Synthesis of ZnO-Ag Nanostructures with Origanum vulgare, Combined with the Solid-State Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. ZnO and ZnO-Ag System Synthesis
2.2. Characterization
3. Results
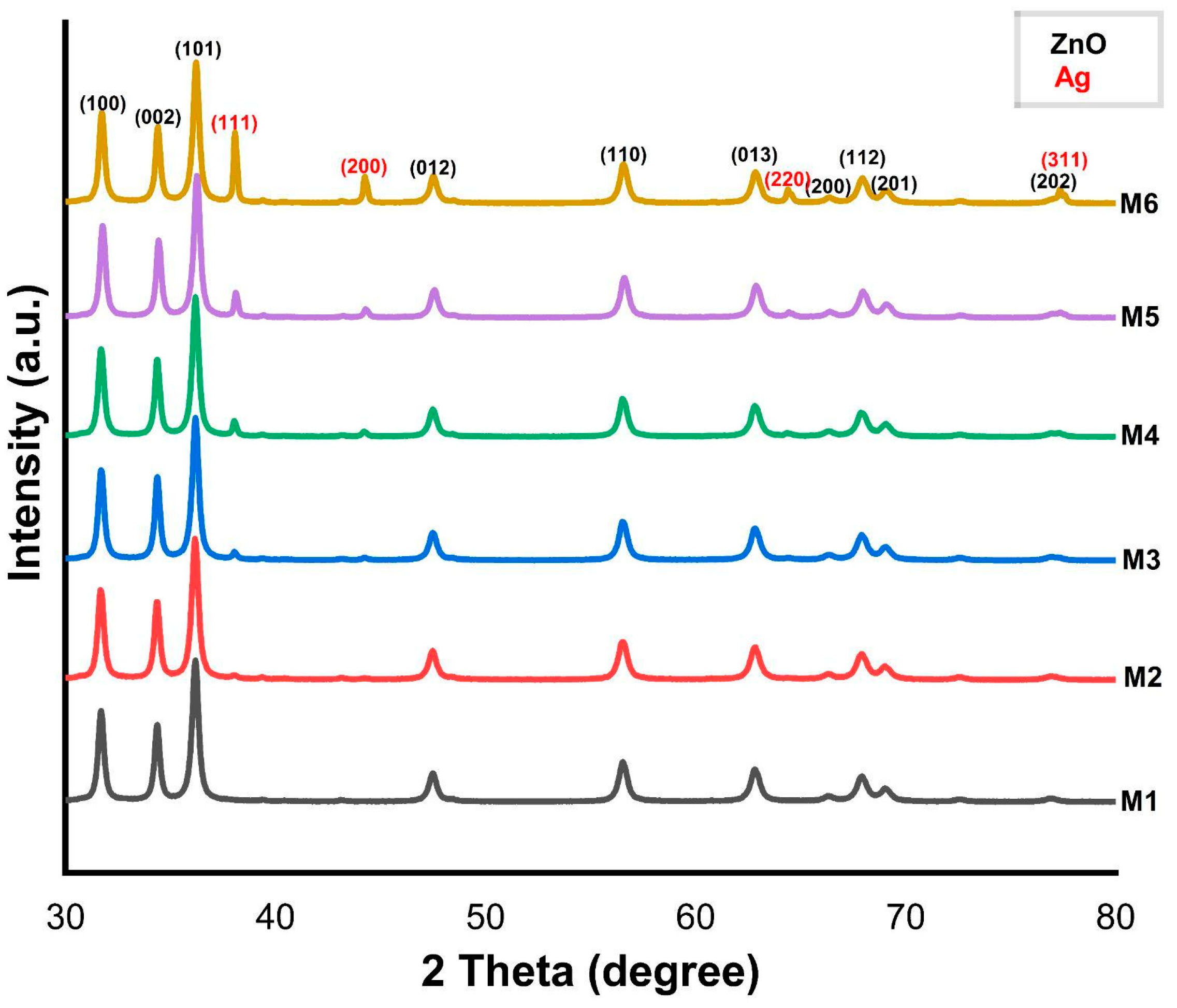
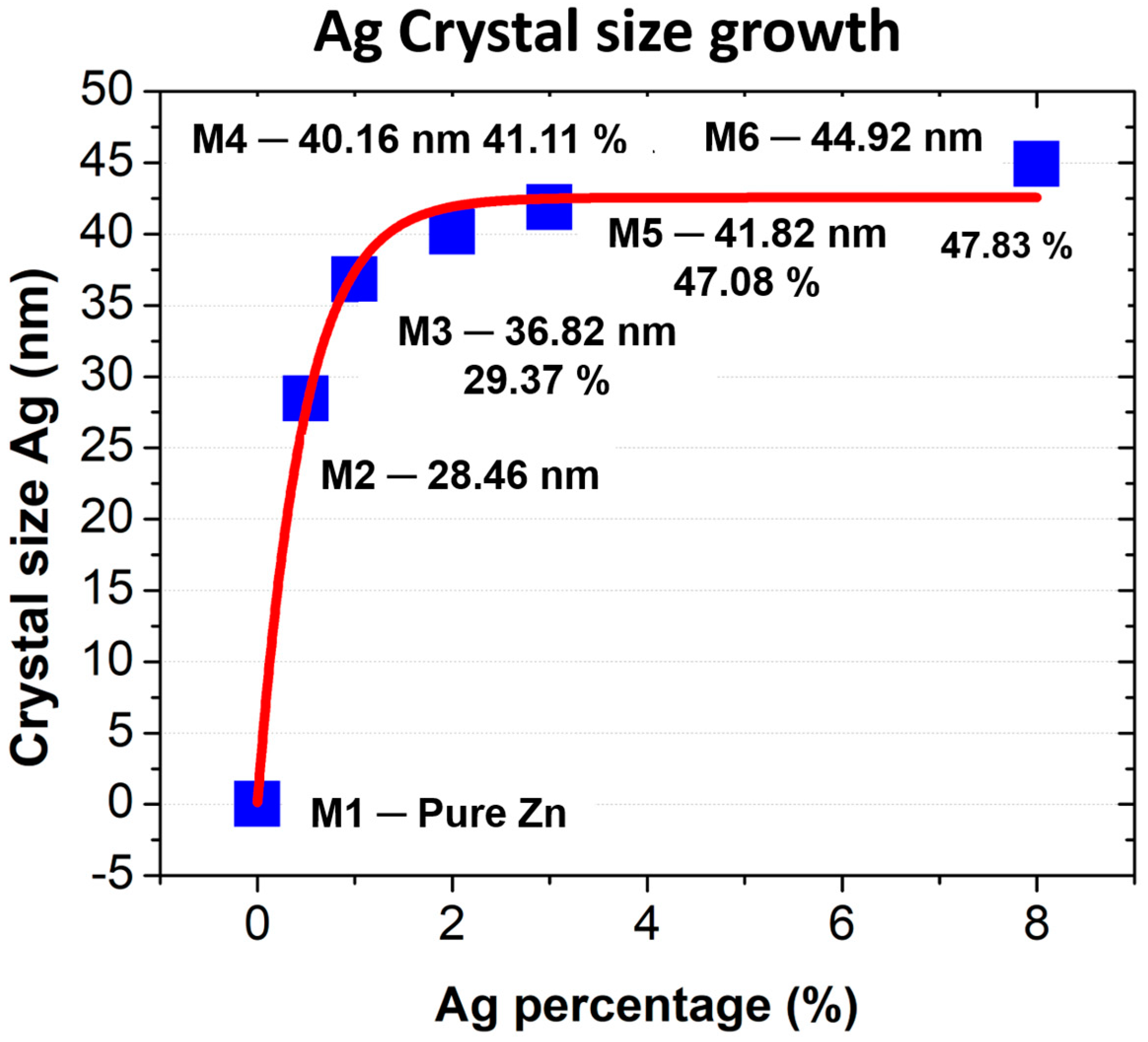
3.1. X-Ray Diffraction
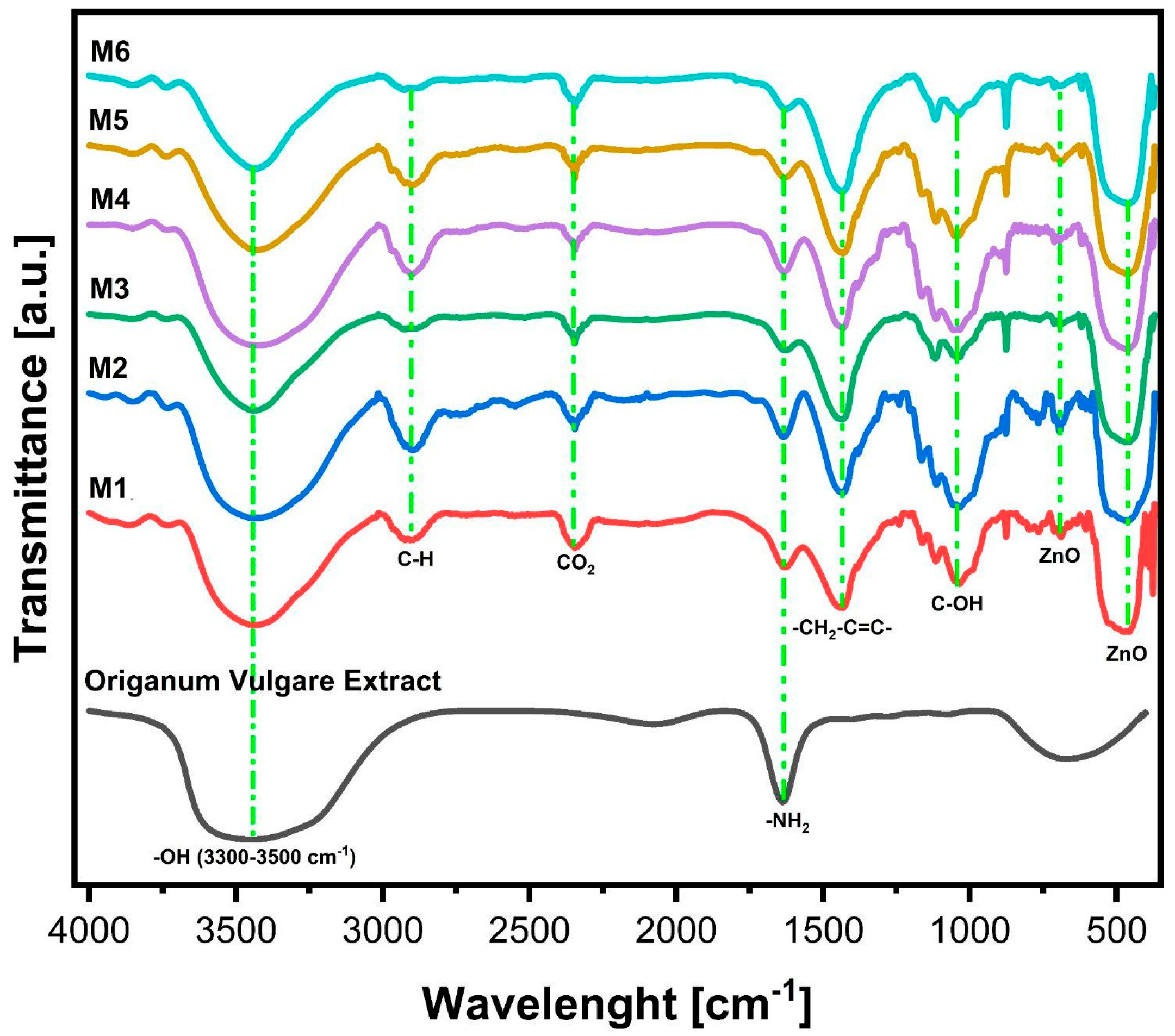
3.2. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
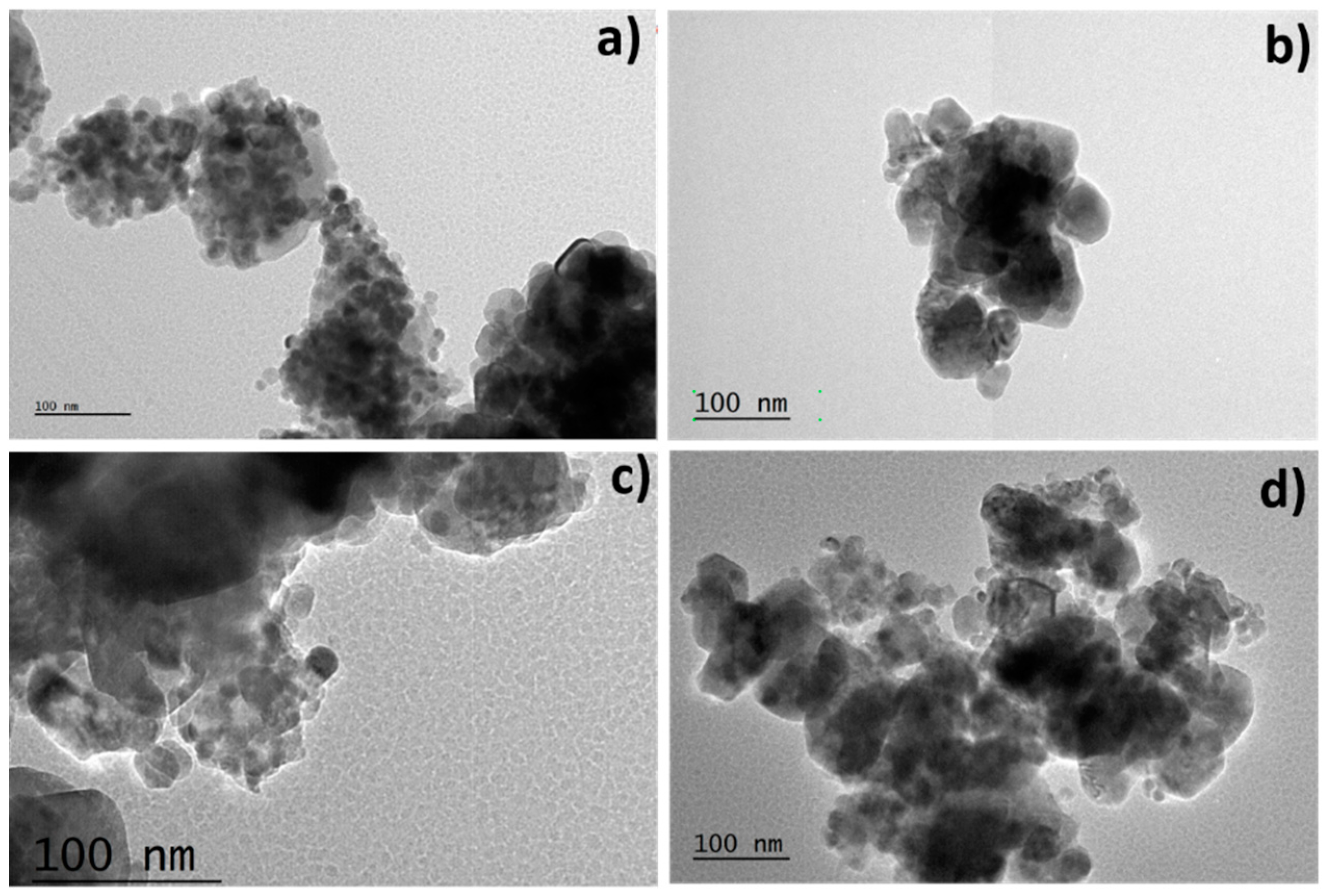
3.3. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
3.4. High-Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy (HRTEM)
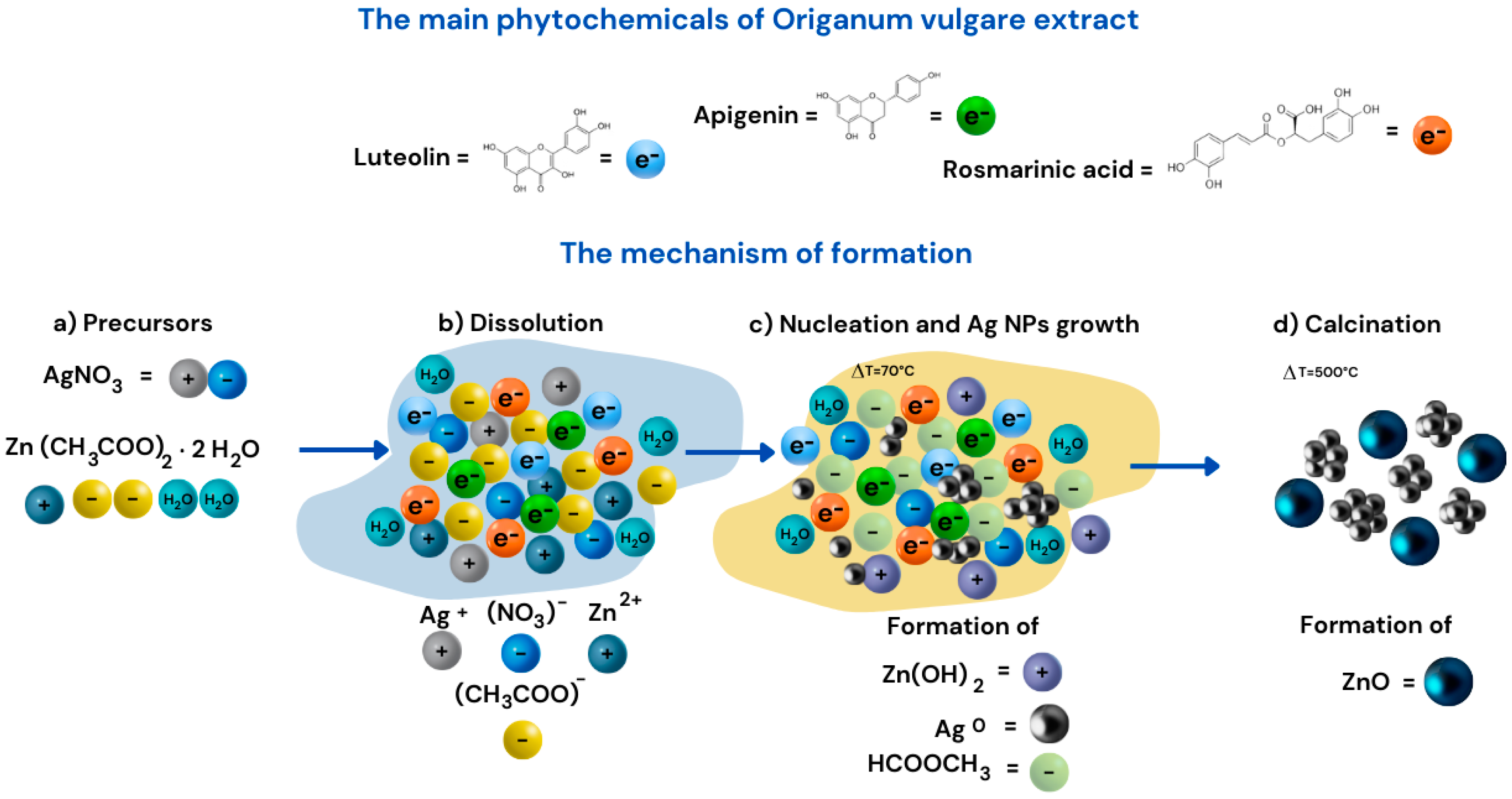
3.5. Reaction Mechanism
4. Discussions
Structural and Morphological Characterization
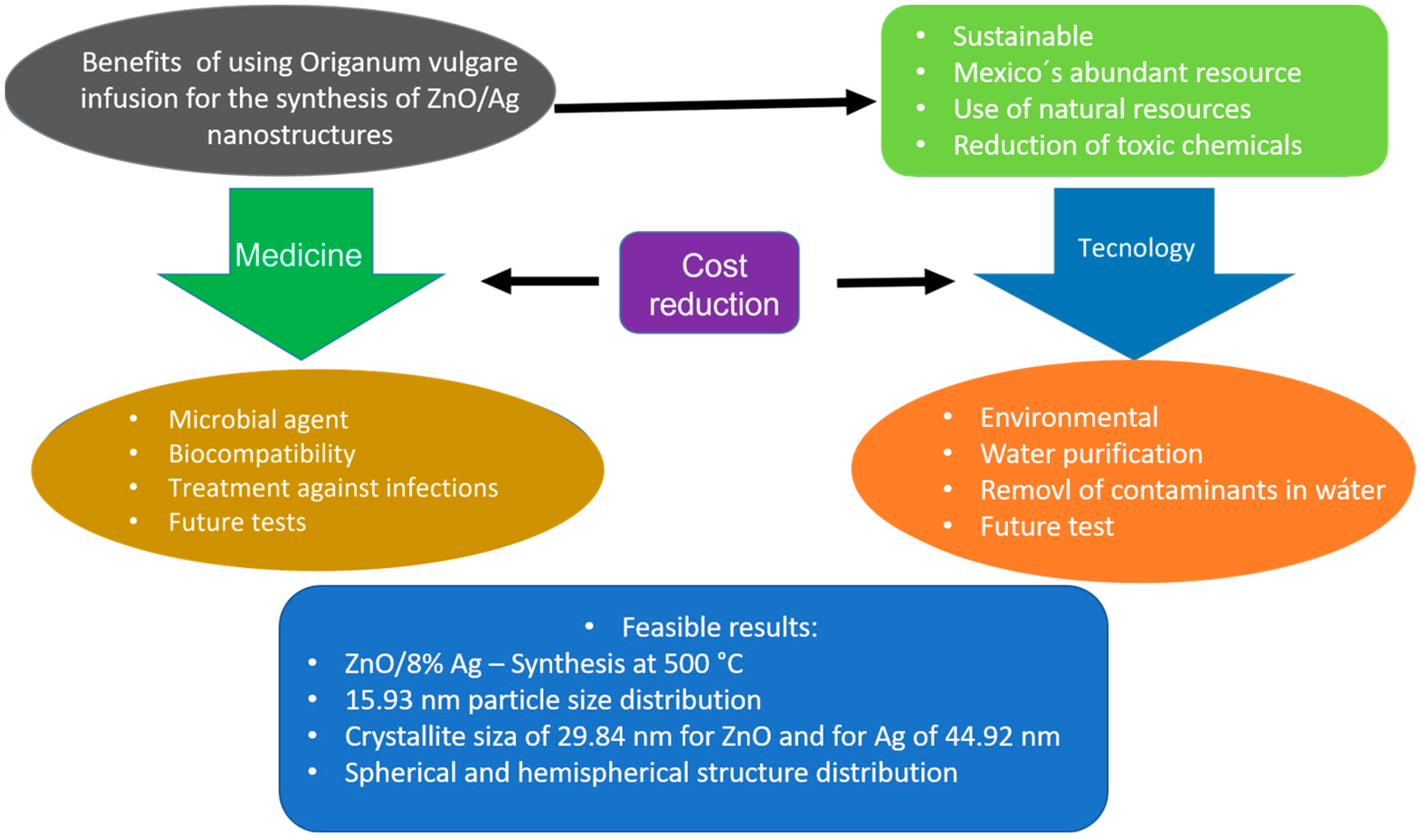
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Özgür, Ü.; Hofstetter, D.; Morkoç, H. ZnO Devices and Applications: A Review of Current Status and Future Prospects. Proc. IEEE 2010, 98, 1255–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayan, B.; Rajesh, K.; Chittaranjan, P. Biomedical applications of zinc oxide nanoparticles. Inorg. Framew. Smart Nanomed. 2018, 6, 239–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galstyan, V.; Comini, E.; Baratto, C.; Faglia, G.; Sberveglieri, G. Nanostructured ZnO chemical gas sensors. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 14239–14244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becheri, A.; Dürr, M.; Nostro, P.L.; Baglioni, P. Synthesis and characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticles: Application to textiles as UV-absorbers. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2008, 10, 679–689. [Google Scholar]
