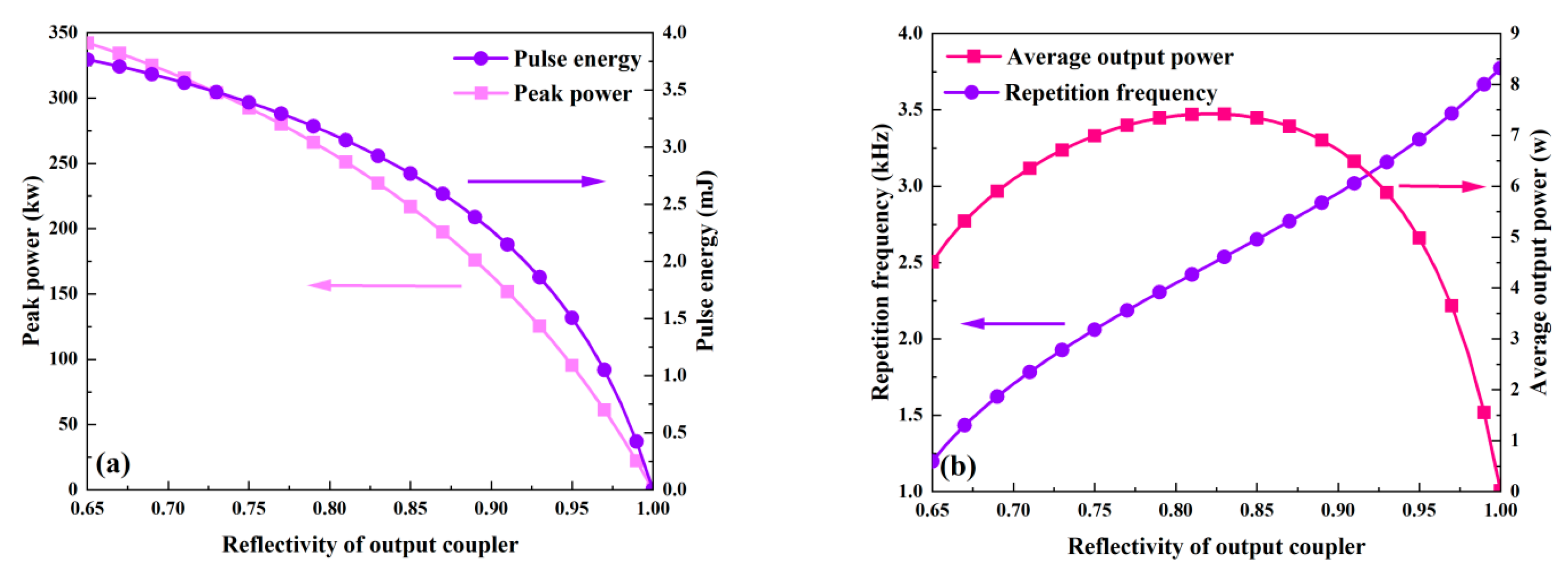
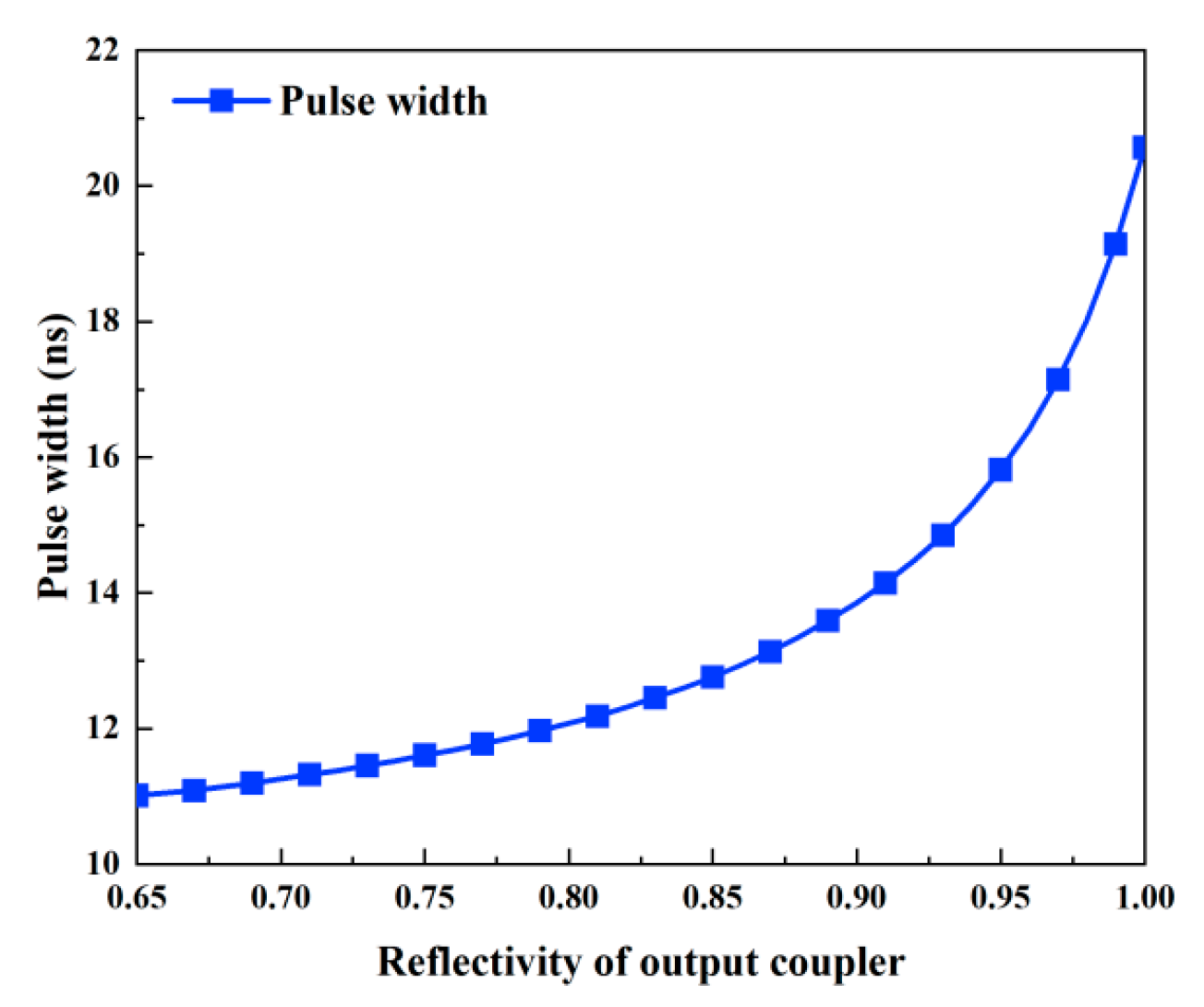
Figure 7 and Figure 8 illustrate how the output coupler’s reflectivity affects the output characteristics. In this case, the output coupler’s reflectivity ranges from 0.65 to 1, and Table 2 lists the values of the other parameters. According to Figure 8, the pulse width grows as the reflectivity rises; in other words, a smaller reflectivity facilitates the achievement of a shorter pulse width. This is because an increase in reflectivity causes the threshold population inversion density to fall (Figure 9) and the intracavity photon lifetime to increase, both of which increase the pulse width. However, as Figure 7a shows, peak power and pulse energy decrease as reflectivity increases. Figure 7b shows that the repetition frequency increases monotonically with reflectivity, while there is an ideal reflectivity at which the average output power reaches its maximum value.
