Performance of Microbially Induced Carbonate Precipitation for Reinforcing Cohesive Soil in the Reservoir Area
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
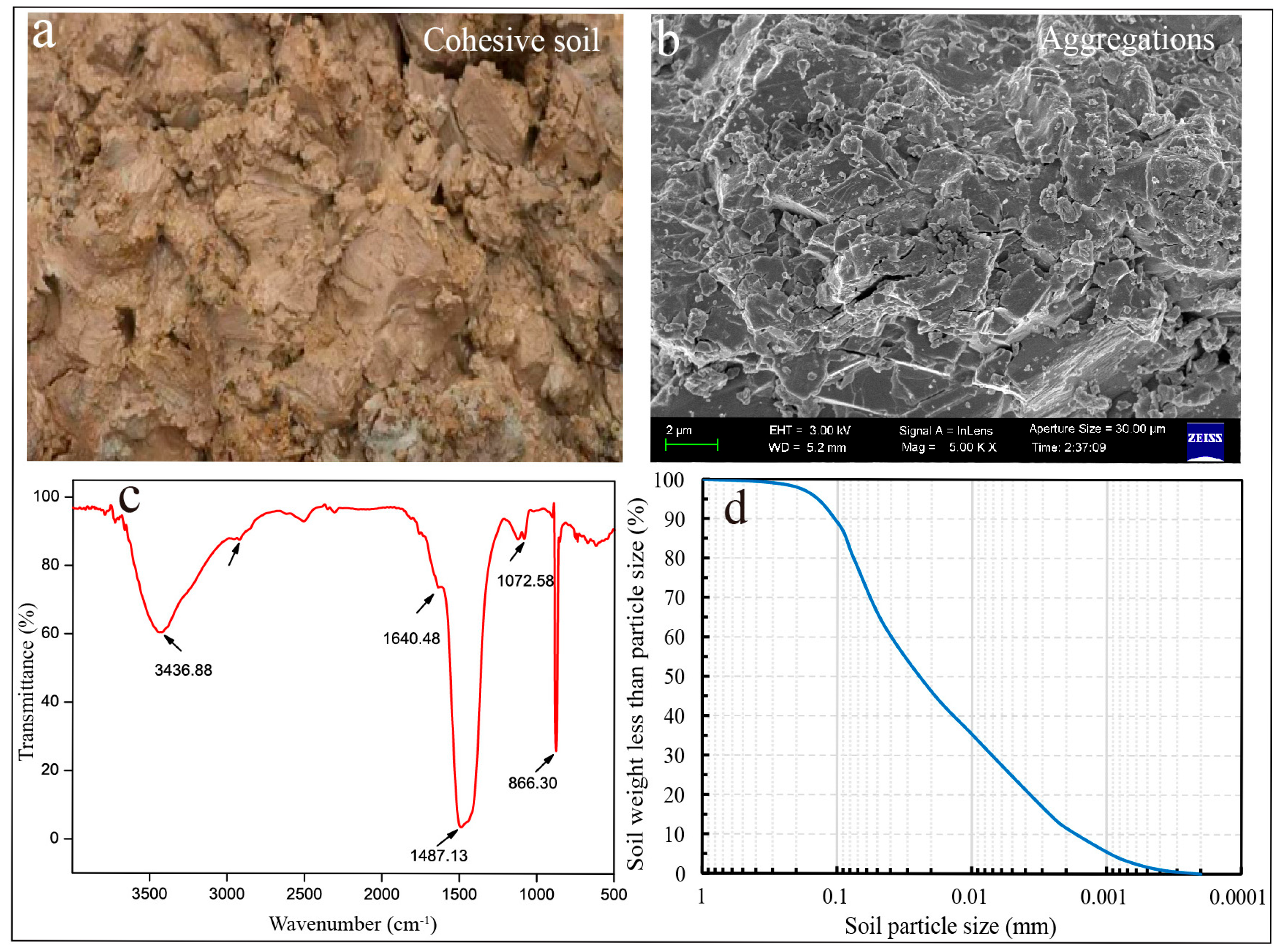
2.1. Source and Characterization of Cohesive Soil
2.2. Bacterial Solution (BS) and Cementing Solution (CS)
2.3. Process of MICP
2.4. Characteristics of Calcium Carbonate
2.5. Mechanical Tests
2.6. Thermal Analysis
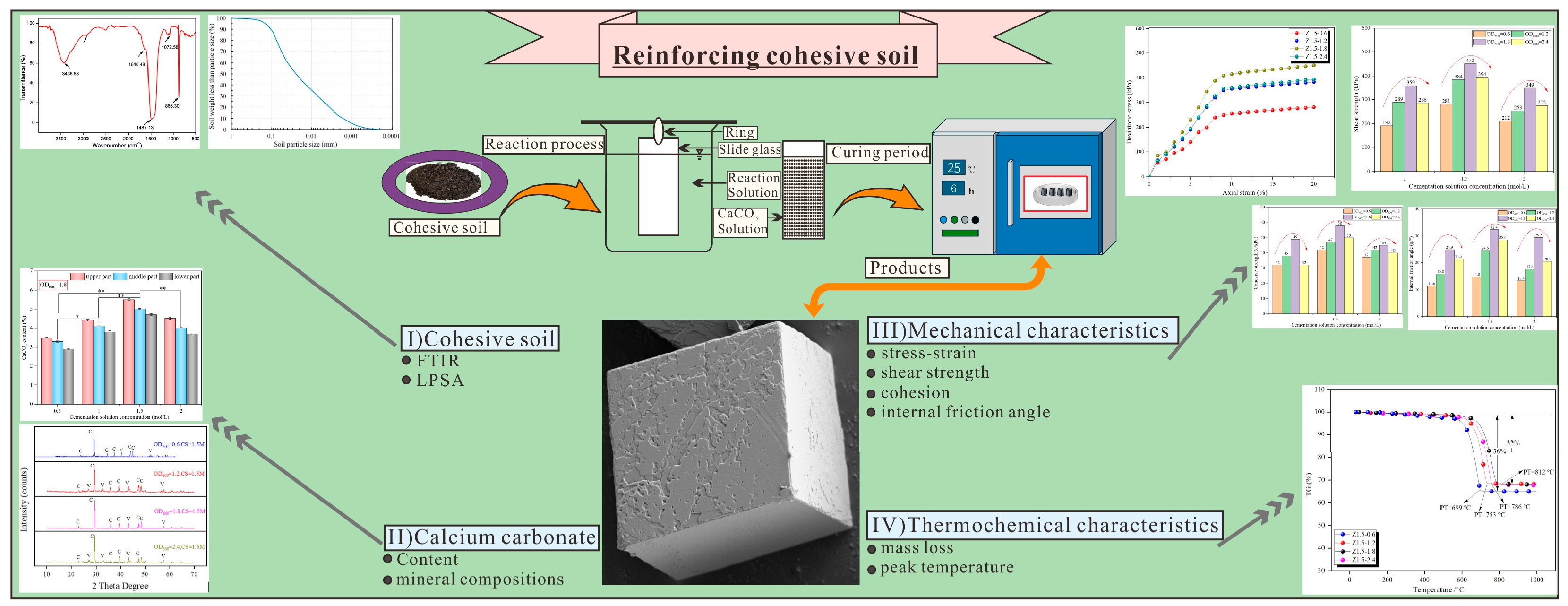
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of Cohesive Soil
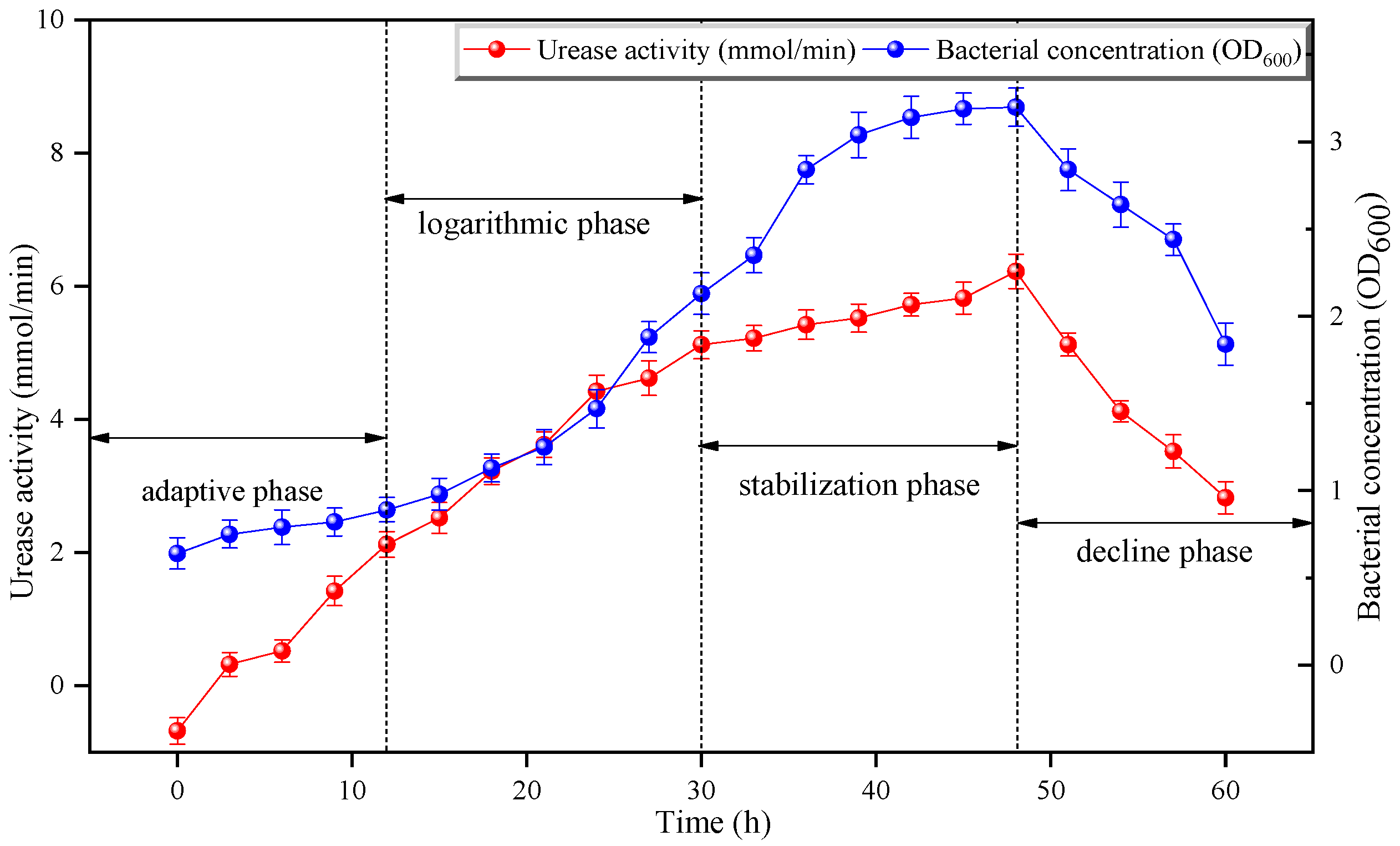
3.2. Bacterial Concentration and Urease Activity of Bacteria
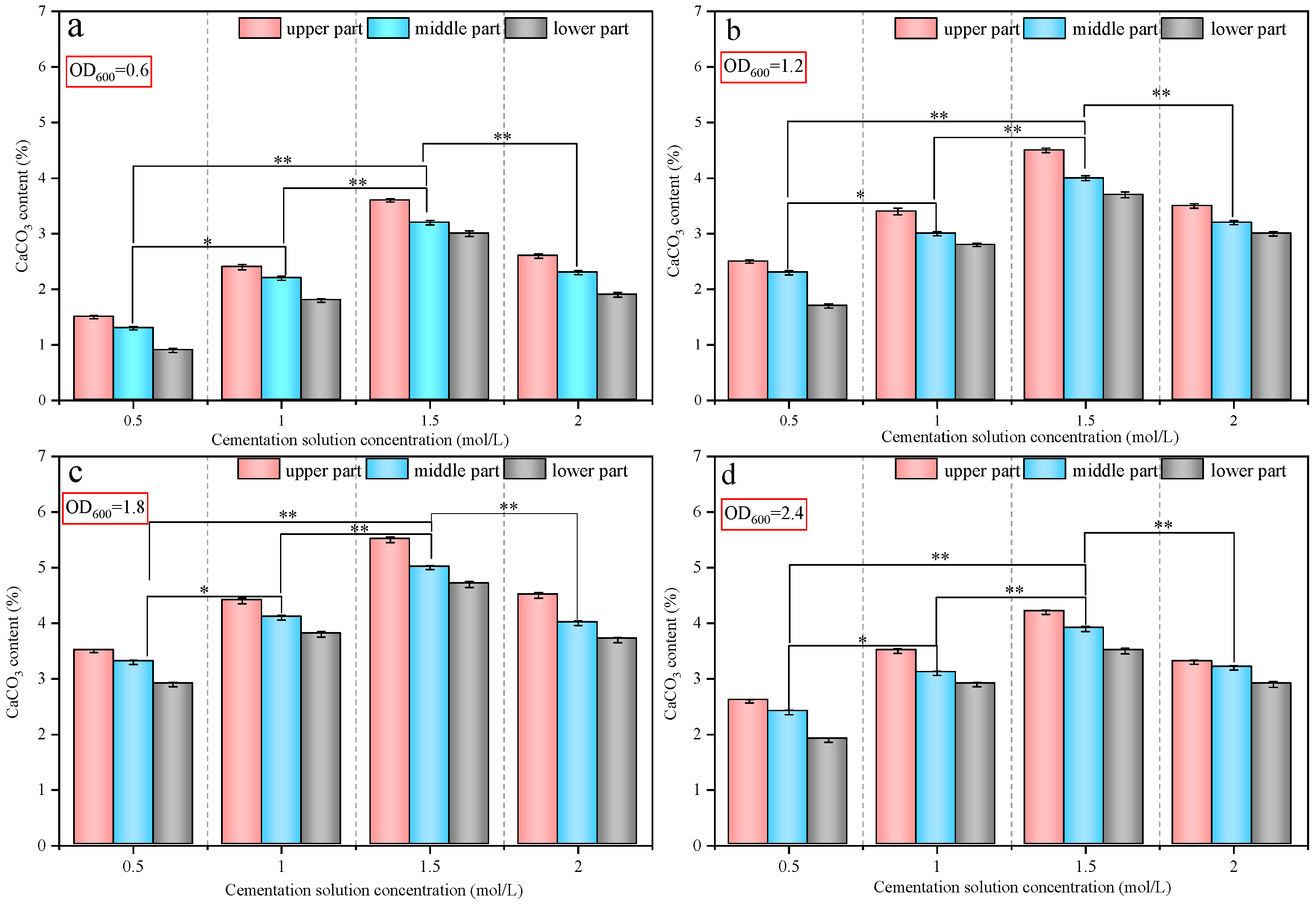
3.3. Calcium Carbonate Content
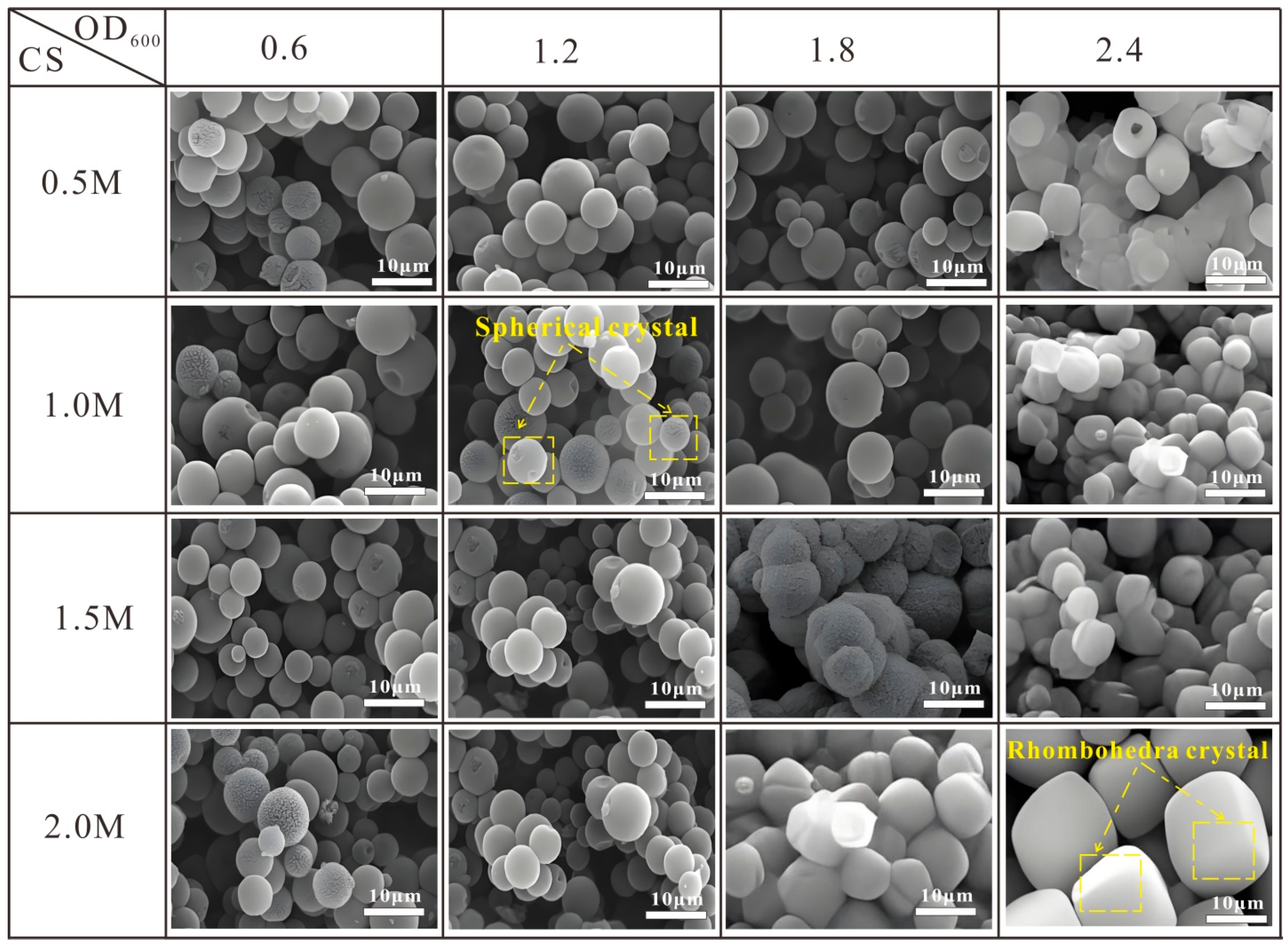
3.4. Morphological Characteristics at Different CS and BS Concentrations
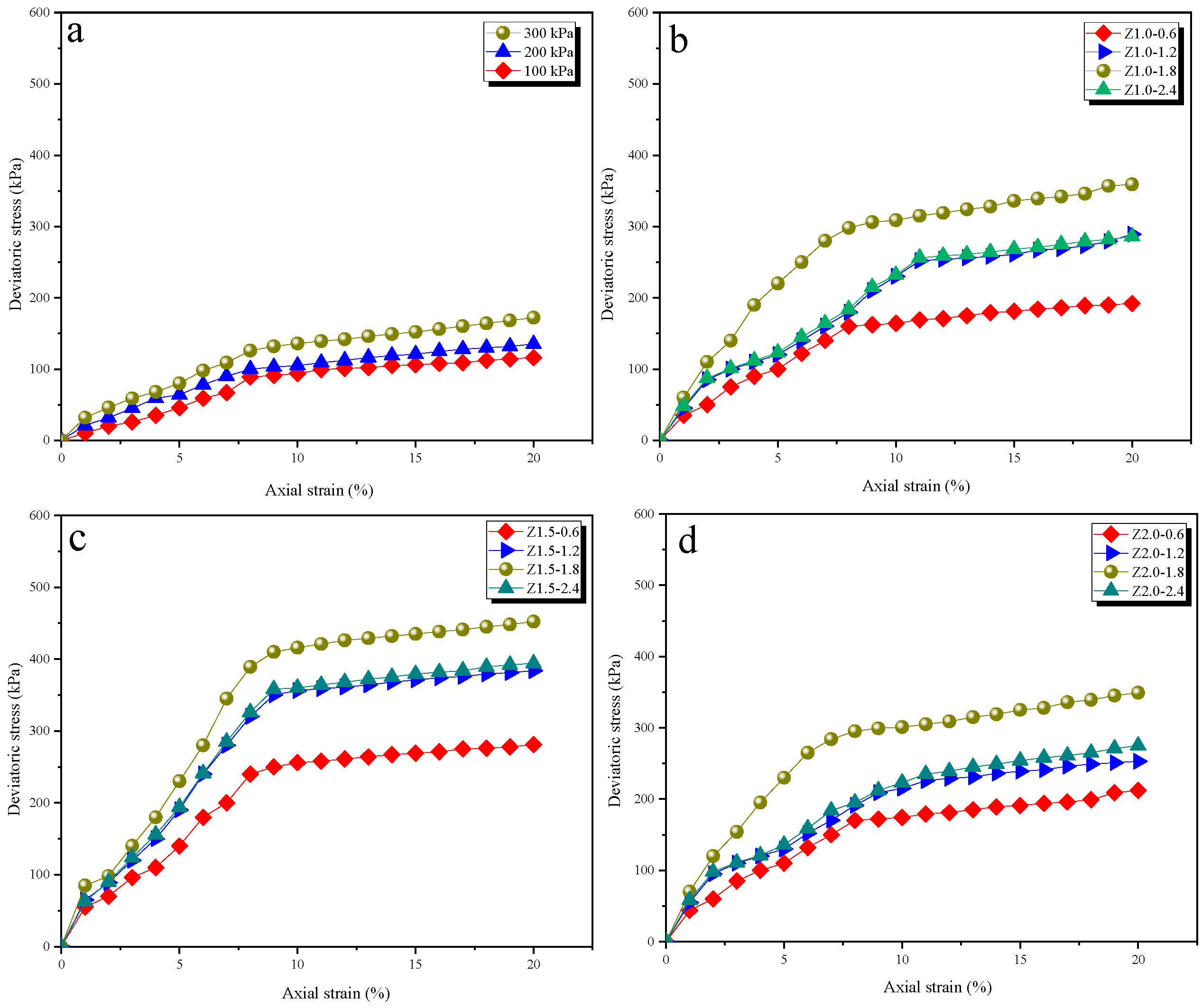
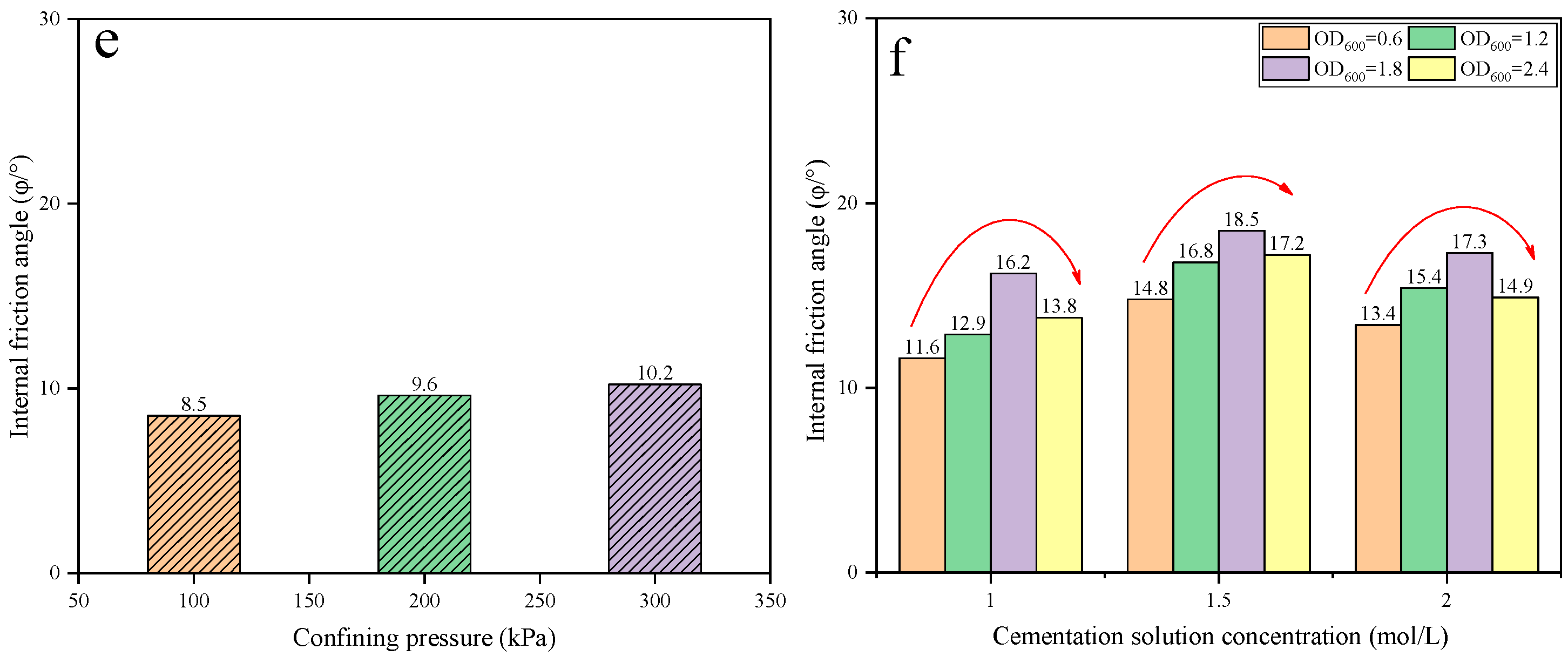
3.5. Mechanical Characteristics
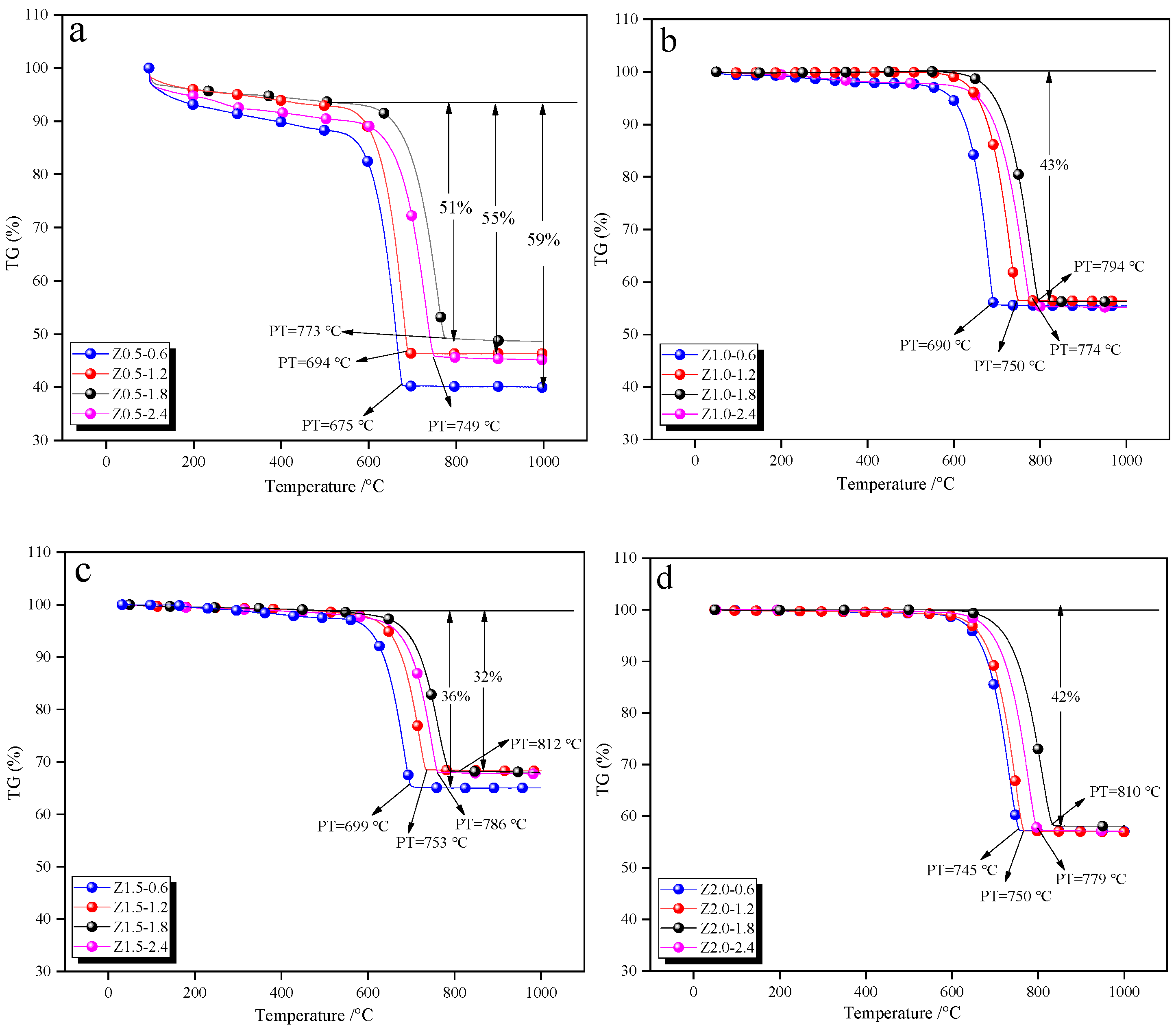
3.6. Thermal Stability Characteristics
4. Discussion
4.1. Comprehensive Evaluation of MICP
4.2. Practical Applications and Future Research Prospects
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.; Wang, G.; Wan, Y.; Yu, X.; Zhao, J.; Shao, J. Recycling of dredged river silt reinforced by an eco-friendly technology as microbial induced calcium carbonate precipitation (MICP). Soils Found. 2022, 62, 101216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouladi, A.S.; Arulrajah, A.; Chu, J.; Horpibulsuk, S. Application of Microbially Induced Calcite Precipitation (MICP) technology in construction materials: A comprehensive review of waste stream contributions. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 388, 131546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, D.; Wang, R.J.; Chen, S.; Li, X. The geochemical and thermodynamic characteristics of waste sand reinforced by microbially induced calcium carbonate precipitation. