Heterogeneous Distribution of Microstructure and Mechanical Properties in M2 High-Speed Steel Fabricated by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
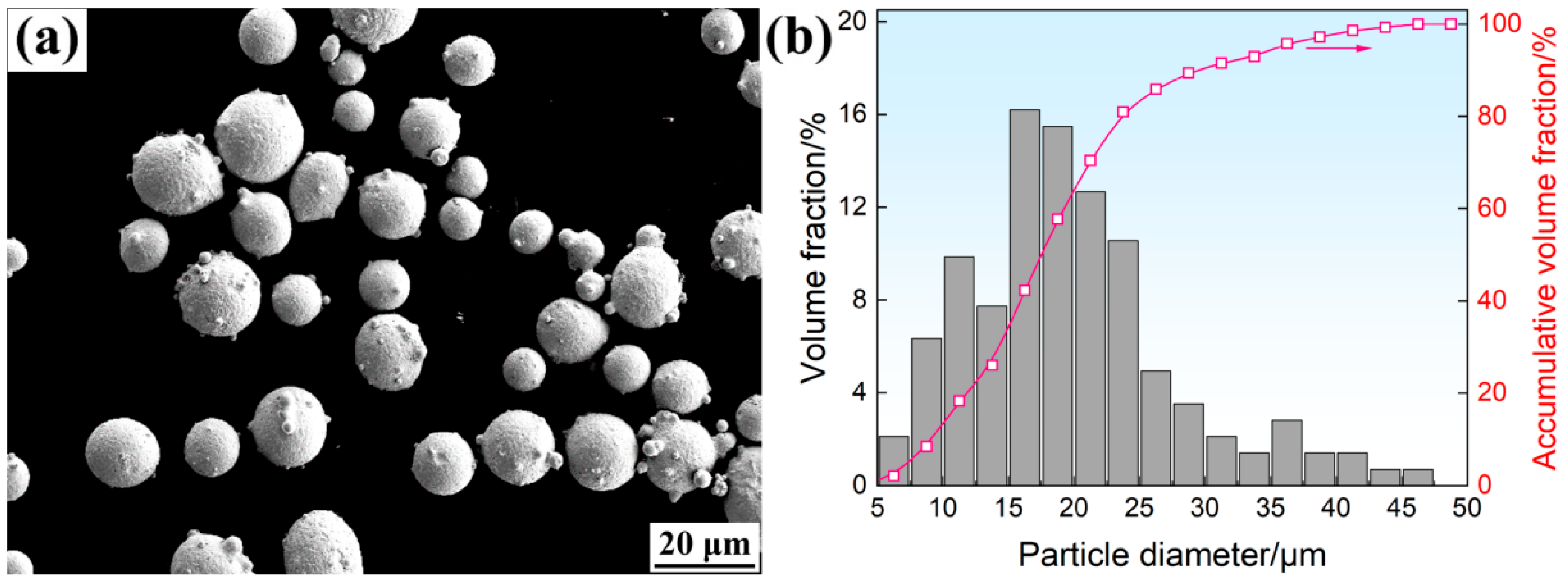