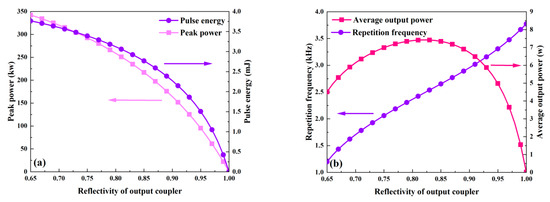
Figure 7.
The dependence of peak power, pulse energy (a), and repetition frequency and average output power (b) on the reflectivity of the output coupler.
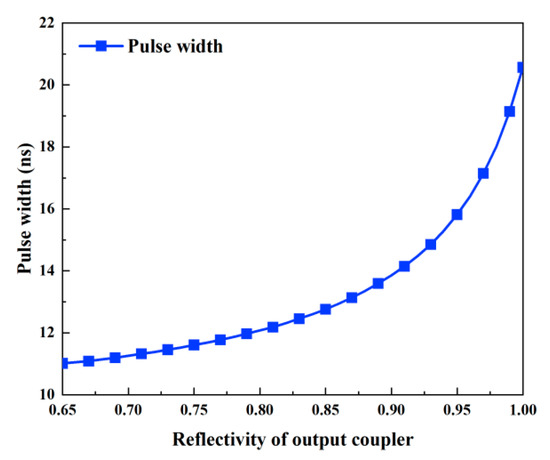
Figure 8.
Pulse width versus the reflectivity of the output coupler.
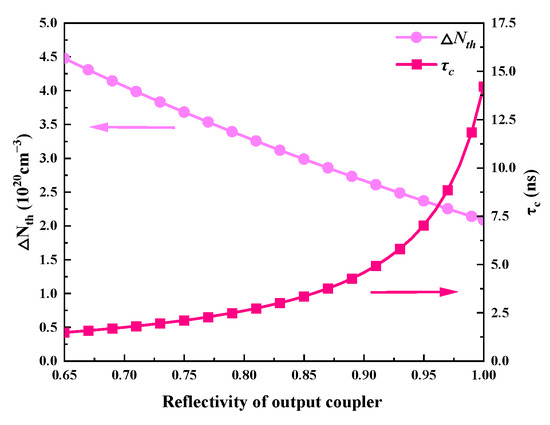
Figure 9.
The dependence of the threshold population inversion density (ΔNth) and intracavity photon lifetime (τc) on the reflectivity of the output coupler.
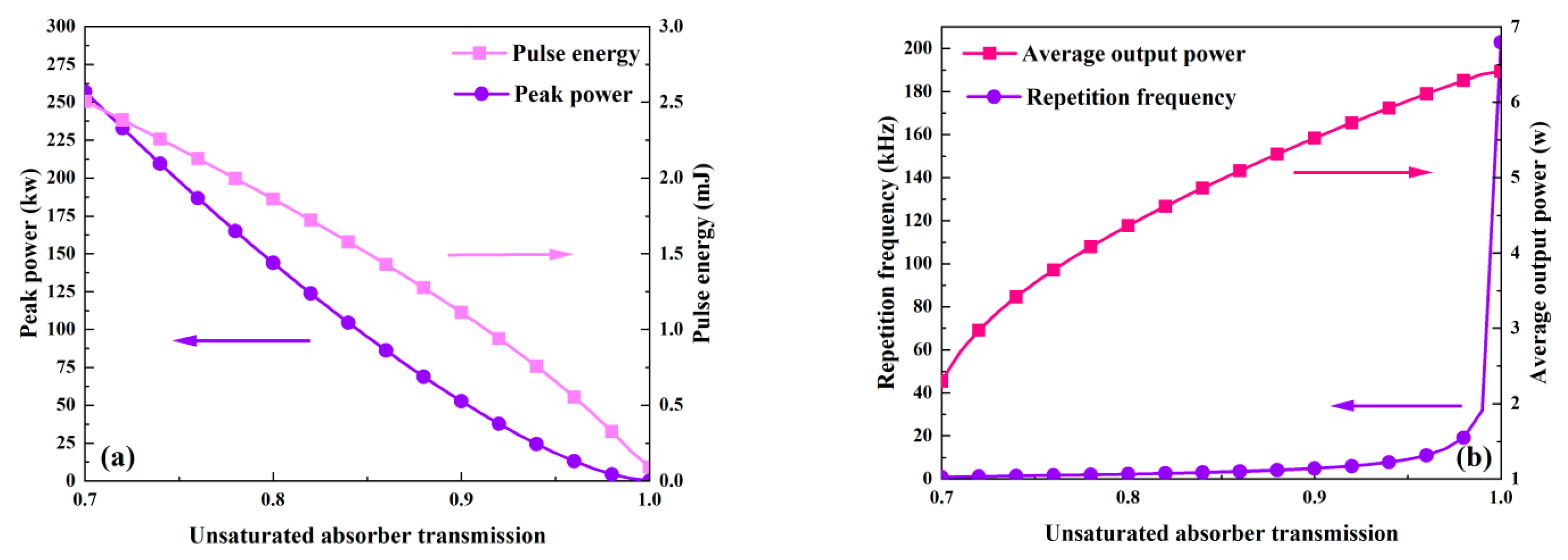
3.3. The Effect of Unsaturated Absorber Transmission on Laser Characteristics
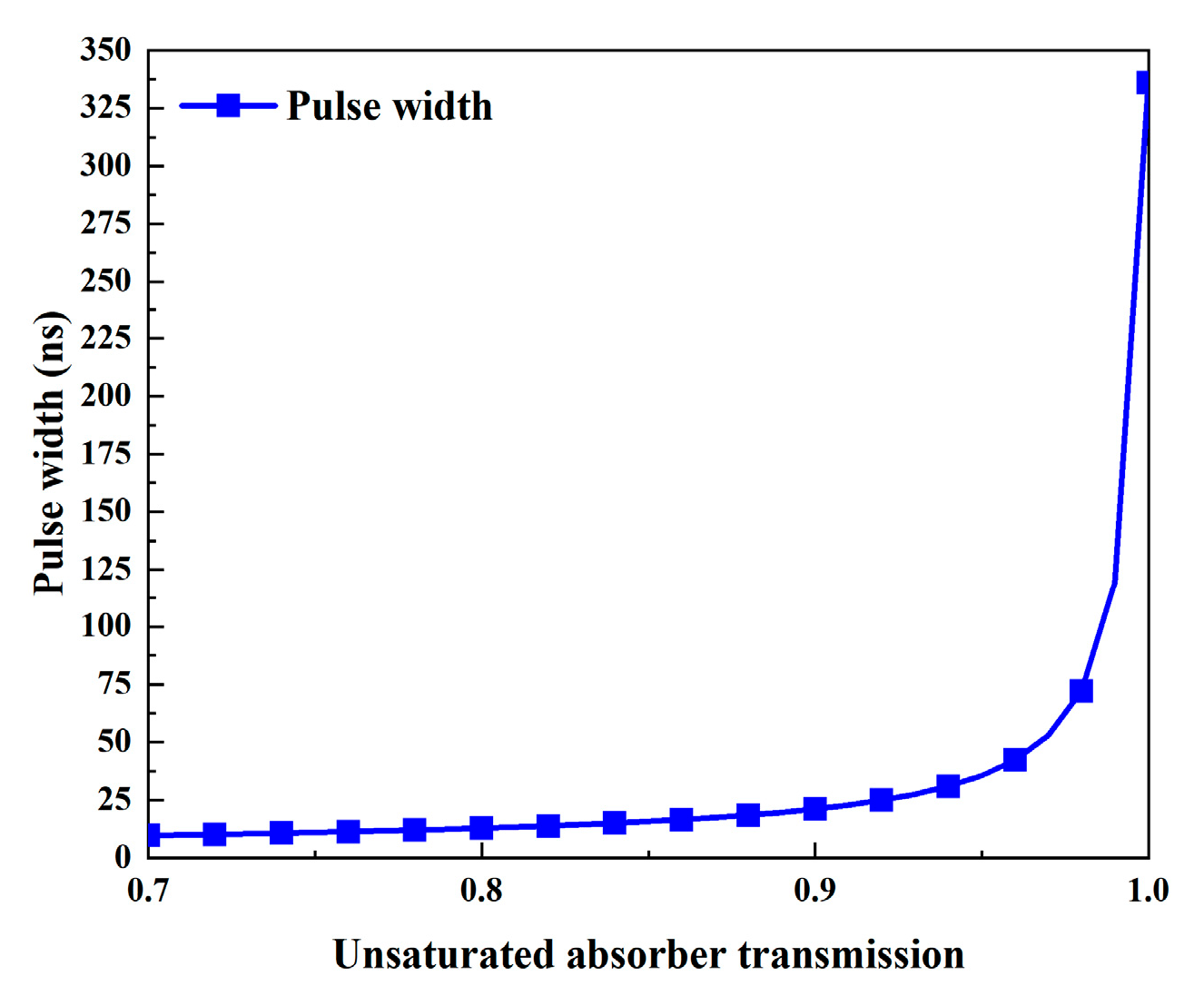
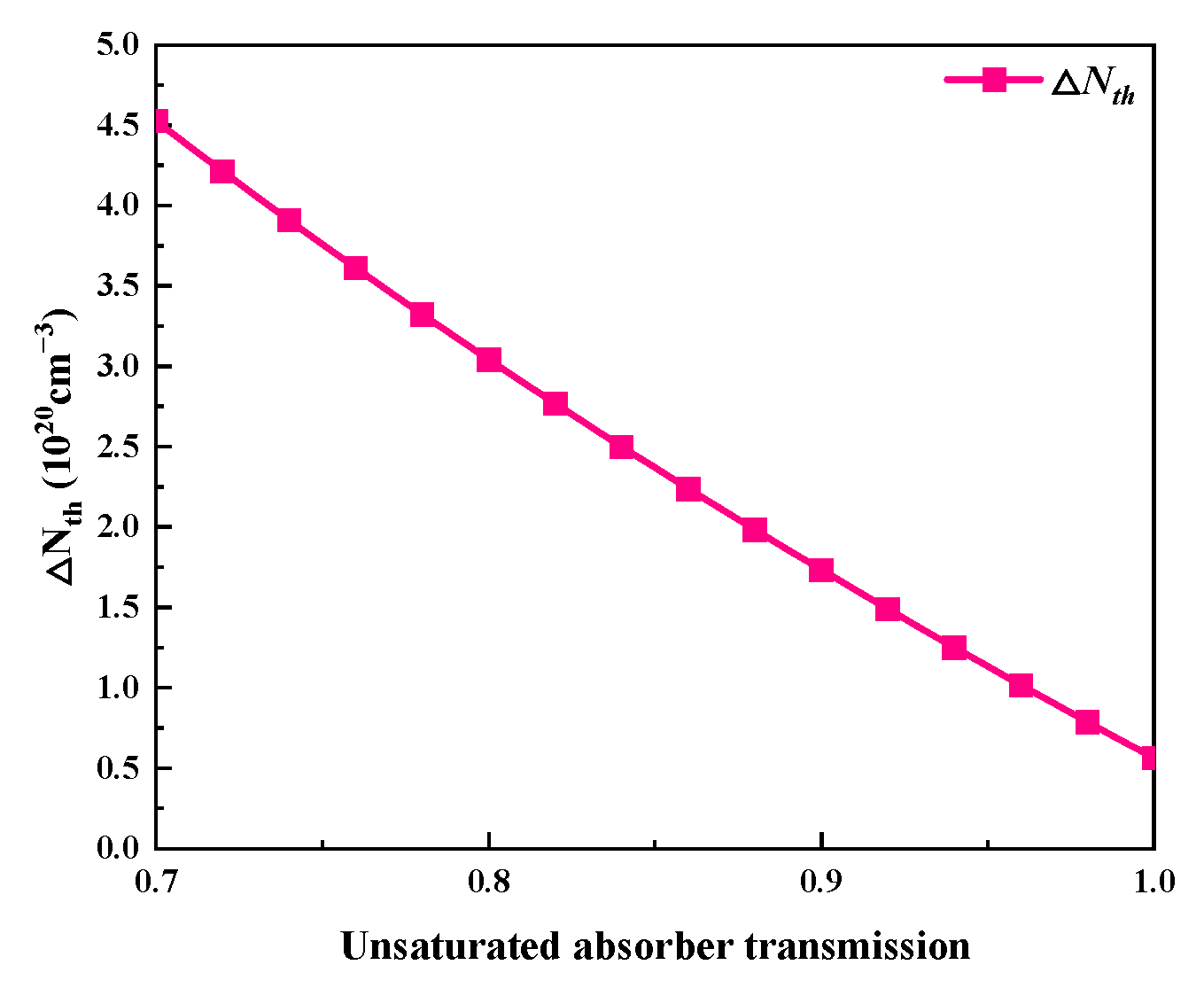
The influence of the unsaturable absorber transmission on the output characteristics is shown in Figure 10 and Figure 11. Here, the unsaturable absorber transmission varies in the range of 0.7~1, and Table 2 makes use of the other