Fabrication and Parameter Optimization of High-Melting-Point Pure Cr by Binder Jetting Additive Manufacturing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiments and Characterization
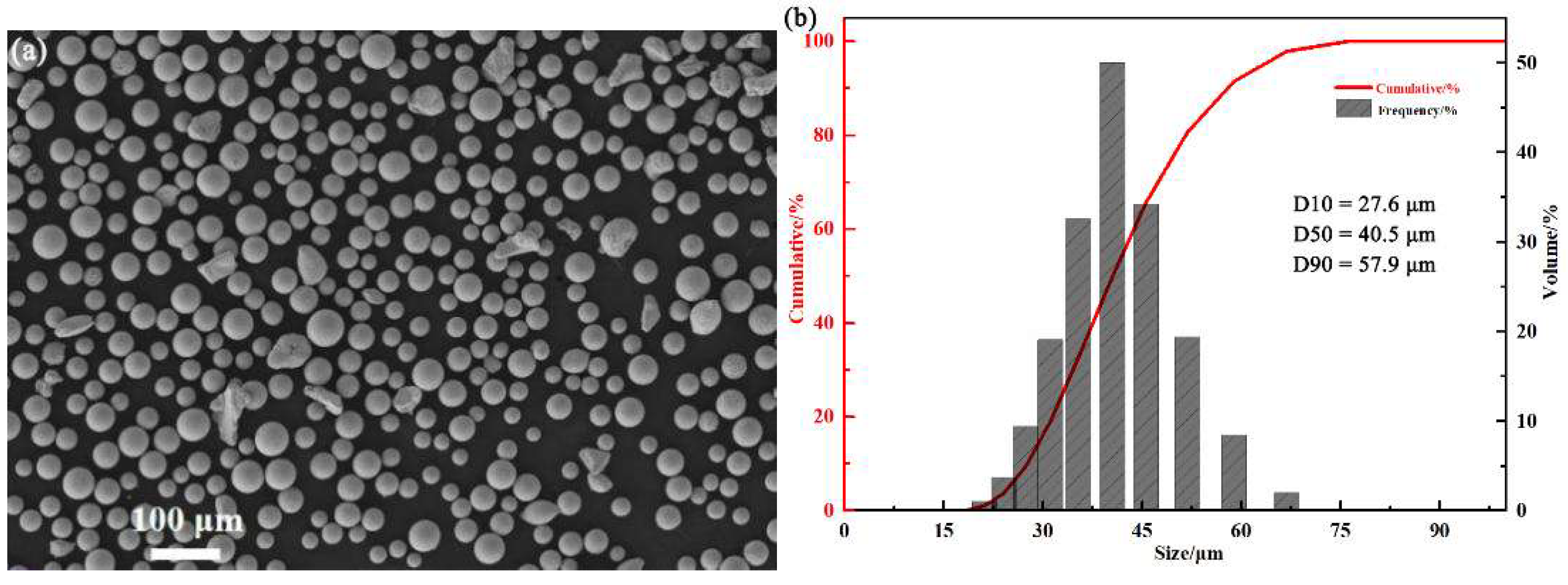
2.1. Materials
2.2. Printing of Cr
2.3. Debinding and Sintering
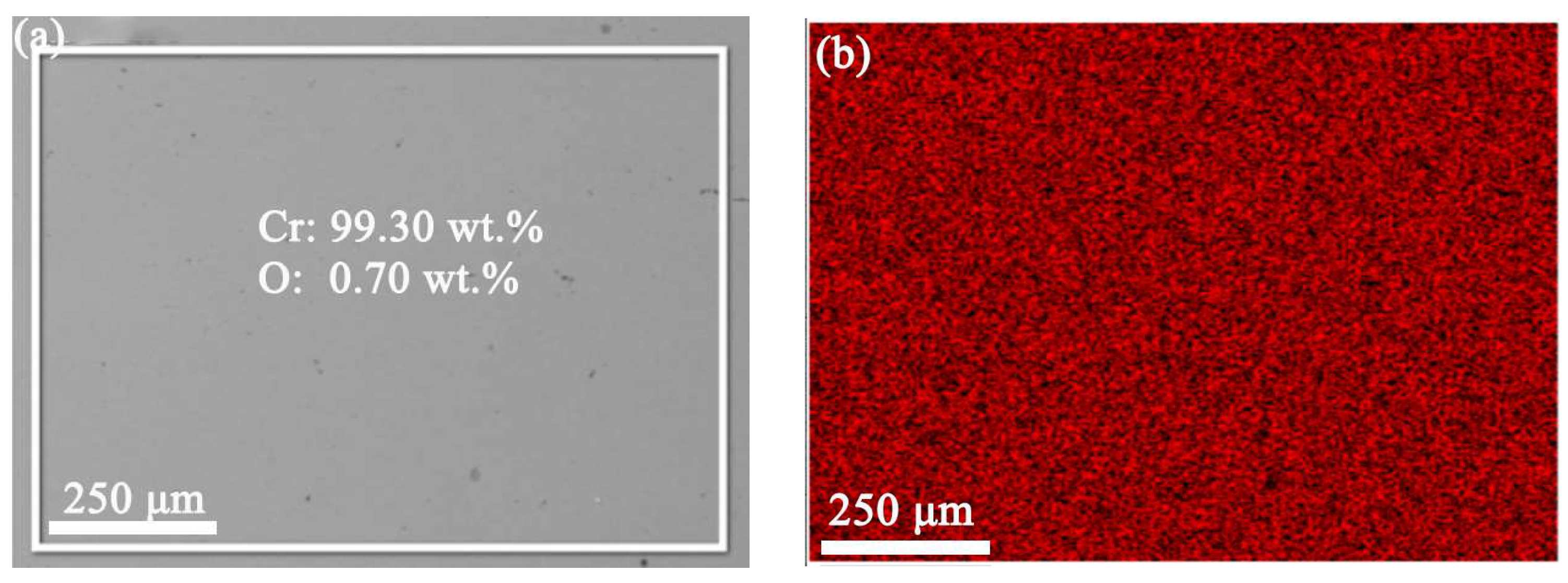
2.4. Microstructure Characterization and Mechanical Properties
3. Results and Discussion
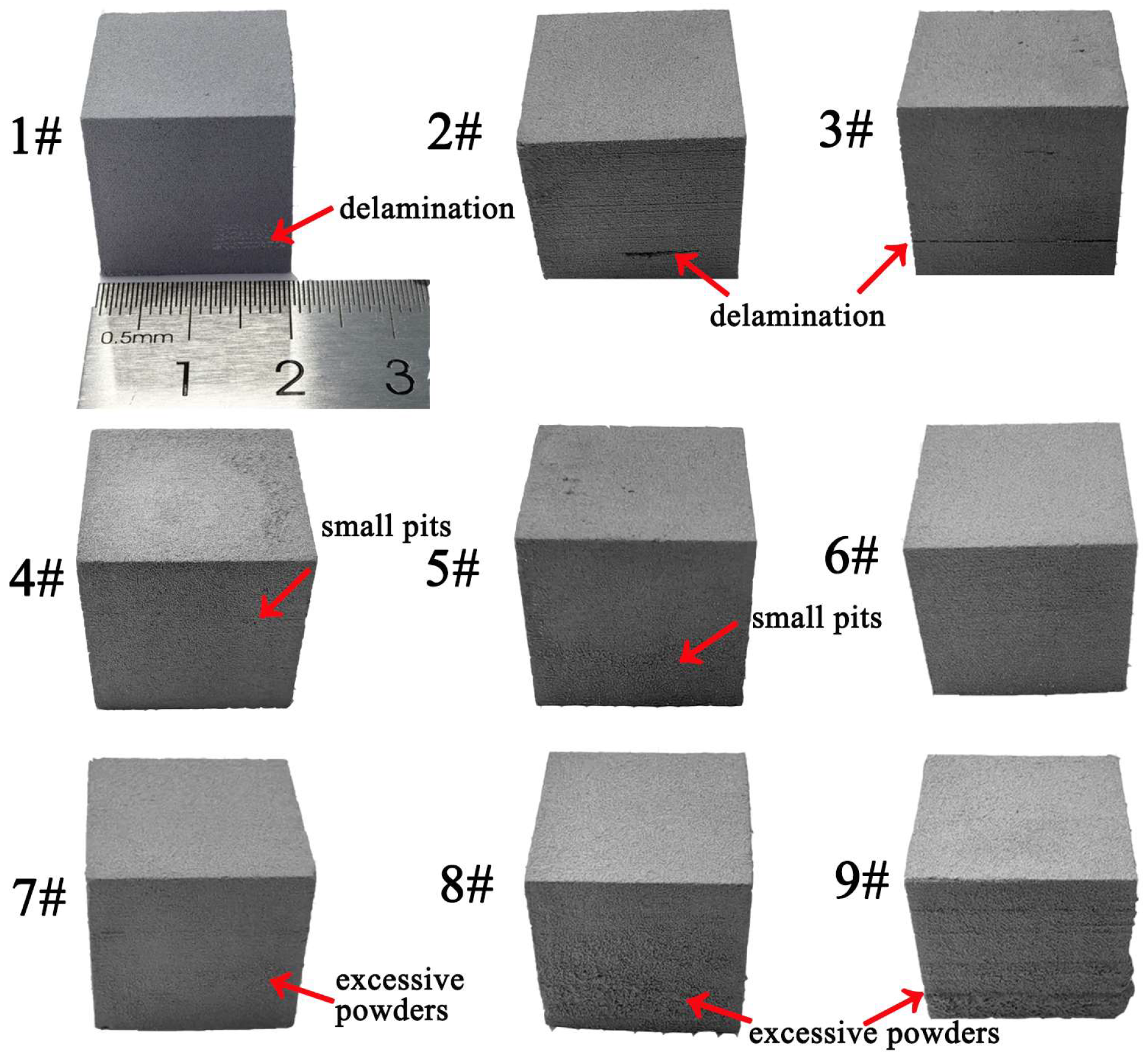
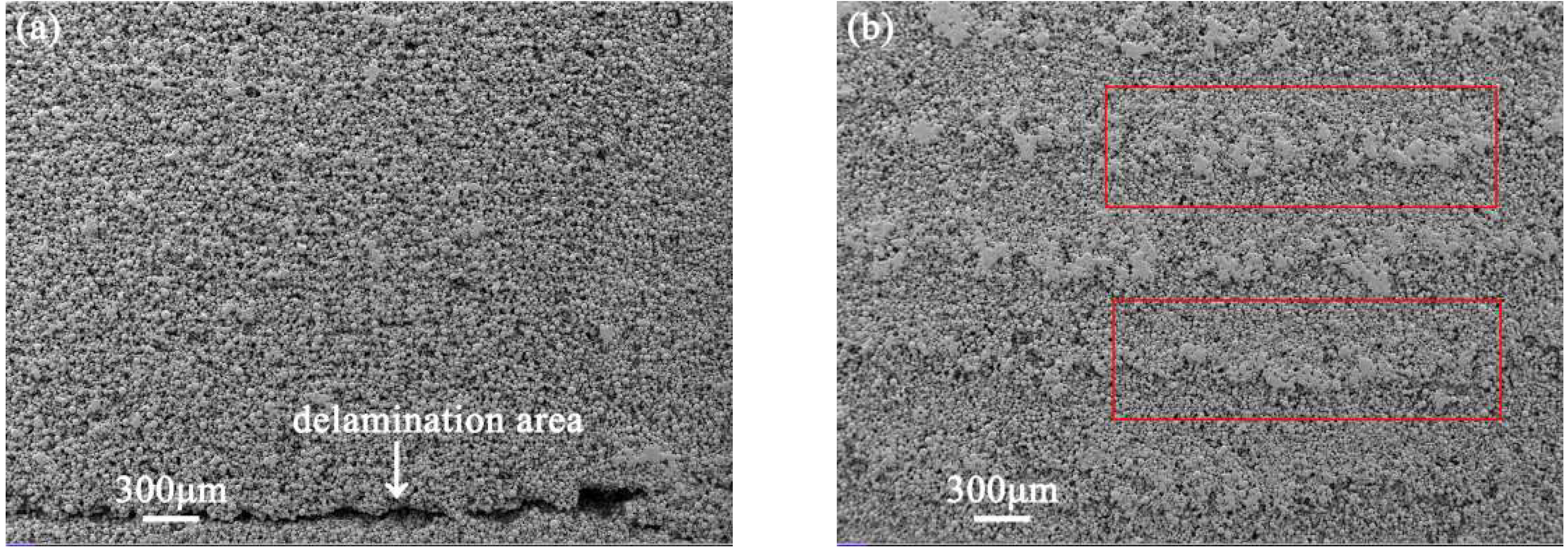
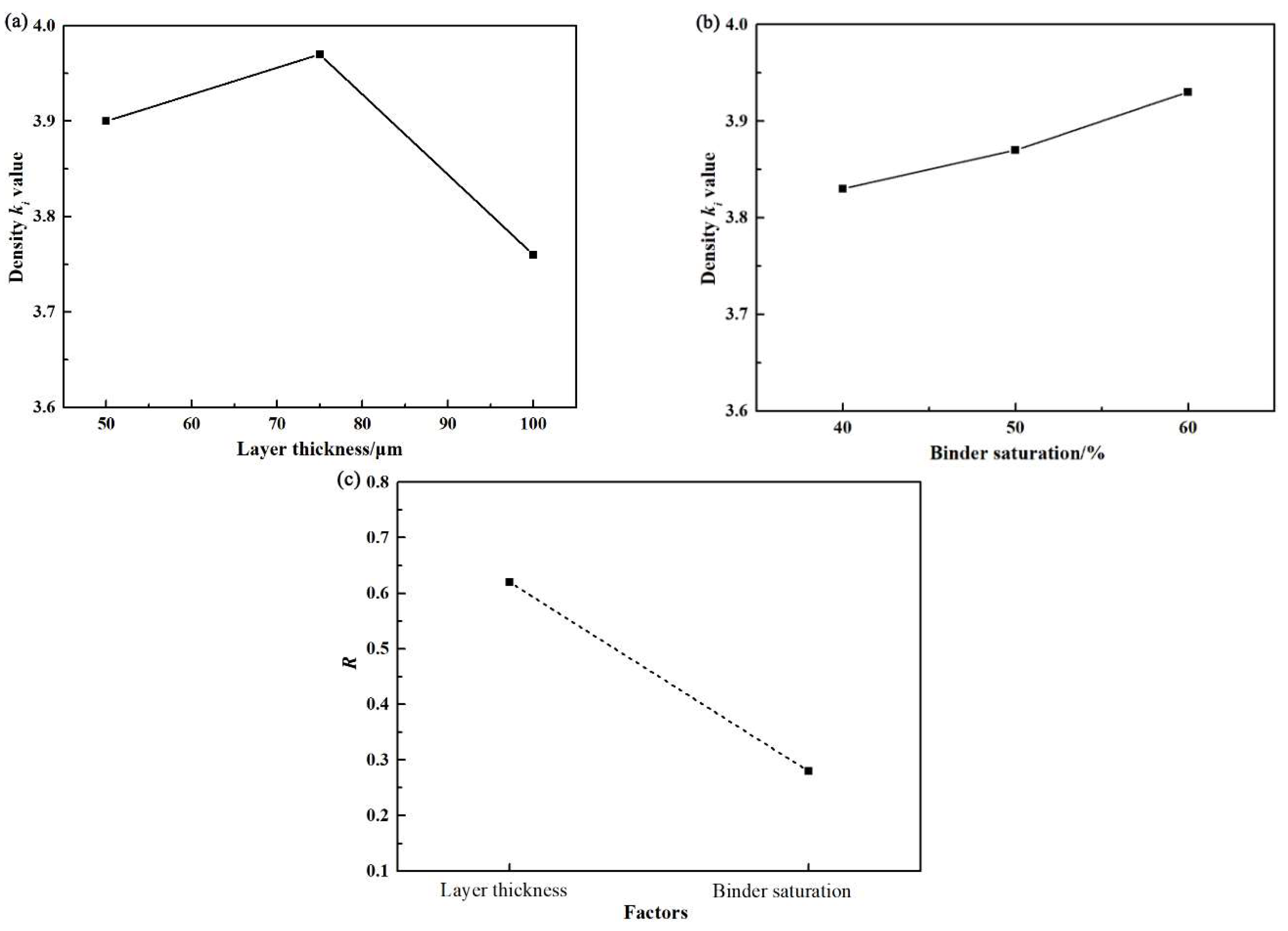
3.1. Effect of Printing Parameters on the Density of Green Parts
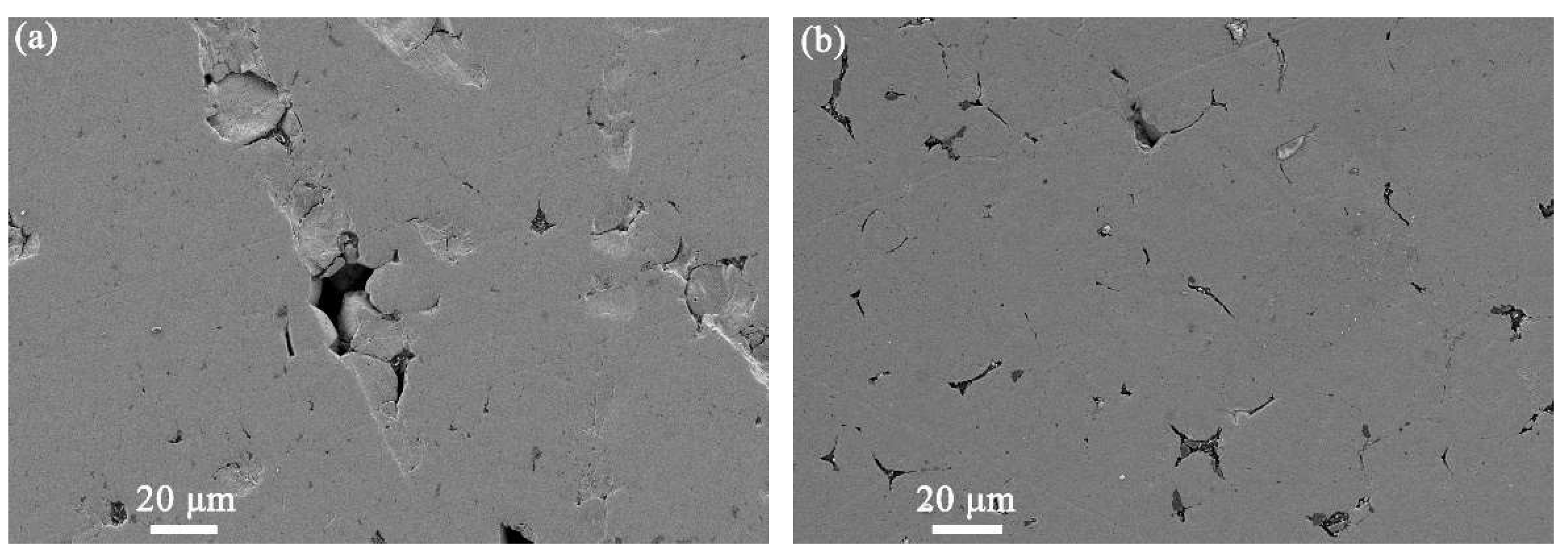
3.2. Effect of Sintering Parameters on Density and Microstructure
3.2.1. Sintering Temperature
3.2.2. Sintering Time
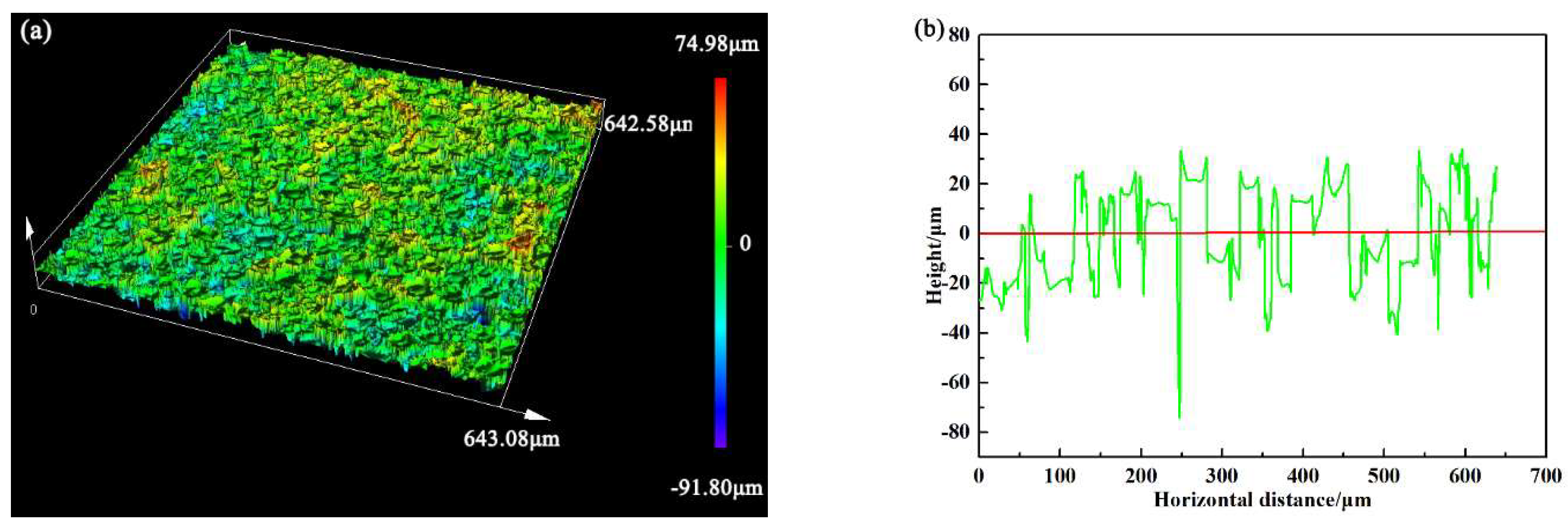
3.3. Surface Roughness and Mechanical Properties
3.3.1. Surface Roughness
3.3.2. Mechanical Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BJ3DP | Binder jet 3D printing method |
References
- Mostafaei, A.; Elliott, A.M.; Barnes, J.E.; Li, F.Z.; Tan, W.D.; Cramer, C.L.; Nandwana, P.; Chmielus, M. Binder jet 3D printing-Process parameters, materials, properties, modeling, and challenges. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2021, 119, 100707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Chen, W.P.; Fu, Z.Q.; Ding, G.X.; Chen, Z.P.; Zhu, D.Z. Binder jet 3D printing of 316L stainless steel: Orthogonal printing and sintering process optimization. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2023, 25, 2200641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanavel, V.; Ashraff Ali, K.S.; Ranganathan, K.; Allen Jeffrey, J.; Ravikumar, M.M.; Rajkumar, S. The roles and applications of additive manufacturing in the aerospace and automobile sector. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 47, 405–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, A.; Marti, B.M.; Sauret-Jackson, V.; Darwood, A. 3D printing in dentistry. Brit. Dent. J. 2015, 219, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, N.; Leu, M.C. Additive manufacturing: Technology, applications and research needs. Front. Mech. Eng. 2013, 8, 215–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buswell, R.A.; Leal de Silva, W.R.; Jones, S.Z.; Dirrenberger, J. 3D printing using concrete extrusion: A roadmap for research. Cem. Concr. Res. 2018, 112, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sames, W.J.; List, F.A.; Pannala, S.; Dehoff, R.R.; Babu, S.S. The metallurgy and processing science of metal additive manufacturing. Int. Mater. Rev. 2016, 61, 315–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, P.; Zocca, A.; Acchar, W.; Günster, J. 3D printing of porcelain by layerwise slurry deposition. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2018, 38, 3395–3400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Pei, X.; Song, P.; Sun, H.; Li, H.; Fan, Y.; Qing, J.; Zhou, X.D. Porous bioceramics produced by inkjet 3D printing: Effect of printing ink formulation on the ceramic macro and micro porous architectures control. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 155, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, S.; Despeisse, M. Additive manufacturing and sustainability: An exploratory study of the advantages and challenges. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 137, 1573–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavropoulos, P.; Foteinopoulos, P. Modelling of additive manufacturing processes: A review and classification. Manuf. Rev. 2018, 5, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farideh, D.; Sadegh, V.; Masoud, A.; Luca, I.; Abdollah, S. In vitro corrosion and bio-tribocorrosion performance of electron beam powder bed fusion Ti6Al4V specimens with lapping and superfinishing treatments. Prog. Addit. Manuf. 2025, 10, 9117–9132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafaei, A.; Stevens, E.L.; Ference, J.J.; Schmidt, D.E.; Chmielus, M. Binder jet printing of partial denture metal framework from metal powder. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2018, 21, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azhari, A.; Marzbanrad, E.; Yilman, D.; Toyserkani, E.; Pope, M.A. Binder-jet powder-bed additive manufacturing (3D printing) of thick graphene-based electrodes. Carbon 2017, 119, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, S.; Manogharan, G. Optimization of binder jetting using Taguchi method. JOM 2017, 69, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atapour, M.; Wang, X.; Persson, M.; Odnevall Wallinder, I.; Hedberg, Y.S. Corrosion and metal release investigations of selective laser melted 316L stainless steel in a synthetic physiological fluid containing proteins and in diluted hydrochloric acid. Electrochim. Acta 2020, 354, 136748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mamun, N.S.; Mairaj Deen, K.; Haider, W.; Asselin, E.; Shabib, I. Corrosion behavior and biocompatibility of additively manufactured 316L stainless steel in a physiological environment: The effect of citrate ions. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 34, 101237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, T.A.; Escobar, J.D.; Shen, J.; Duarte, V.R.; Ribamar, G.G.; Avila, J.A.; Maawad, E.; Schell, N.; Santos, T.G.; Oliveira, J.P. Effect of heat treatments on 316 stainless steel parts fabricated by wire and arc additive manufacturing: Microstructure and synchrotron X-ray diffraction analysis. Addit. Manuf. 2021, 48, 102428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, A. Metallurgy of chromium. Nature 1968, 220, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.F.; Harada, H.; Ro, Y. Chromium and chromium-based alloys: Problems and possibilities for high-temperature service. JOM 2004, 56, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokcekaya, O.; Hayashi, N.; Ishimoto, T.; Ueda, K.; Narushima, T.; Nakano, T. Crystallographic orientation control of pure chromium via laser powder bed fusion and improved high temperature oxidation resistance. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 36, 101624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.; Dong, C.; Ni, X.; Li, X. Corrosion of metallic materials fabricated by selective laser melting. npj Mater. Degrad. 2019, 3, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonsson, B.; Westerlund, A. Oxidation comparison of alumina-forming and chromia-forming commercial alloys at 1100 and 1200 °C. Oxid. Met. 2017, 88, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Footner, P.K.; Holmes, D.R.; Mortimer, D. Oxidation of iron-chromium binary alloys. Nature 1967, 216, 54–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, G. Oxidation of binary FeCr alloys (Fe-2.25Cr, Fe-10Cr, Fe-18Cr