- Cruz, D.M.; Mostafavi, E.; Vernet-Crua, A.; Barabadi, H.; Shah, V.; Cholula-Díaz, J.L.; Guisbiers, G.; Webster, T.J. Green nanotechnology-based zinc oxide (ZnO) nanomaterials for biomedical applications: In review. J. Phys. Mater. 2020, 3, 034005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, S.; Ahmad, M.B.; Hussein, M.Z.; Ibrahim, N.A. Synthesis, antibacterial and thermal studies of cellulose nanocrystal stabilized ZnO-Ag heterostructure nanoparticles. Molecules 2013, 18, 6269–6280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, C.B.; Ng, L.Y.; Mohammad, A.W. A review of ZnO nanoparticles as solar photocatalysts: Synthesis, mechanisms and applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 81 Pt 1, 536–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.; Wang, C.; Ko, H.; Hwang, W.; Chang, K. Synthesis of zinc oxide nanocrystalline powders for cosmetic applications. Ceram. Int. 2010, 36, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Sun, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Li, W.; Li, B.; Huang, X.; Liu, X.; Hu, J. Heterostructures of CuS nanoparticle/ZnO nanorod arrays on carbon fibers with improved visible and solar light photocatalytic properties. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 7304–7313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Cai, L.; Zhang, W. Controlled fabrication and properties of three-dimensional ZnO@ hemimorphite nano-heterostructures. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 14119–14126. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.L.; Sun, Y.G.; Ding, D.R.; Rao, P.H.; Cai, L.Y.; Xu, J.N. Simple synthesis and enhanced photocatalytic performance of La-modified ZnO nanosheet-assembled flower-like microstructures. Funct. Mater. Lett. 2014, 5, 1450052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barcikowski, S.; Compagnini, G. Advanced nanoparticle generation and excitation by lasers in liquids. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 3022–3042. [Google Scholar]
- Amendola, V.; Meneghetti, M. Laser ablation synthesis in solution and size manipulation of noble metal nanoparticles. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2009, 11, 3805–3821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Gökce, B. Laser synthesis and processing of colloids: Fundamentals and applications. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 3990–4103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, Y.H.; Wei, X.W.; Hong, J.M.; Ye, Y. Hydrothermal preparation and optical properties of ZnO nanorods. Mater. Sci. Eng. B Solid-State Mater. Adv. Technol. 2005, 121, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBride, R.A.; Kelly, J.M.; McCormack, D.E. Growth of well-defined ZnO microparticles by hydroxide ion hydrolysis of zinc saltsElectronic supplementary information (ESI) available: SEM images of initial precipitate and of particles formed by Method A. J. Mater. Chem. 2003, 13, 1196–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.H.; Yeh, C.H. Emulsion precipitation of submicron zinc oxide powder. Mater. Lett. 1997, 33, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; E, L.; Ya, J.; Xin, Y. Growth of ZnO nanorods by aqueous solution method with electrodeposited ZnO seed layers. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 255, 5415–6420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghababazadeh, R.; Mazinani, B.; Mirhabibi, A.; Tamizifar, M. ZnO Nanoparticles Synthesised by mechanochemical processing. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2006, 26, 312–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanković, A. Review of 12 Principles of Green Chemistry in Practice. Int. J. Sustain. Green. Energy 2017, 6, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeVierno Kreuder, A.; House-Knight, T.; Whitford, J.; Ponnusamy, E.; Miller, P.; Jesse, N.; Rodenborn, R.; Sayag, S.; Gebel, M.; Aped, I.; et al. A Method for Assessing Greener Alternatives between Chemical Products Following the 12 Principles of Green Chemistry. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 2927–2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalpana, V.N.; Rajeswari, V.D. A Review on Green Synthesis, Biomedical Applications, and Toxicity Studies of ZnO NPs. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2018, 2018, 3569758. [Google Scholar]
- Espitia, P.J.P.; Soares, N.D.F.F.; Coimbra, J.S.D.R.; de Andrade, N.J.; Cruz, R.S.; Medeiros, E.A.A. Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Antimicrobial Activity and Food Packaging Applications. Food Bioprocess. Technol. 2012, 5, 1447–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noohpisheh, Z.; Amiri, H.; Farhadi, S.; Mohammadi-gholami, A. Green synthesis of Ag-ZnO nanocomposites using Trigonella foenum-graecum leaf extract and their antibacterial, antifungal, antioxidant and photocatalytic properties. Spectrochim. Acta-Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2020, 240, 118595. [Google Scholar]