parameters’ values. Figure 10a and Figure 11 show that as the unsaturated absorber transmission increases, the pulse width gradually increases while the peak power and pulse energy monotonically decrease. This is because an increase in unsaturable absorber transmission leads to a reduction in the threshold population inversion density, as shown in Figure 12. Figure 10b illustrates that the average output power and repetition frequency increase in tandem with the unsaturable absorber transmission. The unsaturable absorber transmission has a major influence on the repetition frequency and pulse width, particularly in the area with a large unsaturable absorber transmission (around 1).
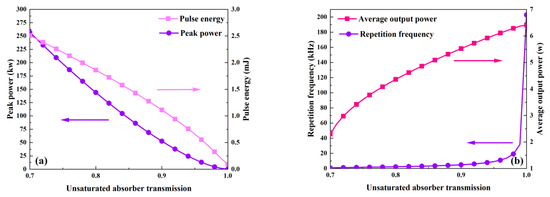
Figure 10.
The dependence of peak power, pulse energy (a), and repetition frequency and average output power (b) on unsaturable absorber transmission.
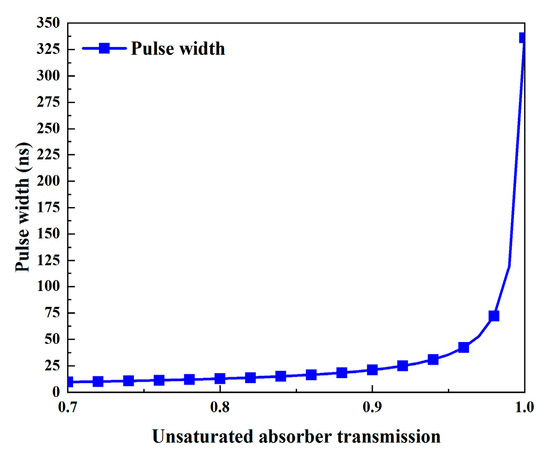
Figure 11.