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2024, 36, 103828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Ju, T.; Meng, Y.; Han, S.; Lin, L.; Jiang, J. A review on the applications of microbially induced calcium carbonate precipitation in solid waste treatment and soil remediation. Chemosphere 2022, 290, 133229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Tang, C.-S.; Jiang, N.-J.; Pan, X.-H.; Liu, B.; Wang, Y.-J.; Shi, B. Microbial induced carbonate precipitation (MICP) technology: A review on the fundamentals and engineering applications. Environ. Earth Sci. 2023, 82, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidanemariam, T.G.; Gebru, K.A.; Kidane Gebretinsae, H. A mini review of enzyme-induced calcite precipitation (EICP) technique for eco-friendly bio-cement production. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 16206–16215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Miao, L.; Tong, T.; Wang, C. Study of the effect of temperature on microbially induced carbonate precipitation. Acta Geotech. 2019, 14, 627–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Yi, J.; Liu, Q.; Cao, A.; Wei, A.; Zhang, K. A self-dissolved grouting reinforcement method for water-rich soft rock roadway. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2022, 81, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Dai, Q.; Lin, X.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, B.; Pan, X.; Peng, Y.; Zhao, G.; Ru, Y.; Zhou, L. Enhancing fiber–matrix interface permeability resistance of natural fiber-reinforced, bio-cemented sand by CaCO3 seed pretreatment. Geomech. Energy Environ. 2023, 35, 100481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Cao, C.; Wu, S. Hydraulic-mechanical properties of loess and its behavior when subjected to infiltration-induced wetting. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2018, 77, 385–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, C.; Lu, X.; Zhu, D.; Liu, L.; Sun, Y.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, W.; Wei, Q. Soil improvement by microbially induced calcite precipitation (MICP): A review about mineralization mechanism, factors, and soil properties. Arab. J. Geosci. 2022, 15, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasekar, A.; Wilkinson, S.; Moy, C.K.S. MICP as a potential sustainable technique to treat or entrap contaminants in the natural environment: A review. Environ. Sci. Ecotechnol. 2021, 6, 100096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Cao, L.; Yang, C. The large deformation mechanism of sewage-treatment plant slope in the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmey, A.H.M.; Aboseidah, A.A.; Gaber, S.; Mahran, F. Characterization and optimization of lipase activity produced by Pseudomonas monteilli 2403-KY120354 isolated from ground beef. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2017, 16, 96–105. [Google Scholar]
- Laity, P.R.; Asare-Addo, K.; Sweeney, F.; Šupuk, E.; Conway, B.R. Using small-angle X-ray scattering to investigate the compaction behaviour of a granulated clay. Appl. Clay Sci. 2015, 108, 149–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dweck, J.; Buchler, P.M.; Coelho, A.C.V.; Cartledge, F.K. Hydration of a Portland cement blended with calcium carbonate. Thermochim. Acta 2000, 346, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, N.; Cong, Z.H.; Sun, X.; Cheng, S.; Nie, Z.H.; Ren, Y.; Liaw, P.K.; Wang, Y.D. An in situ high-energy X-ray diffraction study of micromechanical behavior of multiple phases in advanced high-strength steels. Acta Mater. 