- Mirzaei, H.; Darroudi, M. Zinc oxide nanoparticles: Biological synthesis and biomedical applications. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 907–914. [Google Scholar]
- Sharmila, G.; Thirumarimurugan, M.; Muthukumaran, C. Green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using Tecoma castanifolia leaf extract: Characterization and evaluation of its antioxidant, bactericidal and anticancer activities. Microchem. J. 2019, 145, 578–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamdagni, P.; Khatri, P.; Rana, J.S. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using flower extract of Nyctanthes arbor-tristis and their antifungal activity. J. King Saud. Univ.-Sci. 2018, 30, 168–175. [Google Scholar]
- Thi, T.U.D.; Nguyen, T.T.; Thi, Y.D.; Thi, K.H.T.; Phan, B.T.; Pham, K.N. Green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using orange fruit peel extract for antibacterial activities. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 23899–23907. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, M.J.; Murtaza, G.; Mehmood, A.; Bhatti, T.M. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using leaves extract of Skimmia laureola: Characterization and antibacterial activity. Mater. Lett. 2015, 153, 10–13. [Google Scholar]
- Foroughbakhch, R.; Alvarado-Vázquez, M.; Sánchez, J.; Guzman, M.; Hernandez-Piñero, J.; Rocha, A. Caracterización Polinologico de las especies de Oregano: De los géneros Lippia (Verbenaceae) y Poliomintha (Lamiaceae) de Nuevo León. Cienc. UANL 2014, 17, 49–56. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Perez, E.; Castro-Álvarez, F.; Gutiérrez-Uribe, J.; García-Lara, S. Revision of the production, phytochemical composition, and nutraceutical properties of Mexican oregano. Rev. Mex. Cienc. Agrícolas 2012, 3, 339–353. [Google Scholar]
- Pandia-Estrada, S.; Romero-Santivañez, R.; Céspedes-Chombo, R.; Solari-Godiño, A. Edible films gelatin-based obtained from mahi-mahi skin (Coryphaena hippurus) and oregano extract: Physicochemical, antimicrobial, structural and surface characteristics. Sci. Agropecu. 2021, 12, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajith Kumar, C.R.; Betageri, V.S.; Nagaraju, G.; Pujar, G.H.; Onkarappa, H.S.; Latha, M.S. Synthesis of Core/Shell (ZnO/Ag) Nanoparticles Using Calotropis gigantea and Their Applications in Photocatalytic and Antibacterial Studies. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2020, 30, 3410–3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustapha, S.; Ndamitso, M.M.; Abdulkareem, A.S.; Tijani, J.O. Comparative study of crystallite size using Williamson-Hall and Debye- Comparative study of crystallite size using Williamson-Hall and Debye-Scherrer plots for ZnO nanoparticles. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 045013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elumalai, K.; Velmurugan, S.; Ravi, S.; Kathiravan, V.; Raj, G.A. Bio-approach: Plant mediated synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles and their catalytic reduction of methylene blue and antimicrobial activity. Adv. Powder Technol. 