X-Ray Crystal Structure of the N-Terminal Domain of Staphylococcus aureus Cell-Cycle Protein GpsB
Abstract
1. Introduction
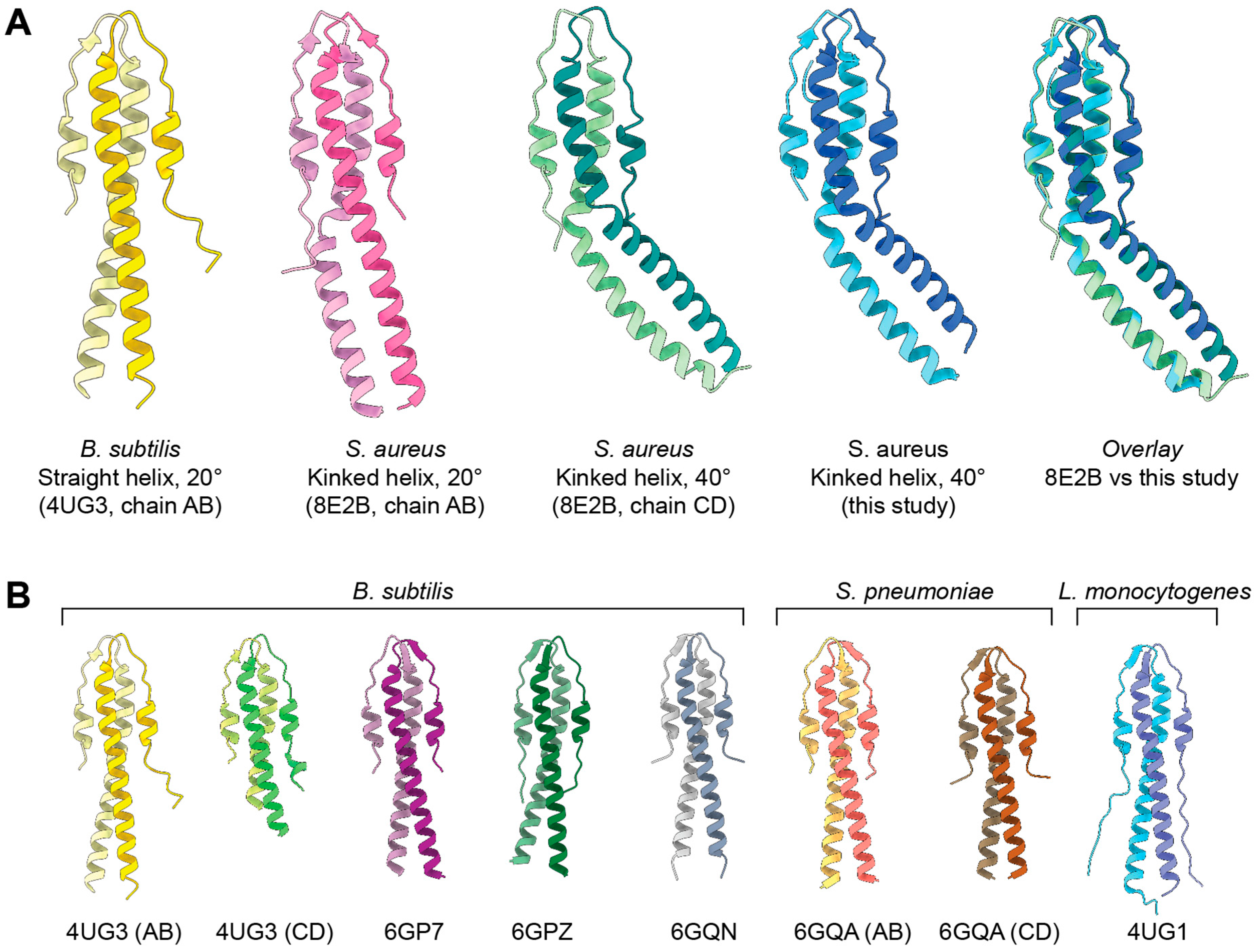
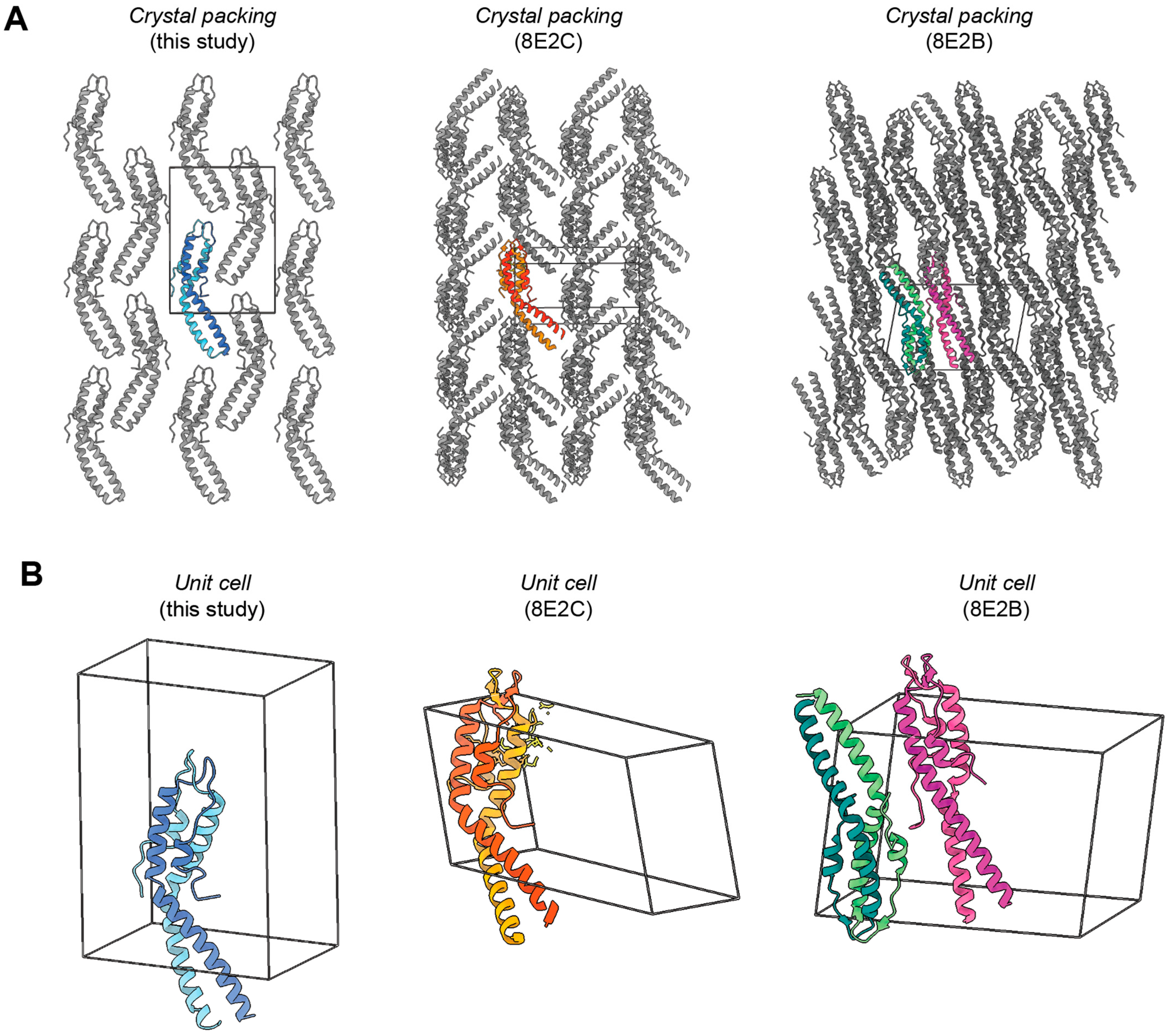
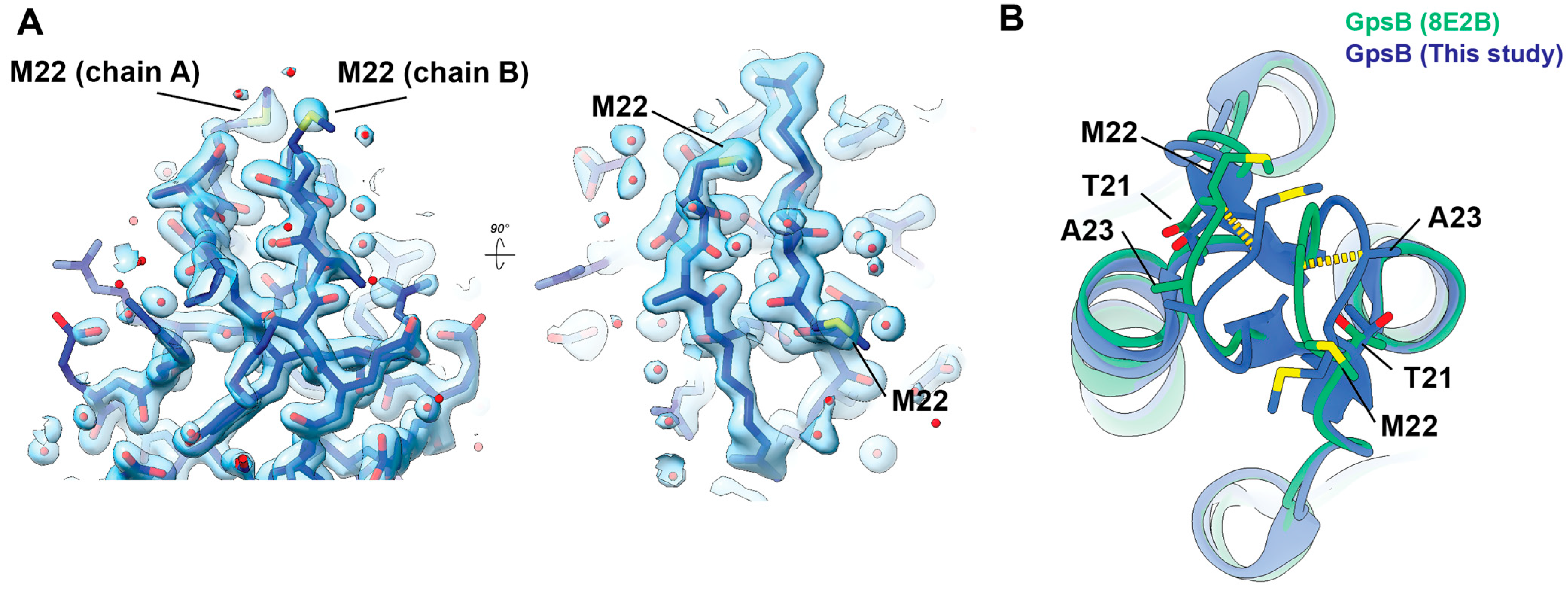
2. Results
3. Conclusions
4. Materials & Methods
4.1. GpsB 1–75 Purification
4.2. GpsB 1–75 Crystallization, Data Collection, and Model Building
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Halbedel, S.; Lewis, R.J. Structural Basis for Interaction of DivIVA/GpsB Proteins with Their Ligands. Mol. Microbiol. 2019, 111, 1404–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammond, L.R.; White, M.L.; Eswara, P.J. ¡vIVA La DivIVA! J. Bacteriol. 2019, 201, e00245-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cleverley, R.M.; Rismondo, J.; Lockhart-Cairns, M.P.; Van Bentum, P.T.; Egan, A.J.; Vollmer, W.; Halbedel, S.; Baldock, C.; Breukink, E.; Lewis, R.J. Subunit Arrangement in GpsB, a Regulator of Cell Wall Biosynthesis. Microb. Drug Resist. 2016, 22, 446–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cleverley, R.M.; Rutter, Z.J.; Rismondo, J.; Corona, F.; Tsui, H.-C.T.; Alatawi, F.A.; Daniel, R.A.; Halbedel, S.; Massidda, O.; Winkler, M.E.; et al. The Cell Cycle Regulator GpsB Functions as Cytosolic Adaptor for Multiple Cell Wall Enzymes. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eswara, P.J.; Brzozowski, R.S.; Viola, M.G.; Graham, G.; Spanoudis, C.; Trebino, C.; Jha, J.; Aubee, J.I.; Thompson, K.M.; Camberg, J.L.; et al. An Essential Staphylococcus aureus Cell Division Protein Directly Regulates FtsZ Dynamics. eLife 2018, 7, e38856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammond, L.R.; Sacco, M.D.; Khan, S.J.; Spanoudis, C.; Hough-Neidig, A.; Chen, Y.; Eswara, P.J. GpsB Coordinates Cell Division and Cell Surface Decoration by Wall Teichoic Acids in Staphylococcus aureus. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0141322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steele, V.R.; Bottomley, A.L.; Garcia-Lara, J.; Kasturiarachchi, J.; Foster, S.J. Multiple Essential Roles for EzrA in Cell Division of Staphylococcus aureus. Mol. Microbiol. 2011, 80, 542–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bottomley, A.L.; Liew, A.T.F.; Kusuma, K.D.; Peterson, E.; Seidel, L.; Foster, S.J.; Harry, E.J. Coordination of Chromosome Segregation and Cell Division in Staphylococcus aureus. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartlett, T.M.; Sisley, T.A.; Mychack, A.; Walker, S.; Baker, R.W.; Rudner, D.Z.; Bernhardt, T.G. FacZ Is a GpsB-Interacting Protein That Prevents Aberrant Division-Site Placement in Staphylococcus aureus. Nat. Microbiol. 2024, 9, 801–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutton, J.A.F.; Cooke, M.; Tinajero-Trejo, M.; Wacnik, K.; Salamaga, B.; Portman-Ross, C.; Lund, V.A.; Hobbs, J.K.; Foster, S.J. The Roles of GpsB and DivIVA in Staphylococcus aureus Growth and Division. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1241249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, S.F.; Saraiva, B.M.; Veiga, H.; Marques, L.B.; Schäper, S.; Sporniak, M.; Vega, D.E.; Jorge, A.M.; Duarte, A.M.; Brito, A.D.; et al. The Role of GpsB in Staphylococcus aureus Cell Morphogenesis. mBio 2024, 15, e03235-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharya, D.; King, A.; McKnight, L.; Horigian, P.; Eswara, P.J. GpsB Interacts with FtsZ in Multiple Species and May Serve as an Accessory Z-Ring Anchor. Mol. Biol. Cell 2025, 36, ar10. [Google Scholar]