2009, 57, 3965–3977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, R.K. Study on shear strength of soil in relation to plant roots as a combind matrix. Int. J. Appl. Sci. Eng. 2013, 1, 103–130. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, W.; Alshameri, B.; Nawaz, M.N.; Qamar, S.U. Experimental study on shear strength behavior and numerical study on geosynthetic-reinforced cohesive soil slope. Innov. Infrastruct. Solut. 2022, 7, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, D.; Yang, F.; Xiang, Q.; Wei, Q.; Jiang, W.; Zhao, J.; Guo, Y. Differences in thermal decomposition and crystallinity of dark organic laminae and light mineral laminae in same stromatolite. Thermochim. Acta 2023, 728, 179576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buza, A.; Türkeş, C.; Arslan, M.; Demir, Y.; Dincer, B.; Nixha, A.R.; Beydemir, Ş. Discovery of novel benzenesulfonamides incorporating 1,2,3-triazole scaffold as carbonic anhydrase I, II, IX, and XII inhibitors. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 239, 124232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Z.; Wang, J.; Zou, R.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X. Hydrothermal synthesis of CeO2 nanoparticles on activated carbon with enhanced desulfurization activity. Energy Fuels 2012, 26, 5879–5886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wei, J.; Ma, C.; Yang, Z.; Li, Z.; Yang, X.; Wang, M.; Zhang, H.; Hu, J.; Zhang, C. Photosynthetic bacteria-based technology is a potential alternative to meet sustainable wastewater treatment requirement? Environ. Int. 2020, 137, 105417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeynali, Y.; Niroumand, H.; Moayed, R.Z. Stabilizing cohesive soils with Micro-and Nano-fly ash as Eco-friendly Materials: An experimental study. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 399, 132490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes, A.S.; Alencar, T.L.; Júnior, R.N.A.; Toma, R.S.; Romero, R.E.; Costa, M.C.G.; Cooper, M.; Mota, J.C.A. Functionality of the porous network of Bt horizons of soils with and without cohesive character. Geoderma 2018, 313, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Liu, J.; Tang, H.; Yan, Z. Study of Zr addition on the composition, crystallite size, microstructure and properties of high-performance nano Cu alloys prepared by mechanical alloying. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2022, 290, 126630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akl, A.A.; El Radaf, I.M.; Hassanien, A.S. Intensive comparative study using X-Ray diffraction for investigating microstructural parameters and crystal defects of the novel nanostructural ZnGa2S4 thin films. Superlattices Microstruct. 2020, 143, 106544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, D.; Yao, W.; Guo, Y.; Wu, C.; Cao, J.; Sun, B. Comparative study on geochemical and thermodynamic characteristics among wormkalk, micrite, thrombolite, and stromatolite. Carbonates Evaporites 2025, 40, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Chou, Y.; Peng, E.; Wang, Y. Solidification of sodium sulfate saline loess by biomineralization of reactive magnesium oxide binder. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 433, 136611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, D.; Yao, W.; Guo, Y.; Chen, Z.; Gui, H.; Zhao, Y. Bioremediation of Heavy Metal-Contaminated Solution and Aged Refuse by Microbially Induced Calcium Carbonate Precipitation: Further Insights into Sporosarcina pasteurii. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Xu, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, S. Disturbed state concept–based model for the uniaxial strain-softening behavior of fiber-reinforced soil. Int. J. Geomech. 