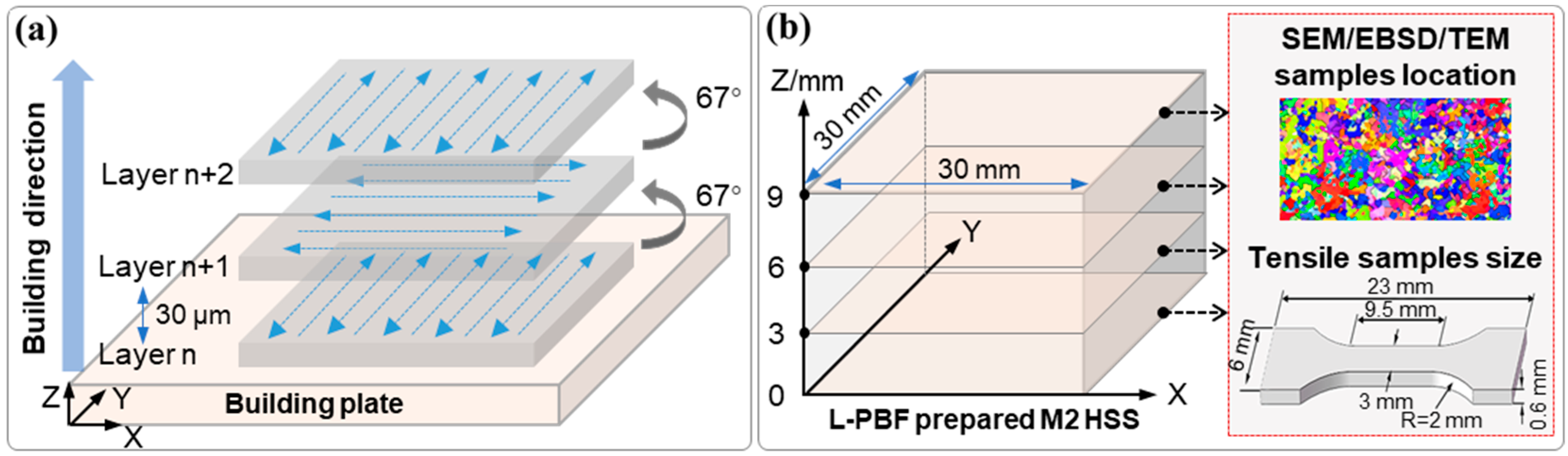
2.1. Materials and L-PBF Processing Parameters
2.2. Characterization
2.3. Hardness and Tensile Tests
3. Results and Discussion
