Influence of Silicon Content on Mechanical and Tribological Properties of FeSi Steels
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Preparation of Experimental Samples
3. Results and Discussion
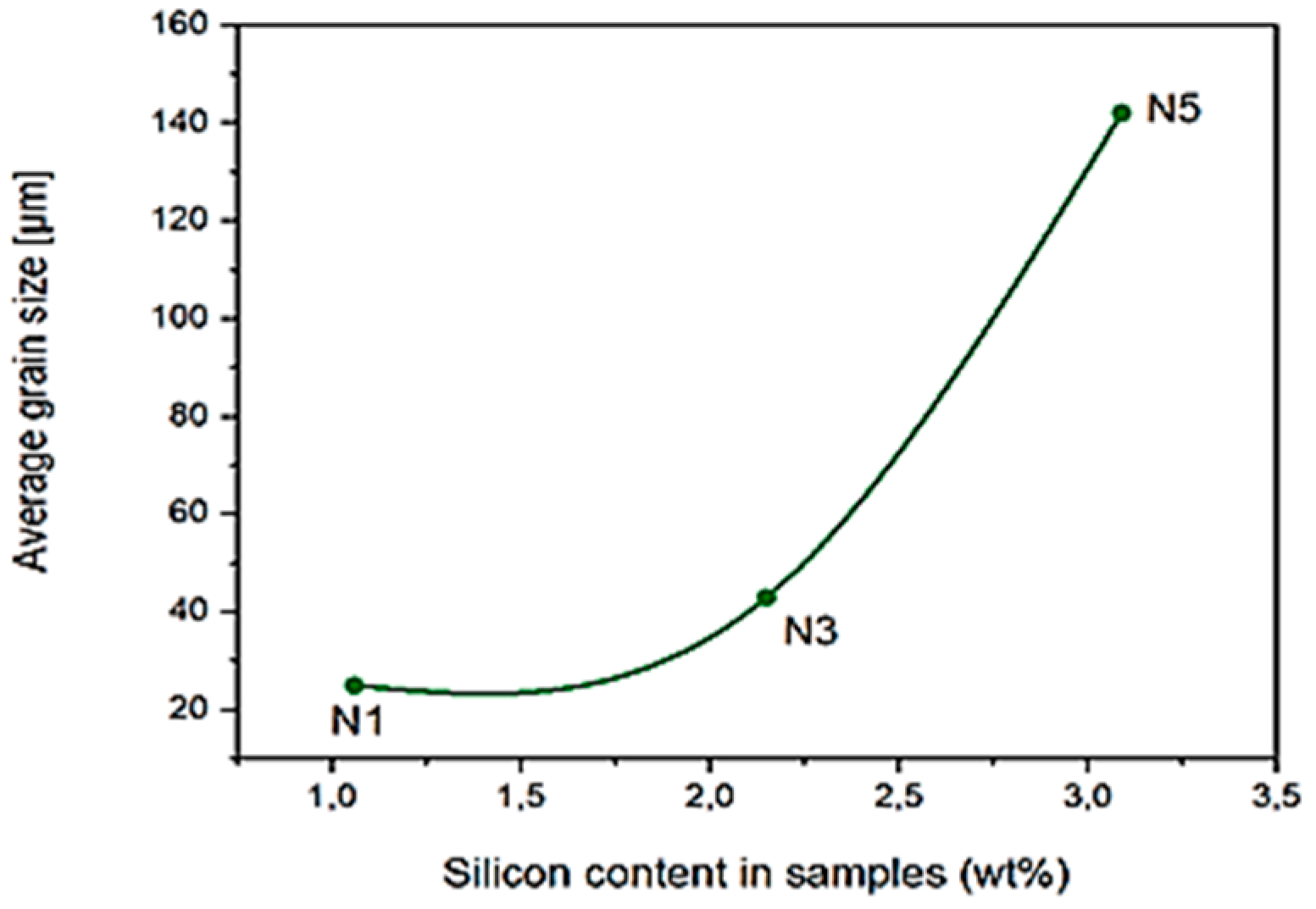
3.1. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties
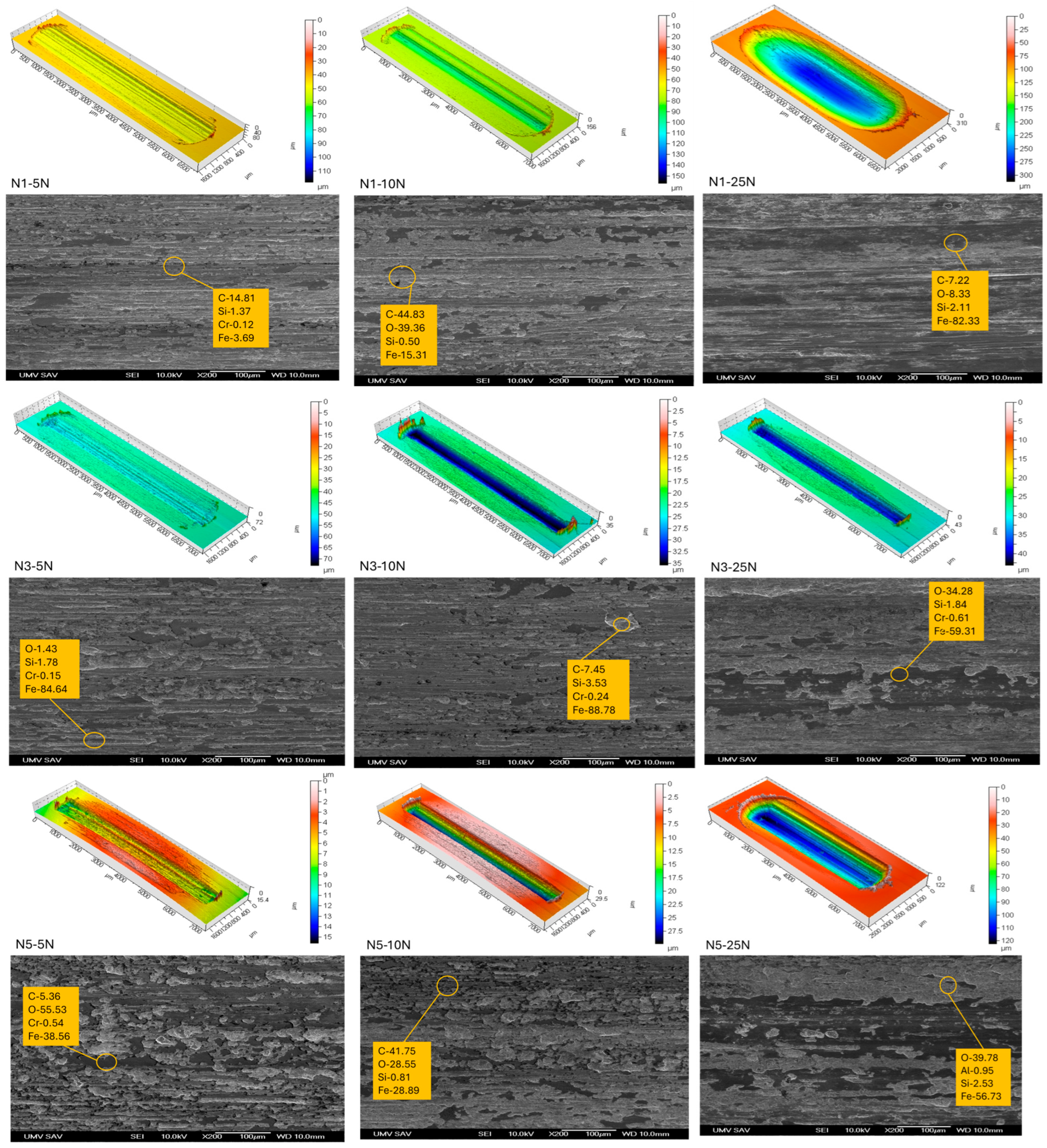
3.2. Tribological Properties
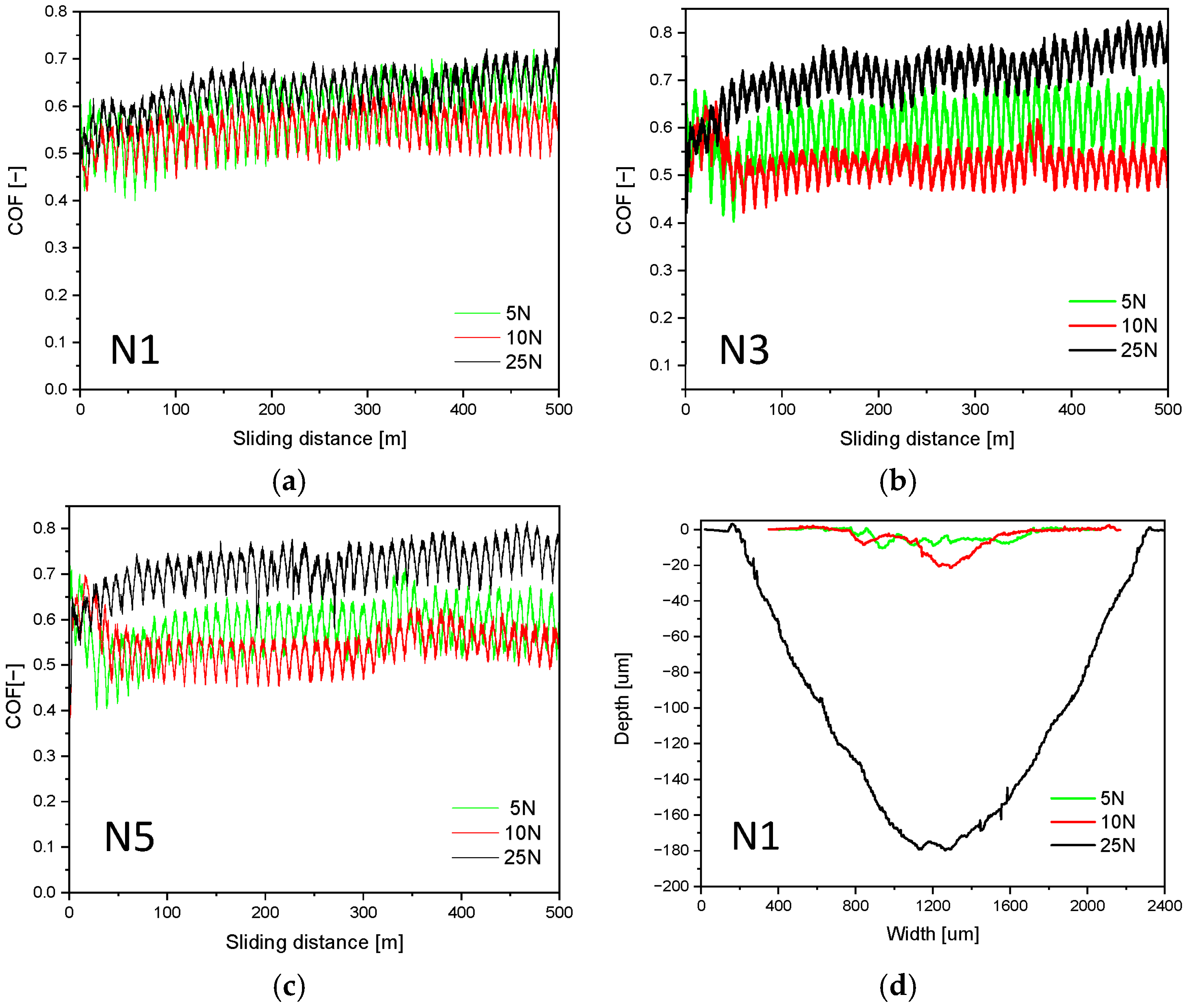
3.2.1. Analysis of the Coefficient of Friction
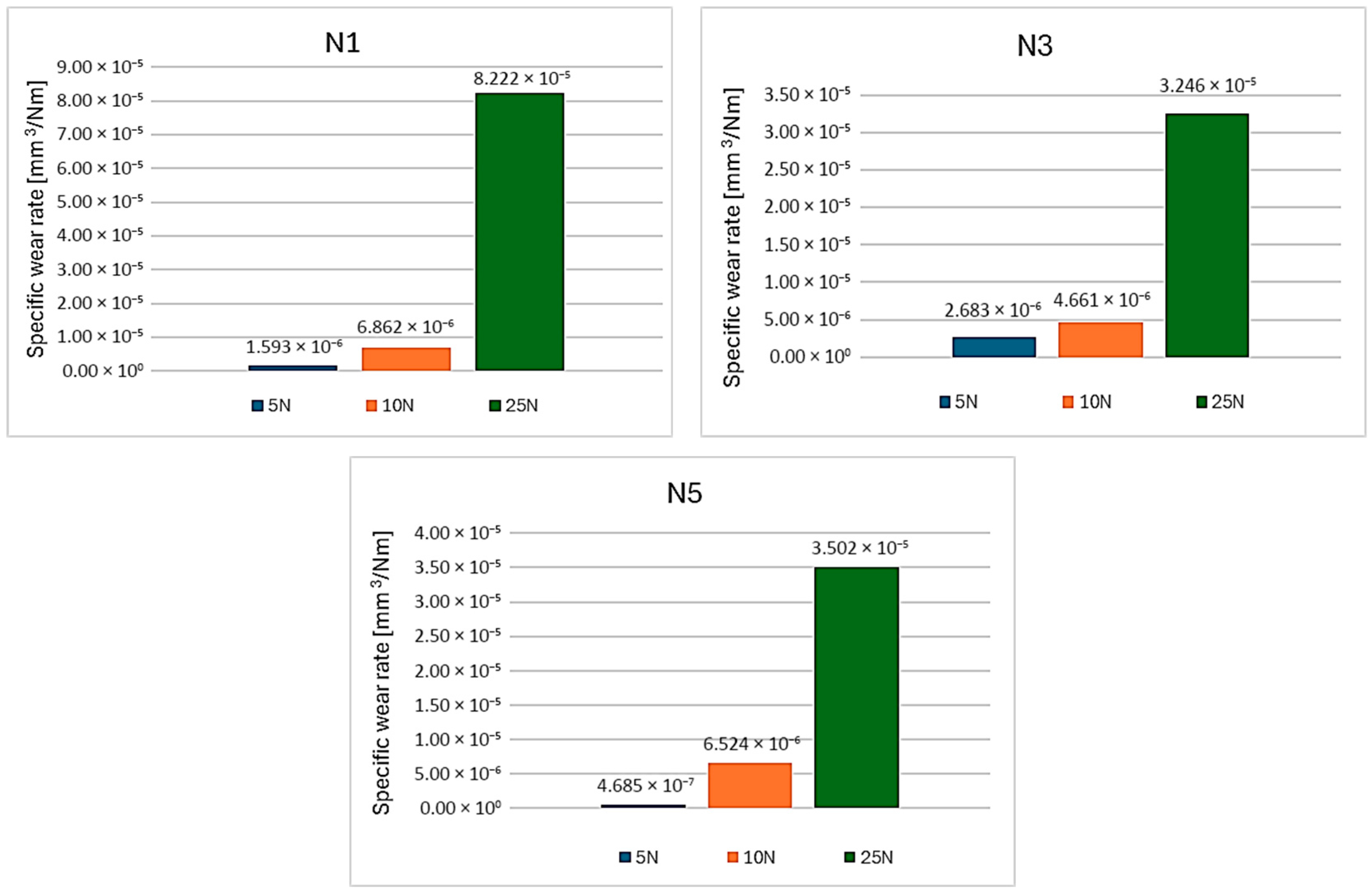
3.2.2. Analysis of Wear Rate
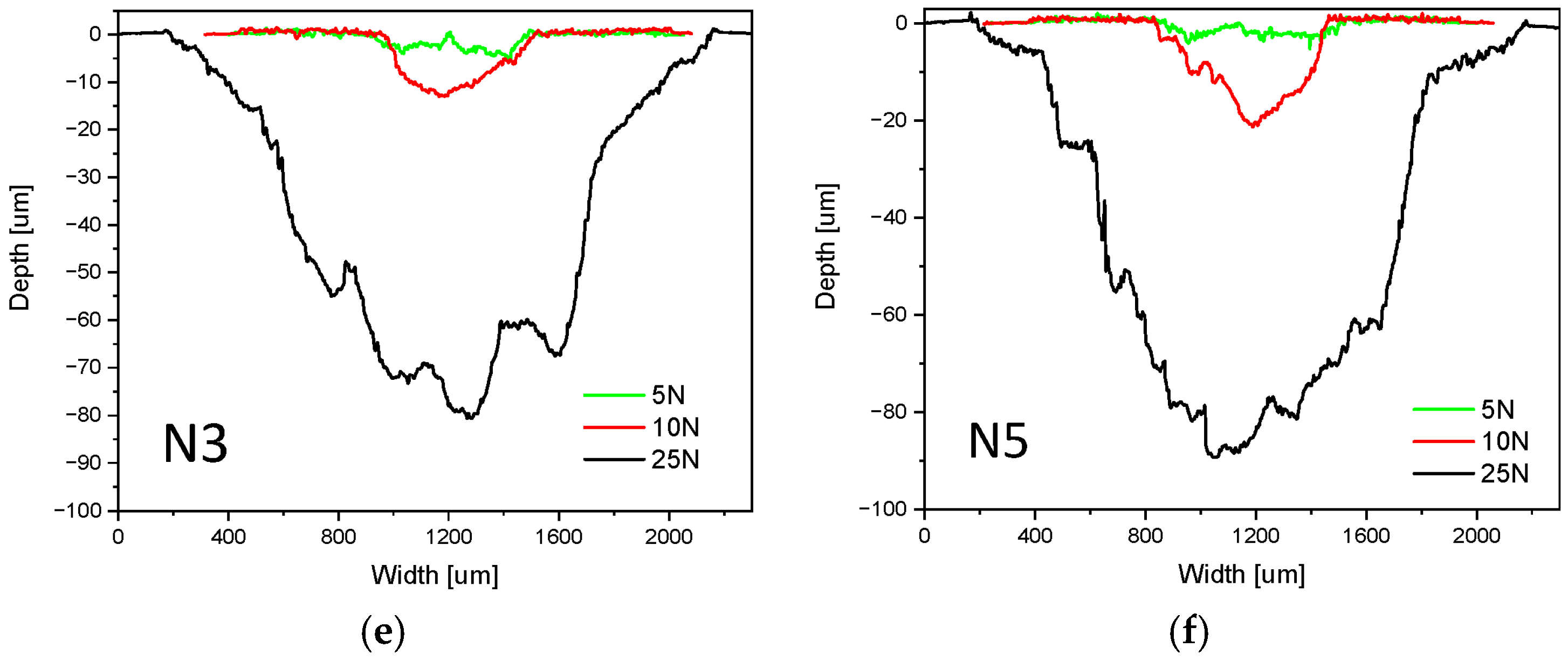
3.2.3. Analysis of Wear Mechanisms
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- He, Y.; Kestens, L.A. The processing, microstructure, texture, and magnetic properties of electrical steels: A review. Int. Mater. Rev. 2025, 70, 