and Fe-25Cr) in O2 and in O2 + H2O environment at 600 °C. Oxid. Met. 2011, 75, 183–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallstrom, S.; Halvarsson, M.; Hoglund, L.; Jonsson, T.; Agren, J. High temperature oxidation of chromium: Kinetic modeling and microstructural investigation. Solid State Ion. 2013, 240, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhavadas, V.; Srivastava, D.; Chadha, U.; Raj, S.A.; Sultan, M.T.H.; Mohamed, F.S.; Shah, A.U.M. A review on metal additive manufacturing for intricately shaped aerospace components. CIRP J. Manuf. Sci. Technol. 2022, 39, 18–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Du, W.; Elwany, A.; Pei, Z.; Ma, C. Metal binder jetting additive manufacturing: A literature review. ASME J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2020, 142, 090801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, L.Y.; Wang, X.L.; Chang, Y.L.; Wang, Y.P. Improving the mechanical performance of Cu-Cr alloy by dissolving Cu in the Cr second phase. Mater. Charact. 2021, 176, 111104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijshoff, H. Drop dynamics in the inkjet printing process. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 36, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Chen, H.; Zhao, Y.F. Process parameters optimization for improving surface quality and manufacturing accuracy of binder jetting additive manufacturing process. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2016, 22, 527–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayazfar, H.; Salarian, M.; Rogalsky, A.; Sarker, D.; Russo, P.; Paserin, V. A critical review of powder-based additive manufacturing of ferrous alloys: Process parameters, microstructure and mechanical properties. Mater. Des. 2018, 144, 98–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amir, M.S.; Harsha, V.R.; Neelapu, C.K.; Lauren, M.N.; Tevis, D.B.J.; Markus, C. Characterizing surface finish and fatigue behavior in binder-jet 3D-printed nickel-based superalloy 625. Addit. Manuf. 2018, 24, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Property | BJ3DP | LPBF |
|---|---|---|
| As-Printed Density | ~50–60% (Green part) | >99% |
| Post-Densified Density | >99% (After sintering/infiltration) | |
| Tensile Strength (Inconel 625) | ~612 MPa (as-sintered), ~700 MPa (aged) | ~900–1100 MPa |
| Elongation (Inconel 625) | ~41% (as-sintered), ~30% (aged) | ~20–30% |
| Surface Roughness (as-built) | ~6 µm Ra (after sintering) | 5–15 µm Ra |
| Support Structures | No Support | Required |
| Typical Build Volume | Up to 2200 × 1200 × 600 mm | Typically < 500 × 500 × 500 mm |
| Material Compatibility | Metals, ceramics, composites | Limited by weldability and reflectivity |
| Element | Ni | Si | Fe | Mn | Mg | Cr |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight percent (wt.%) | 0.025 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.001 | 0.0039 | 99.95 |
| Nominal composition (wt.%) | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | ≥99.9 |
| Experiments Number | Printing Parameters | |
|---|---|---|
| Binder Saturation (%) | Layer Thickness (μm) | |
| 1 | 40 | 100 |
| 2 | 50 | 100 |
| 3 | 60 | 100 |
| 4 | 40 | 75 |
| 5 | 50 | 75 |
| 6 | 60 | 75 |
| 7 | 40 | 50 |
| 8 | 50 | 50 |
| 9 | 60 | 50 |