- Rismondo, J.; Cleverley, R.M.; Lane, H.V.; Großhennig, S.; Steglich, A.; Möller, L.; Mannala, G.K.; Hain, T.; Lewis, R.J.; Halbedel, S. Structure of the Bacterial Cell Division Determinant GpsB and Its Interaction with Penicillin-Binding Proteins. Mol. Microbiol. 2016, 99, 978–998. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sacco, M.D.; Hammond, L.R.; Noor, R.E.; Bhattacharya, D.; McKnight, L.J.; Madsen, J.J.; Zhang, X.; Butler, S.G.; Kemp, M.T.; Jaskolka-Brown, A.C.; et al. Staphylococcus aureus FtsZ and PBP4 Bind to the Conformationally Dynamic N-Terminal Domain of GpsB. eLife 2024, 13, e85579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otwinowski, Z.; Minor, W. [20] Processing of X-Ray Diffraction Data Collected in Oscillation Mode. Methods Enzymol. 1997, 276, 307–326. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McCoy, A.J.; Grosse-Kunstleve, R.W.; Adams, P.D.; Winn, M.D.; Storoni, L.C.; Read, R.J. Phaser Crystallographic Software. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2007, 40 Pt 4, 658–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emsley, P.; Lohkamp, B.; Scott, W.G.; Cowtan, K. Features and Development of Coot. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2010, 66 Pt 4, 486–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liebschner, D.; Afonine, P.V.; Baker, M.L.; Bunkóczi, G.; Chen, V.B.; Croll, T.I.; Hintze, B.; Hung, L.-W.; Jain, S.; McCoy, A.J.; et al. Macromolecular Structure Determination Using X-Rays, Neutrons and Electrons: Recent Developments in Phenix. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D Struct. Biol. 2019, 75, 861–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| PDB ID | 9PV2 |
|---|---|
| Data Reduction | |
| Space group | P212121 |
| Cell dimensions | |
| a, b, c (Å) | 38.373, 55.531, 77.077 |
| α, β, γ (°) | 90, 90, 90 |
| Resolution (Å) * | 45.06–1.75 (1.78–1.75) |
| Rmerge * | 0.073 (0.401) |