353–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, J.; Franke, A.; Fortunati, S. Evolution of Microstructure and Texture for Electrical Steels-Non-Grain Oriented (NGO) vs. Grain Oriented Electrical Steels (GO)-Part 1: NGO. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference Magnetism and Metallurgy WMM20, Rome, Italy, 3–5 February 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y.; O’Malley, R.; Buchely, M.F. Review of Magnetic Properties and Texture Evolution in Non-Oriented Electrical Steels. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 6097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landgraf, F.J.G. Nonoriented electrical steels. JOM 2012, 64, 764–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdi, M.; He, Y.; Hilinski, E.J.; Edrisy, A. Effect of skin pass rolling reduction rate on the texture evolution of a non-oriented electrical steel after inclined cold rolling. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 429, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Liang, Y.; Wen, S.; Wang, S.; Shi, X.; Ye, F.; Lin, J. High-strength low-iron-loss silicon steels fabricated by cold rolling. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2019, 474, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oda, Y.; Kohno, M.; Honda, A. Recent development of non-oriented electrical steel sheet for automobile electrical devices. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2008, 320, 2430–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemke, J.N.; Simonelli, M.; Garibaldi, M.; Ashcroft, I.; Hague, R.; Vedani, M.; Wildman, R.; Tuck, C. Calorimetric study and microstructure analysis of the order-disorder phase transformation in silicon steel built by SLM. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 722, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiso, K.; Akatsu, K. Performance Comparison of High-Speed Motors for Electric Vehicle. World Electr. Veh. J. 2022, 13, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slota, J.; Spišák, E.; Kaščák, L.; Majerníková, J. Experimental and finite element analysis of the shear cutting process of electrical steel sheets under various process conditions. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 651, 012084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami, R.; Butler, D.; Tamimi, S. Manufacturing of non-grain-oriented electrical steels: Review. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2024, 133, 1083–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrovič, D.S. Non-oriented electrical steel sheets. Mater. Technol. 2010, 44, 317–325. [Google Scholar]
- Ros-Yañez, T.; Houbaert, Y.; Fischer, O.; Schneider, J. Production of high silicon steel for electrical applications by thermomechanical processing. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2003, 141, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, J.; Petrov, R.H.; Leunis, E.; Kestens, L. Strain Induced Inward Grain Growth during Recrystallisation in Steel Sheets with BCC Crystal Structure. Mater. Sci. Forum. 2012, 715–716, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- STN EN ISO 6892-1 (ISO 6892-1:2019); Metallic Materials—Tensile Testing—Part 1: Method of Test at Room Temperature. CEN-CENELEC Management Centre: Bruxelles, Belgium, 2019.