2022, 22, 04022092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Chai, S.X.; Zhang, H.Y.; Shi, Q. Mechanical properties of soil reinforced with both lime and four kinds of fiber. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 172, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.-J.; Zheng, J.-J.; Chu, J.; Wu, C.-C.; Lai, H.-J. Bio-mediated calcium carbonate precipitation and its effect on the shear behaviour of calcareous sand. Acta Geotech. 2021, 16, 1377–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Wang, B.; Guo, J.; Guo, H.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Dai, Q. Experimental study on improving hydraulic characteristics of sand via microbially induced calcium carbonate precipitation. Geomech. Energy Environ. 2024, 37, 100519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Q.; Tannant, D.D.; Jing, H.W.; Nunoo, S.; Niu, S.J.; Wang, S.Y. Evolution of cohesion and friction angle during microfracture accumulation in rock. Nat. Hazards 2015, 77, 497–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, D.; Chen, Z.; Sun, B. Thermal Decomposition of Calcium Carbonate at Multiple Heating Rates in Different Atmospheres Using the Techniques of TG, DTG, and DSC. Crystals 2025, 15, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Cai, G.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Liu, K. Evaluation of engineering properties and environmental effect of recycled waste tire-sand/soil in geotechnical engineering: A compressive review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 126, 109831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavari, N.; Tang, A.M.; Pereira, J.