Pulse width versus unsaturated absorber transmission.
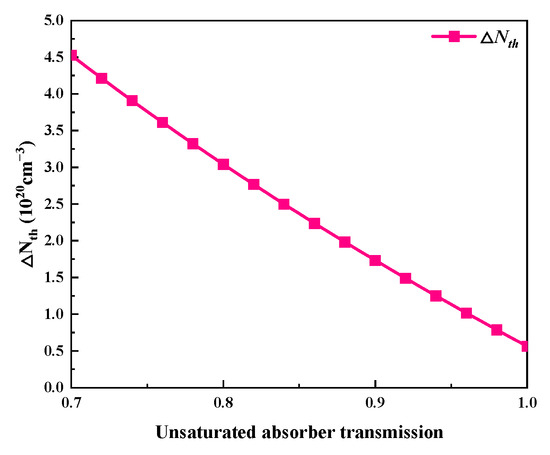
Figure 12.
Threshold population inversion density (ΔNth) versus unsaturated absorber transmission.
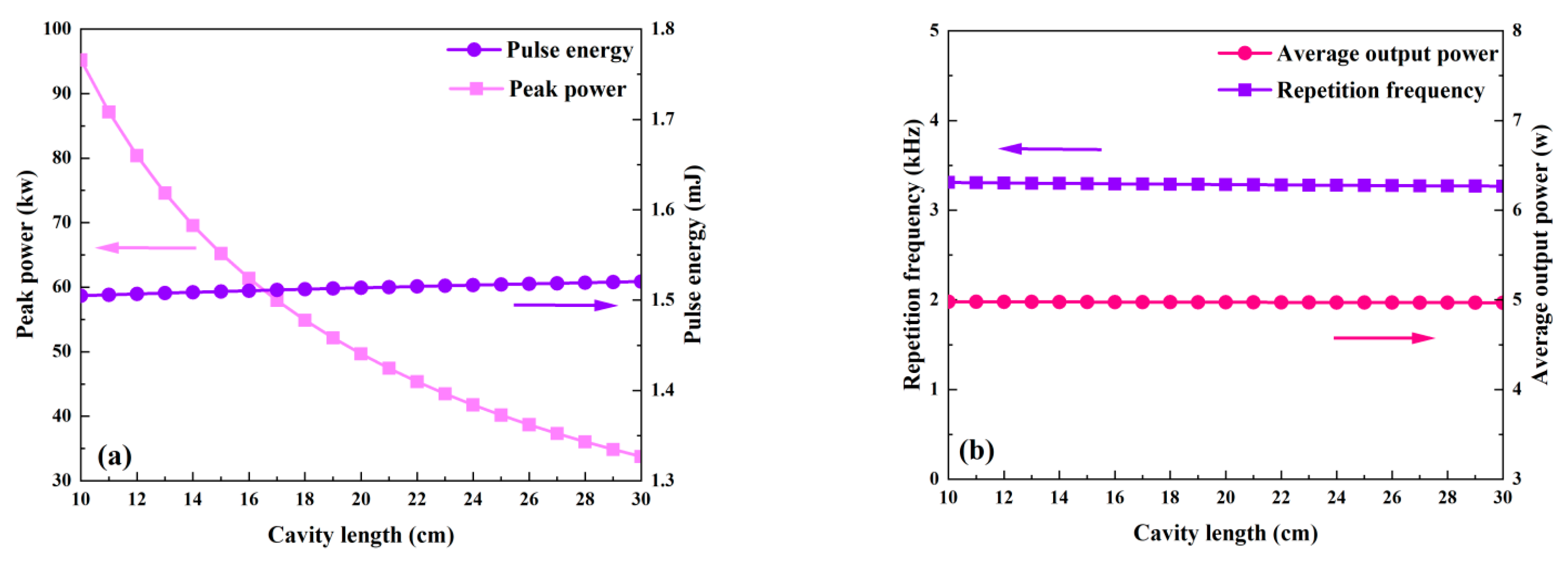
3.4. The Effect of Cavity Length on Laser Characteristics
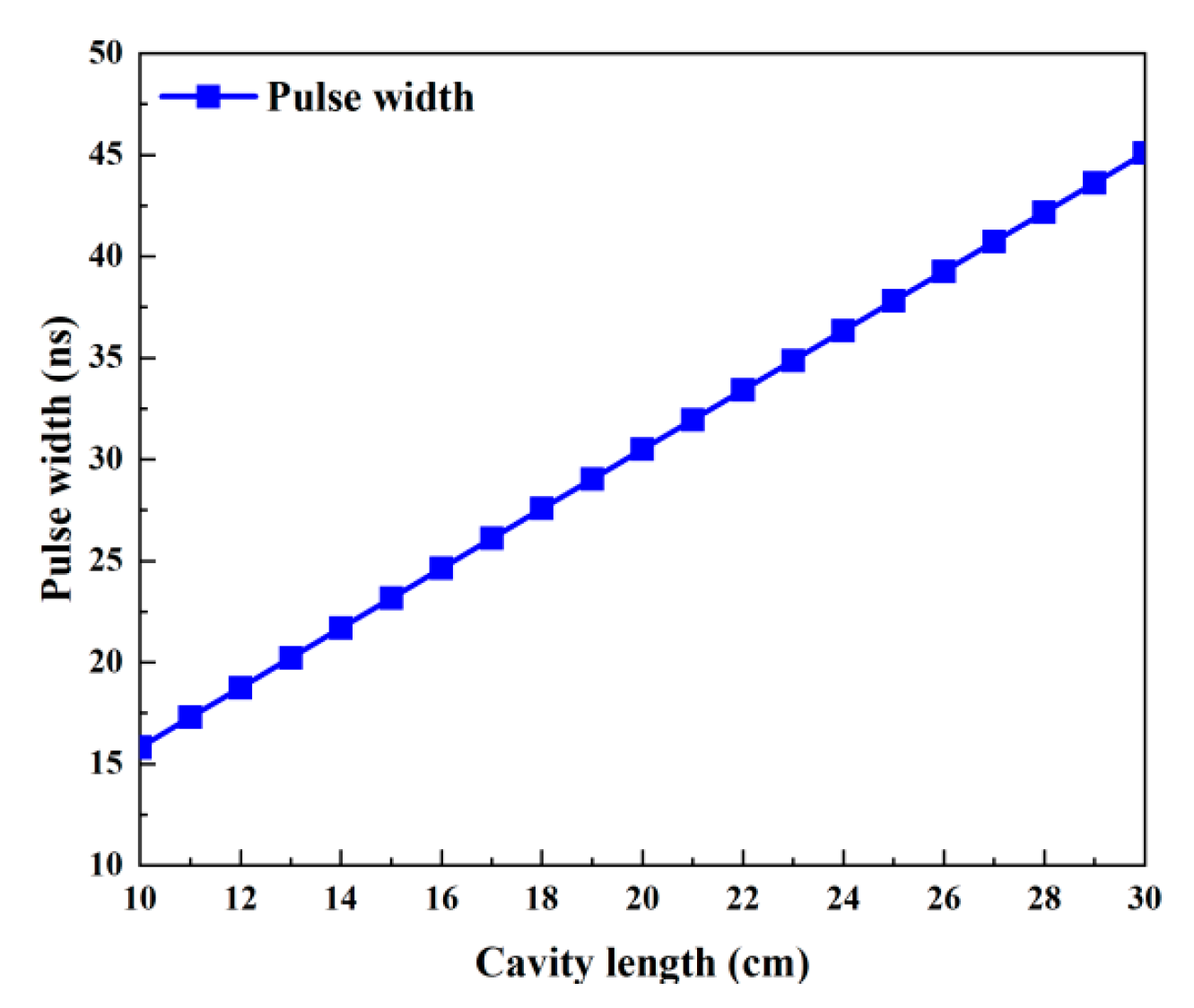
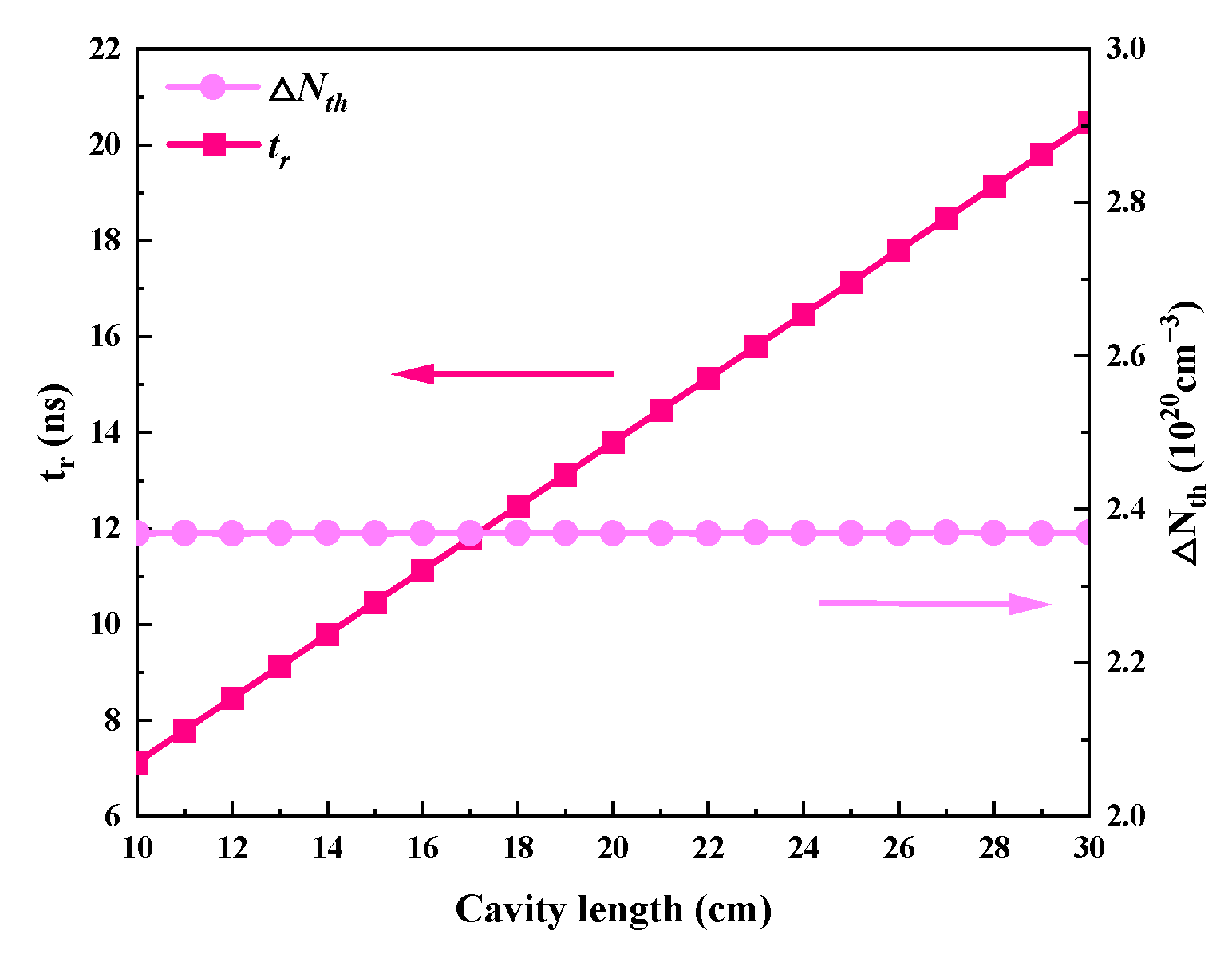
The effects of the cavity’s length, which ranges from 10 to 30 cm, on each of the passive Q-switched laser’s output parameters are shown in Figure 13 and Figure 14. The remaining values are used in Table 2. Because Figure 15 shows that the round-trip time (tr) grows with cavity length, the pulse width in Figure 14 also increases with cavity length. Except for peak power, which decreases as cavity length grows, Figure 