2015, 26, 1639–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slathia, S.; Gupta, T.; Chauhan, R.P. Green synthesis of Ag–ZnO nanocomposite using Azadirachta indica leaf extract exhibiting excellent optical and electrical properties. Phys. B Condens. Matter. 2021, 621, 413287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouladi-Fard, R.; Aali, R.; Mohammadi-Aghdam, S.; Mortazavi-derazkola, S. The surface modification of spherical ZnO with Ag nanoparticles: A novel agent, biogenic synthesis, catalytic and antibacterial activities. Arab. J. Chem. 2022, 15, 103658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatami, M.; Varma, R.S.; Zafarnia, N.; Yaghoobi, H.; Sarani, M.; Kumar, V.G. Applications of green synthesized Ag, ZnO and Ag/ZnO nanoparticles for making clinical antimicrobial wound-healing bandages. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2018, 10, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
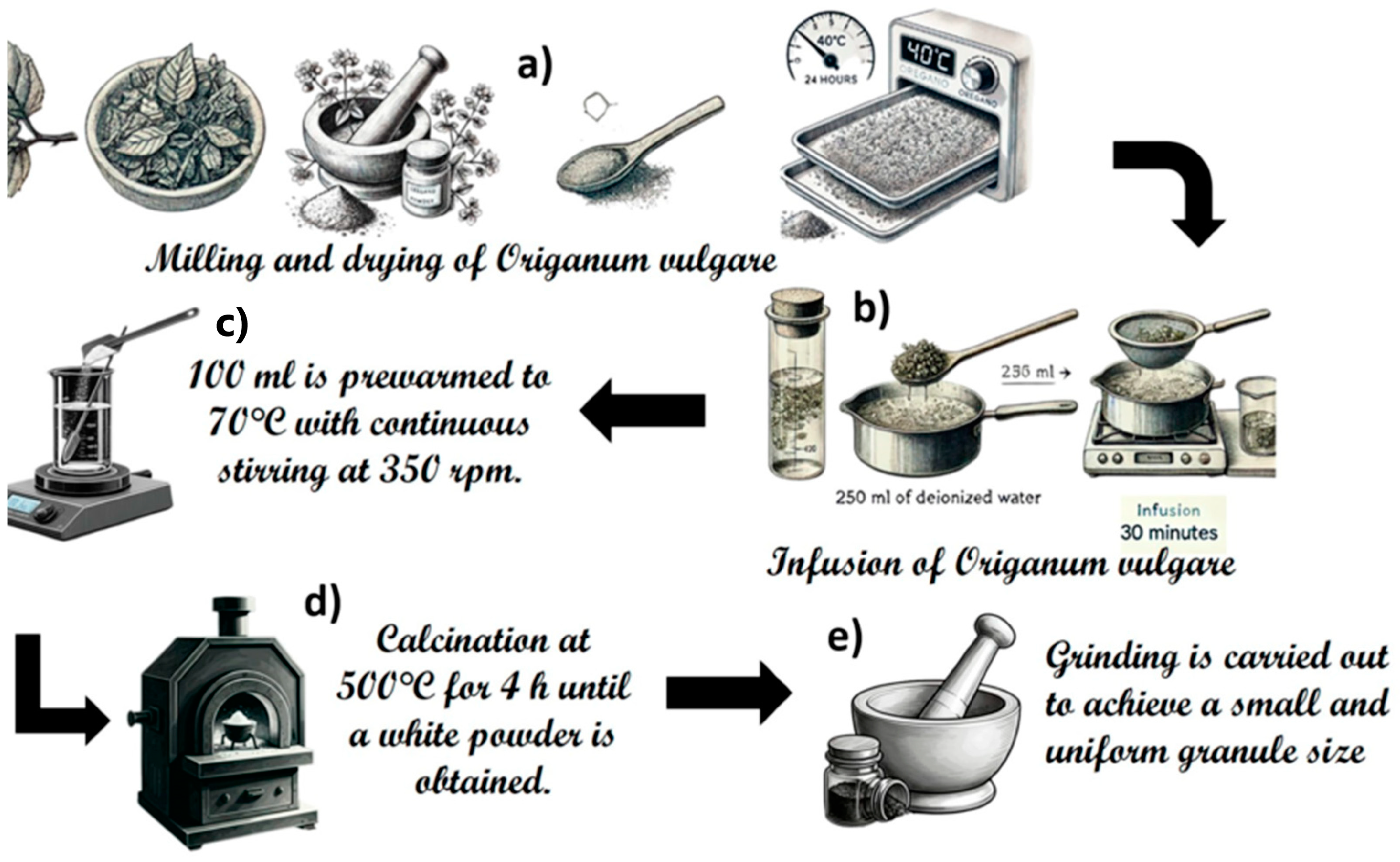

| Sample | Mass mmol ZnO | Mass mmol Ag | Percentage (%) of Ag |
|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | 61.4175 | 0 | 0 |
| M2 | 61.1104 | 0.2317 | 0.5 |
| M3 | 60.8033 | 0.4634 | 1 |
| M4 | 60.1891 | 0.9270 | 2 |
| M5 | 59.5750 | 1.3900 | 3 |
| M6 | 56.5041 | 3.7070 | 8 |
| Samples | ZnO Crystallite Size (nm) | Ag Crystallite Size (nm) |
|---|---|---|
| M1 | 24.9 | ----- |
| M2 | 27.20 | 28.46 |
| M3 | 28.95 | 36.82 |
| M4 | 29.52 | 40.16 |
| M5 | 29.85 | 41.86 |
| M6 | 29.84 | 44.92 |
| Parts of the Plant | Synthesis Method | Synthesis Temperature (°C) | Crystal Size (nm) | Particle Size (nm) | Ag Concentration | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Extract of Calotropis gigantea leaves | Combustion solution | 500 | 38.00 | 100–150 | 5% wt | [33] |