- STN 42 0310 (ISO 6892-1:2016); Metallic Materials—Tensile Testing—Part 1: Method of Test at Room Temperature. CEN-CENELEC Management Centre: Bruxelles, Belgium, 2016.
- STN EN ISO 6507-1; Metallic Materials—Vickers Hardness Test—Part 1: Test Method. CEN-CENELEC Management Centre: Bruxelles, Belgium, 2023.
- Oliver, W.C.; Pharr, G.M. An improved technique for determining hardness and elastic modulus using load and displacement sensing indentation experiments. J. Mater. Res. 1992, 7, 1564–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephenson, E.; Marder, A. The effects of grain size on the core loss and permeability of motor lamination steel. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1986, 22, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, P.; Chromik, R.R.; Knight, A.M.; Wakade, S.G. Effect of metallurgical factors on the bulk magnetic properties of non-oriented electrical steels. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2014, 356, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchings, I.; Shipway, P. Tribology Friction and Wear of Engineering Materials, 2nd ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2017; pp. 106–240. [Google Scholar]
- Hanief, M.; Charoo, M.S. Archard’s wear law revisited to measure accurate wear coefficient considering actual sliding velocity. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 47, 5598–5600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Experimental Sample Designation | Thickness mm | C % | Mn % | Si % | P % | Al % | Cu % | S % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1 | 0.50 | 0.004 | 0.35 | 1.06 | 0.14 | 0.22 | 0.01 | 0.008 |
| N3 | 0.50 | 0.003 | 0.27 | 2.15 | 0.01 | 0.28 | 0.01 | 0.005 |
| N5 | 0.50 | 0.004 | 0.26 | 3.09 | 0.01 | 0.97 | 0.01 | 0.004 |
| Experimental Sample Designation | Rp0.2 MPa | Rm MPa | A, % | Hardeness HV |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1 | 268.28 | 395.83 | 21.32 | 227 |
| N3 | 347.34 | 515.09 | 18.25 | 293 |
| N5 | 450.63 | 574.74 | 15.73 | 361 |
| Sample Designtion | Hardness H [GPa] | Young’s Modulus E [GPa] | Ratio H/E [−] | Ratio H3/E2 [GPa] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1 | 2.11 ± 0.18 | 185.6 ± 14.5 | 0.0114 | 0.00027 |
| N3 | 2.25 ± 0.23 | 180.0 ± 15.0 | 0.0125 | 0.00035 |
| N5 | 2.85 ± 0.12 | 183.5 ± 9.1 | 0.0155 | 0.00069 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Motýľová, M.; Petrišinec, I.; Džunda, R.; Andrejovská, J. Influence of Silicon Content on Mechanical and Tribological Properties of FeSi Steels. Crystals 2025, 15, 1005. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15121005
Motýľová M, Petrišinec I, Džunda R, Andrejovská J. Influence of Silicon Content on Mechanical and Tribological Properties of FeSi Steels. Crystals. 2025; 15(12):1005. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15121005
Chicago/Turabian StyleMotýľová, Marcela, Ivan Petrišinec, Róbert Džunda, and Jana Andrejovská. 2025. "Influence of Silicon Content on Mechanical and Tribological Properties of FeSi Steels" Crystals 15, no. 12: 1005. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15121005
APA StyleMotýľová, M., Petrišinec, I., Džunda, R., & Andrejovská, J. (2025). Influence of Silicon Content on Mechanical and Tribological Properties of FeSi Steels. Crystals, 15(12), 1005. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15121005