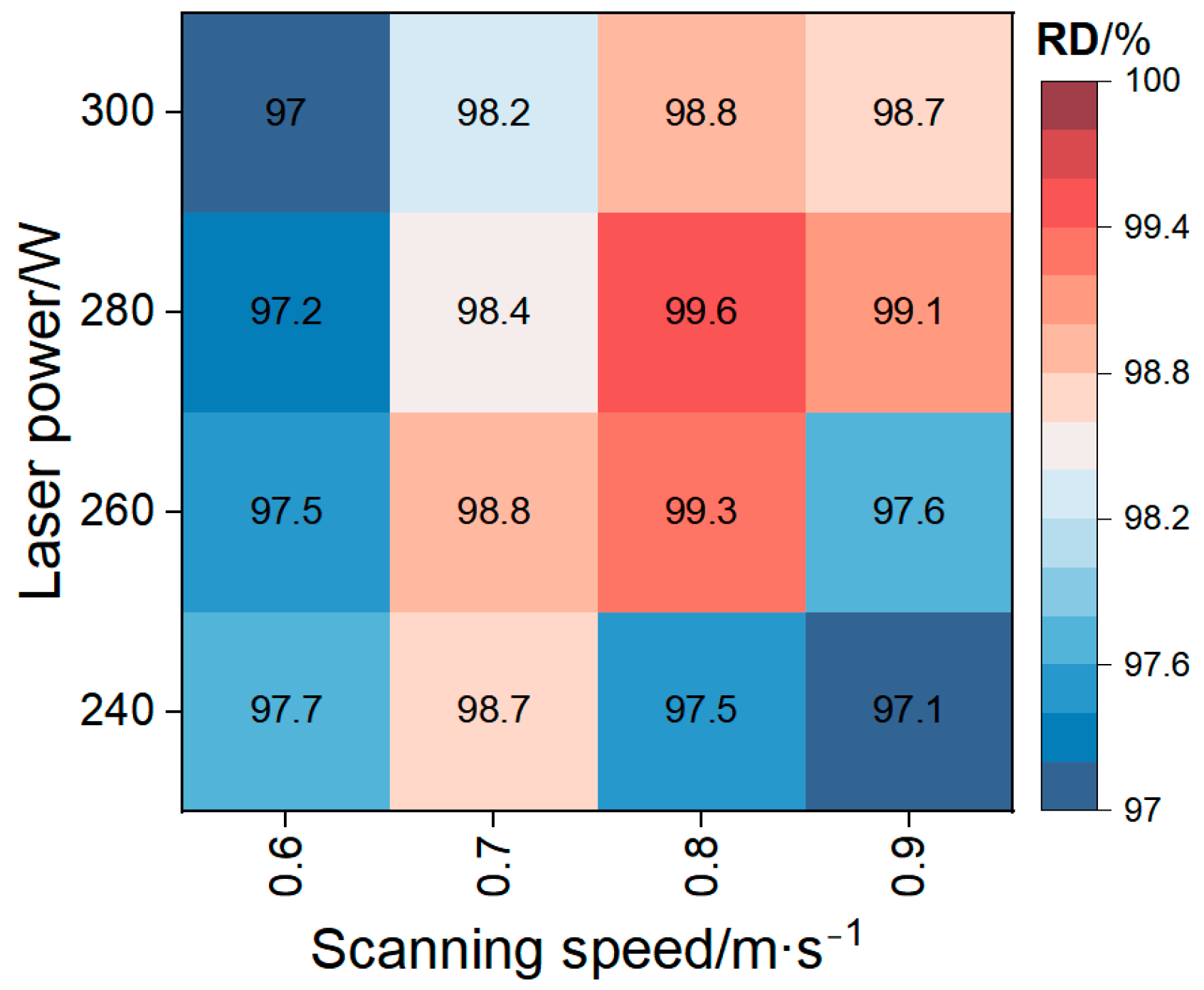
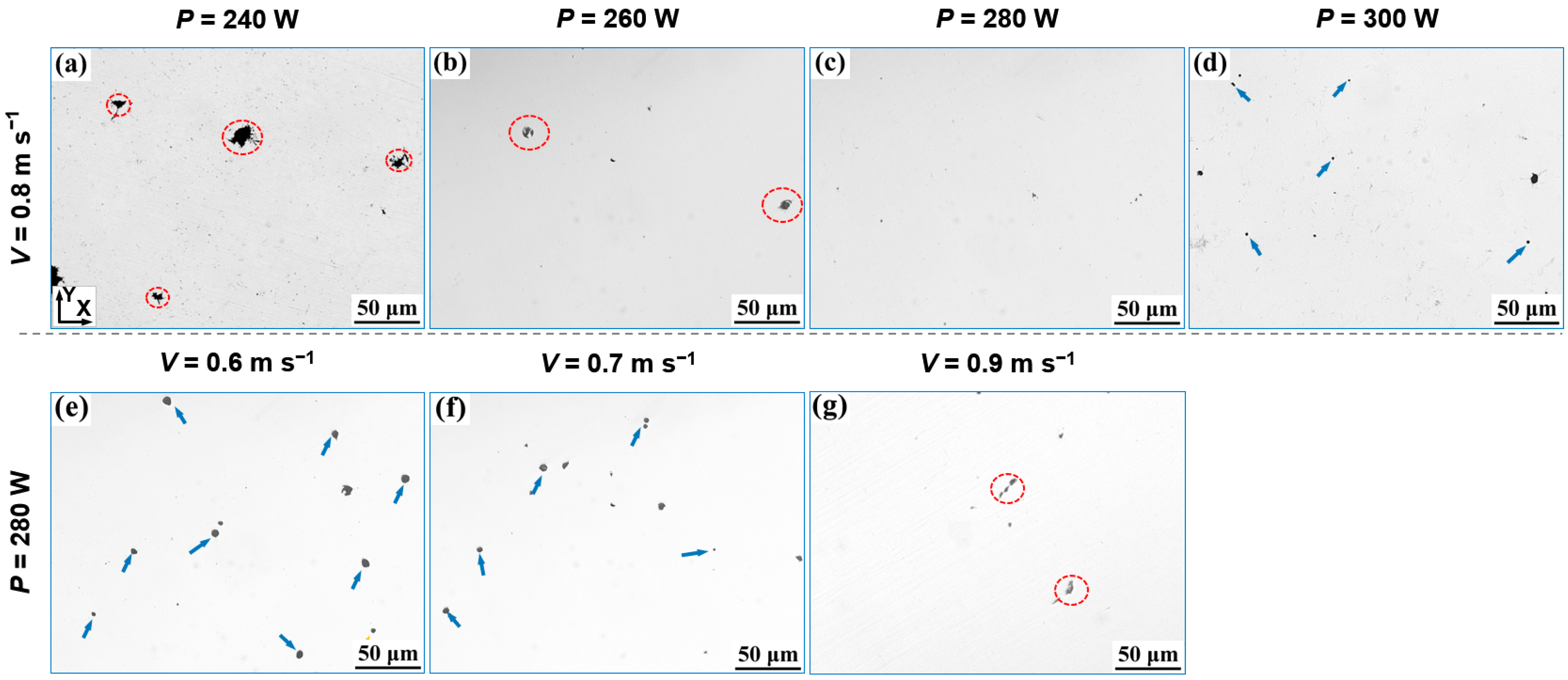
3.1. Relative Density
3.2. Microstructures
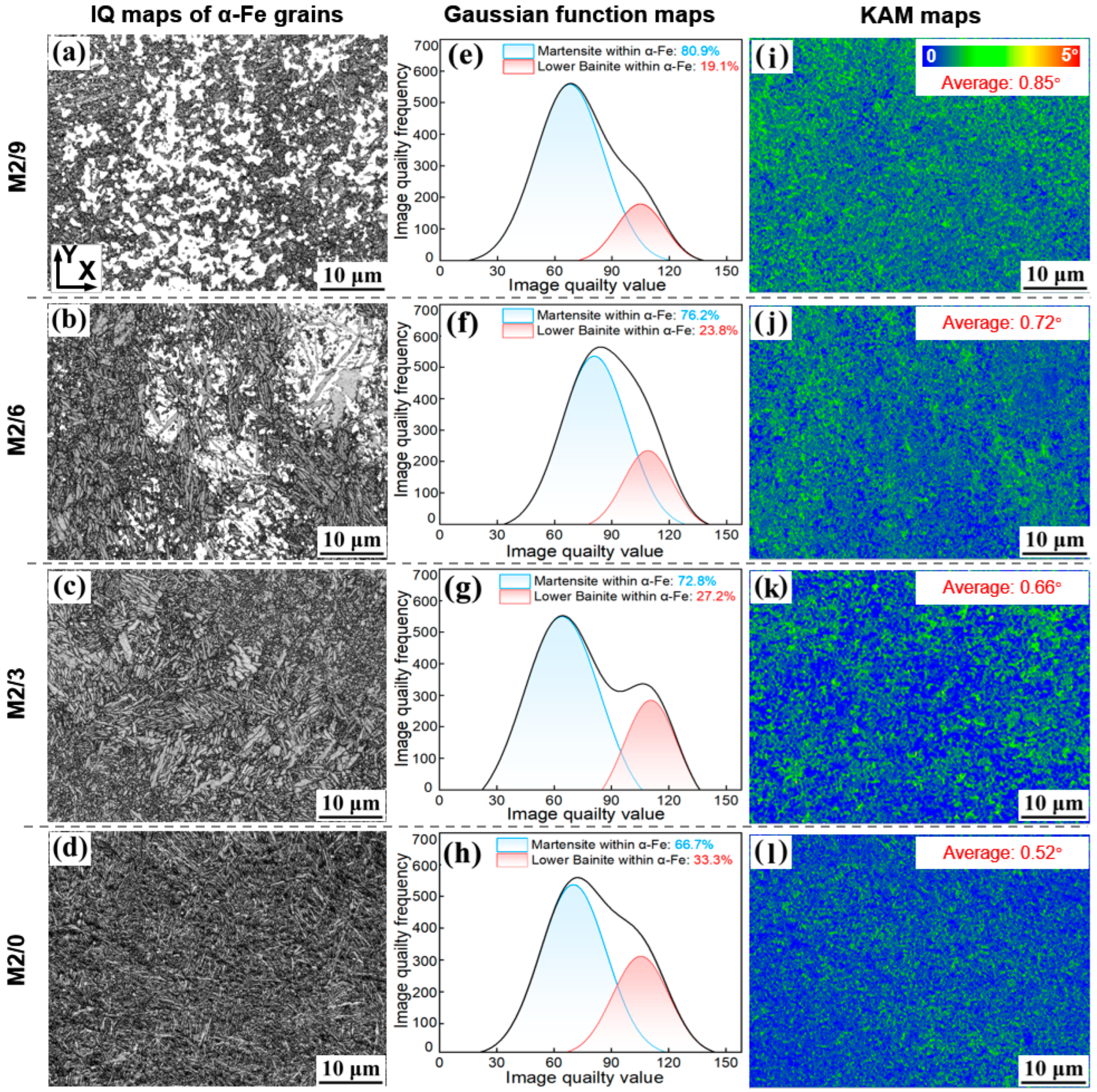
3.2.1. Phase Composition