13 illustrates that the average output power, repetition frequency, and pulse energy are all almost insensitive to cavity length. The peak power falls as the pulse width rises, but the pulse energy, repetition frequency, and average output power essentially remain constant because the threshold population inversion density is independent of the cavity length (Figure 15).
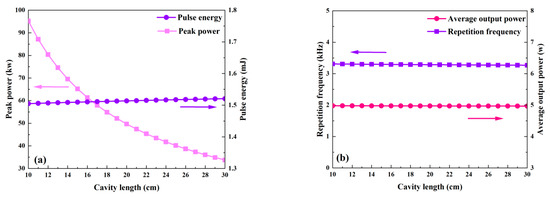
Figure 13.
The dependence of peak power, pulse energy (a), and repetition rate and average output power (b) on cavity length.
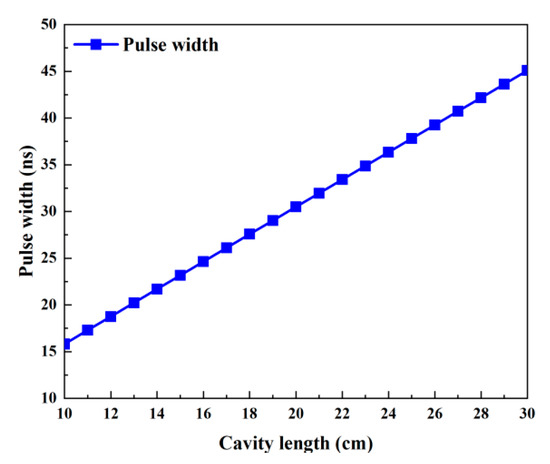
Figure 14.
Pulse width versus cavity length.
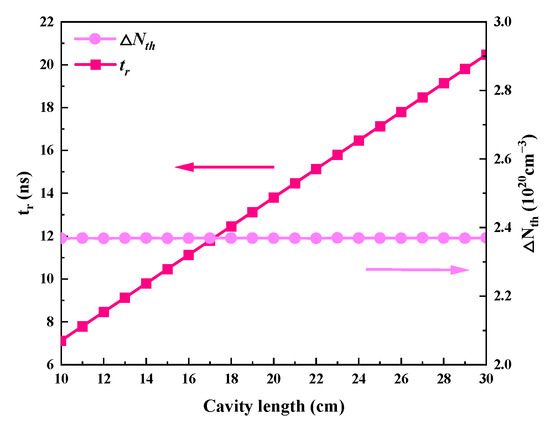
Figure 15.
The dependence of threshold population inversion density (ΔNth) and round-trip time (tr) on cavity length.