| Experiments Number | X-Axis (mm) | Y-Axis (mm) | Z-Axis (mm) | Average Density (g·cm−3) | Average Relative Density (%) | Average Dimensional Deviation (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 20.07 ± 0.05 | 20.14 ± 0.09 | 19.99 ± 0.10 | 3.68 | 51.2% | ±0.22 |
| 2 | 20.08 ± 0.07 | 20.17 ± 0.12 | 19.98 ± 0.08 | 3.76 | 52.3% | ±0.27 |
| 3 | 20.10 ± 0.09 | 20.18 ± 0.13 | 19.95 ± 0.11 | 3.84 | 53.4% | ±0.33 |
| 4 | 20.09 ± 0.06 | 20.20 ± 0.11 | 20.01 ± 0.15 | 3.92 | 54.5% | ±0.30 |
| 5 | 20.06 ± 0.10 | 20.19 ± 0.13 | 20.03 ± 0.17 | 3.96 | 55.1% | ±0.28 |
| 6 | 20.04 ± 0.05 | 20.21 ± 0.17 | 20.06 ± 0.06 | 4.02 | 55.9% | ±0.31 |
| 7 | 20.07 ± 0.06 | 20.22 ± 0.15 | 20.09 ± 0.13 | 3.90 | 54.3% | ±0.38 |
| 8 | 20.08 ± 0.10 | 20.23 ± 0.19 | 20.05 ± 0.08 | 3.88 | 53.9% | ±0.36 |
| 9 | 20.08 ± 0.11 | 20.20 ± 0.20 | 20.08 ± 0.14 | 3.92 | 54.5% | ±0.36 |
| Experiments Number | Factors | Density (g·cm−3) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Binder Saturation (%) | Layer Thickness (μm) | ||
| 1 | 40 | 100 | 3.68 |
| 2 | 50 | 100 | 3.76 |
| 3 | 60 | 100 | 3.84 |
| 4 | 40 | 75 | 3.92 |
| 5 | 50 | 75 | 3.96 |
| 6 | 60 | 75 | 4.02 |
| 7 | 40 | 50 | 3.90 |
| 8 | 50 | 50 | 3.88 |
| 9 | 60 | 50 | 3.92 |
| K1 | 11.50 | 11.28 | |
| K2 | 11.60 | 11.90 | |
| K3 | 11.78 | 11.70 | |
| k1 | 3.83 | 3.76 | |
| k2 | 3.87 | 3.97 | |
| k3 | 3.93 | 3.90 | |
| R | 0.28 | 0.62 | |
| Sintering Parameters | Linear Shrinkage (%) | Volumetric Shrinkage (%) | Density (g·cm−3) | Relative Density (%) | Average Grain Size (μm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X-Axis | Y-Axis | Z-Axis | |||||
| 1500 °C/2.0 h | 4.2 | 4.5 | 4.6 | 12.72 | 5.59 | 78.13 | 21 |
| 1600 °C/3.0 h | 4.3 | 4.7 | 4.7 | 13.08 | 5.83 | 81.59 | 23 |
| 1650 °C/3.0 h | 4.5 | 4.8 | 4.9 | 13.54 | 6.14 | 85.82 | 26 |