3.2.2. Grain Structure
3.2.3. Precipitation
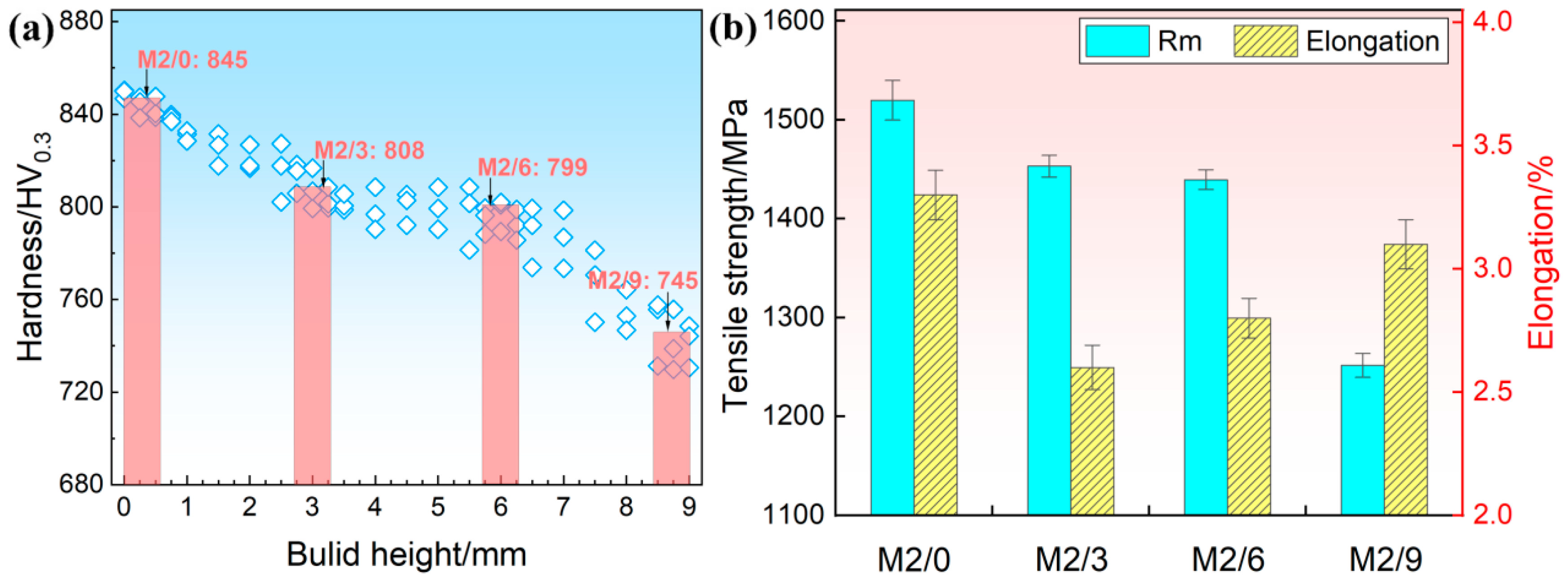
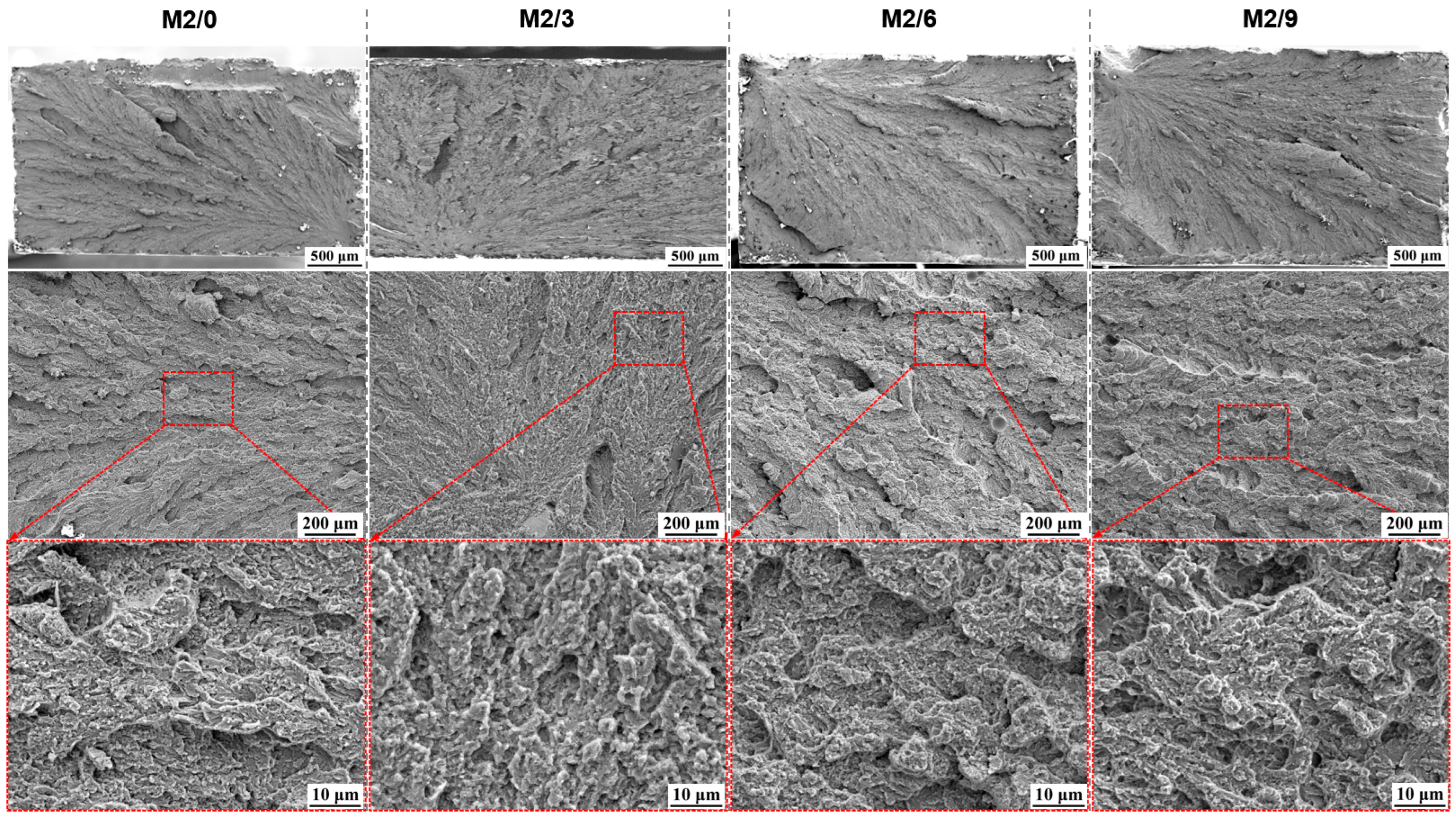
3.3. Hardness and Tensile Properties
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- By optimizing the laser power (280 W) and scanning speed (0.8 m s−1), high-density M2 HSS with a relative density of 99.6% was successfully produced.