3.5. The Effect of the Length of Gain Medium on Laser Characteristics
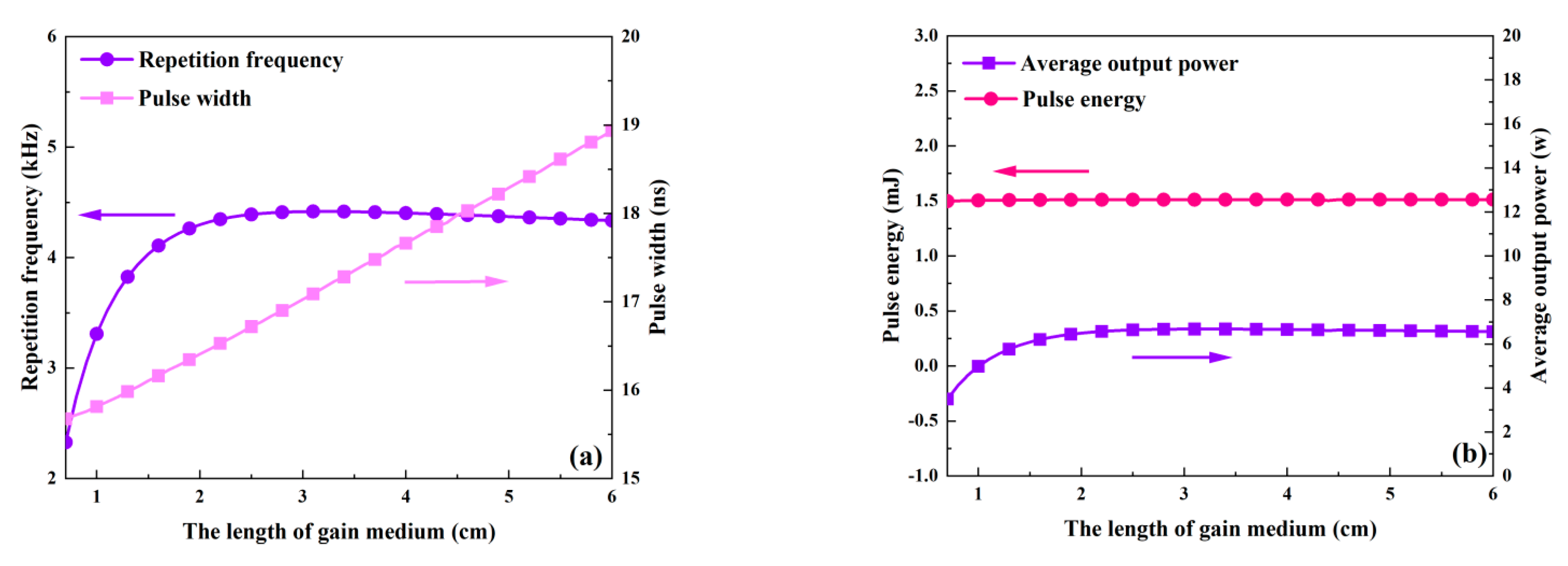
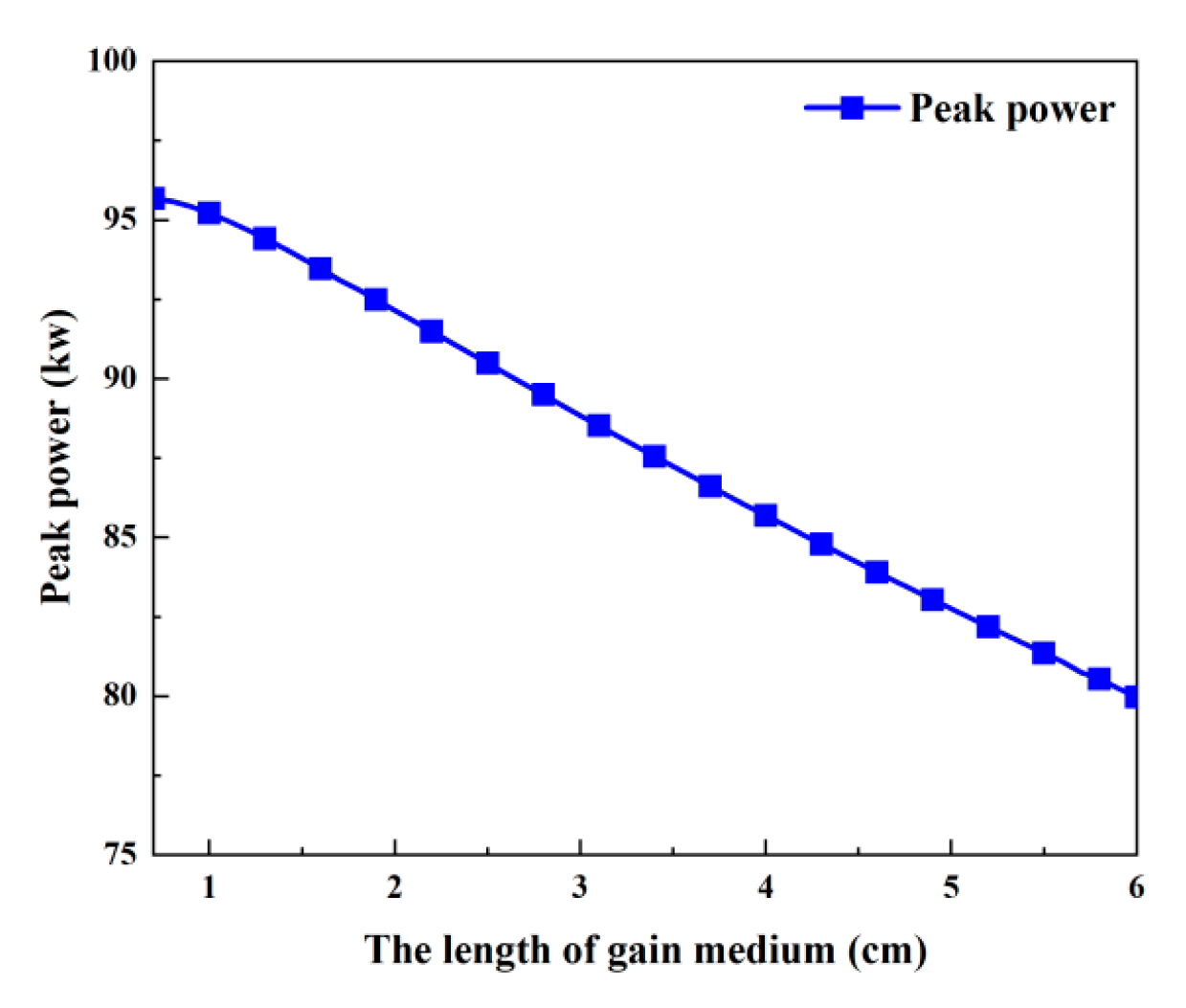
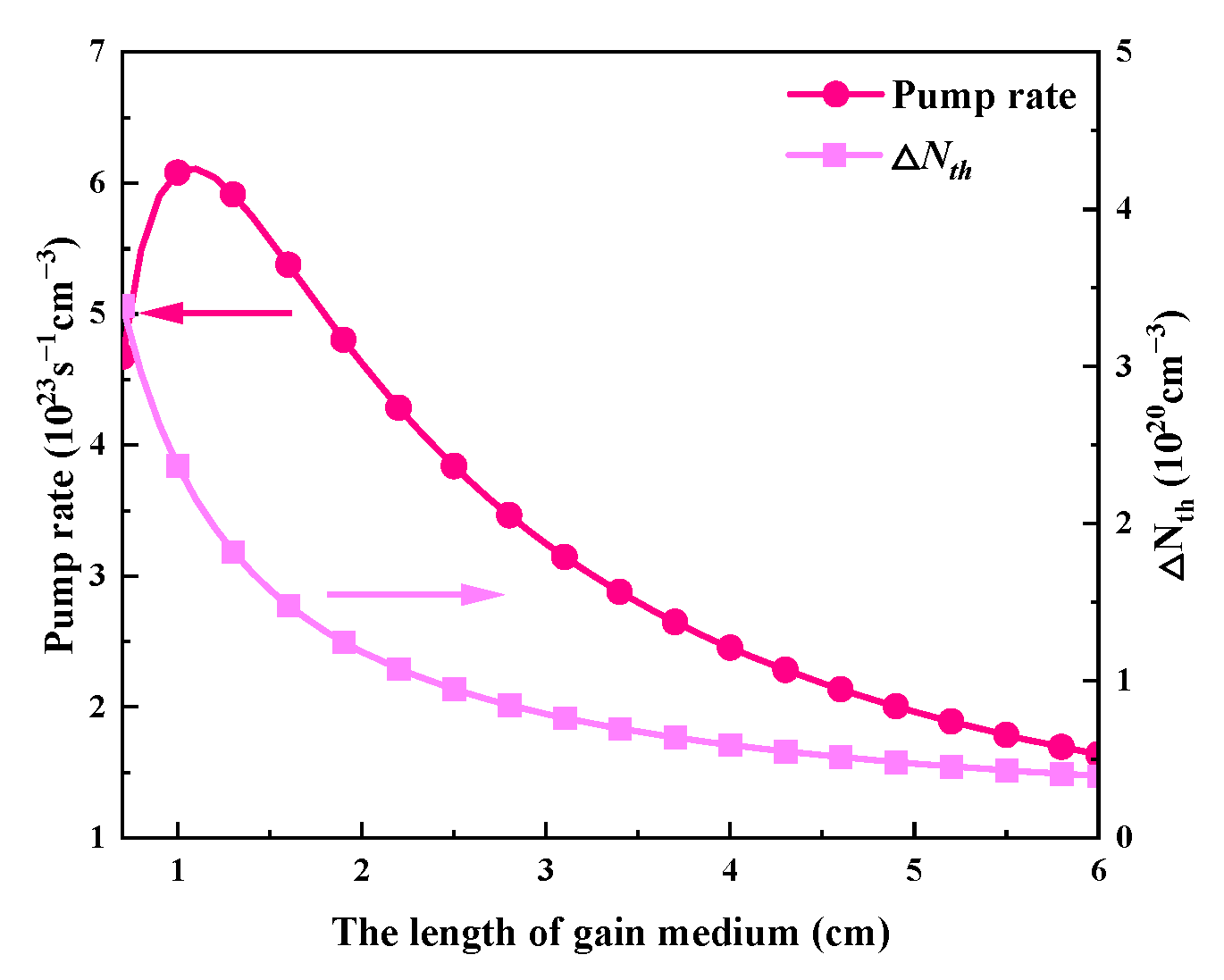
The effects of the gain medium’s length, which ranges from 0.7 to 6 cm, on each of the passive Q-switched laser’s output parameters are shown in Figure 16 and Figure 17. Table 2 uses the remaining values. The pulse width increases as the gain medium lengthens, as seen in Figure 16a, mainly because a longer gain medium results in a longer round-trip time. Both the threshold population inversion density and the pump rate have an impact on the repeat frequency. As the gain medium’s length grows, the pump rate first shows a slight increase and then gradually decreases, while the threshold population inversion density first drops rapidly and then slows down, as seen in Figure 18. According to Figure 16a, these factors cause the repetition frequency to climb quickly initially before tending to remain constant as the gain medium’s length increases. As illustrated in Figure 16b, the average output power will follow a similar trend to the repetition frequency since the pulse energy stays almost constant. But as the length of the gain medium rises, the peak power monotonically decreases, as shown in Figure 17.
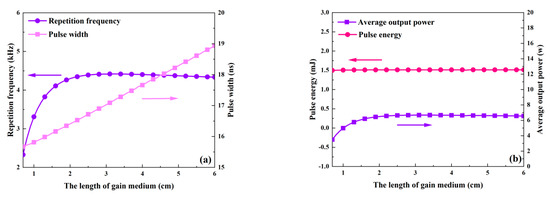
Figure 16.
The dependence of repetition frequency, pulse width (a), and pulse energy and average output power (b) on the length of the gain medium.