-M.; Hassen, G. Effect of temperature on the shear strength of soils and the soil–structure interface. Can. Geotech. J. 2016, 53, 1186–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, L.K.; Sirdesai, N.N.; Sharma, K.M.; Singh, T. Experimental study to examine the independent roles of lime and cement on the stabilization of a mountain soil: A comparative study. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 152, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Shi, Y.; Yu, X.; Xu, H.; Zheng, G.; Yang, S.; He, Y. Failure mechanism and bearing capacity of rigid footings placed on top of cohesive soil slopes in spatially random soil. Int. J. Geomech. 2023, 23, 04023110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Xiao, H.; Li, Z.; Li, Z.; Su, H.; Ouyang, Q. Experimental study on the strength characteristics of expansive soils improved by the MICP method. Geofluids 2022, 2022, 3089820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Han, Y.; Zhang, X.; Sarajpoor, S.; Zhang, S.; Yao, X. Experimental study on permeability and strength characteristics of MICP-treated calcareous sand. Biogeotechnics 2023, 1, 100034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Mou, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhao, B.; Li, J.; Wu, X.; Zhou, M. Study on durability of MICP treated cohesive soils under dry–wet cycle and freeze–thaw cycle. Arab. J. Geosci. 2022, 15, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Souli, H.; Pechaud, Y.; Fleureau, J.-M. Review on engineering properties of MICP-treated soils. Geomech. Eng. 2021, 27, 13–30. [Google Scholar]
- Banik, N.; Sarkar, R.; Uddin, M.E. Assessment of strength and low-strain shear modulus of bio-cemented sand considering MICP treatment. Environ. Earth Sci. 2023, 82, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimian, A.; Hassanlourad, M. Mechanical behaviour of MICP-treated silty sand. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2022, 81, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| No. | Cementing solution Concentration (M) | Bacterial Solution Concentration (OD600) | Temperature (°C) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 25 | 7 |