| 1700 °C/3.0 h | 4.9 | 5.0 | 5.2 | 14.39 | 6.39 | 89.40 | 31 |
| 1800 °C/6.0 h | 5.2 | 5.1 | 5.5 | 14.98 | 6.68 | 93.42 | 34 |
| 1800 °C/9.0 h | 5.6 | 5.5 | 6.1 | 16.23 | 6.96 | 97.35 | 36 |
| Method | Sintering Parameters | Hardness (HV) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| LM | / | 171.20 ± 5.6 | [27] |
| BJ3DP | 1500 °C/2.0 h | 149.92 ± 6.1 | This work |
| BJ3DP | 1600 °C/3.0 h | 156.25 ± 5.9 | This work |
| BJ3DP | 1650 °C/3.0 h | 166.85± 1.8 | This work |
| BJ3DP | 1700 °C/3.0 h | 169.22 ± 2.3 | This work |
| BJ3DP | 1800 °C/6.0 h | 177.50 ± 2.3 | This work |
| BJ3DP | 1800 °C/9.0 h | 184.20 ± 2.0 | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shan, L.; Shi, Y.; Su, X.; Li, W.; Liu, C. Fabrication and Parameter Optimization of High-Melting-Point Pure Cr by Binder Jetting Additive Manufacturing. Crystals 2025, 15, 1012. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15121012
Shan L, Shi Y, Su X, Li W, Liu C. Fabrication and Parameter Optimization of High-Melting-Point Pure Cr by Binder Jetting Additive Manufacturing. Crystals. 2025; 15(12):1012. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15121012
Chicago/Turabian StyleShan, Liyuan, Yandong Shi, Xuming Su, Wenkai Li, and Caiming Liu. 2025. "Fabrication and Parameter Optimization of High-Melting-Point Pure Cr by Binder Jetting Additive Manufacturing" Crystals 15, no. 12: 1012. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15121012
APA StyleShan, L., Shi, Y., Su, X., Li, W., & Liu, C. (2025). Fabrication and Parameter Optimization of High-Melting-Point Pure Cr by Binder Jetting Additive Manufacturing. Crystals, 15(12), 1012. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15121012