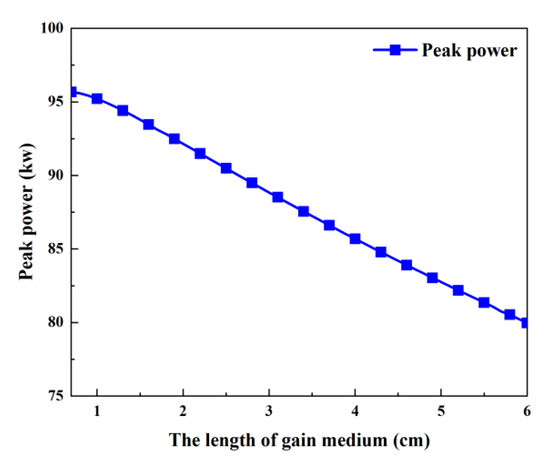
Figure 17.
Peak power versus the length of the gain medium.
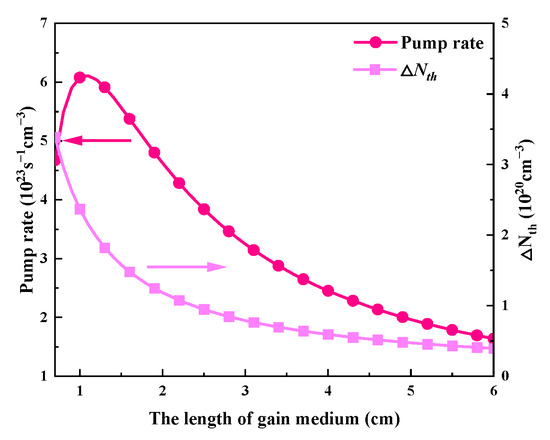
Figure 18.
The dependence of pump rate and threshold population inversion density (ΔNth) on the length of the gain medium.
4. Conclusions
This work establishes a model of a PQS Tm:CaF2 laser using bulk material doped with Cr2+ as a SA. The theory can be used to simulate the pulsed laser manufacturing process and derive the evolution of photon density, effective population inversion density, and total round-trip loss with time. Furthermore, this model is used to thoroughly examine how the laser parameters affect the output characteristics. The study found that it is easier to create high-energy, short-pulse lasers by reducing the reflectivity of the output coupler and the transmission of unsaturated absorbers. It is advantageous to shorten the cavity length to produce a laser with a small pulse width and high peak power. By raising the pump power, a high average power laser with a high repetition frequency can be achieved. The short length gain medium makes it easier to achieve the low repetition frequency, small pulse width, and high peak power of the pulse laser. There is also an optimal output coupler reflectivity for the average output power and optical-to-optical conversion efficiency. This model can help in the design and optimization of other types of thulium-doped SSLs (3F4 → 3H6) which are Q-switched by Cr2+-doped saturable absorbers.