- (2)
- The microstructure of M2 HSS is primarily composed of lath martensite, needle-like lower bainite, and retained austenite, accompanied by a minor fraction (less than 2.9%) of eutectic M6C and M2C carbides. As the build height increases (0 to 9 mm), significant variations in phase composition are observed, along with a corresponding increase in residual stress. Specifically, the area fraction of lower bainite decreases significantly, from 32.1 to 13.1%, while the retained austenite content increases from 0.9 to 29.1%. Meanwhile, the average grain size remains between 1.15 and 1.61 μm.
- (3)
- The heterogeneous distribution of microstructures along the build direction plays a critical role in determining the mechanical properties at different build heights. As the distance from the substrate to the surface increases, both hardness and tensile strength gradually decrease, from 845 HV0.3 and 1520 MPa to 745 HV0.3 and 1251 MPa, respectively. Meanwhile, the elongation value (2.6–3.3%) exhibits a trend of initial decrease and subsequent increase.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xiang, J.; Yang, H.; Zhuang, C. Effect of cooling rate on the characteristics of eutectic carbides in M2Al high-speed steel. Crystals 2025, 15, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.K.; Luo, T.; Zhang, W.; Wang, J. Electron beam melting powder bed forming M2 high speed steel corrosion resistance. J. Powder Metall. Technol. 2025, 4, 391–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Sun, Z.; Wei, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Yang, X.; Tang, H. Research progress on powder bed fusion additive manufacturing of tool and mold steels. Iron Steel 2024, 59, 2–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halfa, H. Characterization of electroslag remelted super hard high speed tool steel containing niobium. Steel Res. Int. 2013, 84, 495–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Hu, L.; Li, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X. Evolution of the microstructure and mechanical properties of powder metallurgical high-speed steel S390 after heat treatment. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 740, 766–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narasimharaju, S.; Zeng, W.; See, T.; Zhu, Z.; Scott, P.; Jiang, X.; Lou, S. A comprehensive review on laser powder bed fusion of steels: Processing, microstructure, defects and control methods, mechanical properties, current challenges and future trends. J. Manuf. Process. 2022, 75, 375–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, F.; Wang, L.; Xiao, Z.; Feng, J.; Zhao, L. Effect of titanium and rare earth microalloying on microsegregation, eutectic carbides of M2 high speed steel during ESR process. J. Rare Earths 2020, 38, 1030–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, A.; Zhao, G.; Suhaimi, H.; Ning, H.; Ghulam, H.; Wei, Z. Readiness of subtractive and additive manufacturing and their sustainable amalgamation from the perspective of Industry 4.0: A comprehensive review. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 111, 2475–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrey, M.; Malekipour, E.; El-Mounayri, H.; Faierson, E.; Agarwal, M. A novel framework of developing a predictive model for powder bed fusion process. 3D Print. Addit. Manuf. 2024, 11, 179–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweizer, F.; Bade, K.; Baldas, L.; Bergdolt, S.; Colin, S.; Deutschbein, C.; Hengsbach, S.; Korvink, J.; Rojas-Cárdenas, M.; Brandner, J. Rarefied gas flows in complex microfluidic 3D-structures fabricated via additive manufacturing. Vacuum 2025, 238, 114213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Liang, X.; Wang, X.; Li, G.; Vanmeense, K.; Xie, J. Alloy design for laser powder bed fusion additive manufacturing: A critical review. Int. J. Extrem. Manuf. 2024, 6, 022002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Luo, L.; Liu, T.; Wang, B.; Luo, L.; Zhao, J.; Wang, L.; Su, Y.; Guo, J.; Fu, H. Tuning process parameters to optimize microstructure and mechanical properties of novel maraging steel fabricated by selective laser melting. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 823, 141740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadroitsev, I.; Krakhmalev, P.; Yadroitsava, I.; Johansson, S.; Smurov, I. Energy input effect on morphology and microstructure of selective laser melting single track from metallic powder. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2013, 213, 606–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, N.; Capuano, L.; Cabeza, S.; Feinaeugle, M.; García-Junceda, A.; Rooij, M.; Matthews, D.; Gibson, I.; Römer, G. Directed energy deposition and characterization of high-carbon high speed steels. Addit. Manuf. 2019, 30, 100838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghdadi, N.; Laleh, M.; Moyle, M.; Primig, S. Additive manufacturing of steels: A review of achievements and challenges. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 64–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, P.; Hariharan, A.; Kini, A.; Kürnsteiner, P.; Raabe, D.; Jägle, E. Steels in additive manufacturing: A review of their microstructure and properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 772, 138633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Careri, F.; Khan, R.H.U.; Alshammari, T.; Attallah, M. Development of a novel heat treatment in L-PBF fabricated high strength A205 Al alloy: Impact on microstructure-mechanical properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2025, 933, 148278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zheng, L.; Xu, W.; Liu, N.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, G. Synergistic impact mechanism of particle size and morphology in superalloy powders for additive manufacturing. Particuology 2024, 95, 279–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 2738:1999; Sintered Metal Materials, Excluding Hardmetals—Permeable Sintered Metal Materials—Determination of Density, Oil Content and Open Porosity. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1999. Available online: https://www.antpedia.com/standard/404749.html (accessed on 23 May 2024).
- Jiao, W.; Li, H.; Feng, H.; Jiang, Z.; Dai, J.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, S.; Chu, M.; Wu, W. Effect of high nitrogen addition on microstructure and mechanical properties of as-cast M42 high speed steel. ISIJ Int. 2020, 60, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 6892-1:2016; Metallic Materials—Tensile Testing—Part 1: Method of Test at Room Temperature. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. Available online: https://www.antpedia.com/standard/7803213.html (accessed on 23 May 2024).
- Liu, S.; Yang, W.; Shi, X.; Li, B.; Duan, S.; Guo, H.; Guo, J. Influence of laser process parameters on the densification, microstructure, and mechanical properties of a selective laser melted AZ61 magnesium alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 808, 151160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Maharma, A.; Patil, S.; Markert, B. Effects of porosity on the mechanical properties of additively manufactured components: A critical review. Mater. Res. Express 2020, 7, 122001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabavi, S.; Dalir, H.; Farshidianfar, A. A comprehensive review of recent advances in laser powder bed fusion characteristics modeling: Metallurgical and defects. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2024, 132, 2233–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Chen, J.; Kang, X.; Zou, J.; Zou, Y.; Shi, W. Coupling effect of substrate thermal properties and droplet geometry on Marangoni instabilities inside an evaporating droplet at quasi-steady state. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2025, 163, 108745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, G.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, L. Gradient in microstructure and mechanical property of selective laser melted AlSi10Mg. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 735, 1414–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Z.; Song, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, W.; Yang, Z.; Mu, M. Effect of cryogenic treatment on the microstructure and mechanical properties of selected laser melted H13 steel. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 21, 5056–5065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Choe, J.; Park, J.; Yu, J.; Kim, S.; Jung, I.; Sung, H. Microstructural effects on the tensile and fracture behavior of selective laser melted H13 tool steel under varying conditions. Mater. Charact. 2019, 155, 109817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Qi, S.; Wang, Y.; Chu, X.; Sun, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Jia, W.; Yang, X.; Liu, S. Microstructural evolution and tribological properties of M2 high-speed steel fabricated under various selective electron beam melting processing parameters. Tribol. Int. 2023, 187, 108749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Cheng, W.; Liu, X. Selective laser melting of 7075 aluminum alloy inoculated by Al-Ti-B: Grain refinement and superior mechanical properties. Vacuum 2022, 200, 111030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.; Yuan, L.; Phillion, A. A 3D simulation of grain structure evolution during powder bed fusion additive manufacturing and subsequent laser rescanning process. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2024, 333, 118603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, R.; Guevara, J.; Inoue, J. In-situ observation of variant pair formation in bainite of low carbon steel by digital holographic microscopy. Acta Mater. 2024, 277, 120212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.; Lee, S.; Hwang, B. In-situ SEM/EBSD investigation of tensile deformation-driven microstructural changes in low-carbon HSLA steels with ferrite-bainite microstructures. Mater. Charact. 