| 2 | 1.0 | 0.6 | 25 | 7 |
| 3 | 1.5 | 0.6 | 25 | 7 |
| 4 | 2.0 | 0.6 | 25 | 7 |
| 5 | 0.5 | 1.2 | 25 | 7 |
| 6 | 1.0 | 1.2 | 25 | 7 |
| 7 | 1.5 | 1.2 | 25 | 7 |
| 8 | 2.0 | 1.2 | 25 | 7 |
| 9 | 0.5 | 1.8 | 25 | 7 |
| 10 | 1.0 | 1.8 | 25 | 7 |
| 11 | 1.5 | 1.8 | 25 | 7 |
| 12 | 2.0 | 1.8 | 25 | 7 |
| 13 | 0.5 | 2.4 | 25 | 7 |
| 14 | 1.0 | 2.4 | 25 | 7 |
| 15 | 1.5 | 2.4 | 25 | 7 |
| 16 | 2.0 | 2.4 | 25 | 7 |
| Particle Size Interval | Sand Particle (0.075–2 mm) | Powder Particle (0.005–0.075 mm) | Clay Particle (<0.005 mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Percentage composition (%) | 19.49% | 56.75% | 23.76% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Zhuang, D.; Hu, R. Performance of Microbially Induced Carbonate Precipitation for Reinforcing Cohesive Soil in the Reservoir Area. Crystals 2025, 15, 540. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15060540
Li X, Zhuang D, Hu R. Performance of Microbially Induced Carbonate Precipitation for Reinforcing Cohesive Soil in the Reservoir Area. Crystals. 2025; 15(6):540. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15060540
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xinfa, Dingxiang Zhuang, and Ru Hu. 2025. "Performance of Microbially Induced Carbonate Precipitation for Reinforcing Cohesive Soil in the Reservoir Area" Crystals 15, no. 6: 540. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15060540
APA StyleLi, X., Zhuang, D., & Hu, R. (2025). Performance of Microbially Induced Carbonate Precipitation for Reinforcing Cohesive Soil in the Reservoir Area. Crystals, 15(6), 540. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15060540