Author Contributions
Writing—original draft, writing—review and editing, data curation, and methodology, M.Y.; investigation and methodology, Z.W.; writing—original draft, methodology, supervision, and funding acquisition, J.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 62205102).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Hałasiński, P.; Lubarska, M.; Lubarski, K.; Jałowska, M. Lasers’ Q-switched treatment in skin and subcutaneous lesions–review. Adv. Dermatol. Allergol. 2023, 40, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Jiang, S.; Yin, X.; Guo, J.; Zhu, X.; Ma, H.; Zhang, G.; Yu, H.; Xiao, Y.; Yang, Y. Long-term effect of transurethral partial cystectomy with a 2-micrometer continuous-wave laser for non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Front. Surg. 2023, 10, 1117997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Jin, P.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, L.; Shen, T. Infrared Image Enhancement: A Review. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2024, 18, 3281–3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shangguan, M.; Liao, Z.; Guo, Y.; Lee, Z. Seabed backscattered signal peak shift and broadening induced by multiple scattering in bathymetric lidar. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2025, 63, 5701214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; He, G.; Yan, F.; Wang, W.; Zhuang, Y. Spatial and Temporal Calibration of Self-Built Panoramic LiDAR in Targetless Environments. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2025, 74, 8504404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Li, J.; Wu, Z.; Li, S.; Han, H.; Li, L. Passively Q-switched operation of a 1.94 µm thulium-doped solid-state laser based on MXene V2CTx. Chin. Opt. Lett. 2023, 21, 021402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebbag, D.; Korenfeld, A.; Ben-Ami, U.; Elooz, D.; Shalom, E.; Noach, S. Diode end-pumped passively Q-switched Tm:YAP laser with 1.85-mJ pulse energy. Opt. Lett. 2015, 40, 1250–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Xu, C.; Wei, Y.; Li, S.; Liu, G.; Li, W.; Fan, D. Continuous-wave and broadly tunable Cr:ZnSe laser pumped by a short wavelength Tm:YLF bulk laser. Chin. Opt. Lett. 2024, 22, 101404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Lu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, H.; Li, Z.; Zhang, P.; Chen, Z. The passive Q-switched and Q-switched mode-locked Nd: GYAP laser based on a novel Bi2O3 saturable absorber. Opt. Laser Technol. 2024, 174, 110620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Yao, B.; Dai, T.; Gao, Y.; Yu, J.; Sun, J. High peak power, high-repetition rate passively Q-switching of a holmium ceramic laser. Laser Phys. 2020, 30, 035004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, W.; Xu, H.; Yang, J.; Qiu, X.; He, T.; An, P.; Bi, C.; Yuan, S.; Wang, M.; Tian, X.; et al. 1.4 W Passively Q-Switched Mode-Locked Tm:CALGO Laser with a MoS2 Saturable Absorber. Photonics 2024, 11, 997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Li, N.; Wu, H.; Liu, H.; Deng, J.; Weng, W.; Li, J.; Lin, W. Obtaining constant sub-25 ns pulse in a Q-switched Tm laser with around 100 kHz repetition frequency. Opt. Laser Technol. 2024, 172, 110478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirov, S.B.; Moskalev, I.S.; Vasilyev, S.; Smolski, V.; Fedorov, V.V.; Martyshkin, D.; Peppers, J.; Mirov, M.; Dergachev, A.; Gapontsev, V. Frontiers of mid-IR lasers based on transition metal doped chalcogenides. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2018, 24, 1601829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirov, S.B.; Fedorov, V.V.; Martyshkin, D.; Moskalev, I.S.; Mirov, M.; Vasilyev, S. Progress in mid-IR lasers based on Cr and Fe-doped II–VI chalcogenides. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 21, 292–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Guo, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, C.; Liu, J.; Su, L. High-efficiency 2 μm continuous-wave laser in laser diode-pumped Tm3+, La3+:CaF2 single crystal. Opt. Lett. 2018, 43, 4300–4303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Jiang, D.; Zhen, Z.; Ma, F.; Zhang, Z.; Su, L. Effect of Tm3+ concentration on structure, spectral properties and cross relaxation of Tm:CaF2 crystal. Opt. Express 2025, 33, 1690–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyapin, A.A.; Fedorov, P.P.; Garibin, E.A.; Malov, A.V.; Osiko, V.V.; Ryabochkina, P.A.; Ushakov, S.N. Spectroscopic, luminescent and laser properties of nanostructured CaF2:Tm materials. Opt. Mater. 2013, 35, 1859–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, C.; Zu, Y.; Fan, X.; Liu, J.; Guo, X.; Qian, X.; Su, L. Efficient continuous-wave, broadly tunable and passive Q-switching lasers based on a Tm3+:CaF2 crystal. Laser Phys. Lett. 2018, 15, 045803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Fan, X.; Liu, J.; Su, L. 1886-nm mode-locked and wavelength tunable Tm-doped CaF2 lasers. Opt. Lett. 2018, 44, 134–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thouroude, R.; Tyazhev, A.; Hideur, A.; Loiko, P.; Camy, P.; Doualan, J.L.; Gilles, H.; Laroche, M. Widely tunable in-band-pumped Tm:CaF2 laser. Opt. Lett. 2020, 45, 4511–4514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, J.; Fan, X.; Peng, Q.; Guo, X.; Jiang, D.; Qian, X.; Su, L. Compact passive Q-switching of a diode-pumped Tm, Y:CaF2 laser near 2 μm. Opt. Laser Technol. 2018, 103, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, F.; Chen, K.; Guo, X.; Liu, J.; Su, L.; Zhang, H. Cu12Sb4S13 nanocrystals as absorbers for a diode-pumped Tm, La:CaF2 2 μm Q-switched laser. Opt. Commun. 2020, 462, 125281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Q.; Liu, W.; Zu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Su, L. Highly efficient dual-wavelength acousto-optically Q-switched Tm, La: CaF2 laser. Chin. Opt. Lett. 2022, 20, 111402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zu, Y.; Guo, X.; Liu, J.; Liu, J.; Su, L. Passively Q-switched operation of a novel Tm3+, La3+ co-doped CaF2 single crystal near 2 µm. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2019, 102, 103010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Qiao, Z.; Xie, G.; Qin, Z.; Zhao, B.; Yu, H.; Su, L.; Ma, J.; Yuan, P.; Qian, L. Spectroscopic characteristics, continuous-wave and mode-locking laser performances of Tm, Y:CaF2 disordered crystal. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 21267–21274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rustad, G.; Stenersen, K. Modeling of laser-pumped Tm and Ho lasers accounting for upconversion and ground-state depletion. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 1996, 32, 1645–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiter, J.; Körner, J.; Pejchal, J.; Yoshikawa, A.; Hein, J.; Kaluza, M.C. Temperature dependent absorption and emission spectra of Tm:CaF2. Opt. Mater. Express 2020, 10, 2142–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strickland, N.M.; Jones, G.D. Site-selective spectroscopy of Tm3+ centers in CaF2:Tm3+. Phys. Rev. B 1997, 56, 10916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J. Numerical modeling of CW-pumped repetitively passively Q-switched Yb:YAG lasers with Cr:YAG as saturable absorber. Opt. Commun. 2003, 226, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degnan, J.J. Theory of the optimally coupled Q-switched laser. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 1989, 25, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Zhao, B.; Ma, W.; Yu, H.; Qian, X.; Kong, L.; Wang, J.; Xie, G.; Wu, A.; Zeng, F.; et al. Optical Spectra Properties and Continuous-Wave Laser Performance of Tm, Y:CaF2 Single Crystals. Int. J. Opt. 2018, 2018, 8592359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).