| Rmeas * | 0.097 (0.378) |
| CC 1/2 * | 0.991 (0.931) |
| I/σI * | 22.7 (2.6) |
| Completeness (%) * | 97.1 (87.0) |
| Total reflections | 113,272 |
| Unique reflections * | 16,728 (721) |
| Redundancy * | 6.8 (5.8) |
| Wilson B-factor (Å2) | 22.46 |
| VM (Å3/Da) | 2.16 |
| Refinement | |
| Resolution (Å) | 45.06–1.75 (1.80–1.75) |
| No. reflections | 16,484 (1195) |
| Rwork/Rfree (%) | 19.75/23.60 (33.49/36.67) |
| No. atoms | |
| Protein | 1225 |
| Water | 144 |
| Mean B-factors | |
| Overall (Å2) | 29.82 |
| Protein (Å2) | 28.74 |
| Water (Å2) | 39.05 |
| R.m.s. deviations | |
| Bond lengths (Å) | 0.004 |
| Bond angles (°) | 0.590 |
| Ramachandran | |
| Favored (%) | 99.30 |
| Allowed (%) | 0.70 |
| Outliers (%) | 0 |
| Rotamer outliers (%) | 0 |
| Clashscore | 9.36 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nicely, N.I.; Bartlett, T.M.; Baker, R.W. X-Ray Crystal Structure of the N-Terminal Domain of Staphylococcus aureus Cell-Cycle Protein GpsB. Crystals 2025, 15, 867. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15100867
Nicely NI, Bartlett TM, Baker RW. X-Ray Crystal Structure of the N-Terminal Domain of Staphylococcus aureus Cell-Cycle Protein GpsB. Crystals. 2025; 15(10):867. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15100867
Chicago/Turabian StyleNicely, Nathan I., Thomas. M. Bartlett, and Richard W. Baker. 2025. "X-Ray Crystal Structure of the N-Terminal Domain of Staphylococcus aureus Cell-Cycle Protein GpsB" Crystals 15, no. 10: 867. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15100867
APA StyleNicely, N. I., Bartlett, T. M., & Baker, R. W. (2025). X-Ray Crystal Structure of the N-Terminal Domain of Staphylococcus aureus Cell-Cycle Protein GpsB. Crystals, 15(10), 867. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15100867