| Extract of Azadirachta indica leaves | hydrothermal | 120 | 21.22 y 23.52 | 60–220 | 10% wt | [36] |
| Extract of Crataegus monogyna | coprecipitation | 500 | 33.8 y 49.6 | 55–77 | 0.002 M | [37] |
| Prosophis fracta and coffee | Eco-friendly | 600 | 16 y 26 | 5–40 | 1 mM | [38] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Munguia Martín, M.P.; Muñoz-Pérez, J.E.; Arenas Alatorre, J.A.; Villaseñor-Cerón, L.S.; Mendoza Anaya, D.; Rodríguez Lugo, V. Synthesis of ZnO-Ag Nanostructures with Origanum vulgare, Combined with the Solid-State Method. Crystals 2025, 15, 313. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15040313
Munguia Martín MP, Muñoz-Pérez JE, Arenas Alatorre JA, Villaseñor-Cerón LS, Mendoza Anaya D, Rodríguez Lugo V. Synthesis of ZnO-Ag Nanostructures with Origanum vulgare, Combined with the Solid-State Method. Crystals. 2025; 15(4):313. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15040313
Chicago/Turabian StyleMunguia Martín, Marco P., Josué E. Muñoz-Pérez, Jesús A. Arenas Alatorre, Lesly S. Villaseñor-Cerón, Demetrio Mendoza Anaya, and Ventura Rodríguez Lugo. 2025. "Synthesis of ZnO-Ag Nanostructures with Origanum vulgare, Combined with the Solid-State Method" Crystals 15, no. 4: 313. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15040313
APA StyleMunguia Martín, M. P., Muñoz-Pérez, J. E., Arenas Alatorre, J. A., Villaseñor-Cerón, L. S., Mendoza Anaya, D., & Rodríguez Lugo, V. (2025). Synthesis of ZnO-Ag Nanostructures with Origanum vulgare, Combined with the Solid-State Method. Crystals, 15(4), 313. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15040313