2023, 206, 113418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, P.; Silveira, A.; Rocha, A.; Stark, A.; Sourmail, T.; Epp, J. Impact of hot and warm deformation on the bainite morphology and kinetics during continuous cooling of low- and medium-C carbide-free bainitic steels. Mater. Des. 2025, 257, 114433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, D.; Paladugu, M.; Hughes, J.; Kapousidou, M.; Islam, U.; Stark, A.; Schell, N.; Jimenez-Melero, E. Formation of lower bainite in a high carbon steel—An in-situ synchrotron XRD study. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 18, 5380–5393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, J.H.; Park, J.; Baek, S.; Ma, N.; Lee, S.; Kim, D. Continuous tempering effect induced PWHT alternative technology using wire arc additivemanufacturing for application in replacing nuclear pressurized water reactor system repairing: CALPHAD, FEM simulation, and EBSD investigation. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 25, 1961–2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhao, X. Effect of scaning speed on microstructure and hardness of M2 high speed steel by direct laser metal deposition. Hot Work. Technol. 2019, 48, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, K.; Shibata, A.; Kimura, Y.; Yamaguchi, M.; Ebihara, K.; Tsuji, N. Effect of carbon segregation at prior austenite grain boundary on hydrogen-related crack propagation behavior in 3Mn-0.2C martensitic steels. Acta Mater. 2024, 280, 120288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Q.; Jiang, S.; Lin, X.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wen, B. High-pressure quenching effect on martensitic transformation characteristics and mechanical properties of low-alloy medium-carbon steel. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 23, 765–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouni, C.T.; Mahadevan, S.; Ravishankar, C.; Albert, S.K.; Das, C.R.; Parida, P.K.; Sagdeo, A. Influence of prior deformation temperature on strain induced martensite formation and its effect on the tensile strengthening behaviour of type 304 SS studied by XRDLPA. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 826, 141960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaus, A.; Kryshtal, A. New insights into the microstructure of M2 high-speed steel. Mater. Charact. 2023, 205, 113313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LI, Y.; Wang, Y.; Niu, J.; Liu, S.; Lin, Y.; Liu, N.; Ma, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J. Microstructure and mechanical properties of M2 high speed steel produced by electron beam melting. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2023, 862, 144327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhang, C.; Qu, F.; Liu, L.; Liu, X. Fe-based metallic glass coatings with suppressed cracks and enhanced wear resistance prepared by extreme high-speed laser cladding. Intermetallics 2024, 175, 108517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| C | Cr | Mo | W | V | Mn | Si | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.8 | 4.1 | 5.1 | 6.5 | 1.9 | 0.3 | 0.2 | Bal. |
| Specimens | M2/0 | M2/3 | M2/6 | M2/9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| γ-Fe content | 1.3% | 5.3% | 19.4% | 25.6% |
| Specimens | Martensite | Lower Bainite | Austenite | M6C, M2C Carbides |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall (within α-Fe) | Overall (within α-Fe) | |||
| M2/0 | 64.4% (66.7%) | 32.1% (33.3%) | 0.9% | 2.6% |
| M2/3 | 66.0% (72.8%) | 24.6% (27.2%) | 6.5% | 2.9% |
| M2/6 | 61.9% (76.2%) | 19.3% (23.8%) | 16.8% | 2% |
| M2/9 | 55.3% (80.9%) | 13.1% (19.1%) | 29.1% | 2.5% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Chu, X.; Liu, S. Heterogeneous Distribution of Microstructure and Mechanical Properties in M2 High-Speed Steel Fabricated by Laser Powder Bed Fusion. Crystals 2025, 15, 917. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15110917
Wei Y, Zhang Y, Li Y, Ren Y, Zhang S, Zhang X, Chu X, Liu S. Heterogeneous Distribution of Microstructure and Mechanical Properties in M2 High-Speed Steel Fabricated by Laser Powder Bed Fusion. Crystals. 2025; 15(11):917. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15110917
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Yingkang, Yufeng Zhang, Yunzhe Li, Yaojia Ren, Shihao Zhang, Xiaotong Zhang, Xin Chu, and Shifeng Liu. 2025. "Heterogeneous Distribution of Microstructure and Mechanical Properties in M2 High-Speed Steel Fabricated by Laser Powder Bed Fusion" Crystals 15, no. 11: 917. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15110917
APA StyleWei, Y., Zhang, Y., Li, Y., Ren, Y., Zhang, S., Zhang, X., Chu, X., & Liu, S. (2025). Heterogeneous Distribution of Microstructure and Mechanical Properties in M2 High-Speed Steel Fabricated by Laser Powder Bed Fusion. Crystals, 15(11), 917. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15110917








